Potential Submerged Macrophytes to Mitigate Eutrophication in a High-Elevation Tropical Shallow Lake—A Mesocosm Experiment in the Andes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
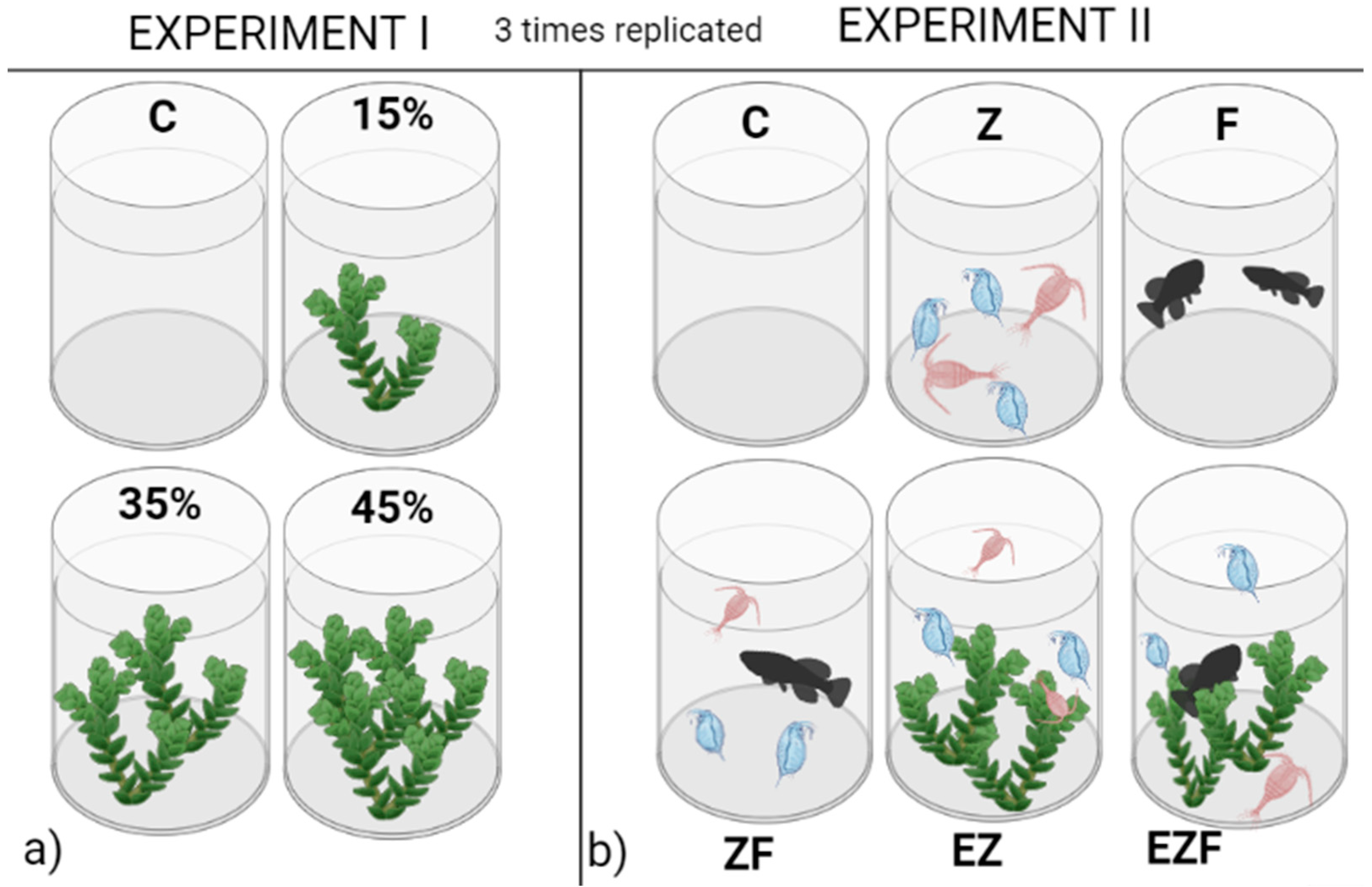
2.2. Experimental Set Up
2.3. Sample Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
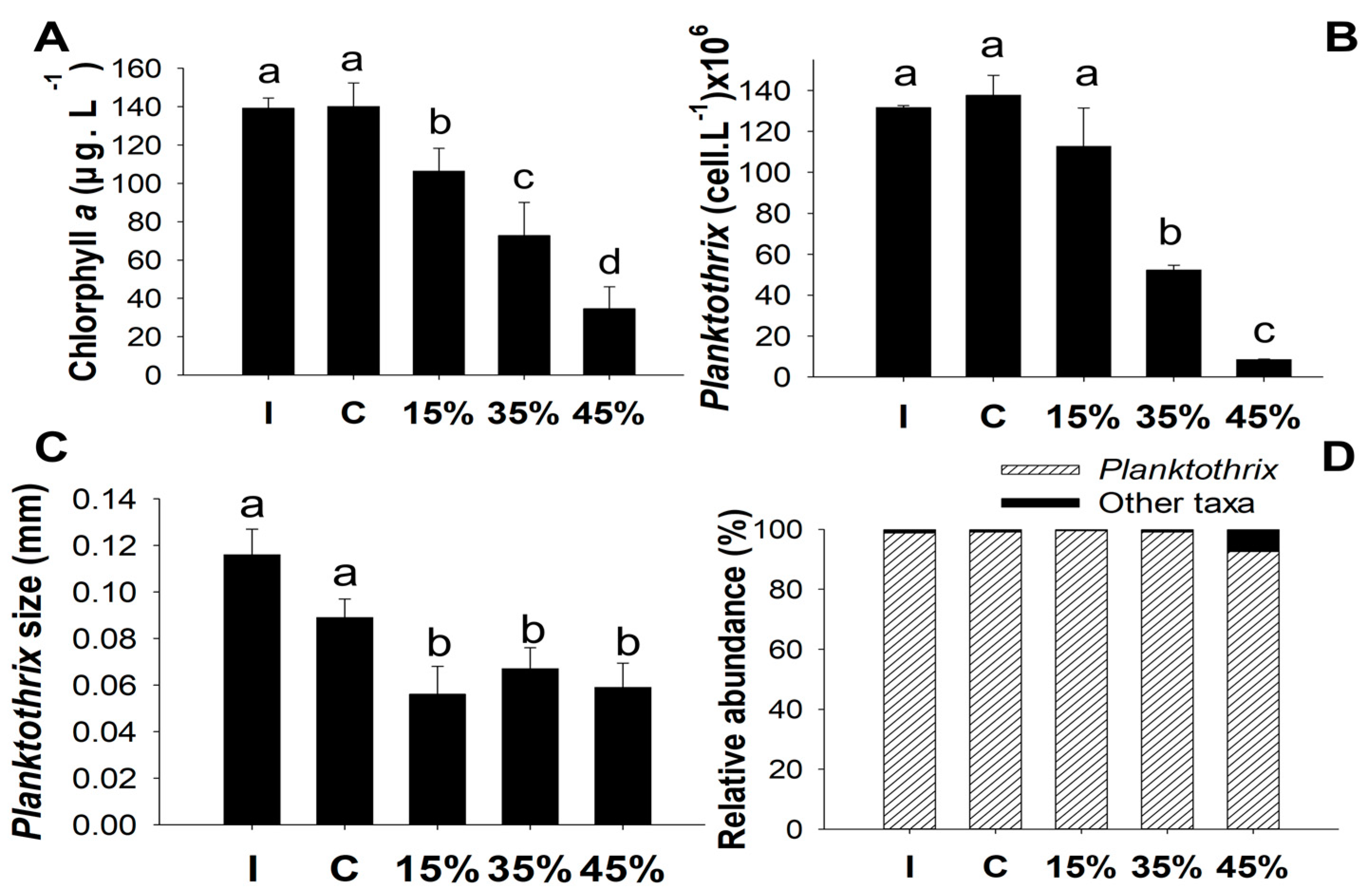
3.1. Experiment 1
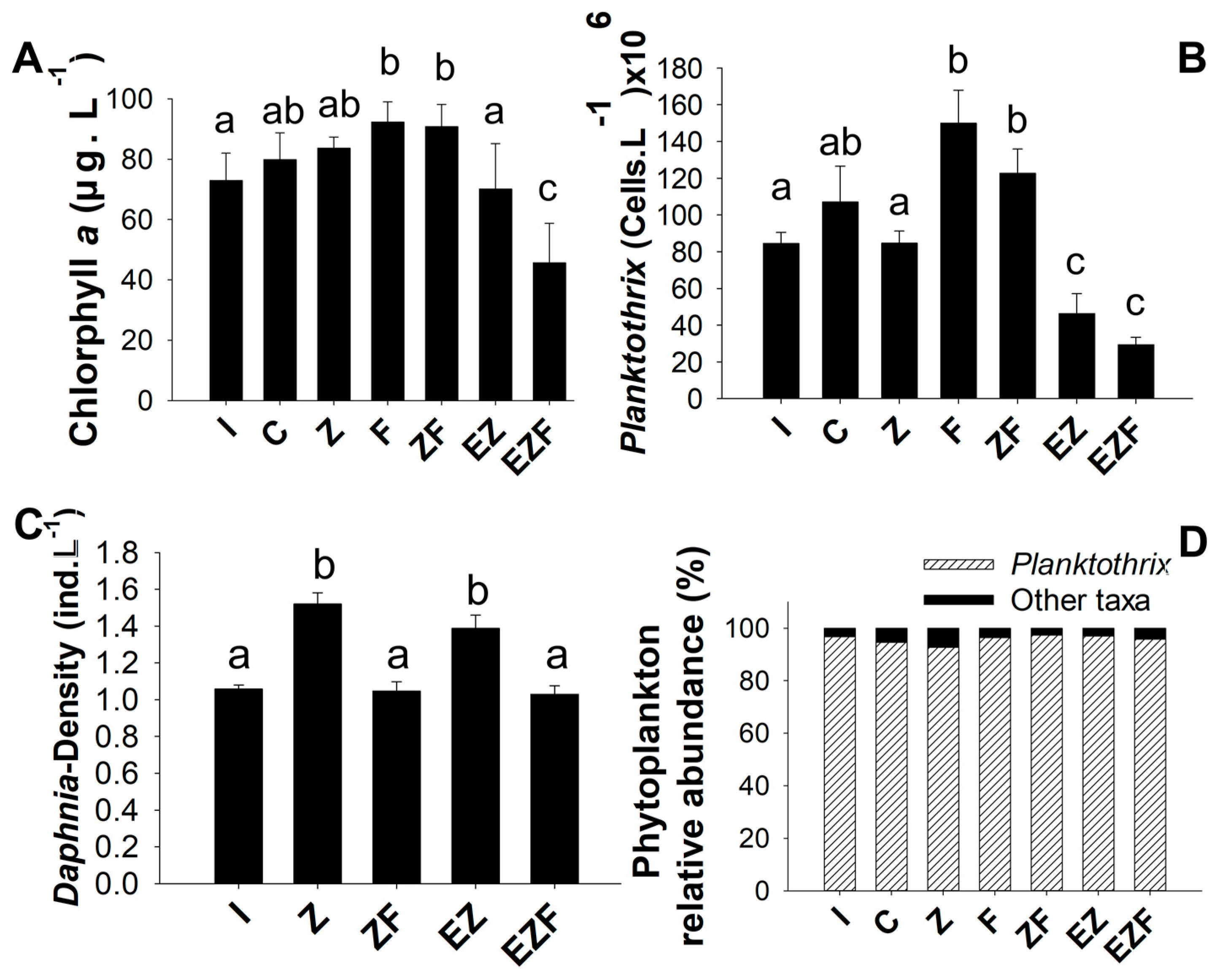
3.2. Experiment 2
4. Discussion
4.1. Phytoplankton Biomass and Total Nutrients with Different Concentrations of Macrophytes
4.2. Effects of Zooplankton on Phytoplankton
4.3. Effects of Fish on Zooplankton and Phytoplankton
4.4. Effects of Fish-Zooplankton and Macrophytes on Phytoplankton
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Experiment I | Experiment II | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CI | 15% | 35% | 45% | CII | F | Z | ZF | EZ | EZF | |
| Phytoplankton biomass | 0.66 ns | −23.6 * | −47.7 *** | −75.2 *** | 9.6 ns | 26.62 *** | 14.76 ns | 24.65 ** | −3.84 ns | −37.34 *** |
| Planktothrix density | 4.4 ns | −14.4 * | −60 *** | −93 *** | 26.7 ns | 77.5 *** | 0.15 ns | 45.18 * | −45.11 * | −65.21 *** |
| Planktothrix relative abundance | 99.12 | 99.53 | 99.10 | 92.55 | 94.57 | 97.04 | 92.68 | 97.28 | 69.93 | 95.76 |
| 30% | −10% | 34 | 9.1 | |||||||
| Daphnia | - | - | - | - | ||||||
| (Chla ug/L) | SD | Growth Rate (u) | SD | Planktothrix (Cell/L) × 106 | SD | Planktothrix Size | SD | TP (µg·L−1) | SD | TN (µg·L−1) | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 139.14 | 5.24 | 131.7 | 0.9 | 0.113 | 0.011 | 89.3 | 21 | 4866 | 750 | ||
| C | 140.06 | 12.28 | 0.0003 | 0.008 | 137.6 | 9.8 | 0.089 | 0.008 | 99 | 96.1 | 5000 | 1000 |
| 15% | 106.26 | 11.99 | −0.027 | 0.010 | 112.7 | 18.8 | 0.059 | 0.01 | 73.3 | 20.8 | 4066 | 1101 |
| 35% | 72.72 | 17.28 | −0.067 | 0.023 | 52.2 | 2.3 | 0.056 | 0.012 | 41.6 | 34.5 | 5666 | 577 |
| 45% | 34.5 | 11.5 | −0.144 | 0.032 | 8.4 | 0.2 | 0.067 | 0.009 | 52.3 | 15.3 | 3133 | 2759 |
| (Chla ug/L) | SD | Growth Rate (u) | SD | Planktothrix (Cell/L) × 106 | SD | TP (µg·L−1) | SD | TN (µg·L−1) | SD | Daphnia (ind L−1) | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 72.8 | 9.1 | 84.4 | 6 | 75 | 21.2 | 4250 | 353.55 | 1.164 | 0.048 | ||
| C | 79.8 | 8.9 | 0.006 | 0.008 | 107 | 19.4 | 75.6 | 46.6 | 5066 | 1006.64 | ||
| Z | 83.6 | 3.7 | 0.018 | 0.006 | 149.9 | 17.8 | 133.3 | 66.5 | 5233. | 251.66 | 1.52 | 0.060 |
| F | 92.2 | 6.7 | 0.009 | 0.003 | 84.5 | 6.6 | 116.6 | 47.2 | 5066 | 115.47 | ||
| ZF | 90.8 | 7.3 | 0.015 | 0.006 | 122.6 | 13.2 | 123.3 | 61.1 | 5666 | 577.35 | 1.04 | 0.051 |
| EZ | 70 | 15 | −0.004 | 0.014 | 46.3 | 10.7 | 93.3 | 15.2 | 5166 | 57.735 | 1.56 | 0.07 |
| EZF | 45.6 | 13 | −0.036 | 0.022 | 29.3 | 3.9 | 79.3 | 35.7 | 4800 | 692.82 | 1.27 | 0.02 |
References
- Smith, V.H.; Tilman, G.D.; Nekola, J.C. Eutrophication: Impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 1999, 100, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilt, S.; Brothers, S.; Jeppesen, E.; Veraart, A.J.; Kosten, S. Translating regime shifts in shallow lakes into changes in ecosystem functions and services. BioScience 2017, 67, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.; Codd, G.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Ibelings, B.W.; Verspagen, J.M.; Visser, P.M. Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, E.; Jensen, J.P.; Jensen, C.; Faafeng, B.; Hessen, D.O.; Søndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.; Brettum, P.; Christoffersen, K. The impact of nutrient state and lake depth on top-down control in the pelagic zone of lakes: A study of 466 lakes from the temperate zone to the arctic. Ecosystems 2003, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargeby, A.; Blindow, I.; Hansson, L.A. Shifts between clear and turbid states in a shallow lake: Multi-causal stress from climate, nutrients and biotic interactions. Arch. Fur. Hydrobiol. 2004, 161, 433–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, W.W.; Boyer, G.L. Health impacts from cyanobacteria harmful algae blooms: Implications for the North American Great Lakes. Harmful. Algae 2016, 54, 194–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Magalhães, V.F.; Soares, R.M.; Azevedo, S.M. Microcystin contamination in fish from the Jacarepaguá Lagoon (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil): Ecological implication and human health risk. Toxicon 2001, 39, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, M.U.; Wilson, A.E.; Leitão, J.I.; Pereira, S.P.; Buley, R.P.; Fernandez-Figueroa, E.G.; Capelo-Neto, J. Environmental factors associated with toxic cyanobacterial blooms across 20 drinking water reservoirs in a semi-arid region of Brazil. Harmful. Algae 2019, 86, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltorti, M.; Ollier, C.D. Geomorphic and tectonic evolution of the Ecuadorian Andes. Geomorphology 2000, 32, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, G.I.; Franco, L.; Delgado, J. Socio-ecological barriers to adaptive management of lake Fuquene, Colombia. Int. J. Des. Nat. Ecodynamics 2012, 7, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velez, M.I.; Salgado, J.; Brenner, M.; Hooghiemstra, H.; Escobar, J.; Boom, A.; Bird, B.; Curtis, J.H.; Temoltzin-Loranca, Y.; Patino, L.F.; et al. Novel responses of diatoms in neotropical mountain lakes to indigenous and post-European occupation. Anthropocene 2021, 34, 100294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, R.; Acosta, F.; Mooij, W.M.; Rejas, D.; Van Damme, P.A. Management of Laguna Alalay: A case study of lake restoration in Andean valleys in Bolivia. Aquat. Ecol. 2007, 41, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolá, R.P.; Bengtsson, L. Long-term and extreme water level variations of the shallow Lake Poopó, Bolivia. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2006, 51, 98–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariano, M.; Huaman, P.; Mayta, E.; Montoya, H.; Chanco, M. Contaminación producida por piscicultura intensiva en lagunas andinas de Junín, Perú. Rev. Peru. De Biol. 2010, 17, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guevara, E.A.; Santander, T.; Espinosa, R.; Graham, C.H. Aquatic bird communities in Andean lakes of Ecuador are increasingly dissimilar over time. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, D.; Dangles, O. Ecology of High Altitude Waters; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Salomón, S.; Rivera-Rondón, C.A.; Zapata, Á.M. Floraciones de cianobacterias en Colombia: Estado del conocimiento y necesidades de investigación ante el cambio global. Rev. De La Acad. Colomb. De Cienc. Exactas Físicas Y Nat. 2020, 44, 376–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Meerhoff, M.; Jacobsen, B.A.; Hansen, R.S.; Søndergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Lauridsen, T.; Mazzeo, N.; Branco, C.W.C. Restoration of shallow lakes by nutrient control and biomanipulation—The successful strategy varies with lake size and climate. Hydrobiologia 2007, 581, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, M.; Jeppesen, E.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Skov, C.; Van Nes, E.H.; Roijackers, R.; Lammens, E.; Portielje, R.O.B. Lake restoration: Successes, failures and long-term effects. J. Appl. Ecol. 2007, 44, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, K.; Chen, F.; Guan, B.; Hu, Y.; Zhong, P.; Tang, Y.; Zhao, X.; He, H.; et al. Restoration of shallow lakes in subtropical and tropical China: Response of nutrients and water clarity to biomanipulation by fish removal and submerged plant transplantation. Water 2016, 8, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, M.; Moss, B. Impact of submerged macrophytes on phytoplankton in shallow freshwater lakes. In The Structuring Role of Submerged Macrophytes in Lakes; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 115–132. [Google Scholar]
- Van Donk, E.; van de Bund, W.J. Impact of submerged macrophytes including charophytes on phyto-and zooplankton communities: Allelopathy versus other mechanisms. Aquat. Bot. 2002, 72, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Søndergaard, M.; Christoffersen, K. (Eds.) The Structuring Role of Submerged Macrophytes in Lakes; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 131. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Yang, K.; Li, S.; Li, G.; Song, L. Submerged vegetation removal promotes shift of dominant phytoplankton functional groups in a eutrophic lake. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 1699–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Hong, Y.; He, Q.; Yu, D.; Liu, C.; Dingshanbayi, H. Greater performance of exotic Elodea nuttallii in response to water level may make it a better invader than exotic Egeria densa during winter and spring. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horppila, J.; Nurminen, L. Effects of submerged macrophytes on sediment resuspension and internal phosphorus loading in Lake Hiidenvesi (southern Finland). Water Res. 2003, 37, 4468–4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzaro, X. Do the trophic cascade hypothesis and classical biomanipulation approaches apply to tropical lakes and reservoirs? Int. Ver. Für Theor. Und Angew. Limnol. Verh. 1997, 26, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerhoff, M.; Iglesias, C.; Teixeira de Mello, F.T.; Clemente, J.M.; Jensen, E.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Jeppesen, E. Effects of habitat complexity on community structure and predator avoidance behaviour of littoral zooplankton in temperate versus subtropical shallow lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, C.; Goyenola, G.; Mazzeo, N.; Meerhoff, M.; Rodo, E.; Jeppesen, E. Horizontal dynamics of zooplankton in subtropical Lake Bianca (Uruguay) hosting multiple Zooplankton predators and aquatic plant refuges. In Shallow Lakes in a Changing World; Springer: Dordrecht, The Nertherlands, 2007; pp. 179–189. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira de Mello, F.; de Oliveira, V.A.; Loverde-Oliveira, S.M.; Huszar, V.L.M.; Barquín, J.; Iglesias, C.; Silva, T.S.F.; Duque-Estrada, C.H.; Silió-Calzada, A.; Mazzeo, N. The structuring role of free-floating plants on the fish community in a tropical shallow lake: An experimental approach with natural and artificial plants. Hydrobiologia 2016, 778, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirós, R. Fish effects on trophic relationships in the pelagic zone of lakes. Hydrobiologia 1997, 361, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinistro, R. Top-down and bottom-up regulation of planktonic communities in a warm temperate wetland. J. Plankton Res. 2010, 32, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderstukken, M.; Mazzeo, N.; Van Colen, W.; Declerck, S.A.; Muylaert, K. Biological control of phytoplankton by the subtropical submerged macrophytes Egeria densa and Potamogeton illinoensis: A mesocosm study. Freshw. Biol. 2011, 56, 1837–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Liu, Z.; He, H.; Zhen, W.; Guan, B.; Chen, F.; Li, K.; Zhong, P.; Teixeira de Mello, F.; Jeppesen, E. Submerged macrophytes facilitate dominance of omnivorous fish in a subtropical shallow lake: Implications for lake restoration. Hydrobiologia 2016, 775, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, C.A.; Moura, A.N. Effects of the manipulation of submerged macrophytes, large zooplankton, and nutrients on a cyanobacterial bloom: A mesocosm study in a tropical shallow reservoir. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunkel, G.; Casallas, J. Limnology of an equatorial high mountain lake—Lago San Pablo, Ecuador: The significance of deep diurnal mixing for lake productivity. Limnologica 2002, 32, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Colen, W.; Portilla, K.; Oña, T.; Wyseure, G.; Goethals, P.; Velarde, E.; Muylaert, K. Limnology of the neotropical high elevation shallow lake Yahuarcocha (Ecuador) and challenges for managing eutrophication using biomanipulation. Limnologica 2017, 67, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; Hosper, S.H.; Meijer, M.L.; Moss, B.; Jeppesen, E. Alternative equilibria in shallow lakes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1993, 8, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setubal, R.B.; Riccardi, N. Long-term effects of fish biomanipulation and macrophyte management on zooplankton functional diversity and production in a temperate shallow lake. Limnology 2020, 21, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, G.D.; Welch, E.B.; Peterson, S.; Nichols, S.A. Restoration and Management of Lakes and Reservoirs; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hilt, S.; Gross, E.M.; Hupfer, M.; Morscheid, H.; Mählmann, J.; Melzer, A.; Poltz, J.; Sandrock, S.; Scharf, E.M.; Schneider, S.; et al. Restoration of submerged vegetation in shallow eutrophic lakes–A guideline and state of the art in Germany. Limnologica 2006, 36, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Lodge, D.M. Effects of submersed macrophytes on ecosystem processes. Aquat. Bot. 1986, 26, 341–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, J.; Zhong, P.; Zhang, X.; Ning, J.; Larsen, S.E.; Chen, D.; Gao, Y.; He, H.; Jeppesen, E. Successful restoration of a tropical shallow eutrophic lake: Strong bottom-up but weak top-down effects recorded. Water Res. 2018, 146, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussner, A. Alien aquatic plant species in European countries. Weed Res. 2012, 52, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Rodríguez, C.A.; Sarma, S.S.S.; Nandini, S. Effect of the allelochemicals from the macrophyte Egeria densa on the competitive interactions of pelagic and littoral cladocerans. Chem. Ecol. 2017, 33, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.B.; Gao, Y.N.; Wang, J.; Liu, B.Y.; Zhou, Q.H.; Zhang, Y.Y. Allelopathic effects of phenolic compounds present in submerged macrophytes on Microcystis aeruginosa. Allelopath. J. 2009, 23, 403–410. [Google Scholar]
- Patton, C.J.; Kryskalla, J.R. Methods of Analysis by the US Geological Survey National Water Quality Laboratory: Evaluation of Alkaline Persulfate Digestion as an Alternative to Kjeldahl Digestion for Determination of Total and DISSOLVED Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Water; No. 4174; US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Denver, CO, USA, 2003; Volume 3.
- Wang, H.; Zhong, G.; Yan, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C. Growth control of cyanobacteria by three submerged macrophytes. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2012, 29, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, S.; Hosomi, M.; Okada, M.; Murakami, A. Control of algal growth by macrophytes and macrophyte-extracted bioactive compounds. Water Sci. Technol. 1996, 34, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erhard, D.; Gross, E.M. Allelopathic activity of Elodea canadensis and Elodea nuttallii against epiphytes and phytoplankton. Aquat. Bot. 2006, 85, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzeo, N.; Rodríguez-Gallego, L.; Kruk, C.; Meerhoff, M.; Gorga, J.; Lacerot, G.; Quintans, F.; Loureiro, M.; Larrea, D.; García-Rodríguez, F. Effects of Egeria densa Planch. beds on a shallow lake without piscivorous fish. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mony, C.; Koschnick, T.J.; Haller, W.T.; Muller, S. Competition between two invasive Hydrocharitaceae (Hydrilla verticillata (Lf)(Royle) and Egeria densa (Planch)) as influenced by sediment fertility and season. Aquat. Bot. 2007, 86, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Z.A. Macrophytes-cyanobacteria allelopathic interactions and their implications for water resources management—A review. Limnologica 2017, 63, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senavirathna, M.D.H.J.; Muhetaer, G.; Atapaththu, K.S.S.; Fujino, T. Egeria densa allelopathy on microcystis aeruginosa under different light intensities and preliminary insight into inter-parameter relationships. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Hong, Y. Algal-bloom control by allelopathy of aquatic macrophytes—A review. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2008, 2, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergalli, J.; Fayolle, S.; Combes, A.; Franquet, E.; Comte, K. Persistence of microcystin production by Planktothrix agardhii (Cyanobacteria) exposed to different salinities. Phycologia 2020, 59, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulderij, G.; Van Nes, E.H.; Van Donk, E. Macrophyte–phytoplankton interactions: The relative importance of allelopathy versus other factors. Ecol. Model. 2007, 204, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brönmark, C.; Weisner, S.E. Indirect effects of fish community structure on submerged vegetation in shallow, eutrophic lakes: An alternative mechanism. In The Dynamics and Use of Lacustrine Ecosystems; Springer: Dordrecht, The Nertherlands, 1992; pp. 293–301. [Google Scholar]
- Lampert, W. Laboratory studies on zooplankton-cyanobacteria interactions. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1987, 21, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrão-Filho, A.S.; Pereira, U.J.; Vilar, M.C.; de Magalhães, L.; Marinho, M.M. Can small-bodied Daphnia control Raphidiopsis raciborskii in eutrophic tropical lakes? A mesocosm experiment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 35459–35473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dussault, G.V.; Kramer, D.L. Food and feeding behavior of the guppy, Poecilia reticulata (Pisces: Poeciliidae). Can. J. Zool. 1981, 59, 684–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfield, D.E., Jr.; Shireman, J.V.; Colle, D.E.; Haller, W.T.; Watkins II, C.E.; Maceina, M.J. Prediction of chlorophyll a concentrations in Florida lakes: Importance of aquatic macrophytes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1984, 41, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, J.P.; Aznarez, C.; Meerhoff, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Baattrup-Pedersen, A.; Yu, C.; Jeppesen, E. Small-sized omnivorous fish induce stronger effects on food webs than warming and eutrophication in experimental shallow lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 148998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira de Mello, F.; Meerhoff, M.; Pekcan-Hekim, Z.; Jeppesen, E. Substantial differences in littoral fish community structure and dynamics in subtropical and temperate shallow lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 1202–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burks, R.L.; Lodge, D.M.; Jeppesen, E.; Lauridsen, T.L. Diel horizontal migration of zooplankton: Costs and benefits of inhabiting the littoral. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 343–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petry, A.C.; Guimarães, T.F.R.; Vasconcellos, F.M.; Hartz, S.M.; Becker, F.G.; Rosa, R.S.; Goyenola, G.; Caramaschi, E.P.; de Astarloa, J.M.D.; Sarmento-Soares, L.M.; et al. Fish composition and species richness in eastern South American coastal lagoons: Additional support for the freshwater ecoregions of the world. J. Fish Biol. 2016, 89, 280–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerhoff, M.; Mazzeo, N.; Moss, B.; Rodríguez-Gallego, L. The structuring role of free-floating versus submerged plants in a subtropical shallow lake. Aquat. Ecol. 2003, 37, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seghers, B.H. Schooling behavior in the guppy (Poecilia reticulata): An evolutionary response to predation. Evolution 1974, 28, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Araújo, F.G.; Peixoto, M.G.; Pinto, B.C.T.; Teixeira, T.P. Distribution of guppies Poecilia reticulata (Peters, 1860) and Phalloceros caudimaculatus (Hensel, 1868) along a polluted stretch of the Paraíba do Sul River, Brazil. Braz. J. Biol. 2009, 69, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilt, S.; Elisabeth Gross, M. Can allelopathically active submerged macrophytes stabilize clear-water states in shallow lakes? Basic Appl. Ecol. 2008, 9, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Treatments | Variables | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phytoplankton Biomass | Planktothrix Density | Planktothrix Size | Nutrients (NP) | Daphnia Density | |
| C | + | + | + | + | − |
| 15% | + | + | + | + | − |
| 35% | + | + | + | + | − |
| 45% | + | + | + | + | − |
| C | + | + | − | + | + |
| Z | + | + | − | + | + |
| F | + | + | − | + | + |
| ZF | + | + | − | + | + |
| EZ | + | + | − | + | + |
| EZF | + | + | − | + | + |
| | | Experiment I | Experiment II | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| df | F | P | df | F | P | |
| Chlorophyll a | 4 | 106.6 | <0.001 | 6 | 23.67 | <0.001 |
| Planktothrix density | 4 | 47.94 | <0.001 | 6 | 34.15 | <0.001 |
| Planktothrix size | 4 | 18.07 | <0.001 | - | - | - |
| TN | 4 | 1.32 | 0.333 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.25 |
| TP | 4 | 0.75 | 0.575 | 6 | 0.77 | 0.6 |
| Daphnia density | - | - | - | 4 | 45.91 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Portilla, K.; Velarde, E.; Decaestecker, E.; Teixeira de Mello, F.; Muylaert, K. Potential Submerged Macrophytes to Mitigate Eutrophication in a High-Elevation Tropical Shallow Lake—A Mesocosm Experiment in the Andes. Water 2023, 15, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15010075
Portilla K, Velarde E, Decaestecker E, Teixeira de Mello F, Muylaert K. Potential Submerged Macrophytes to Mitigate Eutrophication in a High-Elevation Tropical Shallow Lake—A Mesocosm Experiment in the Andes. Water. 2023; 15(1):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15010075
Chicago/Turabian StylePortilla, Karen, Elizabeth Velarde, Ellen Decaestecker, Franco Teixeira de Mello, and Koenraad Muylaert. 2023. "Potential Submerged Macrophytes to Mitigate Eutrophication in a High-Elevation Tropical Shallow Lake—A Mesocosm Experiment in the Andes" Water 15, no. 1: 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15010075
APA StylePortilla, K., Velarde, E., Decaestecker, E., Teixeira de Mello, F., & Muylaert, K. (2023). Potential Submerged Macrophytes to Mitigate Eutrophication in a High-Elevation Tropical Shallow Lake—A Mesocosm Experiment in the Andes. Water, 15(1), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15010075








