Control of Aquatic Weed Eichhornia crassipes Using Florpyrauxifen-benzyl Herbicide—Case Study in Cangkuang Lake (Indonesia)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
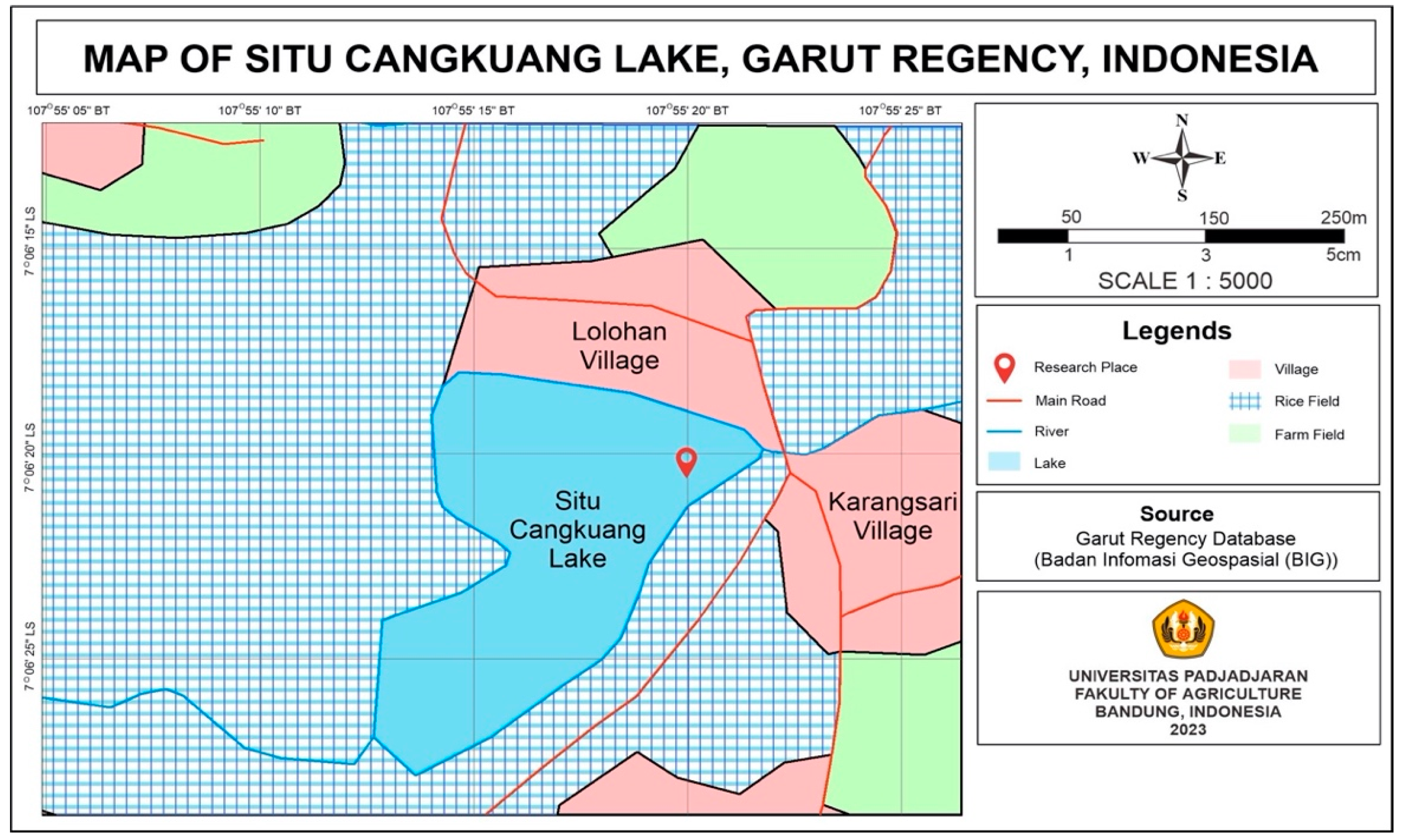
2.1. Study Location
2.2. Plant Materials
2.3. Experimental Design and Herbicide Application
2.4. Water Quality Measurement
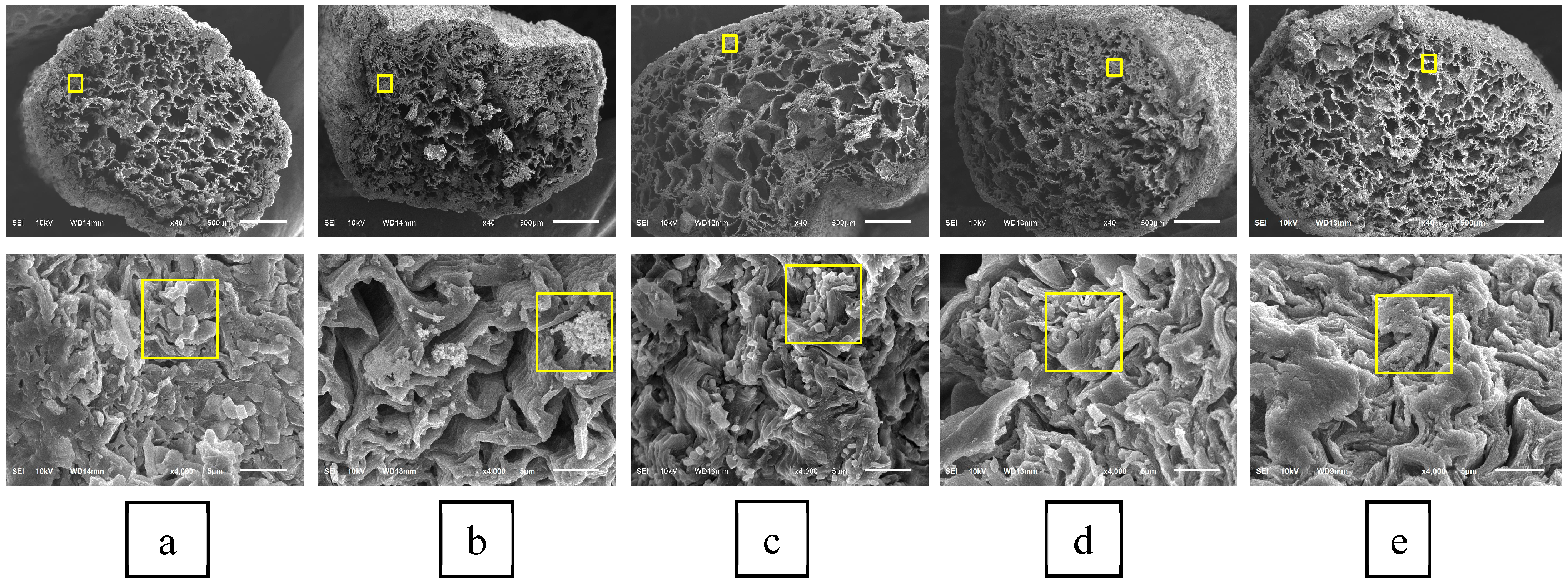
2.5. Morphological Structure and Topography of Water Hyacinth Petioles
2.6. Statistical Analyses for Dose–Response Experiments
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Herbicide on the Weeds E. crassipes
3.1.1. Dry Weight of the Weeds E. crassipes
3.1.2. Growth Reduction of the Weeds E. crassipes
3.2. Effect of Herbicides on Water Quality
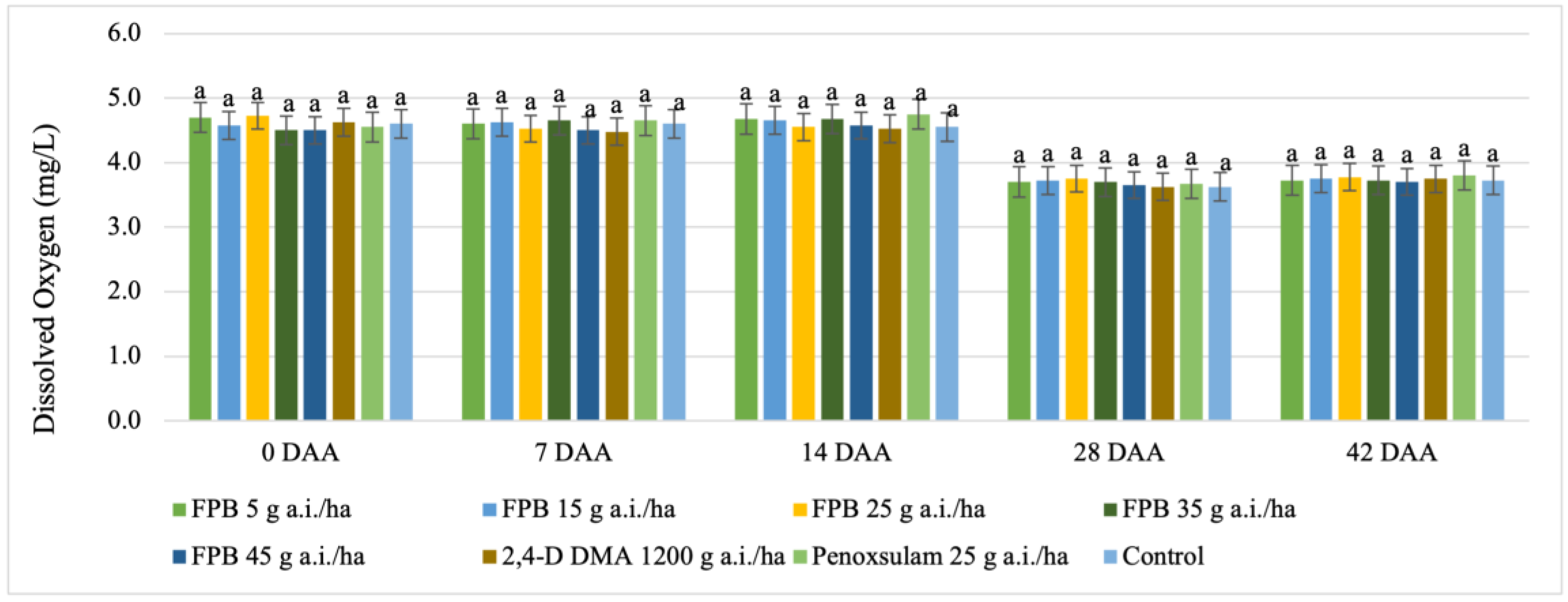
3.2.1. Dissolved Oxygen (DO)
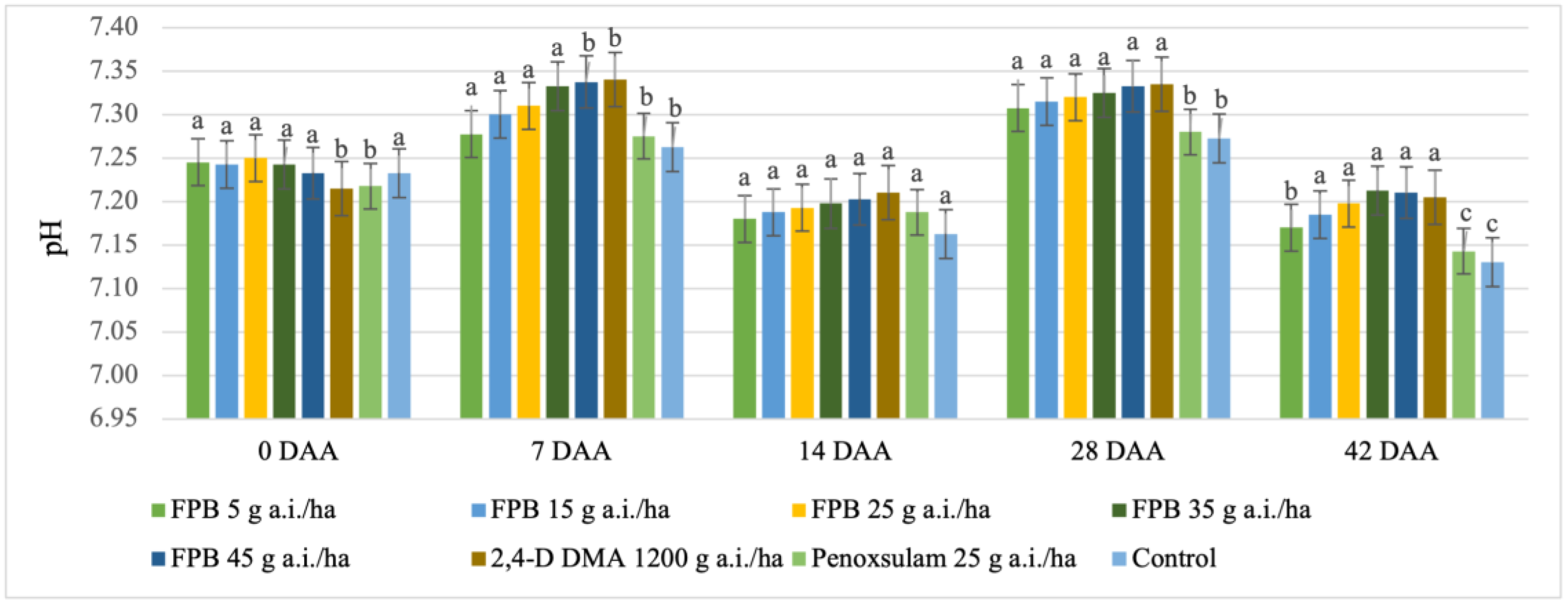
3.2.2. Power of Hydrogen (pH)
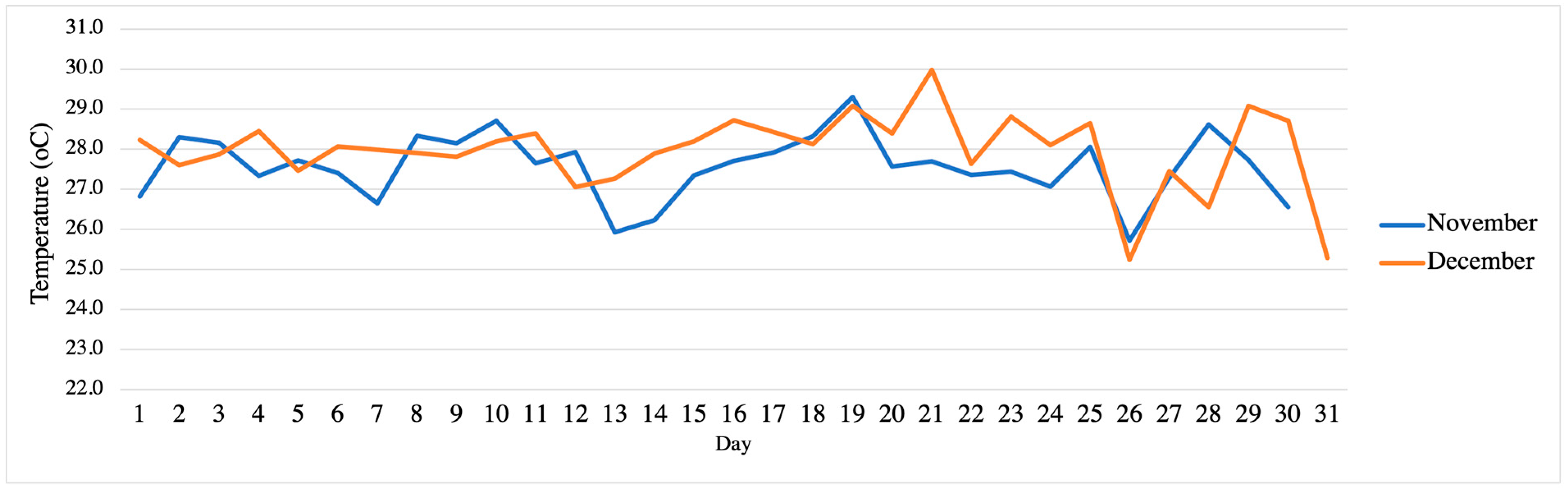
3.2.3. Water Temperature
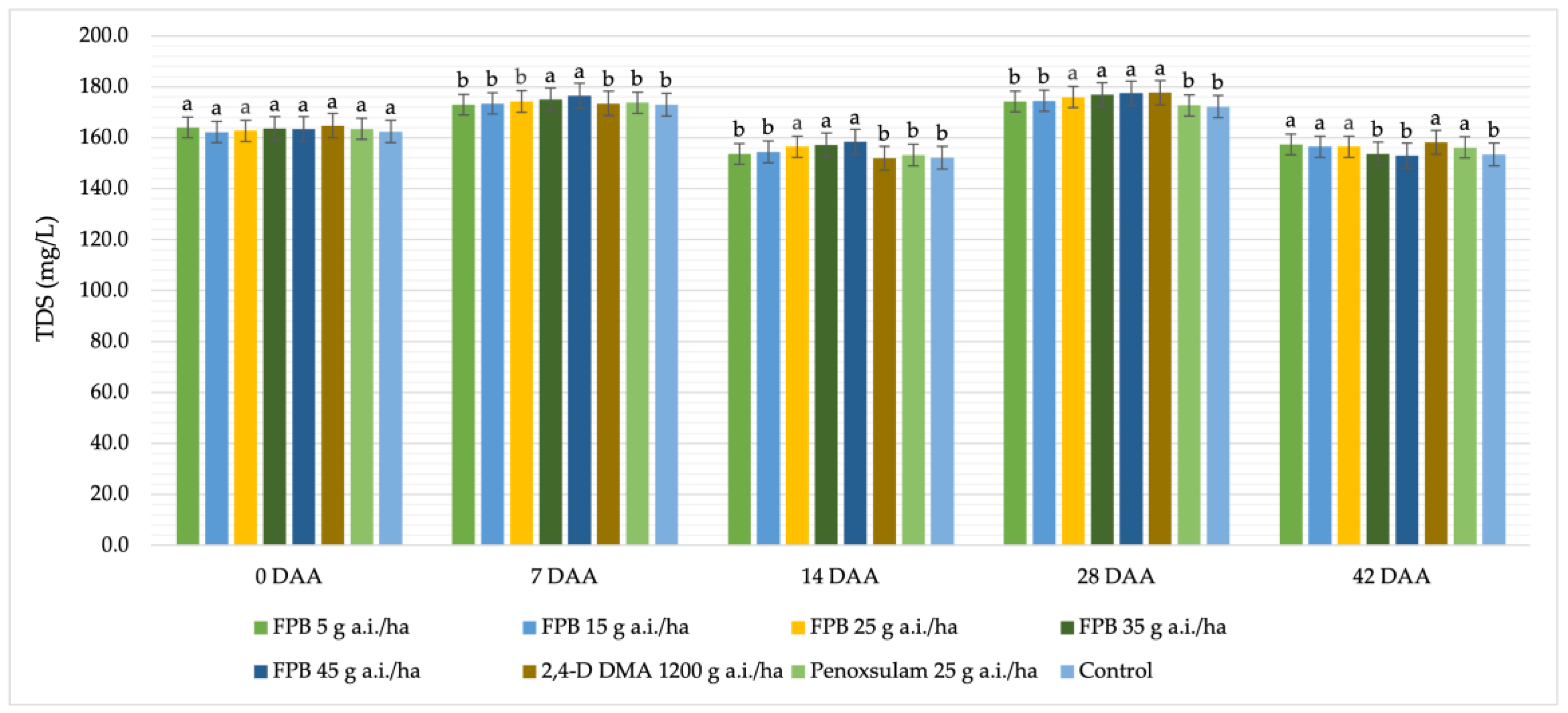
3.2.4. Total Dissolved Solids (TDS)
3.2.5. Ammonia (NH3-N)
4. Discussion
4.1. Efficacy of Florpyrauxifen-benzyl on Eichhornia crassipes
4.2. Herbicide Effect on Water Quality
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, A.; Aggarwal, N.K.; Saini, A.; Yadav, A. Beyond biocontrol: Water hyacinth-Opportunities and challenges. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 9, 26–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, D.Y.; Barrett, S.C.H. Genetic uniformity characterizes the invasive spread of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes), a clonal aquatic plant. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 1774–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayanda, O.I.; Ajayi, T.; Asuwaju, F.P. Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms: Uses, Challenges, Threats, and Prospects. Sci. World J. 2020, 2020, 3452172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miskella, J.J.; Madsen, J.D.; Llaban, A.; Hard, E. Dissolved oxygen under waterhyacinth following herbicide application. J. Aquat. Plant Manag. 2021, 59, 82–89. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaqi, D.; Pranoto, P.; Setyono, P. Estimation of Water Losses Through Evapotranspiration of Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes). Caraka Tani J. Sustain. Agric. 2019, 34, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewantara, E.F.; Purwanto, Y.J.; Setiawan, Y. Management strategy of water hyacinth (Eichornia crassipes) in Jatiluhur Reservoir, West Java. J. Penelit. Sos. Dan Ekon. Kehutan. 2021, 18, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetyo, S.; Anggoro, S.; Soeprobowati, T.R. The Growth Rate of Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms) in Rawapening Lake, Central Java. J. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 22, 222–231. [Google Scholar]
- Putra, R.R.; Khadijah, U.L.S.; Rakhman, C.U. Between Conservation and Tourism Functions: Efforts to Preserve Cangkuang Temple Cultural Heritage as a Cultural Tourism Attraction. In Culture Heritage Tourism, 1st ed.; Khadijah, U.L.S., Hadian, M.S.D., Eds.; Unpad Press: Bandung, Indonesia, 2020; Volume 1, pp. 399–411. [Google Scholar]
- Situ Cangkuang. Available online: https://visitgarut.garutkab.go.id/situ-cangkuang/ (accessed on 19 March 2023).
- De Carvalho, L.B.; Cerveira Junior, W.R. Control of water hyacinth: A short review. Commun. Plant Sci. 2019, 9, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzajani, A.; Nezamabadi, N.; Salavatian, S.M.; Bagheri, S.; Salahi, M.; Rufchaei, R. Chemical control of water hyacinth by some herbicides and their effect on some aquatic invertebrate. Res. Sq. 2022, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Uka, U.N.; Chukwuka, K.S. Chemical control method as a management approach to water hyacinth infestation in Nigeria. Zonas Áridas 2008, 12, 184–190. [Google Scholar]
- Beets, J.; Netherland, M. Mesocosm response of crested floating heart, hydrilla, and two native emergent plants to Florpyrauxifen-benzyl: A new arylpicolinate herbicide. J. Aquat. Plant Manag. 2018, 56, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Madsen, J.; Kyser, G. Herbicides for management of waterhyacinth in the Sacramento-San Joaquin River Delta, California. J. Aquat. Plant Manag. 2020, 58, 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, E.L.C.; Filho, J.T.; Velini, E.D.; Silva, J.R.M.; Tonello, K.C.; Foloni, L.L.; Gonzalez, G.D.D.; Barbosa, A.C.; Freato, T.A. Efficacy of Glyphosate in Water Management and the Effects on Water Quality. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2020, 12, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltham, N.J.; Fixler, S. Aerial herbicide spray to control invasive water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes): Water quality concerns fronting fish occupying a tropical floodplain wetland. Trop. Conserv. Sci. 2017, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamagna, A.M.; Murphy, B.R. Ecological and socio-economic impacts of invasive water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes): A review. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 282–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyser, G.B.; Madsen, J.D.; Miskella, J.; O’brien, J. New herbicides and tank mixes for control of waterhyacinth in the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta. J. Aquat. Plant Manag. 2021, 59, 78–81. [Google Scholar]
- Epp, J.B.; Alexander, A.L.; Balko, T.W.; Buysse, A.M.; Brewster, W.K.; Bryan, K.; Daeuble, J.F.; Fields, S.C.; Gast, R.E.; Green, R.A.; et al. The discovery of ArylexTM active and RinskorTM active: Two novel auxin herbicides. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, E.J.; Ahmed, K.A.; Gannon, T.W.; Richardson, R.J. Absorption and translocation of Florpyrauxifen-benzyl in ten aquatic plant species. Weed Sci. 2021, 69, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, R.; Weimer, M.R.; Morell, M.; Havens, P.L.; Meregalli, G.; Papipeni, S.; Laughin, L.A.; Shan, G. Rinskor active herbicide—A new environtment friendly tool for weed management in rice and aquatic environments. In Recent Highlights in the Discovery and Optimization of Crop Protection Products, 1st ed.; Maienfisch, P., Mangelinckx, S., Eds.; Academic Press Publication Elsevier: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; Volume 1, pp. 511–522. [Google Scholar]
- Grossmann, K. Auxin herbicides: Current status of mechanism and mode of action. Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, K. Auxin herbicide action: Lifting the veil step by step. Plant Signal. Behav. 2007, 2, 421–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florpyrauxifen-Benzyl: New Active Ingredient Review. Available online: https://www.mda.state.mn.us/sites/default/files/inline-files/Florpyrauxifen-benzyl.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Loyant®. Available online: http://agrian-cg-fs1-production.s3.amazonaws.com/pdfs/Loyant1d_MSDS.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Tobias, V.D.; Conrad, J.L.; Mahardja, B.; Khanna, S. Impacts of water hyacinth treatment on water quality in a tidal estuarine environment. Biol. Invasions 2019, 21, 3479–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaenel, B.R.; Buehrer, H.; Uehlinger, U. Effects of aquatic plant management on stream metabolism and oxygen balance in streams. Freshw. Biol. 2000, 45, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, L.E.; Hodges, K.B. Role of aquatic vegetation coverage on hypoxia and sunfish abundance in bays of a eutrophic reservoir. Hydrobiologia 2000, 427, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Devi, P. Water quality guidelines for the management of pond fish culture. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 5, 1980–2009. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, C.E. Water Quality an Introduction, 2nd ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 1–353. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Jetani, K.L.; Yusuzai, S.I.; Sayani, A.N.; Dar, S.A.; Ashraf, M. Effect of sediment and water quality parameters on the productivity of coastal shrimp farm. Pelagia Res. Libr. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res. 2012, 3, 2033–2041. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchini Jr, I.; Cunha-Santino, M.B.; Panhota, R.S. Oxygen uptake from aquatic macrophyte decomposition from Piraju Reservoir (Piraju, SP, Brazil). Braz. J. Biol. 2011, 71, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, A.; Kumar, S. Aquatic weeds management through chemical and manual integration to reduce cost by manual removal alone and its effect on water quality. Indian J. Weed Sci. 2019, 51, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghufron, M.; Rahardja, B.S.; Sari, L.A. The temporal variation of ammonia and nitrite content in extensive ponds with tilapia. AACL Bioflux 2020, 13, 1328–1335. [Google Scholar]
- Climatology of Garut Regency. Available online: https://www.garutkab.go.id/page/klimatologi (accessed on 19 March 2023).
- Unggul, S.Y.; (Garut Space and Atmospheric Technology Test and Observation Center, Garut, West Java, Indonesia). Garut Climate Data November–December 2022. 2022; (phase: Unpublished work). [Google Scholar]
- Auralia, I.O.; Nurruhwati, I.; Herawati, H. Fluctuations of Ammonia and Nitrate Content on Nilem (Osteochilus Sp.) Cultivation Using Diffuser Aerator. Glob. Sci. J. 2018, 6, 946–954. [Google Scholar]
- Ihsan, Y.N.; Azizah, L.; Fellatami, K.; Pribadi, T.D.K. The Effect of Ammonium Concentration Addition to Gracilaria sp. on The Absorption of Mercury. J. Kelaut. Indones. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2022, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation of the Government of the Republic of Indonesia (PP No. 22 of 2021) Concerning the Implementation of Environmental Protection and Management. Available online: https://jdih.setkab.go.id/PUUdoc/176367/PP_Nomor_22_Tahun_2021.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Hilton, H.W. Herbicide tolerant strains of weeds. In Hawaiian Sugar Planters Assocociation Annual Repport; University Press of Hawaii: Honolulu, HI, USA, 1957; pp. 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Dersseh, M.G.; Melesse, A.M.; Tilahun, S.A.; Abate, M.; Dagnew, D.C. Water hyacinth: Review of its impacts on hydrology and ecosystem services-Lessons for management of Lake Tana. In Extreme Hydrology and Climate Variability: Monitoring, Modelling, Adaptation and Mitigation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 237–251. [Google Scholar]
- Final Registration Decision on the New Active Ingredient Florpyrauxifen-Benzyl. Available online: https://www.regulations.gov/document/EPA-HQ-OPP-2016-0560-0065 (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Getsinger, K.D.; Netherland, M.D.; Grue, C.E.; Koschnick, T.J. Improvements in the Use of Aquatic Herbicides and Establishment of Future Research Directions. J. Aquat. Plant Manag. 2008, 46, 32–41. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, R.J.; Haug, E.J.; Netherland, M.D. Response of seven aquatic plants to a new arylpicolinate herbicide. J. Aquat. Plant Manag. 2016, 54, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Mudge, C.R.; Turnage, G.; Netherland, M.D. Effect of Florpyrauxifen-benzyl formulation and rate for waterhyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) control in a mesocosm setting. Invasive Plant Sci. Manag. 2021, 14, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnusamy, C.; Janaki, P.; Arthanari, P.M.; Muthukrishnan, P. Effects of Post-Emergence Herbicides on Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes)-Tank Culture Experiment. Pak. J. Weed Sci. Resour. 2012, 18, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- McCauley, C.L.; McAdam, S.A.M.; Bhide, K.; Thimmapuram, J.; Banks, J.A.; Young, B.G. Transcriptomics in Erigeron canadensis reveals rapid photosynthetic and hormonal responses to auxin herbicide application. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 3701–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, G.; Calderon-Villalobos, L.I.; Prigge, M.; Peret, B.; Dharmasiri, S.; Itoh, H.; Lechner, E.; Gray, W.M.; Bennett, M.; Estelle, M. Complex regulation of the TIR1/AFB family of auxin receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 106, 22540–22545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varanasi, A.; Prasad, P.V.V.; Jugulam, M. Impact of Climate Change Factors on Weeds and Herbicide Efficacy. In Advances in Agronomy, 1st ed.; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; Volume 1, pp. 107–146. [Google Scholar]
- Marlina, N.; Melyta, D. Analysis Effect of Cloud Cover, Wind Speed, and Water Temperature to BOD and DO Concentration Using QUAL2Kw Model (Case Study in Winongo River, Yogyakarta). In MATEC Web of Conferences; ICSBE: Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 2018; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Sondhia, S.; Vishwakarma, K. Herbicides effect on fish mortality and water quality in relation to chemical control of alligator weed. Indian J. Weed Sci. 2017, 49, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamau, A.N.; Njogu, P.; Kinyua, R.; Sessay, M. Sustainability Challenges and Opportunities of Generating Biogas from Water Hyacinth. In Proceedings of the Sustainable Research and Innovation (SRI) Conference, Ndunga Village, Kenya, 6–8 May 2015; African Centre for Technology Studies: Nairobi, Kenya, 2015; pp. 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, Y.R.; Howell, T.; Watson, S.B.; Abernethy, S. On hypoxia and fish kills along the north shore of Lake Erie. J. Great Lakes Res. 2014, 40, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirisu, C.G.; Mafiana, M.O.; Dirisu, G.B.; Amodu, R. Level of pH In Drinking Water of an Oil and Gas Producing Community and Perceived Biological and Health Implications. Eur. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2016, 3, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, J.; Sprague, L. Water-quality trends in US rivers: Exploring effects from streamflow trends and changes in watershed management. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Bhatta, B.; Shrestha, M.; Shrestha, P.K. Integrated assessment of the climate and landuse change impact on hydrology and water quality in the Songkhram River Basin, Thailand. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1610–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Qu, X. Seasonal and Spatial Variation in Hydrochemical Characteristics of a Semi-Arid River Basin, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2015, 21, 845–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koushali, H.P.; Mastouri, R.; Khaledian, M.R. Impact of Precipitation and Flow Rate Changes on the Water Quality of a Coastal River. Shock Vib. 2021, 2021, 6557689. [Google Scholar]
- Weber-Scannell, P.K.; Duffy, L.K. Effects of total dissolved solids on aquatic organisms: A review of literature and recommendation for salmonid species. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.T.; Farooq, Q.U.; Almohamadi, H. Physicochemical Characterization of Natural Rocks and Their Applications for Wastewater Treatment. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.M.; Tang, Z. Identification of Contamynetion Sources and TDS Concentration in Groundwater of Second Biggest City of Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2013, 4, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañedo-Argüelles, M.; Kefford, B.J.; Piscart, C.; Prat, N.; Schäfer, R.B.; Schulz, C.J. Salinisation of rivers: An urgent ecological issue. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 173, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, J.A. Nitrogen biogeochemistry of aquaculture ponds. Aquaculture 1998, 166, 181–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, D.; Emtiazi, G. Ammonium production during the Nitrogen-fixing process by wild Paenibacillus strains and cell-free extract adsorbed on nano TiO2 particles. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 20, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Van Dyke, M.I.; Huck, P.M. Identification of critical contamynents in wastewater effluent for managed aquifer recharge. Chemosphere 2017, 172, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E. General relationship between water quality and aquaculture performance in ponds. In Fish Diseases: Prevention and Control Strategies, 1st ed.; Jeney, G., Ed.; Academic Press Publication Elsevier Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 147–166. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Shang, Z.H.; Wang, G.Y.; You, K.; Mi, D. High concentrations of environmental ammonia induced changes in large-scale loach (Paramisgurnus dabryanus) immunity. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 8614–8622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erguder, T.H.; Boon, N.; Wittebolle, L.; Marzorati, M.; Verstraete, W. Environmental factors shaping the ecological niches of ammonia-oxidizing archaea. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 33, 855–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Guo, X.; Park, H.S. Comparison study of the effects of temperature and free ammonia concentration on nitrification and nitrite accumulation. Process Biochem. 2008, 43, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercante, C.T.; David, G.S.; Rodrigues, C.J.; da Silva, R.J.; do Carmo, C.F. Potential toxic effect of ammonia in reservoirs with tilapiculture in cages. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2018, 6, 256–261. [Google Scholar]
- Tidwell, J. Aquaculture Production Systems, 1st ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 1–421. [Google Scholar]
- Aquatic Life Ambient Water Quality Criteria for Ammonia-Freshwater. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-08/documents/aquatic-life-ambient-water-quality-criteria-for-ammonia-freshwater-2013.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2023).



| Treatment (Herbicide) | Rate (g a.i./ha) | Dry Weight (g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 DAA | 28 DAA | 42 DAA | ||
| Florpyrauxifen-benzyl | 5 | 20.05 c ± 0.48 | 16.67 c ± 0.36 | 13.48 b ± 0.59 |
| Florpyrauxifen-benzyl | 15 | 15.75 d ± 0.33 | 7.04 d ± 0.35 | 0.00 e ± 0.00 |
| Florpyrauxifen-benzyl | 25 | 15.67 d ± 0.51 | 0.00 e ± 0.00 | 0.00 e ± 0.00 |
| Florpyrauxifen-benzyl | 35 | 12.24 e ± 0.89 | 0.00 e ± 0.00 | 0.00 e ± 0.00 |
| Florpyrauxifen-benzyl | 45 | 10.83 e ± 2.17 | 0.00 e ± 0.00 | 0.00 e ± 0.00 |
| 2,4-D DMA | 1200 | 15.71 d ± 1.67 | 7.43 d ± 1.10 | 5.12 d ± 0.13 |
| Penoxsulam | 25 | 23.28 b ± 1.24 | 18.49 b ± 0.92 | 12.30 c ± 0.09 |
| Control | - | 39.07 a ± 1.51 | 42.42 a ± 1.09 | 50.28 a ± 1.07 |
| Treatment (Herbicide) | Rate (g a.i./ha) | Ammonia (NH3-N) (mg/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 21 DAA | 42 DAA | ||
| Florpyrauxifen-benzyl | 5 | 0.0083 ± 0.0027 a | 0.0051 ± 0.0022 a |
| Florpyrauxifen-benzyl | 15 | 0.0086 ± 0.0038 a | 0.0055 ± 0.0023 a |
| Florpyrauxifen-benzyl | 25 | 0.0086 ± 0.0033 a | 0.0057 ± 0.0022 a |
| Florpyrauxifen-benzyl | 35 | 0.0086 ± 0.0038 a | 0.0060 ± 0.0026 a |
| Florpyrauxifen-benzyl | 45 | 0.0087 ± 0.0038 a | 0.0059 ± 0.0024 a |
| 2,4-D DMA | 1200 | 0.0089 ± 0.0039 a | 0.0066 ± 0.0035 a |
| Penoxsulam | 25 | 0.0078 ± 0.0036 a | 0.0055 ± 0.0010 a |
| Control | - | 0.0041 ± 0.0009 b | 0.0050 ± 0.0014 a |
| Water Quality Parameter | Class II | Class III | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| DO | 4 mg/L | 3 mg/L | 3.70–4.75 |
| Temperature | Dev 3 | Dev 3 | 25.3–27.1 °C |
| pH | 6–9 | 6–9 | 7.13–7.34 |
| TDS | 1.000 mg/L | 1.000 mg/L | 153.00–177.50 mg/L |
| Ammonia | 0.2 mg/L | 0.5 mg/L | 0.0050–0.0066 mg/L |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kurniadie, D.; Rezkia, N.N.; Widayat, D.; Widiawan, A.; Duy, L.; Prabowo, D.P. Control of Aquatic Weed Eichhornia crassipes Using Florpyrauxifen-benzyl Herbicide—Case Study in Cangkuang Lake (Indonesia). Water 2023, 15, 1859. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101859
Kurniadie D, Rezkia NN, Widayat D, Widiawan A, Duy L, Prabowo DP. Control of Aquatic Weed Eichhornia crassipes Using Florpyrauxifen-benzyl Herbicide—Case Study in Cangkuang Lake (Indonesia). Water. 2023; 15(10):1859. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101859
Chicago/Turabian StyleKurniadie, Denny, Nita Nur Rezkia, Dedi Widayat, Aditya Widiawan, Le Duy, and Dwi Priyo Prabowo. 2023. "Control of Aquatic Weed Eichhornia crassipes Using Florpyrauxifen-benzyl Herbicide—Case Study in Cangkuang Lake (Indonesia)" Water 15, no. 10: 1859. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101859





