Temperature-Dependent Growth Characteristics and Competition of Pseudanabaena and Microcystis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Stain Selection and Culture Condition
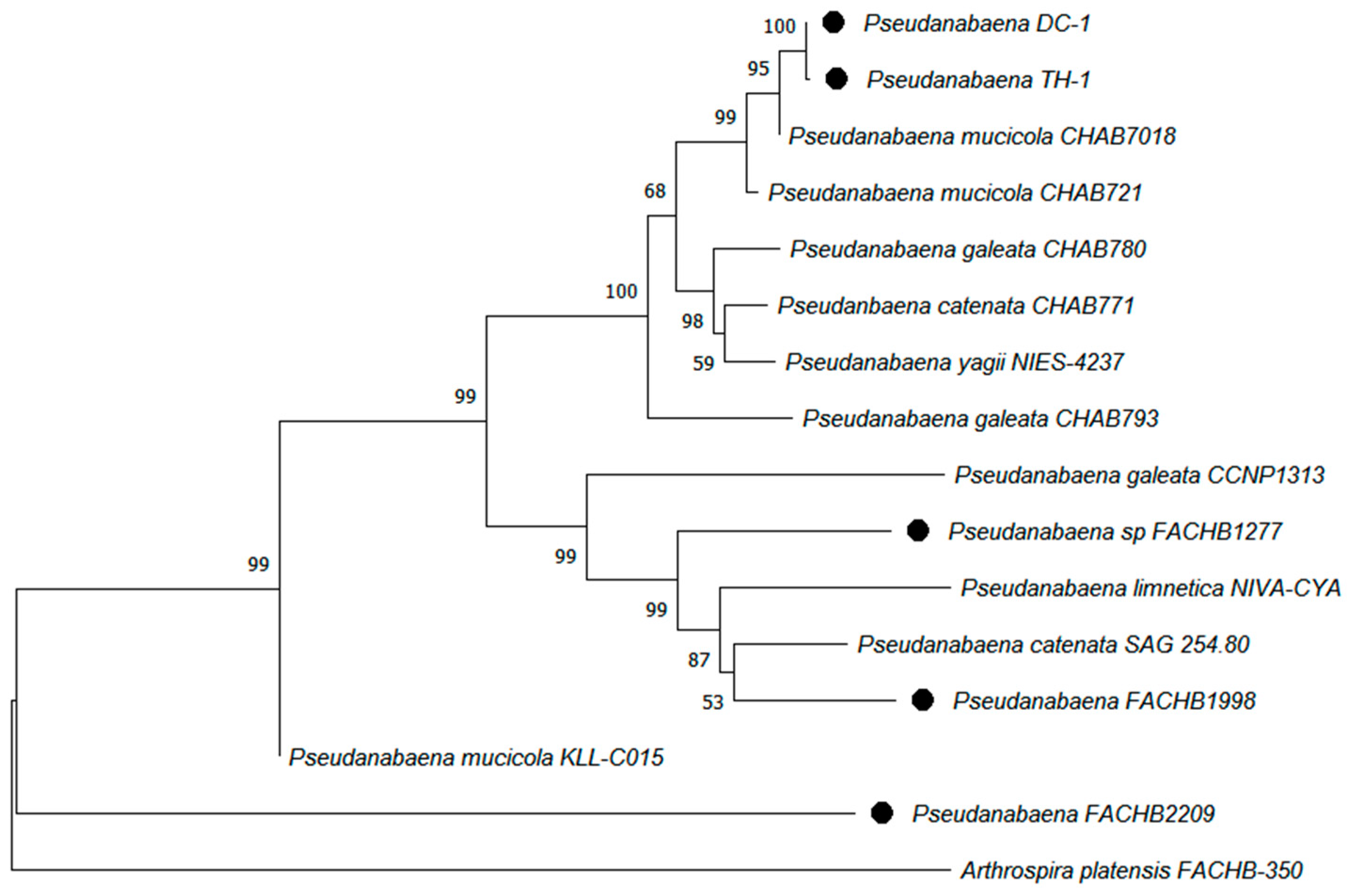
2.2. DNA Extraction, Sequencing, and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. Experimental Design
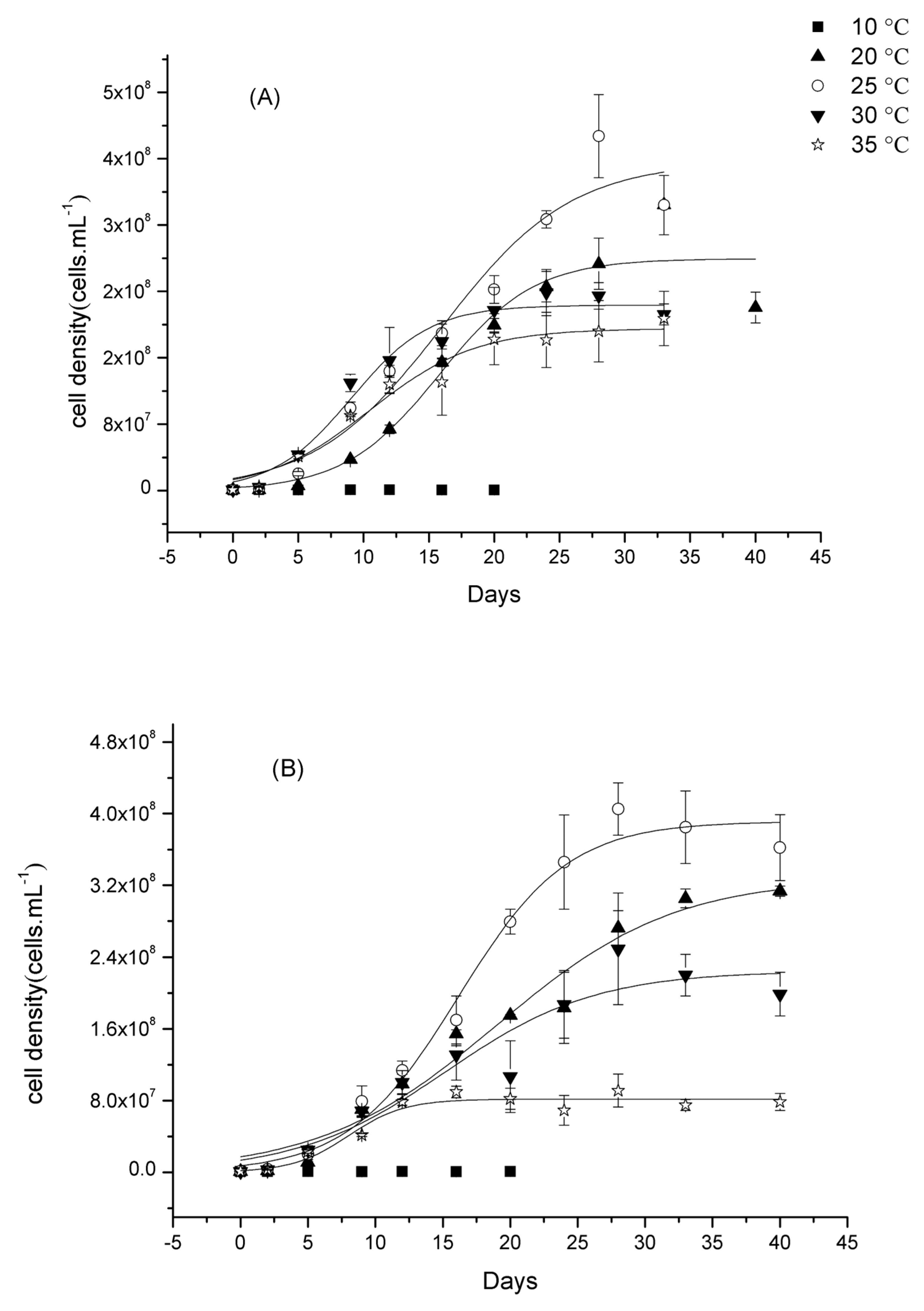
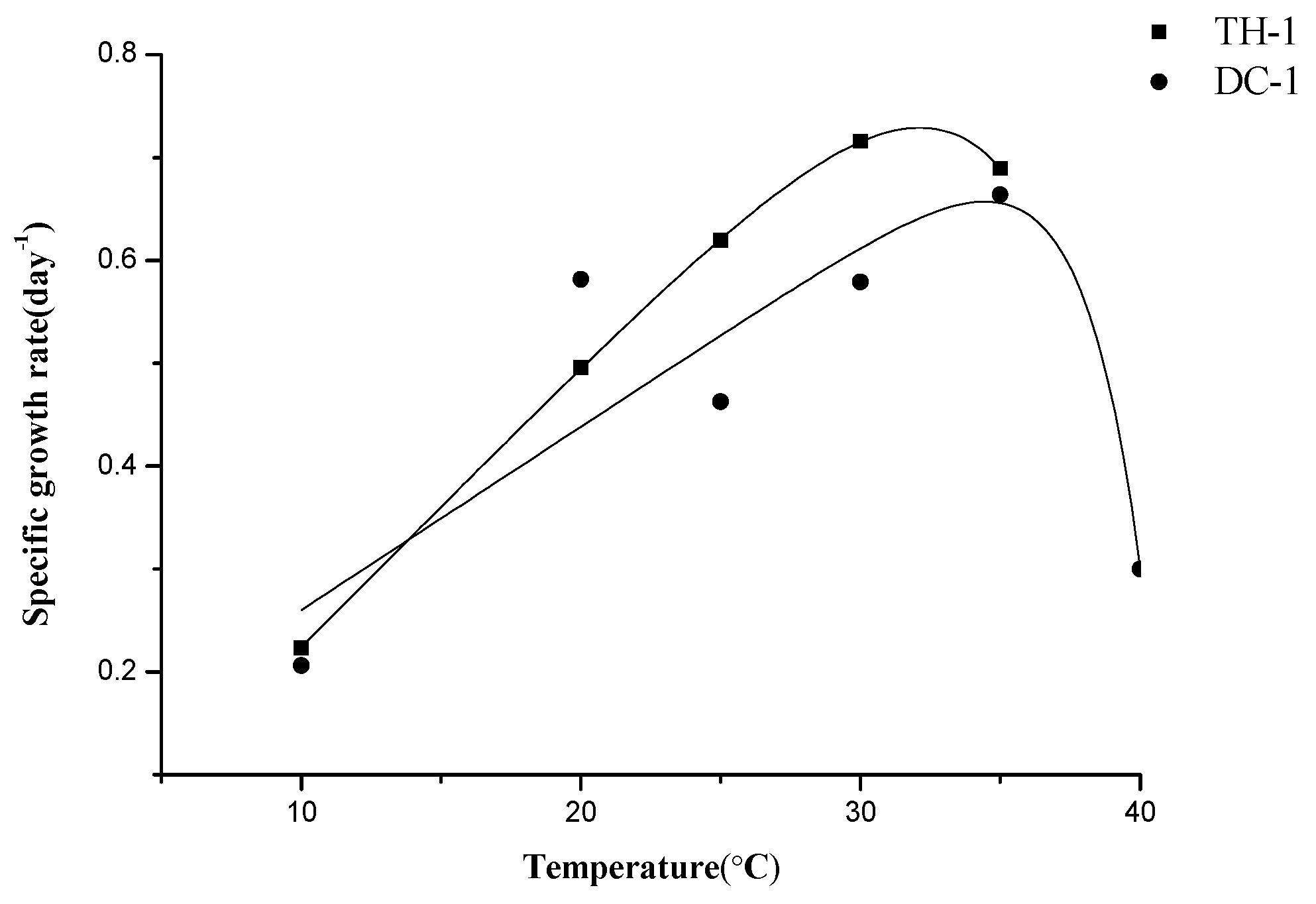
2.4. Growth Characteristics in Mono-Culture
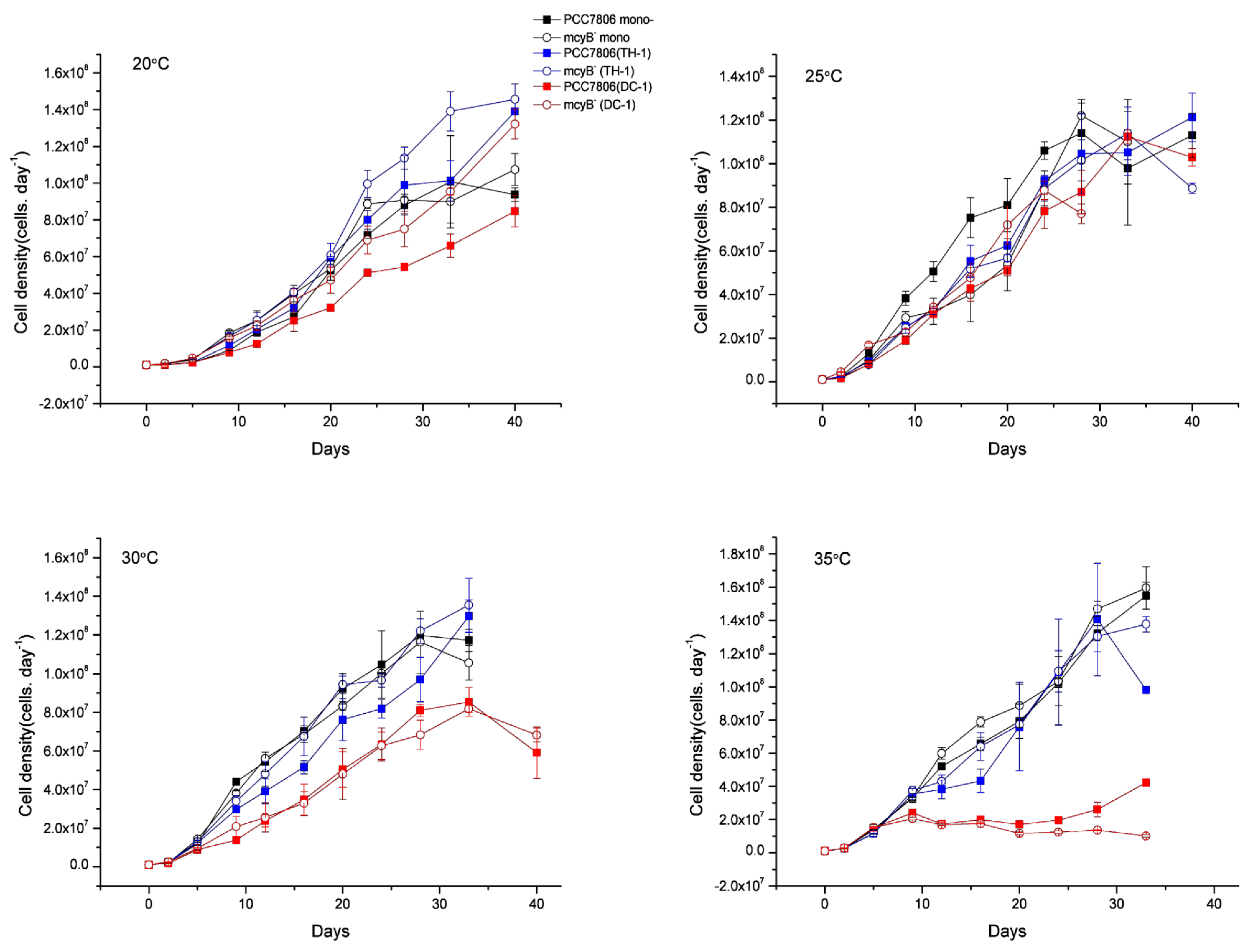
2.5. Interspecies Competition Analyses
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Pseudanabaena
3.2. The Growth of Pseudanabaena in Mono-Culture Experiments at Different Temperature
3.3. The Growth of Microcystis in Mono-Culture Experiments at Different Temperatures
3.4. Dominant Characteristics of Pseudanabaena and Microcystis in Co-Culture at Different Temperatures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.J.; Xu, Y.; Shao, J.H.; Wang, J.; Li, R.H. Genes associated with 2-methylisoborneol biosynthesis in cyanobacteria: Isolation, characterization, and expression in response to light. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, 18665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zheng, L.L.; Li, L.; Song, L.R. 2-Methylisoborneol production characteristics of Pseudanabaena sp. FACHB 1277 isolated from Xionghe Reservoir, China. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 3353–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castenholz, R.W.; Rippka, R.; Herdman, M.; Wilmotte, A. Form-genus XII. Pseudanabaena Lauterborn 1916. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacterilogy, 2nd ed.; Boone, D.R., Castenholz, R.W., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 554–557. [Google Scholar]
- Zwart, G.; Kamst-van Agterveld, M.P.; van der Werff-Staverman, I.; Hagen, F.; Hoogveld, H.L.; Gons, H.J. Molecular characterization of cyanobacterial diversity in a shallow eutrophic lake. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez, B.; Bauer, K.; Bergman, B. Epilithic cyanobacterial communities of a marine tropical beach rock (Heron Island, Great Barrier Reef): Diversity and diazotrophy. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2007, 73, 3656–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acinas, S.G.; Haverkamp, T.H.A.; Huisman, J.; Stal, L.J. Phenotypic and genetic diversification of Pseudanabaena spp. (cyanobacteria). ISME. J. 2009, 3, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villena, M.J.; Romo, S. Effects of nutrients, Fish, Charophytes and algal sediment recruitment on the phytoplankton ecology of a shallow Lake. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2007, 92, 626–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sthapit, E.; Ochs, C.A.; Zimba, P.V. Spatial and temporal variation in phytoplankton community structure in a southeastern U.S. reservoir determined by HPLC and light microscopy. Hydrobiologia 2008, 600, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izaguirre, G.; Taylor, W.; Pasek, J. Off-flavor problems in two reservoirs, associated with planktonic Pseudanabaena species. Water. Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niiyama, Y.; Tuji, A.; Takemoto, K.; Ichise, S. Pseudanabaena foetida sp. Nov. and P. subfoetida sp. Nov. (Cyanophyta/Cyanobacteria) producing 2-methylisoborneol from Japan. Fottea. Olomouc. 2016, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Omar, W.M.W.; Merican, F.M.M.S.; Convey, P.; Foog, C.P.; Najimudin, N. Characterisation of Pseudanabaena amphigranulata (Synechococcales) isolated from a man-made pond, Malaysia: A polyphasic approach. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 3187–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.T.; Tian, C.; Pei, H.Y.; Hu, W.R.; Xie, J. Environmental factors influencing cyanobacteria community structure in Dongping Lake, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 15, 2196–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Liu, Y.S.; Hu, W.R.; Hao, D.P.; Pei, H.Y.; Tian, C.; Wei, J.L.; Feng, Y.W. Seasonal pattern of cyanobacteria community and its relationship with environmental factors: A case study in Luoma Lake, East China. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 57, 6658–6669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.J.; Li, Q.H.; Wang, X.Q.; Han, M.S.; Li, L.; Xiao, J.; Liu, Y.P. Responses of phytoplankton functional groups to environmental factors in the Maixi river, southwest China. J. Limnol. 2018, 77, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.S.; Li, Q.H.; Chen, H.L.; Xiao, J.; Jiang, F. Spatial and temporal variations in cyanobacteria and microcystins in Aha reservoir, Southwest China. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2018, 36, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertos-Fortis, M.; Farnelid, H.M.; Lindh, M.V.; Casini, M.; Andersson, A.; Pinhassi, J.; Legrand, C. Unscrambling cyanobacteria community dynamics related to environmental factors. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.B.; Li, Q.H.; Chen, W.S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, S.H.; Han, M.S.; Brancej, A. The key environmental factors driving the succession of phytoplankton functional groups in Hongfeng reservoir, southwest China. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2022, 40, 1472–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, S.-J.; Cui, Y.S.; Lee, J.J.; Choi, I.-C.; Oh, H.-M.; Ahn, C.-Y. Network analysis reveals succession of Microcystis genotypes accompanying distinctive microbial modules with recurrent patterns. Water Res. 2020, 170, 115326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Hu, L.L.; Shen, W.; Zeng, J.Y.; Li, L.; Song, L.R.; Gan, N.Q. The involvement of α-proteobacteria Phenybacterium in maintaining the dominance of toxic Microcystis blooms in Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 1066–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.L.; Shan, K.; Huang, L.C.; Li, Y.R.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, Q.C.; Song, L.R. Environmental factors associated with cyanobacterial assemblages in a mesotrophic subtropical plateau lake: A focus on bloom toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otten, T.G.; Paerl, H.W.; Dreher, T.W.; Kimmerer, W.J.; Parker, A.E. The molecular ecology of Microcystis sp. blooms in the San Francisco Estuary. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 3619–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedmak, B.; Kosi, G. Microcystins in Slovene freshwaters (Central Europe)-first report. Nat. Toxins 1997, 5, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarmoshenko, L.P.; Kureyshevich, A.V.; Yakushin, V.M. Microcystis botrys and Lemmermanniella flexa-new species of Cyanoprokaryota for the flora of Ukraine in phytoplankton of the Kanev reservoir. Hydrobiol. J. 2013, 49, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, V.; Morais, J.; Vale, M. Microcystins and cyanobacteria trends in a 14 year monitoring of a temperate eutrophic reservoir (Aguieira, Portugal). J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agha, R.; Labrador, M.D.M.; de los Ríos, A.; Quesada, A. Selectivity and detrimental effects of epiphytic Pseudanabaena on Microcystis colonies. Hydrobiologia 2016, 777, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowe, M.A.D.; Mitrovic, S.M.; Lim, R.P.; Furey, A.; Yeo, D.C.J. Tropical cyanobacterial blooms: A review of prevalence, problem taxa, toxins and influencing environmental factors. J. Limnol. 2015, 74, 205–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohary, T.; Fishbein, T.; Shlichter, M.; Naselli-Flores, L. Larger cell or colony size in winter, smaller in summer- a pattern shared by many species of Lake Kinneret phytoplankton. Inland Waters 2017, 7, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Climate change: A catalyst for global expansion of harmful cyanobacterial blooms. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2009, 1, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, P.M.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Sandrini, G.; Stal, L.J.; Matthijs, H.C.P.; Davis, T.W.; Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. How rising CO2 and global warming may stimulate harmful cyanobacterial blooms. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.; Codd, G.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Ibelings, B.W.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Visser, P.M. Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Blooms like it hot. Science 2009, 320, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, C.C.; Iblings, B.W.; Hoffmann, E.P.; Hamilton, D.P.; Brookes, J.D. Eco-physiological adaptations that favour freshwater cyanobacteria in a changing climate. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1394–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anneville, O.; Gammeter, S.; Straile, D. Phosphorus decrease and climate variability: Mediators of synchrony in phytoplankton changes among European peri-alpine lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 1731–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Qin, B.Q.; Paerl, H.W.; Zhang, Y.L.; Ma, J.R.; Chen, Y.W. Earlier and warmer springs increase cyanobacterial (Microcystis spp.) blooms in subtropical Lake Taihu, China. Freshw. Biol. 2014, 59, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.S.; Akbar, S.; Sun, Y.F.; Gu, L.; Zhang, L.; Lyu, K.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Z. Cyanobacterial and dominance and succession: Factors, mechanisms, predictions, and managements. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Otten, T.G. Duelling‘CyanoHABs’: Unravelling the environmental drivers controlling dominance and succession among diazotrophic and non-N2-fixing harmful cyanobacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, K.; Song, L.R.; Chen, W.; Li, L.; Liu, L.M.; Wu, Y.L.; Jia, Y.L.; Zhou, Q.C.; Peng, L. Analysis of environmental divers influencing interspecific variations and associations among bloom-forming cyanobacteria in large, shallow eutrophic lakes. Harmful Algae 2019, 84, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robarts, R.D.; Zohary, T. Temperature effects on photosynthetic capacity, respiration, and growth rates of bloom-forming cyanobacteria. N. Zeal. J. Mar. Fresh 1987, 21, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, T.; Zhang, D.L.; Hu, C.X. Comparative studies on phosphate utilization of two bloom-forming Microcystis spp. (cyanobacteria) isolated from Lake Taihu (China). J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.S.; Zhu, J.; Wang, M.W.; Dong, W.Y. Dominance and growth factors of Pseudanabaena sp. in drinking water source reservoirs, Southern China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.E.; Wilson, W.A.; Hay, M.E. Intraspecific variation in growth and morphology of the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 7386–7389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.L. Polyphasic characterization of four species of Pseudanabaena (Oscillatoriales, Cyanobacteria) from China and insights into polyphyletic divergence within the Pseudanabaena genus. Phytotaxa 2015, 192, 001–012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudi, K.; Skulberg, O.M.; Jakobsen, K.S. Evolution of cyanobacteria by exchange of genetic material among phyletically related strains. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 3453–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratkowsky, D.A.; Lowry, R.K.; McMeekin, T.A.; Stokes, A.N.; Chandler, R.E. Model for bacterial culture growth rate throughout the entire biokinetic temperature range. J. Bacteriol. 1983, 154, 1222–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volterra, V. Fluctuation in the abundance of a species considered mathematically. Nature 1926, 118, 558–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.L.; Yu, G.L.; Song, G.F.; Chang, J.B.; Wan, C.Y.; Li, R.H. Molecular specifificity and detection for Pseudanabaena (cyanobacteria) species based on rbcLX sequences. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2015, 60, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te, S.H.; Tan, B.F.; Thompson, J.R.; Gin, K.Y.H. Relationship of microbiota and cyanobacterial secondary metabolites in Planktothricoides-dominated bloom. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4199–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temraleeva, A.D. Cyanobacterial diversity in the soils of Russian dry steppes and semideserts. Microbiology. 2018, 87, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, H.; Hakim, A.; Morrow, C.D.; Eipers, P.G.; Davila, A.; Andersen, D.T.; Bej, A.K. Comparison of two bioinformatics tools used to characterize the microbial diversity and predictive functional attributes of microbial mats from Lake Obersee, Antarctica. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2017, 140, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Li, R.H. Effects of light and temperature on the odor production of 2-methylisoborneol-producing Pseudanabaena sp. and geosmin-producing Anabaena ucrainica (cyanobacteria). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2015, 58, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romo, S. Growth parameters of Pseudanabaena galeata Böcher in culture under different light and temperature conditions. Algol. Stud. Aichiv. Für. Hydrobiol. Suppl. Vol. 1994, 75, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.L.; Li, Q.; Liu, W.; Zhang, S.S.; Xu, H.Z.; Pei, H.Y. Changes of phytoplankton and water environment in a highly urbanized subtropical lake during the past ten years. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 879, 162985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, H.; Chang, K.-H.; Kusaba, M.; Nakano, S.-I. Temperature-dependent dominance of Microcystis (Cyanophyceae) species: M. aeruginosa and M. wesenbergii. J. Plankton. Res. 2009, 31, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Litchman, E. Effects of temperature and nitrogen availability on the growth of invasive and native cyanobacteria. Hydrobiologia 2016, 763, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.Q.; Mallery, K.; Hong, J.R.; Hondzo, M. Temperature effects on growth and buoyancy of Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Plankton. Res. 2018, 40, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lürling, M.; Eshetu, F.; Faassen, E.J.; Kosten, S.; Huszar, V.L.M. Comparison of cyanobacterial and green algal growth rates at different temperatures. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.F.; Zhou, M.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Meng, Y.Y.; Liu, J.L.; Zuo, Z.J. Effects of high light and temperature on Microcystis aeruginosa cell growth and β-cyclocitral emission. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2020, 192, 110313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Yu, Y.; Shi, X.L. Temperature triggers the annual cycle of Microcystis, comparable results from the laboratory and a large shallow lake. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninio, S.; Lupu, A.; Viner-Mozzini, Y.; Zohary, T.; Sukenik, A. Multiannual variation in Microcystis bloom episodes-temperature drives shift in species composition. Harmful Algae 2020, 92, 101710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.M.; Steinman, A.D.; Tang, X.M.; Xue, Q.J.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Xie, L.Q. Response of bacterial communities to cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms in Lake Taihu, China. Harmful Algae 2017, 68, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Shi, X.L. Interannual and seasonal shift between Microcystis and Dolichospermum: A 7-Year investigation in Lake Chaohu, China. Water 2020, 12, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Li, L.; Zheng, L.L.; Dai, G.Y.; Ma, H.Y.; Shan, K.; Wu, H.D.; Zhou, Q.C.; Song, L.R. Patterns of succession between bloom-forming cyanobacteria Aphanizomenon flos-aquae and Microcystis and related environmental factors in large, shallow Dianchi Lake, China. Hydrobiologia 2016, 765, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conradie, K.R.; Barnard, S. The dynamics of toxic Microcystis strains and microcystin production in two hypertrofic South African reservoirs. Harmful Algae 2012, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.J.; Pan, R.J.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, T.Q.; Fan, J.J. Interspecific competition between Microcystis aeruginosa and Pseudanadaena and their production of T&O compounds. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126509. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]



| Temperature (°C) | Competitive Parameters | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 20 | −0.31 | −1.20 | 0.14 | 0.05 | 2.54 | 3.37 | 3.81 | 3.77 |
| 25 | 0.15 | 1.77 | 0.21 | 0.46 | 5.53 | 5.66 | 4.75 | 6.66 |
| 30 | 0.09 | −1.16 | 0.27 | 0.18 | 2.93 | 2.83 | 2.84 | 2.79 |
| 35 | 0.02 | 0.41 | 0.70 | 1.18 | 1.35 | 0.96 | 0.69 | 2.34 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, L.; Wang, H.; Cui, J.; Zou, W.; Li, J.; Shan, K. Temperature-Dependent Growth Characteristics and Competition of Pseudanabaena and Microcystis. Water 2023, 15, 2404. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132404
Hu L, Wang H, Cui J, Zou W, Li J, Shan K. Temperature-Dependent Growth Characteristics and Competition of Pseudanabaena and Microcystis. Water. 2023; 15(13):2404. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132404
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Lili, Haiyan Wang, Jingzhen Cui, Wansheng Zou, Jie Li, and Kun Shan. 2023. "Temperature-Dependent Growth Characteristics and Competition of Pseudanabaena and Microcystis" Water 15, no. 13: 2404. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132404
APA StyleHu, L., Wang, H., Cui, J., Zou, W., Li, J., & Shan, K. (2023). Temperature-Dependent Growth Characteristics and Competition of Pseudanabaena and Microcystis. Water, 15(13), 2404. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132404







