Effect and Mechanism of Applying Myriophyllum Verticillatum for Reclaimed Water Purification in Urban Rivers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
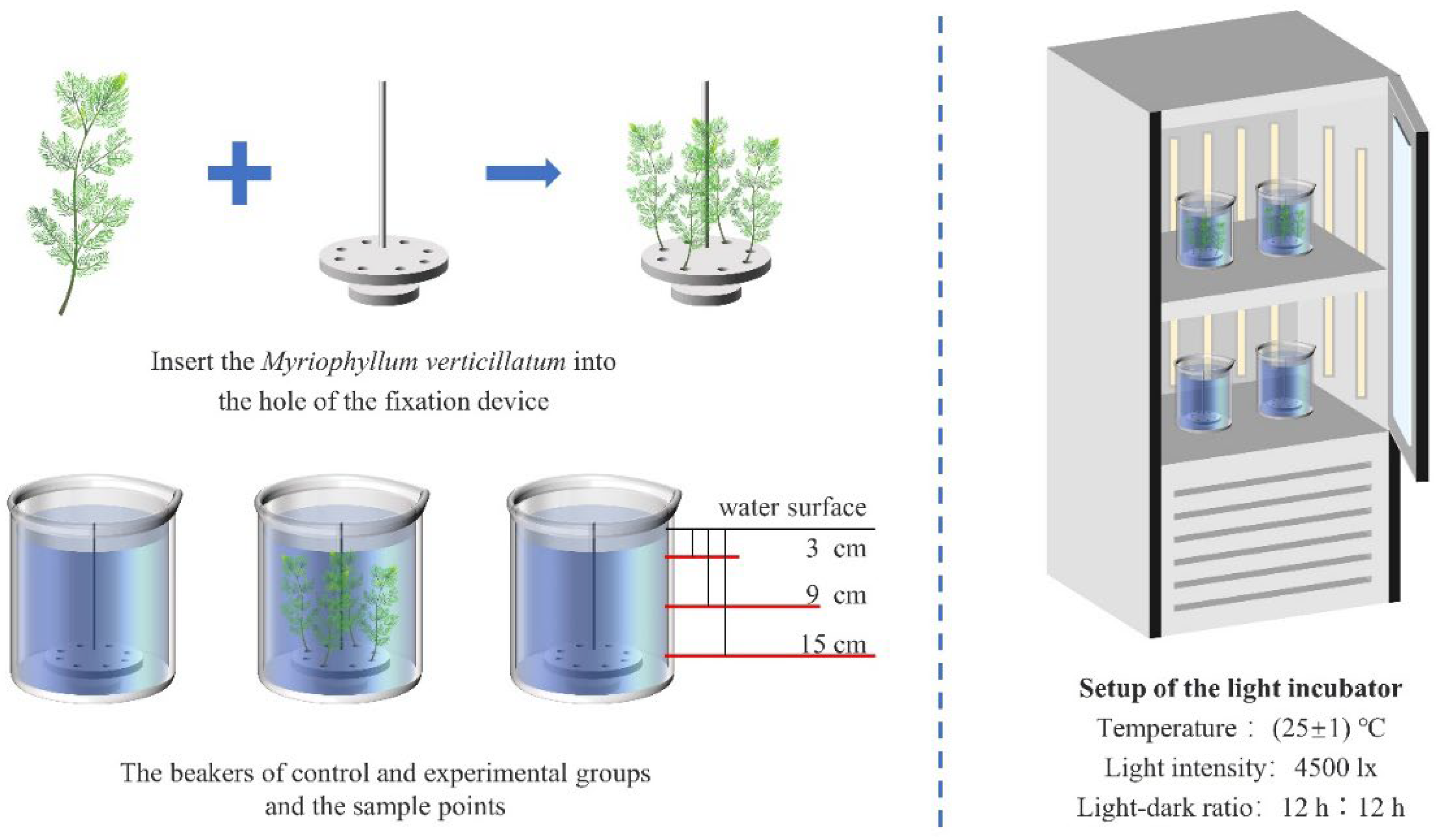
2.1. Experimental Subjects and Condition Settings
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.3. Analysis Methods
2.3.1. Analysis of Water Quality Indicators
2.3.2. Analysis of Plant Growth and Composition
2.3.3. Analysis of Microbial Communities on Plant Surfaces
3. Results and Discussion
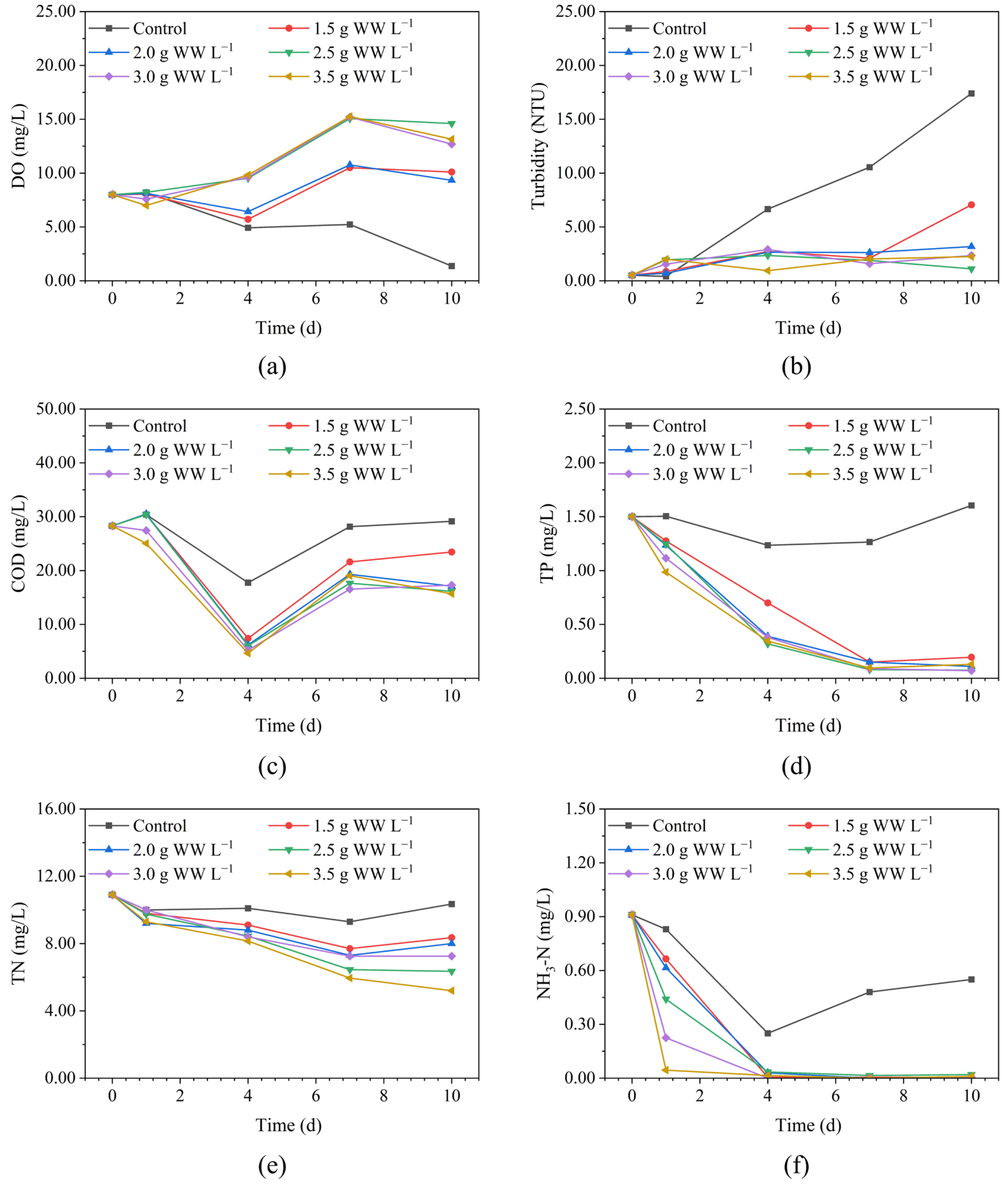
3.1. Water Quality Improvement Performance
3.2. Stem and Leaf Indicators of M. verticillatum with Different Roles in Nutrient Removal
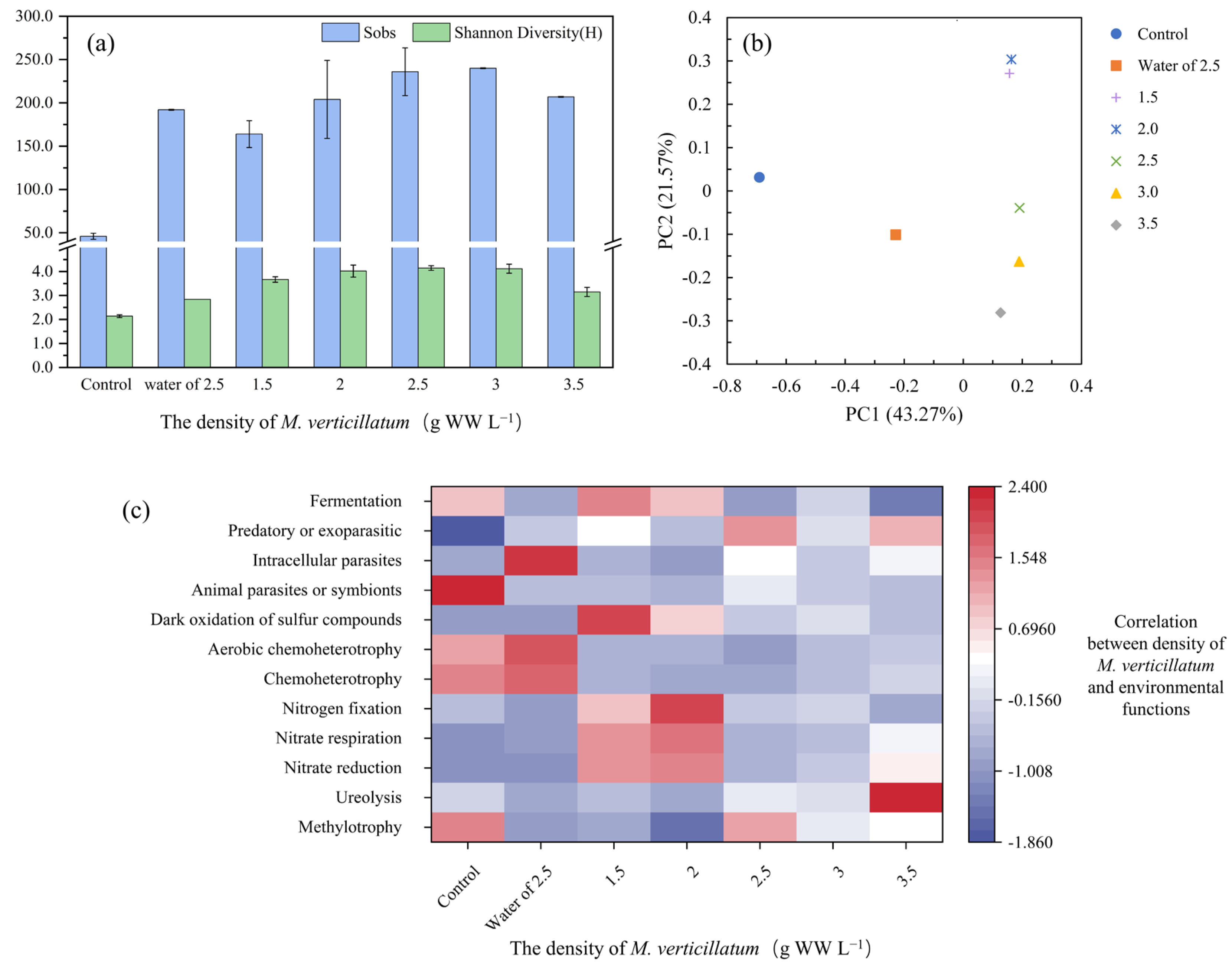
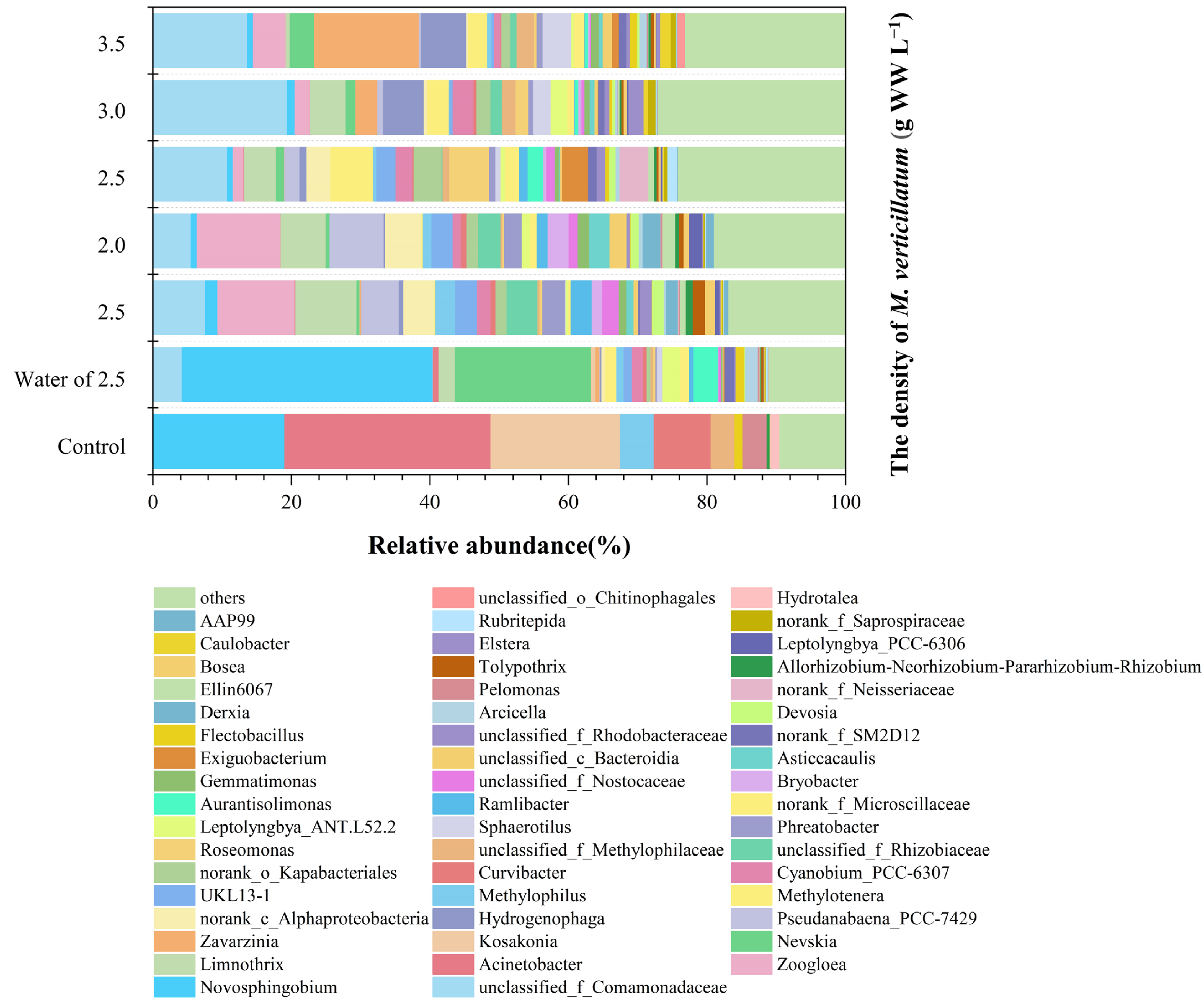
3.3. Analysis of Colonies Attached to the Surface of Myriophyllum verticillatum
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Macura, V.; Štefunková, Z.; Škrinár, A.; Halaj, P. Design of restoration of regulated rivers based on bioindication. Procedia Eng. 2016, 161, 1025–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. The distribution pattern and ecological restoration technology of aquatic plants in a eutrophic water landscape belt. Water Supply 2021, 22, 860–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohl, E.; Lininger, K.B.; Scott, D.N. River beads as a conceptual framework for building carbon storage and resilience to extreme climate events into river management. Biogeochemistry 2018, 141, 365–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.F.; Thorne, C.R.; Castro, J.M.; Kondolf, G.M.; Mazzacano, C.S.; Rood, S.B.; Westbrook, C. Biomic river restoration: A new focus for river management. River Res. Appl. 2019, 36, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Sun, S.; Fu, G.; Hall, J.W.; Ni, Y.; He, L.; Yi, J.; Zhao, N.; Du, Y.; Pei, T.; et al. Pollution exacerbates China’s water scarcity and its regional inequality. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Pei, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Shu, L.; Zhang, H. Twenty years of China’s water pollution control: Experiences and challenges. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.; Adin, A.; Crook, J.; Davis, C.; Hultquist, R.; Jimenez-Cisneros, B.; Kennedy, W.; Sheikh, B.; van der Merwe, B. Climbing the ladder: A step by step approach to international guidelines for water recycling. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 43, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, W.; Lyu, S.; Jiao, W. Perceptions of different stakeholders on reclaimed water reuse: The case of Beijing, China. Sustainability 2015, 7, 9696–9710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wu, G.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Niu, Z.; Hu, H. Characteristics of water quality of municipal wastewater treatment plants in China: Implications for resources utilization and management. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 131, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Zhu, M.; Liu, J.; Weng, B.; Xiang, C.; Gong, J.; Wang, N.; Yang, G. Photovoltaic water lifting and ecological water supplement for Xiang’an water system in Xiamen city. Energy Procedia 2017, 142, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. State Environmental Protection Administration, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Wang, M.; Li, Q.; Fan, G.; Fan, Y.; Zhu, G. Effect of nitrogen nutrients on chlorophyll a and algal density in landscape water supplied with reclaimed water. Water Wastewater Eng. 2010, 46, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, Q.; Lun, Z.; Fan, G.; Zhu, G. The effect of phosphorus nutrients on chlorophyll a and algal density in landscape water supplied with reclaimed water. Water Wastewater Eng. 2009, 45, 112–115. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, Z.A. Macrophytes-cyanobacteria allelopathic interactions and their implications for water resources management—A review. Limnologica 2017, 63, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, K.; Struyf, E.; Vereecken, H.; Viaene, P.; De Doncker, L.; de Deckere, E.; Mostaert, F.; Meire, P. How do macrophyte distribution patterns affect hydraulic resistances? Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Kayaba, Y.; Nishihiro, J.; Takamura, N. Effects of submerged plants on water quality and biota in large-scale experimental ponds. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2008, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Bao, S.; Sima, X.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, W.; Tang, W. Study on the application of integrated eco-engineering in purifying eutrophic river waters. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 94, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oon, Y.; Ong, S.; Ho, L.; Wong, Y.; Dahalan, F.A.; Oon, Y.; Lehl, H.K.; Thung, W.; Nordin, N. Role of macrophyte and effect of supplementary aeration in up-flow constructed wetland-microbial fuel cell for simultaneous wastewater treatment and energy recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, S.; Zhang, S.; Lv, X.; Han, B.; Liu, K.; Qiu, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, P.; Toland, H.; He, Z. Characterization of bacterial community in biofilm and sediments of wetlands dominated by aquatic macrophytes. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 97, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Jin, J.; Dong, Y.; Duan, T.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z. Research progress in submerged plant for purifying water quality. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2012, 30, 72–79. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.; Jia, J.; Chu, Q.; Liu, L. Effect of river ecological restoration by symbiotic system of aquatic plants. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 621, 12086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, Z.; Zhao, R.; Gao, R.; Yun, Y.; Saino, M.; Wang, X. Experimental comparisons of three submerged plants for reclaimed water purification through nutrient removal. Desalin Water Treat. 2016, 57, 12037–12046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Wu, Z.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Yu, D. Carbon gain limitation is the primary mechanism for the elevational distribution limit of myriophyllum in the high-altitude plateau. Front. Plant. Sci. 2018, 9, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Fan, L. Purification of eutrophic water by five aqua-cultured plants in lake Hongfeng, Guiyang, China. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 2019, 24, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Lu, P.; Lu, P.; Huang, M. Correlations between physiological responses of four aquatic plant species and river water quality. Chem. Ecol. 2014, 30, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, I.O.; Izaguirre, I.; Chaparro, G.; Unrein, F.; Sinistro, R.; Pizarro, H.; Rodríguez, P.; de Tezanos Pinto, P.; Lombardo, R.; Tell, G. Water level as the main driver of the alternation between a free-floating plant and a phytoplankton dominated state: A long-term study in a floodplain lake. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 73, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Li, W.; Zhang, M.; Ni, L.; Wang, S. Adaptation of submerged macrophytes to both water depth and flood intensity as revealed by their mechanical resistance. Hydrobiologia 2012, 696, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Meng, F.; Tong, Y.; Chi, J. Effect of plant density on phytoremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons contaminated sediments with Vallisneria spiralis. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 73, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; You, W.; Xie, D.; Yu, D. Turion morphological responses to water nutrient concentrations and plant density in the submerged macrophyte Potamogeton crispus. Sci. Rep. 2015, 4, 7079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambers, H.; Szaniawski, R.; Devisser, R. Respiration for growth, maintenance and ion uptake. An evaluation of concepts, methods, values and their significance. Physiol. Plant. 1983, 58, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Jia, C.; Liang, W.; Hu, S.; Wu, Z. Effects of the submerged macrophyte Ceratophyllum demersum L. on restoration of a eutrophic waterbody and its optimal coverage. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 40, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Hu, W. The research on landscape restoration design of watercourse in mountainous city based on comprehensive management of water environment. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 54, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riis, T.; Tank, J.L.; Reisinger, A.J.; Aubenau, A.; Roche, K.R.; Levi, P.S.; Baattrup Pedersen, A.; Alnoee, A.B.; Bolster, D. Riverine macrophytes control seasonal nutrient uptake via both physical and biological pathways. Freshw. Biol. 2020, 65, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, P.; Prepas, E.; Hamilton, H.; Bothwell, M. Current velocity and its effect on aquatic macrophytes in flowing waters. Ecol. Appl. 1991, 1, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, S.S.S.; Lane, S.N. Nutrient and grazing factors in relation to phytoplankton level in a eutrophic shallow lake: The effect of low macrophyte abundance. Water Res. 2002, 36, 3593–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Qin, B.; Gao, G.; Cai, X. Submerged macrophyte communities and the controlling factors in large, shallow Lake Taihu (China): Sediment distribution and water depth. J. Great Lakes Res. 2014, 40, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodkins, I.; Aguiar, F.; Rivaes, R.; Albuquerque, A.; Rodríguez-González, P.; Ferreira, M.T. Measuring ecological change of aquatic macrophytes in Mediterranean rivers. Limnologica 2012, 42, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neori, A.; Reddy, K.R.; Číšková-Končalová, H.; Agami, M. Bioactive chemicals and biological-biochemical activities and their functions in rhizospheres of wetland plants. Bot. Rev. 2000, 66, 350–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, S.; Luo, J. Nutrient removal processes in freshwater submersed macrophyte systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 350, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, N.E.; Ward, D.P.; Adame, M.F.; Valdez, D.; Bunn, S.E. Influence of aquatic plant architecture on epiphyte biomass on a tropical river floodplain. Aquat. Bot. 2016, 129, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, P.V.; Dell, M.B.O.; Shuford, R.B.E.; Backus, J.G.; Kennedy, W.C. Periphyton responses to experimental phosphorus enrichment in a subtropical wetland. Aquat. Bot. 2001, 71, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietro, K.C.; Chimney, M.J.; Steinman, A.D. Phosphorus removal by the Ceratophyllum/periphyton complex in a south Florida (USA) freshwater marsh. Ecol. Eng. 2006, 27, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastviken, S.K.; Eriksson, P.G.; Ekström, A.; Tonderski, K. Seasonal denitrification potential in wetland sediments with organic matter from different plant species. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2007, 183, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Gu, B.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, T. The role of submerged macrophytes in phytoremediation of arsenic from contaminated water: A case study on Vallisneria natans (Lour.) Hara. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe 2018, 165, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Prasad, S.M. Antioxidant enzyme responses to the oxidative stress due to chlorpyrifos, dimethoate and dieldrin stress in palak (Spinacia oleracea L.) and their toxicity alleviation by soil amendments in tropical croplands. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vymazal, J. Plants used in constructed wetlands with horizontal subsurface flow: A review. Hydrobiologia 2011, 674, 133–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Mu, X.; Han, B.; Zhang, S.; Qiu, C.; Ohore, O.E. Ammonium loading disturbed the microbial food webs in biofilms attached to submersed macrophyte Vallisneria natans. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, H.; Mu, X.; Zhang, S.; Pang, S.; Ohore, O.E. Nitrate application decreased microbial biodiversity but stimulated denitrifiers in epiphytic biofilms on Ceratophyllum demersum. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 269, 110814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, B.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Lu, G.; Dang, Z.; Yin, H. Bacterial communities on soil microplastic at Guiyu, an E-Waste dismantling zone of China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe 2020, 195, 110521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ma, K.; Xu, X.; Alvarezc, P.J.J.; Zhu, L. Understanding of aerobic sludge granulation enhanced by sludge retention time in the aspect of quorum sensing. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 272, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakob, R.P.; Schmidpeter, P.A.M.; Koch, J.R.; Schmid, F.X.; Maier, T. Structural and functional characterization of a novel family of Cyclophilins, the AquaCyps. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e157070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Yan, J.; Wen, J.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, W. Rhamnolipid-enhanced aerobic biodegradation of triclosan (TCS) by indigenous microorganisms in water-sediment systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Chang, Z.; Qiao, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Song, X.; Li, J. Effect of hydraulic retention time on solid-phase denitrification reactor in recirculating aquaculture system. Aquaculture 2021, 543, 736928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, J.; Hou, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, H.; Shi, S.; Ma, F. Enhanced treatment performance of phenol wastewater and membrane antifouling by biochar-assisted EMBR. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 306, 123147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Muñoz-Palazon, B.; Hurtado-Martinez, M.; Mikola, A.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.; Vahala, R.; Gonzalez-Martinez, A. Analysis of microbial communities involved in organic matter and nitrogen removal in a full-scale moving bed biofilm reactor located near the Polar Arctic Circle. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2020, 146, 104830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gu, L.; Hua, Z.; Li, X.; Lu, Y.; Chu, K. Effects of Escherichia coli pollution on decomposition of aquatic plants: Variation due to microbial community composition and the release and cycling of nutrients. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, H.; Kim, M.; Kim, D.; Hyeon, K.K.; Bae, S.; Lee, K.; Chang-Hee, H. Nitrite removal characteristics and application of Bosea sp. isolated from BFT system culture water. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 50, 378–387. [Google Scholar]
- Kviatkovski, I.; Minz, D. A member of the Rhodobacteraceae promotes initial biofilm formation via the secretion of extracellular factor(s). Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 75, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Horiba, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Hiraishi, A. Members of the family comamonadaceae as primary poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)-degrading denitrifiers in activated sludge as revealed by a polyphasic approach. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 3206–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Qiao, W.; Xing, C.; Shen, X.; Hu, D.; Wang, L. A micro-aerobic hydrolysis process for sludge in situ reduction: Performance and microbial community structure. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 173, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustakhimov, I.; Kalyuzhnaya, M.G.; Lidstrom, M.E.; Chistoserdova, L. Insights into denitrification in methylotenera mobilis from denitrification pathway and methanol metabolism mutants. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 2207–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, M.; Canchaya, C.; Tauch, A.; Chandra, G.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Chater, K.F.; van Sinderen, D. Genomics of actinobacteria: Tracing the evolutionary history of an ancient phylum. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Res. 2007, 71, 495–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.T. Methylobacter and methylophilus microbial consortium for aerobic denitrification and PAH(Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon) degradation. J. Korean Soc. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 24, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyuhznaya, M.G.; Martens-Habbena, W.; Wang, T.; Hackett, M.; Stolyar, S.M.; Stahl, D.A.; Lidstrom, M.E.; Chistoserdova, L. Methylophilaceae link methanol oxidation to denitrification in freshwater lake sediment as suggested by stable isotope probing and pure culture analysis. Env. Microbiol. Rep. 2009, 1, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Yu, L.; Yang, Z.; Li, M.; Clough, T.; Wrage-Mönnig, N.; Hu, C.; Liu, B.; Chen, S.; Zhou, S. Electrodes donate electrons for nitrate reduction in a soil matrix via DNRA and denitrification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 2002–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Huang, W.; Sheu, S. Derxia lacustris sp. nov., a nitrogen-fixing bacterium isolated from a freshwater lake. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Micr 2013, 63, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.; Chu, L.; Wang, J. Biological treatment of actual petrochemical wastewater using anaerobic/anoxic/oxic process and the microbial diversity analysis. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2016, 100, 10193–10202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.; He, W.; Li, C.; Wang, F.; Crittenden, J.C.; Feng, Y. Remediation of nitrate contamination by membrane hydrogenotrophic denitrifying biofilm integrated in microbial electrolysis cell. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, W.; Gao, N.; Xia, M.; Dai, J.; Yu, D.; Qiu, D. Physiological characteristics and systematic classification of the Zoogloea species and their role in the activated sludge. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2016, 22, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Q.; Cheng, J.; Sun, S. New ammonium nitrogen-fixing bacteria Kosakonia radicincitans GXGL-4A, useful for preparing microbial fertilizer, promoting crop growth and preventing water eutrophication.
- Jia, L.; Jiang, B.; Huang, F.; Hu, X. Nitrogen removal mechanism and microbial community changes of bioaugmentation subsurface wastewater infiltration system. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 294, 122140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Li, Y. Study on the feasibility of enhancing the biodegradation of aniline wastewater by polyvinyl alcohol-sodium alginate gel pellets embedded activated sludge. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2022, 39, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, E.; Liu, Y.; Ouyang, J.; Wang, X. Effects of different wastewater characteristics and treatment techniques on the bacterial community structure in three pharmaceutical wastewater treatment systems. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Water Quality Indicators | COD | TP | TN | NH3-H |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentrations at point N1 in River L replenished with reclaimed water | 15–29 mg L−1 | 0.11–1.40 mg L−1 | 4.56–18.8 mg L−1 | 0.05–3.50 mg L−1 |
| Experimental water | 19.38 ± 1.58 mg L−1 | 0.49 ± 0.17 mg L−1 | 11.31 ± 3.50mg L−1 | 0.93 ± 0.51 mg L−1 |
| Artificially configured agents | C12H22O11 | NH4H2PO4 | KNO3 | (NH4)2SO4 |
| Initial | Terminal | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | 3.5 | ||
| TN (mg g−1 DW) | 33.27 ± 0.04 | 39.75 ± 0.41 | 38.02 ± 1.58 | 40.31 ± 0.33 | 39.56 ± 1.50 | 40.45 ± 0.29 |
| TN content growth rate | — | 19.47% | 14.27% | 21.16% | 18.89% | 21.57% |
| TP (mg g−1 DW) | 0.66 ± 0.03 | 0.83 ± 0.04 | 0.86 ± 0.04 | 0.80 ± 0.01 | 0.81 ± 0.03 | 0.86 ± 0.02 |
| TP content growth rate | — | 26.52% | 30.30% | 21.21% | 22.73% | 30.30% |
| N/P | 0.0198 | 0.0210 | 0.0226 | 0.0198 | 0.0205 | 0.0213 |
| Family | Genus | Environmental Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Hyphomonadaceae | UKL13-1 | Degradation of organic matter and hydrocarbons [49] Denitrification [50] Secretion of extracellular proteins and biofilm formation [51] |
| Caulobacteraceae | Caulobacter | Secretion of extracellular polymers [50] Adapts to and may be able to degrade triclosan (TCS) [52] |
| Rhizobiaceae | g__unclassified_f__Rhizobiaceae | Denitrification [53] |
| Devosiaceae | Devosia | Secretion of extracellular polymers [54] Nitrification [55,56] |
| Beijerinckiaceae | Bosea | Removal of nitrite [57] |
| Rhodobacteraceae | g__unclassified_f__Rhodobacteraceae | Promotes initial biofilm formation [58] |
| Comamonadaceae | g__unclassified_f__Comamonadaceae | Denitrification [59] |
| Comamonadaceae | Ramlibacter | Anaerobic or partly anaerobic bacteria grown via the reduction of oxygen anions, such as sulfate, perchlorate, nitrate, and nitrite [60] |
| Methylophilaceae | Methylotenera | Methanol oxidation and denitrification [61] Nitrogen fixation and degradation of simple alkanes [62] |
| Methylophilaceae | Methylophilus | Promotes aerobic denitrification and PAH biodegradation [63] |
| Methylophilaceae | g__unclassified_f__Methylophilaceae | Methanol oxidation and denitrification [64] |
| Alcaligenaceae | Derxia | Nitrate reduction [65] |
| Nitrogen fixation [66] | ||
| Nitrosomonadaceae | Ellin6067 | Ammonia oxidation [67] |
| Rhodocyclaceae | Zoogloea | TN removal [68] |
| COD, nitrogen, and phosphorus removal [69] | ||
| Enterobacteriaceae | Kosakonia | Ammonium nitrogen fixation [70] |
| Gemmatimonadaceae | Gemmatimonas | Nitrogen removal [71] |
| Microscillaceae | g__norank_f__Microscillaceae | Nitrification [72] |
| Saprospiraceae | g__norank_f__Saprospiraceae | Nutrient removal [73] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, L.; Lin, X.; Li, S.; Sun, D.; Fang, H.; Xu, J.; Huang, J.; Li, G. Effect and Mechanism of Applying Myriophyllum Verticillatum for Reclaimed Water Purification in Urban Rivers. Water 2023, 15, 2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132331
Zhu L, Lin X, Li S, Sun D, Fang H, Xu J, Huang J, Li G. Effect and Mechanism of Applying Myriophyllum Verticillatum for Reclaimed Water Purification in Urban Rivers. Water. 2023; 15(13):2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132331
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Liping, Xiaohu Lin, Shiyi Li, Danyan Sun, Haifeng Fang, Jingcheng Xu, Juwen Huang, and Guangming Li. 2023. "Effect and Mechanism of Applying Myriophyllum Verticillatum for Reclaimed Water Purification in Urban Rivers" Water 15, no. 13: 2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132331
APA StyleZhu, L., Lin, X., Li, S., Sun, D., Fang, H., Xu, J., Huang, J., & Li, G. (2023). Effect and Mechanism of Applying Myriophyllum Verticillatum for Reclaimed Water Purification in Urban Rivers. Water, 15(13), 2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15132331








