Assessment of Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers by Integrating Statistical and Graphical Techniques: Quaternary Aquifer, West Nile Delta, Egypt
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Analytical Techniques
2.3. Cluster Analysis and Saturation Index (SI)
2.4. Seawater Intrusion Quality Index (SWI)
3. Results and Discussions
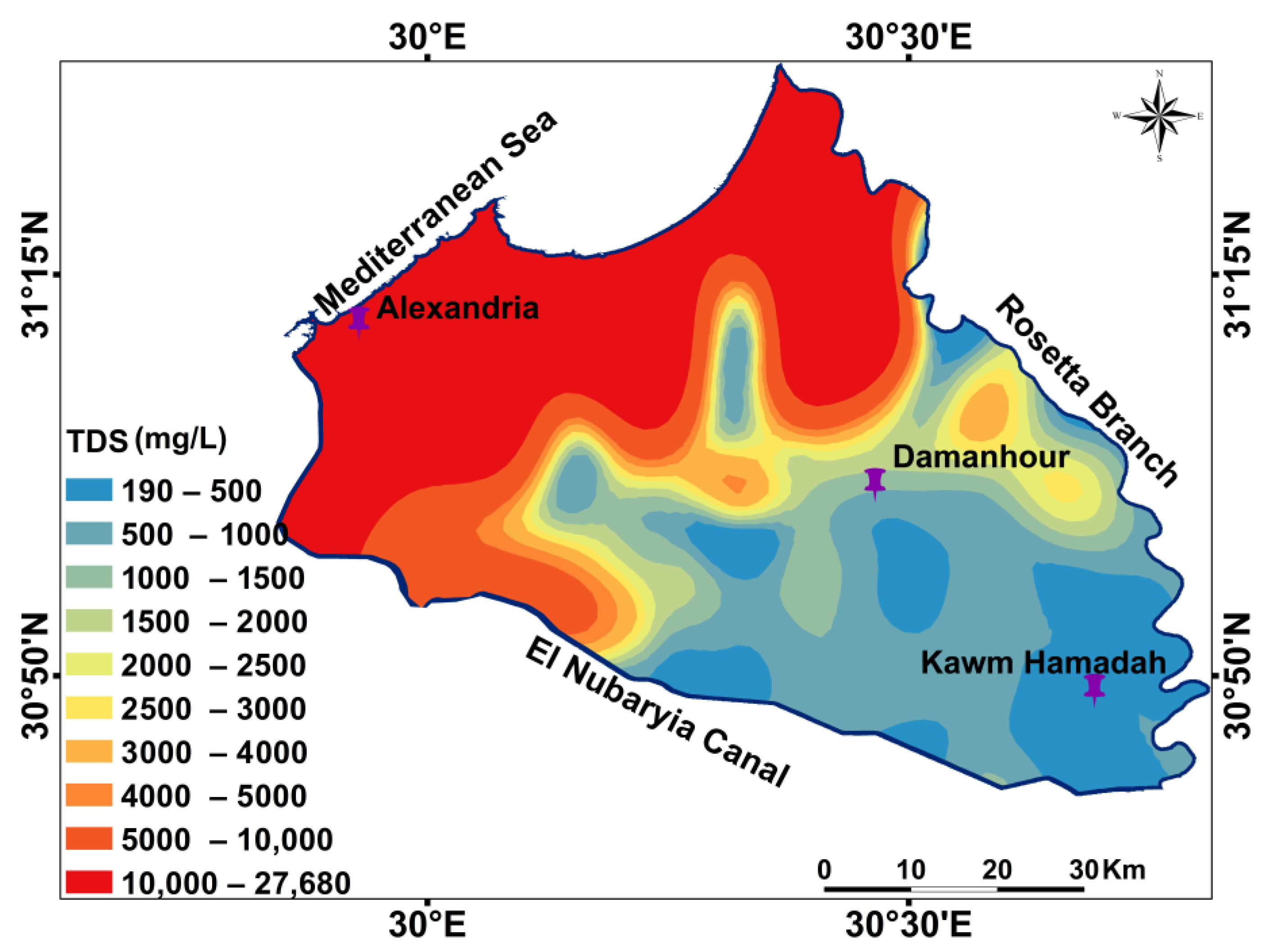
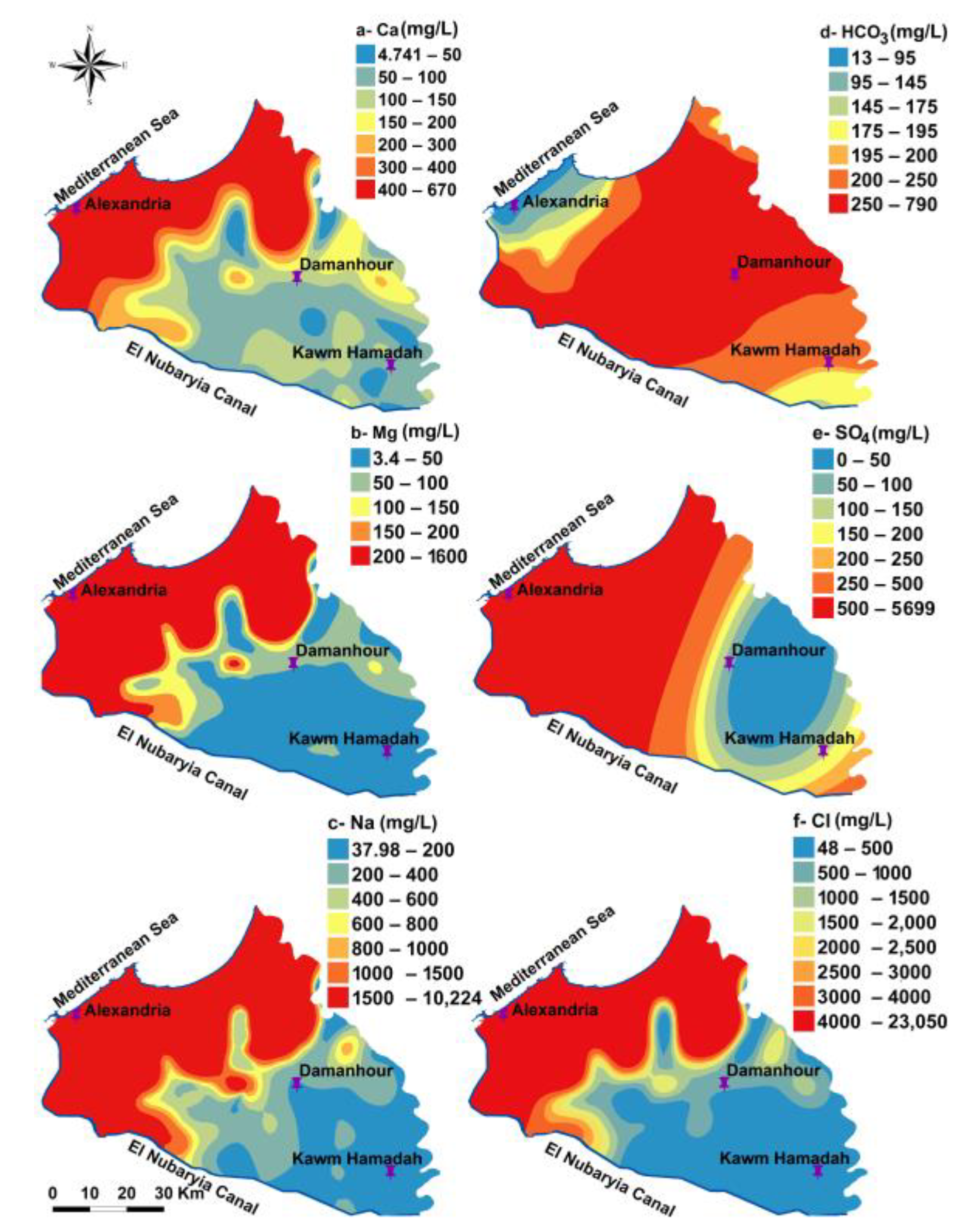
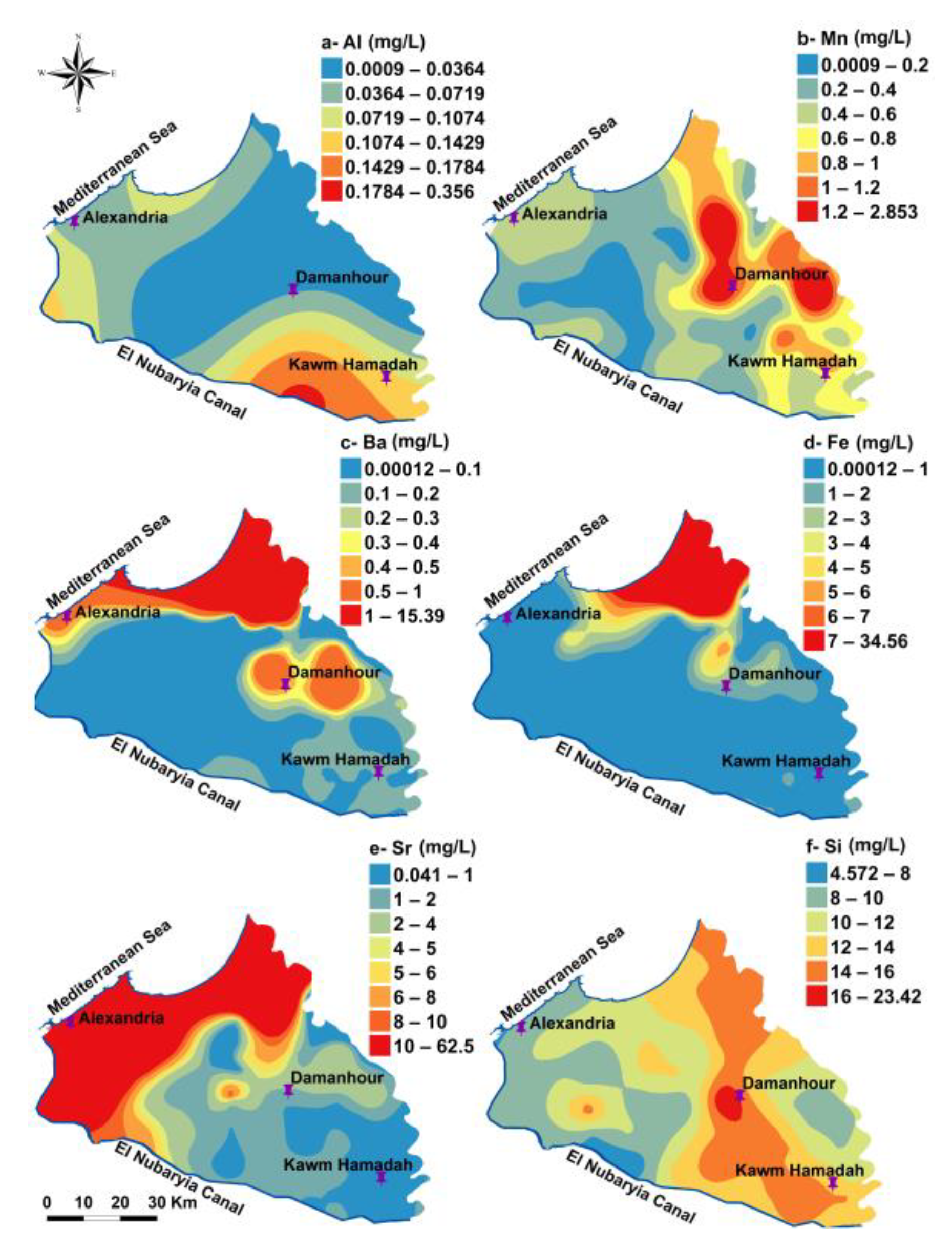
3.1. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Spatial Distribution
3.2. Hydrochemical Classification
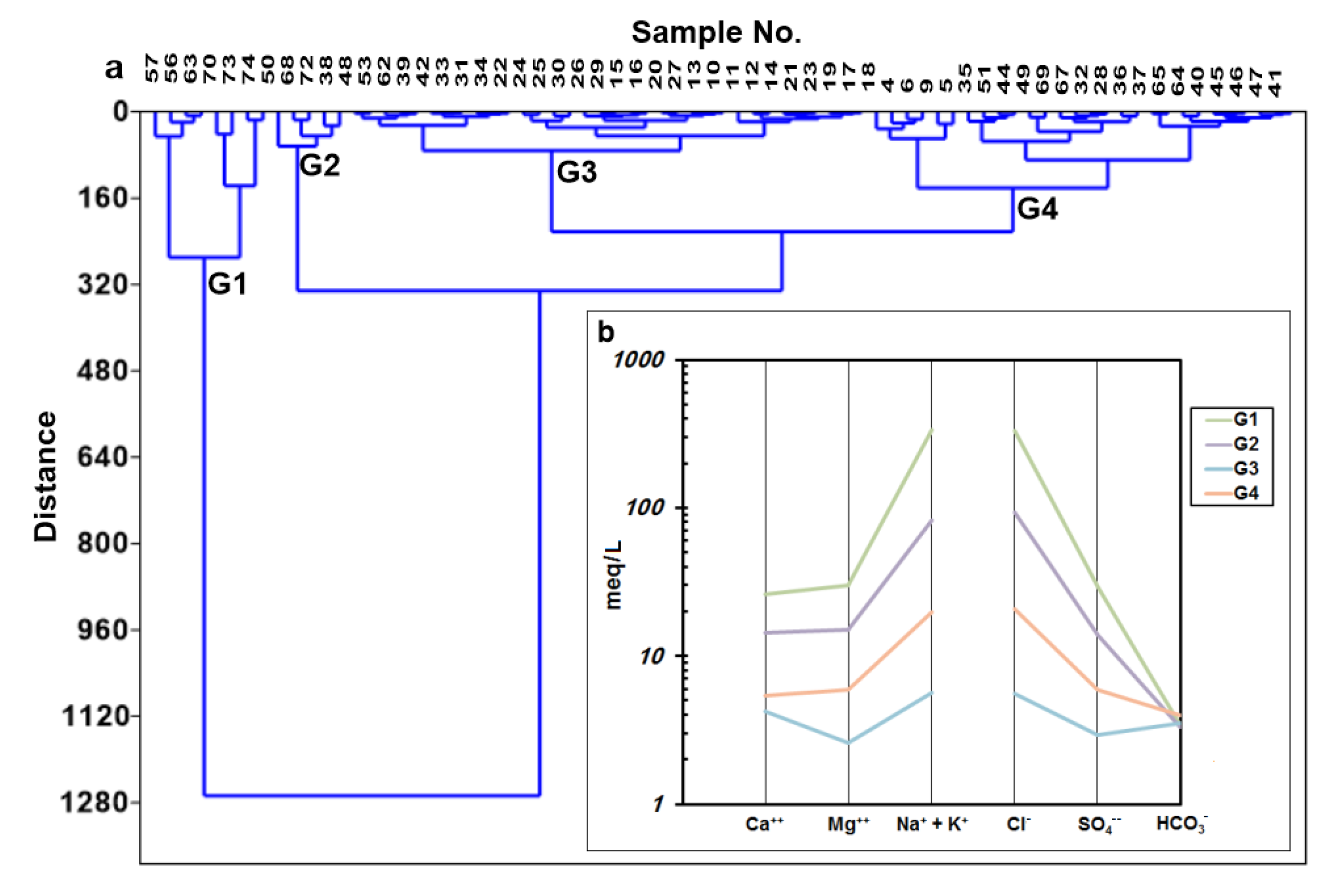
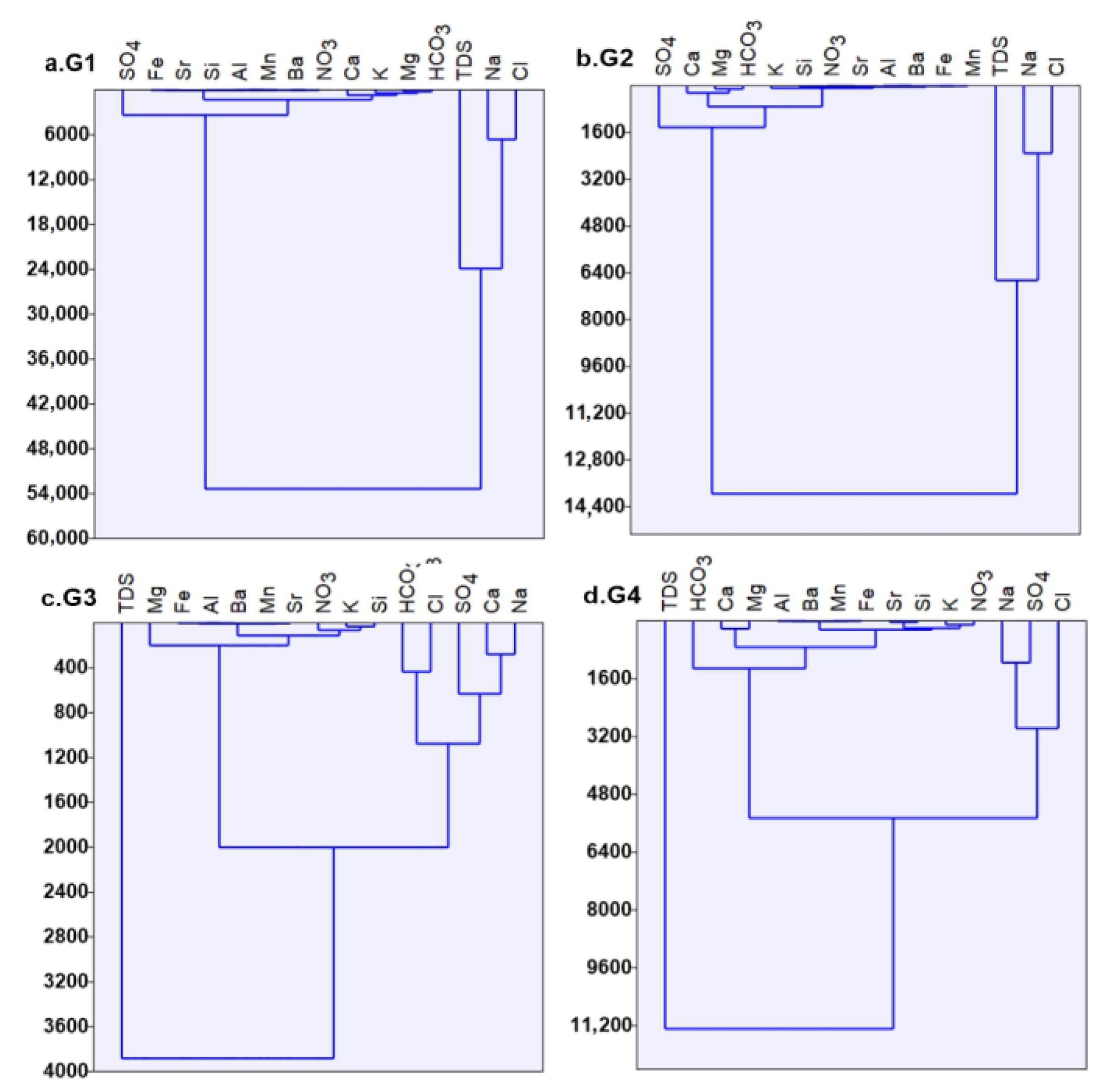
3.2.1. Cluster Analysis
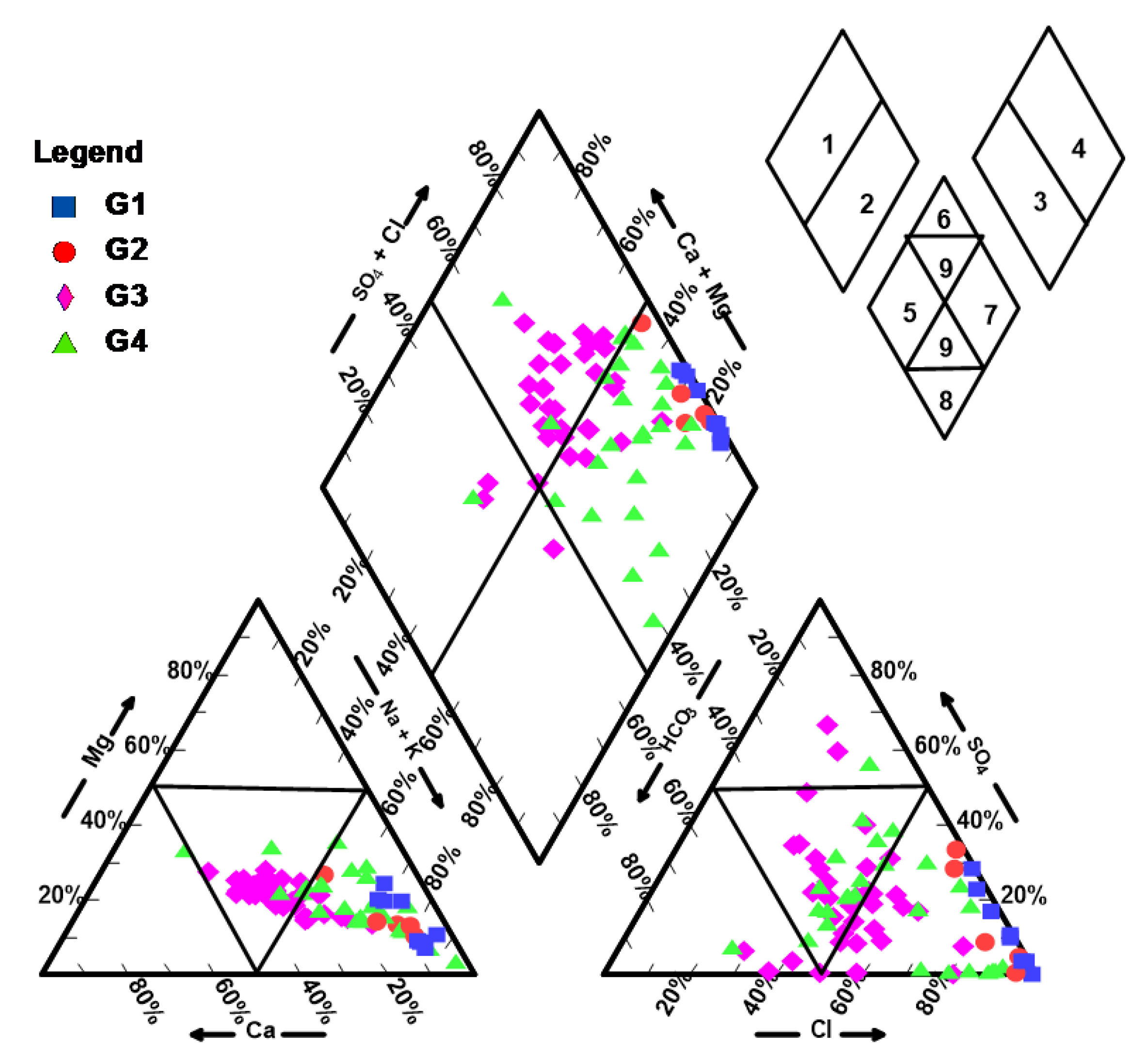
3.2.2. Piper’s (Trilinear) Diagram
3.2.3. Statistical Ions Classification
3.3. Saturation Index (SI)
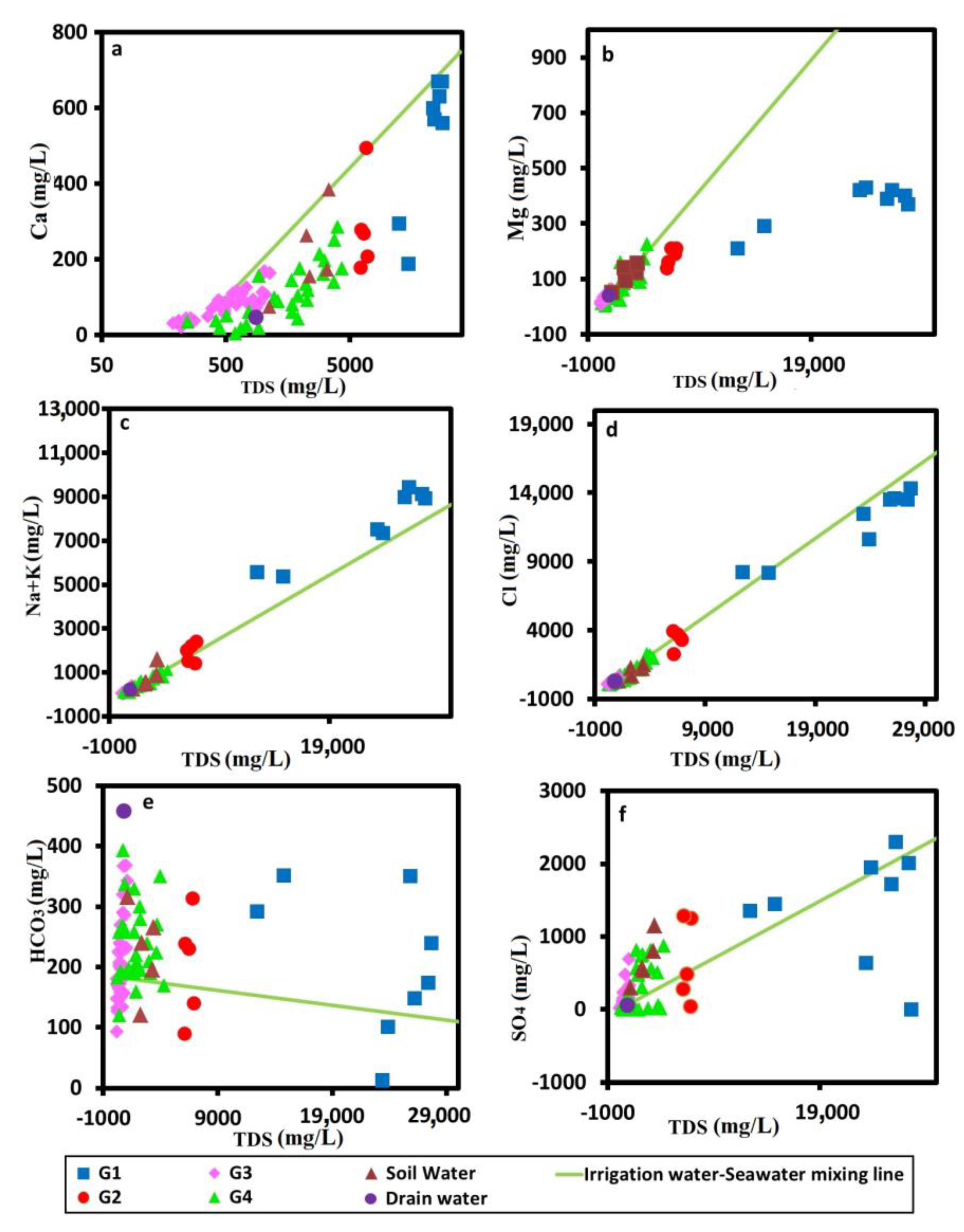
3.4. Hydrogeochemical Processes
Ions-TDS Relationships
- Gibbs diagram
- TDS vs. Ca, Mg, Na + K, Cl, HCO3, and SO4
3.5. Seawater Intrusion Quality Index (SWI)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.; Miao, J.; Hu, B.X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Z. Hydrogeochemical characterization and groundwater quality assessment in intruded coastal brine aquifers (Laizhou Bay, China). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 21073–21090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makri, P.; Stathopoulou, E.; Hermides, D.; Kontakiotis, G.; Zarkogiannis, S.D.; Skilodimou, H.D.; Bathrellos, G.D.; Antonarakou, A.; Scoullos, M. The Environmental Impact of a Complex Hydrogeological System on Hydrocarbon-Pollutants’ Natural Attenuation: The Case of the Coastal Aquifers in Eleusis, West Attica, Greece. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Osta, M.; Masoud, M.; Alqarawy, A.; Elsayed, S.; Gad, M. Groundwater Suitability for Drinking and Irrigation Using Water Quality Indices and Multivariate Modeling in Makkah Al-Mukarramah Province, Saudi Arabia. Water 2022, 14, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, Z.E.-S.; Abdelrahman, k.; Kováčiková, S.; Badran, O.M. Use of various statistical techniques to assess the vertical and lateral change in the groundwater chemistry of Quaternary aquifer in an irrigated highly populated area. J. King Saud Univ. -Sci. 2021, 33, 101556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Salem, H.S.; Gemail, K.S.; Junakova, N.; Ibrahim, A.; Nosair, A.M. An Integrated Approach for Deciphering Hydrogeochemical Processes during Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers. Water 2022, 14, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Yousfi, Y.; Himi, M.; El Ouarghi, H.; Elgettafi, M.; Benyoussef, S.; Gueddari, H.; Aqnouy, M.; Salhi, A.; Alitane, A. Hydrogeochemical and statistical approach to characterize groundwater salinity in the Ghiss-Nekkor coastal aquifers in the Al Hoceima province, Morocco. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 19, 100818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makri, P.; Hermides, D.; Kontakiotis, G.; Zarkogiannis, S.D.; Besiou, E.; Janjuhah, H.T.; Antonarakou, A. Integrated Ecological Assessment of Heavily Polluted Sedimentary Basin within the Broader Industrialized Area of Thriassion Plain (Western Attica, Greece). Water 2022, 14, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibaj, M.; Javadi, A.A.; Akrami, M.; Ke, K.-Y.; Farmani, R.; Tan, Y.-C.; Chen, A.S. Modelling seawater intrusion in the Pingtung coastal aquifer in Taiwan, under the influence of sea-level rise and changing abstraction regime. Hydrogeol. J. 2020, 28, 2085–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusty, P.; Farooq, S.H. Seawater intrusion in the coastal aquifers of India—A review. HydroResearch 2020, 3, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendiran, T.; Sabarathinam, C.; Chandrasekar, T.; Panda, B.; Mathivanan, M.; Nagappan, G.; Natesan, D.; Ghai, M.; Kumar Singh, D.; Alagappan, R. Geochemical variations due to salinization in groundwater along the southeast coast of India. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajji, S.; Allouche, N.; Bouri, S.; Aljuaid, A.M.; Hachicha, W. Assessment of Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers Using Multivariate Statistical Analyses and Hydrochemical Facies Evolution-Based Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 19, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Elhamid, H.F.; Abd-Elaty, I.; Hussain, M.S. Mitigation of seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers using coastal earth fill considering future sea level rise. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 23234–23245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Elhamid, H.F.; Abd-Elaty, I.; Sherif, M.M. Effects of Aquifer Bed Slope and Sea Level on Saltwater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers. Hydrology 2019, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Koriem, M.A.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Antar, A.S.; Ewis, M.A.; He, Z.; Kheir, A.M.S. Seawater intrusion impacts on groundwater and soil quality in the northern part of the Nile Delta, Egypt. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yihdego, Y.; Al-Weshah, R.A. Assessment and Prediction of Saline Sea Water Transport in Groundwater Using 3-D Numerical Modelling. Environ. Process. 2017, 4, 49–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodzadeh, D.; Ketabchi, H.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Simmons, C.T. Conceptualization of a fresh groundwater lens influenced by climate change: A modeling study of an arid-region island in the Persian Gulf, Iran. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermides, D.; Makri, P.; Kontakiotis, G.; Antonarakou, A. Advances in the Coastal and Submarine Groundwater Processes: Controls and Environmental Impact on the Thriassion Plain and Eleusis Gulf (Attica, Greece). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Liang, C.-Z.; Chung, T.-S.; Weber, M.; Staudt, C.; Maletzko, C. Combination of forward osmosis (FO) process with coagulation/flocculation (CF) for potential treatment of textile wastewater. Water Res. 2016, 91, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llamas, M.R.; Martínez-Santos, P. Intensive Groundwater Use: Silent Revolution and Potential Source of Social Conflicts. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2005, 131, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, M.M.R.; Hermans, T.; Van Camp, M.; Hossain, D.; Islam, M.; Ahmed, N.; Bhuiyan, M.A.Q.; Karim, M.M.; Walraevens, K. Identifying the Major Hydrogeochemical Factors Governing Groundwater Chemistry in the Coastal Aquifers of Southwest Bangladesh Using Statistical Analysis. Hydrology 2022, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escolero, O.; Marin, L.E.; Domínguez-Mariani, E.; Torres-Onofre, S. Dynamic of the freshwater–saltwater interface in a karstic aquifer under extraordinary recharge action: The Merida Yucatan case study. Environ. Geol. 2007, 51, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vengadesan, M.; Lakshmanan, E. Management of Coastal Groundwater Resources. In Coastal Management; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 383–397. ISBN 978-0-12-810473-6. [Google Scholar]
- Torres Martínez, J.A.; Mora, A.; Ramos Leal, J.A.; Morán Ramírez, J.; Arango Galván, C.; Mahlknecht, J. Constraining a density-dependent flow model with the transient electromagnetic method in a coastal aquifer in Mexico to assess seawater intrusion. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 2955–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, S.; Vinodh, K.; Johnson Babu, G.; Gowtham, B.; Arulprakasam, V. Integrated seawater intrusion study of coastal region of Thiruvallur district, Tamil Nadu, South India. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vann, S.; Puttiwongrak, A.; Suteerasak, T.; Koedsin, W. Delineation of Seawater Intrusion Using Geo-Electrical Survey in a Coastal Aquifer of Kamala Beach, Phuket, Thailand. Water 2020, 12, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Hwang, S. A Borehole-Based Approach for Seawater Intrusion in Heterogeneous Coastal Aquifers, Eastern Part of Jeju Island, Korea. Water 2020, 12, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, T.; Paepen, M. Combined Inversion of Land and Marine Electrical Resistivity Tomography for Submarine Groundwater Discharge and Saltwater Intrusion Characterization. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sae-Ju, J.; Chotpantarat, S.; Thitimakorn, T. Hydrochemical, geophysical and multivariate statistical investigation of the seawater intrusion in the coastal aquifer at Phetchaburi Province, Thailand. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2020, 191, 104165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, A.; Ledo, J.J.; Linde, N.; Luquot, L.; Bellmunt, F.; Folch, A.; Marcuello, A.; Queralt, P.; Pezard, P.A.; Martínez, L.; et al. Time-lapse cross-hole electrical resistivity tomography (CHERT) for monitoring seawater intrusion dynamics in a Mediterranean aquifer. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 2121–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefelnasr, A.; Sherif, M. Impacts of Seawater Rise on Seawater Intrusion in the Nile Delta Aquifer, Egypt. Groundwater 2014, 52, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrouk, M.; Jonoski, A.; HP Oude Essink, G.; Uhlenbrook, S. Impacts of Sea Level Rise and Groundwater Extraction Scenarios on Fresh Groundwater Resources in the Nile Delta Governorates, Egypt. Water 2018, 10, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrouk, M.; Jonoski, A.; Oude Essink, G.; Uhlenbrook, S. Assessing the Fresh–Saline Groundwater Distribution in the Nile Delta Aquifer Using a 3D Variable-Density Groundwater Flow Model. Water 2019, 11, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, M.; El Osta, M.; Alqarawy, A.; Elsayed, S.; Gad, M. Evaluation of groundwater quality for agricultural under different conditions using water quality indices, partial least squares regression models, and GIS approaches. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, M.; Sefelnasr, A.; Javadi, A. Incorporating the concept of equivalent freshwater head in successive horizontal simulations of seawater intrusion in the Nile Delta aquifer, Egypt. J. Hydrol. 2012, 464–465, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, Z.E.; Al Temamy, A.M.; Salah, M.K.; Kassab, M. Origin and characteristics of brackish groundwater in Abu Madi coastal area, Northern Nile Delta, Egypt. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 178, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, Z.E.-S.; Osman, O.M. Use of major ions to evaluate the hydrogeochemistry of groundwater influenced by reclamation and seawater intrusion, West Nile Delta, Egypt. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 3675–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Deek, M.; Nessim, R. Organic pollutants in Abu Qir Bay. J. High Inst. Public Health 1995, 25, 221–226. [Google Scholar]
- Armanuos, A.M.; Negm, A. Integrated Groundwater Modeling for Simulation of Saltwater Intrusion in the Nile Delta Aquifer, Egypt. In Groundwater in the Nile Delta; Negm, A.M., Ed.; The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 489–544. ISBN 978-3-319-94283-4. [Google Scholar]
- Allam, A.R.; Saaf, E.-J.; Dawoud, M.A. Desalination of brackish groundwater in Egypt. Desalination 2003, 152, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawoud, M.A.; Darwish, M.M.; El-Kady, M.M. GIS-Based Groundwater Management Model for Western Nile Delta. Water Resour. Manag. 2005, 19, 585–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, W. Environmental Management of Groundwater Resources in the Nile Delta Region. Ph.D. Thesis, Cairo University, Cairo, Egypt, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Awad, S.R.; El Fakharany, M.A.; Hagran, N.M. Environmental Impact on Water Resources at the Northwestern Part of the Nile Delta, Egypt. J. Am. Sci. 2015, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, Z.E.; Sefelnasr, A.M.; Hasan, S.S. Assessment of groundwater vulnerability for pollution using DRASTIC Index, young alluvial plain, Western Nile Delta, Egypt. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS. Earth Resources Observation And Science (EROS) Center Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) 1 Arc-Second Global; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Salem, Z.E.; Hasan, S.S. Use of GALDIT model and HFE-Diagram to assess seawater intrusion vulnerability in West Nile Delta, Egypt. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Arabi, N.E.; Morsy, W.S. Applying integrated ground- and surface-water management (case study: Nubaryia Basin, West Delta, Egypt). J. Am. Sci. 2013, 9, 43–53. [Google Scholar]
- REGWA. The Groundwater in a Study Area Southern of Wadi El Farigh; REGWA: Cairo, Egypt, 1993; p. 74. [Google Scholar]
- Domenico, P.A.; Schwartz, F.W. Physical and Chemical Hydrogeology, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998; ISBN 978-0-471-59762-9. [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch, W.J.; Siegel, R. Groundwater Geochemistry: Fundamentals and Applications to Contamination; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997; ISBN 978-1-00-306994-2. [Google Scholar]
- HACH. Chemical Procedures Explained; Hach Technical Center for Applied Analytical Chemistry: Loveland, CO, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- US EPA. Method 200.7: Determination of Metals and Trace Elements in Water and Wastes by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/esam/method-2007-determination-metals-and-trace-elements-water-and-wastes-inductively-coupled (accessed on 7 March 2023).
- Okiongbo, K.S.; Douglas, R.K. Evaluation of major factors influencing the geochemistry of groundwater using graphical and multivariate statistical methods in Yenagoa city, Southern Nigeria. Appl. Water Sci. 2015, 5, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfy, M.E.; Lashin, A.; Faraj, T.; Alataway, A.; Tarawneh, Q.; Al-Bassam, A. Quantitative hydro-geophysical analysis of a complex structural karst aquifer in Eastern Saudi Arabia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dişli, E.; Gülyüz, N. Hydrogeochemical investigation of an epithermal mineralization bearing basin using multivariate statistical techniques and isotopic evidence of groundwater: Kestanelik Sub-Basin, Lapseki, Turkey. Geochemistry 2020, 80, 125661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Li, P.; He, X.; Su, F.; Elumalai, V. Hydrogeochemical Processes Affecting Groundwater Chemistry in the Central Part of the Guanzhong Basin, China. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 80, 74–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Tian, R.; Liu, R. Solute Geochemistry and Multivariate Analysis of Water Quality in the Guohua Phosphorite Mine, Guizhou Province, China. Expo Health 2019, 11, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, P.; Wang, D.; Ren, X.; Wei, M. Statistical and multivariate statistical techniques to trace the sources and affecting factors of groundwater pollution in a rapidly growing city on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2020, 26, 1603–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, S.R.; Parkhurst, D.L. PHREEQCI—A Graphical User Interface to the Geochemical Model PHREEQC; Fact Sheet; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2002; Volume 031–032.
- Tomaszkiewicz, M.; Abou Najm, M.; El-Fadel, M. Development of a groundwater quality index for seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 57, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Postma, D. (Eds.) Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2005; ISBN 978-0-429-15232-0. [Google Scholar]
- Kreitler, C.W. Geochemical Techniques for Identifying Sources of Ground-Water Salinization; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993; ISBN 978-1-56670-000-9. [Google Scholar]
- Panteleit, B.; Hamer, K.; Kringel, R.; Kessels, W.; Schulz, H.D. Geochemical processes in the saltwater–freshwater transition zone: Comparing results of a sand tank experiment with field data. Environ. Earth Sci 2011, 62, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaky, A.; Atta, S.; El Hassanein, A.; Khallaf, K. Hydrogeochemistry of Groundwater in the Western Nile Delta Aquifers, Egypt; Cairo University: Giza, Egypt, 2007; Volume 19, pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Winslow, A.G.; Kister, L.R. Saline-Water Resources of Texas; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1956.
- Abdel Baki, A. Hydrogeological and Hydrochemical Studies on the Area West of Rosetta Branch and South El Nasr Canal. Ph.D. Thesis, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Piper, A. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1944, 25, 914–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaky, A.M.; El Hasanein, A.S.; Atta, S.A.; Khallaf, K.M. Nile and Groundwater Interaction in the Western Nile Delta, Egypt. In The Nile Delta; Negm, A.M., Ed.; The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 55, pp. 33–62. ISBN 978-3-319-56122-6. [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz, B.; Singurindy, O.; Lowell, R.P. Mixing-driven diagenesis and mineral deposition: CaCO3 precipitation in salt water–fresh water mixing zones: Mixing-Driven Diagenesis. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drevaliene, G.; Karro, E.; Mokrik, R.; Savitskaja, L. The origin of barium in the Cambrian–Vendian aquifer system, North Estonia. Est. J. Earth Sci. 2009, 58, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawson, J.; Siade, A.; Sun, J.; Neidhardt, H.; Berg, M.; Prommer, H. Quantifying Reactive Transport Processes Governing Arsenic Mobility after Injection of Reactive Organic Carbon into a Bengal Delta Aquifer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 8471–8480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, A.; Gustafsson, J.P.; Neidhardt, H.; Halder, D.; Kundu, A.K.; Chatterjee, D.; Berner, Z.; Bhattacharya, P. Role of competing ions in the mobilization of arsenic in groundwater of Bengal Basin: Insight from surface complexation modeling. Water Res. 2014, 55, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosono, T.; Hossain, S.; Shimada, J. Hydrobiogeochemical evolution along the regional groundwater flow systems in volcanic aquifers in Kumamoto, Japan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marandi, A.; Shand, P. Groundwater chemistry and the Gibbs Diagram. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 97, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.K.; De Maio, M.; Singh, P.K.; Singh, A.K. Hydrogeochemical characterization and groundwater quality assessment in a coal mining area, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouderbala, A.; Gharbi, B.Y. Hydrogeochemical characterization and groundwater quality assessment in the intensive agricultural zone of the Upper Cheliff plain, Algeria. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.; Koh, D.-C.; Jung, H.; Lee, J. The Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Groundwater Subjected to Seawater Intrusion in the Archipelago, Korea. Water 2020, 12, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussien, R.A. Groundwater Quality Index Studies for Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifer Ras Sudr, Egypt Using Geographic Information System. Sciences 2015, 5, 209–222. [Google Scholar]




| Parameter | Used Instrument | Analyzing Techniques | Analyzing Place |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric conductance Ec (mS/cm) | Hach’s Portable conductivity/ Total dissolved solids (TDS) | The typical analytical methods explained by HACH [50] | Field |
| Total dissolved solids TDS (mg/L) | |||
| Temperature (°C) | |||
| Hydrogen ion activity (pH) | Portable Consort pH Meter (Model p 314) | ||
| SO4 and NO3 | Hach’s Direct Reading (DR/2000) Spectrophotometer | Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, Tanta University | |
| Cl and HCO3 | Hach’s Digital Titrator Model 16900-01 | ||
| Na, K, Ca, Mg, Al, Ba, Fe, Mn, Sr, and Si | ICP (Inductive Coupled Plasma Optima 7000 DV) | EPA method 200.7 by USEPA [51] | Center of Scientific Research and Measurements, Tanta University |
| Parameter | Min | Max | Av | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TDS (mg/L) | 190 | 27,680 | 3806.2 | 7001.4 |
| EC (ms/cm) | 0.38 | 55.3 | 7.1 | 12.3 |
| pH | 5.05 | 8.7 | 7.1 | 0.8 |
| TH (mg/L) | 25.93 | 3315 | 762.8 | 839.4 |
| Ca (mg/L) | 4.74 | 670 | 153.6 | 159.5 |
| Mg (mg/L) | 3.43 | 430 | 92.3 | 110.9 |
| Na (mg/L) | 37.98 | 9200 | 1156.7 | 2339.8 |
| K (mg/L) | 2.34 | 337.7 | 34.8 | 68.4 |
| HCO3 (mg/L) | 13.02 | 394 | 222.6 | 74.1 |
| SO4 (mg/L) | 0 | 2300 | 365.7 | 517.7 |
| Cl (mg/L) | 48 | 14,300 | 1844.1 | 3647.6 |
| NO3 (mg/L) | 0 | 202 | 22.9 | 36.6 |
| Al (mg/L) | 9 × 10−4 | 0.36 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Ba (mg/L) | 12 × 10−5 | 15.39 | 0.3 | 1.7 |
| Fe (mg/L) | 12 × 10−5 | 34.56 | 1.1 | 4.1 |
| Mn (mg/L) | 9 × 10−4 | 2.853 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Si (mg/L) | 4.57 | 23.42 | 12.1 | 3.9 |
| Sr (mg/L) | 0.04 | 62.5 | 4.6 | 11.1 |
| Water Class | Salt Concentration (mg/L) | No. of Wells | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fresh | >1000 | 40 | 53 |
| Slightly saline | 1000–3000 | 16 | 21 |
| Moderately saline | 3000–10,000 | 11 | 15 |
| Very saline | 10,000–35,000 | 8 | 11 |
| Brine | <35,000 | - | - |
| Parameter | G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TDS mg/L | 22,686.75 | 6486.4 | 597.94 | 1829.1 |
| Ca meq/L | 26.09 | 14.27 | 4.24 | 5.37 |
| Mg meq/L | 30.12 | 14.97 | 2.57 | 5.94 |
| Na meq/L | 329.78 | 82.24 | 5.51 | 19.17 |
| K meq/L | 5.18 | 0.72 | 0.17 | 0.56 |
| HCO3 meq/L | 3.42 | 187 | 3.49 | 3.95 |
| SO4 meq/L | 29.71 | 13.94 | 2.92 | 5.93 |
| Cl meq/L | 332.59 | 92.92 | 5.6 | 20.91 |
| Si mg/L | 12.63 | 12.89 | 11.31 | 10.59 |
| Al mg/L | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| Ba mg/L | 0.12 | 3.11 | 0.13 | 0.24 |
| Fe mg/L | 0.25 | 10.01 | 0.55 | 1.47 |
| Mn mg/L | 0.49 | 1.55 | 0.49 | 0.88 |
| Sr mg/L | 0.80 | 28.01 | 1.97 | 6.14 |
| No. | Aragonite | Calcite | Dolomite | Witherite | Anhydrite | Gypsum | Barite | Halite | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | Min | −1.7 | −1.6 | −2.7 | −8.4 | −1.3 | −0.9 | −2.5 | −3.1 |
| Max | 0.2 | 0.3 | 1.0 | −3.6 | −0.4 | 0.0 | 2.5 | −2.2 | |
| Av | −0.7 | −0.6 | −0.8 | −5.5 | −0.7 | −0.4 | −0.1 | −2.7 | |
| SI > 1% | 12.5 | 25 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 57.2 | 0 | |
| SI < 1% | 87.5 | 75 | 75 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 42.8 | 100 | |
| G2 | Min | −1.9 | −1.7 | −3.1 | −8.6 | −2.2 | −1.9 | −2.7 | −4.2 |
| Max | 1.1 | 1.2 | 2.5 | −3.7 | −0.8 | −0.6 | −0.7 | −3.8 | |
| Av | −0.5 | −0.4 | −0.5 | −6.0 | −1.4 | −1.1 | −1.5 | −3.9 | |
| SI > 1% | 40 | 40 | 40 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| SI < 1% | 60 | 60 | 60 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| G3 | Min | −1.1 | −1.0 | −1.9 | −6.4 | −3.8 | −3.5 | −4.2 | −7.2 |
| Max | 1.2 | 1.3 | 2.6 | −1.8 | −1.1 | −0.7 | 0.7 | −5.4 | |
| Av | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.9 | −2.9 | −2.1 | −1.8 | −0.2 | −6.3 | |
| SI > 1% | 84.90 | 87.90 | 87.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 63.7 | 0 | |
| SI < 1% | 15.10 | 12.10 | 12.1 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 36.3 | 100 | |
| G4 | Min | −1.9 | −1.7 | −3.4 | −8.0 | −3.8 | −3.5 | −3.3 | −7.1 |
| Max | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.7 | −1.8 | −1.2 | −0.8 | 1.2 | −4.4 | |
| Av | −0.8 | −0.6 | −1.1 | −5.2 | −2.1 | −1.8 | −1.2 | −5.4 | |
| SI > 1% | 22.6 | 25.9 | 22.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 25.9 | 0 | |
| SI < 1% | 77.4 | 74.1 | 77.4 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 74.1 | 100 | |
| No. | Sylvite | Hematite | Pyrolusite | Albite | Anorthite | K-feldspar | Kaolinite | Quartz | |
| G1 | Min | −4.6 | −2.7 | −1.8 | −4.4 | −12.1 | −4.3 | −1.8 | 0.1 |
| Max | −3.7 | 16.5 | 2.9 | 0.1 | −4.3 | 0.6 | 4.8 | 0.7 | |
| Av | −4.0 | 10.6 | 0.7 | −2.2 | −7.7 | −1.6 | 1.3 | 0.4 | |
| SI > 1% | 0 | 87.5 | 0 | 25 | 0 | 25 | 50 | 100 | |
| SI < 1% | 100 | 12.5 | 100 | 75 | 100 | 75 | 50 | 0 | |
| G2 | Min | −5.7 | 1.7 | −0.4 | −2.9 | −8.4 | −2.9 | 1.1 | 0.1 |
| Max | −4.9 | 20.3 | 0.4 | −1.7 | −5.1 | −1.1 | 1.7 | 0.5 | |
| Av | −5.4 | 9.7 | 0.1 | −2.5 | −6.9 | −2.2 | 1.4 | 0.3 | |
| SI > 1% | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | |
| SI < 1% | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | |
| G3 | Min | −7.9 | 5.5 | −0.2 | −3.8 | −6.6 | −2.6 | 0.7 | 0.1 |
| Max | −6.4 | 20.3 | 2.1 | 0.1 | −0.7 | 1.3 | 5.8 | 0.5 | |
| Av | −7.1 | 15.0 | 1.1 | −1.0 | −2.2 | 0.1 | 3.6 | 0.3 | |
| SI > 1% | 0 | 100 | 0 | 5.8 | 0 | 79.5 | 100 | 100 | |
| SI < 1% | 100 | 0 | 100 | 94.2 | 100 | 20.5 | 0 | 0 | |
| G4 | Min | −7.6 | 1.1 | −0.6 | −4.6 | −9.6 | −3.8 | 0.5 | −0.1 |
| Max | −4.9 | 21.2 | 2.7 | −0.6 | −1.6 | 0.0 | 6.4 | 0.5 | |
| Av | −6.4 | 11.4 | 0.5 | −2.9 | −6.5 | −2.0 | 1.7 | 0.2 | |
| SI > 1% | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 88 | |
| SI < 1% | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 12 | |
| TDS | EC | Ca | Mg | Na | K | HCO3 | SO4 | Cl | NO3 | Al | Ba | Fe | Mn | Si | Sr | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TDS | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| EC | 0.9 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| Ca | 0.9 | 0.9 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Mg | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 1 | ||||||||||||
| Na | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1 | |||||||||||
| K | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 1 | ||||||||||
| HCO3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 1 | |||||||||
| SO4 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 1 | ||||||||
| Cl | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 1 | |||||||
| NO3 | −0.1 | −0.1 | −0.1 | 0.0 | −0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | −0.1 | 1 | ||||||
| Al | −0.2 | −0.2 | −0.2 | −0.3 | −0.2 | −0.1 | −0.1 | −0.1 | −0.2 | −0.1 | 1 | |||||
| Ba | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.4 | −0.1 | 0.5 | 0.4 | −0.1 | −0.1 | 1 | ||||
| Fe | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.4 | −0.1 | 0.5 | 0.4 | −0.1 | −0.1 | 0.9 | 1 | |||
| Mn | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | −0.1 | −0.1 | 0.2 | −0.1 | 0.1 | −0.2 | −0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 1 | ||
| Si | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | −0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | −0.2 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 1 | |
| Sr | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.6 | −0.1 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.1 | −0.2 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 1 |
| Water Type | GQISWI Based on Worldwide Literature | Typical GQISWI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | |
| Fresh water | 73.5 | 90.1 | 82.7 | 75 | 100 |
| Mixed groundwater | 47.8 | 79.9 | 63.4 | 50 | 75 |
| Saline groundwater | 4.8 | 58.8 | 27.5 | 10 | 50 |
| Seawater | 3.1 | 9.2 | 5.8 | 0 | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hasan, S.S.; Salem, Z.E.; Sefelnasr, A. Assessment of Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers by Integrating Statistical and Graphical Techniques: Quaternary Aquifer, West Nile Delta, Egypt. Water 2023, 15, 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101803
Hasan SS, Salem ZE, Sefelnasr A. Assessment of Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers by Integrating Statistical and Graphical Techniques: Quaternary Aquifer, West Nile Delta, Egypt. Water. 2023; 15(10):1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101803
Chicago/Turabian StyleHasan, Samia S., Zenhom E. Salem, and Ahmed Sefelnasr. 2023. "Assessment of Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers by Integrating Statistical and Graphical Techniques: Quaternary Aquifer, West Nile Delta, Egypt" Water 15, no. 10: 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15101803





