Shallow Water Bathymetry Mapping from ICESat-2 and Sentinel-2 Based on BP Neural Network Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Areas and Data
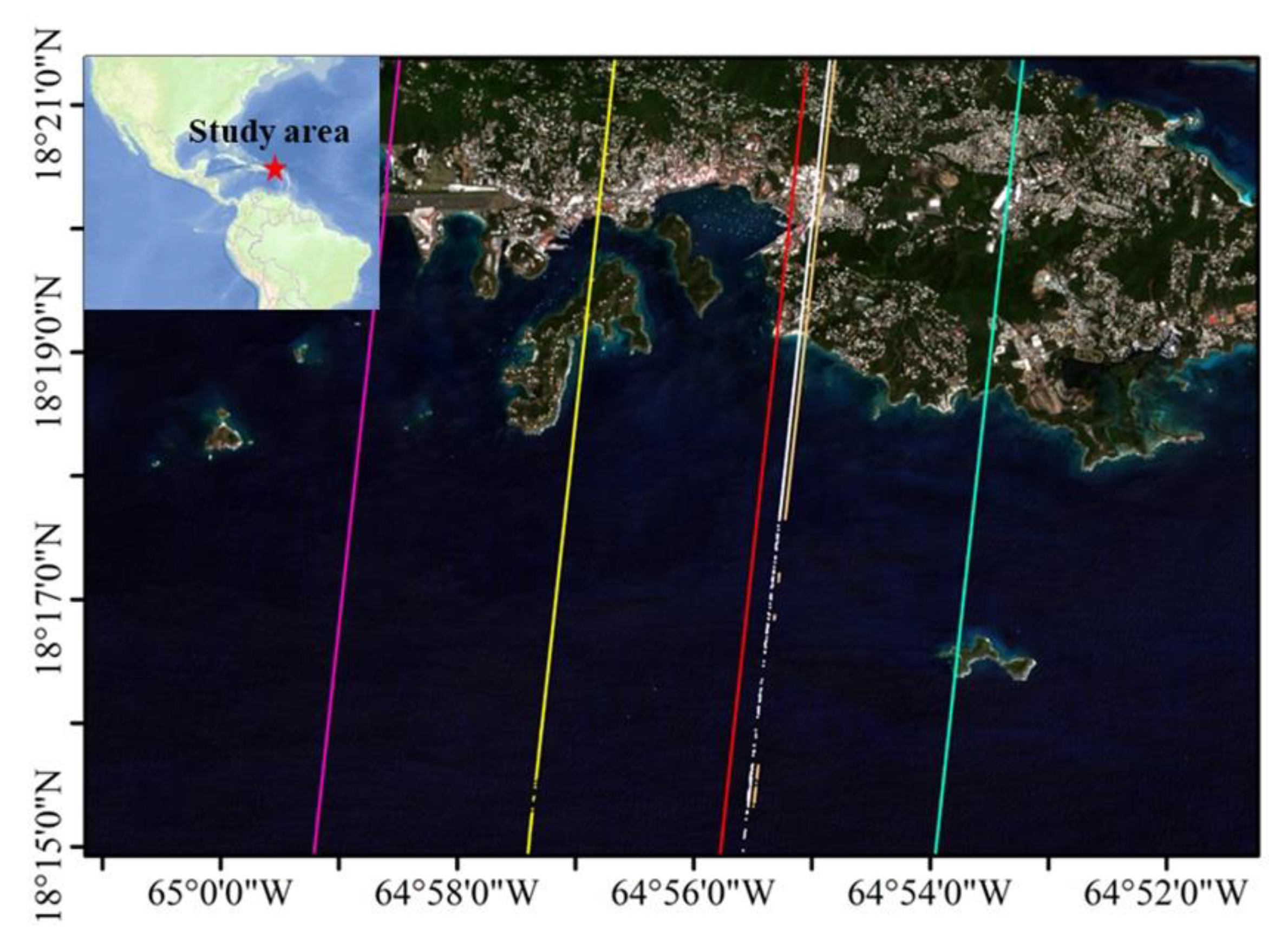
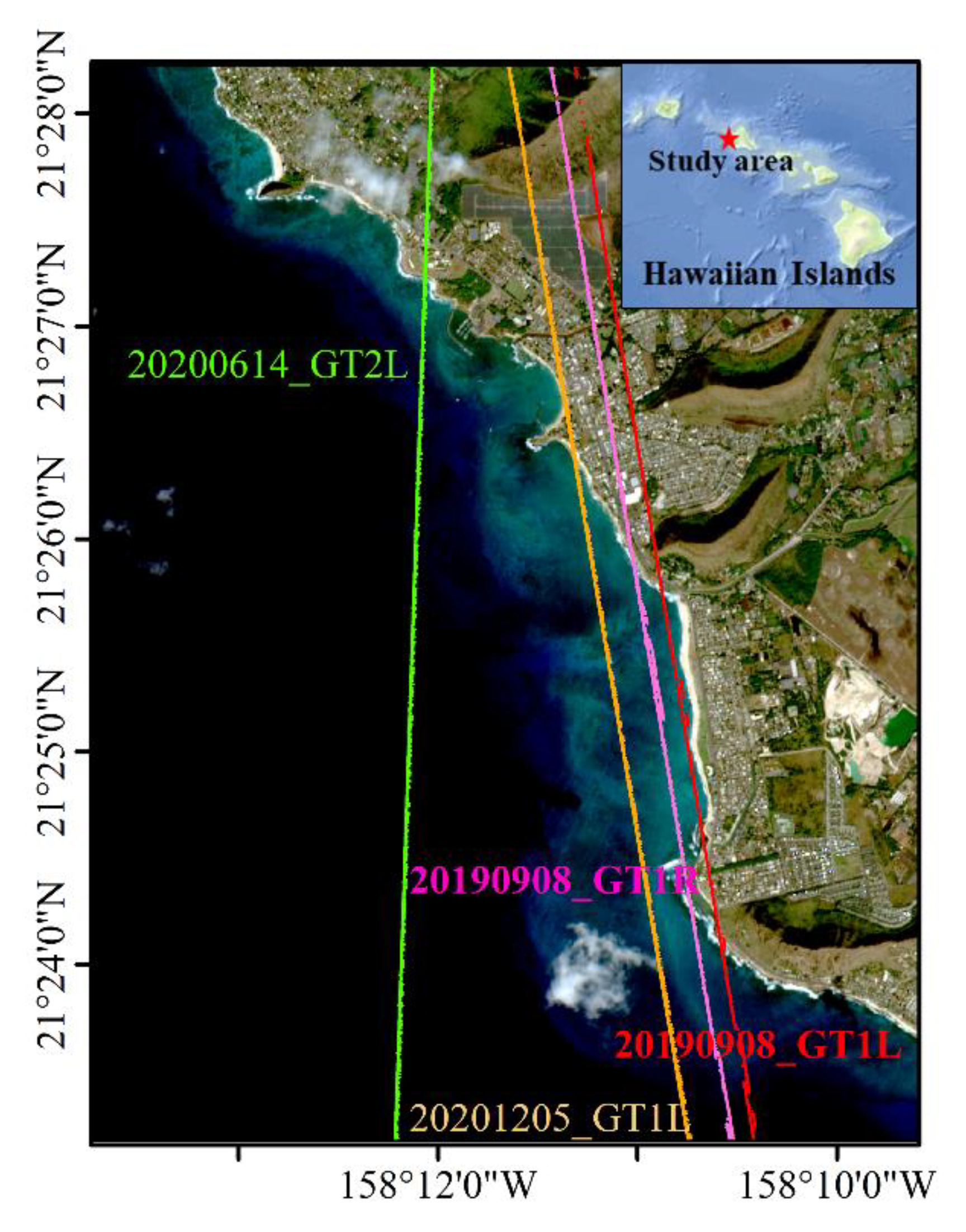
2.1.1. Study Areas and In-Situ Bathymetric Data
2.1.2. ICESat-2 Data
2.1.3. Sentinel-2 Satellite Image
2.2. Methods
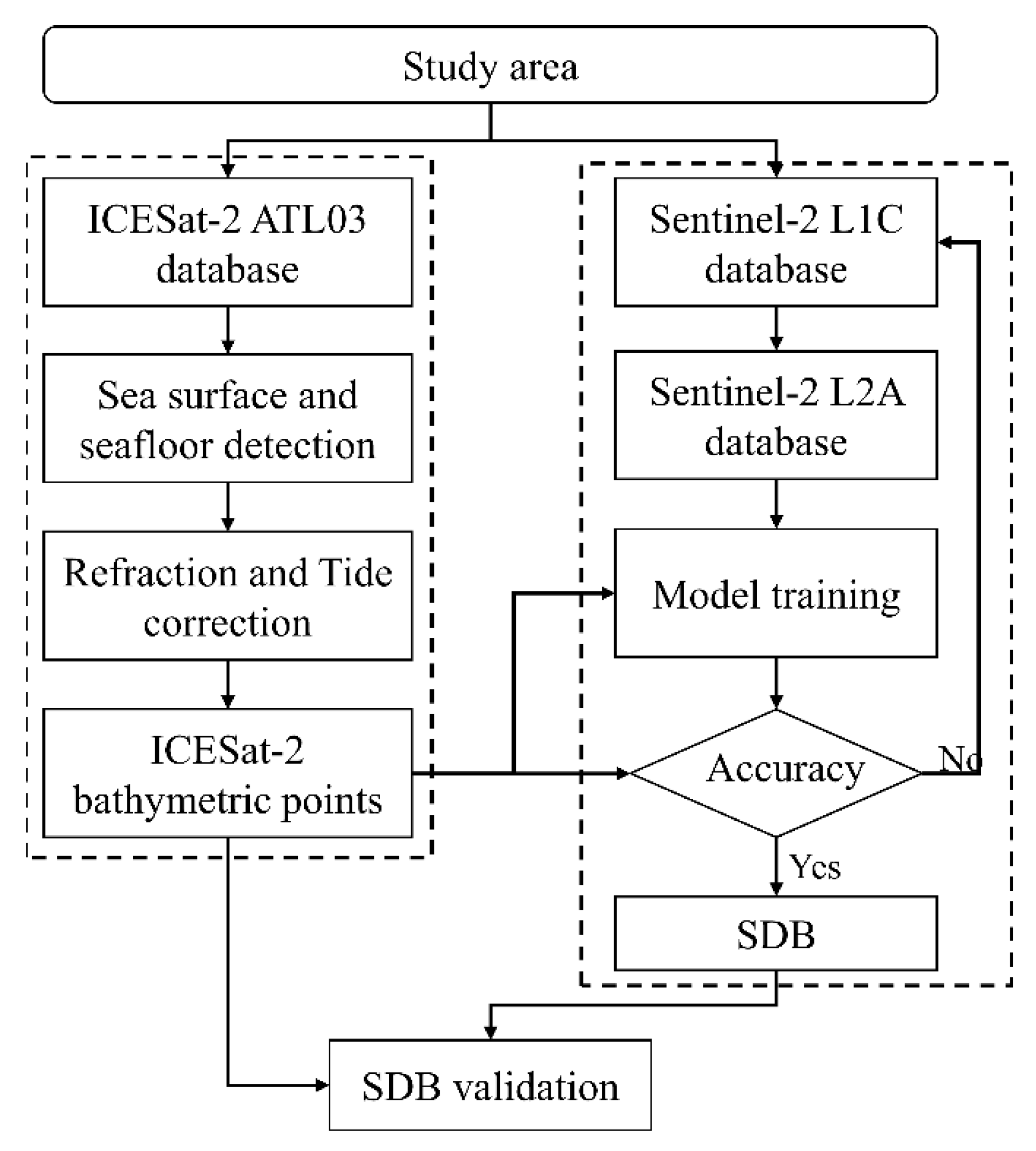
2.2.1. Shallow Water Bathymetry Mapping
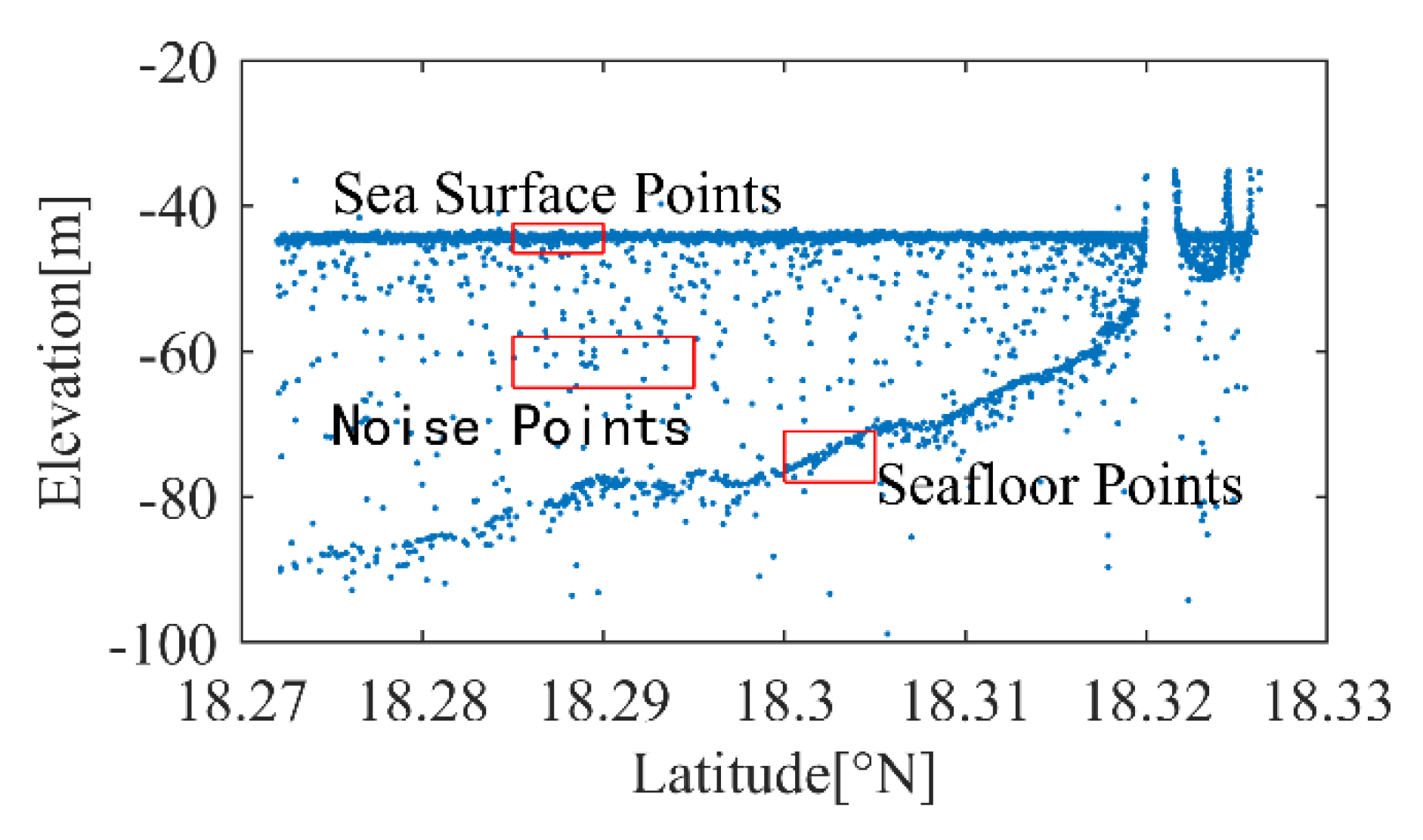
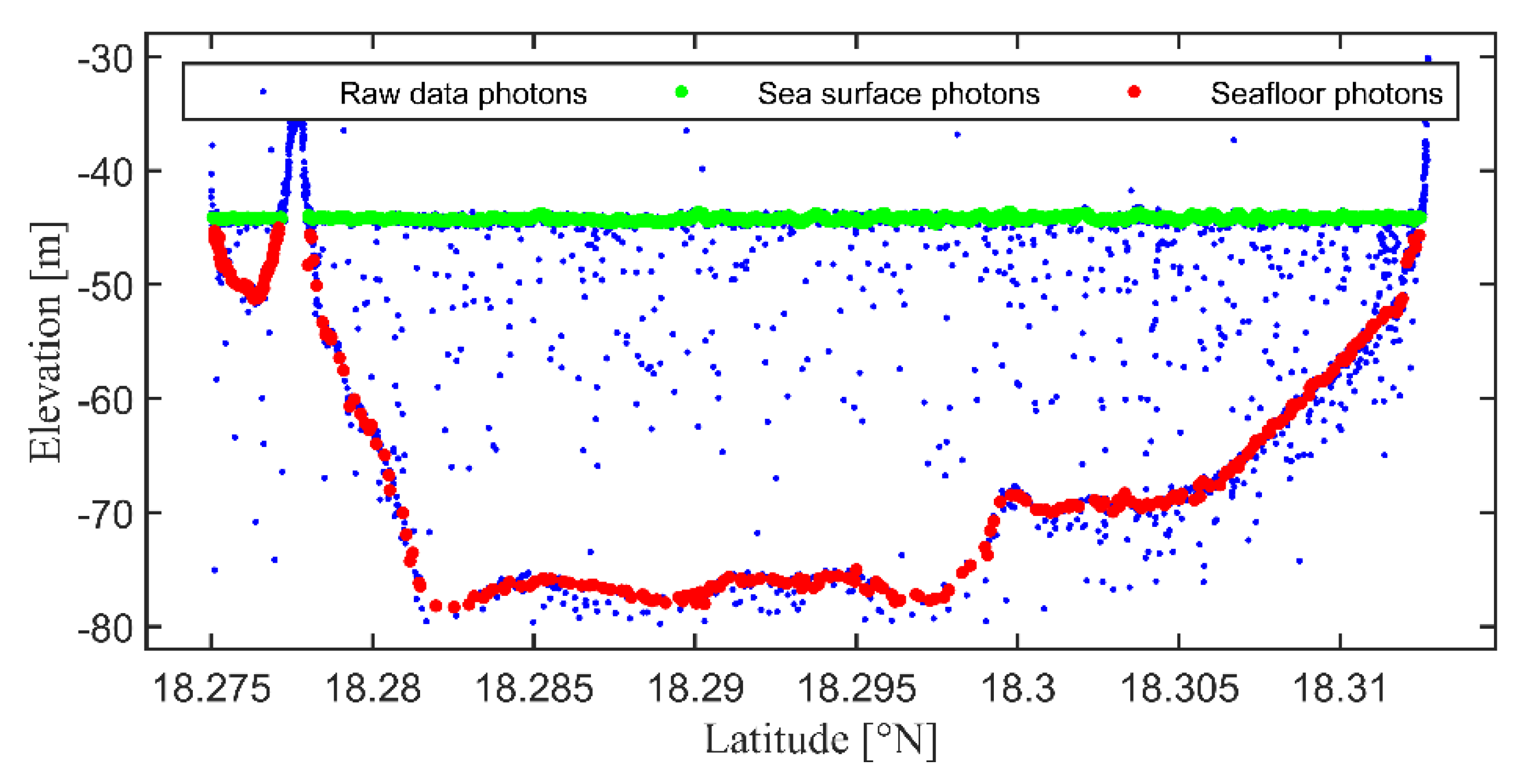
2.2.2. Detection of ICESat-2 Bathymetry Points
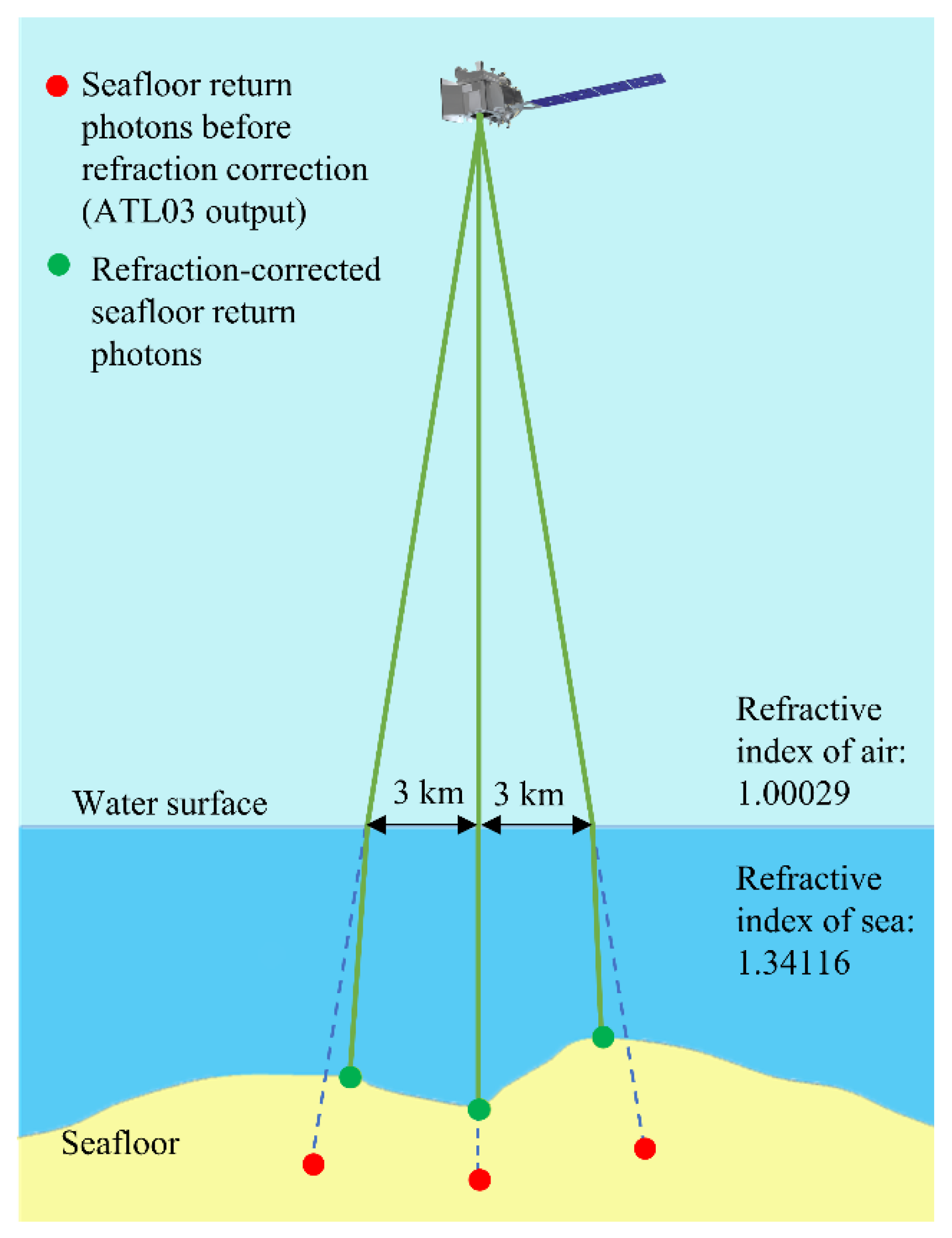
2.2.3. Refraction Correction
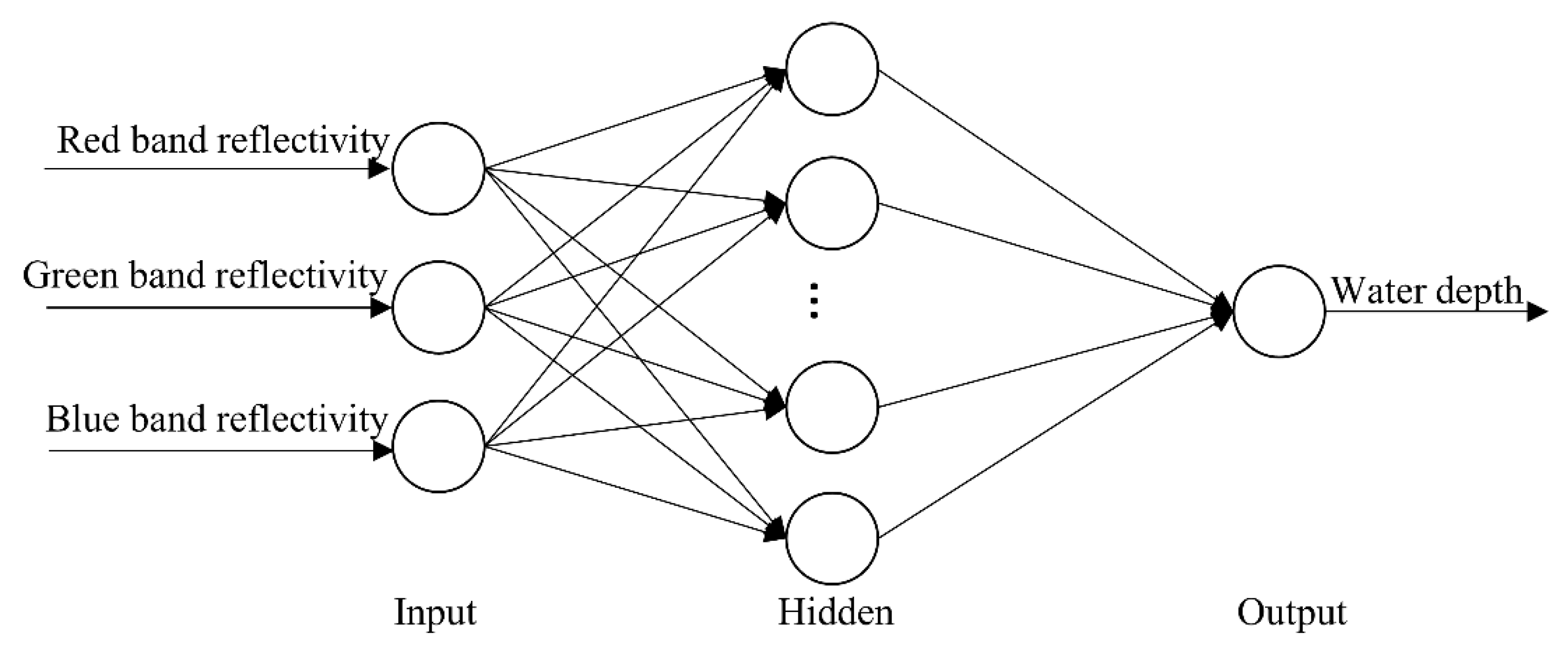
2.2.4. Satellite-Derived Bathymetry Based on BP Neural Network Model
3. Results and Analysis
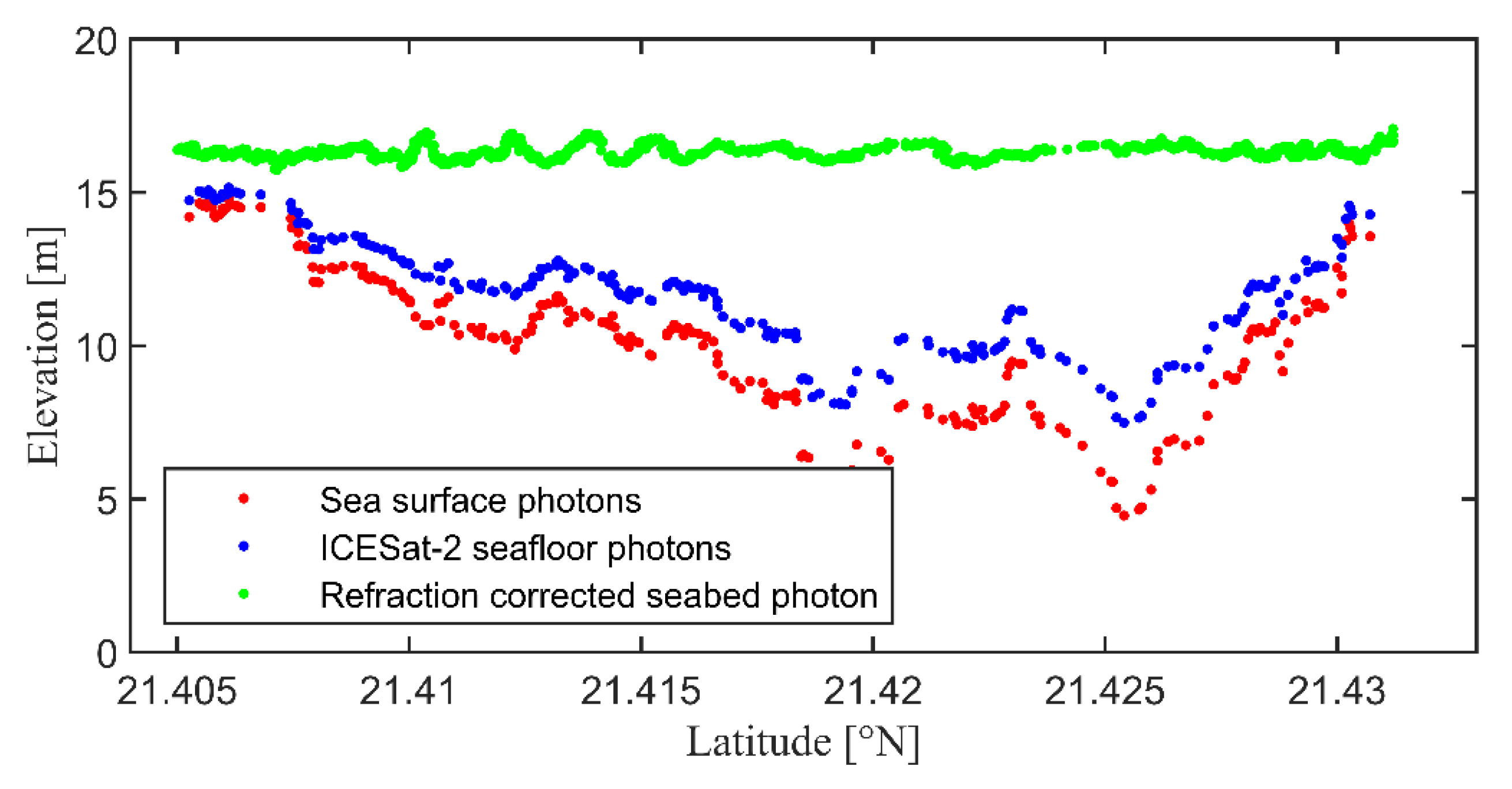
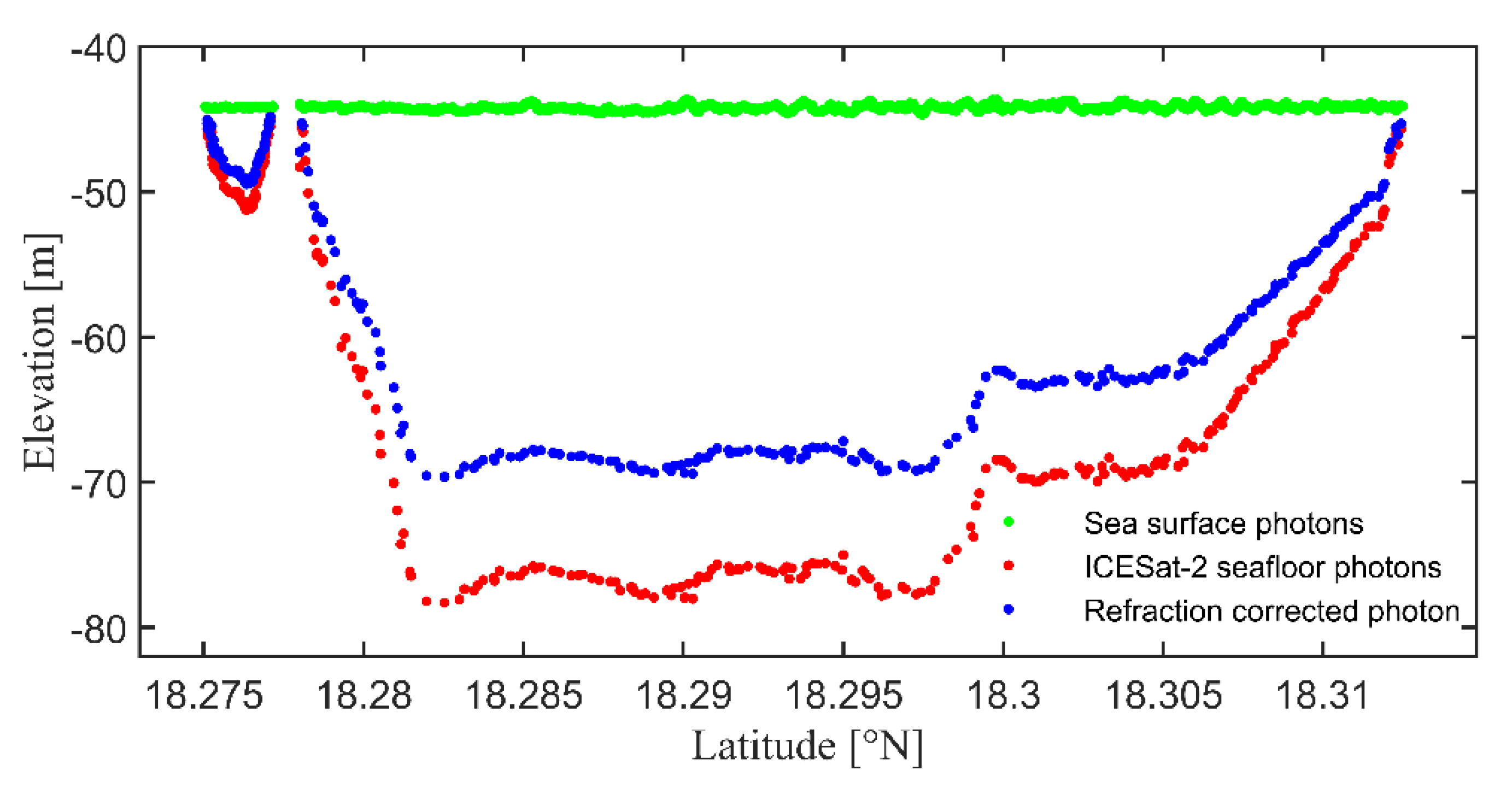
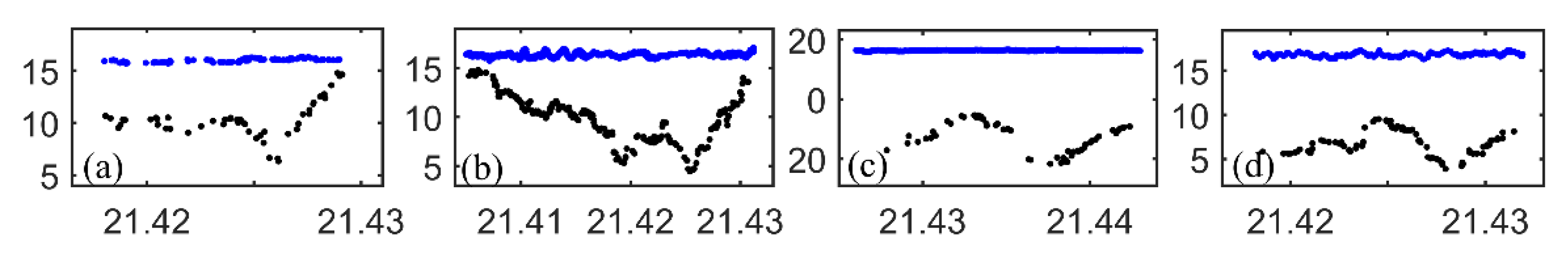
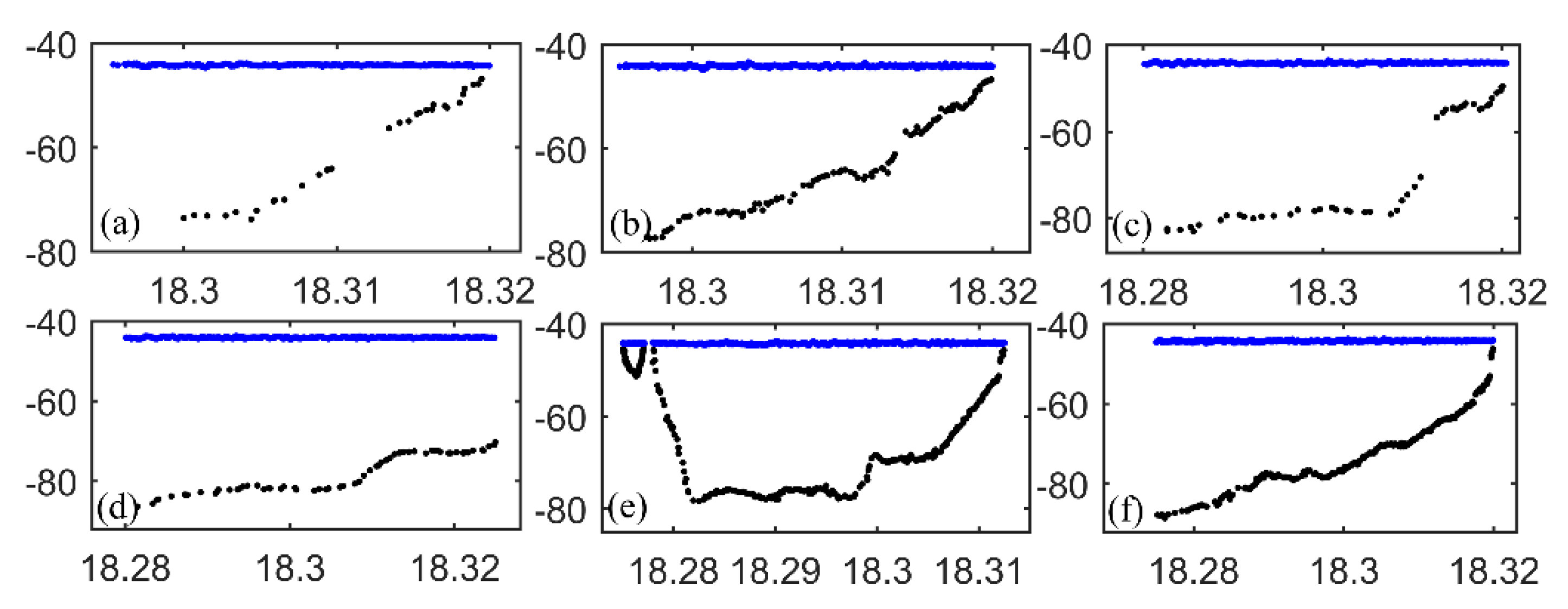
3.1. ICESat-2 Bathymetric Points
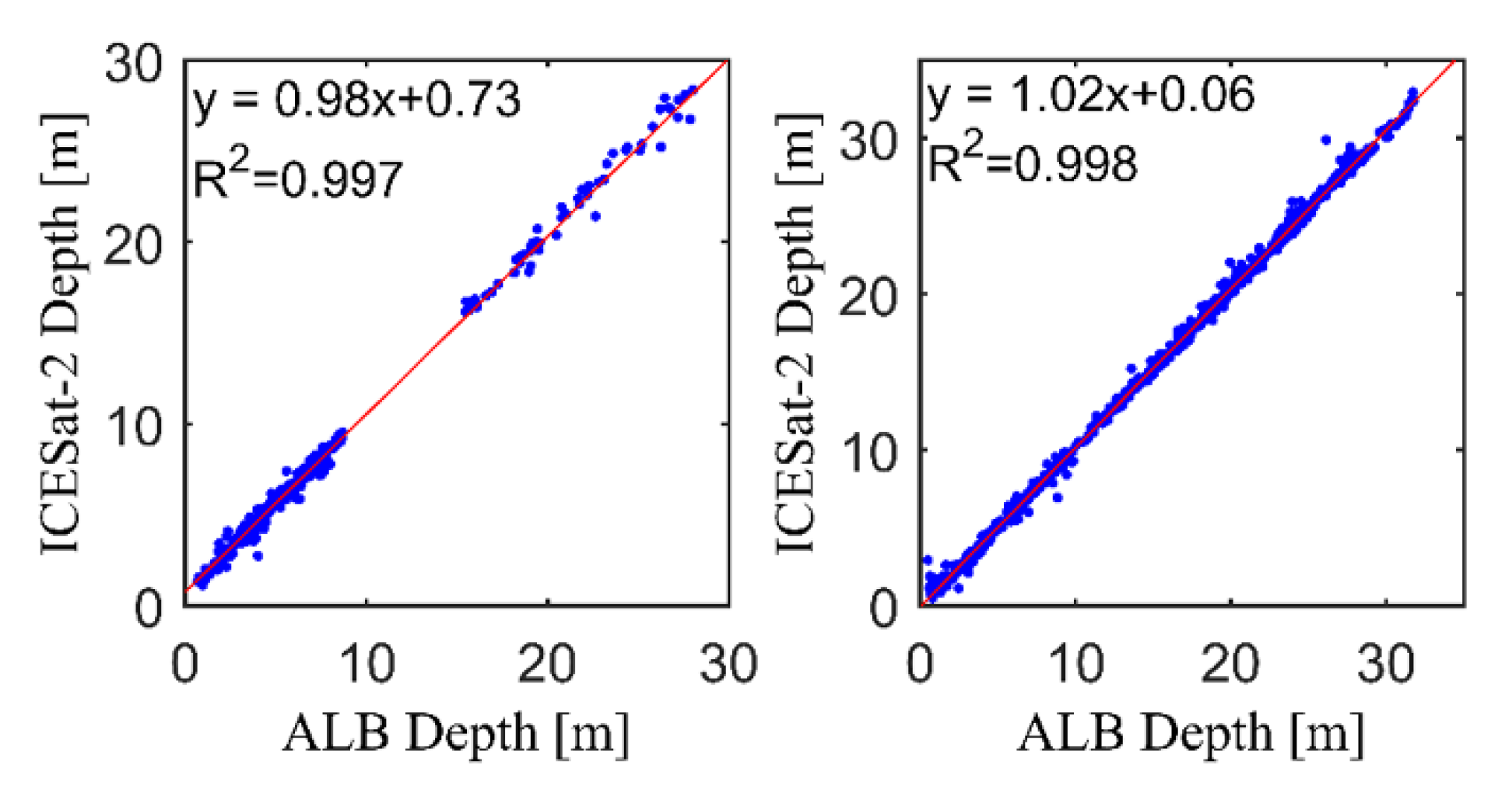
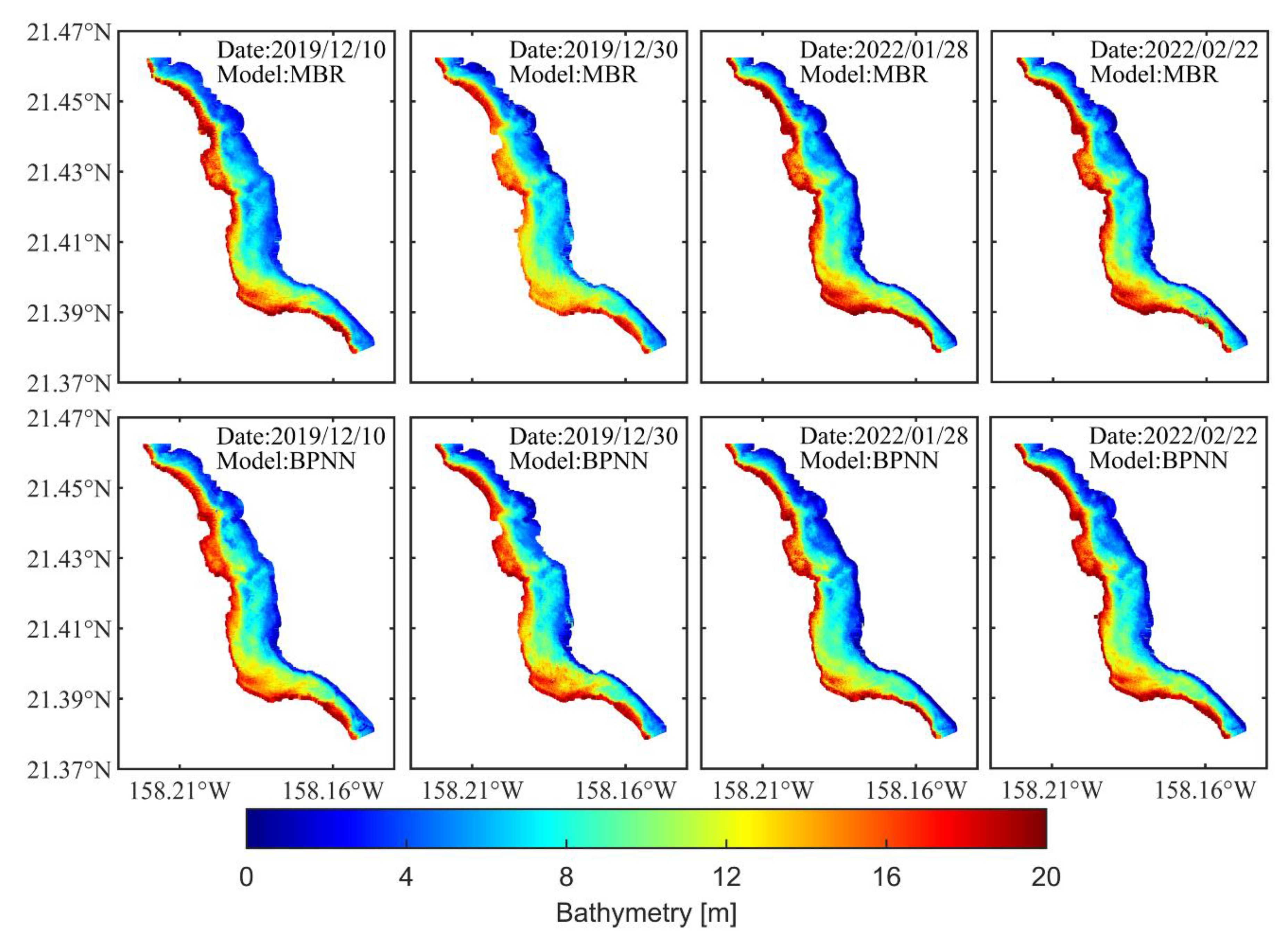
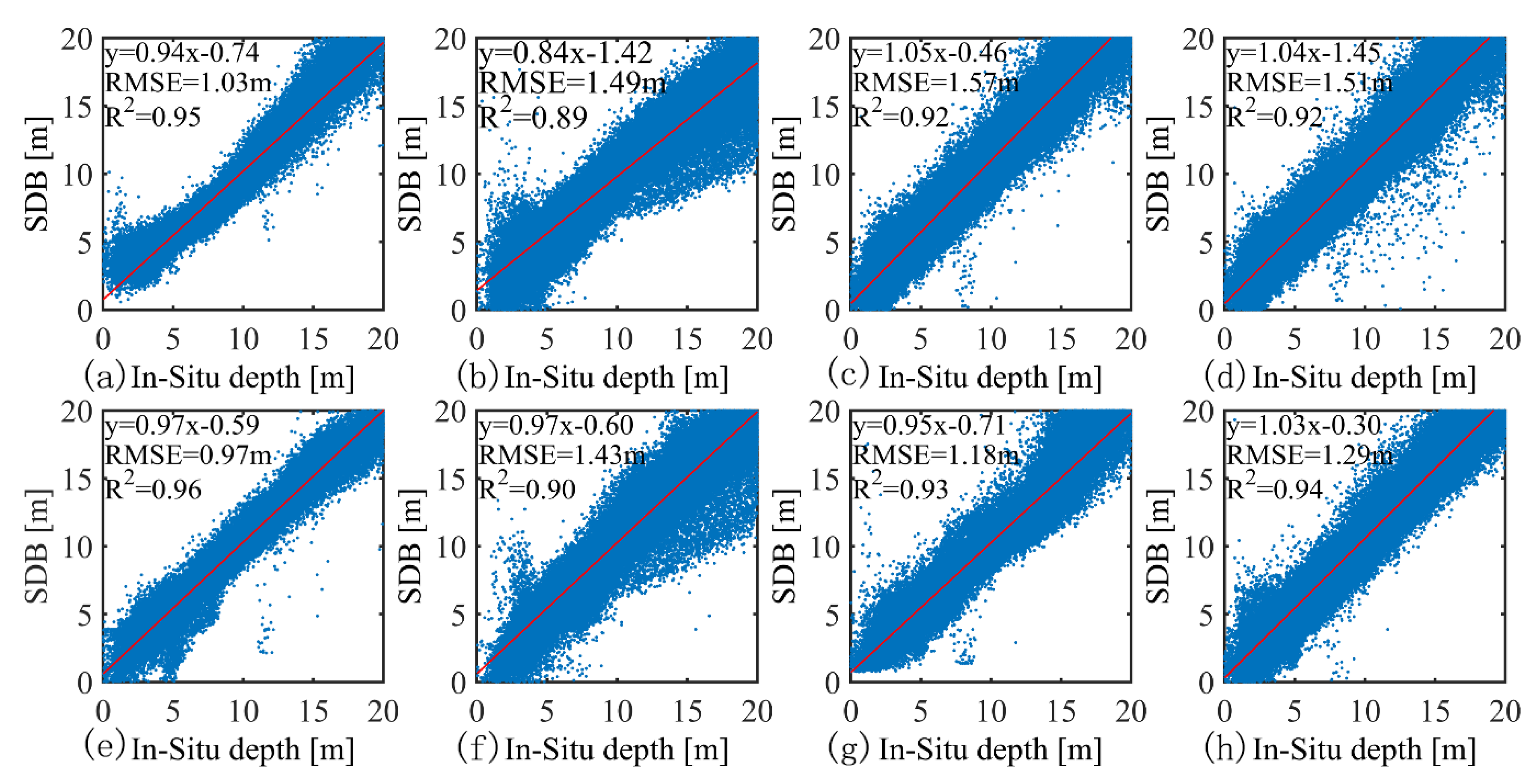
3.2. Satellite-Derived Bathymetry with Sentinel-2 Imagery
4. Discussion
4.1. ICESat-2 Bathymetric Error
4.2. Satellite Bathymetric Error
4.3. Error Correction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nicholls, R.J.; Cazenave, A. Sea-Level Rise and Its Impact on Coastal Zones. Science 2010, 328, 1517–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Mumby, P.J.; Hooten, A.J.; Steneck, R.S.; Greenfield, P.; Gomez, E.; Harvell, C.D.; Sale, P.F.; Edwards, A.J.; Caldeira, K.; et al. Coral Reefs Under Rapid Climate Change and Ocean Acidification. Science 2007, 318, 1737–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.H.; Ouyang, Y.Z.; Wang, A.X. Status and Development Tendency for Seafloor Terrain Measurement Technology. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2017, 46, 1786–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.Y. Progress in Shallow Water Depth Mapping from Optical Remote Sensing. Advances in Marine Science 2018, 36, 331–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, Y.N.; Ma, Z.L. A Bathymetric Extraction Approach Through Refraction and Inversion from Overlapped Or-thoimages. Hydrogr. Surv. Charting 2019, 39, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCombs, M.P.; Mulligan, R.P.; Boegman, L. Offshore wind farm impacts on surface waves and circulation in Eastern Lake Ontario. Coast. Eng. 2014, 93, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J. Application of single-beam and multi-beam bathymetric systems for underwater topographic surveys in shallow waters. Surv. World 2021, 3, 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L. Analysis of comparison between single sounding system and shallow multi-beam sounding system used in bathymetric surveying. Heilongjiang Hydraul. Sci. Technol. 2018, 46, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Q.; Zhou, W.J.; Ju, Z.X.; Lin, X.F. Analysis of the combined application of single- and multi-beam systems for shallow area measurements. China Water Transp. Sci. Technol. Waterw. 2018, 5, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legleiter, C.J.; Overstreet, B.T.; Glennie, C.L.; Pan, Z.; Fernandez-Diaz, J.C.; Singhania, A. Evaluating the capabilities of the CASI hyperspectral imaging system and Aquarius bathymetric LiDAR for measuring channel morphology in two distinct river environments. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2016, 41, 344–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, H.; Sinclair, M. The successful application of Airborne LiDAR Bathymetry surveys using latest technology. In Proceedings of the 2012 Oceans, Yeosu, Republic of Korea, 21–24 May 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramnath, V.; Feygels, V.; Kalluri, H.; Smith, B. CZMIL (Coastal Zone Mapping and Imaging Lidar) bathymetric performance in diverse littoral zones. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2015, Washington, DC, USA, 19–22 October 2015; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Z. Research on SAR Remote Sensing Imaging Mechanism and Inversion of Typical Shallow Water Topography. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 10 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.; Huang, W.G.; Zhou, C.B.; Yang, J.S.; Shi, A.Q.; Li, D.L. Simulation study of sea bottom topography mapping by spaceborne SAR. Haiyang Xuebao 2001, 1, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Al Najar, M.; Benshila, R.; El Bennioui, Y.; Thoumyre, G.; Almar, R.; Bergsma, E.W.J.; Delvit, J.-M.; Wilson, D.G. Coastal Bathymetry Estimation from Sentinel-2 Satellite Imagery: Comparing Deep Learning and Physics-Based Approaches. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, M.J.; Otis, D.B.; Hughes, D.; Muller-Karger, F.E. Automated high-resolution satellite-derived coastal bathymetry mapping. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 107, 102693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Chu, S.; Cheng, L.; Ji, C.; Li, M.; Shen, W. Satellite-derived bathymetry using Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2A images: Assessment of atmospheric correction algorithms and depth derivation models in shallow waters. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, B.C.; Fang, Y.; Jiang, Z.Z.; Gao, L.; Hu, H.Y. Water Depth Measurement from the Fusion of ICESat-2 Laser Satellite and Optical Remote Sensing Image. Hydrogr. Surv. Charting 2020, 40, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.H. Research on bathymetry technology based on multibeam sonar system. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2018, 16, 36–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Lu, B.; Wen, W.; Ding, J.S. Comparison of Sounding Accuracy Between Multi-beam Sonar Systems EM1002S and GeoSwath. Coast. Eng. 2013, 32, 56–64. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.L. Establishment for The Model of Submarine Terrain with Sonar System and DGPS. J. Earth Sci. Environ. 1998, 2, 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, B.C. A Study of Remotely-Sensed Data Processing in Bathymetry. Ph.D. Thesis, Information Engineering University, Zhengzhou, China, 22 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ranndal, H.; Christiansen, P.S.; Kliving, P.; Andersen, O.B.; Nielsen, K. Evaluation of a Statistical Approach for Extracting Shallow Water Bathymetry Signals from ICESat-2 ATL03 Photon Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forfinski-Sarkozi, N.A.; Parrish, C.E. Analysis of MABEL Bathymetry in Keweenaw Bay and Implications for ICESat-2 ATLAS. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, H.-J.; Huang, C.-Y.; Jasinski, M.; Li, Y.; Gao, H.; Yamanokuchi, T.; Wang, C.-G.; Chang, T.-M.; Ren, H.; Kuo, C.-Y.; et al. A semi-empirical scheme for bathymetric mapping in shallow water by ICESat-2 and Sentinel-2: A case study in the South China Sea. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 178, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Le, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yan, Q.; Dong, Y.; Han, W.; Wang, L. Nearshore bathymetry based on ICESat-2 and multispectral images: Comparison between Sentinel 2, Landsat 8, and testing Gaofen-2. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 2449–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Deng, R.; Liang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Xiong, L.; Liu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Tang, D. A downscaled bathymetric mapping approach combining multitemporal Landsat-8 and high spatial resolution imagery: Demonstrations from clear to turbid waters. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 180, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrish, C.E.; Magruder, L.A.; Neuenschwander, A.L.; Forfinski-Sarkozi, N.; Alonzo, M.; Jasinski, M. Validation of ICESat-2 ATLAS Bathymetry and Analysis of ATLAS’s Bathymetric Mapping Performance. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fredericks, X.; Kranenburg, C.; Nagle, D.B. EAARL-B Submerged Topography? Saint Thomas, U.S. Virgin Islands, 2014; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustin, S. Classification of benthic composition in a coral reef environment using spectral unmixing. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2007, 1, 011501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasinski, M.; Stoll, J.; Hancock, D.; Robbins, J.; Nattala, J.; Pavelsky, T.; Morrison, J.; Ondrusek, M.; Parrish, C.; Jones, B.; et al. Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD) for Inland Water Data Products ATL13, Version 4; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, T.; Brenner, A.; Hancock, D.; Robbins, J.; Saba, J.; Harbeck, K.; Gibbons, A.; Lee, J.; Luthcke, S.; Rebold, T.; et al. ATLAS/ICESat-2 L2A Global Geolocated Photon Data, Version 4; NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2021; Available online: https://nsidc.org/sites/default/files/atl03-v004-userguide.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Jasinski, M.F.; Stoll, J.D.; Cook, W.B.; Ondrusek, M.; Stengel, E.; Brunt, K. Inland and Near-Shore Water Profiles Derived from the High-Altitude Multiple Altimeter Beam Experimental Lidar (MABEL). J. Coast. Res. 2016, 76, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, H.; Jasinski, M.F.; Zhang, S.; Stoll, J.D. Deriving High-Resolution Reservoir Bathymetry From ICESat-2 Prototype Photon-Counting Lidar and Landsat Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 7883–7893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusch, M.; del Bello, U.; Carlier, S.; Colin, O.; Fernandez, V.; Gascon, F.; Hoersch, B.; Isola, C.; Laberinti, P.; Martimort, P.; et al. Sentinel-2: ESA’s Optical High-Resolution Mission for GMES Operational Services. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, I.; Stumpf, R.P. On the use of Sentinel-2 satellites and lidar surveys for the change detection of shallow bathymetry: The case study of North Carolina inlets. Coast. Eng. 2021, 169, 103936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Main-Knorn, M.; Pflug, B.; Louis, J.; Debaecker, V.; Müller-Wilm, U.; Gascon, F. Sen2Cor for Sentinel-2. Proc. SPIE 2017, 10427, 1042704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, N.; Liu, Z.; Yang, B.; Yang, F.; Wang, X.H.; Li, S. Satellite-derived bathymetry using the ICESat-2 lidar and Sentinel-2 imagery datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 250, 112047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casal, G.; Monteys, X.; Hedley, J.; Harris, P.; Cahalane, C.; McCarthy, T. Assessment of empirical algorithms for bathymetry extraction using Sentinel-2 data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 2855–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, M.; Simis, S.; Martinez-Vicente, V.; Poser, K.; Bresciani, M.; Alikas, K.; Spyrakos, E.; Giardino, C.; Ansper, A. Assessment of atmospheric correction algorithms for the Sentinel-2A MultiSpectral Imager over coastal and inland waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 267–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturges, H.A. The Choice of a Class Interval. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1926, 21, 65–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, C. The Optical Properties of Water. In Handbook of Optics, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1995; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Neuenschwander, A.L.; Magruder, L.A. The Potential Impact of Vertical Sampling Uncertainty on ICESat-2/ATLAS Terrain and Canopy Height Retrievals for Multiple Ecosystems. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, G.; Xu, D.; Meng, Y. Dynamic Evolution Analysis of Desertification Images Based on BP Neural Network. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 5645535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrada, M.; Zurita, G.; Cabrera, D.; Sánchez, R.-V.; Artés, M.; Li, C. Fault diagnosis in spur gears based on genetic algorithm and random forest. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 70–71, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyzenga, D.R. Passive remote sensing techniques for mapping water depth and bottom features. Appl. Opt. 1978, 17, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klonowski, W.M.; Fearns, P.R.C.S.; Lynch, M.J. Retrieving key benthic cover types and bathymetry from hyperspectral imagery. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2007, 1, 011505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, R.P.; Holderied, K.; Sinclair, M. Determination of water depth with high-resolution satellite imagery over variable bottom types. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q. Research on Water Depth Inversion Method of Multispectral Remote Sensing Image. Ph.D. Thesis, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai, China, 30 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z. Study on Bathymetry Inversion Models Using Multispectral or Hyperspectral Data and Bathyorographical Mapping Technology. Ph.D. Thesis, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao, China, 10 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Amidror, I. Scattered data interpolation methods for electronic imaging systems: A survey. J. Electron. Imaging 2002, 11, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hedley, J.D.; Roelfsema, C.; Brando, V.; Giardino, C.; Kutser, T.; Phinn, S.; Mumby, P.J.; Barrilero, O.; Laporte, J.; Koetz, B. Coral reef applications of Sentinel-2: Coverage, characteristics, bathymetry and benthic mapping with comparison to Landsat 8. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 598–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, S.; Hedley, J.D.; Lavender, S. Sun Glint Correction of High and Low Spatial Resolution Images of Aquatic Scenes: A Review of Methods for Visible and Near-Infrared Wavelengths. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 697–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hedley, J.D.; Harborne, A.R.; Mumby, P.J. Technical note: Simple and robust removal of sun glint for mapping shallow-water benthos. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 2107–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casal, G.; Harris, P.; Monteys, X.; Hedley, J.; Cahalane, C.; McCarthy, T. Understanding satellite-derived bathymetry using Sentinel 2 imagery and spatial prediction models. GIScience Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, I.; Stumpf, R.P. Retrieval of nearshore bathymetry from Sentinel-2A and 2B satellites in South Florida coastal waters. Estuarine, Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 226, 106277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahtmäe, E.; Kutser, T. Airborne mapping of shallow water bathymetry in the optically complex waters of the Baltic Sea. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 025012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Date | Ground Track | MAE (m) | MRE | RMSE (m) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019/09/08 | 1L | 0.32 | 8% | 0.35 | 0.92 |
| 2019/09/08 | 1R | 0.31 | 7% | 0.39 | 0.97 |
| 2020/06/14 | 2L | 0.47 | 2% | 0.58 | 0.98 |
| 2020/12/05 | 1L | 0.51 | 7% | 0.55 | 0.93 |
| Date | Ground Track | MAE (m) | MRE | RMSE (m) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018/11/22 | 1L | 0.37 | 3% | 0.54 | 0.99 |
| 2018/11/22 | 1R | 0.32 | 2% | 0.43 | 0.99 |
| 2018/11/22 | 2R | 0.52 | 3% | 0.71 | 0.99 |
| 2018/11/22 | 3R | 0.34 | 1% | 0.41 | 0.99 |
| 2019/02/21 | 1L | 0.26 | 2% | 0.37 | 0.99 |
| 2019/02/21 | 2L | 0.41 | 2% | 0.54 | 0.99 |
| Date | MBR | BPNN | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | RMSE (m) | R2 | N | RMSE (m) | R2 | |
| 2019/12/10 | 87065 | 1.03 | 0.95 | 88322 | 0.97 | 0.96 |
| 2019/12/30 | 134134 | 1.49 | 0.89 | 128952 | 1.43 | 0.90 |
| 2022/01/28 | 129175 | 1.57 | 0.92 | 130786 | 1.18 | 0.93 |
| 2022/02/22 | 133228 | 1.51 | 0.92 | 133228 | 1.29 | 0.94 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, X.; Jin, X.; Jin, S. Shallow Water Bathymetry Mapping from ICESat-2 and Sentinel-2 Based on BP Neural Network Model. Water 2022, 14, 3862. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233862
Guo X, Jin X, Jin S. Shallow Water Bathymetry Mapping from ICESat-2 and Sentinel-2 Based on BP Neural Network Model. Water. 2022; 14(23):3862. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233862
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Xiaozu, Xiaoyi Jin, and Shuanggen Jin. 2022. "Shallow Water Bathymetry Mapping from ICESat-2 and Sentinel-2 Based on BP Neural Network Model" Water 14, no. 23: 3862. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233862
APA StyleGuo, X., Jin, X., & Jin, S. (2022). Shallow Water Bathymetry Mapping from ICESat-2 and Sentinel-2 Based on BP Neural Network Model. Water, 14(23), 3862. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233862







