Spatiotemporal Variation in Saline Soil Properties in the Seasonal Frozen Area of Northeast China: A Case Study in Western Jilin Province
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
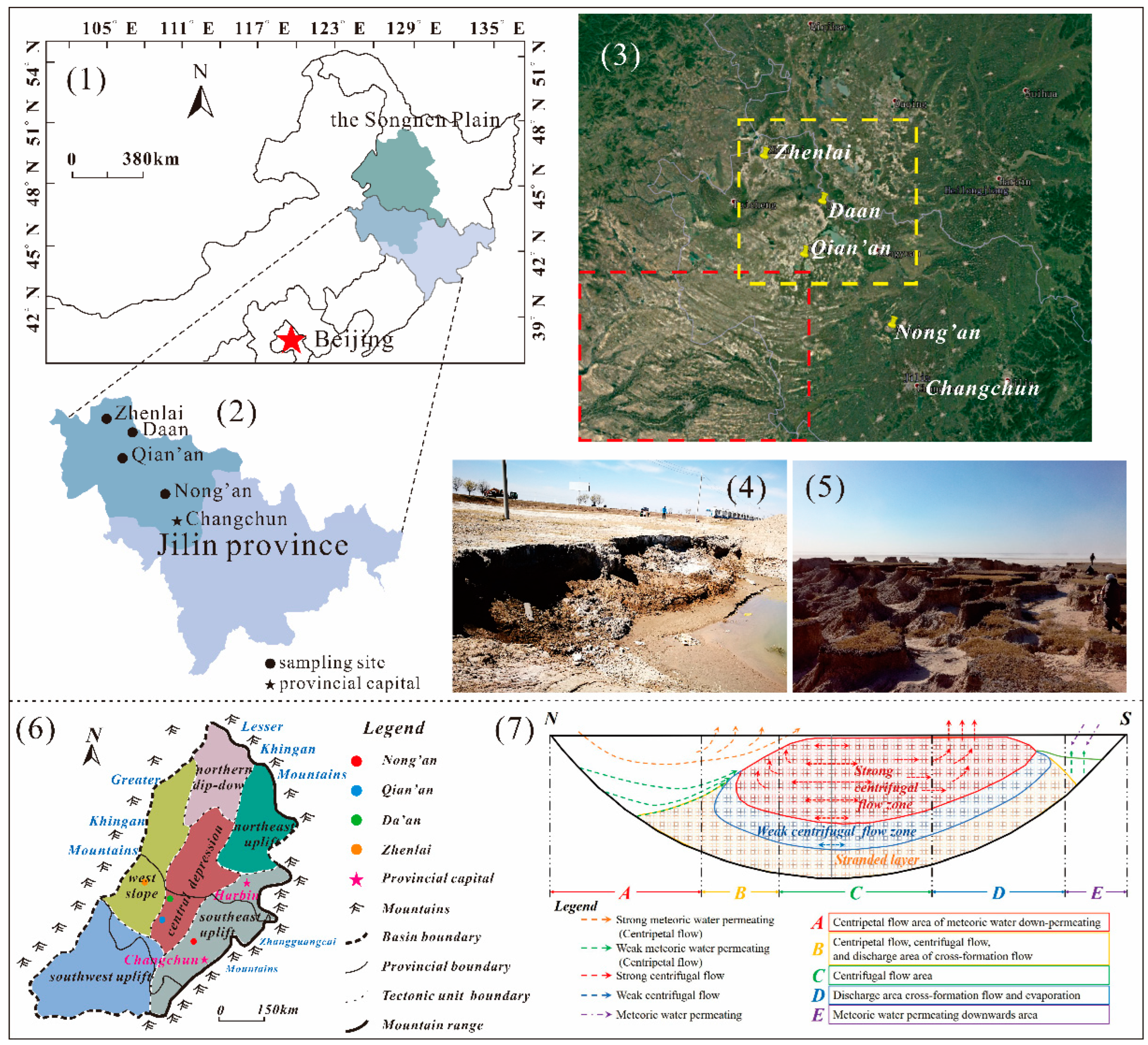
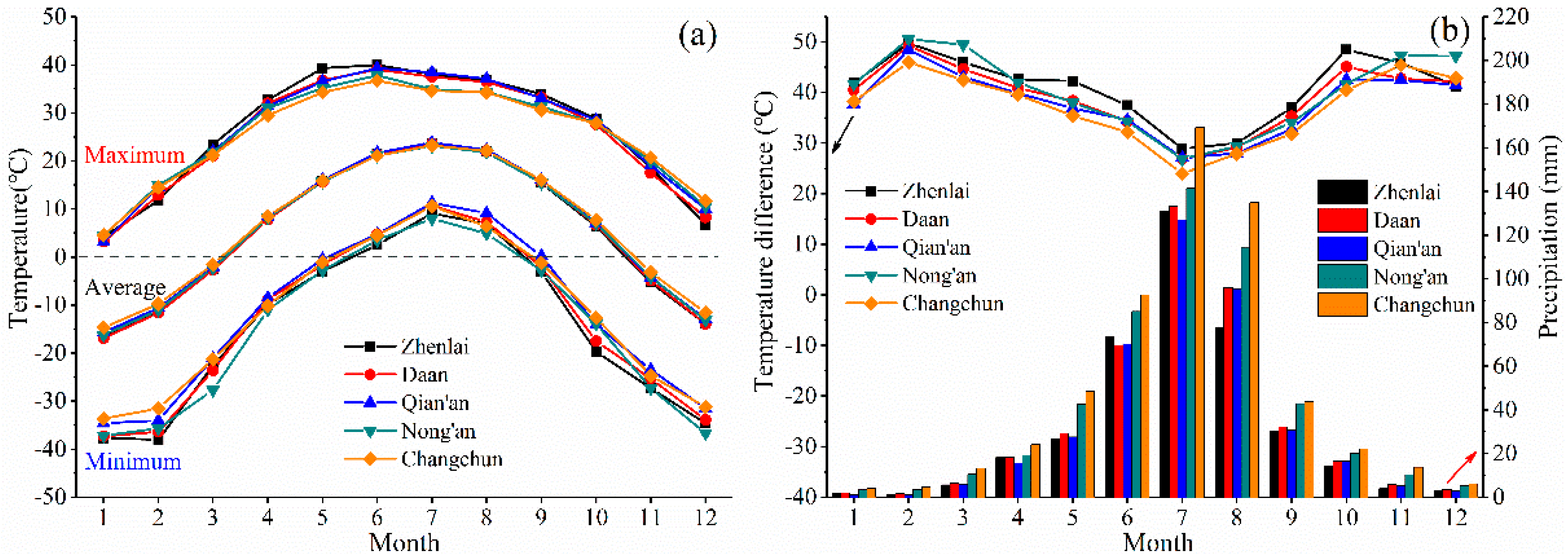
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Soil Samples
2.3. Methods
3. Results and Discussions
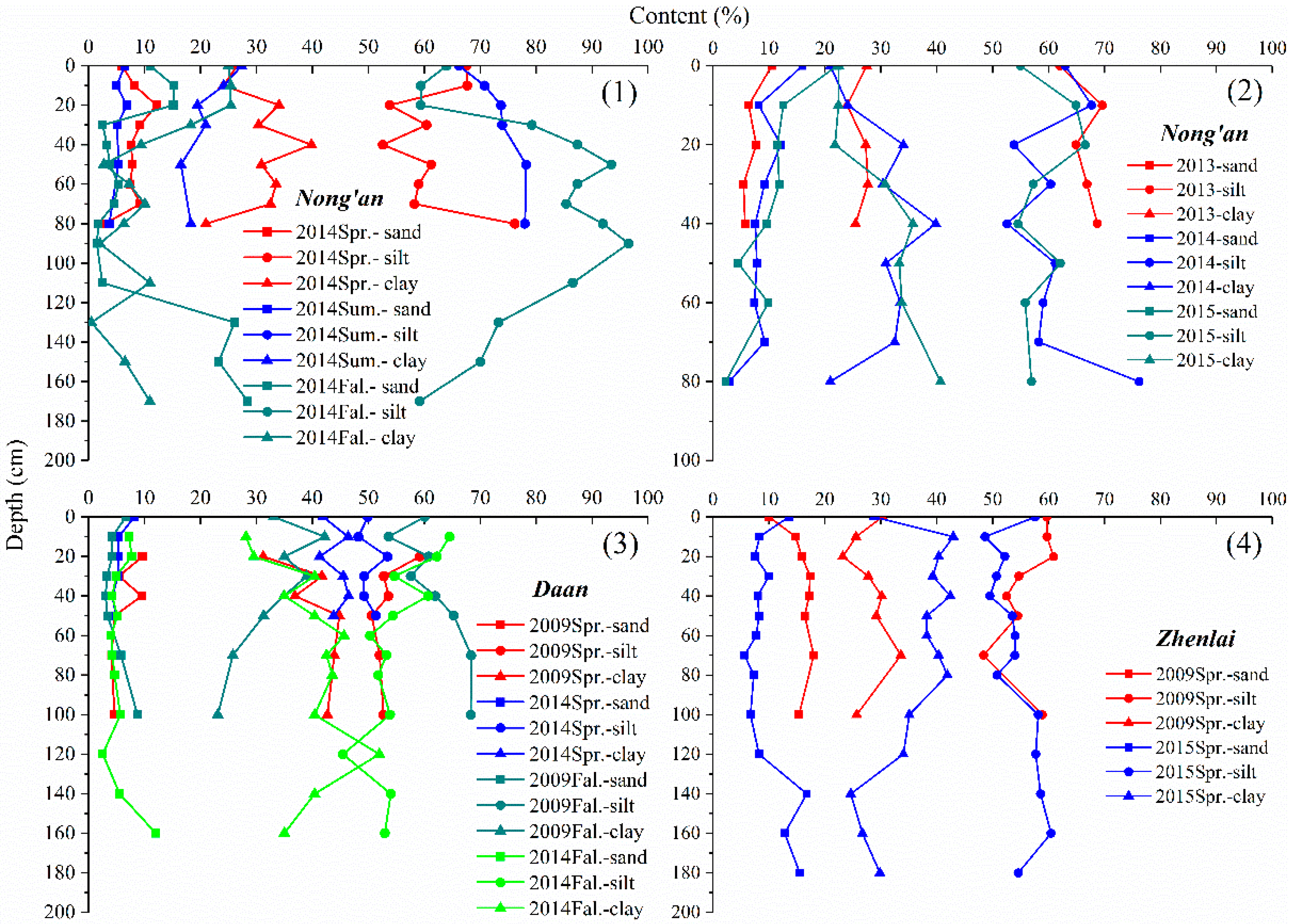
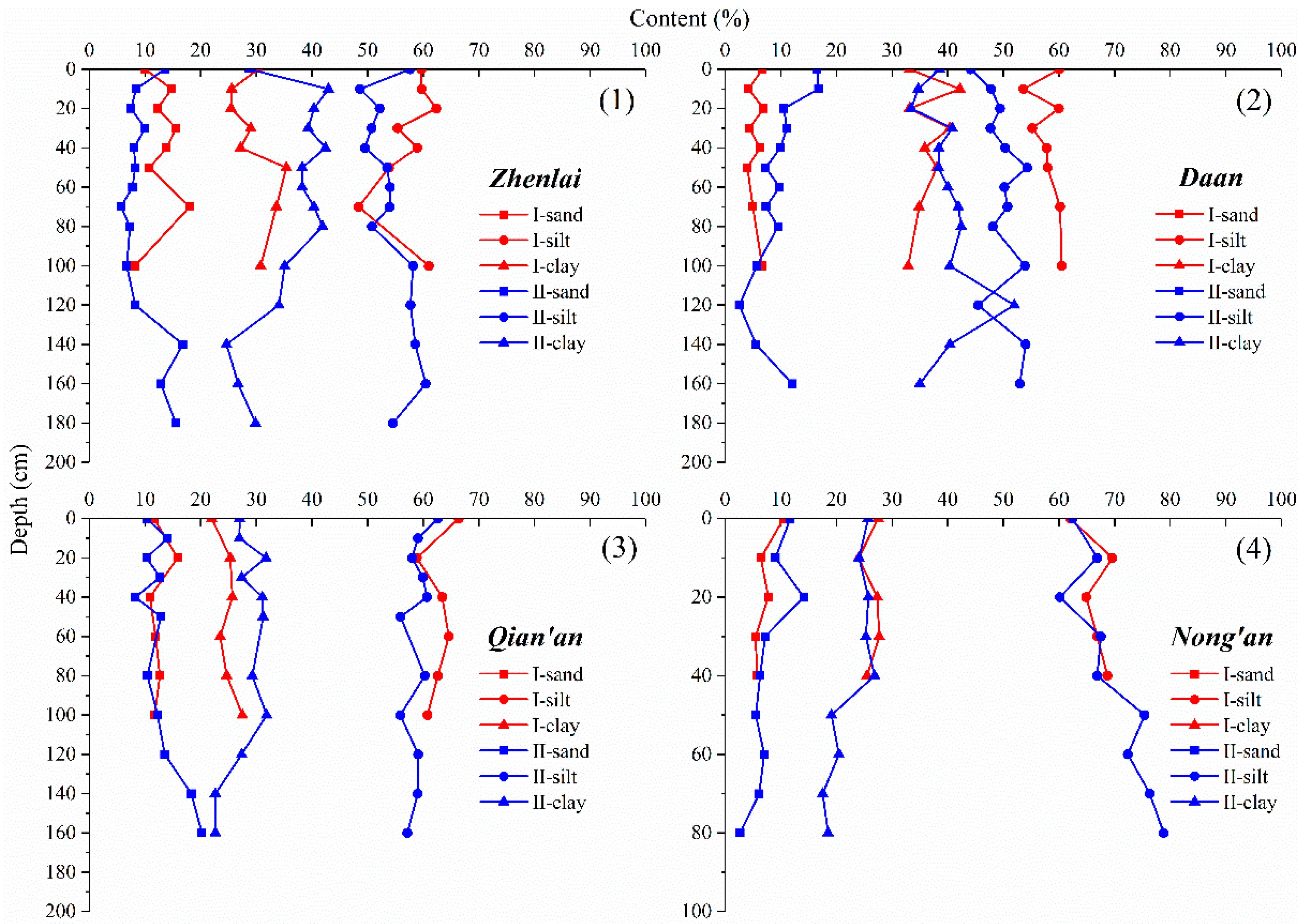
3.1. Analysis of Grain Size Composition
3.2. Analysis of Mineral Composition
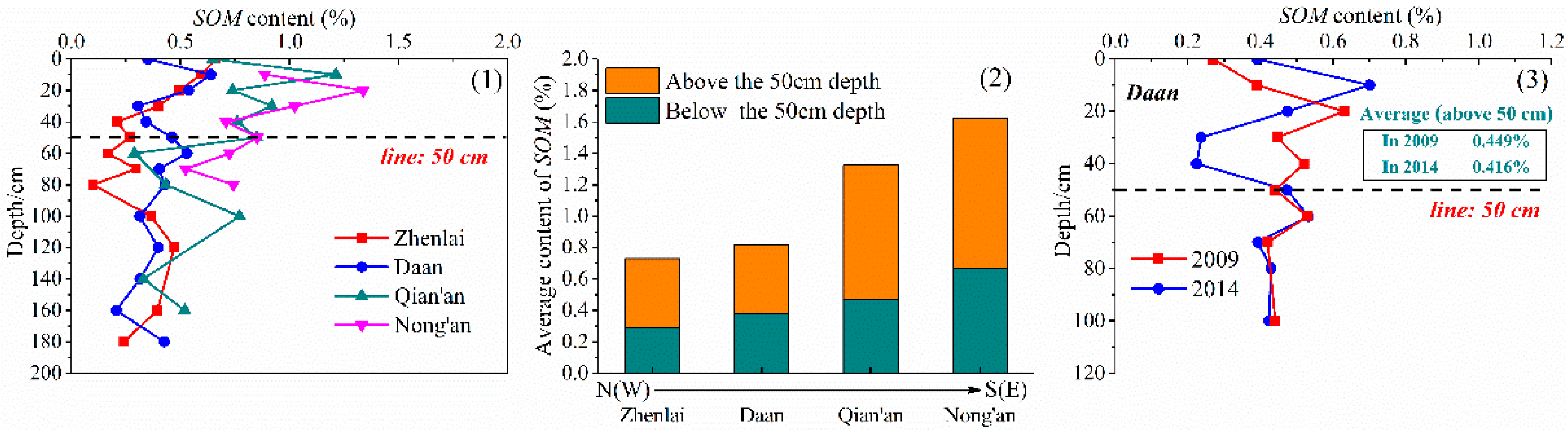
3.3. Analysis of SOM
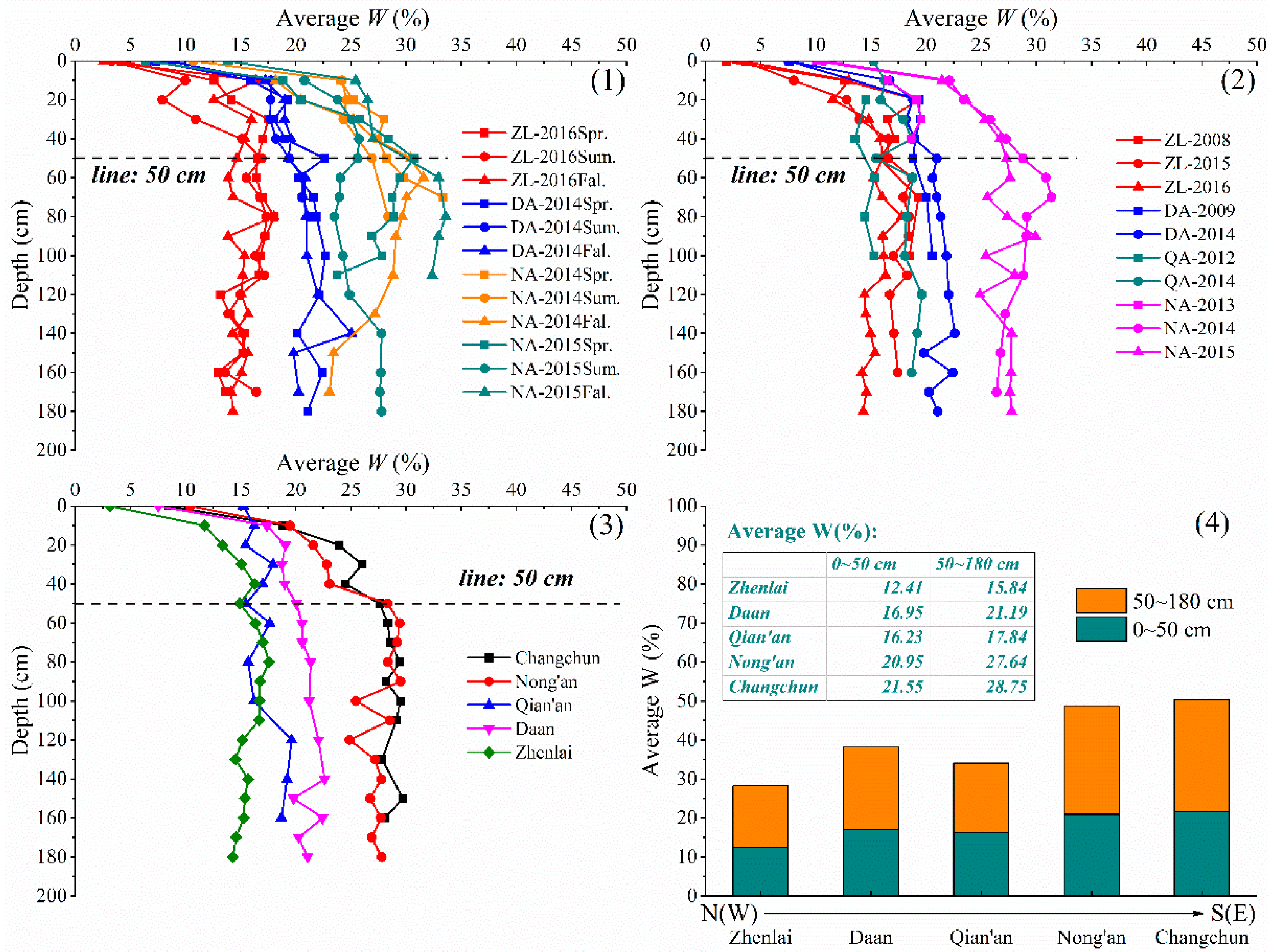
3.4. Analysis of W
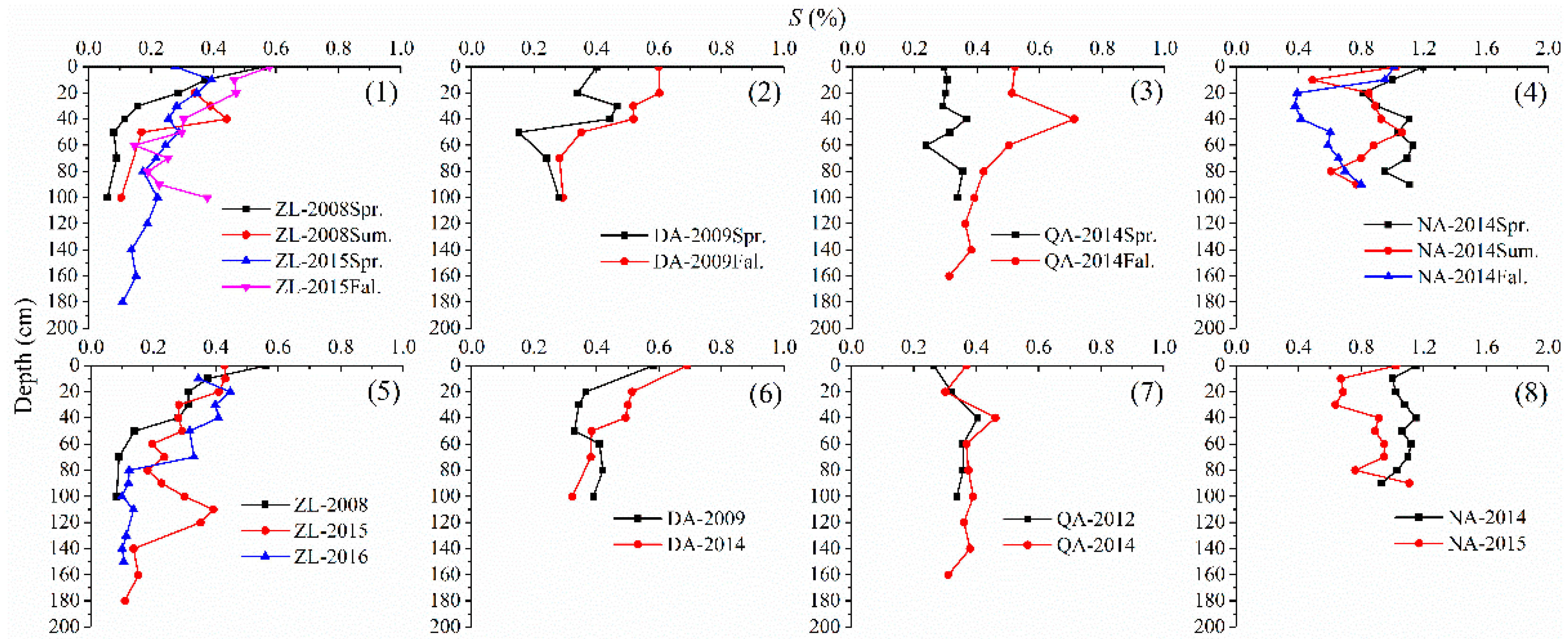
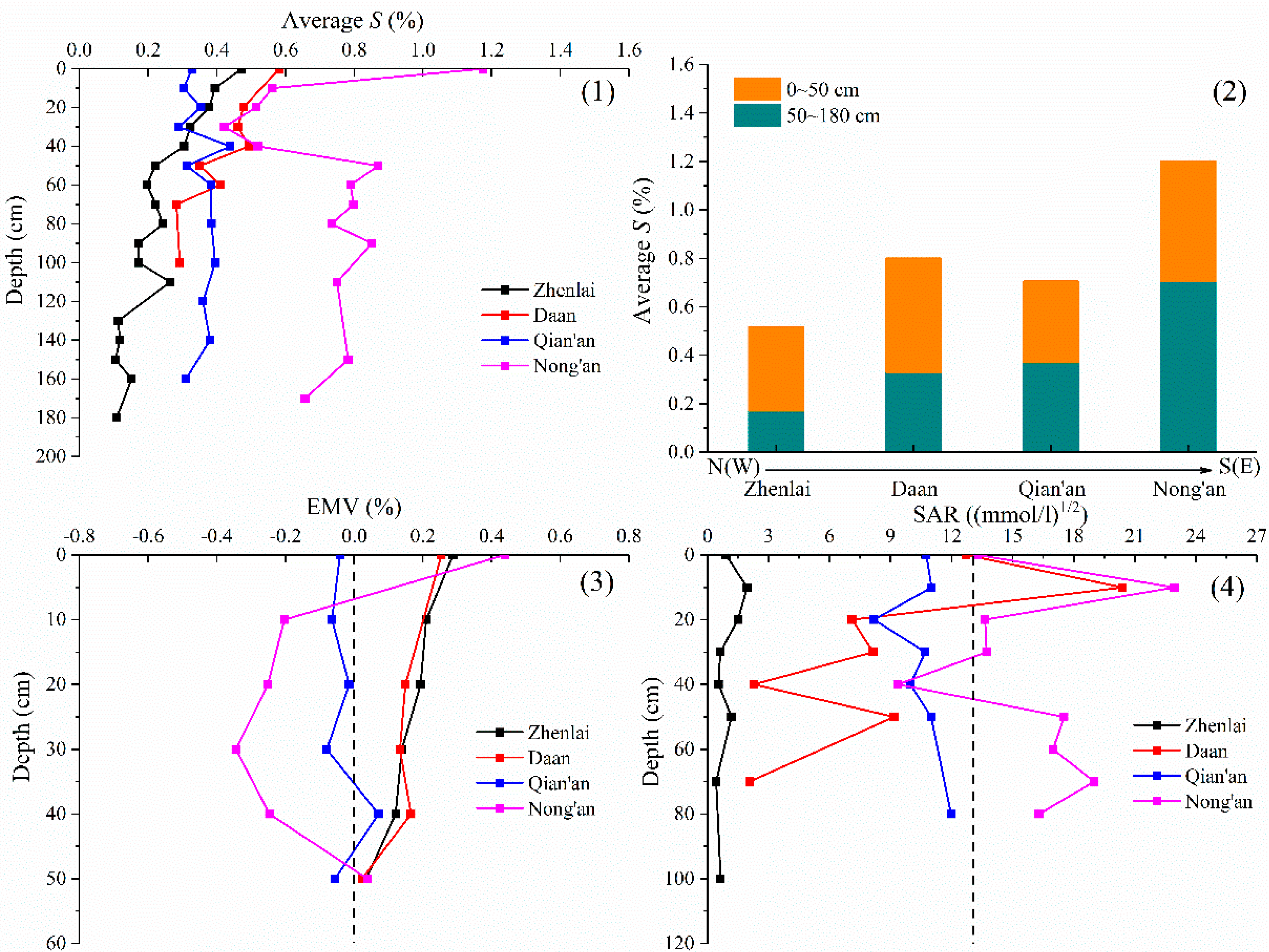
3.5. Analysis of S
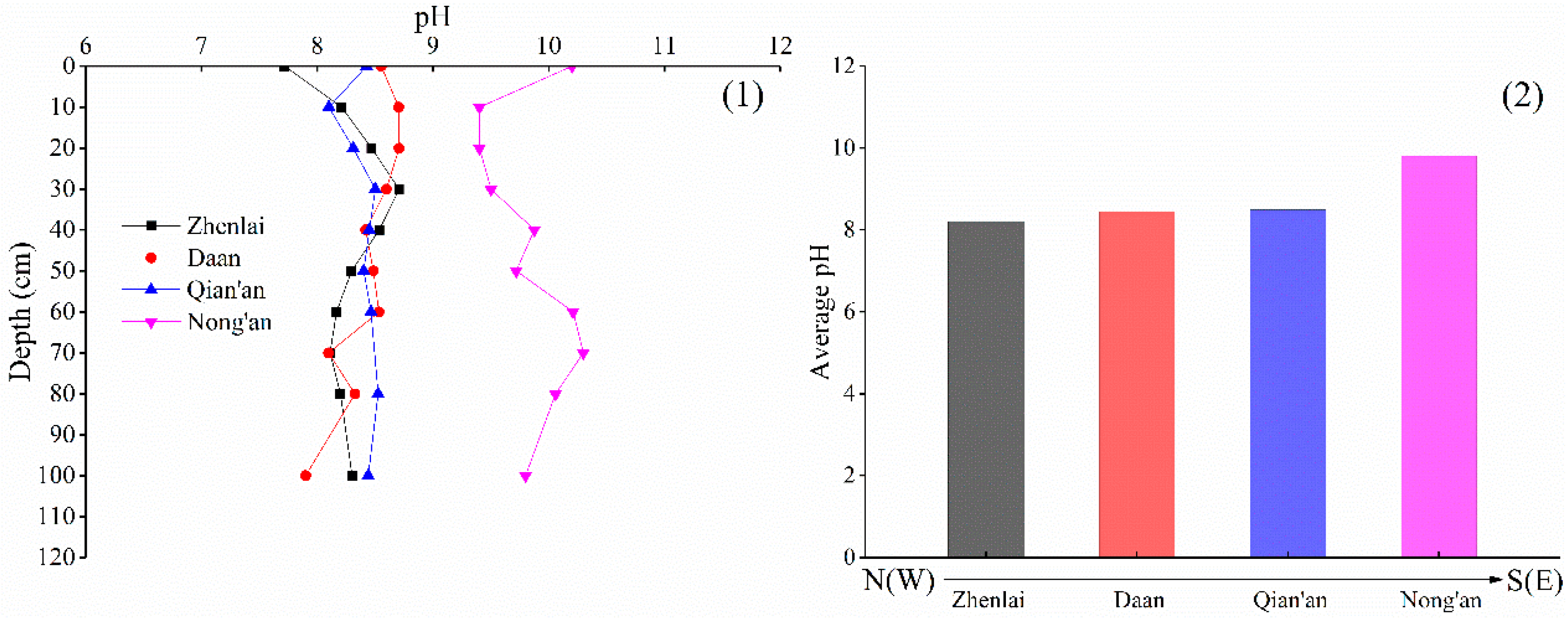
3.6. Analysis of pH
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The soil properties W, SOM, and S showed obvious stratification characteristics in the longitudinal profile. (i) The first layer, ranging from 0 to 50 cm, was greatly affected by the external environment, and the W and S fluctuated significantly with the seasons. The SOM decreased with the decrease in humus content in relation to depth. (ii) The second layer, below 50 cm, was relatively less affected by the external environment and tended to be stable, with relatively high W and low S and SOM.
- (2)
- Grain–size composition and mineral composition had no obvious stratification in the longitudinal profile. In the study area, silt was the main constituent in the grain–size composition, followed by clay, and sand was the least. The sand content changed relatively little in relation to depth, while the silt and clay content fluctuated significantly, and there seemed to be a mirror relationship between them. Moreover, the secondary minerals accounted for less than 25% of the mineral composition and increased in relation to depth, which coincided with the variation in clay content.
- (3)
- The soil properties in the study area changed significantly with space. In the S(E) study area, the precipitation was relatively abundant, and the average values of W, SOM, S, and pH in the soil were large. Under leaching, the shallow soil was desalted, and the salt storage in the deep soil was high. In the N(W) study area, evaporation and freeze–thaw played a dominant role in salt migration, and the salt state in the soil transformed from desalination into accumulation. In addition, the crystallization degree of the clay minerals tended to increase in the N(W)–S(E) direction, indicating that the relatively hot and humid climates in the S(E) were more conducive to the crystallization of the clay minerals.
- (4)
- The process of soil salinization was also accompanied by soil alkalization in the study area, but salinization was more common and serious than alkalization. In summary, this study provided valuable insights into the spatiotemporal variation in soil properties in Western Jilin province, and the findings could help develop effective strategies for soil management in this area.
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, T.; Milne, E. Carbon storage in a wolfberry plantation chronosequence established on a secondary saline land in an arid irrigated area of Gansu Province, China. J. Arid Land 2018, 10, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekkouche, M.S.; Bessaim, M.M.; Maliki, M.; Missoum, H.; Bendani, K.; Laredj, N. Enhanced electrokinetic removal of problematic salts in arid and semi-arid areas. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2020, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J. Development and Prospect of the research on salt-affacted soils in China. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2008, 45, 837–845. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.W.; Cao, C.J.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, W.L.; Shen, J.J.; Chen, Y.T.; Gu, F.F.; Han, M.X.; Rocchi, I. Utilization of bioethanol industry recycled waste for sustainable soil improvement: A win-win application. Eng. Geol. 2021, 289, 106192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, B. Present status of saline soil resources and countermeasures for improvement and utilization in China. Shandong Agric. Sci. 2015, 47, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Lin, S.; Han, Y.; Cheng, S.; Wang, N. Relationship between the Shear Strength and Microscopic Pore Parameters of Saline Soil with Different Freeze-Thaw Cycles and Salinities. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cao, Y.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y.; Duan, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Qu, Y. Relationships between Temporal and Spatial Changes in Lakes and Climate Change in the Saline-Alkali Concentrated Distribution Area in the Southwest of Songnen Plain, Northeast China, from 1985 to 2015. Water 2020, 12, 3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Tang, J.; Lin, N. Relationship between saline-alkali soil formation and neotectonic movement in Songnen Plain, China. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Seki, K.; Miyazaki, T.; Ishihama, Y. The causes of soil alkalinization in the Songnen Plain of Northeast China. Paddy Water Environ. 2009, 7, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Tang, J. Study on the environment evolution and the analysis of causes to land salinization and desertification in Songnen plain. Quat. Sci. 2005, 25, 474–483. [Google Scholar]
- Ilyushin, Y.V.; Asadulagi, M.-A.M. Development of a Distributed Control System for the Hydrodynamic Processes of Aquifers, Taking into Account Stochastic Disturbing Factors. Water 2023, 15, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pershin, I.M.; Papush, E.G.; Malkov, A.V.; Kukharova, T.V.; Spivak, A.O. Operational Control of Underground Water Exploitation Regimes. In Proceedings of the 2019 III International Conference on Control in Technical Systems (CTS), St. Petersburg, Russia, 30 October–1 November 2019; pp. 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martirosyan, K.V.; Chernyshev, A.B.; Martirosyan, A.V.; Tatyana, K.V. Formation of the Anterior Heating Function under the Action of Uniformly Distributed Sources. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Conference of Russian Young Researchers in Electrical and Electronic Engineering (EIConRus), St. Petersburg and Moscow, Russia, 27–30 January 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, G.; Niu, C. Experimental study on grain size and soluble salt of saline soil in western Jilin Province, China. Sci. Cold Arid Reg. 2015, 7, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Han, Y.; Han, M.; Shen, J.; Kong, Y.; Zhang, X. Crystallization variations in clay minerals with latitude in Jilin Province, China: A climate perspective. Clays Clay Miner. 2019, 67, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, J.; Wu, X. Present situation and tendency of saline-alkali soil in west Jilin Province. J. Geogr. Sci. 2001, 11, 321–328. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Qiu, S.; Deng, W. Study on the secondary saline-alkalization of land in Songnen Plain. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 1998, 18, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yu, T.; Zhang, X. Basic properties of saline soil in Da’an, western Jilin, China. Sci. Cold Arid Reg. 2015, 7, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shu, C.; Fujii, M.; Wu, Y.; Sun, D.A.; Ye, P.; Bao, Y. Numerical and Experimental Study on Water-Heat-Salt Transport Patterns in Shallow Bare Soil with Varying Salt Contents under Evaporative Conditions: A Comparative Investigation. J. Hydrol. 2023, 129564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Han, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. Evolution process of the microstructure of saline soil with different compaction degrees during freeze-thaw cycles. Eng. Geol. 2022, 304, 106699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chang, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Cao, C.; Zheng, W.; Bao, Y.; Rocchi, I. Use of Sulfur-Free Lignin as a novel soil additive: A multi-scale experimental investigation. Eng. Geol. 2020, 269, 105551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Yu, T.; Bao, S.; Wang, G.; Zhou, X.; Niu, C. A study of soil dispersivity in Qian’an, western Jilin Province of China. Sci. Cold Arid Reg. 2015, 7, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhai, E.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Lu, Y. A study on frost heave and thaw settlement of soil subjected to cyclic freeze-thaw conditions based on hydro-thermal-mechanical coupling analysis. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2021, 188, 103296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, K.; Kilic, S. Spatial variability of salinity and alkalinity of a field having salination risk in semi-arid climate in northern Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 127, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallarino, A.P.; Wittry, D.J. Efficacy of Grid and Zone Soil Sampling Approaches for Site-Specific Assessment of Phosphorus, Potassium, pH, and Organic Matter. Precis. Agric. 2004, 5, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhou, S.L.; Zhao, Q.G. Evaluation of spatial and temporal changes of soil quality based on geostatistical analysis in the hill region of subtropical China. Geoderma 2003, 115, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Senge, M.; Ito, K.; Onishi, T.; Yoshiyama, K. Experimental evaluation of irrigation methods for soil desalinization. Paddy Water Environ. 2015, 13, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Xu, C.; Wu, J.; Huang, J. Soil salt leaching under different irrigation regimes: HYDRUS-1D modelling and analysis. J. Arid Land 2014, 6, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaran, S.; Sonkamble, S.; Krishnakumar, K.; Mondal, N.C. Integrated approach for demarcating subsurface pollution and saline water intrusion zones in SIPCOT area: A case study from Cuddalore in Southern India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 5121–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, Y.; Yano, T.; Honna, T.; Yammoto, S.; Inosako, K. Causes of farmland salinization and remedial measures in the Aral Sea basin—Research on water management to prevent secondary salinization in rice-based cropping system in and land. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 85, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Wang, Q.; Fu, H.; Wang, J.; Han, Y.; Shen, J.; Lin, S. Effect of freeze-thaw cycles on the mechanical properties and constitutive model of saline soil. Geomech. Eng. 2021, 27, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, Q.; Kong, Y.; Cheng, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, N. Experiments on the initial freezing point of dispersive saline soil. Catena 2018, 171, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yu, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Song, S. A study of water migration characteristics of soda alkaline saline soils in western jilin province. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2018, 27, 2216–2224. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Shu, C.; Wu, Y.; Ye, P.; Du, D. Advances of coupled water-heat-salt theory and test techniques for soils in cold and arid regions: A review. Geoderma 2023, 432, 116378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhai, E.; Ye, P. Coupling analysis of the heat-water dynamics and frozen depth in a seasonally frozen zone. J. Hydrol. 2021, 593, 125603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhai, E.; Wu, Y.; Sun, D.a.; Lu, Y. Theoretical and Numerical Analyses on Hydro-Thermal-Salt-Mechanical Interaction of Unsaturated Salinized Soil Subjected to Typical Unidirectional Freezing Process. Int. J. Geomech. 2021, 21, 04021104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.; Cheng, J.; Jin, A. Origin and Evolution of the Hydrodynamics in Sedimentary Basins—A case study of the Songliao Basin. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2006, 24, 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Peng, W.; Li, C.; Xu, X.; Fan, J. Evolution Law of the Properties of Saline Soil in Western Jilin Province Under Multi Field Effect. Journal of Jilin University. Earth Sci. Ed. 2017, 47, 807–817. [Google Scholar]
- Bing, H.; He, P.; Zhang, Y. Cyclic freeze-thaw as a mechanism for water and salt migration in soil. Env. Ment. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.D.; Ye, P.; Wu, Y.J.; Zhai, E.C. Experimental study on simultaneous heat-water-salt migration of bare soil subjected to evaporation. J. Hydrol. 2022, 609, 127710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Zhenlai | Daan | Qian’an | Nong’an | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In 2008 | ∗∗∗ | |||
| In 2009 | ∗∗∗ | |||
| In 2012 | ∗∗ | |||
| In 2013 | ∗∗∗∗∗∗∗∗ | |||
| In 2014 | ∗∗∗ | ∗∗∗∗ | ∗∗∗∗∗∗∗ | |
| In 2015 | ∗∗∗∗ | ∗ | ∗∗∗∗ | |
| In 2016 | ∗∗∗∗∗∗ | |||
| Count (batches) | 13 | 7 | 6 | 19 |
| Elevation (m) | 133.5 | 129.9 | 123.6 | 193.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Fu, H. Spatiotemporal Variation in Saline Soil Properties in the Seasonal Frozen Area of Northeast China: A Case Study in Western Jilin Province. Water 2023, 15, 1812. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101812
Shen J, Chen Y, Wang Q, Fu H. Spatiotemporal Variation in Saline Soil Properties in the Seasonal Frozen Area of Northeast China: A Case Study in Western Jilin Province. Water. 2023; 15(10):1812. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101812
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Jiejie, Yating Chen, Qing Wang, and Huicheng Fu. 2023. "Spatiotemporal Variation in Saline Soil Properties in the Seasonal Frozen Area of Northeast China: A Case Study in Western Jilin Province" Water 15, no. 10: 1812. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101812
APA StyleShen, J., Chen, Y., Wang, Q., & Fu, H. (2023). Spatiotemporal Variation in Saline Soil Properties in the Seasonal Frozen Area of Northeast China: A Case Study in Western Jilin Province. Water, 15(10), 1812. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101812






