The Mediterranean Killifish Aphanius fasciatus (Valenciennes, 1821) (Teleostei: Cyprinodontidae) as a Sentinel Species for Protection of the Quality of Transitional Water Environments: Literature, Insights, and Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
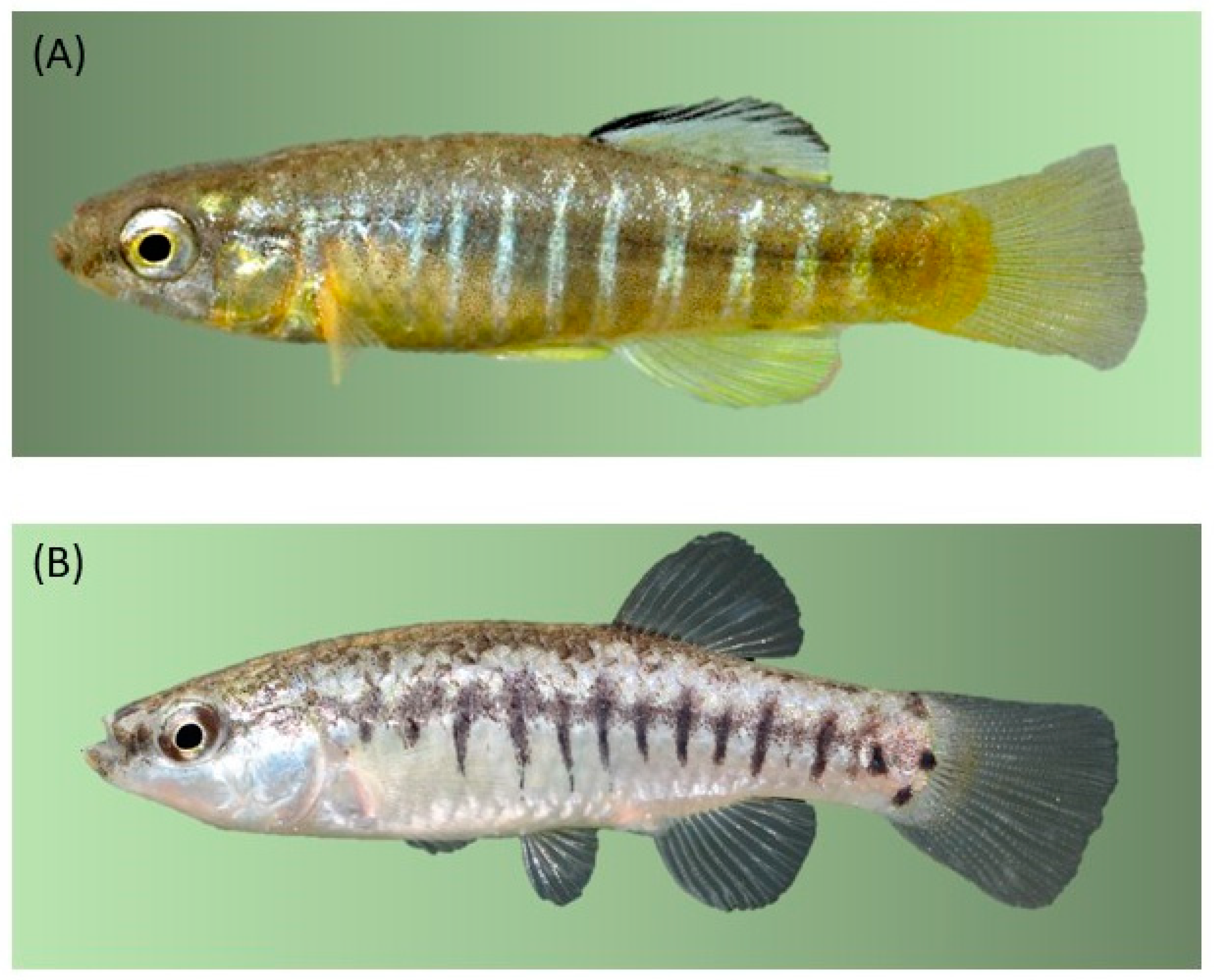
2. Aphanius fasciatus: Biology, Habitat Preference, Distribution, and Conservation Status
3. Aphanius fasciatus as Sentinel Species for the Ecotoxicological Risk of Coastal Lagoons
A. fasciatus as Sentinel Species for Metal Pollution
4. Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Facca, C.; Cavraro, F.; Franzoi, P.; Malavasi, S. Lagoon Resident Fish Species of Conservation Interest According to the Habitat Directive (92/43/CEE): A Review on Their Potential Use as Ecological Indicator Species. Water 2020, 12, 2059. [Google Scholar]
- Gilby, B.L.; Olds, A.D.; Connolly, R.M.; Yabsley, N.A.; Maxwell, P.S.; Tibbetts, I.; Schoeman, D.S.; Schlacher, T.A. Umbrellas can work under water: Using threatened species as indicator and management surrogates can improve coastal conservation. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 199, 132–140. [Google Scholar]
- Andolina, C.; Franzoi, P.; Cavraro, F.; Jackson, A.L.; Mazzola, A.; Vizzini, S. Trophic adaptability shapes isotopic niche of the resident fish Aphanius fasciatus across lagoon habitats. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 264, 107685. [Google Scholar]
- Kottelat, M.; Freyhof, J. Handbook of European Freshwater Fishes; Kottelat, Cornol and Freyhof: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lionetto, M.G.; Caricato, R.; Giordano, M.E. Pollution biomarkers in the framework of marine biodiversity conservation: State of art and perspectives. Water 2021, 13, 1847. [Google Scholar]
- Gouveia, D.; Almunia, C.; Cogne, Y.; Pible, O.; Degli-Esposti, D.; Salvador, A.; Cristobal, S.; Sheehan, D.; Chaumot, A.; Geffard, O.; et al. Ecotoxicoproteomics: A decade of progress in our understanding of anthropogenic impact on the environment. J. Proteom. 2019, 198, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bianco, P.G.; Ahnelt, H.; Economidis, P.S. The freshwater fishes from eastern and large Mediterranean islands with comments on their safety status. Acta Univ. Carol. Biol. 1996, 40, 45–60. [Google Scholar]
- Por, F.D. The Legacy of Tethys: An Aquatic Biogeography of the Levant; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Maltagliati, F. Genetic divergence in natural populations of the Mediterranean brackish-water killifish Aphanius fasciatus. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 179, 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Toro, M.A.; Caballero, A. Characterization and conservation of genetic diversity in subdivided populations. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1367–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Valdesalici, S.; Langeneck, J.; Barbieri, M.; Castelli, A.; Maltagliati, F. Distribution of natural populations of the killifish Aphanius fasciatus (Valenciennes, 1821) (Teleostei: Cyprinodontidae) in Italy: Past and current status, and future trends. It. J. Zool. 2015, 82, 212–223. [Google Scholar]
- Cimmaruta, R.; Scialanca, F.; Luccioli, F.; Nascetti, G. Genetic diversity and environmental stress in Italian populations of the cyprinodont fish Aphanius fasciatus. Oceanol. Acta 2003, 26, 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- European Environmental Agency (EEA). Report under the Article 17 of the Habitats Directive, Period 2007–2012; EEA: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2015.
- De Mitri, R. Pesci e crostacei decapodi del bacino di Acquatina (Lecce). Thalass. Salentina 2004, 27, 21–32. [Google Scholar]
- Denitto, F. (Department Biological and Environmental Sciences and Technologies, University of Salento, Lecce, Italy). Personal communication, 2002.
- Zonno, V. (Department Biological and Environmental Sciences and Technologies, University of Salento, Lecce, Italy). Personal communication, 2012.
- Bianchi, C.N. (Department for the Study of the Territory and its Resources, University of Genoa, Genoa, Italy). Personal communication, 1994.
- Costa, O.G. Genere Lebia. In Fauna del Regno di Napoli. Pesci. Parte Prima; Stabilimento Tipografico Fr. Azzolino: Napoli, Italy, 1850; pp. 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Cavicchioli, G. Considerazioni bio-ecologiche sopra Aphanius fasciatus Valenciennes (Cyprinodontidae). Boll. Zool. 1962, 29, 713–719. [Google Scholar]
- Baldacconi, R. (Department Zoology, University of Bari, Bari, Italy). Personal communication, 2013.
- Tigano, C.; Ferrito, V. Studio biometrico e morfologico in popolazioni di Aphanius fasciatus (Nardo) dell’Adriatico e di Sicilia (Pisces, Cyprinodontidae). Nova Thalass. 1984, 6, 679–680. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrito, V.; Maltagliati, F.; Maceri, A.; Adorno, A.; Tigano, C. Morphological and genetic variation in four Italian populations of Lebias fasciata (Teleostei, Cypridontidae). Ital. J. Zool. 2003, 70, 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrito, V.; Mannino, M.C.; Pappalardo, A.M.; Tigano, C. Morphological variation among populations of Aphanius fasciatus Nardo, 1827 (Teleostei, Cyprinodontidae) from the Mediterranean. J. Fish Biol. 2007, 70, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Manzo, C. Fish Assemblages in Three Mediterranean Coastal Lagoons: Structure, Functioning and Spatio-Temporal Dynamics. Ph.D. Thesis, Università di Roma “Tor Vergata”, Rome, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cepollaro, F. (Department Biology, University of Padua, Padua, Italy). Personal communication, 2006.
- Valdesalici, S. (Associazione Italiana Killifish, Viano, Italy). Personal communication, 2008.
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gönenç, I.E.; Wolflin, J.P. Coastal Lagoons Ecosystem Processes and Modeling for Sustainable Use and Development; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, A.; Brito, A.C.; Icely, J.D.; Derolez, V.; Clara, I.; Angus, S.; Schernewski, G.; Inacio, M.; Lillebø, A.I.; Sousa, A.I.; et al. Assessing, quantifying and valuing the ecosystem services of coastal lagoons. J. Nat. Conserv. 2018, 44, 50–65. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, M.V.; Helali, M.A.; Zaaboub, N.; Boukef-BenOmrane, I.; Frontalini, F.; Reis, D.; Portela, H.; Clemente, I.M.; Nogueira, L.; Pereira, E.; et al. Organic matter quantity and quality, metals availability and foraminiferal assemblages as environmental proxy applied to the Bizerte Lagoon (Tunisia). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 105, 161–179. [Google Scholar]
- Lacoste, E.; Jones, A.; Callier, M.; Klein, J.; Lagarde, F.; Derolez, V. A Review of Knowledge on the Impacts of Multiple Anthropogenic Pressures on the Soft-Bottom Benthic Ecosystem in Mediterranean Coastal Lagoons. Estuaries Coast. 2023, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeónLeon, V.M.; Moreno-GonzálezGonzalez, R.; GarcíaGarcia, V.; Campillo, J.A. Impact of flash flood events on the distribution of organic pollutants in surface sediments from a Mediterranean coastal lagoon (Mar Menor, SE Spain). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 4284–4300. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Salem, F.; Ben Said, O.; Cravo-Laureau, C.; Mahmoudi, E.; Bru, N.; Monperrus, M.; Duran, R. Bacterial community assemblages in sediments under high anthropogenic pressure at Ichkeul Lake/Bizerte Lagoon hydrological system, Tunisia. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 644–656. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chambers, J.E.; Boone, J.S.; Carr, R.L.; Chambers, H.W.; Straus, D.L. Biomarkers as predictors in health and ecological risk assessment. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Manag. 2002, 8, 165–176. [Google Scholar]
- Connon, R.E.; Geist, J.; Werner, I. Effect-based tools for monitoring and predicting the ecotoxicological effects of chemicals in the aquatic environment. Sensors 2012, 12, 12741–12771. [Google Scholar]
- Hook, S.E.; Gallagher, E.P.; Batley, G.E. The role of biomarkers in the assessment of aquatic ecosystem health. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2014, 10, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kroon, F.; Streten, C.; Harries, S. A protocol for identifying suitable biomarkers to assess fish health: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174762. [Google Scholar]
- Varanasi, U.; Stein, J.E. Disposition of xenobiotic chemicals and metabolites in marine organisms. Environ. Health Perspect. 1991, 90, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kessabi, K.; Hwas, Z.; Sassi, A.; Said, K.; Messaoudi, I. Heavy metal accumulation and histomorphological alterations in Aphanius fasciatus (Pisces, Cyprinodontidae) from the Gulf of Gabes (Tunisia). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 14099–14109. [Google Scholar]
- Lionetto, M.G.; Giordano, M.E.; Caricato, R.; Pascariello, M.F.; Marinosci, L.; Schettino, T. Biomonitoring of heavy metal contamination along the salento Coast (Italy) by metallothionein evaluation in Mytilus galloprovincialis and Mullus barbatus. Aquat. Conserv. 2001, 11, 305–310. [Google Scholar]
- Calisi, A.; Lionetto, M.G.; Lemanni, A.; De Lorenzis, E.; Schettino, T. Metallothionein induction in the coelomic fluid of the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris following heavy metal exposure: A short report. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 109386. [Google Scholar]
- Samuel, M.S.; Datta, S.; Khandge, R.S.; Selvarajan, E. A state of the art review on characterization of heavy metal binding metallothioneins proteins and their widespread applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145829. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, N.; Yamamoto, M.; Watanabe, K.; Kambegawa, A.; Hattori, A. Both mercury and cadmium directly influence calcium homeostasis resulting from the suppression of scale bone cells: The scale is a good model for the evaluation of heavy metals in bone metabolism. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2004, 22, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messaoudi, I.; Kessabi, K.; Kacem, A.; Said, K. Incidence of spinal deformities in natural populations of Aphanius fasciatus Nardo, 1827 from the Gulf of Gabes, Tunisia. Afr. J. Ecol. 2009, 3, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slooff, W. Skeletal anomalies in fish from polluted surface waters. Aquat. Toxicol. 1982, 2, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, B.G.; Tanabe, S.; Tatsukawa, R.; Ogawa, K.; Miyako, G. Temporal changes of morphological abnormalitiesand parasitic infestation in fishes from the river Nagaragawa, Japan. Nippon. Suisan Gakkaishi 1989, 55, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Whittle, D.M.; Sergeant, D.B.; Huestis, S.Y.; Hyatt, W.H. Food chain accumulation of PCDF isomers in the Great Lakesaquatic community. Chemosphere 1992, 25, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, T.; Kobayashi, E.; Suwazono, Y. Mirei Uetani, Mitsuhiro Oishi, Hideaki Nakagawa, Koji Nogawa. Estimation of cumulative cadmium intake causing Itai–itai disease. Toxicol. Lett. 2005, 159, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetto, M.G.; Caricato, R.; Giordano, M.E. Pollution biomarkers in environmental and human biomonitoring. Open Biomark. J. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Martínez, L.; Martínez-Subiela, S.; Cerón, J.J.; Tecles, F.; Eckersall, P.D.; Oravcova, K.; Tvarijonaviciute, A. Biomarkers of health and welfare: A One Health perspective from the laboratory side. Res. Vet. Sci. 2020, 128, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annabi, A.; Said, K.; Messaoudi, I. Cadmium: Bioaccumulation, histopathology and detoxifying mechanisms in Fish. Am. J. Res. Comm. 2013, 1, 60–79. [Google Scholar]
- Mosesso, P.; Angeletti, D.; Pepe, G.; Pretti, C.; Nascetti, G.; Bellacima, R.; Cimmaruta, R.; Jha, A.N. The use of cyprinodont fish, Aphanius fasciatus, as a sentinel organism to detect complex genotoxic mixtures in the coastal lagoon ecosystem. Mutat. Res. 2012, 742, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebbio, C.; Carere, C.; Nascetti, G.; Bellisario, B.; Mosesso, P.; Cimmaruta, R.; Angeletti, D. Interspecies variation in DNA damage induced by pollution. Curr. Zool. 2014, 60, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, N.M.; Whitehead, A. Functional genomics to assess biological responses to marine pollution at physiological and evolutionary timescales: Toward a vision of predictive ecotoxicology. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2016, 15, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terzibasi-Tozzini, E.; Cellerino, A. Nothobranchius annual killifishes. EvoDevo 2020, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtze, S.; Gorshkova, E.; Braude, S.; Cellerino, A.; Dammann, P.; Hildebrandt, T.B.; Hoeflich, A.; Hoffmann, S.; Koch, P.; Terzibasi-Tozzini, E.; et al. Alternative Animal Models of Aging Research. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 660959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Solano, A.; Nester, T.L.; Perea, S.; Doadrio, I. Complete mitochondrial genome of the Spanish toothcarp, Aphanius iberus (Valenciennes, 1846) (Actinopterygii, Aphaniidae) and its phylogenetic position within the Cyprinodontiformes order. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 2953–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

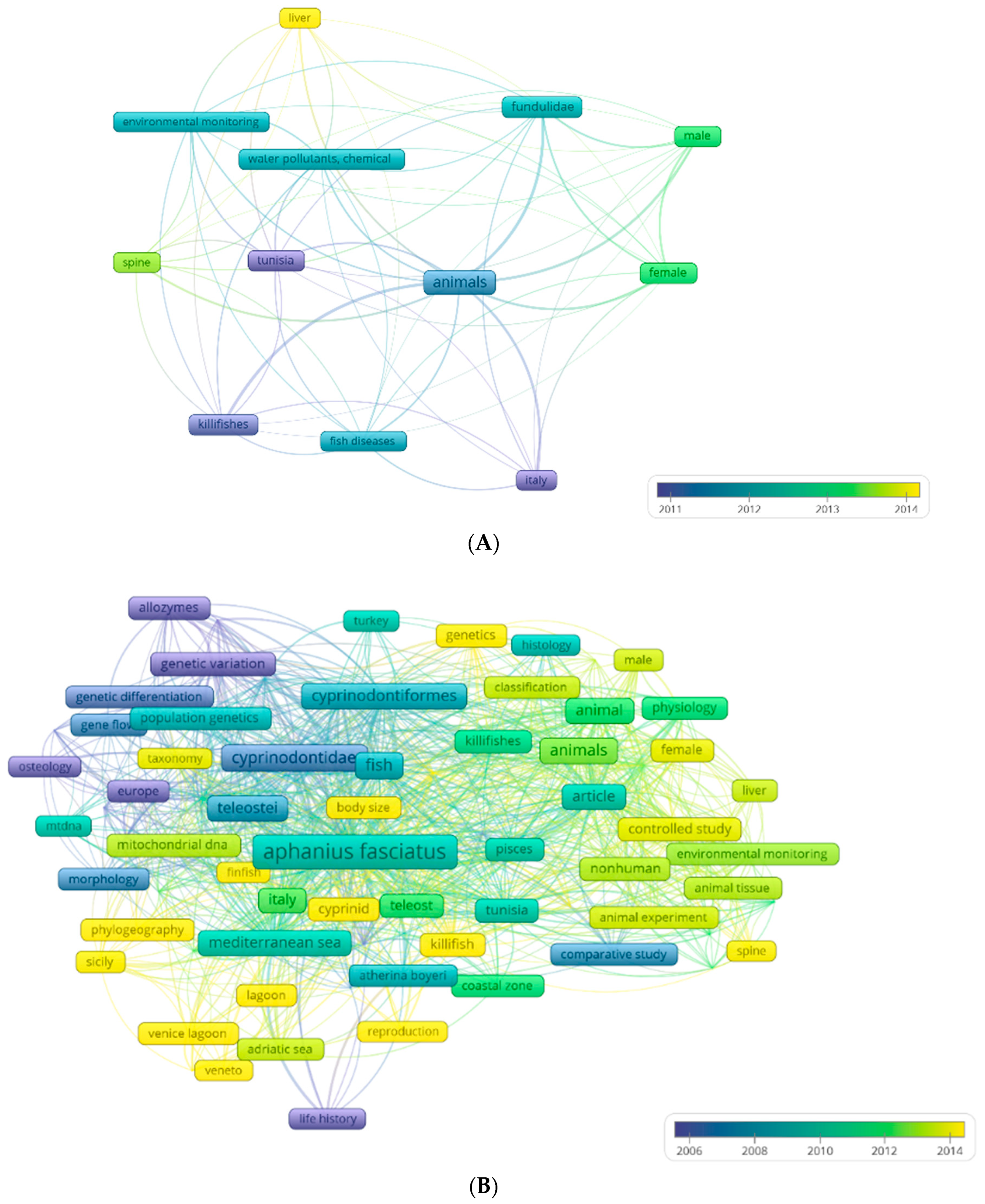
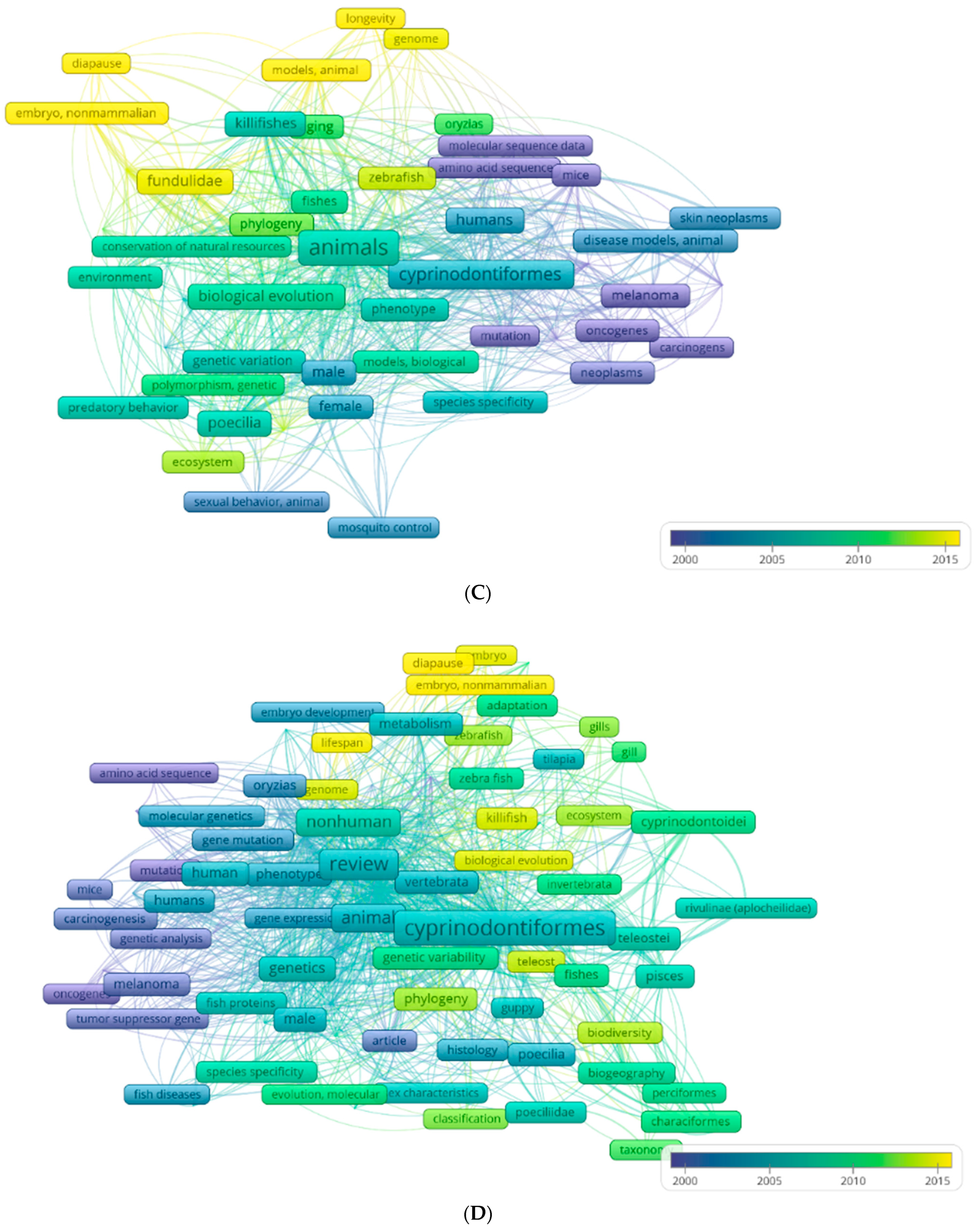
| Order (Suborder) | Family | Genus | Species | Sequenced Genomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyprinodontiformes (killifish and others) | 66 | |||
| (Aplocheiloidei) | Rivulidae (New World rivulines) | Austrofundulus | Austrofundulus limnaeus | 1 £ |
| Kryptolebias | Kryptolebias brasiliensis | 1 £ | ||
| Kryptolebias gracilis | 1 £ | |||
| Kryptolebias hermaphroditus | 1 $ | |||
| Kryptolebias marmoratus (mangrove rivulus) | 2 $ | |||
| Kryptolebias ocellatus (sardinita) | 1 £ | |||
| Nematolebias | Nematolebias whitei (Rio pearlfish) | 1 $ | ||
| Nothobranchiidae | Aphyosemion | Aphyosemion australe (lyretail killifish) | 1 £ | |
| Callopanchax | Callopanchax toddi | 1 £ | ||
| Nothobranchius | Nothobranchius furzeri (turquoise killifish) | 6 £ | ||
| Nothobranchius kuhntae (Beira killifish) | 2 £ | |||
| Aplocheilidae (rivulines) | Pachypanchax | Pachypanchax playfairii (golden panchax) | 1 £ | |
| (Cyprinodontoidei) | Anablepidae | Anableps | Anableps anableps (largescale foureyes) | 2 $ |
| Aphaniidae | Aphanius | Aphanius iberus (Spanish toothcarp) | 1 £ | |
| Fluviphylacidae | - | - | - | |
| Goodeidae (goodeids) | Girardinichthys | Girardinichthys multiradiatus | 1 $ | |
| Cyprinodontidae (killifish) | Cyprinodon | Cyprinodon brontotheroides | 1 £ | |
| Cyprinodon variegatus (sheepshead minnow) | 1 £ | |||
| Cyprinodon nevadensis (Amargosa pupfish) | 1 £ | |||
| Cyprinodon tularosa | 1 & | |||
| Poeciliidae (livebearers) | Alfaro | Alfaro cultratus | 1 £ | |
| Brachyrhaphis | Brachyrhaphis roseni | 1 £ | ||
| Brachyrhaphis terrabensis | 1 £ | |||
| Gambusia | Gambusia holbrooki (eastern mosquitofish) | 1 £ | ||
| Gambusia affinis (western mosquitofish) | 2 $ | |||
| Girardinus | Girardinus metallicus (metallic livebearer) | 1 £ | ||
| Micropoecilia | Micropoecilia bifurca | 1 £ | ||
| Phalloptychus | Phalloptychus januarius | 1 & | ||
| Poecilia | Poecilia mexicana (shortfin molly) | 1 £ | ||
| Poecilia formosa (Amazon molly) | 3 £ | |||
| Poecilia latipinna (sailfin molly) | 1 £ | |||
| Poecilia gillii (Gill’s molly) | 1 £ | |||
| Poecilia reticulata (guppy) | 2 $ | |||
| Poecilia wingei | 1 £ | |||
| Poecilia picta (swamp guppy) | 2 & | |||
| Poeciliopsis | Poecilopsis turrubanensis | 1 £ | ||
| Poecilopsis paucimaculata | 1 £ | |||
| Poecilopsis occidentalis (Gila topminnow) | 1 £ | |||
| Poecilopsis infans (Lerma livebearer) | 1 £ | |||
| Poecilopsis prolifica (blackstripe livebearer) | 2 £ | |||
| Poecilopsis gracilis (portohole livebearer) | 2 & | |||
| Poecilopsis retropinna | 1 £ | |||
| Poecilopsis turneri (blackspotted livebearer) | 2 & | |||
| Poecilopsis presidionis (Sinaloa livebearer) | 1 £ | |||
| Xiphophorus | Xiphophorus hellerii (green swordtail) | 2 $ | ||
| Xiphophorus couchianus (Monterrey platyfish) | 1 $ | |||
| Xiphophorus maculatus (southern platyfish) | 2 $ | |||
| Profundulidae (Middle American killifish) | - | - | - | |
| Pandanodontidae | - | - | - | |
| Procatopodidae | - | - | - | |
| Fundulidae (topminnows) | Fundulus | Fundulus heteroclitus (mummichog) | 2 $ | |
| Valenciidae | - | - | - |
| Entrez Records | |
|---|---|
| Database Name | Number of Relevant Data Available |
| Nucleotide | 453 |
| Protein | 211 |
| Popset | 29 |
| PubMed Central | 31 |
| Identical Protein Groups | 79 |
| Taxonomy | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lionetto, M.G.; Zonno, V.; Schiavone, R.; Giordano, M.E.; Barca, A.; Belmonte, G.; Verri, T. The Mediterranean Killifish Aphanius fasciatus (Valenciennes, 1821) (Teleostei: Cyprinodontidae) as a Sentinel Species for Protection of the Quality of Transitional Water Environments: Literature, Insights, and Perspectives. Water 2023, 15, 2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152721
Lionetto MG, Zonno V, Schiavone R, Giordano ME, Barca A, Belmonte G, Verri T. The Mediterranean Killifish Aphanius fasciatus (Valenciennes, 1821) (Teleostei: Cyprinodontidae) as a Sentinel Species for Protection of the Quality of Transitional Water Environments: Literature, Insights, and Perspectives. Water. 2023; 15(15):2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152721
Chicago/Turabian StyleLionetto, Maria Giulia, Vincenzo Zonno, Roberta Schiavone, Maria Elena Giordano, Amilcare Barca, Genuario Belmonte, and Tiziano Verri. 2023. "The Mediterranean Killifish Aphanius fasciatus (Valenciennes, 1821) (Teleostei: Cyprinodontidae) as a Sentinel Species for Protection of the Quality of Transitional Water Environments: Literature, Insights, and Perspectives" Water 15, no. 15: 2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152721
APA StyleLionetto, M. G., Zonno, V., Schiavone, R., Giordano, M. E., Barca, A., Belmonte, G., & Verri, T. (2023). The Mediterranean Killifish Aphanius fasciatus (Valenciennes, 1821) (Teleostei: Cyprinodontidae) as a Sentinel Species for Protection of the Quality of Transitional Water Environments: Literature, Insights, and Perspectives. Water, 15(15), 2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152721









