Assessment of Integrated Soil and Water Conservation Practices on Soil Erosion Risk in a Typical Red-Beds Watershed in South China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
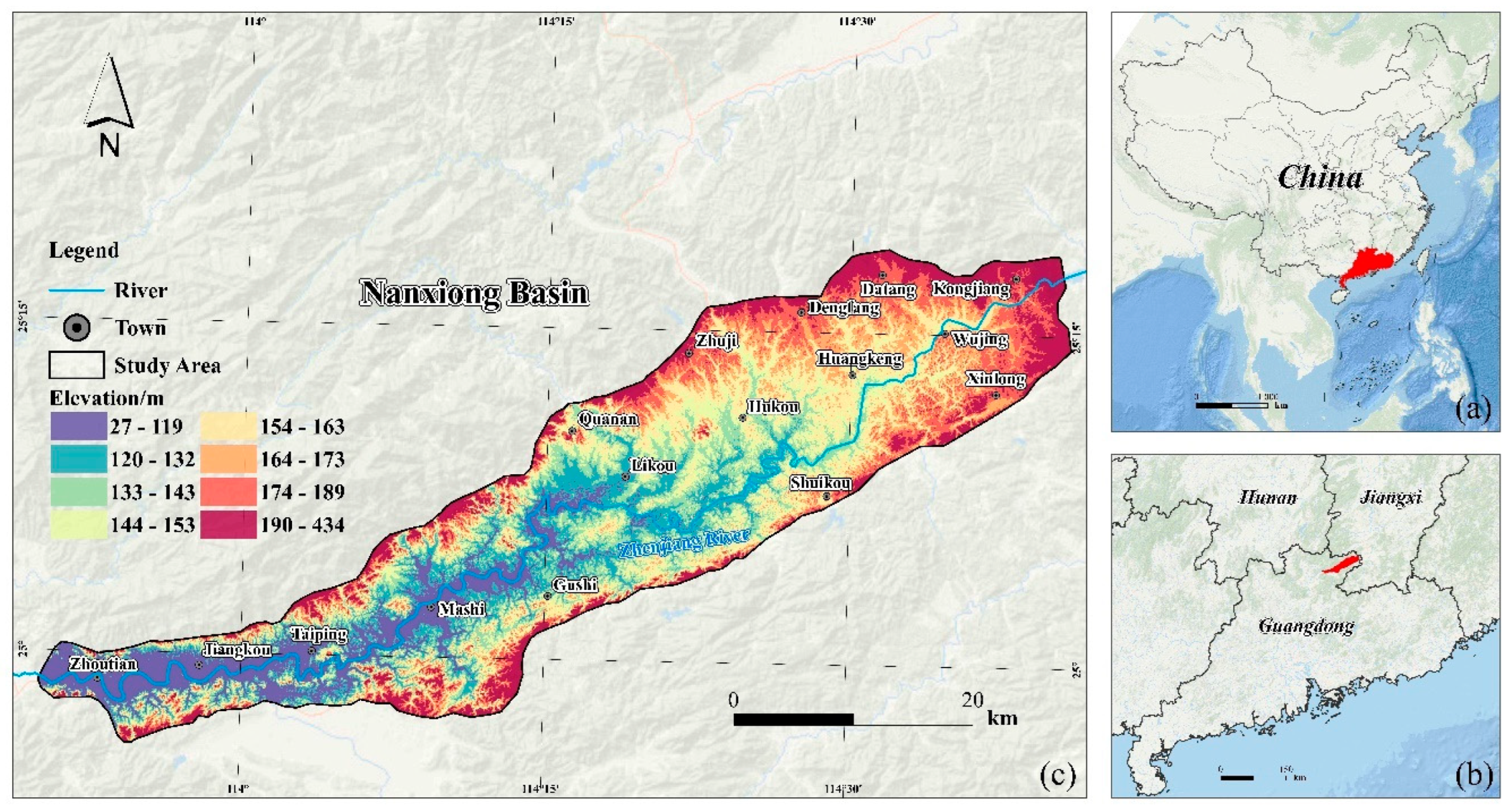
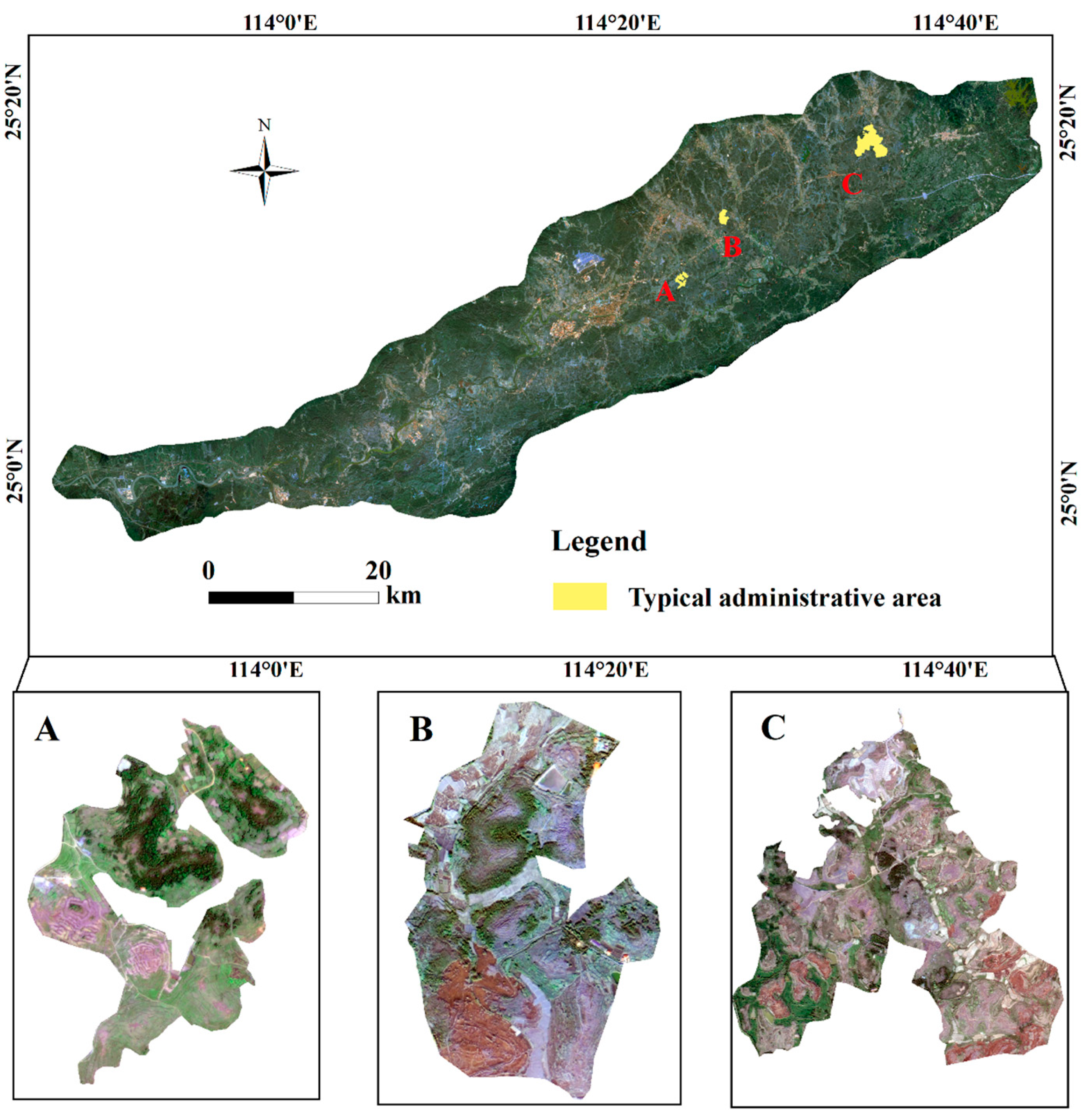
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Sources of Information and Pre-Processing
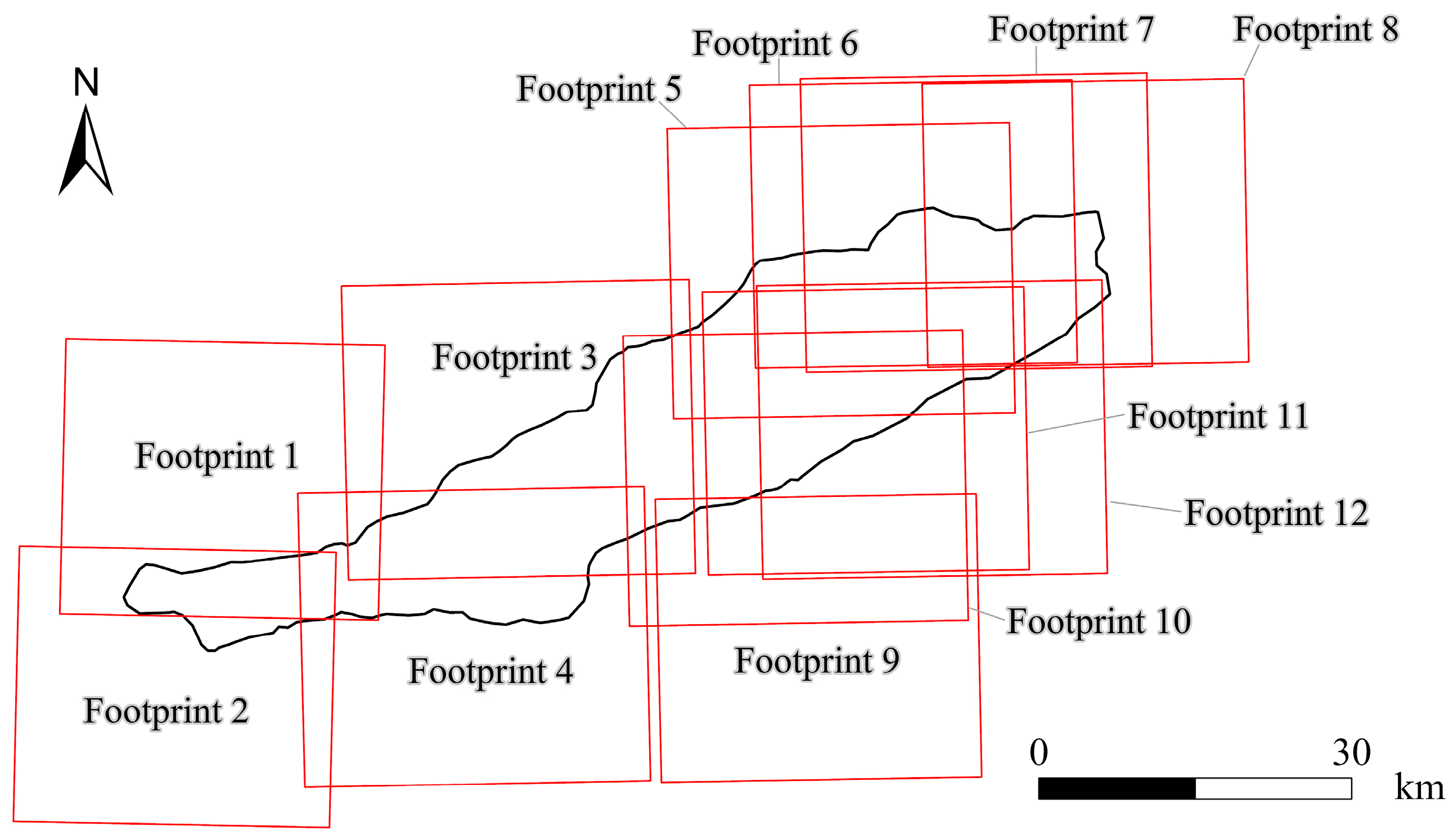
2.2.1. Remote Sensing Data
2.2.2. Other Data Materials
2.3. Research Methods
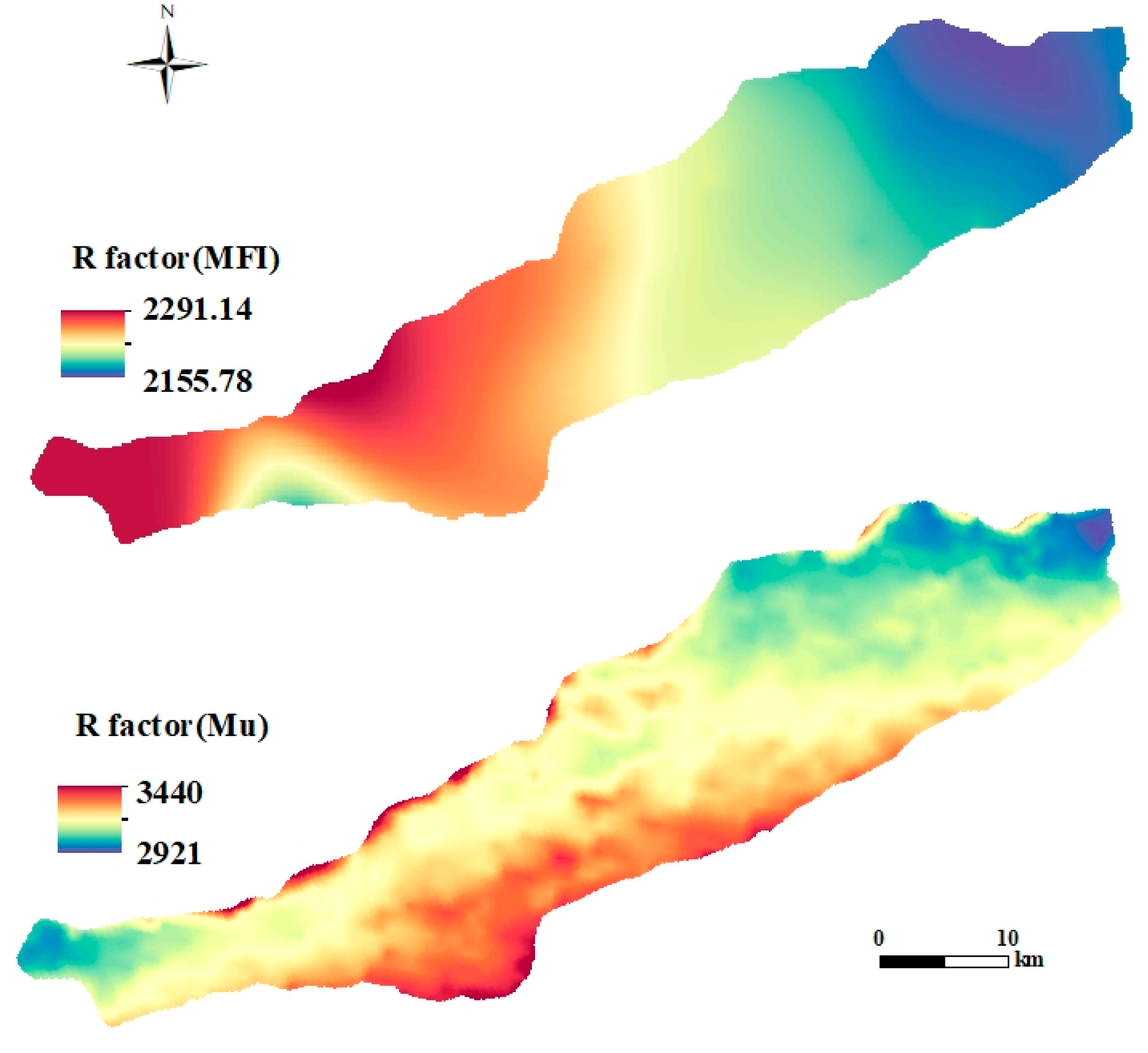
2.3.1. Rainfall Erosivity Factor (R)
2.3.2. Soil Erodibility Factor (K)
2.3.3. Slope Length–Steepness Factor (LS)
2.3.4. Vegetation Cover and Management Factors (C)
2.3.5. Conservation Practice Factor (P)
2.3.6. Erosion Intensity Classification
2.3.7. Soil and Water Conservation Measures
3. Results
3.1. Dynamics of Single Factors
3.1.1. Rainfall Erosivity Factor (R)
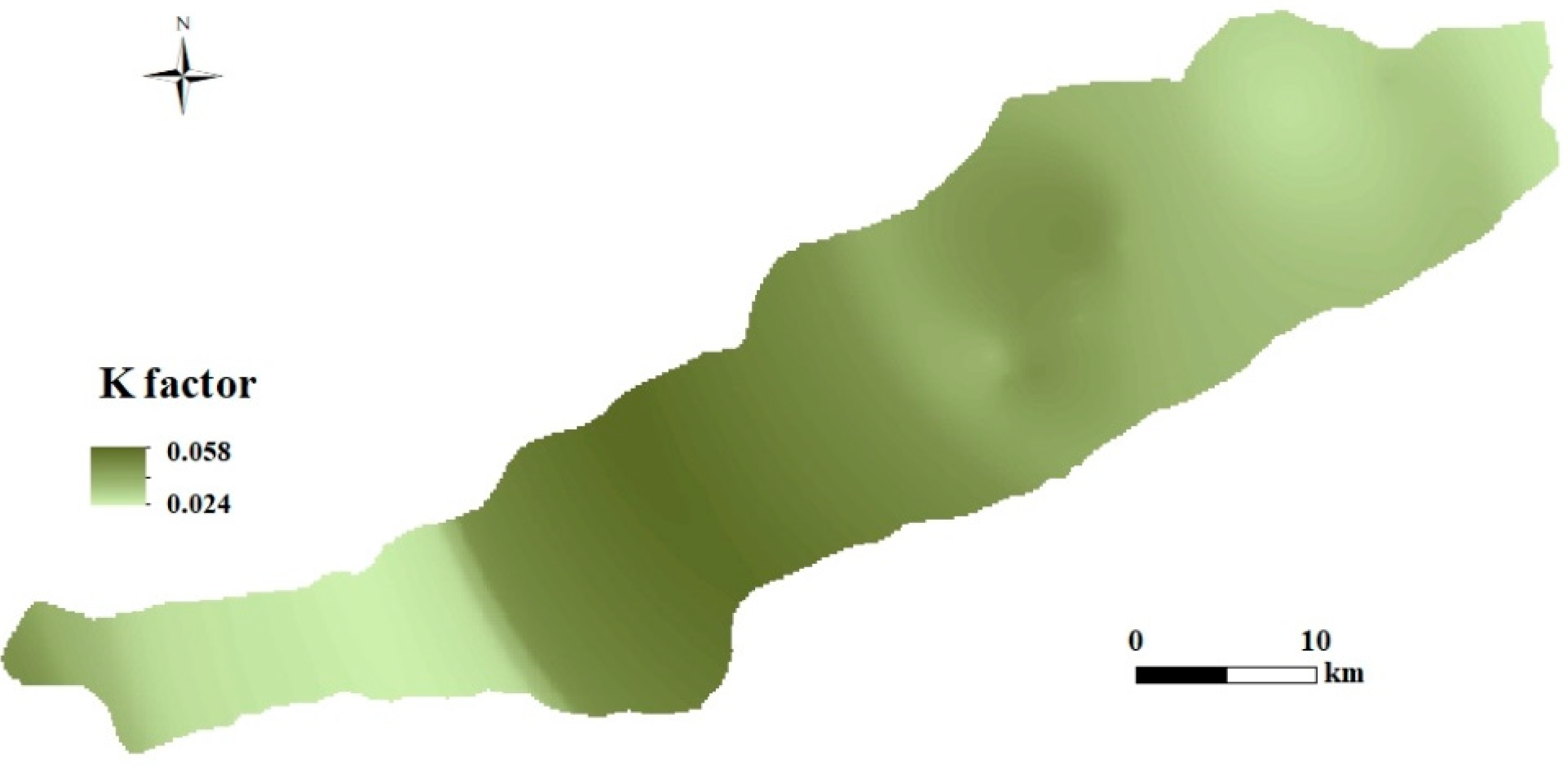
3.1.2. Soil Erodibility Factor (K)
3.1.3. Slope Length–Steepness Factor (LS)
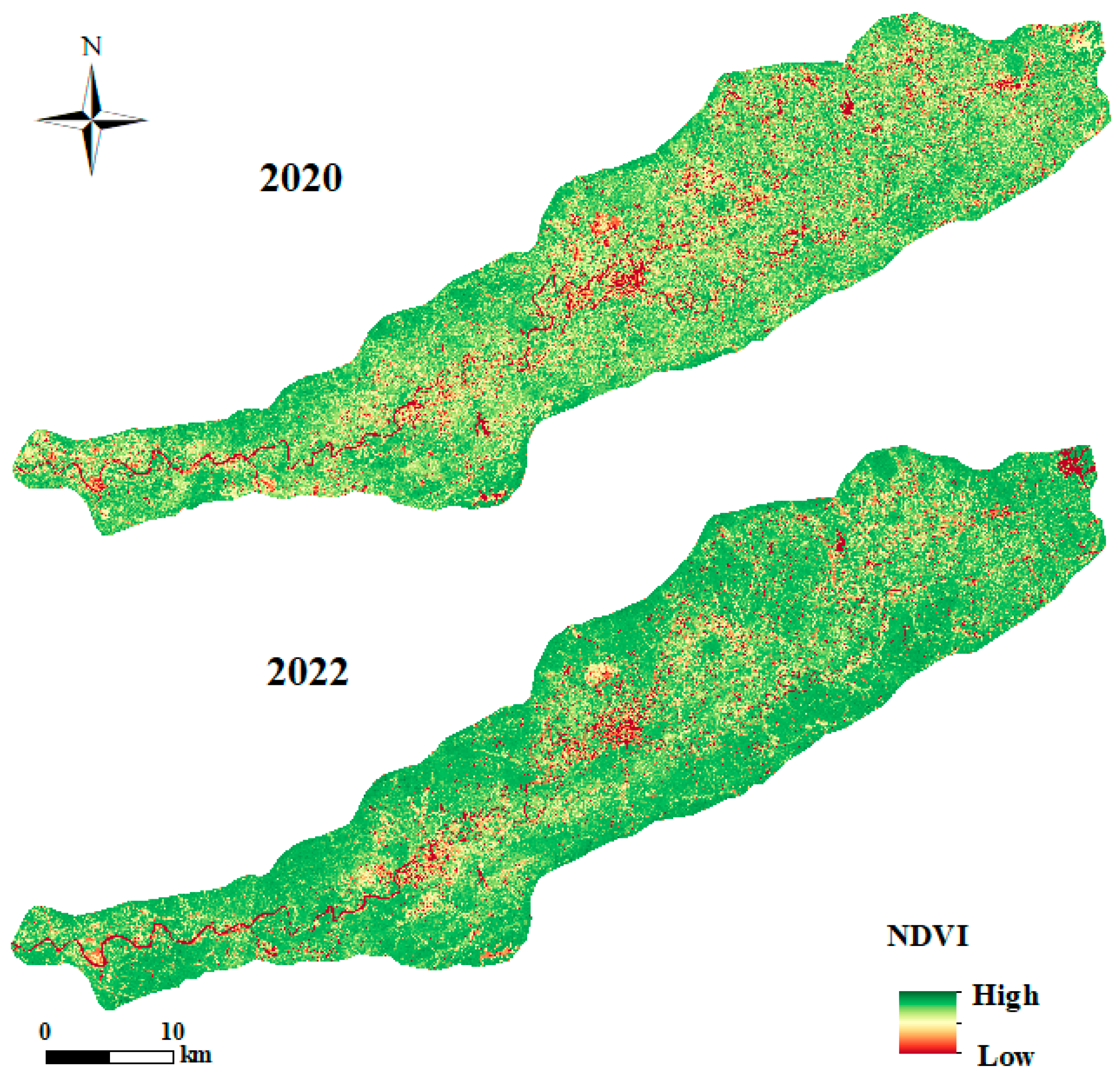
3.1.4. Vegetation Cover and Management Factor (C)
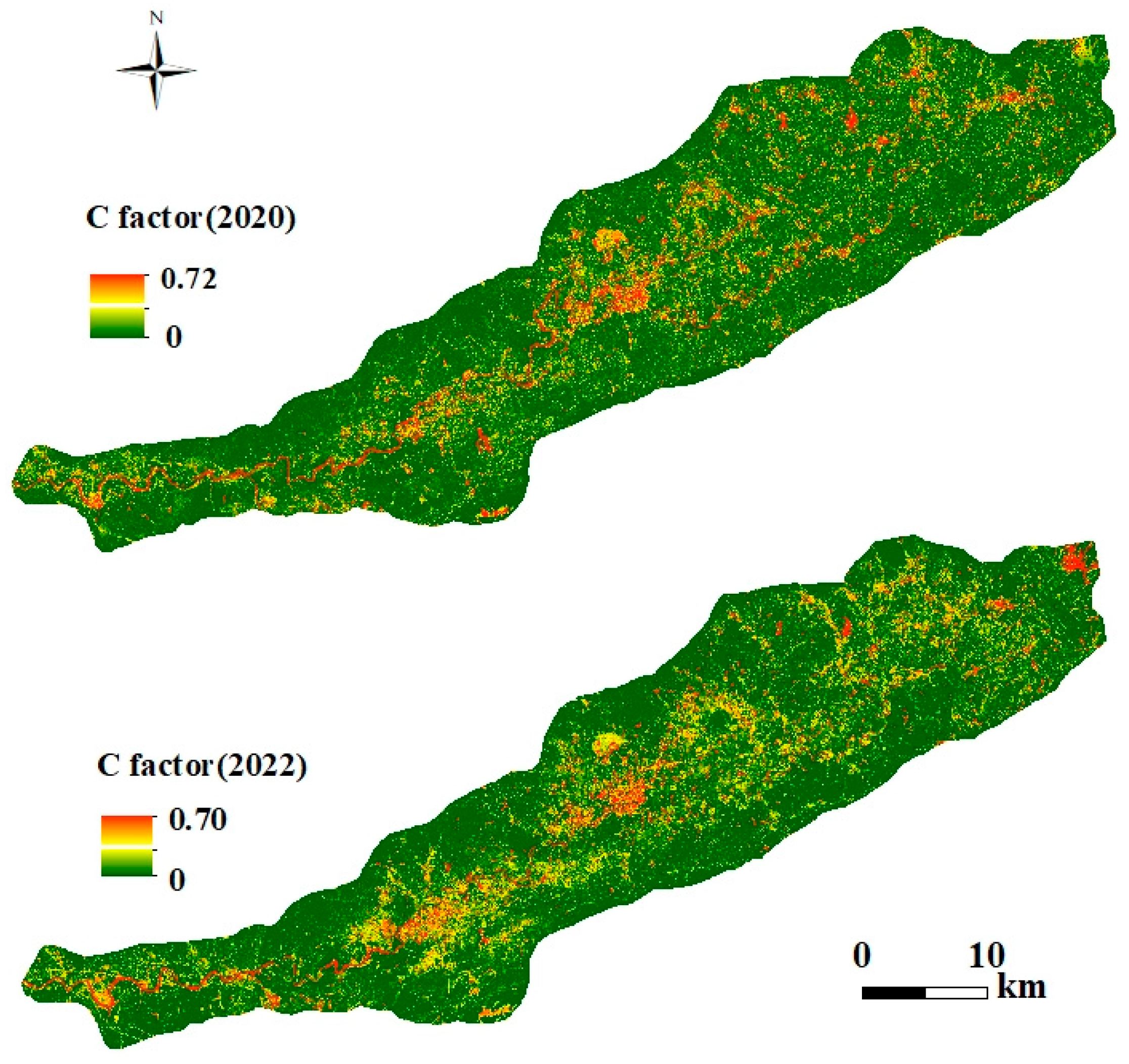
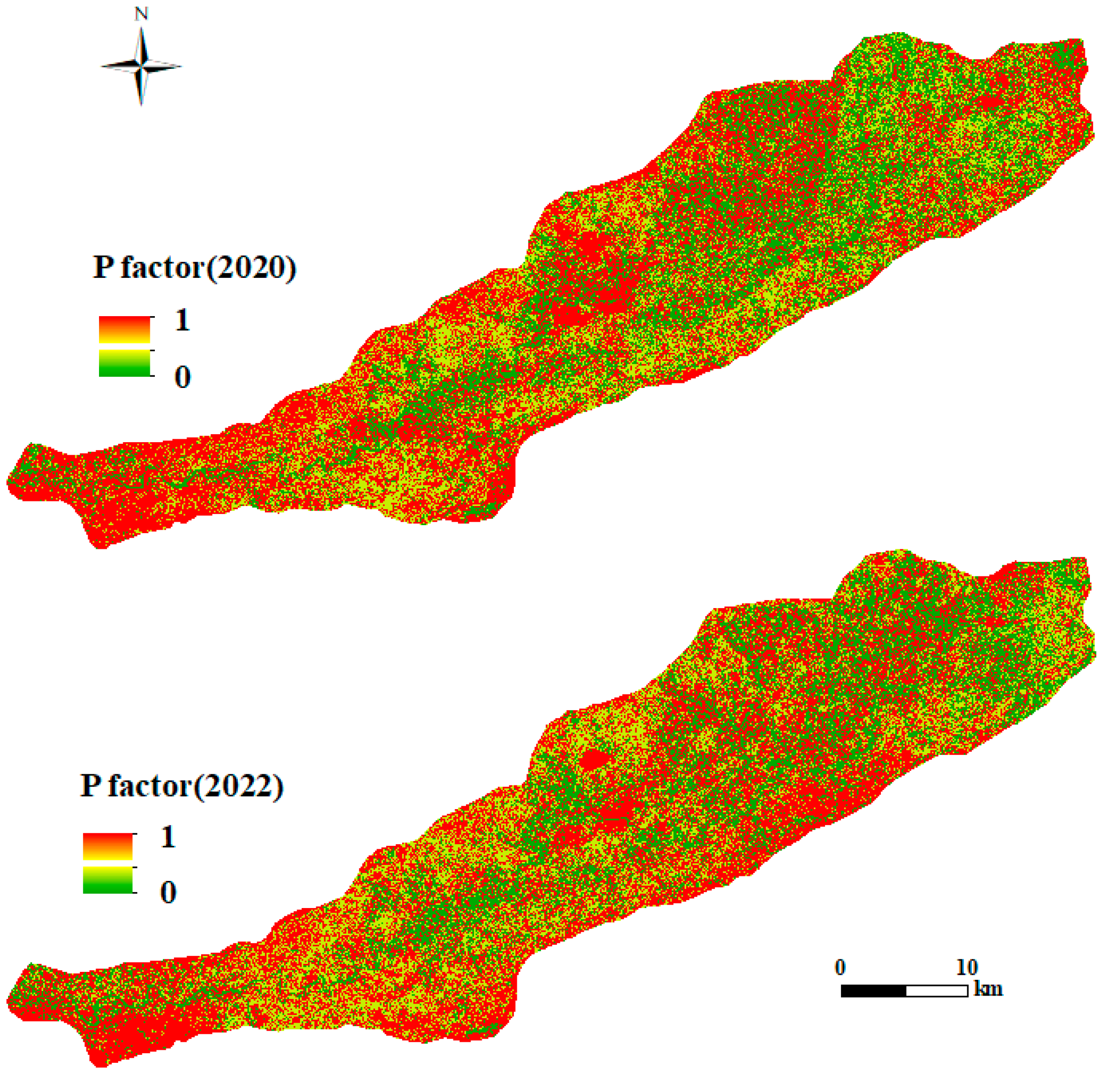
3.1.5. Conservation Practice Factor (P)
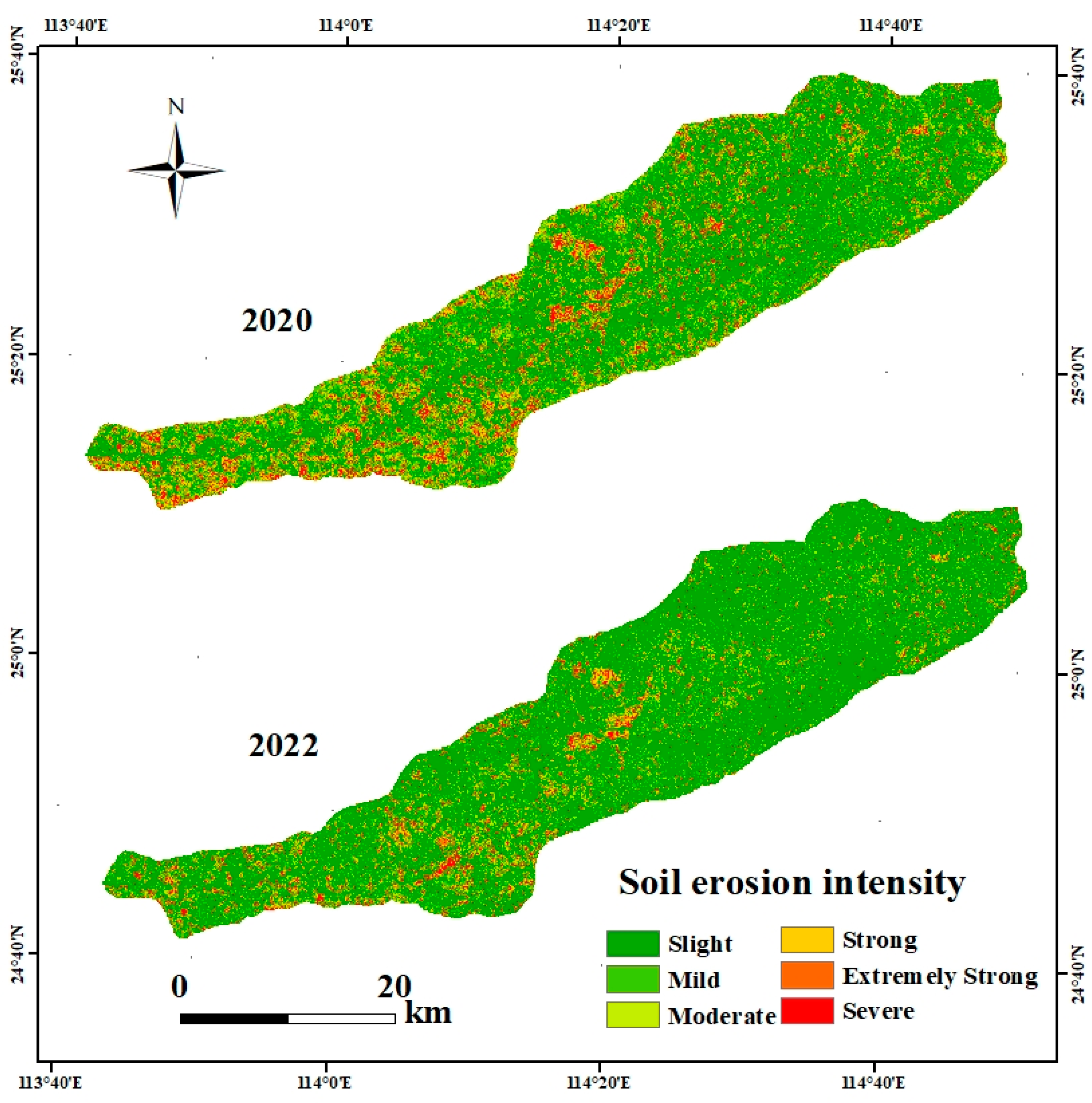
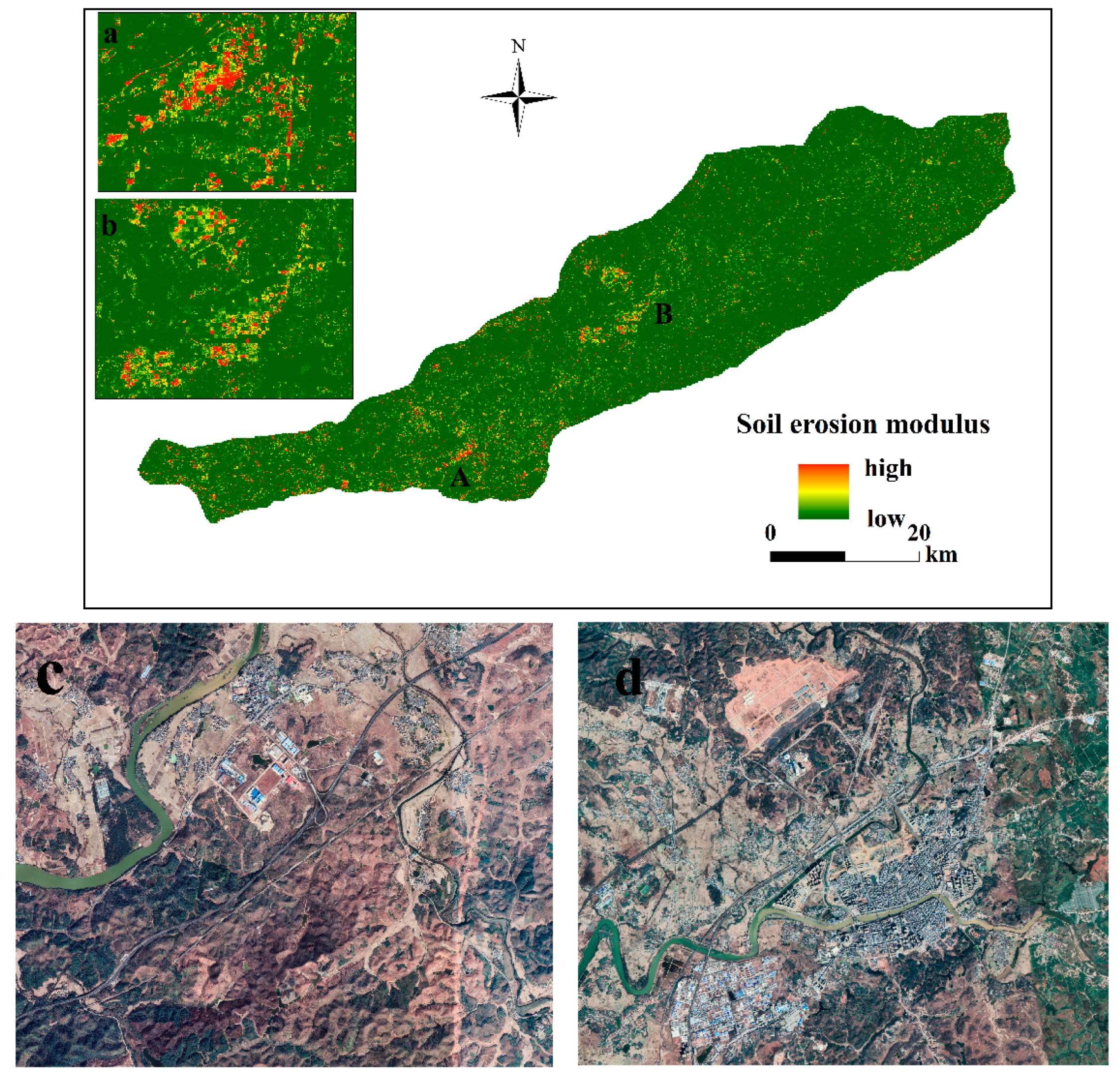
3.2. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Soil Erosion
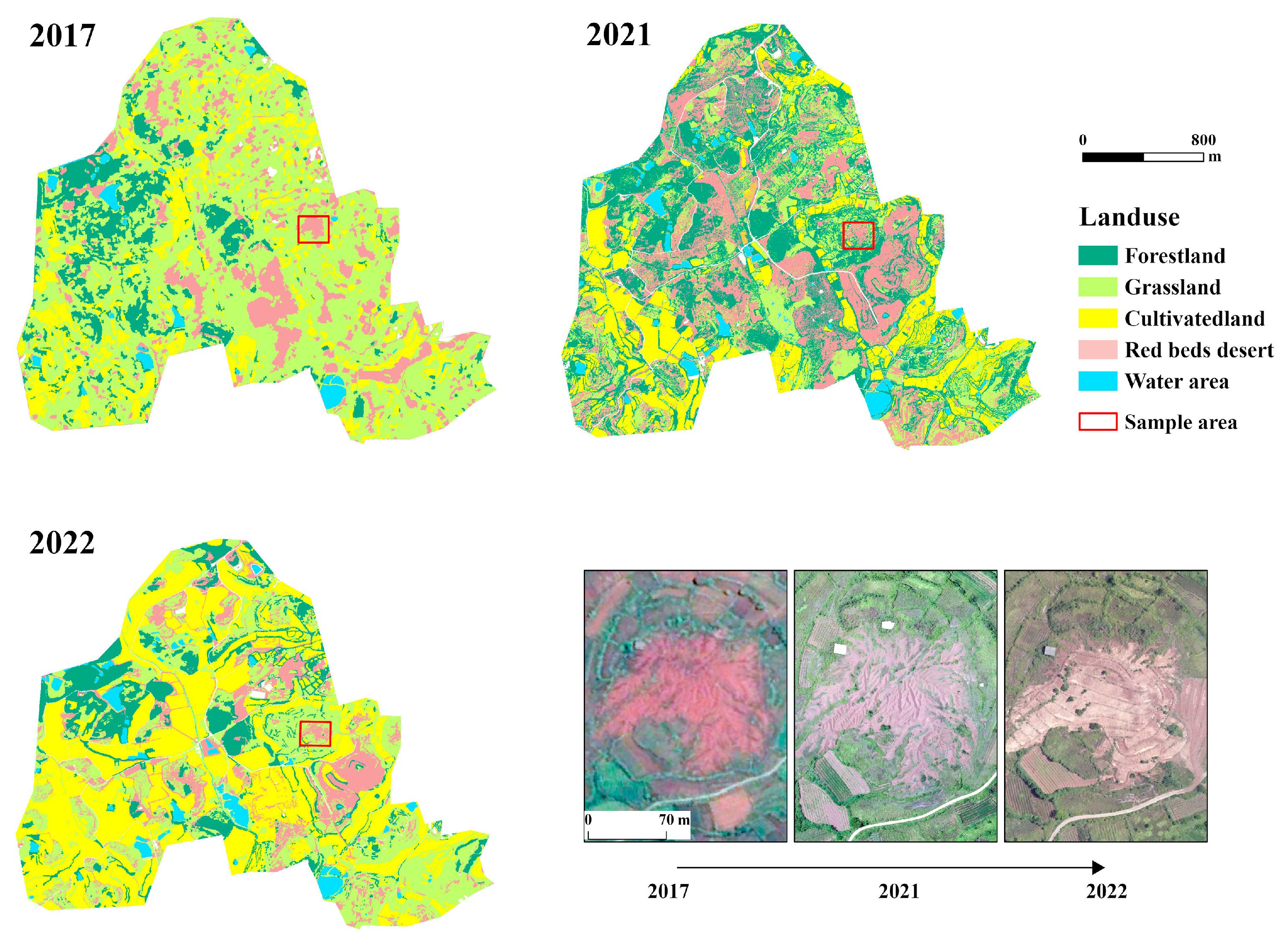
3.3. Consequences of Ecological Restoration in Representative Areas with Conservation Practices
4. Discussion
4.1. Uncertainty and Applicability of the RUSLE Model
4.2. Major Factors Affecting Soil Erosion
4.2.1. Rainfall
4.2.2. Steepness
4.2.3. Land use
4.2.4. Socioeconomic Activities
4.3. Effectiveness of Water and Soil Erosion Control Engineering
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yi, L.; Zuo, L.; Wen, Q.; Liu, F.; Xu, J.; Hu, S.; Liu, B. Assessment of Soil Erosion Change and Its Relationships with Land Use/Cover Change in China from the End of the 1980s to 2010. CATENA 2016, 137, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Fang, H. Impacts of Climate Change on Water Erosion: A Review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 163, 94–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, M.; Philippidis, G.; Ferrari, E.; Borrelli, P.; Lugato, E.; Montanarella, L.; Panagos, P. A Linkage between the Biophysical and the Economic: Assessing the Global Market Impacts of Soil Erosion. Land Use Policy 2019, 86, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiyamurthi, S.; Ramya, M.; Saravanan, S.; Subramani, T. Estimation of Soil Erosion for a Semi-Urban Watershed in Tamil Nadu, India Using RUSLE and Geospatial Techniques. Urban Clim. 2023, 48, 101424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Han, Y.; Wu, H.; Liu, F.; Liu, Z. Application of the Source–Sink Landscape Method in the Evaluation of Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution: First Estimation of an Orchard-Dominated Area in China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 252, 106910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Q. Review and prospects of scientific research on soil erosion in China. Chin. J. Nat. 2008, 30, 12–16+63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. Analyses of Affecting Factors of Soil Erosion and Its Harms in China. J. Agric. Eng. 2000, 16, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, T.; Cheng, S.; Li, Z. Progress of soil erosion models in recent 30 years. J. Sediment Res. 2023, 48, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Cai, Q.; Ke, Q. Major Achievements and Future Key Fields of Soil Erosion Research in China. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 42, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Peng, C.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, M.; Wang, H.; Peng, S.; He, H. Modelling the Impacts of Climate and Land Use Changes on Soil Water Erosion: Model Applications, Limitations and Future Challenges. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 250, 109403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Mu, X.; Holden, J.; Wu, Y.; Irvine, B.; Wang, F.; Gao, P.; Zhao, G.; Sun, W. Comparison of Soil Erosion Models Used to Study the Chinese Loess Plateau. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 170, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning, U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1978, Agriculture Handbook No. 537. Available online: https://topsoil.nserl.purdue.edu/usle/AH_537.pdf (accessed on 6 April 2023).
- Xia, L.; Bi, R.; Song, X.; Lv, C. Dynamic Changes in Soil Erosion Risk and Its Driving Mechanism: A Case Study in the Loess Plateau of China. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 72, 1312–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.G. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, C.; Vega, J.A. Evaluation of the Rusle and Disturbed Wepp Erosion Models for Predicting Soil Loss in the First Year after Wildfire in NW Spain. Environ. Res. 2018, 165, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista, P.V.G.; Davies, J.; Silva, M.L.N.; Quinton, J.N. On the Evaluation of Soil Erosion Models: Are We Doing Enough? Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 197, 102898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Joseph, S.; Thrivikramji, K.P. Assessment of Soil Erosion in a Tropical Mountain River Basin of the Southern Western Ghats, India Using RUSLE and GIS. Geosci. Front. 2018, 9, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Fu, T.; Gao, H.; Qi, F. Spatio-temporal variations in soil erosion and its influence factors in Taihang Mountain area based on RUSLE modeling. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2022, 30, 1064–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Jiang, X.; Ren, L.; Tang, X.; Xiao, X. Quantitative Evaluation of Soil Erosion in the Huaihe River Basin Based on RUSLE Model. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 52, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Jiang, X.; Pan, J.; Yang, S.; Zhang, C. GIS-Based Spatial Analysis and Evaluation of Soil Erosion in the Huaihe River Basin. Soils 2007, 39, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Du, C.; Zhang, L.; Du, Y.; Li, S. Research Trends and Hotspots in Soil Erosion from 1932 to 2013: A Literature Review. Scientometrics 2015, 105, 743–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Qiu, J.; Cao, B.; Cai, S.; Niu, K.; Yang, X. Mapping Soil Erosion Dynamics (1990–2020) in the Pearl River Basin. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnashar, A.; Zeng, H.; Wu, B.; Fenta, A.A.; Nabil, M.; Duerler, R. Soil Erosion Assessment in the Blue Nile Basin Driven by a Novel RUSLE-GEE Framework. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phinzi, K.; Ngetar, N.S. Land Use/Land Cover Dynamics and Soil Erosion in the Umzintlava Catchment (T32E), Eastern Cape, South Africa. Trans. R. Soc. S. Afr. 2019, 74, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Hou, X.; Yang, X. Characteristics of Watershed Dynamic Sediment Delivery Based on Improved RUSLE Model. CATENA 2022, 219, 106602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Dai, E.; Wu, C. Spatial and Temporal Evolution Characteristics and Driving Factors of Soil Conservation Services on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. CATENA 2023, 221, 106766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G. Several Ideas Related to Soil Erosion Research. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 34, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Shi, Y.; Cao, Q.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, B. Soil erosion evaluation of Liudaogou catchment in the Loess Plateau during the past 30 years. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 18, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jia, Y.; Fan, H. Spatial distribution characteristics of sediment connectivity and soil erosion in a small watershed in brown soil hilly region of low mountains in western Liaoning Province, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 34, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhaske, S.N.; Pathak, K.; Dash, S.S.; Nayak, D.B. Assessment and Management of Soil Erosion in the Hilltop Mining Dominated Catchment Using GIS Integrated RUSLE Model. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 294, 112987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, Y.S.; Endalamaw, N.T.; Sinshaw, B.G.; Atinkut, H.B. Modeling Soil Erosion Using RUSLE and GIS at Watershed Level in the Upper Beles, Ethiopia. Environ. Chall. 2021, 2, 100009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection, Chinese Academy of Sciences. National Zoning of Ecological Functions (Revised Version), Beijing, China, 2015. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/bgg/201511/W020151126550511267548.pdf (accessed on 21 March 2023).
- Shao, S.; Wang, G.; Liao, L.; Li, H.; Huang, G. Research and practice of ecological protection and restoration of the mountain-river-forest-farmland-lake-grassland system in Nanling mountains area, northern Guangdong Province. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2020, 10, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wu, Z. A Preliminary Study on the Characteristics and the Distribution of Red Beds. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 2003, 42, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H. A Survey of the Danxia Landform Research in China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2000, 20, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Yan, L.; Chen, Z.; SIMONSON, S.; Luo, G. A preliminary study of desertification in red beds in the humid region of Southern China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2015, 70, 1699–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Zhong, P.; Zhang, Z. Study on Soil and Water Loss Control and Development and Utilization of Purple Sand Shale Region in the Upper Stream of Beijiang River. Soil Water Conserv. China 2007, 6, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
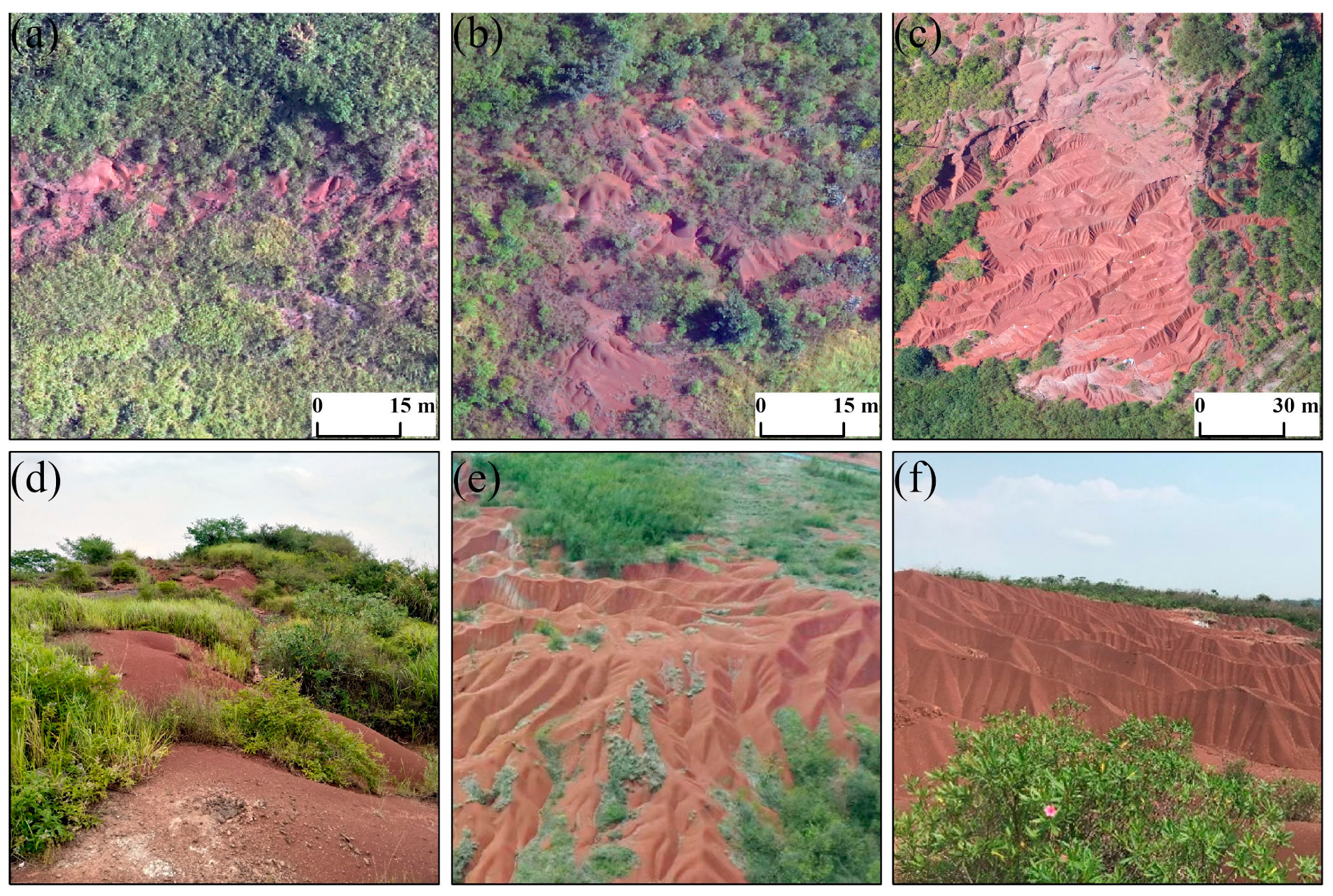
- Chen, J.; Yu, S.; Fu, J.; Xu, G. Soil Quality Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Different Land Use in the Red Bed Landform Region of South China: Taking Nanxiong Basin as An Example. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2022, 31, 918–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Guan, H.; He, W. GF-2 Satellite Remote Sensing Technology. Spacecr. Recovery Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinzi, K.; Ngetar, N.S. The Assessment of Water-Borne Erosion at Catchment Level Using GIS-Based RUSLE and Remote Sensing: A Review. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2019, 7, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Xiong, K.; Xiao, H. Multi-Time Scale Variability of Rainfall Erosivity and Erosivity Density in the Karst Region of Southern China, 1960–2017. CATENA 2021, 197, 104977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando, D.; Romana, M.G. Estimating the Rainfall Erosivity Factor from Monthly Precipitation Data in the Madrid Region (Spain). J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2015, 63, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Gertner, G.; Liu, X.; Anderson, A. Uncertainty Assessment of Soil Erodibility Factor for Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation. CATENA 2001, 46, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Erosion-Productivity Impact Calculator (EPIC) Model: A Case History. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 1990, 329, 421–428. [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Tresch, S.; Meusburger, K. Modification of the RUSLE Slope Length and Steepness Factor (LS-Factor) Based on Rainfall Experiments at Steep Alpine Grasslands. MethodsX 2019, 6, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Zhang, X.C. (John); Liu, B. Effects of DEM Resolutions on Soil Erosion Prediction Using Chinese Soil Loss Equation. Geomorphology 2021, 384, 107706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmet, P.J.J.; Govers, G. A gis procedure for automatically calculating the usle ls factor on topographically complex landscape units. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1996, 51, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Y.; Nearing, M.A.; Shi, P.J.; Jia, Z.W. Slope Length Effects on Soil Loss for Steep Slopes. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1759–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, Y.; Liu, X.; Cao, L.; Zheng, F. Calculation and macroscopic distribution of soil erodibility K values in water erosion zones in China. Soil Water Conserv. China 2013, 35–40+79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Knijff, J.M.; Jones, R.J.A.; Montanarella, L. Soil Erosion Risk: Assessment in Europe. EUROPEAN SOIL DATA CENTRE, European Commission, 2000. Available online: https://esdac.jrc.ec.europa.eu/content/soil-erosion-risk-assessment-europe (accessed on 6 April 2023).
- Gong, W.; Liu, T.; Duan, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, X.; Qiu, Z. Estimating the Soil Erosion Response to Land-Use Land-Cover Change Using GIS-Based RUSLE and Remote Sensing: A Case Study of Miyun Reservoir, North China. Water 2022, 14, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Zhu, Z.; Yue, Q.; He, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Hao, F.; Guo, W.; Chen, L.; Liu, M. Soil Erosion Assessment by RUSLE with Improved P Factor and Its Validation: Case Study on Mountainous and Hilly Areas of Hubei Province, China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2021, 9, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Xu, H.; Lin, N.; He, H.; Zeng, H. RUSLE-based quantitative study on the soil erosion of the Hetian basin area in County Changting, Fujian Province, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 2974–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, K.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Yao, H. The Characteristics of Spatial-temporal Differentiation of Soil Erosion Based on RUSLE Model: A Case Study of Chaoyang City, Liaoning Province. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2015, 35, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China. Soil Erosion Classification and Grading Standard: SL190-2007, Beijing, China, 2008. Available online: https://slgcfy.ylvtc.cn/__local/D/6F/D7/6C04DCAF303494B02D6DBB6E965_8A1D4E97_BC696.pdf (accessed on 17 January 2023).
- Dabral, P.P.; Baithuri, N.; Pandey, A. Soil Erosion Assessment in a Hilly Catchment of North Eastern India Using USLE, GIS and Remote Sensing. Water Resour Manag. 2008, 22, 1783–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Rahaman, S.; Aruchamy, S.; Jegankumar, R.; Abdul Ajeez, S. Estimation of Annual Avergfe Soil Loss, Based on RUSLE Model in Kallar Water Watershed, Bhavani Basin, Tamil Nadu, India. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2015, II-2/W2, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
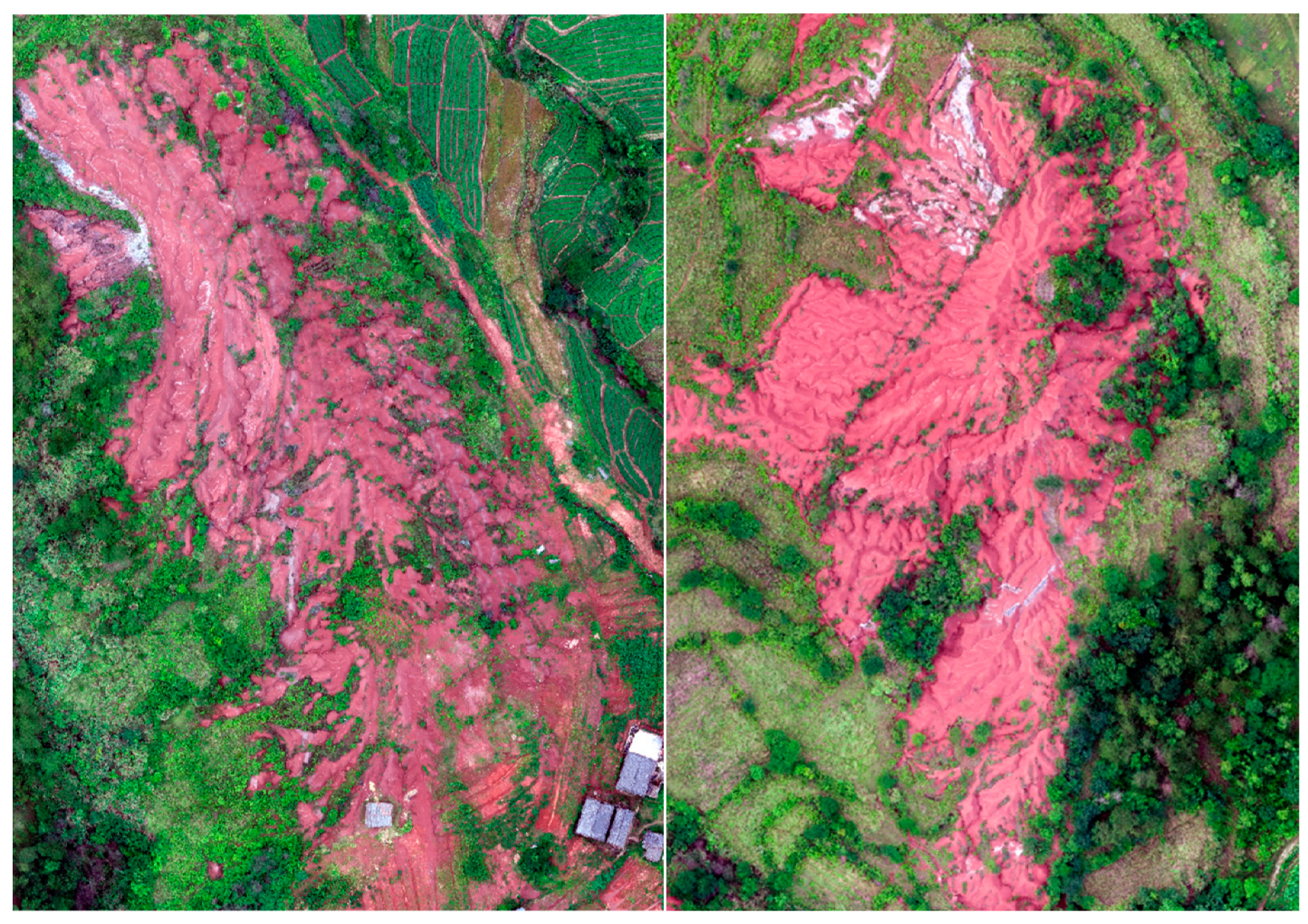
- Yan, L.; Kasanin-Grubin, M. Land Degradation and Management of Red Beds in China: Two Case Studies. J. Mt. Sci. 2019, 16, 2591–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Rainfall Energy and Its Relationship to Soil Loss. Trans. AGU 1958, 39, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frédéric, F. CLIMAT ET ÉROSION: La Relation Entre l’érosion du sol par l’eau et les Précipitations Atmosphériques; Presses Universitaires: Paris, France, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Mezősi, G.; Bata, T. Estimation of the Changes in the Rainfall Erosivity in Hungary. J. Environ. Geogr. 2016, 9, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teng, M.; Huang, C.; Wang, P.; Zeng, L.; Zhou, Z.; Xiao, W.; Huang, Z.; Liu, C. Impacts of Forest Restoration on Soil Erosion in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Li, P.; Ren, Z.; Xiao, L. Effect of Slope Gradient on the Process of Runoff and Sediment Yieldand Water-Sediment Relationon the Loess Slope. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 27, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C. Effects of Land Use Changes on Soil Erosion in a Fast Developing Area. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 1549–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Parameter | 1 m Resolution Panchromatic/4 m Resolution Multispectral Camera | |
|---|---|---|
| Spectral range | Panchromatic | 0.45~0.90 μm |
| Multispectral | 0.45~0.52 μm | |
| ID | Land Use | mCla/% (<0.002 mm) | mSil/% (0.002~0.05 mm) | mSan/% (0.05~2.0 mm) | C% | K/(Mg·ha·h·MJ−1·mm−1·ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | red beds desert | 16.99 | 3.00 | 80.01 | 0.56 | 0.036 |
| 2 | 15.90 | 3.97 | 80.13 | 1.03 | 0.037 | |
| 3 | 12.98 | 7.99 | 79.04 | 0.46 | 0.048 | |
| 4 | 13.91 | 8.45 | 77.64 | 0.16 | 0.049 | |
| 5 | 13.98 | 0.50 | 85.52 | 0.18 | 0.024 | |
| 6 | 14.49 | 1.50 | 71.51 | 1.09 | 0.045 | |
| 7 | 42.96 | 16.49 | 52.59 | 1.25 | 0.056 | |
| 8 | grassland | 19.49 | 9.00 | 72.55 | 0.51 | 0.045 |
| 9 | 13.97 | 33.44 | 72.57 | 0.81 | 0.041 | |
| 10 | 18.97 | 8.49 | 74.03 | 0.53 | 0.036 | |
| 11 | 18.45 | 8.98 | 71.51 | 1.18 | 0.035 | |
| 12 | 10.00 | 28.49 | 55.60 | 1.02 | 0.053 | |
| 13 | 16.98 | 8.99 | 55.07 | 3.60 | 0.043 | |
| 14 | 19.49 | 9.00 | 65.59 | 2.03 | 0.040 | |
| 15 | 10.48 | 33.92 | 51.10% | 1.17 | 0.052 | |
| 16 | 16.48 | 28.46 | 73.54 | 2.12 | 0.037 | |
| 17 | 20.44 | 13.96 | 62.02 | 1.52 | 0.051 | |
| 18 | 19.46 | 29.44 | 59.22 | 0.99 | 0.053 | |
| 19 | woodland | 16.00 | 11.50 | 59.63 | 1.88 | 0.042 |
| 20 | 16.48 | 9.99 | 75.50 | 2.29 | 0.035 | |
| 21 | 13.49 | 24.49 | 57.65 | 1.10 | 0.043 | |
| 22 | 15.42 | 25.36 | 31.07 | 0.91 | 0.034 | |
| 23 | 20.43 | 19.94 | 61.57 | 1.65 | 0.028 | |
| 24 | 17.00 | 7.50 | 27.54 | 1.90 | 0.024 | |
| 25 | 19.93 | 22.42 | 29.64 | 1.67 | 0.027 | |
| 26 | 48.95 | 19.98 | 59.69 | 2.81 | 0.050 | |
| 27 | 32.94 | 5.49 | 55.00 | 2.25 | 0.056 | |
| 28 | 68.47 | 4.00 | 44.98 | 1.18 | 0.039 | |
| 29 | 60.38 | 9.98 | 70.04 | 2.70 | 0.046 | |
| 30 | 15.43 | 24.88 | 34.14 | 1.17 | 0.040 | |
| 31 | farmland | 14.00 | 31.00 | 72.51 | 0.74 | 0.039 |
| 32 | 35.20 | 19.83 | 58.51 | 1.56 | 0.048 | |
| 33 | 16.48 | 13.48 | 61.52 | 1.12 | 0.055 | |
| 34 | 49.39 | 16.46 | 64.56 | 0.92 | 0.050 | |
| 35 | 20.49 | 20.99 | 84.01 | 1.05 | 0.029 | |
| 36 | 16.47 | 18.97 | 40.13 | 1.02 | 0.049 | |
| 37 | 14.47 | 45.40 | 35.12 | 1.51 | 0.058 | |
| 38 | 18.47 | 46.42 | 40.16 | 0.50 | 0.056 | |
| 39 | 17.95 | 41.89 | 40.55 | 0.88 | 0.038 |
| Erosion Category | Before Treatment (2020) | After Treatment (2022) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (km2) | Proportion (%) | Erosion Rate (t km−2 yr−1) | Total Erosion (t yr−1) | Area (km2) | Proportion (%) | Erosion Rate (t km−2 yr−1) | Total Erosion (t yr−1) | |
| Slight | 712.8 | 65.54% | 77.0 | 54,885.6 | 907.8 | 80.96% | 53.7 | 48,748.9 |
| Mild | 196.6 | 18.08% | 1223.3 | 240,500.8 | 109.5 | 9.77% | 1208.3 | 132,308.9 |
| Moderate | 58.5 | 5.38% | 3563.6 | 208,470.6 | 35.5 | 3.17% | 3573 | 126,841.5 |
| Strong | 30.9 | 2.84% | 6333.1 | 195,692.8 | 19.4 | 1.73% | 6340.2 | 122,999.9 |
| Extremely strong | 32.9 | 3.03% | 10,946.2 | 360,129.9 | 20.7 | 1.85% | 10902.8 | 225,688.0 |
| Severe | 55.8 | 5.13% | 48,802.4 | 2,723,173.9 | 28.4 | 2.53% | 43213.8 | 1,227,271.9 |
| 2022 | Slight | Mild | Moderate | Strong | Extremely Strong | Severe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | |||||||
| Slight | 633.17 | 157.46 | 47.61 | 24.08 | 22.96 | 28.58 | |
| Mild | 50.88 | 31.41 | 13.83 | 7.80 | 7.96 | 9.73 | |
| Moderate | 17.10 | 10.01 | 5.27 | 3.63 | 4.14 | 5.22 | |
| Strong | 8.53 | 5.21 | 2.80 | 2.05 | 2.83 | 4.22 | |
| Extremely strong | 7.86 | 5.09 | 2.72 | 2.03 | 2.90 | 6.24 | |
| Severe | 7.01 | 6.37 | 3.35 | 2.30 | 2.97 | 11.62 | |
| Chengping Village | Changshi Village | Youshan Town | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Erosion/(t km−2yr−1) | Total Erosion/(t yr−1) | Soil Erosion/(t km−2yr−1) | Total Erosion/(t yr−1) | Soil Erosion/(t km−2yr−1) | Total Erosion/(t yr−1) | |
| before treatment | 30.71 | 24.87 | 20.09 | 15.47 | 45.86 | 199.03 |
| after treatment | 13.32 | 10.79 | 4.75 | 3.66 | 12.71 | 55.16 |
| Slope Range (°) | Area (km2) | Erosion Modulus (t·km−2·yr−1) | Slight (km2) | Mild (km2) | Moderate (km2) | Strong (km2) | Extremely Strong (km2) | Severe (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0°~5° | 571.0 | 1181.8 | 517.6 | 54.6 | 22.1 | 12.2 | 11.8 | 9.5 |
| 5°~8° | 249.8 | 1899.5 | 179.6 | 25.7 | 9.3 | 5.5 | 5.9 | 6.9 |
| 8°~15° | 244.67 | 2731.7 | 168.9 | 28.1 | 9.3 | 5.3 | 5.8 | 9.3 |
| 15°~25° | 72.9 | 4251.6 | 47.3 | 10.4 | 3.2 | 1.8 | 2.0 | 4.1 |
| >25° | 9.5 | 8656.6 | 5.6 | 1.6 | 0.6 | 0 | 0.4 | 1.1 |
| Land Use Types | Slight | Mild | Moderate | Strong | Extremely Strong | Severe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glass land | 236.60 | 30.90 | 8.70 | 4.43 | 4.06 | 4.57 |
| Cultivated land | 232.17 | 17.18 | 7.22 | 3.95 | 3.74 | 3.81 |
| Forest | 192.22 | 18.55 | 4.44 | 2.19 | 1.98 | 2.55 |
| Construction land | 59.95 | 15.79 | 10.45 | 7.32 | 8.49 | 9.3 |
| Red-beds desert | 156.38 | 36.33 | 12.79 | 6.75 | 6.92 | 9.5 |
| Water | 42.28 | 1.79 | 0.87 | 0.56 | 0.69 | 1.26 |
| Land Use Type | Average Steepness/(°) | NDVI | Rainfall Erosivity/(MJ·mm·ha−1·ha−1·yr−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivated land | 3.6 | 0.5 | 333.0 |
| Forest | 9.5 | 0.7 | 335.4 |
| Grassland | 7.0 | 0.7 | 336.4 |
| Red-beds desert | 5.6 | 0.4 | 335.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Yang, X.; Xu, G.; Fu, J.; Cai, S.; Mu, X.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Li, L.; et al. Assessment of Integrated Soil and Water Conservation Practices on Soil Erosion Risk in a Typical Red-Beds Watershed in South China. Water 2023, 15, 2613. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142613
Xu Y, Yang X, Xu G, Fu J, Cai S, Mu X, Zhou T, Zhang W, Chen J, Li L, et al. Assessment of Integrated Soil and Water Conservation Practices on Soil Erosion Risk in a Typical Red-Beds Watershed in South China. Water. 2023; 15(14):2613. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142613
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yue, Xiankun Yang, Guoliang Xu, Jiafang Fu, Shirong Cai, Xiaolin Mu, Tao Zhou, Wenxin Zhang, Jiaxin Chen, Likuan Li, and et al. 2023. "Assessment of Integrated Soil and Water Conservation Practices on Soil Erosion Risk in a Typical Red-Beds Watershed in South China" Water 15, no. 14: 2613. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142613






