Microplastics in Ship Sewage and Solutions to Limit Their Spread: A Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
- BW and GW/galley waters can be collected in a storage tank and discharged to the port for further treatment.
- BW can be ground, disinfected, and discharged directly into the sea with GW/galley water.
- GW/galley water can be kept in dedicated tanks and periodically discharged directly into the sea.
- GW can be cleaned and used for a toilet flushing system [30].
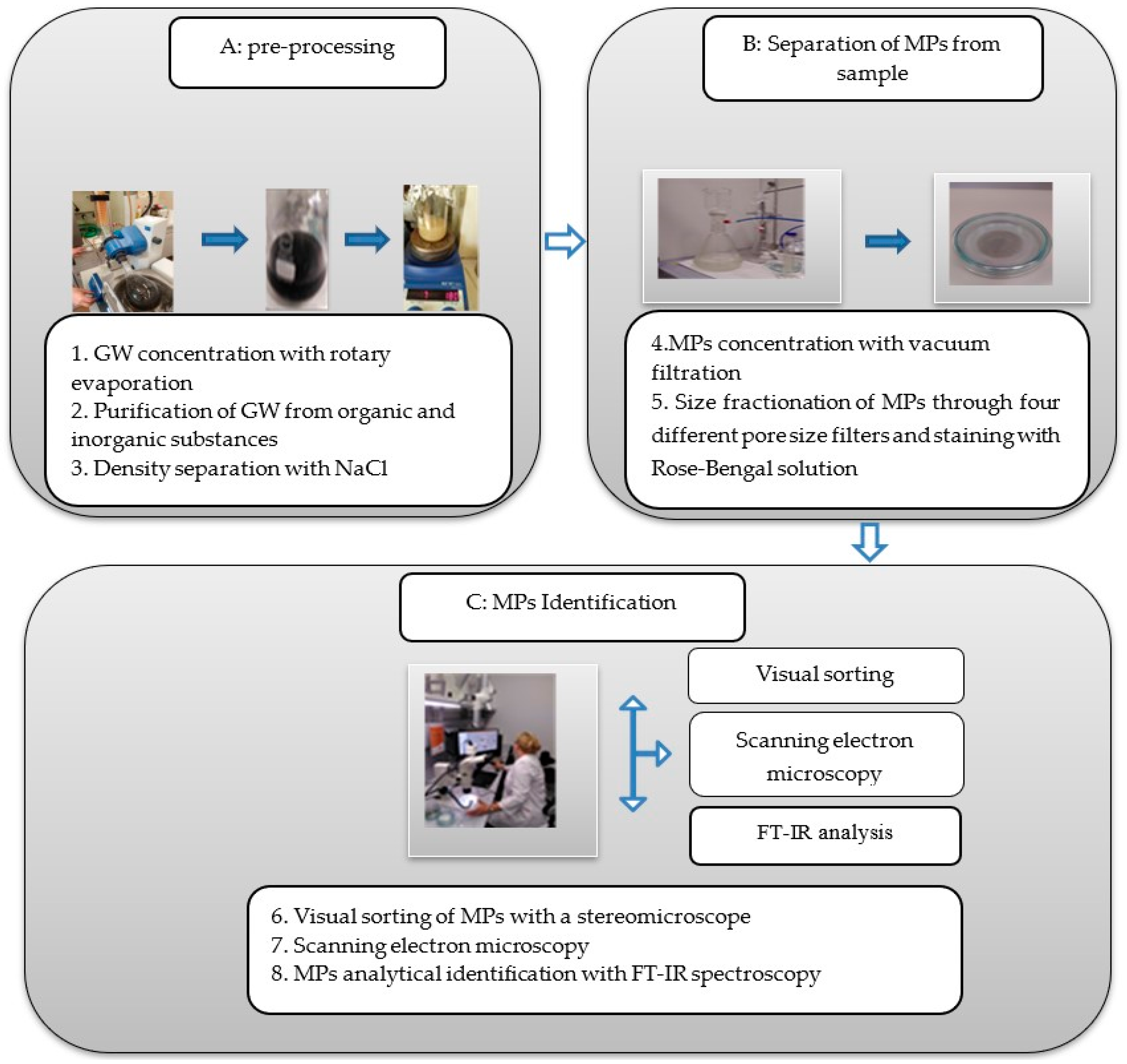
2. Materials and Methods
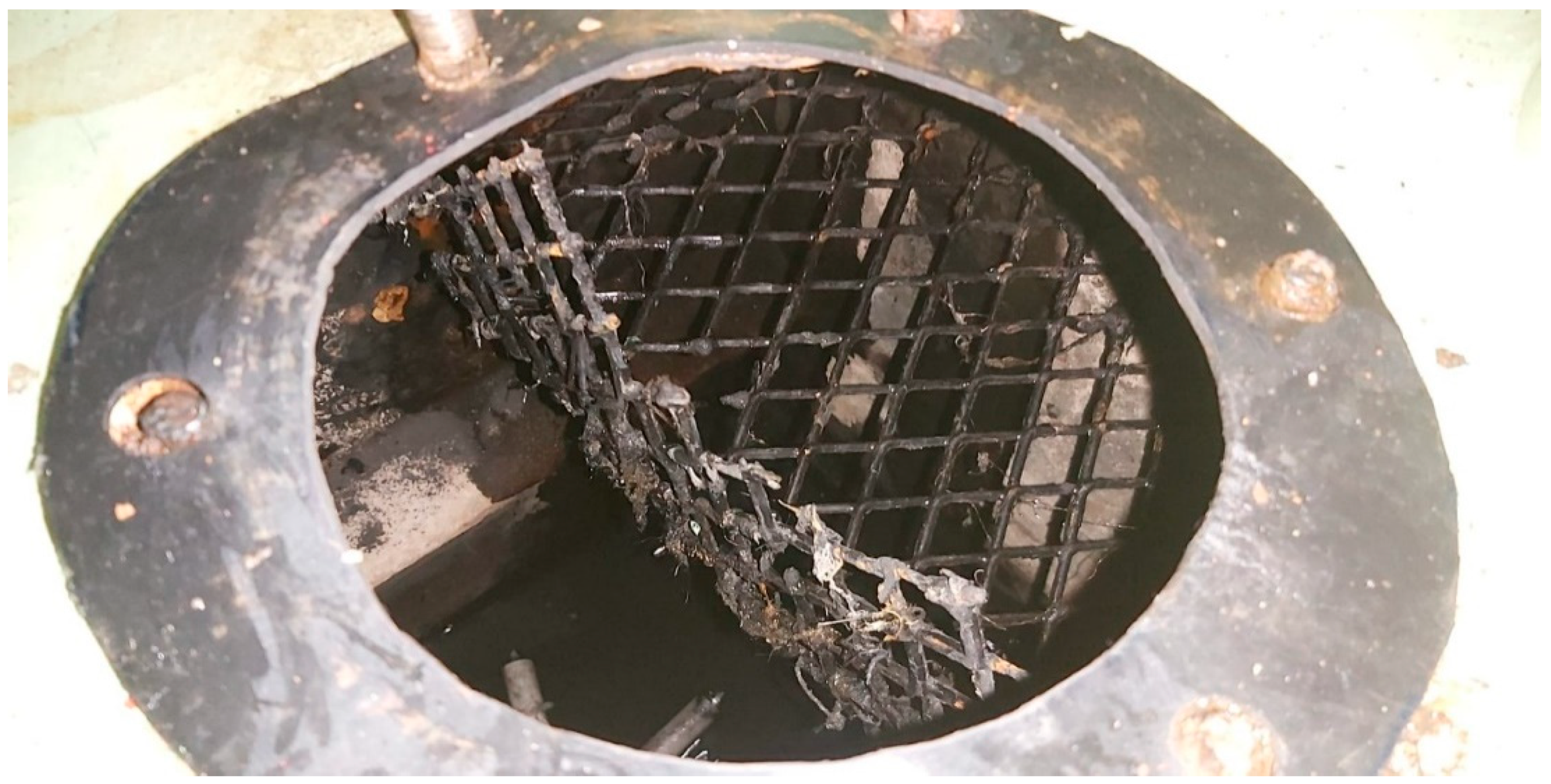
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. Grey Water Sample Processing and MPs Identification Methods
2.3. Statistics
2.4. Quality Assurance and Quality Control
3. Results
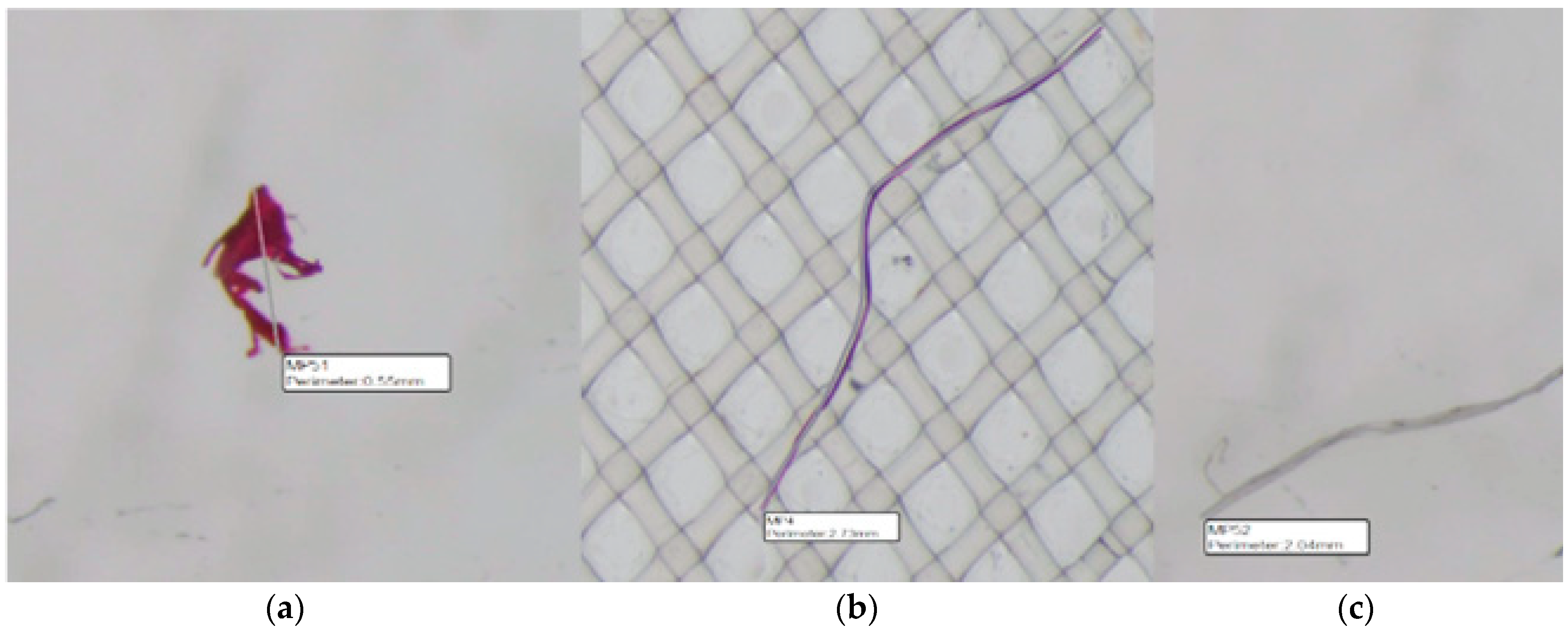
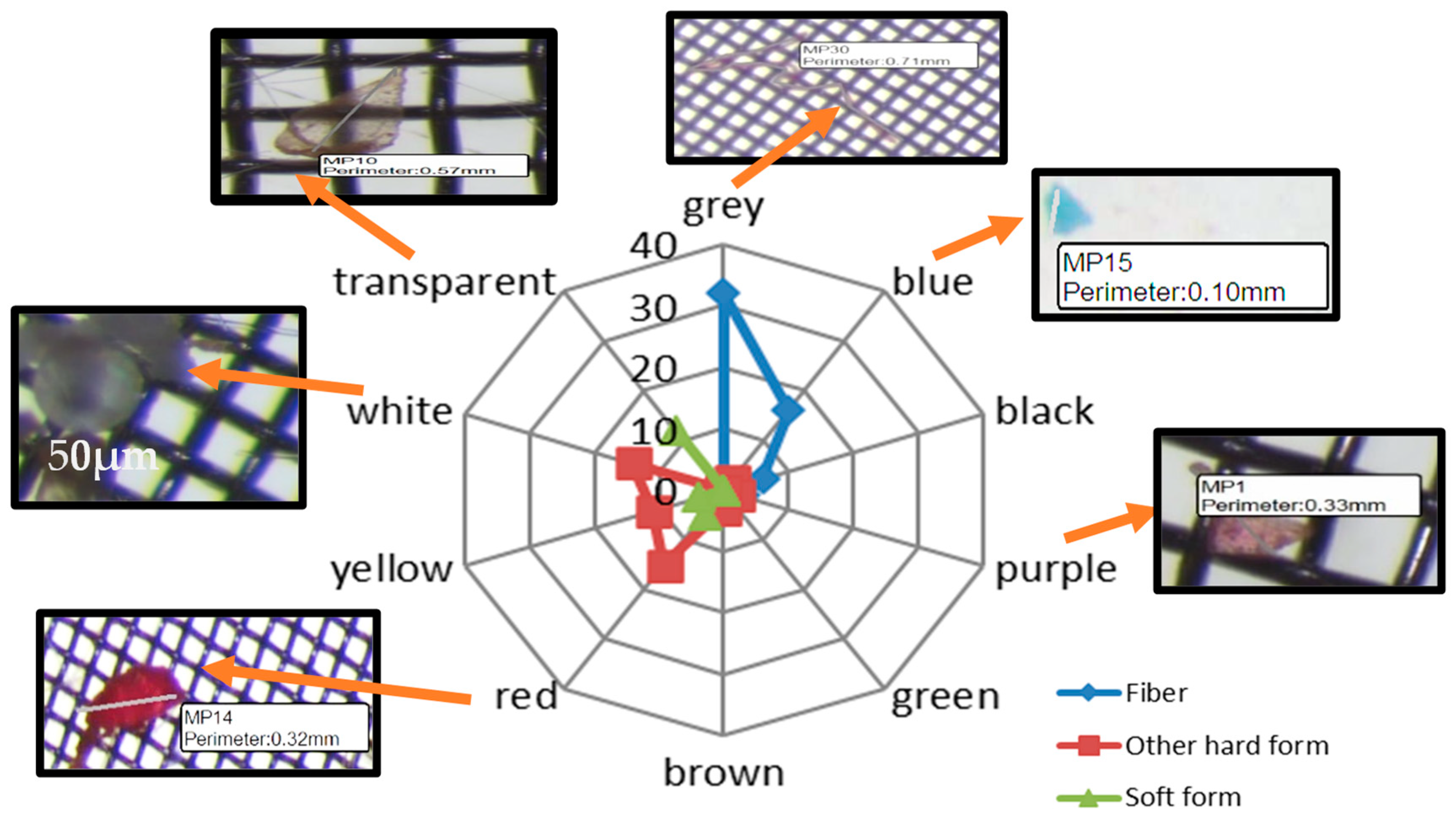
3.1. Microplastic Visual Sorting Analysis Results
3.2. Microplastics Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis Results
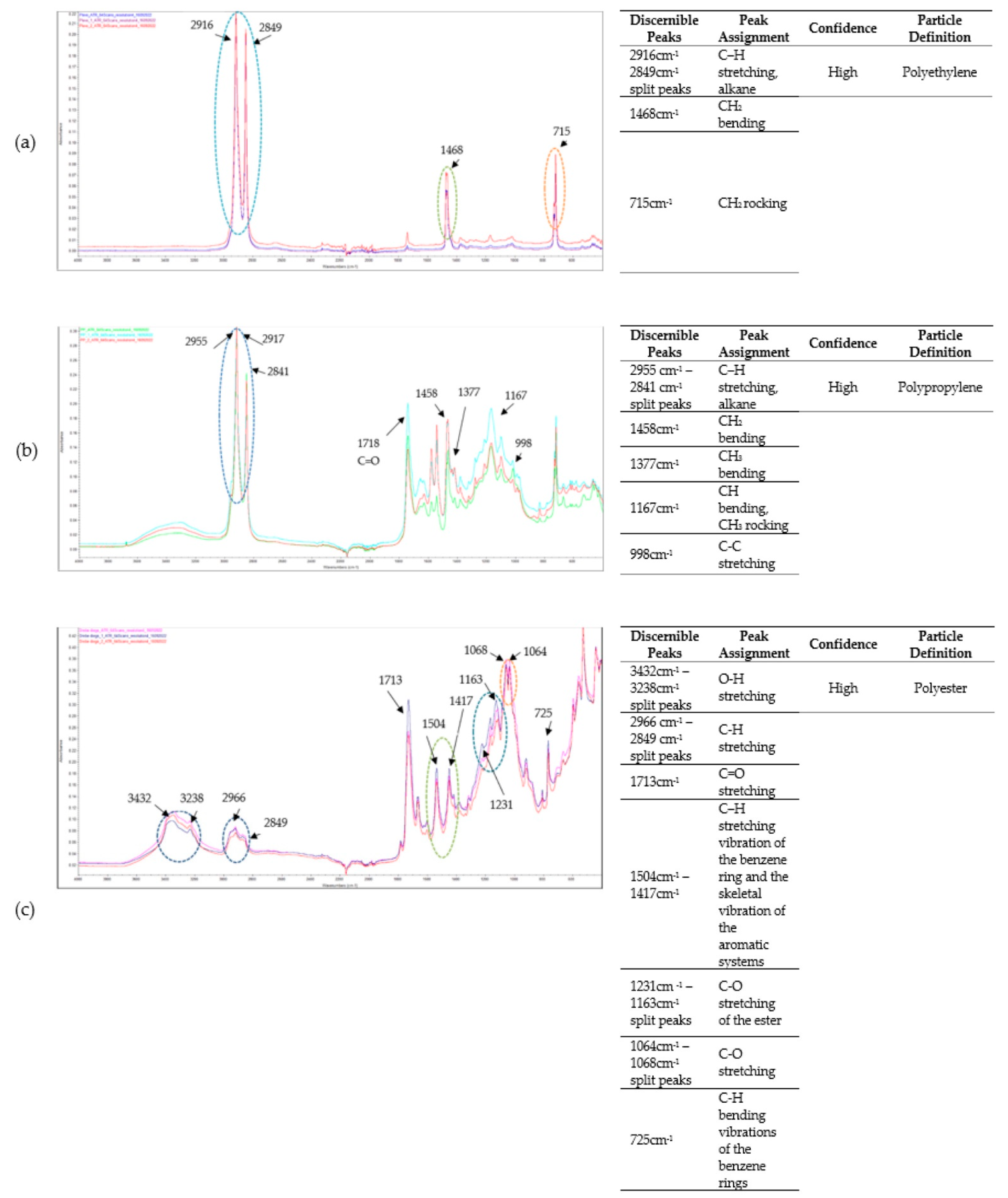
3.3. Microplastics Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy Analysis Results
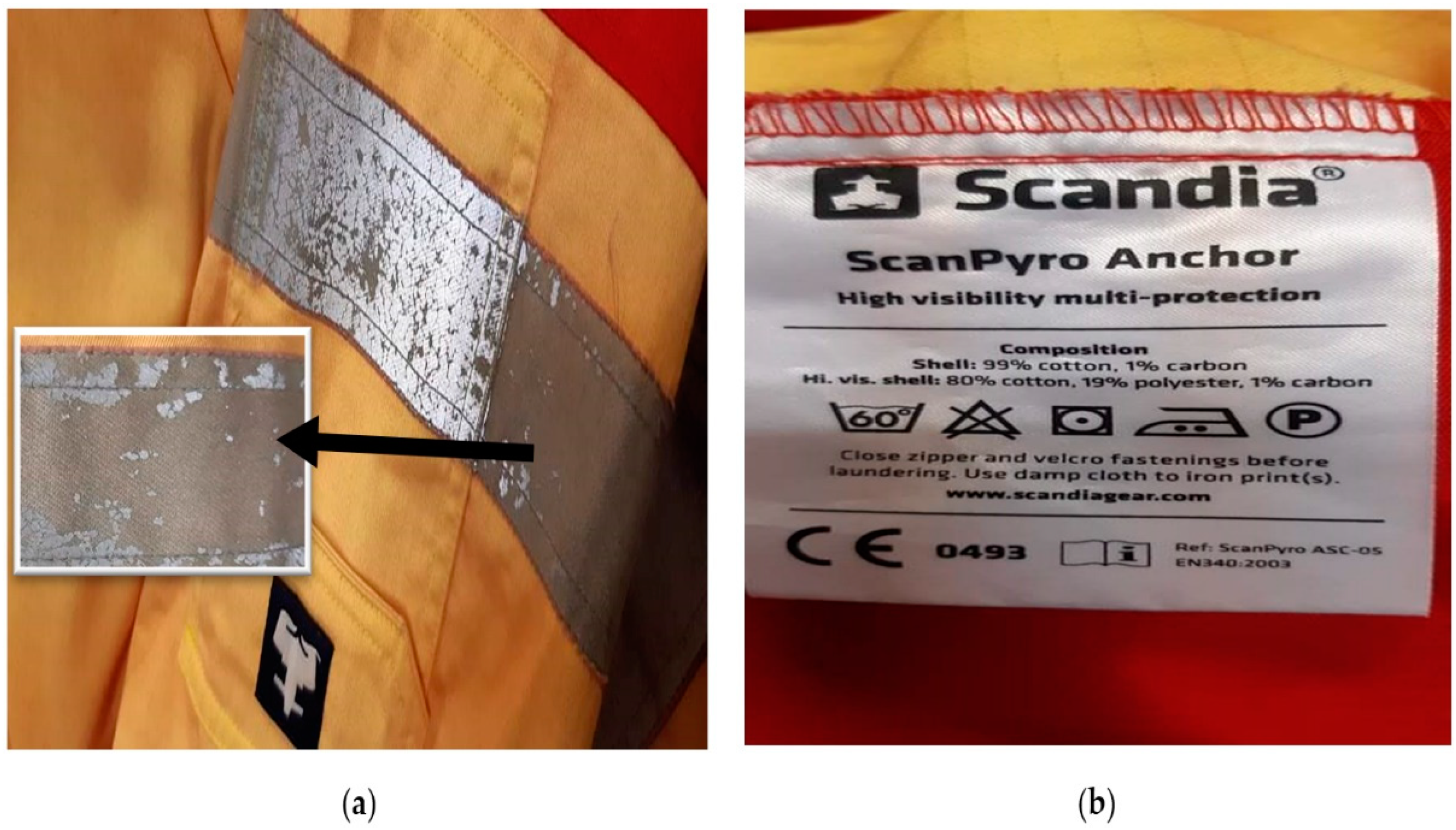
3.4. Improvement Solution for Ship Sewage Treatment Plant
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davidson, N.C.; van Dam, A.A.; Finlayson, C.M.; McInnes, R.J. Worth of Wetlands: Revised Global Monetary Values of Coastal and Inland Wetland Ecosystem Services. Mar. Freshwater Res. 2019, 70, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Review of Maritime Transport 2020; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2020; p. 159. Available online: https://unctad.org/system/files/official-document/rmt2020_en.pdf (accessed on 6 August 2022).
- Chen, W.; Beavis, M.; Jost, O. The Magic of Sewage Treatment Plant Type Tests. The Maritime Executive. 2021. Available online: https://maritime-executive.com/corporate/the-magic-of-sewage-treatment-plant-type-tests (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- FanpLESStic-Sea. Review of Existing Policies and Research Related to Microplastics; FanpLESStic-Sea: Rostock, Germany, 2019; Available online: https://helcom.fi/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/FanpLESStic-sea-Microplastics-Policy-and-Research-Review.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the Marine Environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statista Annual Production of Plastics Worldwide from 1950 to 2020. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/282732/global-production-of-plastics-since-1950/ (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, Use, and Fate of All Plastics Ever Made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GESAMP. Sources, Fate and Effects of Microplastics in the Marine Environment: Part Two of a Global Assessment” (Kershaw, P.J., and Rochman, C.M., Eds). (IMO/FAO/UNESCO-IOC/UNIDO/WMO/IAEA/UN/ UNEP/UNDP Joint Group of Experts on the Scientific Aspects of Marine Environmental Protection). Rep. Stud. GESAMP No. 93; International Maritime Organization: London, UK, 2016; p. 220. Available online: http://www.gesamp.org/site/assets/files/1275/sources-fate-and-effects-of-microplastics-in-the-marine-environment-part-2-of-a-global-assessment-en.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- GESAMP. Guidelines for the Monitoring and Assessment of Plastic Litter and Microplastics in the Ocean; International Maritime Organization: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Essel, R.; Engel, L.; Carus, M.; Ahrens, D.R.H. Sources of Microplastics Relevant to Marine Protection in Germany; (TEXTE 64/2015. Project No. 31969. Report No. (UBA-FB) 002147/E); Umwelt Bundesamt: Dessau-Roßlau, Germany, 2015; p. 48. [Google Scholar]
- Guerranti, C.; Martellini, T.; Perra, G.; Scopetani, C.; Cincinelli, A. Microplastics in Cosmetics: Environmental Issues and Needs for Global Bans. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 68, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, H.A. Plastic in Cosmetics: Are We Polluting the Environment through Our Personal Care?: Plastic Ingredients That Contribute to Marine Microplastic Litter; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2015; ISBN 978-92-807-3466-9. [Google Scholar]
- Mintenig, S.M.; Int-Veen, I.; Löder, M.G.J.; Primpke, S.; Gerdts, G. Identification of Microplastic in Effluents of Waste Water Treatment Plants Using Focal Plane Array-Based Micro-Fourier-Transform Infrared Imaging. Water Res. 2017, 108, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Fu, D.; Qi, H.; Lan, C.Q.; Yu, H.; Ge, C. Micro- and Nano-Plastics in Marine Environment: Source, Distribution and Threats—A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norwegian Environment Agency (Miljødirektoratet). Sources of Microplastic Pollution to the Marine Environment; Norwegian Environment Agency (Miljødirektoratet): Oslo, Norway, 2014; p. 86. Available online: https://www.miljodirektoratet.no/globalassets/publikasjoner/M321/M321.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastics as Contaminants in the Marine Environment: A Review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, M.; Lebreton, L.C.M.; Carson, H.S.; Thiel, M.; Moore, C.J.; Borerro, J.C.; Galgani, F.; Ryan, P.G.; Reisser, J. Plastic Pollution in the World’s Oceans: More than 5 Trillion Plastic Pieces Weighing over 250,000 Tons Afloat at Sea. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodall, L.C.; Sanchez-Vidal, A.; Canals, M.; Paterson, G.L.J.; Coppock, R.; Sleight, V.; Calafat, A.; Rogers, A.D.; Narayanaswamy, B.E.; Thompson, R.C. The Deep Sea Is a Major Sink for Microplastic Debris. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2014, 1, 140317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, J.; Friot, D. Primary Microplastics in the Oceans: A Global Evaluation of Sources; Lundin, C.G., Matos de Sousa, J., Eds.; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-2-8317-1827-9. [Google Scholar]
- Browne, M.A.; Crump, P.; Niven, S.; Teuten, E.; Tonkin, A.; Galloway, T.; Thompson, R. Accumulation of Microplastic on Shorelines Woldwide: Sources and Sinks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9175–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic Waste Inputs from Land into the Ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Näkki, P.; Setälä, O.; Lehtiniemi, M. Seafloor Sediments as Microplastic Sinks in the Northern Baltic Sea—Negligible Upward Transport of Buried Microplastics by Bioturbation. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherrington, D.C.; Darrah, D.C.; Hann, S.; Cole, G.; Corbin, M. Study to Support the Development of Measures to Combat a Range of Marine Litter Sources; Eunomia Research & Consulting Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 2016; p. 432. Available online: https://mcc.jrc.ec.europa.eu/documents/201606243248.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- International Maritime Organization. Progress Report of the GESAMP Working Group on Sea-Based Sources of Marine Litter (Secretariat); International Maritime Organization: London, UK, 2020; p. 126. [Google Scholar]
- Kalnina, R.; Ivaninoka, I. Treatment Methods of Ships Sewage. In Proceedings of the 24th International Scientific Conference Transport Means 2020, Kaunas University of Technology, Palanga, Lithuania, 30 September–2 October 2020; Volume 2, p. 514. [Google Scholar]
- International Maritime Organization. Marpol: Articles, Protocols, Annexes, Unified Interpretations of the International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships, 1973, As Modified by the Protocol of 1978 Relating Thereto; International Maritime Organization: London, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-92-801-1657-1. [Google Scholar]
- International Maritime Organization Resolution MEPC.201(62). Amendments to the Annex of the Protocol of 1978 Relating to the International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships; International Maritime Organization: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ytreberg, E.; Eriksson, M.; Maljutenko, I.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Johansson, L.; Granhag, L. Chemicals and Nutrients in Grey Water from Ships; HELCOM: Helsinki, Finland, 2019; p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Nellesen, T.; Broeg, K.; Dorgeloh, E.; Joswig, M.; Heitmüller, S. A Technical Guidance for the Handling of Wastewater in Ports of the Baltic Sea Special Area under MARPOL Annex IV. Available online: https://helcom.fi/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/Technical-guidance-for-the-handling-of-wastewater-in-ports.pdf (accessed on 26 September 2022).
- European Maritime Safety Agency. The Management of Ship-Generated Waste On-Board Ships; CE Delft: Delft, The Netherlands, 2017; p. 90. Available online: https://cedelft.eu/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2021/04/CE_Delft_7i85_The_Management_of_Ship-Generated_Waste_On-board_Ships_Def.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2022).
- Kalnina, R.; Demjanenko, I.; Gorbacenko, D.; Priednieks, V.; Baronins, J. Nutrient Analysis of Food Waste from Ships’ Greywater in the Baltic Sea. Water 2021, 13, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mausra, B.; Foster, A. Laboratory Methods for the Analysis of Microplastics in the Marine Environment; NOAA Marine Debris Division: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2015; p. 39. Available online: https://marinedebris.noaa.gov/sites/default/files/publications-files/noaa_microplastics_methods_manual.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2022).
- Gies, E.A.; LeNoble, J.L.; Noël, M.; Etemadifar, A.; Bishay, F.; Hall, E.R.; Ross, P.S. Retention of Microplastics in a Major Secondary Wastewater Treatment Plant in Vancouver, Canada. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löder, M.G.J.; Kuczera, M.; Mintenig, S.; Lorenz, C.; Gerdts, G.; Löder, M.G.J.; Kuczera, M.; Mintenig, S.; Lorenz, C.; Gerdts, G. Focal Plane Array Detector-Based Micro-Fourier-Transform Infrared Imaging for the Analysis of Microplastics in Environmental Samples. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 563–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Azzawi, M.S.M.; Kefer, S.; Weißer, J.; Reichel, J.; Schwaller, C.; Glas, K.; Knoop, O.; Drewes, J.E. Validation of Sample Preparation Methods for Microplastic Analysis in Wastewater Matrices—Reproducibility and Standardization. Water 2020, 12, 2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebezeit, G.; Liebezeit, E. Synthetic Particles as Contaminants in German Beers. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2014, 31, 1574–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, W.J.; Hong, S.H.; Eo, S.E. Identification Methods in Microplastic Analysis: A Review. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Chemicals Agency. Restriction Proposal for Intentionally Added Microplastics in the EU. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/lv/-/restriction-proposal-for-intentionally-added-microplastics-in-the-eu-update (accessed on 2 October 2022).
- Lister, J.; Poulsen, R.T.; Ponte, S. Orchestrating Transnational Environmental Governance in Maritime Shipping. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2015, 34, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.-H.; Lun, V.Y.H.; Wong, C.W.Y.; Cheng, T.C.E. Green Shipping Practices in the Shipping Industry: Conceptualization, Adoption, and Implications. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2011, 55, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, L.; Feng, H. Green Strategic Planning Approach for International Shipping Activities. Sustainability 2020, 12, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnina, R.; Demjanenko, I.; Suraja, K. Perspective of Sustainable Shipping—Eco-Ships. In Proceedings of the 25th International Scientific Conference, Transport Means 2021, Kaunas University of Technology, Kaunas, Lithuania, 6–8 October 2021; Volume 2, p. 426. [Google Scholar]
- International Maritime Organization. Hull Scrapings and Marine Coatings as a Source of Microplastics; International Maritime Organization: London, UK, 2019; p. 33. Available online: https://wwwcdn.imo.org/localresources/en/OurWork/Environment/Documents/Hull%20Scrapings%20final%20report.pdf (accessed on 8 October 2022).
- Hwang, D.-J. The IMO Action Plan to Address Marine Plastic Litter from Ships and Its Follow-Up Timeline. J. Int. Marit. Saf. Environ. Aff. Shipp. 2020, 4, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, A.; Aleixo, M.; De Pablo, H.; Lopes, C.; Raimundo, J. Microplastics in Wastewater: Microfiber Emissions from Common Household Laundry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 26643–26649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramasamy, R.; Aragaw, T.A.; Balasaraswathi Subramanian, R. Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluent and Microfiber Pollution: Focus on Industry-Specific Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 51211–51233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesa, F.S.; Turra, A.; Checon, H.H.; Leonardi, B.; Baruque-Ramos, J. Laundering and Textile Parameters Influence Fibers Release in Household Washings. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suaria, G.; Achtypi, A.; Perold, V.; Lee, J.; Pierucci, A.; Bornman, T.; Aliani, S.; Ryan, P. Microfibers in Oceanic Surface Waters: A Global Characterization. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay8493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivakumar, N.; Madhusudan, P.; Daniel, S.C.G.K. Chapter 15—Nanomaterials for Smart Food Packaging. In Handbook of Nanomaterials for Industrial Applications; Mustansar Hussain, C., Ed.; Micro and Nano Technologies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 260–270. ISBN 978-0-12-813351-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ashton, K.; Holmes, L.; Turner, A. Association of Metals with Plastic Production Pellets in the Marine Environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 2050–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, L.A.; Turner, A.; Thompson, R.C. Adsorption of Trace Metals to Plastic Resin Pellets in the Marine Environment. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 160, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, M.; Anjum, S.; Hano, C.; Anjum, I.; Abbasi, B.H. An Overview of the Applications of Nanomaterials and Nanodevices in the Food Industry. Foods 2020, 9, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ytreberg, E.; Eriksson, M.; Maljutenko, I.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Johansson, L.; Hassellöv, I.-M.; Granhag, L. Environmental Impacts of Grey Water Discharge from Ships in the Baltic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 152, 110891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasundaram, B.; King, P.E.; Shackley, S. The Effects of Zinc on Postfertilization Development in Eggs of Clupea harengus L. Aquat. Toxicol. 1984, 5, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Choi, W. Solid-Phase Photocatalytic Degradation of PVC–TiO2 Polymer Composites. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2001, 143, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galletti, A.; Seo, S.; Joo, S.H.; Su, C.; Blackwelder, P. Effects of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Derived from Consumer Products on the Marine Diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 21113–21122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi Khaneghah, A.; Hashemi, S.M.B.; Limbo, S. Antimicrobial Agents and Packaging Systems in Antimicrobial Active Food Packaging: An Overview of Approaches and Interactions. Food Bioprod. Process. 2018, 111, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerstin, H.-R.; Schlich, K.; Wenzel, A. TiO2 Nanoparticles—Relationship between Dispersion Preparation Method and Ecotoxicity in the Algal Growth Test. Umweltwiss. Schadst.-Forsch. 2010, 22, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Lao, Y.; Lv, X.; Tao, Y.; Huang, B.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; Cai, Z. TiO2 Nanoparticles in the Marine Environment: Physical Effects Responsible for the Toxicity on Algae Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherchi, C.; Gu, A. Impact of Titanium Dioxide Nanomaterials on Nitrogen Fixation Rate and Intracellular Nitrogen Storage in Anabaena Variabilis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8302–8307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szefer, P. Metal Pollutants and Radionuclides in the Baltic Sea—An Overview. Oceanologia 2002, 44, 129–178. [Google Scholar]
- Gheorghe, S.; Stoica, C.; Vasile, G.G.; Nita-Lazar, M.; Stanescu, E.; Lucaciu, I.E.; Gheorghe, S.; Stoica, C.; Vasile, G.G.; Nita-Lazar, M.; et al. Metals Toxic Effects in Aquatic Ecosystems: Modulators of Water Quality; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-953-51-2882-3. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, N.B.; Legros, S.; Von der Kammer, F.; Hofmann, T.; Baun, A. The Potential of TiO2 Nanoparticles as Carriers for Cadmium Uptake in Lumbriculus Variegatus and Daphnia Magna. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 118–119, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magni, S.; Binelli, A.; Pittura, L.; Avio, C.G.; Della Torre, C.; Parenti, C.C.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. The Fate of Microplastics in an Italian Wastewater Treatment Plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano, M.C.; Pawlak, J.J.; Daystar, J.; Ankeny, M.; Cheng, J.J.; Venditti, R.A. Microfibers Generated from the Laundering of Cotton, Rayon and Polyester Based Fabrics and Their Aquatic Biodegradation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulmine, J.V.; Janissek, P.R.; Heise, H.M.; Akcelrud, L. Polyethylene Characterization by FTIR. Polym. Test. 2002, 21, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.R.; Horgen, F.D.; Orski, S.V.; Rodriguez, C.V.; Beers, K.L.; Balazs, G.H.; Jones, T.T.; Work, T.M.; Brignac, K.C.; Royer, S.-J.; et al. Validation of ATR FT-IR to Identify Polymers of Plastic Marine Debris, Including Those Ingested by Marine Organisms. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chércoles Asensio, R.; San Andrés Moya, M.; de la Roja, J.M.; Gómez, M. Analytical Characterization of Polymers Used in Conservation and Restoration by ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 2081–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowrey, A.; Haynes, J.; Marcott, C. Group Frequency Assignments for Major Infrared Bands Observed in Common Synthetic Polymers. In Physical Properties of Polymers Handbook; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 395–406. [Google Scholar]
- Gardette, M.; Perthue, A.; Gardette, J.-L.; Janecska, T.; Földes, E.; Pukánszky, B.; Therias, S. Photo- and Thermal Oxidation of Polyethylene: Comparison of Mechanisms and Influence of Unsaturation Content. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 2383–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewert, B.; Plassmann, M.; MacLeod, M. Pathways for Degradation of Plastic Polymers Floating in the Marine Environment. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Hay, J.N.; Jenkins, M.J. FTIR Spectroscopic Analysis of Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) on Crystallization. Eur. Polym. J. 2012, 48, 1586–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Causin, V.; Marega, C.; Schiavone, S.; Guardia, V.D.; Marigo, A. Forensic Analysis of Acrylic Fibers by Pyrolysis–Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2006, 75, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, I.; Kiumarsi, A.; Parvinzadeh Gashti, M.; Rashidian, R. Atmospheric-Air Plasma Enhances Coating of Different Lubricating Agents on Polyester Fiber. Eur. Phys. J.-Appl. Phys. 2011, 56, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, K.L.; Lyons, M. Plasma Surface Modification of Polymers: Relevance to Adhesion; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-1-4665-6341-4. [Google Scholar]
- Peets, P.; Leito, I.; Pelt, J.; Vahur, S. Identification and Classification of Textile Fibres Using ATR-FT-IR Spectroscopy with Chemometric Methods. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 173, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, Y.; Isobe, T.; Takada, H.; Kanehiro, H.; Ohtake, C.; Kaminuma, T. Plastic Resin Pellets as a Transport Medium for Toxic Chemicals in the Marine Environment. Environ Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatmullina, L.; Chubarenko, I. Transport of Marine Microplastic Particles: Why Is It so Difficult to Predict? Anthr. Coasts 2019, 2, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberbeckmann, S.; Osborn, A.; Duhaime, M. Microbes on a Bottle: Substrate, Season and Geography Influence Community Composition of Microbes Colonizing Marine Plastic Debris. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalkanen, J.-P.; Johansson, L.; Wilewska-Bien, M.; Granhag, L.; Ytreberg, E.; Eriksson, K.M.; Yngsell, D.; Hassellöv, I.-M.; Magnusson, K.; Raudsepp, U.; et al. Modeling of Discharges from Baltic Sea Shipping; Copernicus Publications: Göttingen, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- International Maritime Organization. Revision of MARPOL Annex IV and Associated Guidelines to Introduce Provisions for Record-Keeping and Measures to Confirm the Lifetime Performance of Sewage Treatment Plants; International Maritime Organization: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rocklöv, J.; Sjödin, H.; Wilder-Smith, A. COVID-19 Outbreak on the Diamond Princess Cruise Ship: Estimating the Epidemic Potential and Effectiveness of Public Health Countermeasures. J. Travel Med. 2020, 27, taaa030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Graywater Discharges from Vessels; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; p. 68. Available online: https://www3.epa.gov/npdes/pubs/vgp_graywater.pdf (accessed on 8 October 2022).
- Ivaninoka, I. Analysis of Sewage Treatment and Control System for Passenger Ships in the Baltic Sea. Master Thesis, Latvian Maritime Academy, Riga, Latvia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.-J.; Hu, H.-Y.; Tang, F.; Li, Y.; Lu, S.-Q.; Lu, Y. Inactivation and Reactivation of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria by Chlorination in Secondary Effluents of a Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2775–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E. Advantages and Disadvantages of Techniques Used for Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanags, M.; Mežule, L.; Spule, A.; Kostjukovs, J.; Šmits, K.; Tamm, A.; Juhna, T.; Vihodceva, S.; Käämbre, T.; Baumane, L.; et al. Rapid Catalytic Water Disinfection from Earth Abundant Ca2Fe2O5 Brownmillerite. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2021, 5, 2100130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkola, O. Estimating Microplastic Concentrations and Loads in Cruise Ship Grey Waters. Master’s Thesis, Aalto University, Espoo, Finland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kalnina, R.; Demjanenko, I.; Drunka, R.; Smilgainis, K. Photocatalytic Disinfection: Direction for the Treatment of Ship “Greywater” from Pathogens and Difficult-to-Degrade Organic Compounds. In Proceedings of the 26th International Scientific Conference, Transport Means 2022, Kaunas University of Technology, Kaunas, Lithuania, 5–7 October 2022. [Google Scholar]





| Identified Particles in Grey Water and Treated Sewage Samples | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Morphotypes MP Particles | Shape of Fibres | Another Hard Matrix | Soft Matrix (Film) | ||||
| Applied Filter Mesh Opening Size Range, µm | 0.7–100 | 100–300 | 0.7–100 | 100–300 | 0.7–100 | 100–300 | |
| The number of MPs per 1 L in tested samples | GW1 | 20 | 8 | 10 | 14 | 5 | 10 |
| TS1 | 11 | 3 | 9 | 12 | 5 | 8 | |
| GW2 | 23 | 9 | 8 | 17 | 7 | 9 | |
| TS2 | 11 | 5 | 6 | 16 | 5 | 6 | |
| GW3 | 27 | 5 | 8 | 14 | 8 | 12 | |
| TS3 | 22 | 5 | 7 | 12 | 2 | 3 | |
| GW4 | 28 | 11 | 10 | 14 | 3 | 5 | |
| TS4 | 19 | 10 | 8 | 13 | 2 | 1 | |
| GW5 | 29 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 2 | 8 | |
| TS5 | 20 | 9 | 10 | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| Total number of MP particles, pcs. | 211 | 74 | 88 | 138 | 41 | 63 | |
| Average number of MP particles, pcs. | 21 | 7 | 9 | 14 | 4 | 6 | |
| Percentage of all detected MP particles, % | 34 | 12 | 14 | 23 | 7 | 10 | |
| GW Samples | Particles/L | TS Sample | Particles/L | Percentage of All Retained Particles, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GW1 | 67 | TS1 | 48 | 28 |
| GW2 | 73 | TS2 | 49 | 33 |
| GW3 | 74 | TS3 | 51 | 30 |
| GW4 | 71 | TS4 | 53 | 25 |
| GW5 | 75 | TS5 | 53 | 29 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalnina, R.; Demjanenko, I.; Smilgainis, K.; Lukins, K.; Bankovics, A.; Drunka, R. Microplastics in Ship Sewage and Solutions to Limit Their Spread: A Case Study. Water 2022, 14, 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223701
Kalnina R, Demjanenko I, Smilgainis K, Lukins K, Bankovics A, Drunka R. Microplastics in Ship Sewage and Solutions to Limit Their Spread: A Case Study. Water. 2022; 14(22):3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223701
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalnina, Renate, Ieva Demjanenko, Kristaps Smilgainis, Kristaps Lukins, Arnis Bankovics, and Reinis Drunka. 2022. "Microplastics in Ship Sewage and Solutions to Limit Their Spread: A Case Study" Water 14, no. 22: 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223701
APA StyleKalnina, R., Demjanenko, I., Smilgainis, K., Lukins, K., Bankovics, A., & Drunka, R. (2022). Microplastics in Ship Sewage and Solutions to Limit Their Spread: A Case Study. Water, 14(22), 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223701






