Sediment Source Fingerprinting and Its Control Strategies of the Lakes in Jiuzhaigou World Natural Heritage Site
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
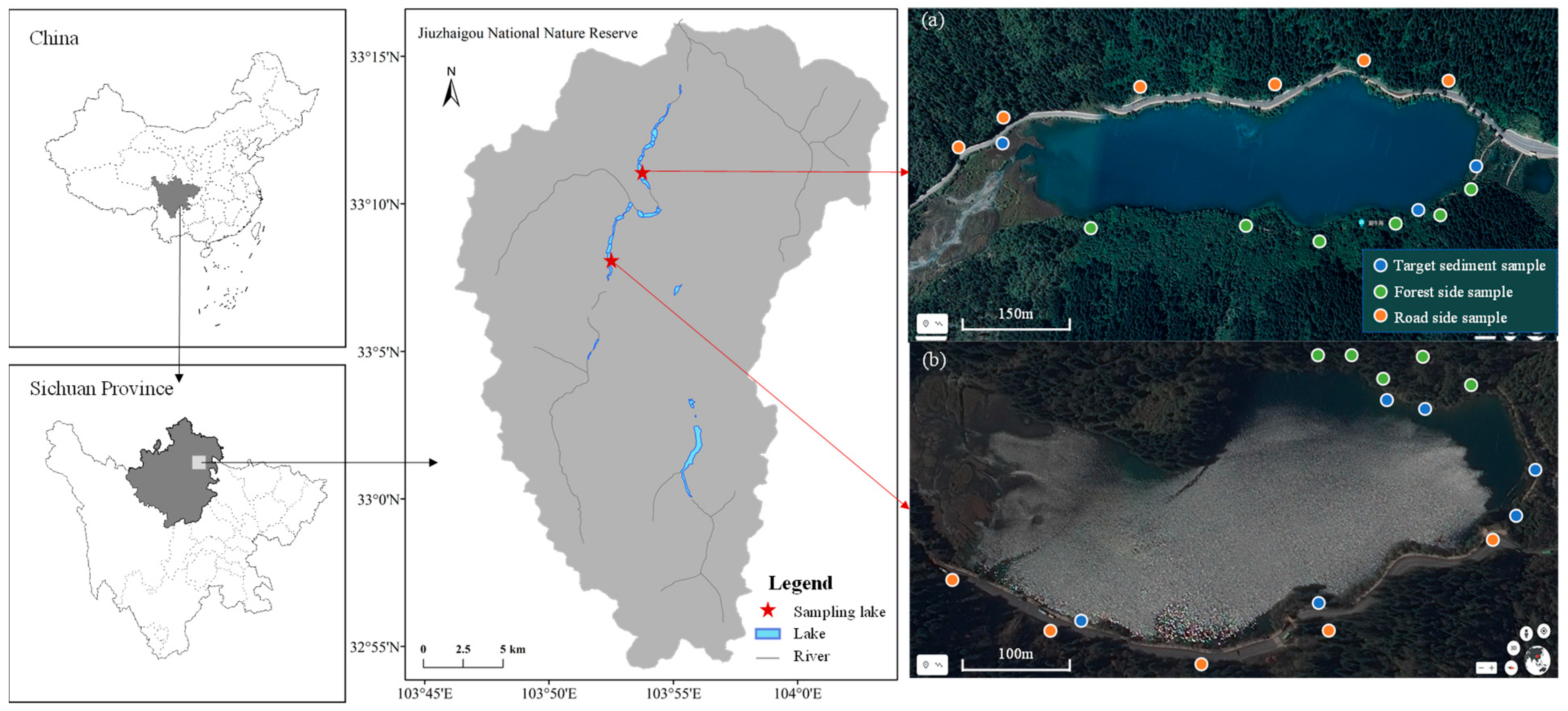
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Laboratory Analysis
2.2.1. Sampling
2.2.2. Laboratory Analysis
2.2.3. Acquisition and Processing of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Images
2.3. Sediment Fingerprinting Analysis
2.3.1. Selection of the Optimum Composite Fingerprints
2.3.2. Multivariate Mixed Model of Compound Fingerprint Recognition Technology
2.3.3. Reliability Test of Sediment Source Discrimination
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Identification and Screening of Fingerprint Factors of Lake Sediment Sources
3.2. The Best Combination of Fingerprint Factors for Lake Sediment Sources
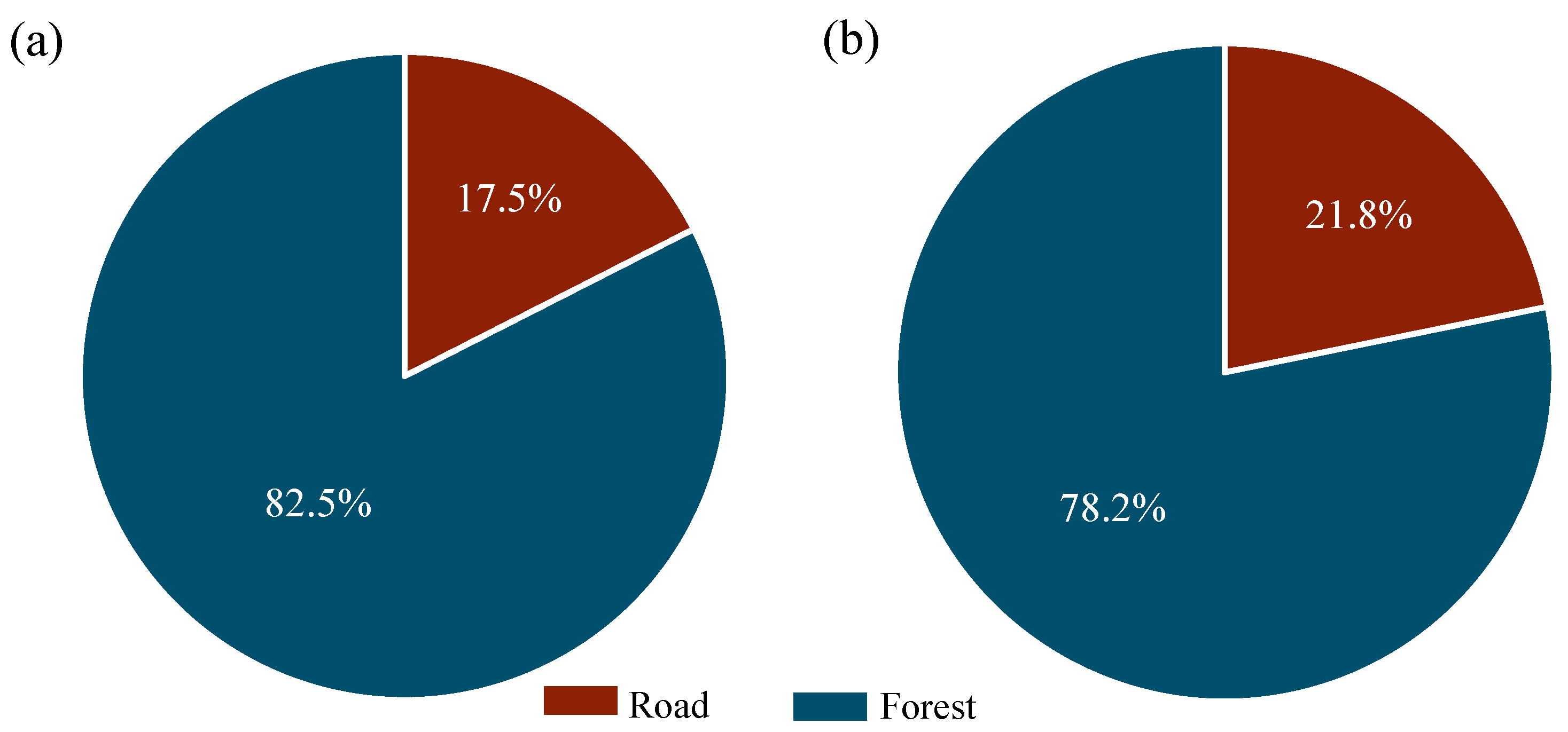
3.3. Sediment Contribution and Reliability of Lake Sediment Sources
3.4. Measures and Countermeasures for Alleviating Sedimentation in Jiuzhaigou Lakes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, K.R.; Venter, O.; Fuller, R.A.; Allan, J.R.; Maxwell, S.L.; Negret, P.J.; Watson, J.E.M. One-third of global protected land is under intense human pressure. Science 2018, 360, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Pan, Y.; Cao, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, Q.; Wang, B.; Pang, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Deng, G. Detecting early signs of envi-ronmental degradation in protected areas: An example of Jiuzhaigou Nature Reserve, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 91, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Hu, X.; Li, S.; Huang, C.; Tang, Y. Anthropogenic effect on deposition dynamics of lake sediments based on 137Cs and 210Pbex techniques in Jiuzhaigou National Nature Reserve, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Deng, G.; Wang, L.; Cao, Y.; Pang, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, B.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Xu, R. Effects of in situ phosphorus enrichment on the benthos in a subalpine karst stream and implications for bioassessment in nature reserves. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 73, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, B.W.; Xu, J.X.; Cao, Y.; Deng, G.P.; Pang, W.T.; Wang, Q.X. Phytoplankton community structure and ecological evaluation in summer, Lake Changhai of Jiuzhaigou National Nature Reserve. J. Lake Sci. 2020, 32, 1088–1099, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Du, J.; Tang, Y.; Qiao, X.; Bossard, C.; Deng, G. Challenges for sustainable tourism at the Jiuzhaigou World Natural Heritage site in western China. Nat. Resour. Forum 2013, 37, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.S.; Huang, C.; Yi, S.J.; Wu, C.H. Study on seismic fault and source rupture tectonic dynamic mechanism of Jiuzhaigou MS7. 0 earthquake. J. Eng. Geol. 2017, 25, 1141–1150, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, K.; Zhan, Y.; Issaak, P.; Du, J.; Di, B.F. Detecting surface deformation and calculating colluvial materials: The case of the 2017 Jiuzhaigou earthquake. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2019, 28, 184–191, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Klages, M.G.; Hsieh, Y.P. Suspended Solids Carried by the Gallatin River of Southwestern Montana: II. Using Mineralogy for Inferring Sources. J. Environ. Qual. 1975, 4, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, G.J.; Wilding, L.P. Mineralogy and Related Parameters of Fluvial Suspended Sediments in Northwestern Ohio. J. Environ. Qual. 1976, 5, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E.; Peart, M.R.; Oldfield, F.; Thompson, R. Suspended sediment sources identified by magnetic measurements. Nature 1979, 281, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E.; Owens, P.; Leeks, G.J.L. Fingerprinting suspended sediment sources in the catchment of the River Ouse, Yorkshire, UK. Hydrol. Process. 1999, 13, 955–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E.; Woodward, J.C. Use of a field-based water elutriation system for monitoring the in-situ particle-size charac-teristics of fluvial suspended sediment. Water Res. 1993, 27, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peart, M.R.; Walling, D.E. Fingerprinting sediment source: The example of a drainage basin in Devon, UK. In Proceedings of the Drainage Basin Sediment Delivery, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 4–8 August 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Laceby, J.P.; Evrard, O.; Smith, H.G.; Blake, W.H.; Olley, J.M.; Minella, J.P.; Owens, P.N. The challenges and opportunities of addressing particle size effects in sediment source fingerprinting: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 169, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walden, J.; Slattery, M.C.; Burt, T.P. Use of mineral magnetic measurements to fingerprint suspended sediment sources: Ap-proaches and techniques for data analysis. J. Hydrol. 1997, 202, 353–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Carreras, N.; Udelhoven, T.; Krein, A.; Gallart, F.; Iffly, J.F.; Ziebel, J.; Hoffmann, L.; Pfister, L.; Walling, D.E. The use of sediment colour measured by diffuse reflectance spectrometry to determine sediment sources: Application to the Attert River catchment (Luxembourg). J. Hydrol. 2010, 382, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.F.; Papanicolaou, A.N. The Use of Carbon and Nitrogen Isotopes to Study Watershed Erosion Processes. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2007, 43, 1047–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosrati, K.; Govers, G.; Ahmadi, H.; Sharifi, F.; Amoozegar, M.A.; Merckx, R.; Vanmaercke, M. An exploratory study on the use of enzyme activities as sediment tracers: Biochemical fingerprints? Int. J. Sediment Res. 2011, 26, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koiter, A.J.; Owens, P.N.; Petticrew, E.L.; Lobb, D.A. The behavioural characteristics of sediment properties and their implications for sediment fingerprinting as an approach for identifying sediment sources in river basins. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2013, 125, 24–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evrard, O.; Poulenard, J.; Nemery, J.; Ayrault, S.; Gratiot, N.; Duvert, C.; Prat, C.; Lefèvre, I.; Philippe Bonté, P.; Esteves, M. Tracing sediment sources in a tropical highland catchment of central Mexico by using conventional and alternative finger-printing methods. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroese, J.S.; Batista, P.V.G.; Jacobs, S.R.; Breuer, L.; Quinton, J.N.; Rufino, M.C. Agricultural land is the main source of stream sediments after conversion of an African montane forest. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmady-Birgani, H.; Agahi, E.; Ahmadi, S.J.; Erfanian, M. Sediment Source Fingerprinting of the Lake Urmia Sand Dunes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Voli, M.T.; Wegmann, K.W.; Bohnenstiehl, D.R.; Leithold, E.; Osburn, C.L.; Polyakov, V. Fingerprinting the sources of sus-pended sediment delivery to a large municipal drinking water reservoir: Falls Lake, Neuse River, North Carolina, USA. J. Soils Sediments 2013, 13, 1692–1707. [Google Scholar]
- Fatahi, A.; Gholami, H.; Esmaeilpour, Y.; Fathabadi, A. Fingerprinting the spatial sources of fine-grained sediment deposited in the bed of the Mehran River, southern Iran. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; You, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, J. Case study on debris-flow hazard mitigation at a world natural heritage site, Jiuzhaigou Valley, Western China. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2020, 11, 1782–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.P. Study of Tourism Geosciences Landscape Formation and Protection of Jiuzhaigou World Natural Heritage Site. Ph.D. Thesis, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, China, 2011. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, Y.B.; Xu, R.L.; Yang, R.; Xu, X.Q. A discussion of sustainable development of tourism in Jiuzhaigou World Heritage Site. World Nat. Cult. Herit. 2012, 1, 78–81, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Klorvuttimontara, S.; McClean, C.J.; Hill, J.K. Evaluating the effectiveness of Protected Areas for conserving tropical forest butterflies of Thailand. Biol. Conserv. 2011, 144, 2534–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X. Study on the Response of Jiuzhaigou to Regional Air Pollution. Ph.D. Thesis, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China, 2012. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cai, C. Jiuzhaigou Nature Protection Area Forest Self-Control Water Source Economic Value Research. Master’s Thesis, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu, China, 2007; p. 58, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.Y.; Zhang, X.P.; Zeng, Z.Y. Biodiversity of Jiuzhaigou Nature Reserve; Sichuan Science and Technology Press: Chengdu, China, 2007; (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.T.; Chong, C.X.; Tang, B.X.; Liu, S.Q.; Liu, S.J. Basic characteristics, formation and evolution of Jiuzhaigou landform. Geography 1989, 2, 1–12, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.X. Tne formation and development of travertine landscape in natural scenery of northwest Sichuan. Mt. Res. 1988, 6, 54–60, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J. On bio-effects on the development of karst dammed lakes in limestone areas, minshan mountain range, NW Sichuan. J. Lake Sci. 1993, 5, 32–39, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yan, C.H.; Wang, B.; Zou, Z.D.; Yu, L.Y.; Huang, W.B.; Qiu, G.Y. Characteristics of nighttime sap flow and its partition in a mixed forest in Jiuzhaigou valley. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2020, 56, 732–738, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.Y.; Wan, X.N.; Fan, X.; Guo, J.Q.; Gu, J.R. Adynamic analog of water environmental system in Jiuzhaigou valley. Acta Geol. Sichuan 2002, 22, 16–20, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Seyler, B.C.; Di, B.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Y. Impact of earthquakes on natural area-driven tourism: Case study of China’s Jiuzhaigou National Scenic Spot. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 58, 102216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossard, C.C.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Rose, A.; Tang, Y. New patterns of establishment and growth of Picea, Abies and Betula tree species in subalpine forest gaps of Jiuzhaigou National Nature Reserve, Sichuan, southwestern China in a changing environment. For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 356, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.C.H.; Li, R.L.; Du, J.; Jiang, B.Q.; Shi, C.; Mao, P.; Qiu, G.Y.; Shen, X.X. Assessment of the current situation of lake siltation and swamping in the Jiuzhaigou World Natural Heritage Site after the earthquake. J. Lake Sci. 2021, 33, 1832–1843, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Collins, A.; Walling, D.; Leeks, G. Source type ascription for fluvial suspended sediment based on a quantitative composite fingerprinting technique. Catena 1997, 29, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poleto, C.; Merten, G.H.; Minella, J.P. The identification of sediment sources in a small urban watershed in southern Brazil: An application of sediment fingerprinting. Environ. Technol. 2009, 30, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.Y. Study on Sediment Sources in Small Catchments on the Loess Plateau Using Composite Fingerprinting. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwest University of Agriculture and Forestry Science and Technology, Yangling, China, 2017; p. 119, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Collins, A.L.; Zhang, Y.; Walling, D.E.; Grenfell, S.E.; Smith, P. Tracing sediment loss from eroding farm tracks using a ge-ochemical fingerprinting procedure combining local and genetic algorithm optimisation. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 5461–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Yang, Y.J.; Yu, Q.G.; Chen, C.; Li, B.; Luo, X.; Li, L.P.; Wang, J.X.; Ouyang, M. Analysis of sediment source of Shuanghe reservoir catchment using combined fingerprinting technique. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 40, 142–148, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Mi, Y. The Research of the Relationship of the Soil Erosion and Sediment Source of Dashiba Reservoir Basin in Yunnan. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing, China, 2015; p. 63, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, M.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y. Fingerprinting sediment sources in the water-wind erosion crisscross region on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Geoderma 2018, 337, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.L.; Blackwell, M.; Boeckx, P.; Chivers, C.-A.; Emelko, M.; Evrard, O.; Foster, I.; Gellis, A.; Gholami, H.; Granger, S.; et al. Sediment source fingerprinting: Benchmarking recent outputs, remaining challenges and emerging themes. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 4160–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laceby, J.P.; Olley, J. An examination of geochemical modelling approaches to tracing sediment sources incorporating distri-bution mixing and elemental correlations. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 1669–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wen, A.B.; Yan, D.C.; Shi, Z.L. Quantifying catchment scale sediment source using composite fingerprinting technique. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 94–104, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Niethammer, U.; James, M.; Rothmund, S.; Travelletti, J.; Joswig, M. UAV-based remote sensing of the Super-Sauze landslide: Evaluation and results. Eng. Geol. 2012, 128, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Q.; Cui, P.; Tang, B.X.; Liu, S.Q. Civil engineering techniques for debris flow control in national parks. Chin. J. Geol. Hazard Control 2006, 2, 79–84, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Blake, W.H.; Wallbrink, P.J.; Doerr, S.H.; Shakesby, R.A.; Humphreys, G.S.; English, P.; Wilkinson, S. Using geochemical stratigraphy to indicate post-fire sediment and nutrient fluxes into a water supply reservoir, Sydney, Australia. IAHS Publi. 2006, 306, 363–370. [Google Scholar]

| Arrow Bamboo Lake | Rhino Lake | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latent Fingerprint Factor | H-Value | p-Value | H-Value | p-Value |
| TP | 1.159 | 0.560 | 4.593 | 0.101 |
| Water Content | 1.734 | 0.420 | 4.543 | 0.103 |
| pH | 0.189 | 0.910 | 6.055 | 0.048 * |
| Salt Content | 0.052 | 0.974 | 2.072 | 0.355 |
| C% | 1.922 | 0.382 | 6.802 | 0.033 * |
| N% | 0.228 | 0.892 | 4.692 | 0.096 |
| Clay% | 0.193 | 0.908 | 4.308 | 0.116 |
| Silt% | 1.699 | 0.428 | 6.352 | 0.042 * |
| Sand% | 1.42 | 0.491 | 4.945 | 0.084 |
| Ti | 0.735 | 0.692 | 4.308 | 0.116 |
| Cr | 4.412 | 0.110 | 4.857 | 0.088 |
| Co | 0.934 | 0.627 | 4.692 | 0.096 |
| Ni | 2.369 | 0.306 | 5.736 | 0.057 |
| Cu | 0.171 | 0.918 | 6.407 | 0.041 * |
| Zn | 2.946 | 0.229 | 6.879 | 0.032 * |
| Sr | 2.929 | 0.231 | 6.879 | 0.032 * |
| Cd | 10.816 | 0.004 * | 4.209 | 0.122 |
| Sn | 8.722 | 0.013 * | 4.308 | 0.116 |
| Sb | 7.729 | 0.021 * | 2.945 | 0.229 |
| Pb | 0.735 | 0.692 | 5.231 | 0.073 |
| Na | 8.782 | 0.012 * | 9.692 | 0.008 * |
| K | 11.016 | 0.004 * | 9.692 | 0.008 * |
| Mg | 3.400 | 0.183 | 9.308 | 0.010 * |
| Ca | 2.059 | 0.357 | 9.308 | 0.010 * |
| Al | 8.647 | 0.013 * | 9.692 | 0.008 * |
| Mn | 2.147 | 0.342 | 5.967 | 0.051 |
| Fe | 8.647 | 0.013 * | 9.308 | 0.010 * |
| Lake | Step | Fingerprints | Single Factor Discrimination Accuracy | Wilk’s Lambda | Cumulative Discrimination Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arrow Bamboo Lake | 1 | Cd | 62.5% | 0.603 | 62.5% |
| 2 | K | 81.3% | 0.176 | 88.9% | |
| Rhino Lake | 1 | K | 64.6% | 0.011 | 64.6% |
| 2 | Al | 71.3% | 0.016 | 75.9% | |
| 3 | Fe | 59.4% | 0.012 | 92.3% | |
| 4 | Na | 67.2% | 0.002 | 100% |
| Lake | Index | Sediment source | Predicted Group Membership | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forest | Road | ||||
| Arrow Bamboo Lake | Count | Forest | 4 | 0 | 4 |
| Road | 1 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Discrimination accuracy (%) | Forest | 100% | 0 | 100% | |
| Road | 20% | 80% | 100% | ||
| Rhino Lake | Count | Forest | 6 | 0 | 6 |
| Road | 0 | 6 | 6 | ||
| Discrimination accuracy (%) | Forest | 100% | 0 | 100% | |
| Road | 0 | 100% | 100% | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, X.; Li, R.; Du, J.; Jiang, X.; Qiu, G. Sediment Source Fingerprinting and Its Control Strategies of the Lakes in Jiuzhaigou World Natural Heritage Site. Water 2022, 14, 3954. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233954
Shen X, Li R, Du J, Jiang X, Qiu G. Sediment Source Fingerprinting and Its Control Strategies of the Lakes in Jiuzhaigou World Natural Heritage Site. Water. 2022; 14(23):3954. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233954
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Xiaoxue, Ruili Li, Jie Du, Xianchenghao Jiang, and Guoyu Qiu. 2022. "Sediment Source Fingerprinting and Its Control Strategies of the Lakes in Jiuzhaigou World Natural Heritage Site" Water 14, no. 23: 3954. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233954
APA StyleShen, X., Li, R., Du, J., Jiang, X., & Qiu, G. (2022). Sediment Source Fingerprinting and Its Control Strategies of the Lakes in Jiuzhaigou World Natural Heritage Site. Water, 14(23), 3954. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233954







