VMD-GP: A New Evolutionary Explicit Model for Meteorological Drought Prediction at Ungauged Catchments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Global Drought Data
3. Methods
3.1. The Standardized Precipitation and Evapotranspiration Index
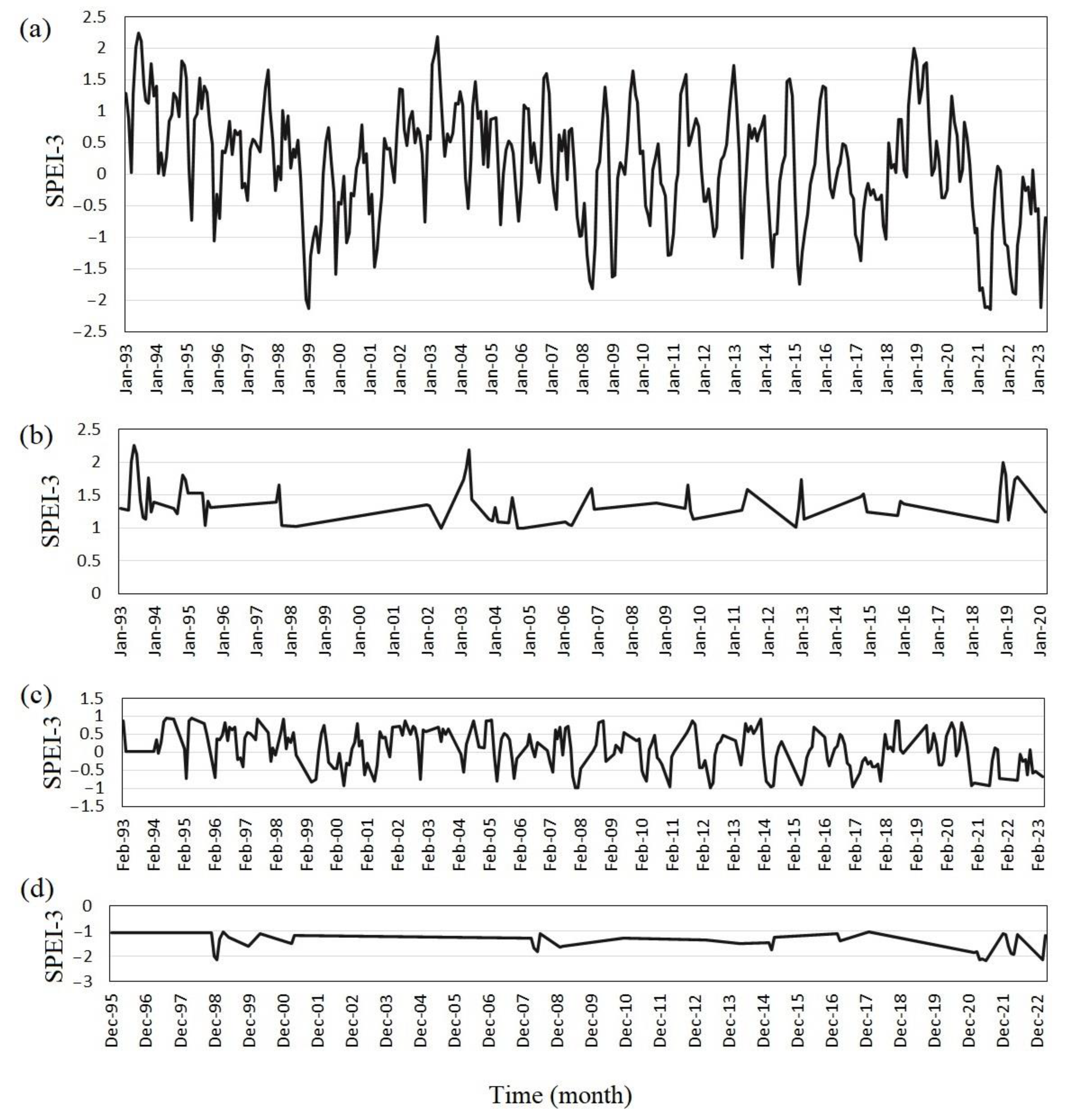
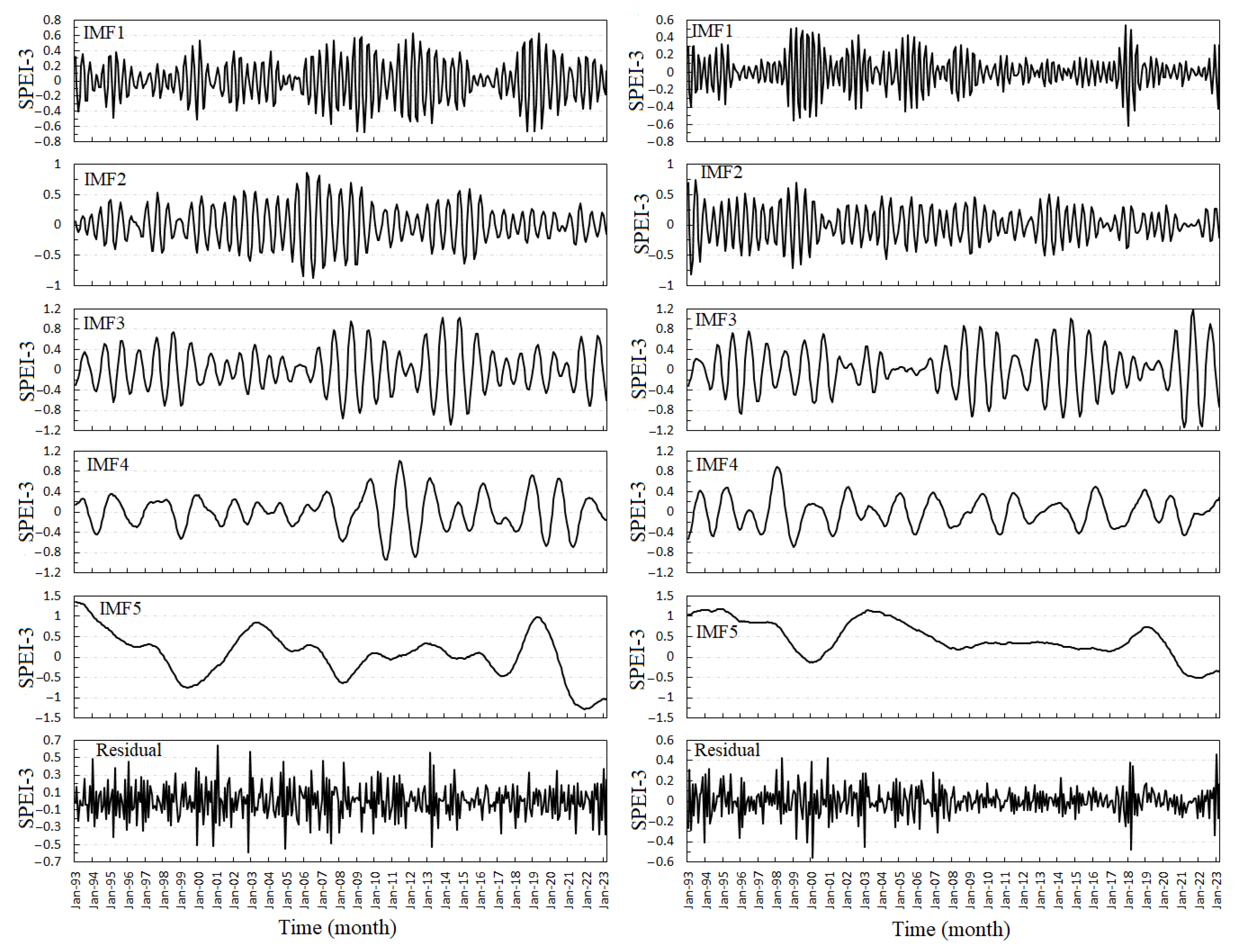
3.2. Variational Mode Decomposition (VMD)
3.3. State-of-the-Art Genetic Programming and Gene Expression Programming
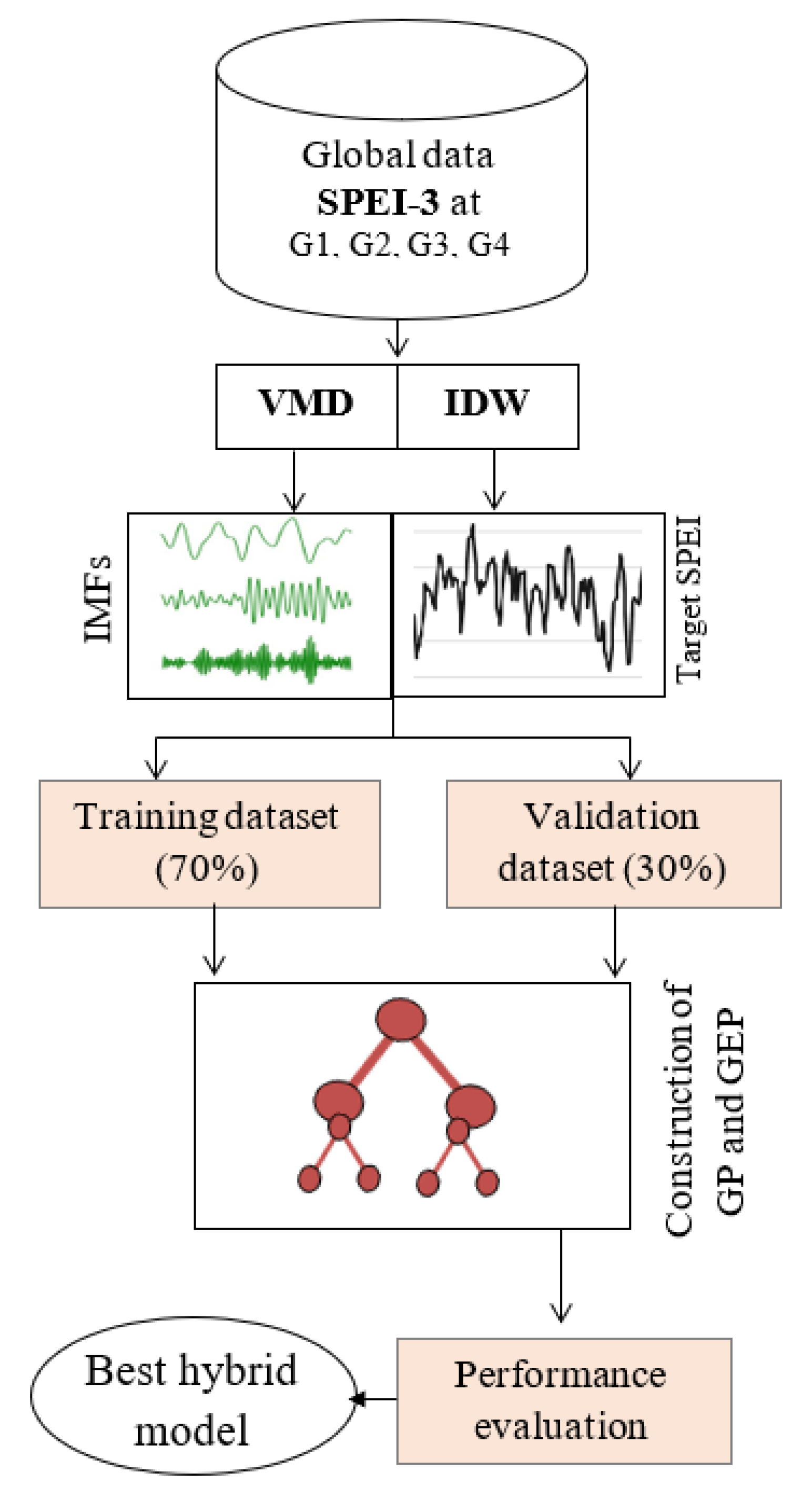
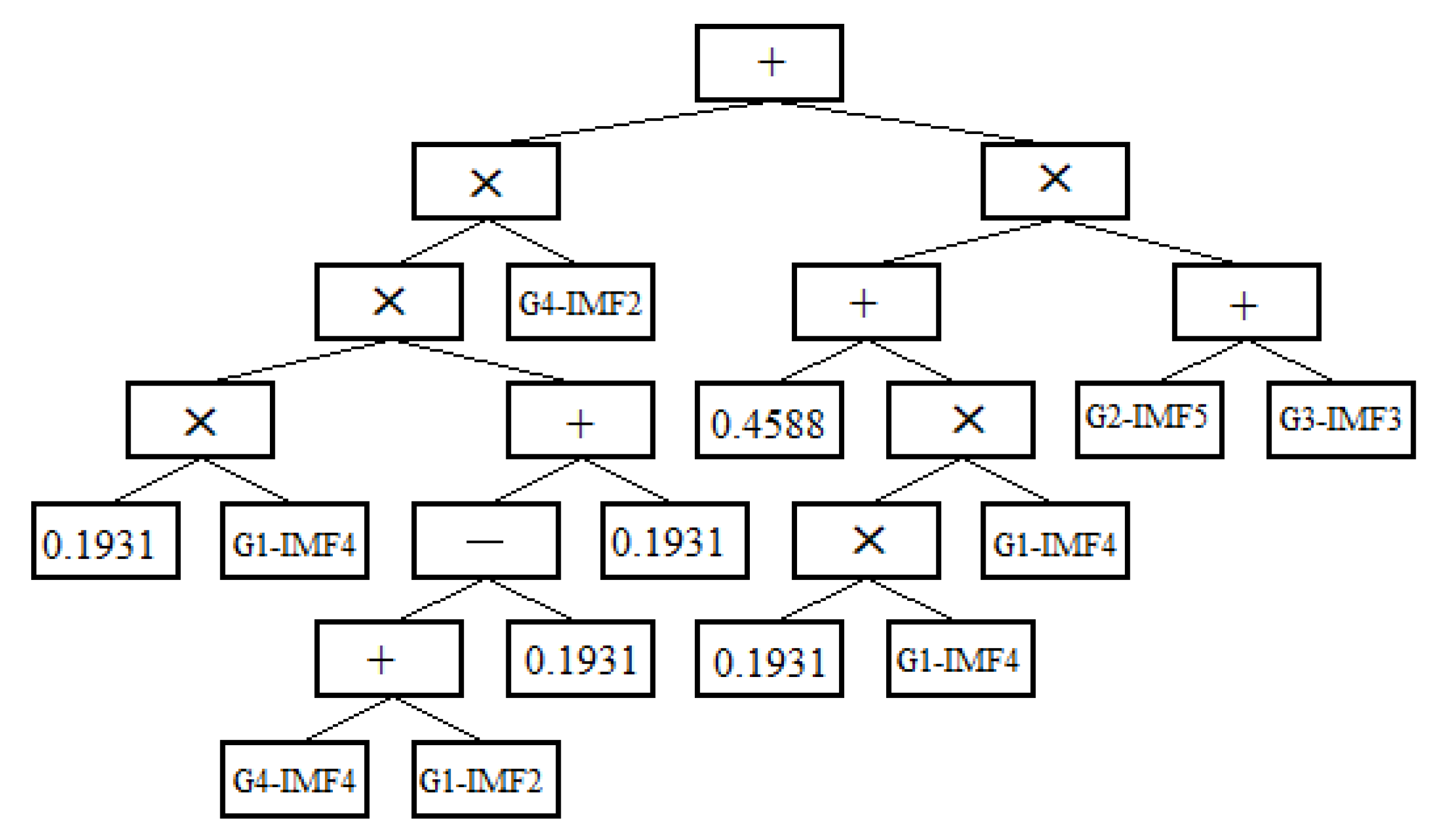
3.4. The Proposed Hybrid VMD-GP Model
3.5. Performance Evaluation
4. Results
4.1. Temporal Variation of SPEI-3 at Erbil
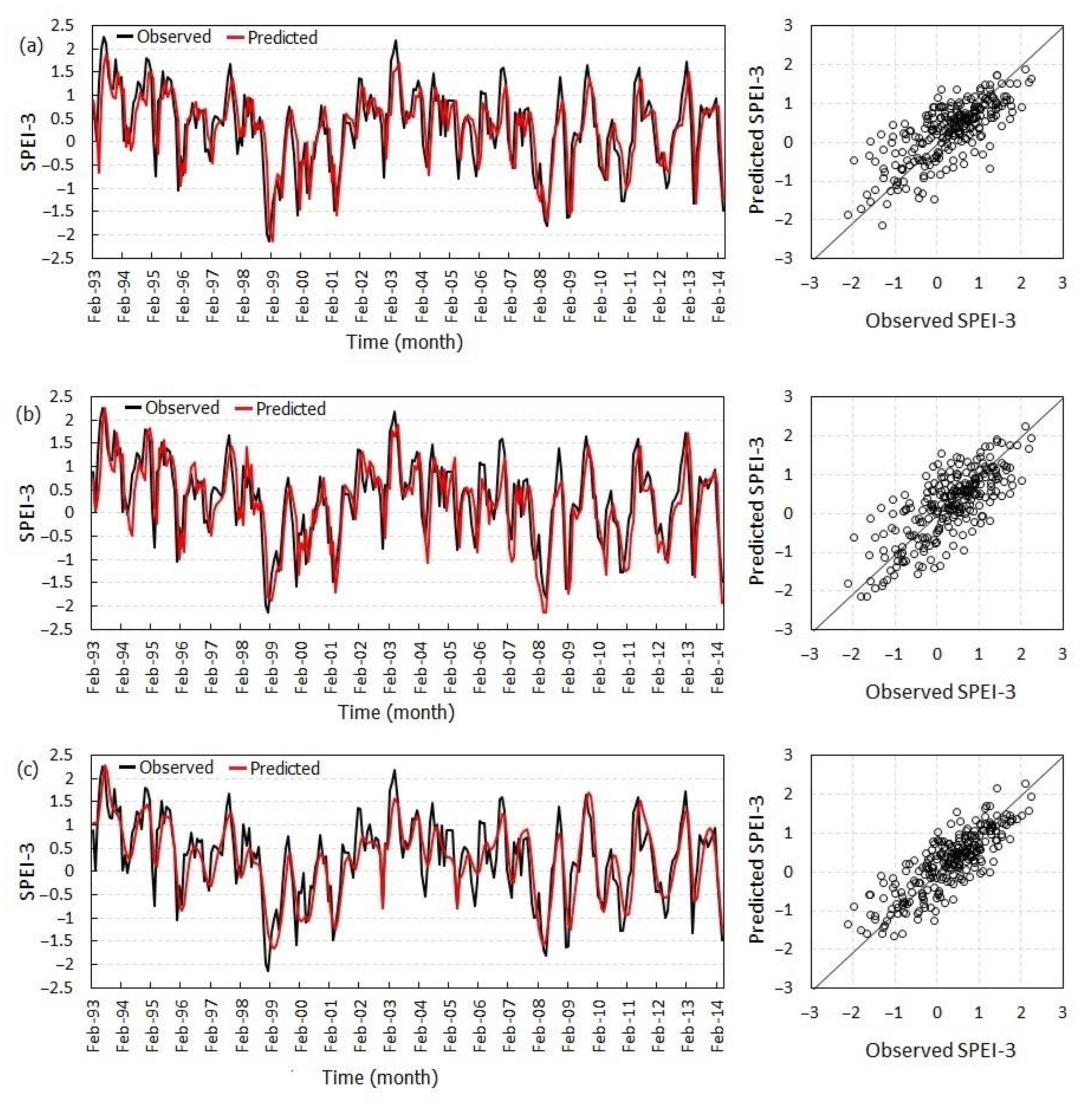
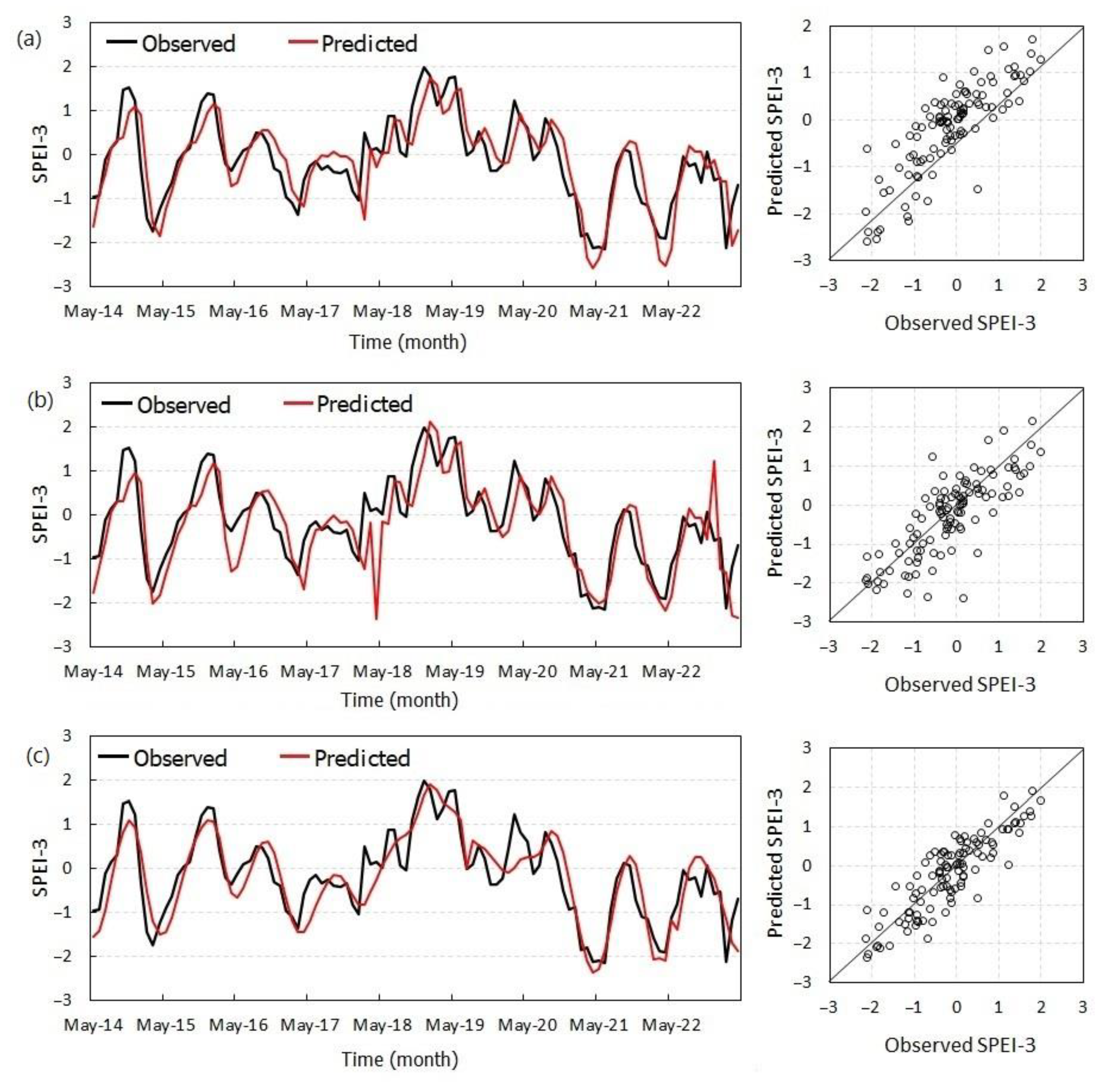
4.2. Benchmark Models
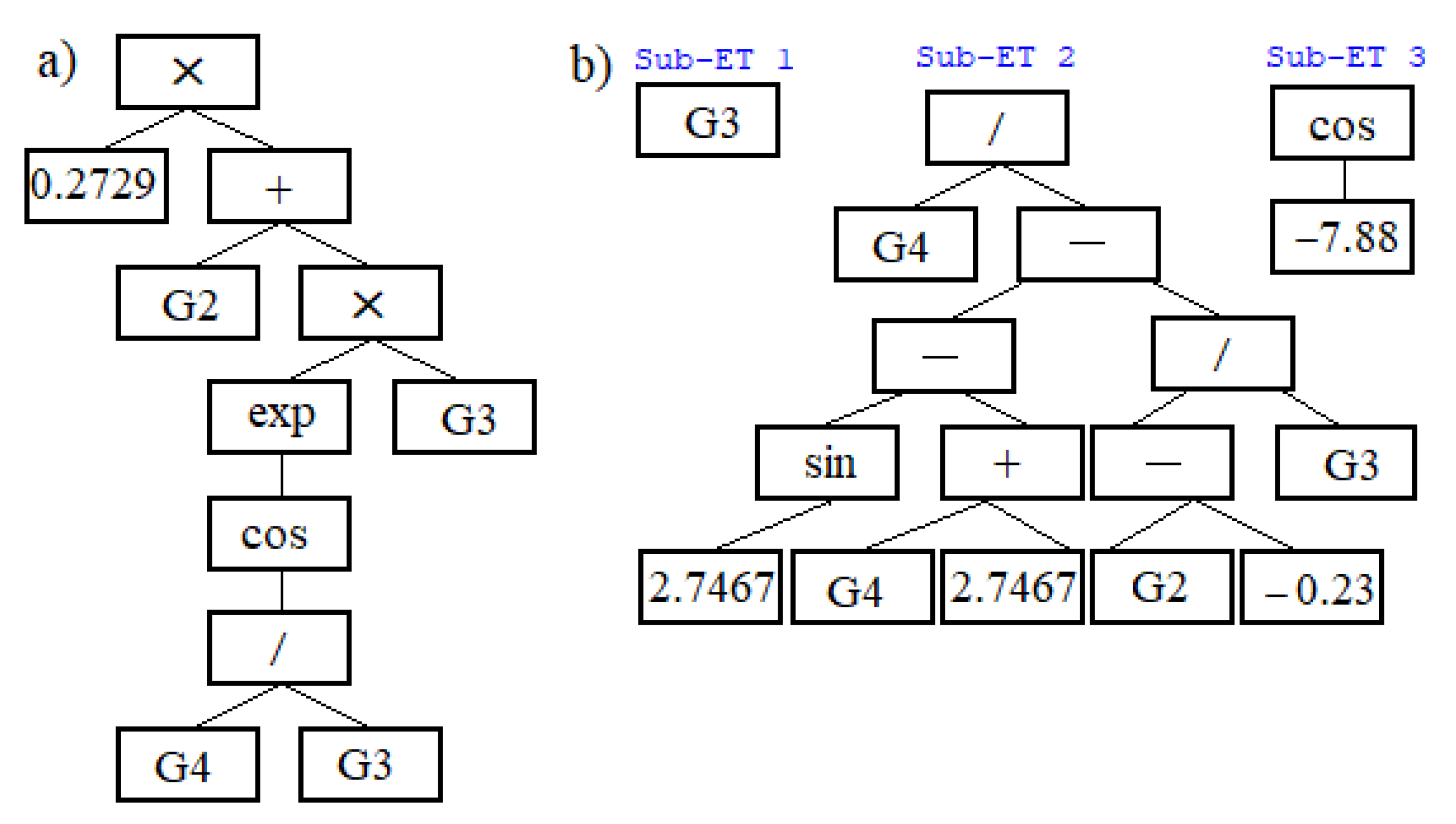
4.3. The Proposed VMD-GP Model
4.4. Models’ Comparison
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Xu, C.; Guo, S.; Chen, X. Toward Monitoring Short-Term Droughts Using a Novel Daily Scale, Standardized Antecedent Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index. J. Hydrometeorol. 2020, 21, 891–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Zscheischler, J.; Guo, S.; Chen, X.A. Standardized index for assessing sub-monthly compound dry and hot conditions with application in China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 1587–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Peng, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Ding, Y.; et al. The Impacts of Climate Change on Water Resources and Agriculture in China. Nature 2010, 467, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Sang, L.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, D. The isotopes of precipitation have climate change signal in arid Central Asia. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2023, 225, 104103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.; Zhou, W.; Li, T. Impact of the Indian Ocean Dipole on Evolution of the Subsequent ENSO: Relative Roles of Dynamic and Thermodynamic Processes. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 3591–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, M.E.; Lloyd, E.A.; Oreskes, N. Assessing Climate Change Impacts on Extreme Weather Events: The Case for an Alternative (Bayesian) Approach. Clim. Chang. 2017, 144, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Zhang, B.; Shao, S.; Hao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z. Risk assessment and zoning of flood disaster in Wuchengxiyu Region, China. Urban Clim. 2023, 49, 101562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, M.; Yin, Z.; Yin, L.; Zheng, W. Impact of dam construction on precipitation: A regional perspective. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2022, 74, 877–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, L.; Zhong, X.; Yao, T.; Qi, J.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Y. Quantifying the major drivers for the expanding lakes in the interior Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Qiu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, D.; Tang, B.; Cao, M. Elevation dependence of landslide activity induced by climate change in the eastern Pamirs. Landslides 2023, 20, 1115–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedri, R.; Piechota, T. Future Colorado River Basin Drought and Surplus. Hydrology 2022, 9, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolway, R.I.; Kraemer, B.M.; Lenters, J.D.; Merchant, C.J.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Sharma, S. Global Lake Responses to Climate Change. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghrebi, M.; Noori, R.; Mehr, A.D.; Lak, R.; Darougheh, F.; Razmgir, R.; Kløve, B. Spatiotemporal changes in Iranian rivers’ discharge. Elem. Sci. Anth. 2023, 11, 00002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wambura, F.J.; Dietrich, O. Analysis of Agricultural Drought Using Remotely Sensed Evapotranspiration in a Data-Scarce Catchment. Water 2020, 12, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danandeh Mehr, A.; Vaheddoost, B.; Mohammadi, B. ENN-SA: A Novel Neuro-Annealing Model for Multi-Station Drought Prediction. Comput. Geosci. 2020, 145, 104622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Huang, N.; Niu, Z.; Qin, Y.; Pei, J.; Wang, J. Mapping Winter Crops in China with Multi-Source Satellite Imagery and Phenology-Based Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, M.; Yin, Z.; Liu, X.; Yin, L.; Zheng, W. Remote sensing and geostatistics in urban water-resource monitoring: A review. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClean, F.; Dawson, R.; Kilsby, C. Intercomparison of Global Reanalysis Precipitation for Flood Risk Modelling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2023, 27, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Beguería, S.; López-Moreno, J.I. A Multiscalar Drought Index Sensitive to Global Warming: The Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Xu, C.Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, H. Similarity and Difference of Global Reanalysis Datasets (WFD and APHRODITE) in Driving Lumped and Distributed Hydrological Models in a Humid Region of China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 542, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyyedi, H.; Anagnostou, E.N.; Beighley, E.; McCollum, J. Hydrologic Evaluation of Satellite and Reanalysis Precipitation Datasets over a Mid-Latitude Basin. Atmos. Res. 2015, 164–165, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, F.; Li, J.; Liu, W.; Mao, T.; Xiong, Z.; Shangguan, W. Assessment of Agricultural Drought Using Soil Water Deficit Index Based on ERA5-Land Soil Moisture Data in Four Southern Provinces of China. Agriculture 2021, 11, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhmatova, N.; Arushanov, M.; Shardakova, L.; Nishonov, B.; Taryannikova, R.; Rakhmatova, V.; Belikov, D.A. Evaluation of the Perspective of ERA-Interim and ERA5 Reanalyses for Calculation of Drought Indicators for Uzbekistan. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Domínguez-Castro, F.; Reig, F.; Tomas-Burguera, M.; Peña-Angulo, D.; Latorre, B.; El Kenawy, A. A global drought monitoring system and dataset based on ERA5 reanalysis: A focus on crop-growing regions. Geosci. Data J. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa Alee, M.; Danandeh Mehr, A.; Akdegirmen, O.; Nourani, V. Drought Assessment across Erbil Using Satellite Products. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, M.; Ahmadalipour, A.; Moradkhani, H. Apprehensive Drought Characteristics over Iraq: Results of a Multidecadal Spatiotemporal Assessment. Geosciences 2018, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jasim, A.I.; Awchi, T.A. Regional Meteorological Drought Assessment in Iraq. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, S.O.; Kovács, F.; Tobak, Z. Spatiotemporal Assessment of Vegetation Indices Aand Land Cover for Erbil City And Its Surrounding Using Modis Imageries. J. Environ. Geogr. 2017, 10, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suliman, A.H.A.; Awchi, T.A.; Al-Mola, M.; Shahid, S. Evaluation of Remotely Sensed Precipitation Sources for Drought Assessment in Semi-Arid Iraq. Atmos. Res. 2020, 242, 105007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Timimi, Y.K.; George, L.E.; Al-Jiboori, M.H. Drought Risk Assessment in Iraq Using Remote Sensing And GIS Techniques. Iraqi J. Sci. 2012, 53, 1078–1082. [Google Scholar]
- Almamalachy, Y.S.; Al-Quraishi, A.M.F.; Moradkhani, H. Agricultural Drought Monitoring Over Iraq Utilizing MODIS Products. Environ. Remote Sens. GIS Iraq 2020, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Juboori, A.M. Prediction of Hydrological Drought in Semi-Arid Regions Using a Novel Hybrid Model. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 37, 3657–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danandeh Mehr, A.; Tur, R.; Çalışkan, C.; Tas, E. A Novel Fuzzy Random Forest Model for Meteorological Drought Classification and Prediction in Ungauged Catchments. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2020, 177, 5993–6006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehr, A.D.; Sorman, A.U.; Kahya, E.; Afshar, M. Climate Change Impacts on Meteorological Drought Using SPI and SPEI: Case Study of Ankara, Turkey. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2019, 65, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomiretskiy, K.; Zosso, D. Variational Mode Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Feng, F.; Zhu, J.; Wu, C.; Zhang, G. A Method for Determining Intrinsic Mode Function Number in Variational Mode Decomposition and Its Application to Bearing Vibration Signal Processing. Shock. Vib. 2020, 8304903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lin, J.; Liu, Z.; Wu, W. A Modified Scale-Space Guiding Variational Mode Decomposition for High-Speed Railway Bearing Fault Diagnosis. J. Sound Vib. 2019, 444, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, U.; Pal, S. Empirical Mode Decomposition vs. Variational Mode Decomposition on ECG Signal Processing: A Comparative Study. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics ICACCI, Jaipur, India, 21–24 September 2016; pp. 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koza, J.R. Genetic Programming as a Means for Programming Computers by Natural Selection. Stat. Comput. 1994, 4, 87–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babovic, V.; Keijzer, M. Genetic Programming as a Model Induction Engine. J. Hydroinform. 2000, 2, 35–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kisi, O.; Dailr, A.H.; Cimen, M.; Shiri, J. Suspended Sediment Modeling Using Genetic Programming and Soft Computing Techniques. J. Hydrol. 2012, 450–451, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C. Gene Expression Programming: Mathematical Modeling by an Artificial Intelligence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 21. [Google Scholar]
- Searson, D.P. GPTIPS 2: An Open-Source Software Platform for Symbolic Data Mining. In Handbook of Genetic Programming Applications; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 551–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brameier, M.; Banzhaf, W.; Banzhaf, W. Linear Genetic Programming; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandomi, A.H.; Alavi, A.H. Multi-Stage Genetic Programming: A New Strategy to Nonlinear System Modeling. Inf. Sci. 2011, 181, 5227–5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad-Azari, S.; Bozorg-Haddad, O.; Loáiciga, H.A. State-of-Art of Genetic Programming Applications in Water-Resources Systems Analysis. Environ. Monit. Assess 2020, 192, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzali, I.; Vanneschi, L.; Bakurov, I.; Silva, S.; Ivaldi, M.; Giacobini, M. Towards the Use of Vector Based GP to Predict Physiological Time Series. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 89, 106097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Althoff, D.; Rodrigues, L.N. Goodness-of-fit criteria for hydrological models: Model calibration and performance assessment. J. Hydrol. 2021, 600, 126674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrnjica, B.; Danandeh Mehr, A. Optimized Genetic Programming Applications; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2018; p. 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Prasad, R.; Xiang, Y.; Khan, M.; Ahsan Farooque, A.; Zong, T.; Yaseen, Z.M. Variational Mode Decomposition Based Random Forest Model for Solar Radiation Forecasting: New Emerging Machine Learning Technology. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 6700–6717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Wu, J.; Cui, H.; Hu, T. Drought prediction based on feature-based transfer learning and time series imaging. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 101454–101468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danandeh Mehr, A.; Rikhtehgar Ghiasi, A.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Sorman, A.U.; Abualigah, L. A Novel Intelligent Deep Learning Predictive Model for Meteorological Drought Forecasting. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2023, 14, 10441–10455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danandeh Mehr, A.; Torabi Haghighi, A.; Jabarnejad, M.; Safari, M.J.S.; Nourani, V. A New Evolutionary Hybrid Random Forest Model for SPEI Forecasting. Water 2022, 14, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, R.; Yılmaz, H.; Danandeh Mehr, A. Multitemporal Meteorological Drought Forecasting Using Bat-ELM. Acta Geophys. 2022, 70, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

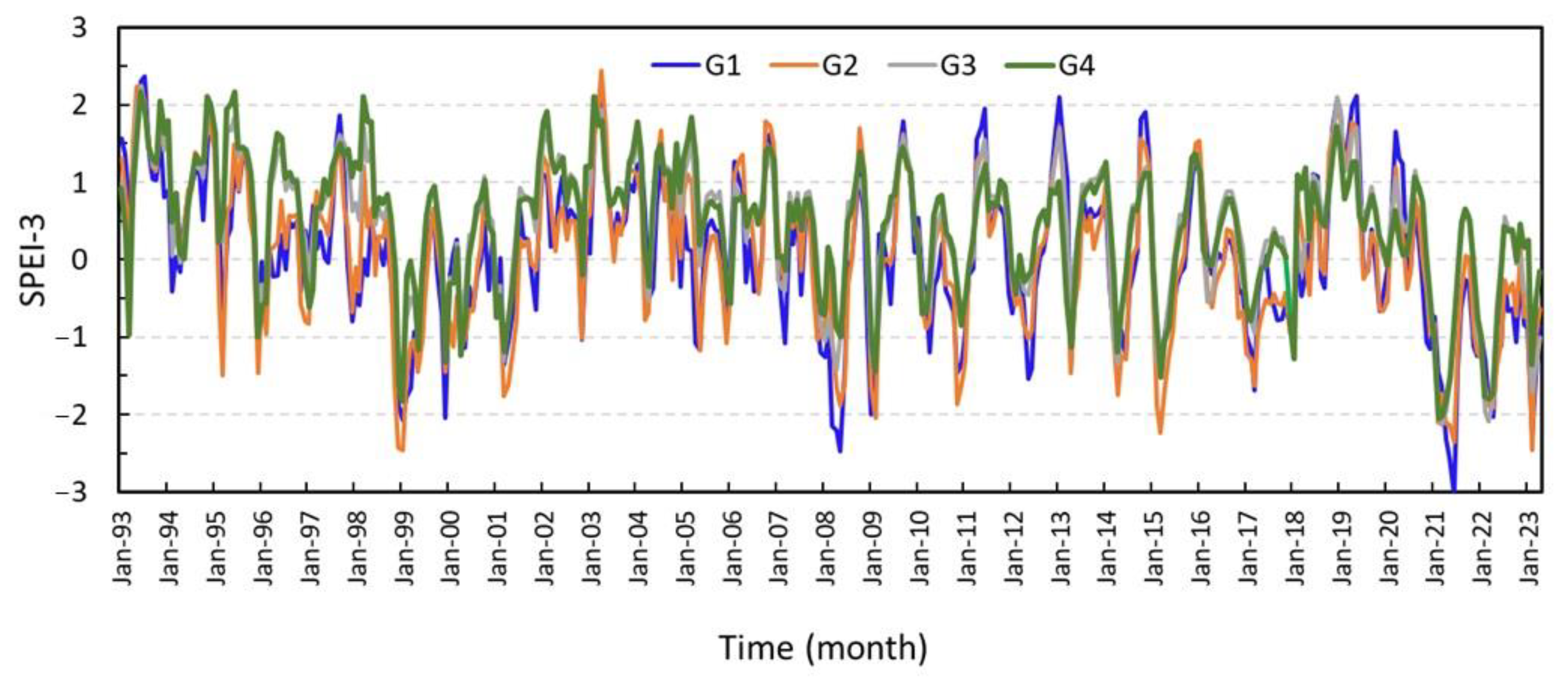

| Grid Point | Distance * (km) | Long. | Lat. | Min | Max | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 24.22 | 43.75 | 36.25 | −3.035 | 2.363 | 0.053 |
| G2 | 22.30 | 44.25 | 36.25 | −2.462 | 2.449 | 0.067 |
| G3 | 53.60 | 43.75 | 35.75 | −2.132 | 2.257 | 0.440 |
| G4 | 52.85 | 44.25 | 35.75 | −2.048 | 2.174 | 0.458 |
| Parameter | GP | GEP |
|---|---|---|
| Population size | 500 | 500 |
| Mutation Rate | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Crossover Rate | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| Reproduction rate | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Maximum genes (trees) | 1 | 3 |
| Maximum number of generations | 1000 | 1000 |
| Max tree depth | 7 | 5 |
| Linking function | NA * | Addition |
| Tree initialization | Half and Half | Half and Half |
| Selection method | Rank selection | Rank selection |
| Function set elements | +, −, ×, ÷, sin, cos, Exp | +, −, ×, ÷, sin, cos, Exp |
| Training | Testing | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Models | RMSE | NSE | KGE | RMSE | NSE | KGE |
| GP | 0.586 | 0.528 | 0.703 | 0.549 | 0.673 | 0.803 |
| GEP | 0.611 | 0.485 | 0.620 | 0.639 | 0.557 | 0.113 |
| VMD-GP | 0.487 | 0.674 | 0.735 | 0.476 | 0.754 | 0.532 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Danandeh Mehr, A.; Reihanifar, M.; Alee, M.M.; Vazifehkhah Ghaffari, M.A.; Safari, M.J.S.; Mohammadi, B. VMD-GP: A New Evolutionary Explicit Model for Meteorological Drought Prediction at Ungauged Catchments. Water 2023, 15, 2686. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152686
Danandeh Mehr A, Reihanifar M, Alee MM, Vazifehkhah Ghaffari MA, Safari MJS, Mohammadi B. VMD-GP: A New Evolutionary Explicit Model for Meteorological Drought Prediction at Ungauged Catchments. Water. 2023; 15(15):2686. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152686
Chicago/Turabian StyleDanandeh Mehr, Ali, Masoud Reihanifar, Mohammad Mustafa Alee, Mahammad Amin Vazifehkhah Ghaffari, Mir Jafar Sadegh Safari, and Babak Mohammadi. 2023. "VMD-GP: A New Evolutionary Explicit Model for Meteorological Drought Prediction at Ungauged Catchments" Water 15, no. 15: 2686. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152686
APA StyleDanandeh Mehr, A., Reihanifar, M., Alee, M. M., Vazifehkhah Ghaffari, M. A., Safari, M. J. S., & Mohammadi, B. (2023). VMD-GP: A New Evolutionary Explicit Model for Meteorological Drought Prediction at Ungauged Catchments. Water, 15(15), 2686. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152686








