Agroclimatic Zone-Based Analysis of Rainfall Variability and Trends in the Wabi Shebele River Basin, Ethiopia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
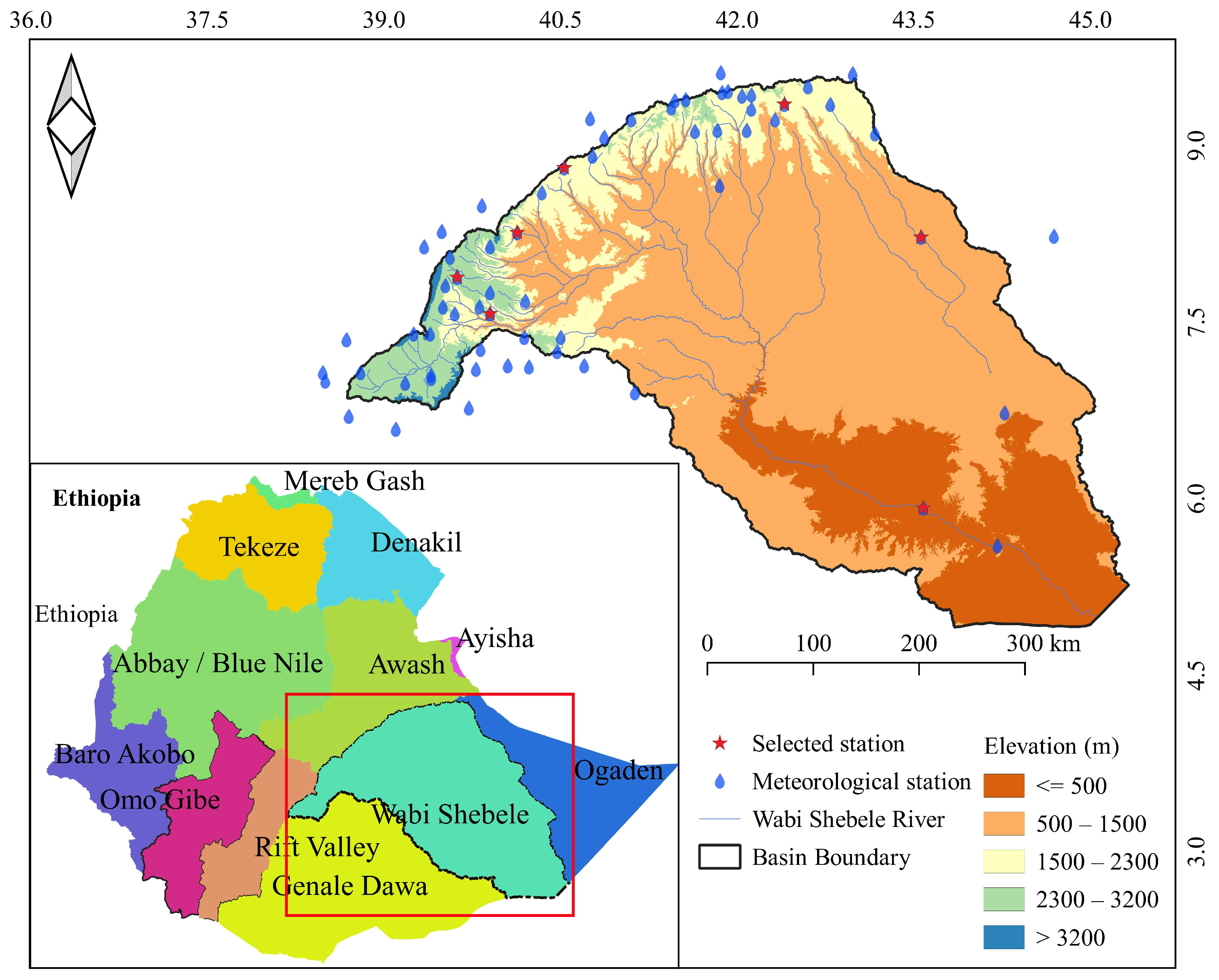
2.1. Study Area
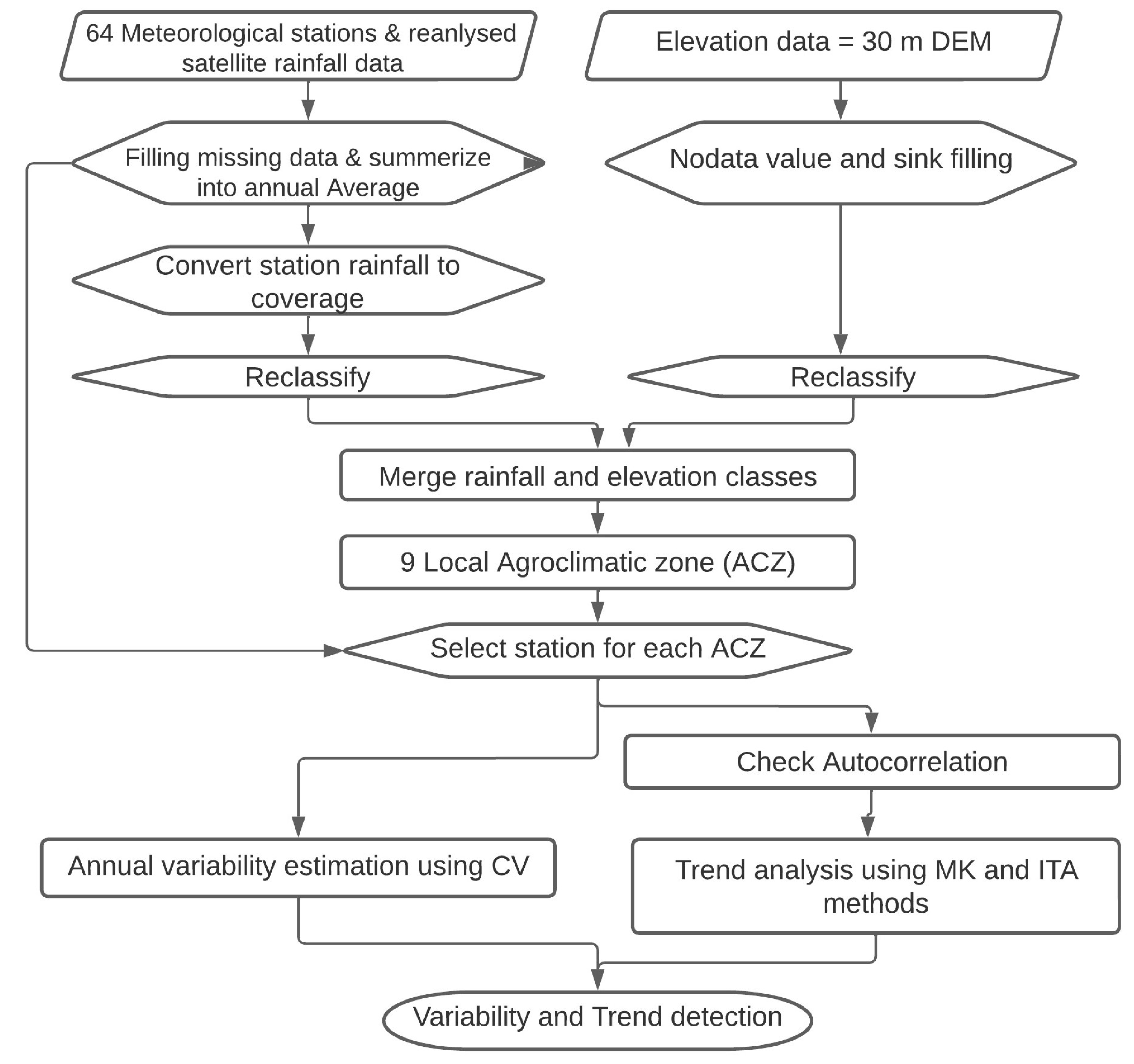
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Data Source and Preparation
2.2.2. Agroclimatic Zonation
2.2.3. Rainfall Seasonal and Annual Variability
2.2.4. Rainfall Trend Analysis
3. Results
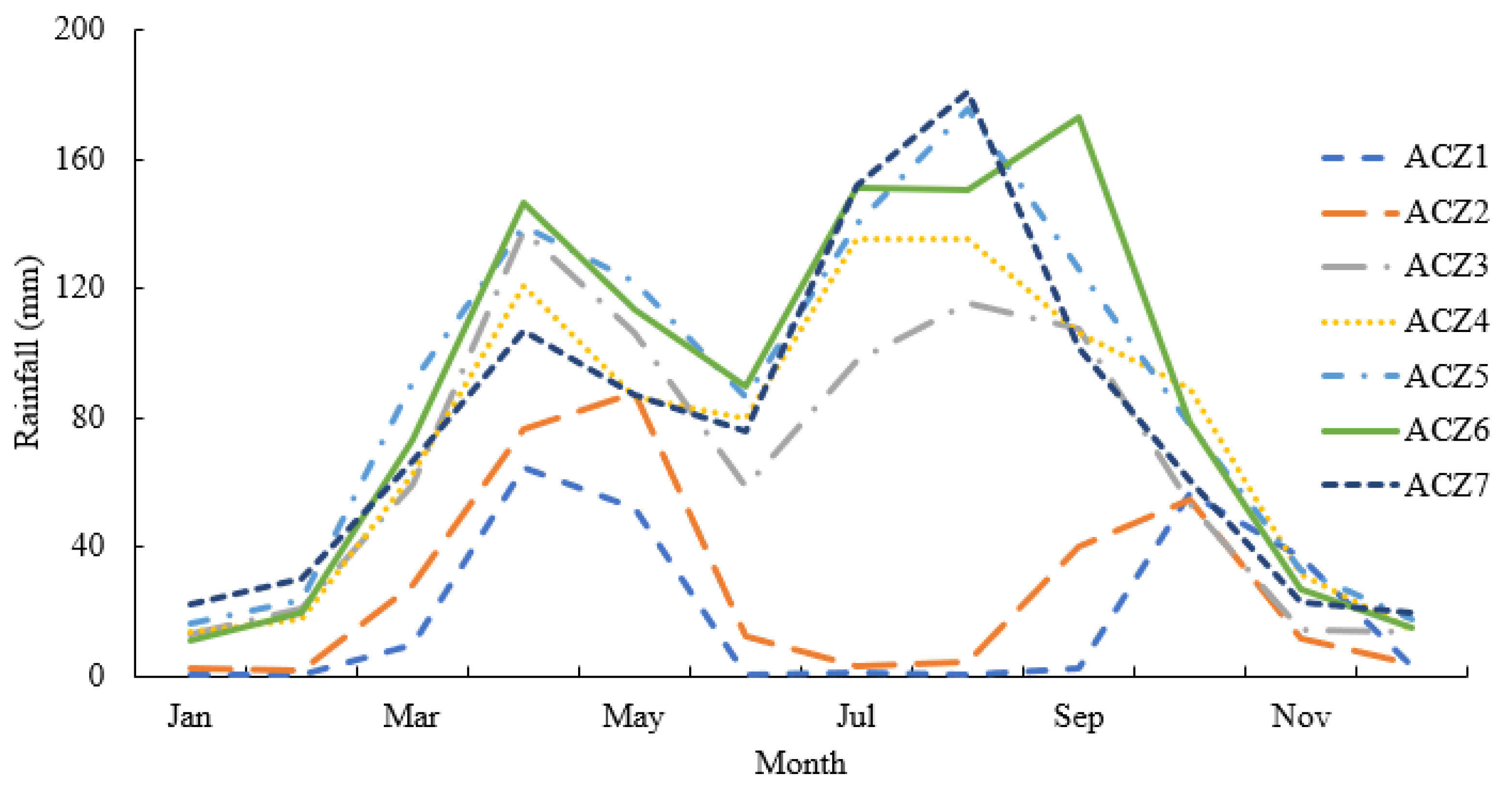
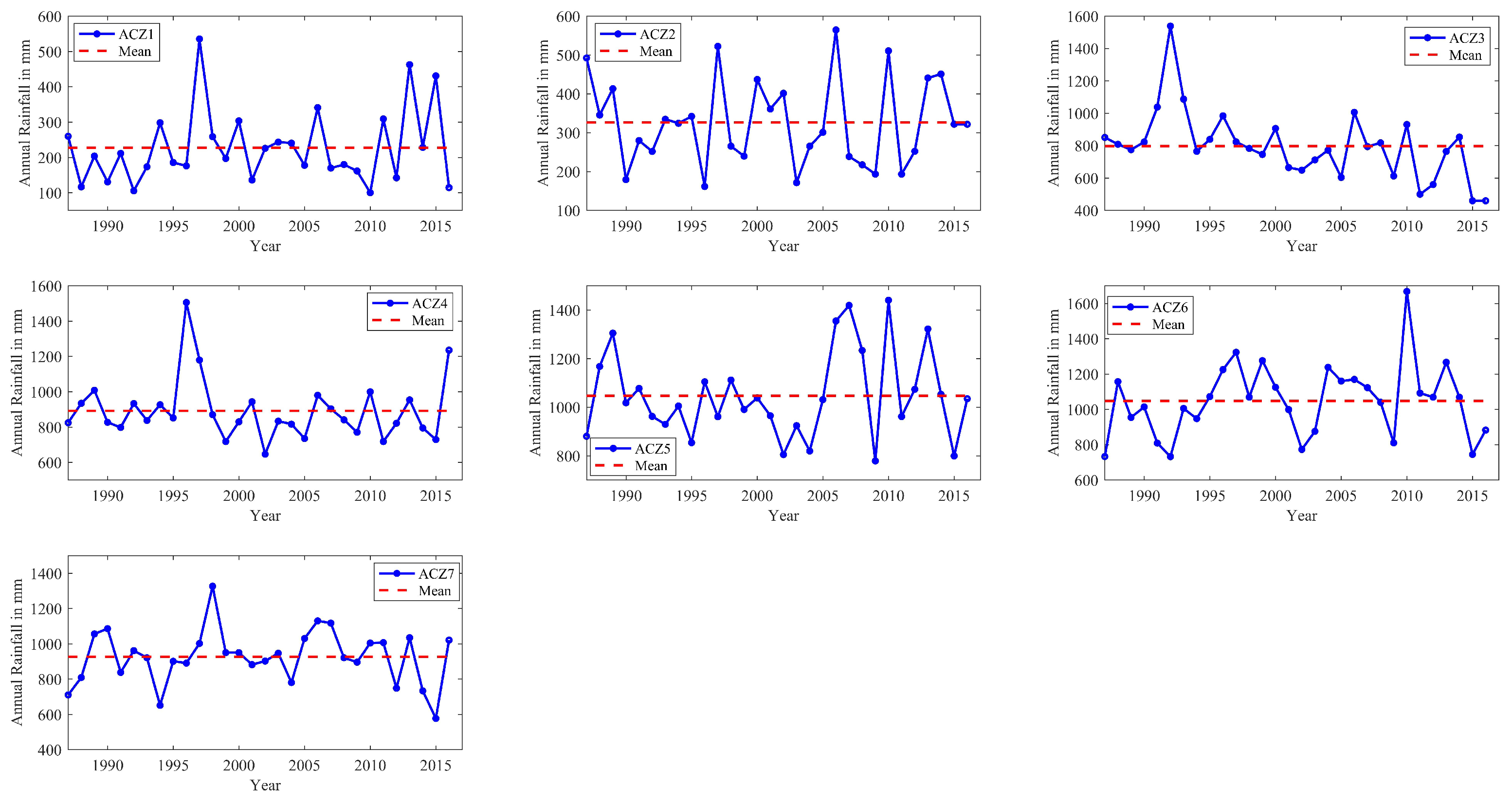
3.1. Rainfall Distribution and Variability
3.2. Trend Analysis
3.2.1. MK and Sen’s Slope Test
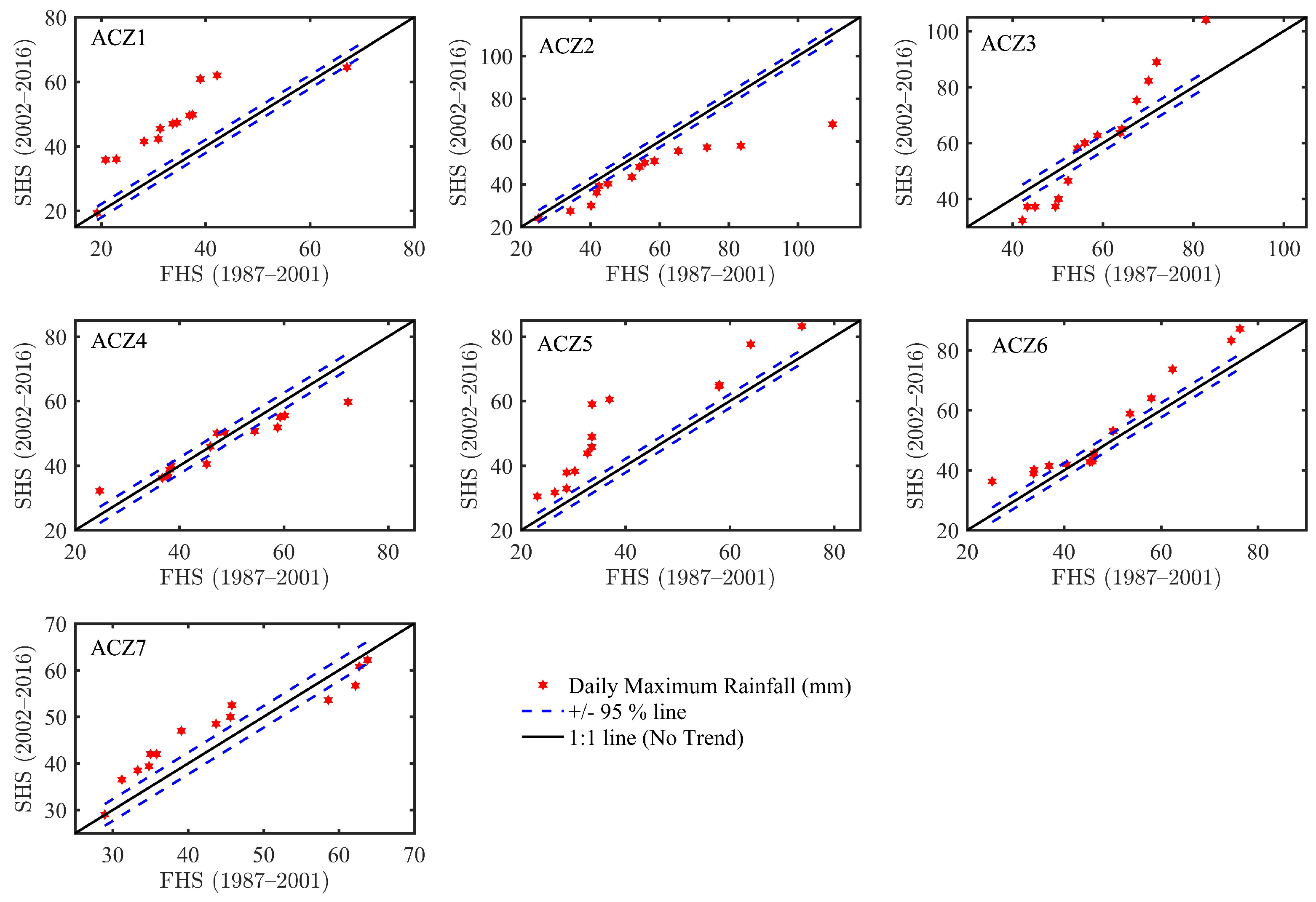
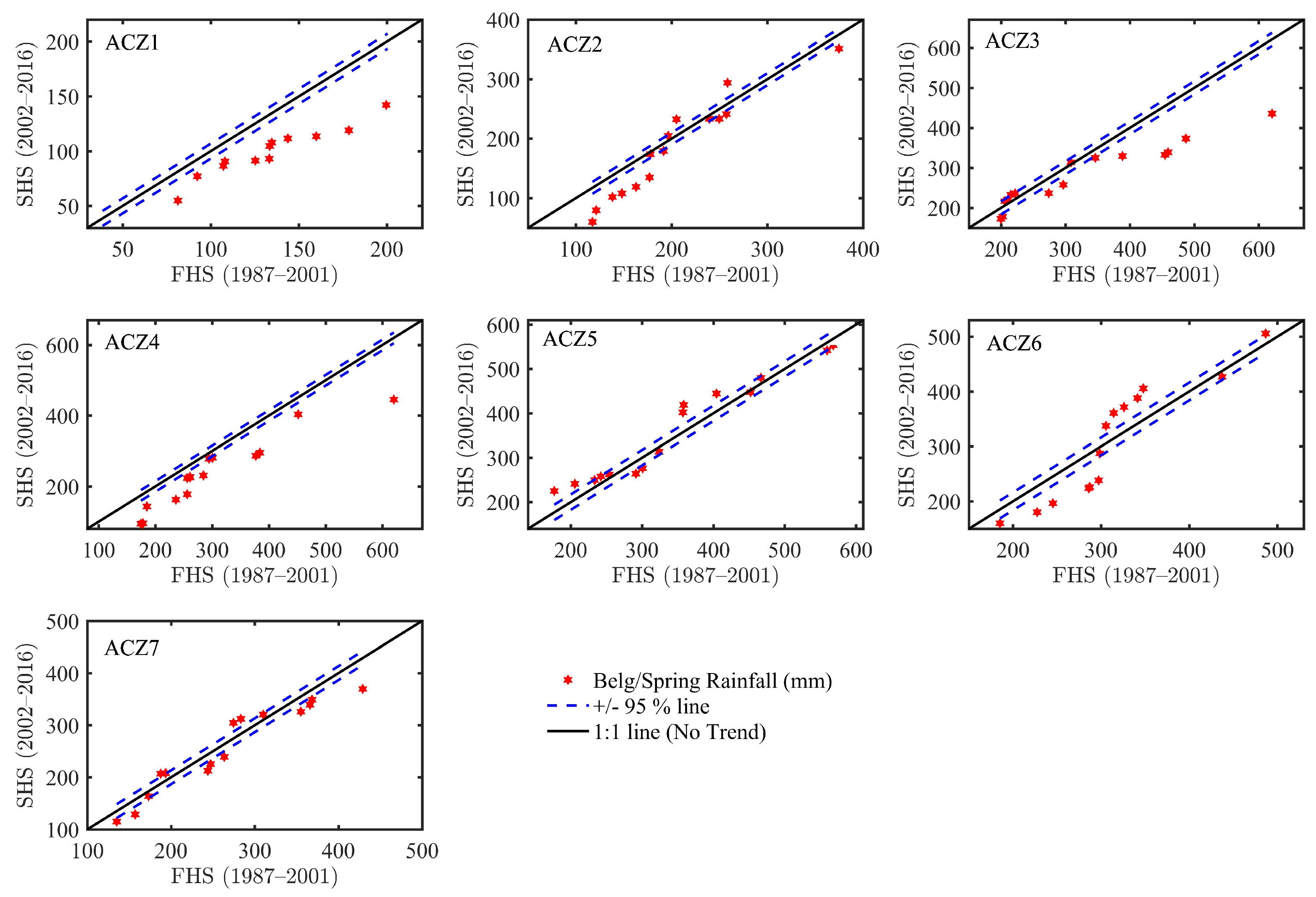
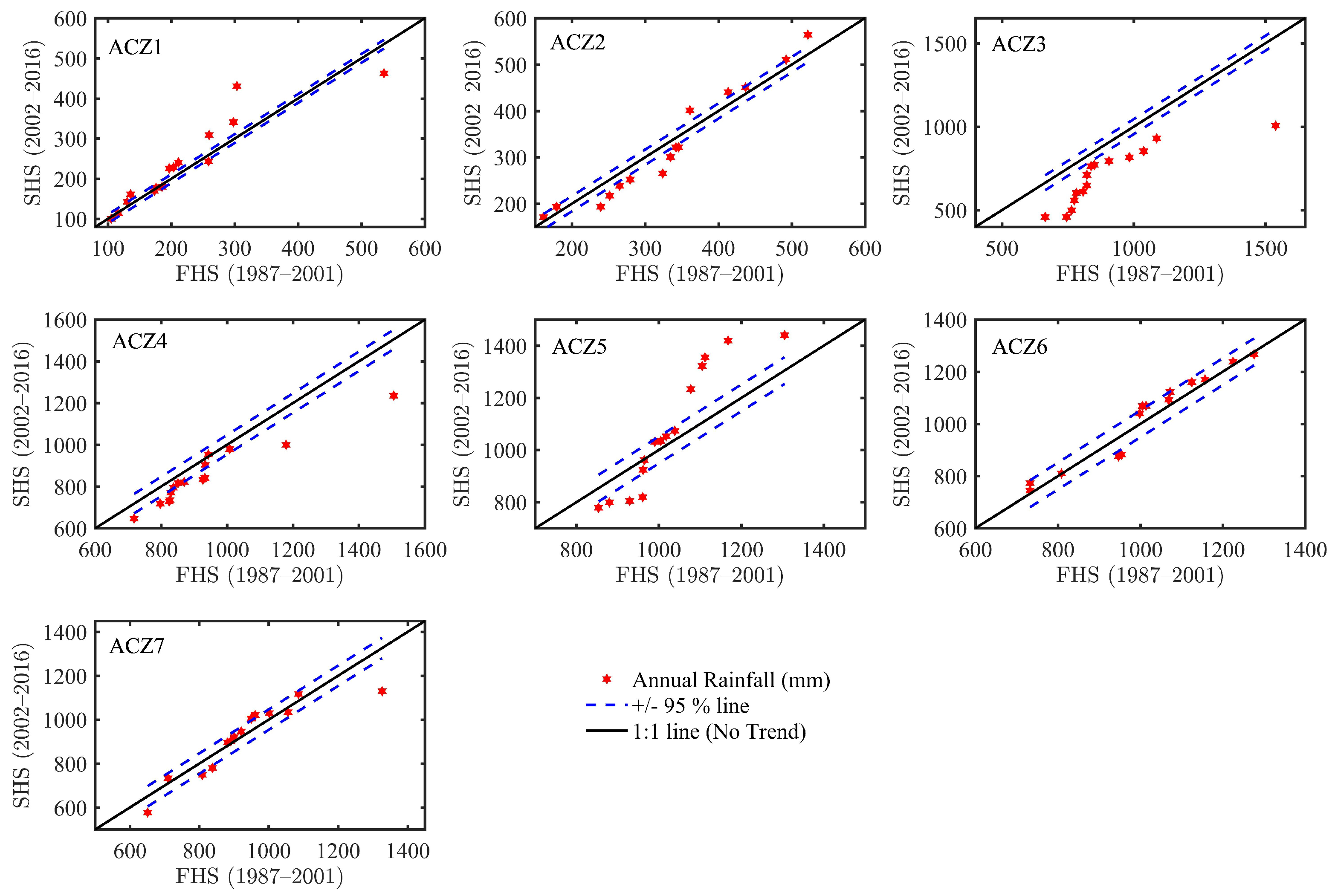
3.2.2. ITA Method
4. Discussion
4.1. Rainfall Variability in the Basin
4.2. Rainfall Trend
MK and ITA Method Comparison
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Eds.; Technical Report; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021; in press. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The State of Food and Agriculture: Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security; Report; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability; Part A: Global and Sectoral Aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Technical Report; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, W.H.; Senay, G.B.; Singh, A. Trends and spatial distribution of annual and seasonal rainfall in Ethiopia. Int. J. Climatol. 2008, 28, 1723–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degefu, M.A.; Bewket, W. Variability, trends, and teleconnections of stream flows with large-scale climate signals in the Omo-Ghibe River Basin, Ethiopia. Environ. Monit. Assess 2017, 189, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addisu, S.; Selassie, Y.G.; Fissha, G.; Gedif, B. Time series trend analysis of temperature and rainfall in lake Tana Sub-basin, Ethiopia. Environ. Syst. Res. 2015, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Admassu, S.; Seid, A.H. Analysis of rainfall trend in Ethiopia. Eth. J. Sci. Technol. 2006, 3, 15–30. [Google Scholar]
- NMSA. Climate Change National Adaptation Programme of Action (NAPA) of Ethiopia; Technical Report; National Meteorological Agency: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2007.
- Alemayehu, A.; Maru, M.; Bewket, W.; Assen, M. Spatiotemporal variability and trends in rainfall and temperature in Alwero watershed, western Ethiopia. Environ. Syst. Res. 2020, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Men, B.H.; Lin, C.K. Impact analysis of climate change on water resources. Procedia Eng. 2011, 24, 643–648. [Google Scholar]
- Hänsel, S.; Petzold, S.; Matschullat, J. Precipitation trend analysis for Central Eastern Germany. In Bioclimatology and Natural Hazards; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, H.B. Non-Parametric Test Against Trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the Regression Coefficient Based on Kendall’s Tau. JASA 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aamir, E.; Hassan, I. Trend analysis in precipitation at individual and regional levels in Baluchistan, Pakistan. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 414, 012042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ademe, D.; Ziatchik, B.F.; Tesfaye, K.; Simane, B.; Alemayehu, G.; Adgo, E. Climate trends and variability at adaptation scale: Patterns and perceptions in an agricultural region of the Ethiopian Highlands. Weather. Clim. Extrem. 2020, 29, 100263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Tang, D.; Wang, T.; Wang, M.; Wagan, B. Precipitation trends over time using Mann-Kendall and spearman’s Rho tests in swat river basin, Pakistan. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015, 431860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alemu, Z.A.; Dioha, M.O. Climate change and trend analysis of temperature: The case of Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Environ. Syst. Res. 2020, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayable, G.; Amare, G.; Alemu, G.; Gashaw, T. Spatiotemporal variability and trends of rainfall and its association with Pacific Ocean Sea surface temperature in West Harerge Zone, Eastern Ethiopia. Environ. Syst. Res. 2021, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhane, A.; Hadgu, G.; Worku, W.; Abrha, B. Trends in extreme temperature and rainfall indices in the semi-arid areas of Western Tigray, Ethiopia. Environ. Syst. Res. 2020, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Edwards, D.R. Long-term trend analysis of precipitation and air temperature for Kentucky, United States. Climate 2016, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degefu, M.A.; Bewket, W. Trends and spatial patterns of drought incidence in the Omo-Ghibe River Basin, Ethiopia. Geogr. Ann. Ser. Phys. Geogr. 2015, 97, 395–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orke, Y.A.; Li, M.H. Hydroclimatic variability in the bilate watershed, ethiopia. Climate 2021, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şen, Z. Innovative Trend Analysis Methodology. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2012, 17, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alifujiang, Y.; Abuduwaili, J.; Maihemuti, B.; Emin, B.; Groll, M. Innovative trend analysis of precipitation in the Lake Issyk-Kul Basin, Kyrgyzstan. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gedefaw, M.; Yan, D.; Wang, H.; Qin, T.; Girma, A.; Abiyu, A.; Batsuren, D. Innovative trend analysis of annual and seasonal rainfall variability in Amhara Regional State, Ethiopia. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harka, A.E.; Jilo, N.B.; Behulu, F. Spatial-temporal rainfall trend and variability assessment in the Upper Wabe Shebelle River Basin, Ethiopia: Application of innovative trend analysis method. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2021, 37, 100915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şen, Z. Hydrological trend analysis with innovative and over-whitening procedures. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2017, 62, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caloiero, T. Evaluation of rainfall trends in the South Island of New Zealand through the innovative trend analysis (ITA). Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2020, 139, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaw, A.; Simane, B.; Hassen, A.; Bantider, A. Variability and time series trend analysis of rainfall and temperature in northcentral Ethiopia: A case study in Woleka sub-basin. Weather. Clim. Extrem. 2018, 19, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taye, M.; Simane, B.; Zaitchik, B.F.; Selassie, Y.G.; Setegn, S. Rainfall variability across the agro-climatic zones of a tropical highland: The case of the jema watershed, northwestern ethiopia. Environments 2019, 6, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esayas, B.; Simane, B.; Teferi, E.; Ongoma, V.; Tefera, N. Trends in extreme climate events over three agroecological zones of Southern Ethiopia. Adv. Meteorol. 2018, 2018, 7354157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyene, A.N. Precipitation and Temperature Trend Analysis in Mekelle city, Northern Ethiopia, the Case of Illala Meteorological Station. J. Earth Sci. Clim. Chang. 2015, 7, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banerjee, A.; Chen, R.; Meadows, M.E.; Singh, R.B.; Mal, S.; Sengupta, D. An analysis of long-term rainfall trends and variability in the uttarakhand himalaya using google earth engine. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tekleab, S.; Mohamed, Y.; Uhlenbrook, S. Hydro-climatic trends in the Abay/Upper Blue Nile basin, Ethiopia. Phys. Chem. Earth 2013, 61, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weldegerima, T.M.; Zeleke, T.T.; Birhanu, B.S.; Zaitchik, B.F.; Fetene, Z.A. Analysis of Rainfall Trends and Its Relationship with SST Signals in the Lake Tana Basin, Ethiopia. Adv. Meteorol. 2018, 2018, 5869010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eshetu, M. Hydro-Climatic Variability and Trend Analysis of Modjo River Watershed, Awash River Basin of Ethiopia. Hydrol. Curr. Res. 2020, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Shawul, A.A.; Chakma, S. Trend of extreme precipitation indices and analysis of long-term climate variability in the Upper Awash basin, Ethiopia. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2020, 140, 635–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadese, M.T.; Kumar, L.; Koech, R.; Zemadim, B. Hydro-climatic variability: A characterisation and trend study of the Awash River Basin, Ethiopia. Hydrology 2019, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrehiwot, T. Assessing the evidence of climate variability in the northern part of Ethiopia. J. Dev. Agric. Econ. 2013, 5, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bekele-Tesemma, A. Useful Trees and Shrubs for Ethiopia: Identification, Propagation and Management in 17 Agro-Ecological Zones; Technical Report; RELMA in ICRAF Project: Nairobi, Kenya, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersson, H. A homogeneity test applied to precipitation data. Int. J. Climatol. 1986, 6, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettitt, A.N. A Non-Parametric Approach to the Change-Point Problem. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C Appl. Stat. 1979, 28, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzopy, K.A.; Chaturvedi, A.K.; Chandrana, K.M.; Gopinath, G.; Naveena, K.; Surendran, U. Trend analysis of long-term rainfall and temperature data for Ethiopia. S. Afr. Geogr. J. 2020, 103, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, K.H. Enhancing the effectiveness of prewhitening in trend analysis of hydrologic data. J. Hydrol. 2009, 368, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Pilon, P.; Phinney, B.; Cavadias, G. The influence of autocorrelation on the ability to detect trend in hydrological series. Hydrol. Process. 2002, 16, 1807–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, K.H.; Rao, A.R. A modified Mann-Kendall trend test for autocorrelated data. J. Hydrol. 1998, 204, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Pilon, P. A comparison of the power of the t test, Mann-Kendall and bootstrap tests for trend detection. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2004, 49, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patakamuri, S.K.; O’Brien, N. Modified Versions of Mann Kendall and Spearman’s Rho Trend Tests; R Package ‘Modifiedmk’. 2021. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/modifiedmk/index.html (accessed on 7 August 2022).
- Patakamuri, S.K.; Das, B. R Package ‘Trendchange’: Innovative Trend Analysis and Time-Series Change Point Analysis Version 1.2. 2022. Available online: https://www.skpatakamuri.com/_files/ugd/8339fc_71634dfc92794ccea524fa36bfb1d529.pdf?index=true (accessed on 7 August 2022).
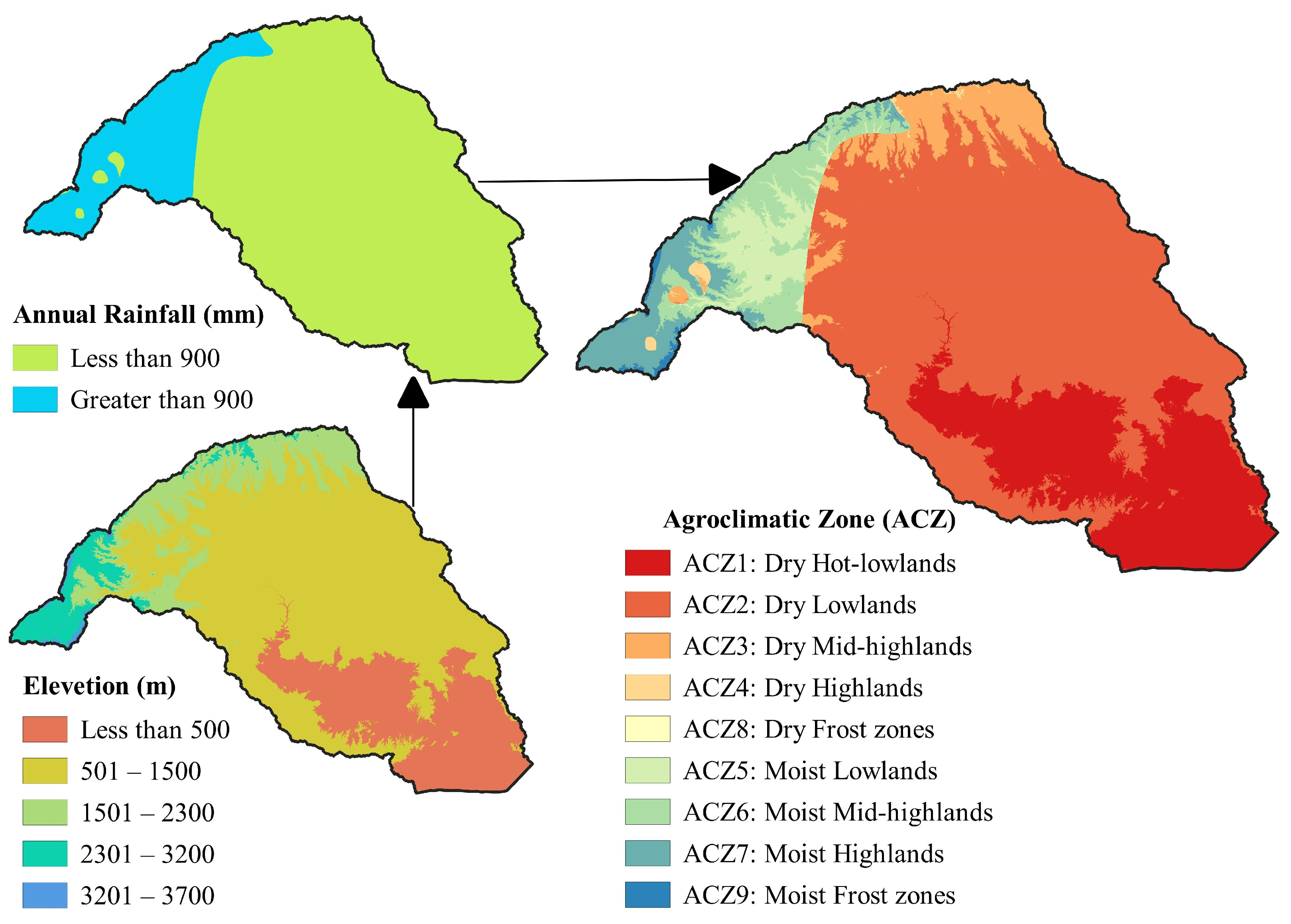


| ACZ: Agroclimatic Zones | MAR (mm) | Elevation (m) | Area | Selected Station | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Km2 | % | Site | Latitude | Longitude | Elevation (m) | |||
| ACZ1: Dry Bereha (Hot-lowlands) | Less than 900 (Dry = Arid and Semi-Arid) | <500 | 42,113.71 | 22.20 | Gode | 5.92 | 43.58 | 290 |
| ACZ2: Dry Kolla (Lowlands) | 500–1500 | 104,350.7 | 55.00 | Degahabour | 8.22 | 43.56 | 1070 | |
| ACZ3: Dry Weyna Dega (Midlands) | 1500–2300 | 11,973.94 | 6.31 | Gursum | 9.35 | 42.4 | 1900 | |
| ACZ4: Dry Dega (Highlands) | 2300–3200 | 795.35 | 0.42 | Indeto | 7.57 | 39.9 | 2416 | |
| ACZ8: Dry Wurch (Frost zones) | 3200–3700 | 37.46 | 0.02 | Not Available | ||||
| ACZ5: Moist Kolla (Lowlands) | Greater than 900 (Moist = humid) | 500–1500 | 7599.37 | 4.01 | Gololcha | 8.26 | 40.13 | 1372 |
| ACZ6: Moist Weyna Dega (Midlands) | 1500–2300 | 12,489 | 6.59 | Bedessa | 8.91 | 40.77 | 1703 | |
| ACZ7: Moist Dega (Highlands) | 2300–3200 | 9335.57 | 4.92 | Arsi Robe | 7.88 | 39.62 | 2441 | |
| ACZ9: Moist Wurch (Frost zones) | 3200–3700 | 960.6 | 0.51 | Not Available | ||||
| Total Area | 189,655.7 | 100 | ||||||
| Zone | Spring | Summer | Annual | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pettitt | SNHT | Pettitt | SNHT | Pettitt | SNHT | |
| ACZ1 | 0.19 | 0.36 | 0.3 | 0.21 | 0.74 | 0.63 |
| ACZ2 | 0.51 | 0.08 | 0.56 | 0.69 | 0.21 | 0.78 |
| ACZ3 | 0.31 | 0.14 | 0.25 | 0.04 * | 0.02 * | 0.11 |
| ACZ4 | 0.04 * | 0.13 | 0.27 | 0.46 | 0.54 | 0.35 |
| ACZ5 | 0.53 | 0.13 | 0.69 | 0.49 | 0.82 | 0.42 |
| ACZ6 | 0.02 * | 0.93 | 0.68 | 0.11 | 0.29 | 0.36 |
| ACZ7 | 0.73 | 0.33 | 0.23 | 0.04 * | 0.41 | 0.59 |
| Temporal Scale | Spatial Zone | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Variance | SD | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daily Maximum | ACZ1 | 19.2 | 106.6 | 47.0 | 485.7 | 22.0 | 46.9 |
| ACZ2 | 24.0 | 110.0 | 49.8 | 324.1 | 18.0 | 36.1 | |
| ACZ3 | 32.3 | 104.0 | 58.8 | 289.7 | 17.0 | 29.0 | |
| ACZ4 | 24.7 | 84.0 | 49.2 | 182.8 | 13.5 | 27.5 | |
| ACZ5 | 23.1 | 90.6 | 48.4 | 379.8 | 19.5 | 40.3 | |
| ACZ6 | 25.1 | 95.0 | 51.5 | 291.2 | 17.1 | 33.2 | |
| ACZ7 | 28.9 | 129.6 | 50.0 | 385.2 | 19.6 | 39.2 | |
| Belg/Spring | ACZ1 | 26.9 | 300.4 | 126.4 | 3378.2 | 58.1 | 46.0 |
| ACZ2 | 59.9 | 374.8 | 192.1 | 5597.7 | 74.8 | 39.0 | |
| ACZ3 | 172.7 | 620.8 | 302.9 | 11,528.2 | 107.4 | 35.4 | |
| ACZ4 | 94.3 | 620.1 | 269.6 | 12,519.6 | 111.9 | 41.5 | |
| ACZ5 | 176.7 | 568.1 | 352.4 | 13,764.8 | 117.3 | 33.3 | |
| ACZ6 | 160.0 | 818.4 | 333.3 | 17,183.4 | 131.1 | 39.3 | |
| ACZ7 | 115.0 | 429.0 | 260.3 | 7020.0 | 83.8 | 32.2 | |
| Kiremt/Summer | ACZ1 | 0.0 | 338.8 | 95.5 | 6966.1 | 83.5 | 87.4 |
| ACZ2 | 16.7 | 299.3 | 106.7 | 5397.0 | 73.5 | 68.9 | |
| ACZ3 | 154.8 | 631.7 | 379.4 | 11,143.4 | 105.6 | 27.8 | |
| ACZ4 | 275.9 | 851.3 | 456.0 | 15,727.2 | 125.4 | 27.5 | |
| ACZ5 | 334.0 | 1009.7 | 527.8 | 17,850.9 | 133.6 | 25.3 | |
| ACZ6 | 181.5 | 882.2 | 563.7 | 23,640.9 | 153.8 | 27.3 | |
| ACZ7 | 205.3 | 801.4 | 510.2 | 12,350.2 | 111.1 | 21.8 | |
| Annual | ACZ1 | 100.1 | 535.3 | 227.2 | 11,275.1 | 106.2 | 46.7 |
| ACZ2 | 161.4 | 564.3 | 326.3 | 12,731.6 | 112.8 | 34.6 | |
| ACZ3 | 459.1 | 1538.4 | 797.2 | 45,085.9 | 212.3 | 26.6 | |
| ACZ4 | 646.1 | 1505.2 | 892.0 | 29,667.9 | 172.2 | 19.3 | |
| ACZ5 | 778.4 | 1440.3 | 1047.2 | 33,181.4 | 182.2 | 17.4 | |
| ACZ6 | 732.4 | 1667.5 | 1047.4 | 42,891.4 | 207.1 | 19.8 | |
| ACZ7 | 576.9 | 1326.3 | 926.0 | 23,943.1 | 154.7 | 16.7 |
| No | Zones | Daily Maximum | Spring | Summer | Annual | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z-Value | Sen’s Slope | Z-Value | Sen’s Slope | Z-Value | Sen’s Slope | Z-Value | Sen’s Slope | ||
| 1 | ACZ1 | 2.78 ** | 1.02 | −0.82 | −1.00 | 1.53 | 3.27 | 0.46 | 0.85 |
| 2 | ACZ2 | −1.62 | −0.53 | −0.62 | −0.85 | 0.14 | 0.16 | −0.29 | −0.59 |
| 3 | ACZ3 | −0.66 | −0.28 | −1.03 | −2.38 | −2.00 * | −3.97 | −8.59 ** | −12.3 |
| 4 | ACZ4 | 0.80 | 0.15 | −2.32 * | −4.11 | 1.46 | 3.36 | −0.86 | −1.96 |
| 5 | ACZ5 | 2.66 ** | 0.72 | −0.25 | −0.47 | 1.46 | 3.33 | 0.21 | 0.97 |
| 6 | ACZ6 | 3.28 ** | 0.52 | −0.36 | −1.1 | 1.36 | 5.84 | 0.77 | 3.73 |
| 7 | ACZ7 | 0.57 | 0.18 | −0.86 | −2.22 | 1.61 | 3.65 | 0.32 | 1.54 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toni, A.T.; Malcherek, A.; Kassa, A.K. Agroclimatic Zone-Based Analysis of Rainfall Variability and Trends in the Wabi Shebele River Basin, Ethiopia. Water 2022, 14, 3699. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223699
Toni AT, Malcherek A, Kassa AK. Agroclimatic Zone-Based Analysis of Rainfall Variability and Trends in the Wabi Shebele River Basin, Ethiopia. Water. 2022; 14(22):3699. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223699
Chicago/Turabian StyleToni, Abebe Teklu, Andreas Malcherek, and Asfaw Kebede Kassa. 2022. "Agroclimatic Zone-Based Analysis of Rainfall Variability and Trends in the Wabi Shebele River Basin, Ethiopia" Water 14, no. 22: 3699. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223699
APA StyleToni, A. T., Malcherek, A., & Kassa, A. K. (2022). Agroclimatic Zone-Based Analysis of Rainfall Variability and Trends in the Wabi Shebele River Basin, Ethiopia. Water, 14(22), 3699. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223699






