Isotope-Based Early-Warning Model for Monitoring Groundwater–Leachate Contamination Phenomena: First Quantitative Assessments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The field monitoring system can acquire physical and geochemical quantities related to the phenomenon and share them with the monitoring system;
- Analysis and forecasting methods describe the landfill evolution, predict its behavior and identify critical events based on alert thresholds (if available);
- The warnings and dissemination of alert messages to notify the relevant authorities about the forecasted critical event;
- Action plans and measures are to be activated based on the forecasting results obtained by applying the numerical model.
2. Materials and Methods
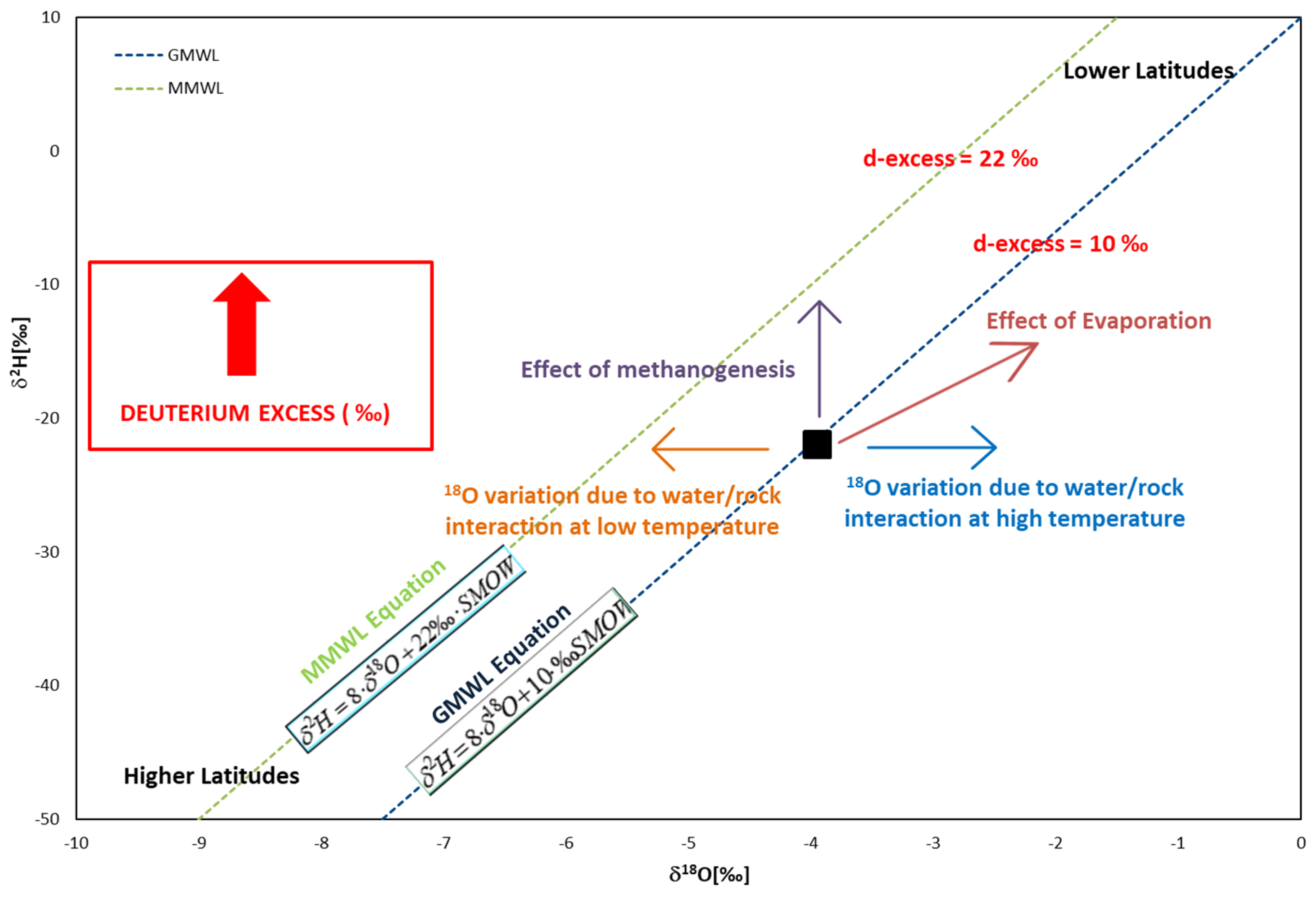
2.1. The Model
dREF = d2H − 8.21d18O = 18.15‰ (d-REFtheo) for reference of d-excess (Pian dell’Elmo station)
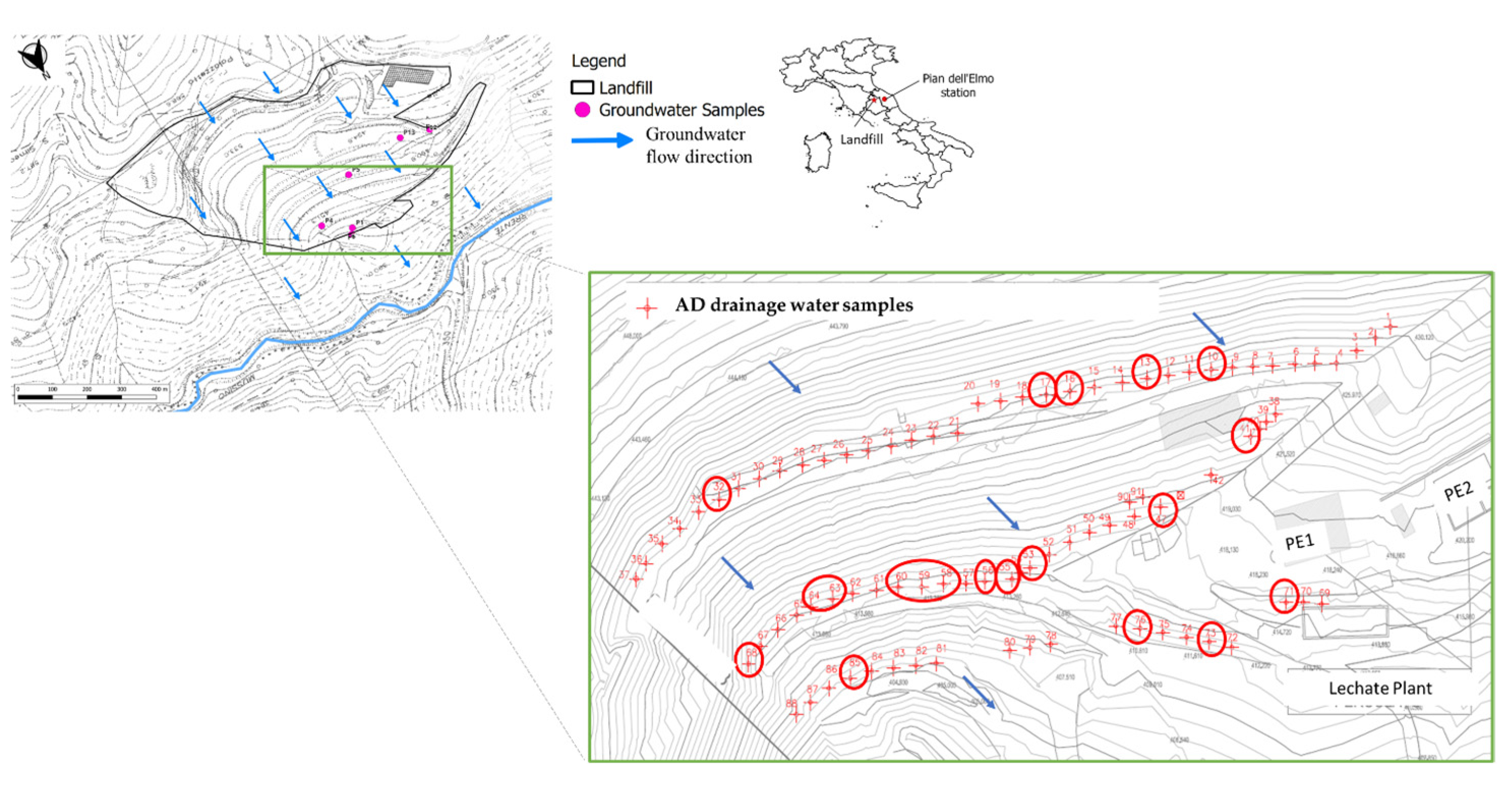
2.2. Study Area and Sampling Data
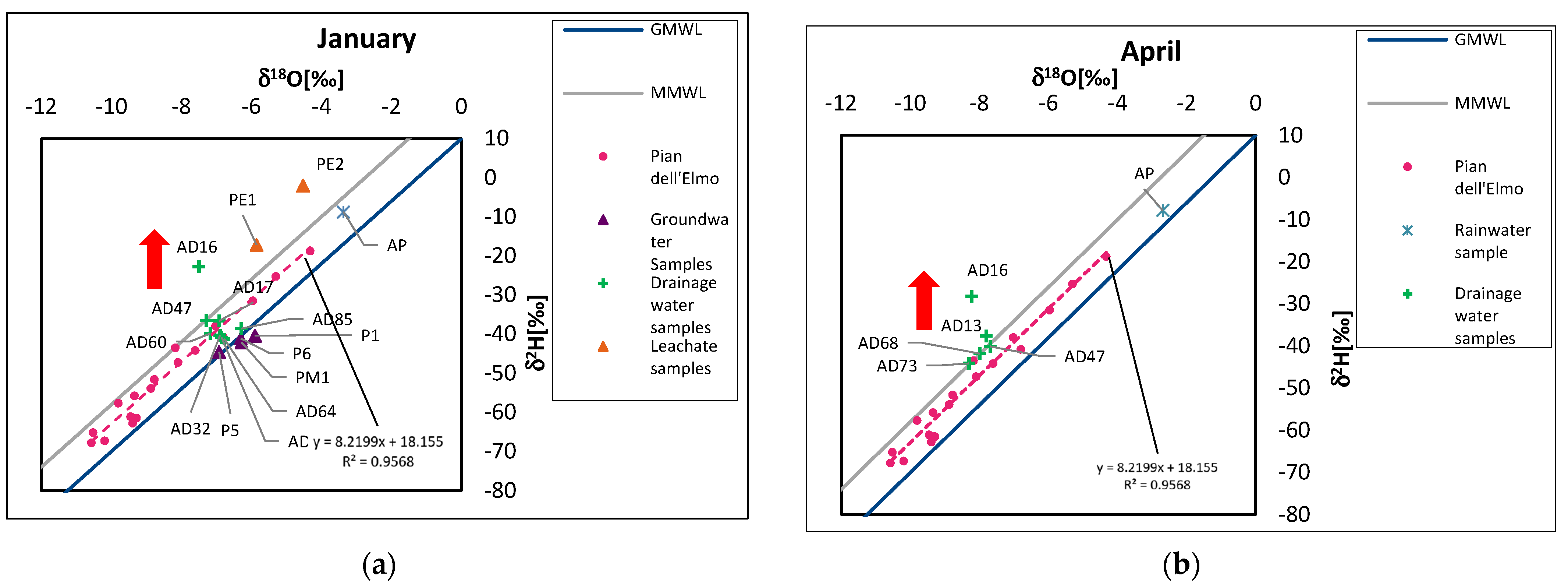
2.2.1. d2H and d18O Isotopes
2.2.2. Trace Elements Concentration: d2H and d18O
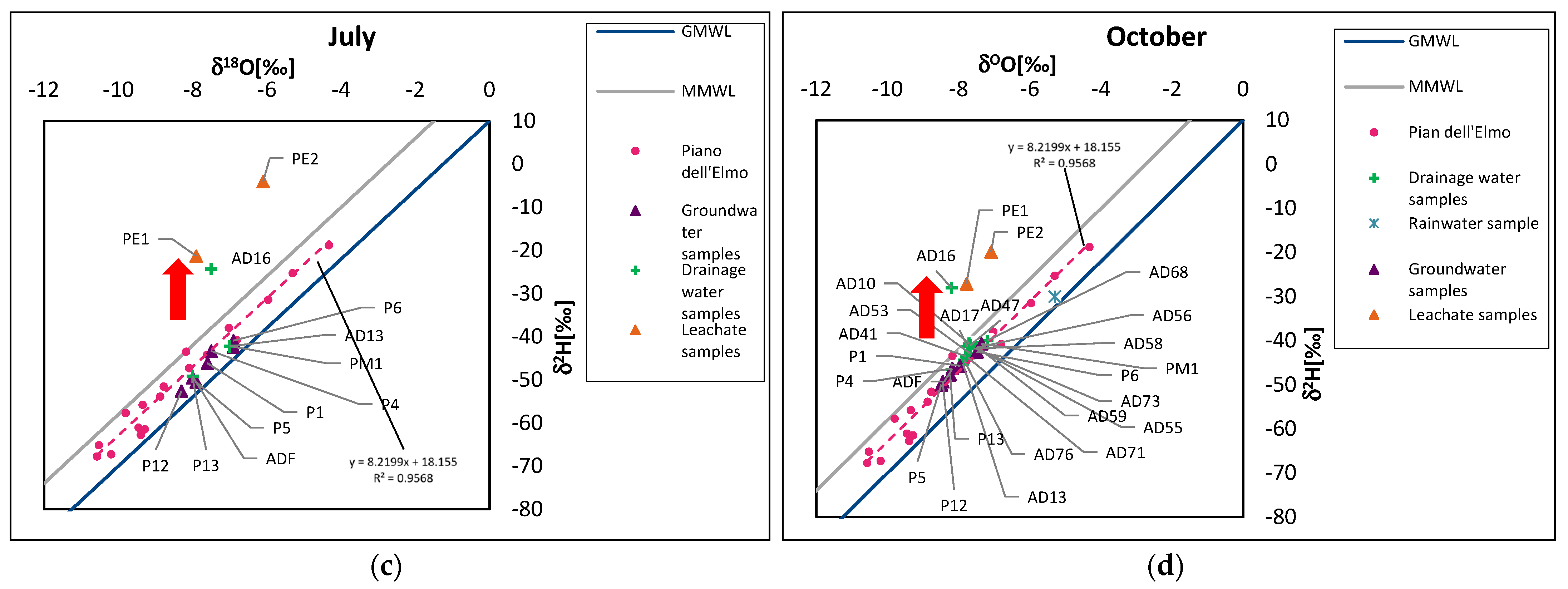
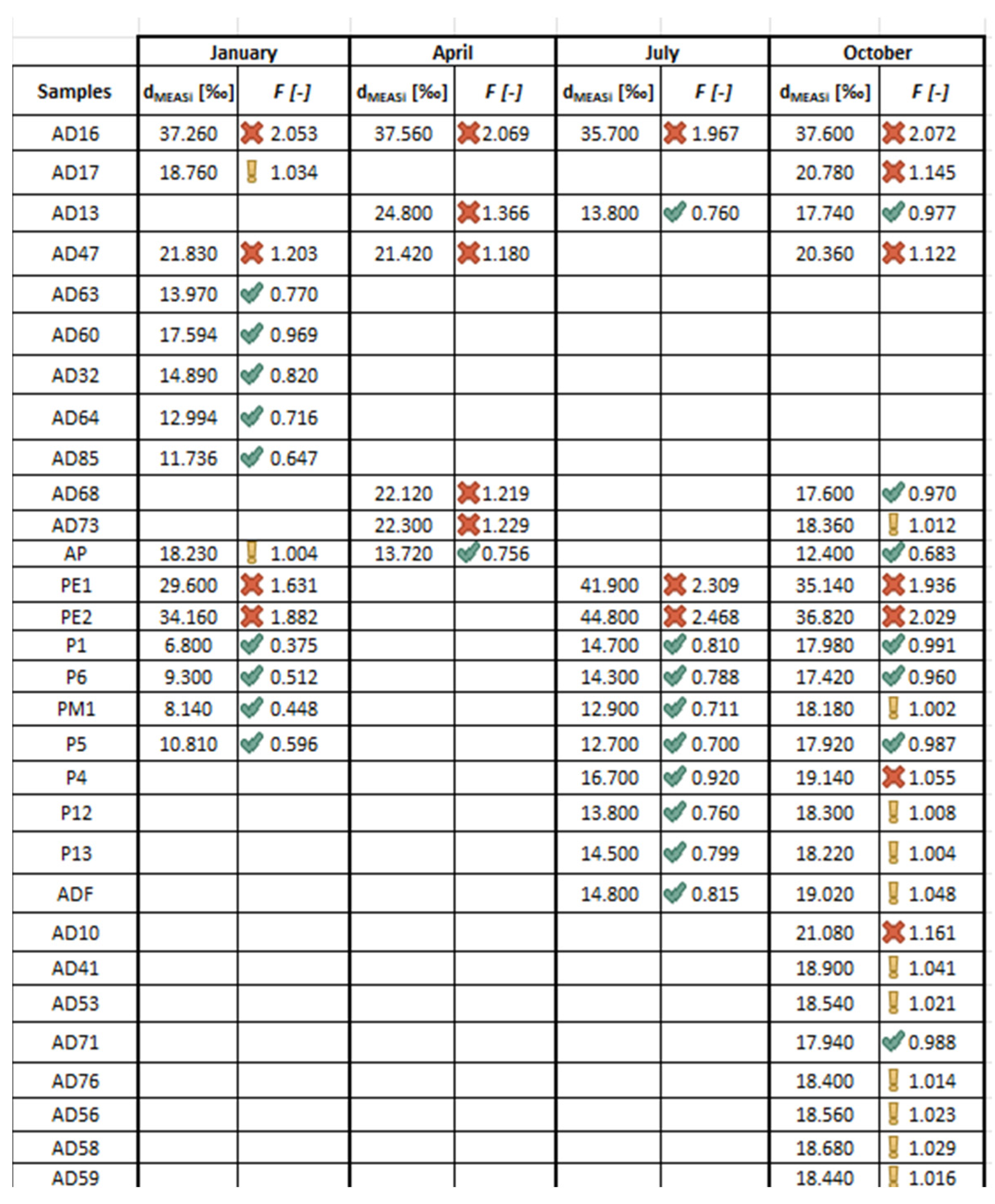
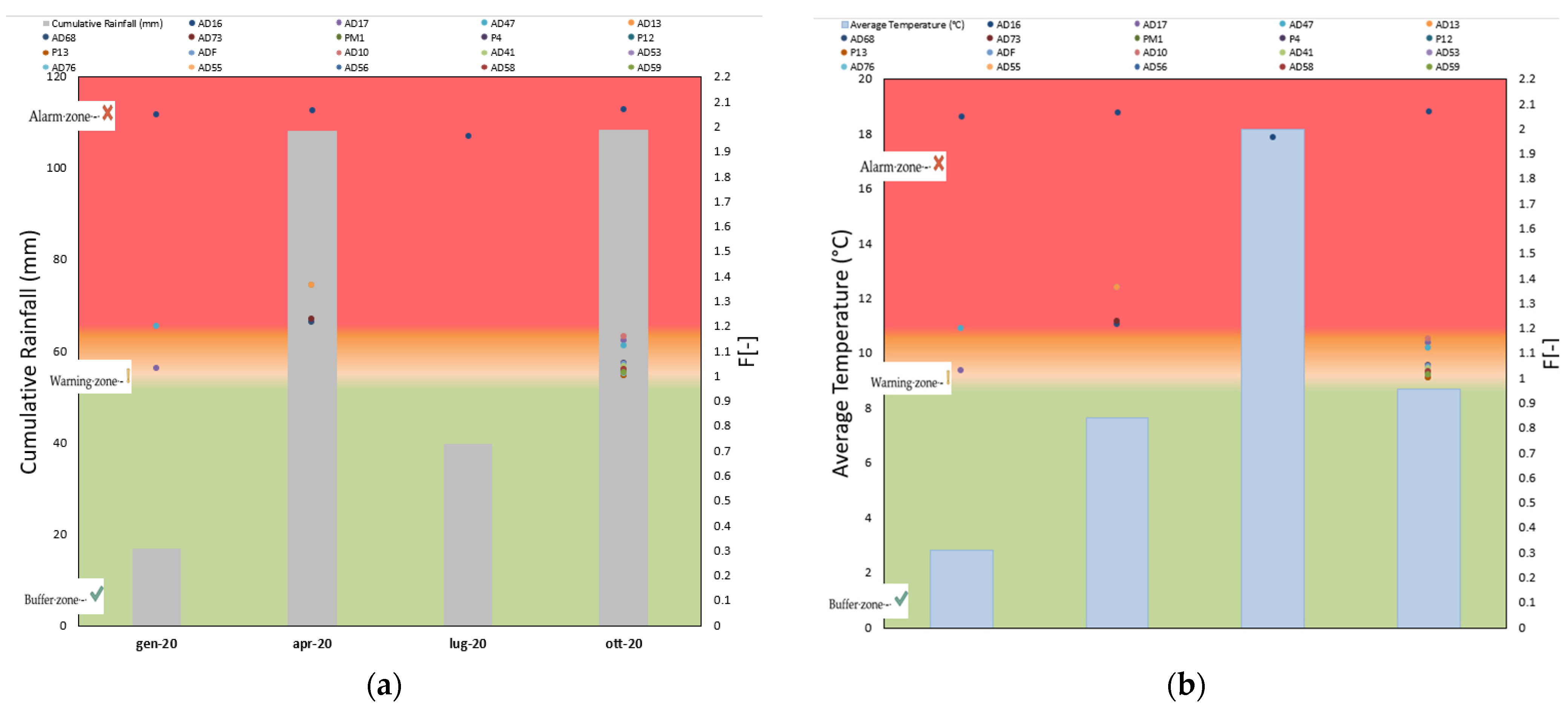
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abu Jabal, M.S.; Abustan, I.; Rozaimy, M.R.; El Najar, H. The deuterium and oxygen-18 isotopic composition of the groundwater in Khan Younis City, southern Gaza Strip (Palestine). Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M. Isotopes in hydrology and hydrogeology. Water 2019, 11, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calligaris, C.; Mezga, K.; Slejko, F.F.; Urbanc, J.; Zini, L. Groundwater characterization by means of conservative (δ18O and δ2H) and non-conservative (87Sr/86Sr) isotopic values: The classical karst region aquifer case (Italy–Slovenia). Geosciences 2018, 8, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrei, F.; Barbieri, M.; Sappa, G. Application of 2H and18O isotopes for tracing municipal solid waste landfill contamination of groundwater: Two Italian case histories. Water 2021, 13, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankoh, A.A.; Derkyi, N.S.A.; Frazer-Williams, R.A.D.; Laar, C.; Kamara, I. A review on the application of isotopic techniques to trace groundwater pollution sources within developing countries. Water 2022, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijewardhana, R.; Senarathne, S.; Jayawardana, C.K.; Edirisinghe, V.; Wijesekara, H.; Mannapperuma, N. Evaluation of the effect of landfill leachate on surface and groundwater quality: A case study in tropical Sri Lanka using the evidence of stable isotopes. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froehlich, K.; Gibson, J.; Aggarwal, P. Deuterium excess in precipitation and its climatological significance. In Proceedings of the Study of Environmental Change Using Isotope Techniques, Vienna, Austria, 23–27 April 2001; pp. 54–66. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopec, B.G.; Feng, X.; Posmentier, E.S.; Sonder, L.J. Seasonal Deuterium Excess Variations of Precipitation at Summit, Greenland, and their Climatological Significance. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 72–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bershaw, J.; Hansen, D.D.; Schauer, A.J. Deuterium excess and 17O-excess variability in meteoric water across the Pacific Northwest, USA. Tellus Ser. B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2020, 72, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gat, J.R.; Carmi, I. Evolution of the Isotopic Composition of Atmospheric Waters in the Mediterranean Sea Area. J. Geophys. Res. 1970, 75, 3039–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gat, J.R.; Carmi, I. Effect of climate changes on the precipitation patterns and isotopic composition of water in a climate transition zone: Case of the Eastern Mediterranean Sea area. In The Influence of Climate Change and Climatic Variability on the Hydrologic Regime and Water Resources; International Association Hydrological Sciences Publication Vancouver: Wallingford, UK, 1987; pp. 513–524. [Google Scholar]
- Bajjali, W. Spatial variability of environmental isotope and chemical content of precipitation in Jordan and evidence of slight change in climate. Appl. Water Sci. 2012, 2, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hackley, L.C.; Liu, C.I.; Coleman, D.D. Environmental Isotope Characteristics of Landfill Leachates and Gases. Groundwater 1996, 34, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasechko, S. Global Isotope Hydrogeology―Review. Rev. Geophys. 2019, 57, 835–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Medeiros Engelmann, P.; dos Santos, V.H.J.M.; Barbieri, C.B.; Augustin, A.H.; Ketzer, J.M.M.; Rodrigues, L.F. Environmental monitoring of a landfill area through the application of carbon stable isotopes, chemical parameters and multivariate analysis. Waste Manag. 2018, 76, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varjani, S.; Gnansounou, E.; Baskar, G.; Pant, D. Waste Bioremediation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; ISBN 9789811074127. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Hashim, M.A.; Gupta, B. Sen Contemporary environmental issues of landfill leachate: Assessment and remedies. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 472–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wimmer, B.; Hrad, M.; Huber-Humer, M.; Watzinger, A.; Wyhlidal, S.; Reichenauer, T.G. Stable isotope signatures for characterising the biological stability of landfilled municipal solid waste. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 2083–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujiindiyati, E.R. Application of deuterium and oxygen-18 to trace leachate movement in Bantar Gebang sanitary landfill. Atom Indones. 2011, 37, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castañeda, S.S.; Sucgang, R.J.; Almoneda, R.V.; Mendoza, N.D.S.; David, C.P.C. Environmental isotopes and major ions for tracing leachate contamination from a municipal landfill in Metro Manila, Philippines. J. Environ. Radioact. 2012, 110, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morasch, B.; Richnow, H.H.; Schink, B.; Vieth, A.; Meckenstock, R.U. Carbon and hydrogen stable isotope fractionation during aerobic bacterial degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 5191–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Froehlich, K.; Kralik, M.; Papesch, W.; Rank, D.; Scheifinger, H.; Stichler, W. Deuterium excess in precipitation of Alpine regions—Moisture recycling. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2008, 44, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonfiantini, R. La composizione isotopica della precipitazioni. Rend. Soc. Ital. Mineral. Petrol. 1983, 38, 1175–1187. [Google Scholar]
- Kerfoot, H.B.; Baker, J.A.; Burt, D.M. The use of isotopes to identify landfill gas effects on groundwater. J. Environ. Monit. 2003, 5, 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meckenstock, R.U.; Morasch, B.; Griebler, C.; Richnow, H.H. Stable isotope fractionation analysis as a tool to monitor biodegradation in contaminated acquifers. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2004, 75, 215–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.S.; Ko, K.S.; Kim, E.Y. Application of stable isotopes and dissolved ions for monitoring landfill leachate contamination. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 1387–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboyeji, O.S.; Eigbokhan, S.F. Evaluations of groundwater contamination by leachates around Olusosun open dumpsite in Lagos metropolis, southwest Nigeria. Environ. Manag. 2016, 183, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisi, B.; Raco, B.; Dotsika, E. Groundwater contamination studies by environmental isotopes: A review. Handb. Environ. Chem. 2016, 40, 115–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porowska, D. Identification of groundwater contamination zone around a reclaimed landfill using carbon isotopes. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teh, Y.A.; Silver, W.L.; Conrad, M.E.; Borglin, S.E.; Carlson, C.M. Carbon isotope fractionation by methane-oxidizing bacteria in tropical rain forest soils. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2006, 111, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, E.L.; Cifuentes, L.A.; Cozzarelli, I.M. Anaerobic methane oxidation in a landfill-leachate plume. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2436–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, J.C.; Frew, R.D.; Van Hale, R. Can stable isotopes be used to monitor landfill leachate impact on surface waters? J. Geochem. Explor. 2006, 88, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansgaard, W. Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bershaw, J. Controls on deuterium excess across Asia. Geosciences 2018, 8, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bates, B.L.; McIntosh, J.C.; Lohse, K.A.; Brooks, P.D. Influence of groundwater flowpaths, residence times and nutrients on the extent of microbial methanogenesis in coal beds: Powder River Basin, USA. Chem. Geol. 2011, 284, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazioli, A. Landfill investigation using tritium and isotopes as pollution tracers. AQUA Mundi 2011, 18, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, J.E.; Quarmby, J.; Stephenson, T. Role of micronutrients in activated sludge-based biotreatment of industrial effluents. Biotechnol. Adv. 1999, 17, 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünal, B.; Perry, V.R.; Sheth, M.; Gomez-Alvarez, V.; Chin, K.J.; Nüsslein, K. Trace elements affect methanogenic activity and diversity in enrichments from subsurface coal bed produced water. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
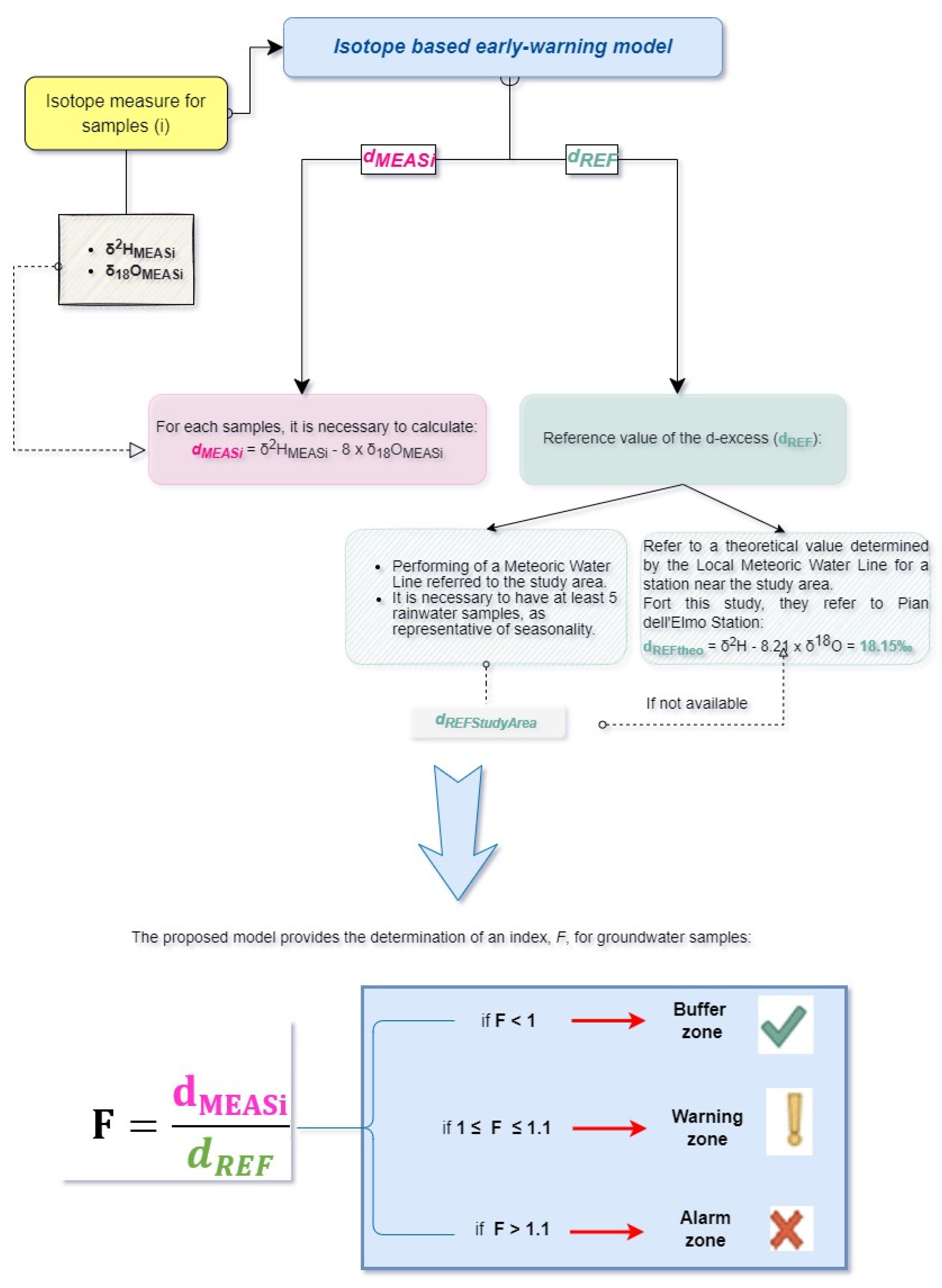
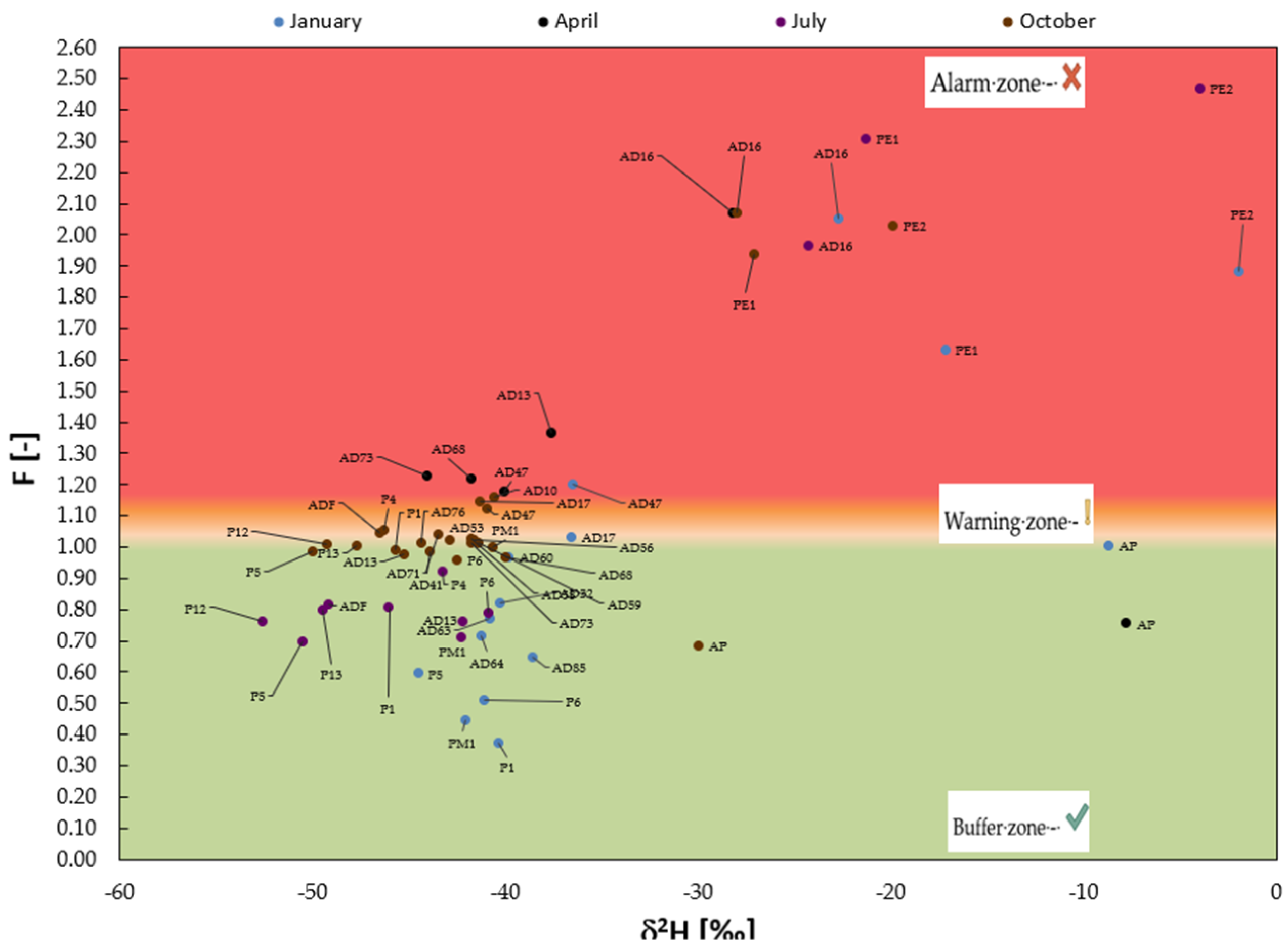

| Values | Zones |
|---|---|
| F > 1.1 (+10%) | Alarm zone— |
| 1 (+1%) ≤ F ≤ 1.1 (+10%) | Warning zone—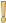 |
| F < 1 (+1%) | Buffer zone—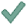 |
| January | April | ||||
| Samples | ‰d(2H) ± 1 ‰ (VSMOW) | ‰d(18O) ± 0.05 ‰ (VSMOW) | Samples | ‰d(2H) ± 1 ‰ (VSMOW) | ‰d(18O) ± 0.05 ‰ (VSMOW) |
| AD16 | −22.7 | −7.5 | AD16 | −28.2 | −8.22 |
| AD17 | −36.6 | −6.92 | AD13 | −37.6 | −7.8 |
| AD47 | −36.5 | −7.29 | AD47 | −40.1 | −7.69 |
| AD63 | −40.8 | −6.85 | AD68 | −41.8 | −7.99 |
| AD60 | −39.8 | −7.178 | AD73 | −44.1 | −8.3 |
| AD32 | −40.3 | −6.9 | AP | −7.8 | −2.69 |
| AD64 | −41.2 | −6.778 | |||
| AD85 | −38.56 | −6.287 | |||
| AP | −8.73 | −3.37 | |||
| PE1 | −17.2 | −5.85 | |||
| PE2 | −2 | −4.52 | |||
| P1 | −40.4 | −5.9 | |||
| P6 | −41.1 | −6.3 | |||
| PM1 | −42.1 | −6.28 | |||
| P5 | −44.55 | −6.92 | |||
| July | October | ||||
| Samples | ‰d(2H) ± 1 ‰ (VSMOW) | ‰d(18O) ± 0.05 ‰ (VSMOW) | Samples | ‰d(2H) ± 1 ‰ (VSMOW) | ‰d(18O) ± 0.05 ‰ (VSMOW) |
| AD13 | −42.2 | −7 | AP | −30 | −5.3 |
| AD16 | −24.3 | −7.5 | AD10 | −40.6 | −7.71 |
| P1 | −46.1 | −7.6 | AD16 | −28 | −8.2 |
| P4 | −43.3 | −7.5 | AD17 | −41.3 | −7.76 |
| P5 | −50.5 | −7.9 | AD41 | −43.5 | −7.8 |
| P6 | −40.9 | −6.9 | AD47 | −41 | −7.67 |
| P12 | −52.6 | −8.3 | AD53 | −42.9 | −7.68 |
| PM1 | −42.3 | −6.9 | AD68 | −40 | −7.2 |
| P13 | −49.5 | −8 | AD71 | −43.9 | −7.73 |
| ADF | −49.2 | −8 | AD76 | −44.4 | −7.85 |
| PE1 | −21.3 | −7.9 | AD55 | −41.6 | −7.52 |
| PE2 | −4 | −6.1 | AD56 | −41.6 | −7.52 |
| AD58 | −41.8 | −7.56 | |||
| AD59 | −41.4 | −7.48 | |||
| AD73 | −41.8 | −7.52 | |||
| AD13 | −45.3 | −7.88 | |||
| ADF | −46.5 | −8.19 | |||
| P1 | −45.7 | −7.96 | |||
| P4 | −46.3 | −8.18 | |||
| P5 | −50 | −8.49 | |||
| P6 | −42.5 | −7.49 | |||
| PM1 | −40.7 | −7.36 | |||
| P12 | −49.3 | −8.45 | |||
| P13 | −47.7 | −8.24 | |||
| PE1 | −27.1 | −7.78 | |||
| PE2 | −19.9 | −7.09 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sappa, G.; Barbieri, M.; Andrei, F. Isotope-Based Early-Warning Model for Monitoring Groundwater–Leachate Contamination Phenomena: First Quantitative Assessments. Water 2023, 15, 2646. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142646
Sappa G, Barbieri M, Andrei F. Isotope-Based Early-Warning Model for Monitoring Groundwater–Leachate Contamination Phenomena: First Quantitative Assessments. Water. 2023; 15(14):2646. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142646
Chicago/Turabian StyleSappa, Giuseppe, Maurizio Barbieri, and Francesca Andrei. 2023. "Isotope-Based Early-Warning Model for Monitoring Groundwater–Leachate Contamination Phenomena: First Quantitative Assessments" Water 15, no. 14: 2646. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142646
APA StyleSappa, G., Barbieri, M., & Andrei, F. (2023). Isotope-Based Early-Warning Model for Monitoring Groundwater–Leachate Contamination Phenomena: First Quantitative Assessments. Water, 15(14), 2646. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142646









