RCCC-WBM Model for Calculating the Impact of Abrupt Temperature Change and Warming Hiatus on Surface Runoff in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Profiles of the Regions of Interest, Data, and Methods
2.1. Profiles of the Regions of Interest
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Data Processing and the Method Employed
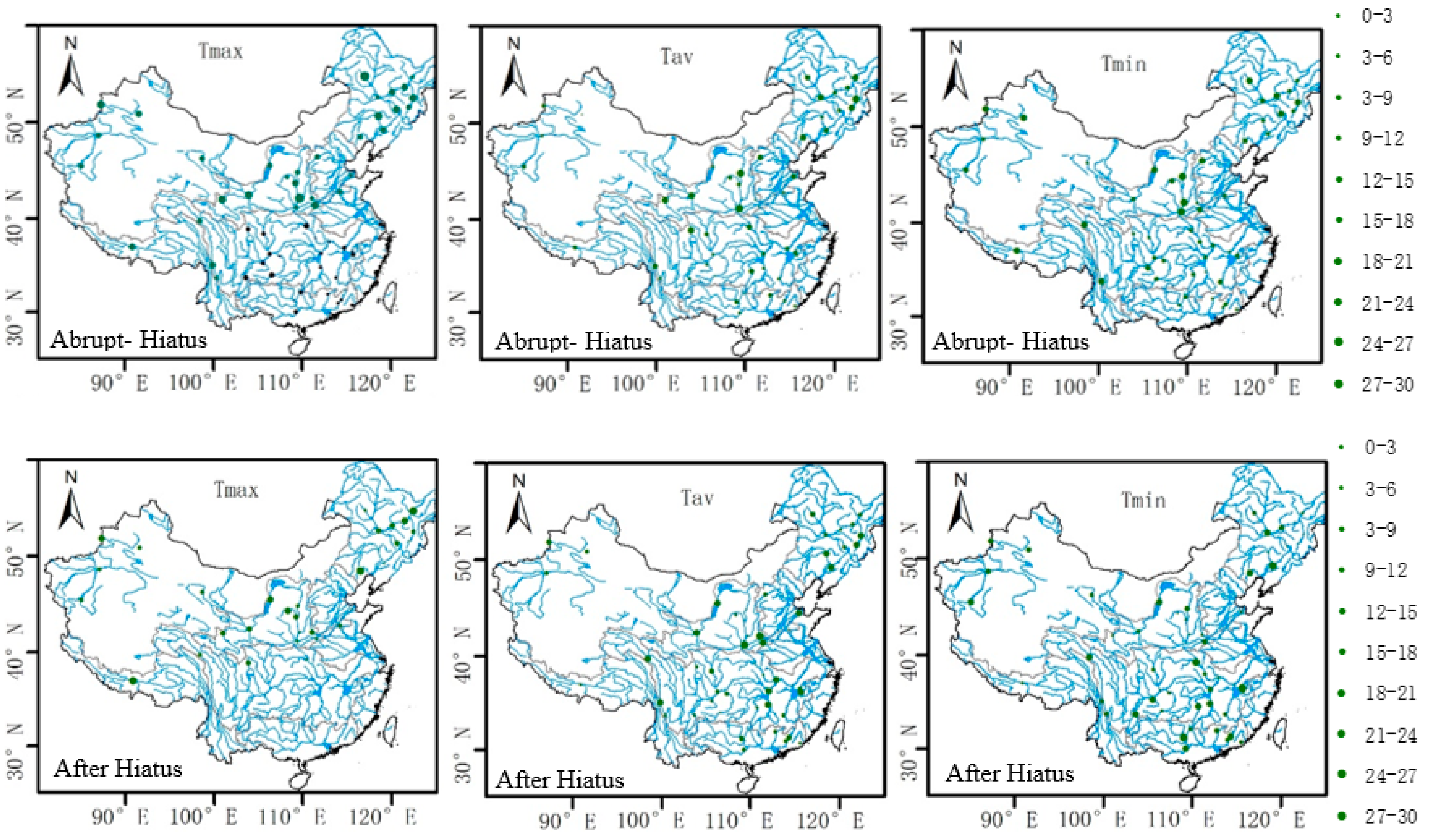
3. Analysis and Results
3.1. Multiyear Variation in Runoff
3.2. Diagnosis of Points of Abrupt Change in Measured Runoff in China
3.3. RCCC-WBM Model Parameter Calibration and Natural Runoff Process Simulation
3.4. Effects of Abrupt Temperature Change and Warming Hiatus on Surface Runoff
4. Results and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhenxin, B.A.; Jianyun, Z.H.; Xiaolin, Y.A.; Guoqing, W.A.; Ruimin, H.E.; Tiesheng, G.U.; Yanli, L.I. Quantitative assessment of the attribution of runoff change caused by four factors in the Haihe River basin. Adv. Water Sci. 2021, 32, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burn, D.H.; Cunderlik, J.M. Hydrological trends and variability in the Liard River basin. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2004, 49, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cayan, D.R.; Dettinger, M.D.; Kammerdiener, S.A.; Caprio, J.M.; Peterson, D.H. Changes in the onset of spring in the western United States. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2001, 82, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.J.; Dong, X.H.; Zeng, Q.; Wei, C.; Yu, D.; Bo, H.J.; Guo, J. Long-term runoff change trend of Yalong River basin under future climate change scenarios. Clim. Change Res. 2019, 15, 596–606, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Fyfe, J.C.; Meehl, G.A.; England, M.H.; Mann, M.E.; Santer, B.D.; Flato, G.M.; Hawkins, E.; Gillett, N.P.; Xie, S.P.; Kosaka, Y. Making sense of the early-2000s warming slow-down. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.T.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Wang, S.P.; Strauss, P.; Yao, A. Appling SWAT model to explore the impact of changes in landuse and climate on the streamflow in a watershed of northern China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 1559–1567. [Google Scholar]
- Binbin, H.U.; Chengyuan, H.A.; Ruonan, L.I.; Hua, Z.H. Research progress on the quantitative methods of calculating contribution rates of climate change and human activities to surface runoff changes. J. Nat. Resour. 2018, 33, 899–910. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.Q.; Zhang, J.Y.; Thomas, C.P. Identifying contributions of climate change and human activity to changes in runoff using epoch detection and hydrologic simulation. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2013, 18, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Ghosh, S.; Pathak, A.; Sahai, A.K. Hydrologic impacts of climate change: Comparisons between hydrological parameter uncertainty and climate model uncertainty. J. Hydrol. 2018, 566, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, G.Y.; Wu, D.Y.; Zhong, Y.X.; Zeng, F.H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.L. Progress in development and applications of SWAT model. J. Hohai Univ. 2012, 40, 243–251. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Y.C.; Zhong, Y.J.; Wu, S.F.; Shen, Y.P.; Wang, G.Y.; La, C.F.; Song, J. Analysis and comparison of responses of runoff to climate change in typical rivers on the southern and northern slopes of the Tianshan Mountains. J. Desert Res. 2011, 31, 254–260. [Google Scholar]
- Leem, H.; Baed, H. Climate change impact assessment on green and blue Water over Asian Monsoon Region. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 2407–2427. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, L.; Hong, Y.; McPherson, R.; Shafer, M.; Gade, D.; Williams, D.; Chen, S.; Lilly, D. Climate change and hydrological response in the Trans-State Oologah Lake watershed—Evaluating dynamically downscaled NARCCAP and statistically downscaled CMIP3 simulations with VIC model. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 3291–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.M.; Zhang, D. Temporal and spatial change analysis of the sensitivity of potential evapotranspiration to meteorological influencing factors in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2011, 66, 579–588. [Google Scholar]
- Naik, P.K.; Jay, D.A. Distinguishing human and climate influences on the Columbia River: Changes in mean flow and sediment transport. J. Hydrol. 2011, 404, 259–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J. River flow forecasting through conceptual models: Part 1: A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Liu, P.; Gao, S.; Xia, J.; Chen, J.; Cheng, L. Improving hydrological projection performance under contrasting climatic conditions using spatial coherence through a hierarchical Bayesian regression framework. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 3405–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piniewski, M.; Voss, F.; Bärlund, I.; Okruszko, T.; Kundzewicz, Z. Effect of modelling scale on the assessment of climate change impact on river runoff. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 737–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, L.J.; Zhengf, L.; Yin, R.S. Variation trend analysis of precipitation and runoff in Yanhe River Basin during 1952–2008. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2011, 25, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Roos, M. A Trend of Decreasing Snowmelt Runoff in Northern California; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1991; pp. 29–36.
- Roos, M. Possible changes in California snowmelt patterns. In Proceedings of the Fourth Pacific Climate Workshop, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 22–26 March 1987; pp. 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Setegn, S.G.; Rayner, D.; Melesse, A.M.; Dargahi, B.; Srinivasan, R. Impact of climate change on the hydroclimatology of Lake Tana Basin, Ethiopia. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W04511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Y. Managing water for sustainable utilization as China warms. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Nat. Resour. 2019, 17, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.Q.; Zhang, J.Y.; Jin, J.L.; Liu, Y.L.; He, R.M.; Bao, Z.X.; Liu, C.S.; Li, Y. Regional calibration of a water balance model for estimating stream flow in ungauged areas of the Yellow River basin. Quat. Int. 2014, 336, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, J. Impact assessment of Climate Anomalies on water resources in the Middle Yellow River using a grid hydrological model and its application. Adv. Water Sci. 2000, 11, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.C.; Wang, G.X.; Song, C.L. Study on the law of runoff retreat in the Threeriver Headwaters region. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin. Resour. Environ. 2018, 27, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Y.L.; Pang, Z.H. What is the primary factor controlling trend of Glacier No. 1 runoff in the Tianshan Mountains: Temperature or precipitation change? Hydrol. Res. 2017, 48, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Xun, S.; Lai, D.; Fan, Y.; Li, Z. Changes in daily climate extremes in the arid area of northwestern China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 112, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Wen, Q.H.; Wu, Y. Penalized maximal t test for detecting undocumented mean change in climate data series. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2007, 46, 916–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.X.; Zhang, G.X.; Yin, X.R. Analysis of runoff change and its influencing factors in Nenjiang River Basin in recent 50 years. Adv. Water Sci. 2009, 20, 416–421. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.W.; Zhang, S.L.; Xu, X.Y. Attribution analysis for runoff decline in Yellow River Basin during past fifty years based on Budyko hypothesis. Sci. Sin. Tech. 2015, 45, 1024–1034. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, G.H.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X. Uncertainty assessment of climate change impacts on the hydrology of small prairie wetlands. J. Hydrol. 2011, 396, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.X. Study on Climate Change in Southwestern China; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zipper, S.C.; Motew, M.; Booth, E.G.; Chen, X.; Qiu, J.; Kucharik, C.J.; Carpenter, S.R.; Loheide, S.P., II. Continuous separation of land use and climate effects on the past and future water balance. J. Hydrol. 2018, 565, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zakwan, M.; Ahmad, Z. Trend analysis of hydrological parameters of Ganga River. Arab. J. Geosci. 2023, 14, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, S.; Lone, M.A.; Goel, N.K.; Zakwan, M. Trend Analysis of Hydro-Meteorological Parameters in the Jhelum River Basin, North Western Himalayas. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2021, 148, 1417–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okkan, U.; Ersoy, Z.B.; Kumanlioglu, A.A.; Fistikoglu, O. Embedding machine learning techniques into a conceptual model to improve monthly runoff simulation: A nested hybrid rainfall-runoff modeling. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumanlioglu, A.A.; Fistikoglu, O. Performance enhancement of a conceptual hydrological model by integrating artificial intelligence. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2019, 24, 04019047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, M.; Yang, W.; Lindsay, J.; Tolson, B.; Dehnavi, M.M. A review of parallel computing applications in calibrating watershed hydrologic models. Environ. Model. Softw. 2022, 151, 105370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Hydrological Station | Rate on a Regular Basis | Validation Period | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Data Series | ENS/% | ER/% | The Data Series | ENS/% | ER/% | |
| Ben Zilan | 1956–1985 | 83.12 | 2.92 | 1986–1995 | 83.51 | 5.24 |
| Cun Tan | 1956–1985 | 68.93 | 1.15 | 1986–1996 | 84.61 | 5.19 |
| Han Kou | 1956–1965 | 71.48 | 1.72 | 1966–1970 | 62.28 | 3.24 |
| Du Fengkeng | 1956–1970 | 72.5 | 2.84 | 1971–1980 | 74.37 | 5.73 |
| Hu Shan | 1956–1970 | 76.26 | 0.82 | 1971–1980 | 77.56 | 2.17 |
| Cheng Lingji | 1956–1965 | 79.04 | 2.17 | 1966–1975 | 64.31 | 4.8 |
| Hu Kou | 1956–1975 | 63.33 | 2.51 | 1976–1989 | 73.7 | 4.78 |
| Gui Gang | 1956–1985 | 63.32 | 0.93 | 1986–1996 | 75.63 | 2.95 |
| Gui Lin | 1956–1990 | 75.98 | 3.49 | 1991–2003 | 65.25 | 3.99 |
| He Yuan | 1956–1962 | 73.02 | 3.64 | 1963–1968 | 80.48 | 5.66 |
| Heng Shan | 1956–1985 | 80.71 | 1.03 | 1986–1998 | 80.76 | 2.88 |
| Chao An | 1956–1965 | 64.13 | 3.9 | 1966–1970 | 79.47 | 5.99 |
| Plump reservoir | 1956–1970 | 66.51 | 0.37 | 1971–1985 | 77.55 | 2.7 |
| Harbin | 1956–1974 | 71.69 | 0.33 | 1975–1984 | 74.45 | 1.9 |
| Jiamusi | 1956–1970 | 71.41 | 1.55 | 1971–1985 | 83.58 | 2.65 |
| Chao Yang | 1956–1970 | 80.53 | 2.06 | 1971–1985 | 81.21 | 2.77 |
| Zhimen Da | 1956–1965 | 75.45 | 4.46 | 1966–1970 | 85.46 | 5.83 |
| Shi Gu | 1956–1970 | 76.37 | 2.06 | 1971–1985 | 85.69 | 5.77 |
| Lengshui Jiang | 1956–1970 | 68.24 | 1.17 | 1971–1980 | 60.44 | 4.22 |
| Xiang Tan | 1956–1970 | 72.88 | 1.91 | 1971–1980 | 61.36 | 2.73 |
| Tong Guan | 1956–1980 | 71.63 | 0.83 | 1981–1990 | 77.33 | 1.22 |
| Li Jin | 1956–1970 | 83.98 | 2.68 | 1971–1979 | 61.69 | 3.41 |
| Wenjia Chuan | 1956–1980 | 83.03 | 4.3 | 1981–1991 | 82.32 | 5.23 |
| Run Chen | 1956–1965 | 64.2 | 0.86 | 1966–1970 | 67.05 | 2.41 |
| Mudan Jiang | 1956–1970 | 69.48 | 0.22 | 1971–1987 | 75.97 | 3.05 |
| Wang Ben | 1956–1960 | 65.2 | 2.99 | 1961–1965 | 66.54 | 4.28 |
| Tangnai Hai | 1956–1980 | 72.84 | 3.34 | 1981–1990 | 63.19 | 4.17 |
| Lan Zhou | 1956–1970 | 80.46 | 0.91 | 1971–1985 | 80.06 | 4.54 |
| Shizui Shan | 1956–1970 | 83.31 | 1.32 | 1971–1985 | 79.88 | 4.95 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Ma, L.; Liu, T.; Sun, B.; Chen, Y.; Qiao, Z. RCCC-WBM Model for Calculating the Impact of Abrupt Temperature Change and Warming Hiatus on Surface Runoff in China. Water 2023, 15, 2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142522
Huang X, Ma L, Liu T, Sun B, Chen Y, Qiao Z. RCCC-WBM Model for Calculating the Impact of Abrupt Temperature Change and Warming Hiatus on Surface Runoff in China. Water. 2023; 15(14):2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142522
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xing, Long Ma, Tingxi Liu, Bolin Sun, Yang Chen, and Zixu Qiao. 2023. "RCCC-WBM Model for Calculating the Impact of Abrupt Temperature Change and Warming Hiatus on Surface Runoff in China" Water 15, no. 14: 2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142522
APA StyleHuang, X., Ma, L., Liu, T., Sun, B., Chen, Y., & Qiao, Z. (2023). RCCC-WBM Model for Calculating the Impact of Abrupt Temperature Change and Warming Hiatus on Surface Runoff in China. Water, 15(14), 2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142522





