The Preparation of a Lignosulfonate/Chitosan–Graphene Oxide Hydrogel Biosorbent to Effectively Remove Cr(VI) from Wastewater: Adsorption Performance and Mechanisms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Synthesis of LCGH
2.3. Characterizations
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
2.5. Reusability Study
3. Results and Discussion
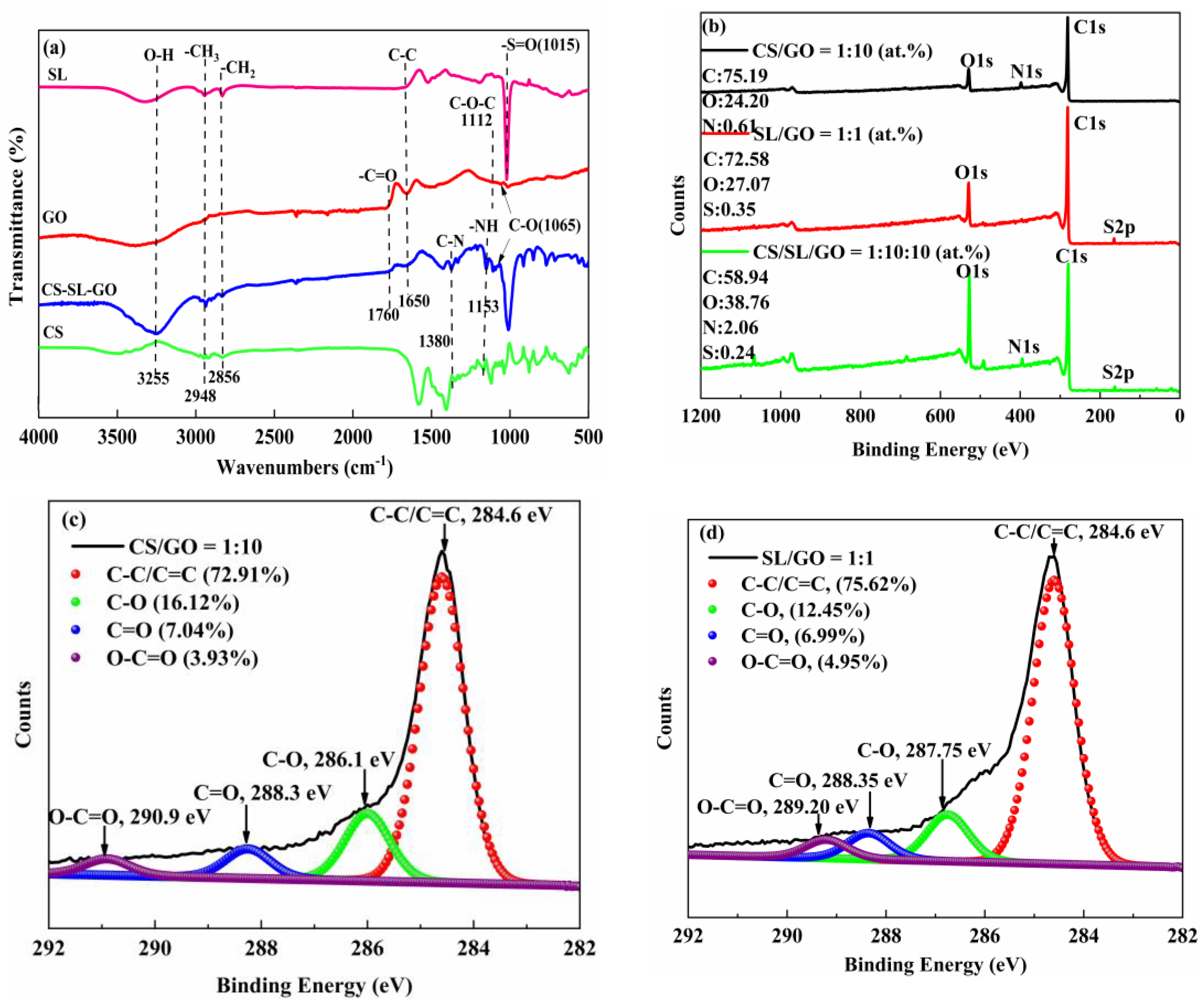
3.1. Characterization of LCGH
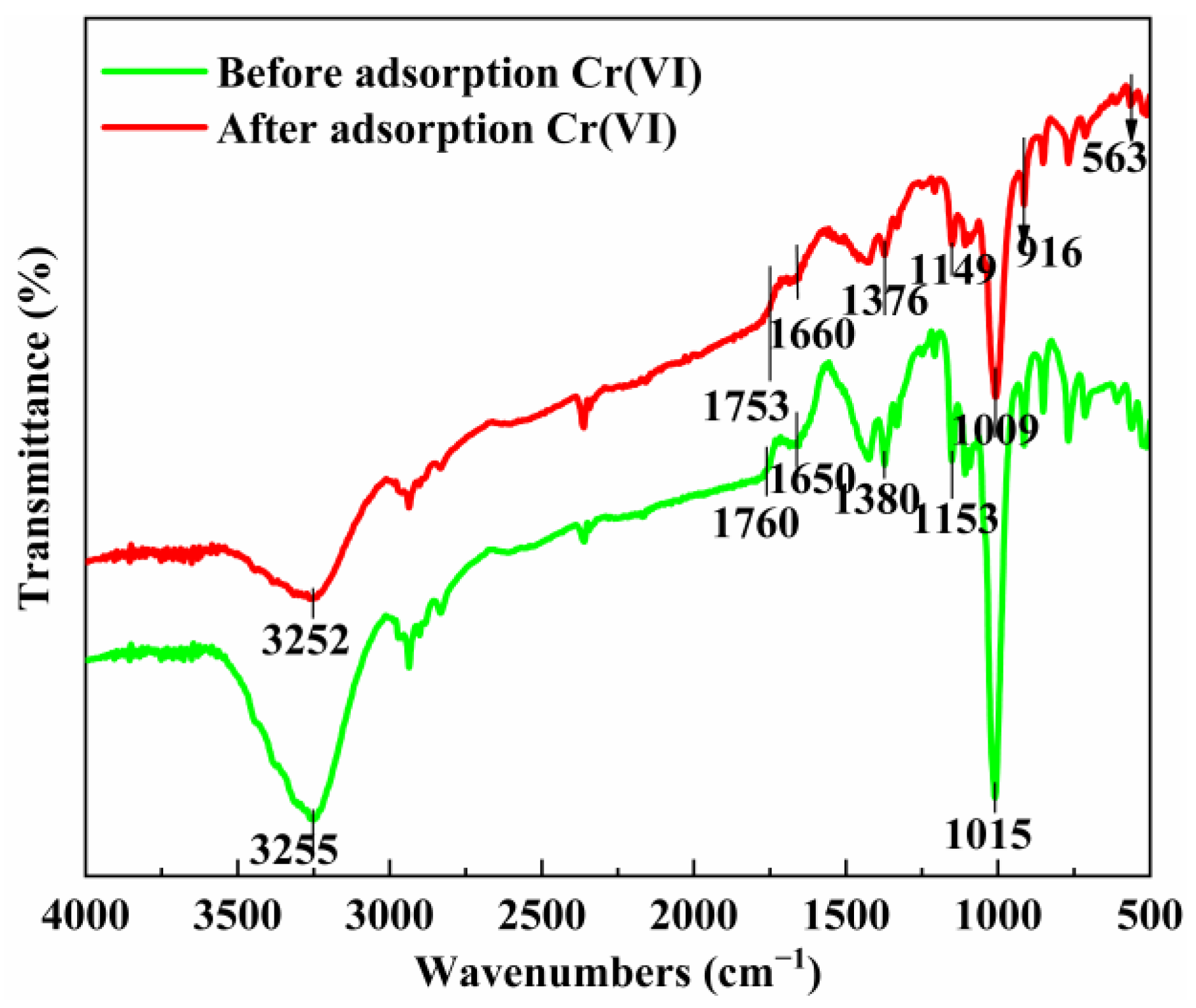
3.1.1. FT-IR
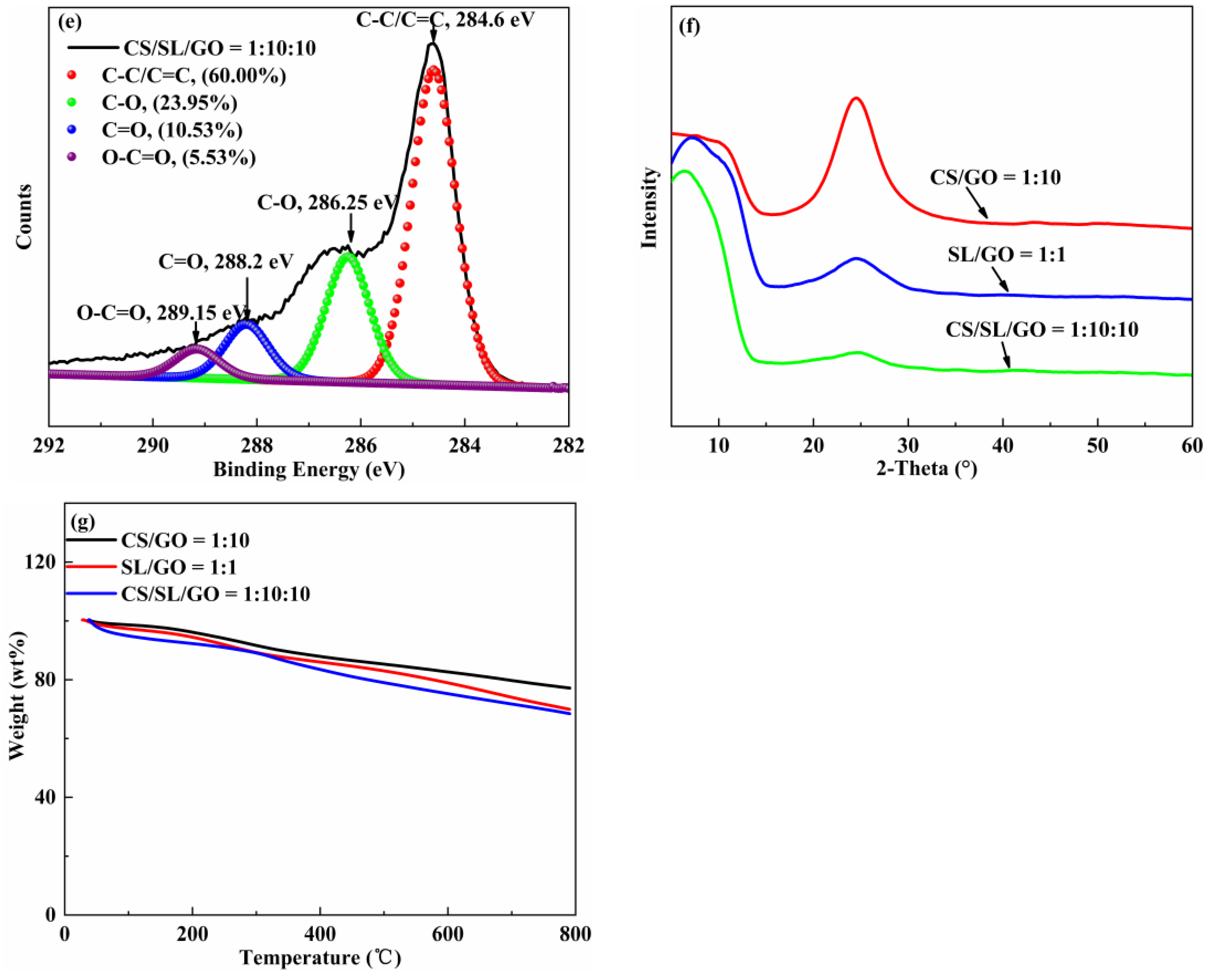
3.1.2. XPS
3.1.3. XRD
3.1.4. TGA
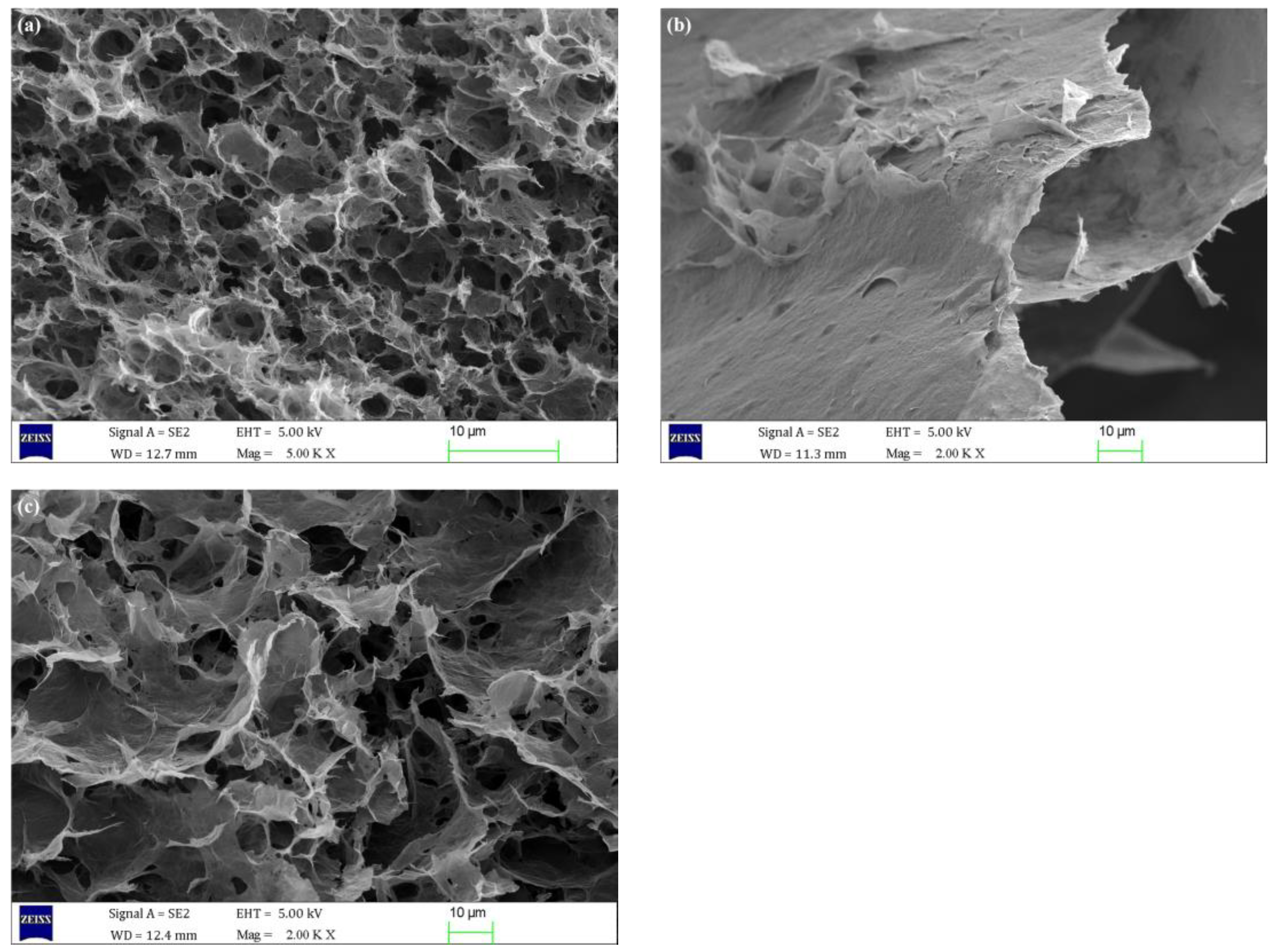
3.1.5. SEM
3.2. Adsorption Experiments
3.2.1. The Effect of Mass Ratio of CS/SL/GO
3.2.2. Influence of pH
3.2.3. Isoelectric Point Analysis
3.3. Theoretical Study of Cr(VI) Adsorption on LCGH
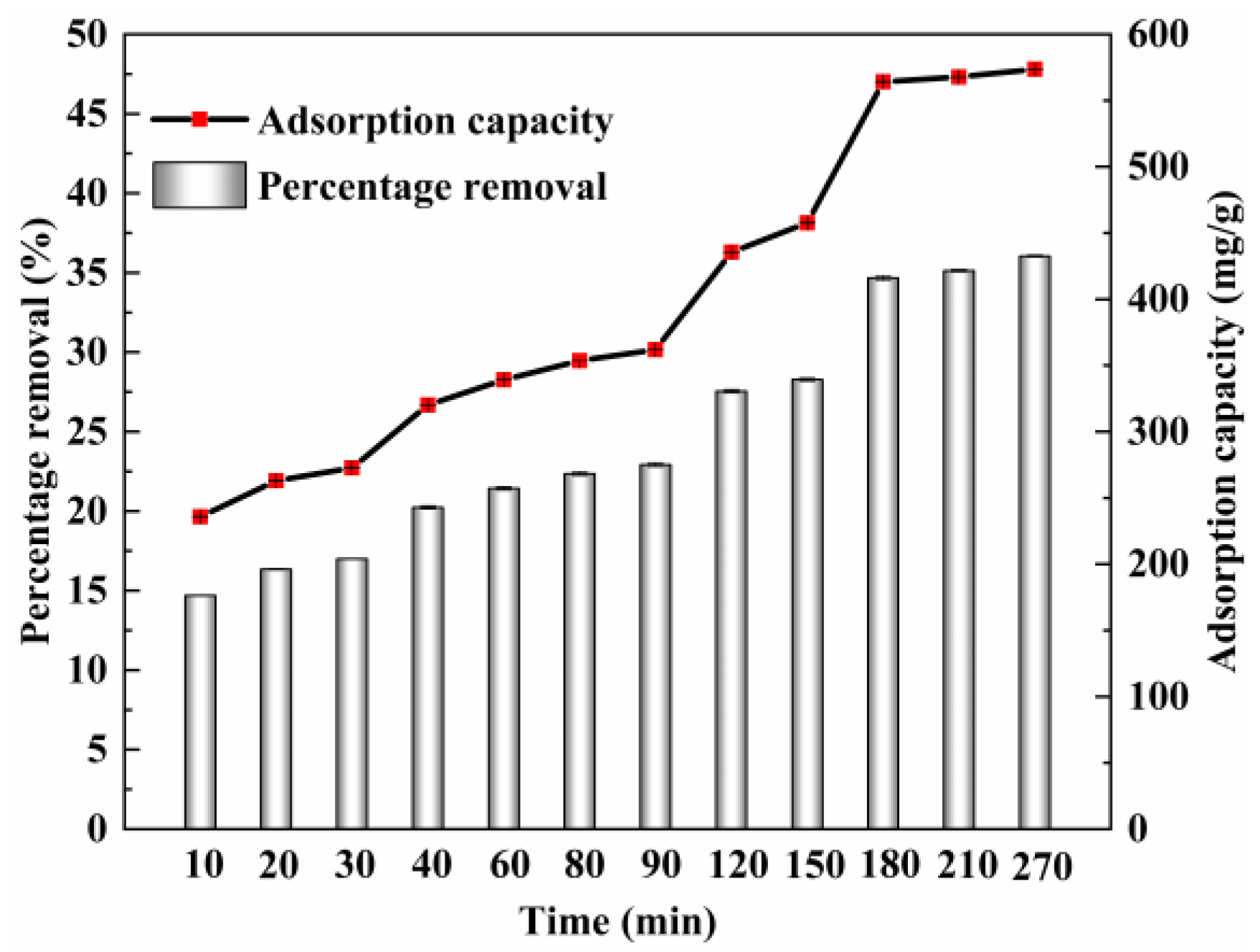
3.3.1. Adsorption Kinetics
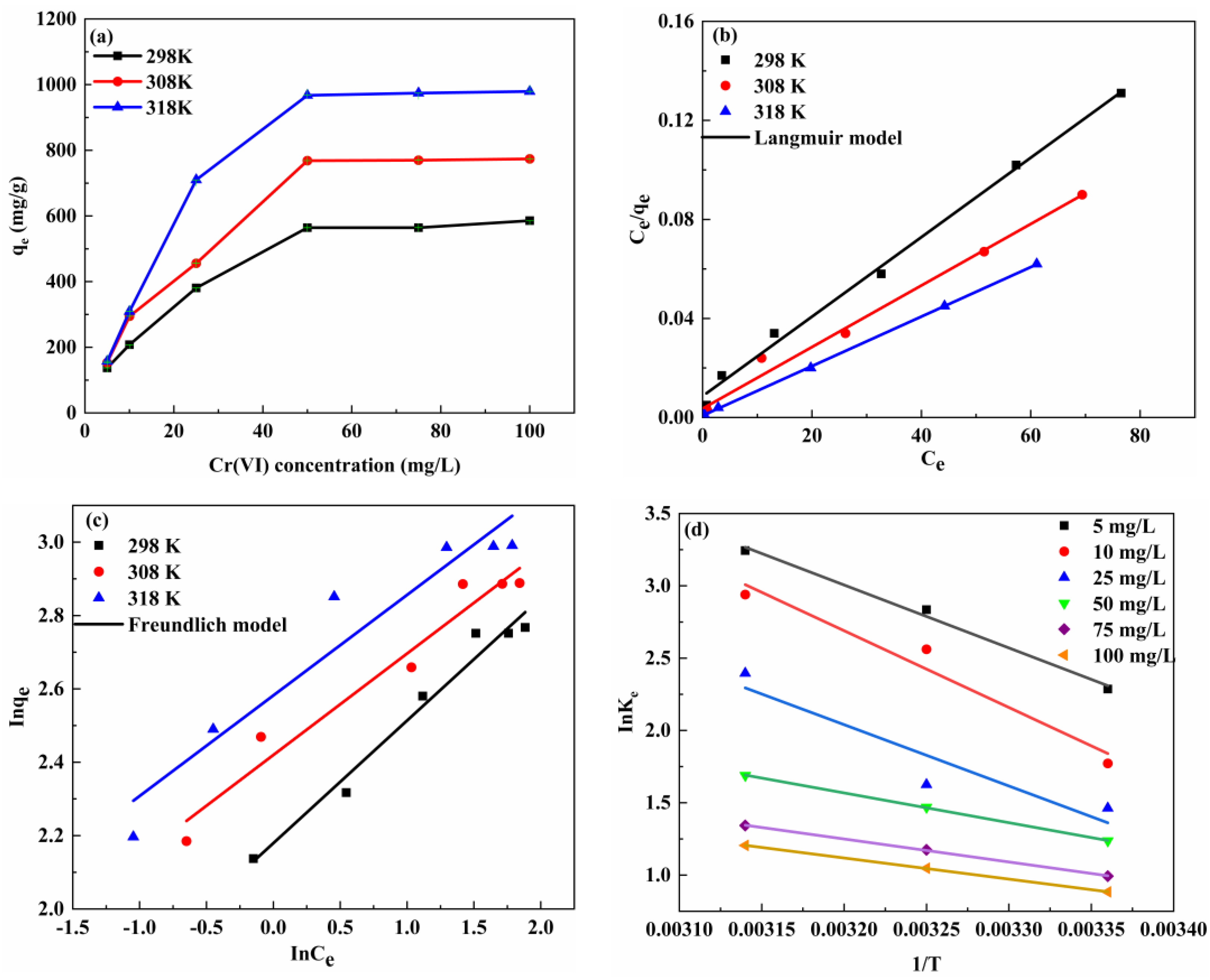
3.3.2. Analysis of Adsorption Isotherms
3.3.3. Adsorption Thermodynamics
3.4. Adsorption Mechanism
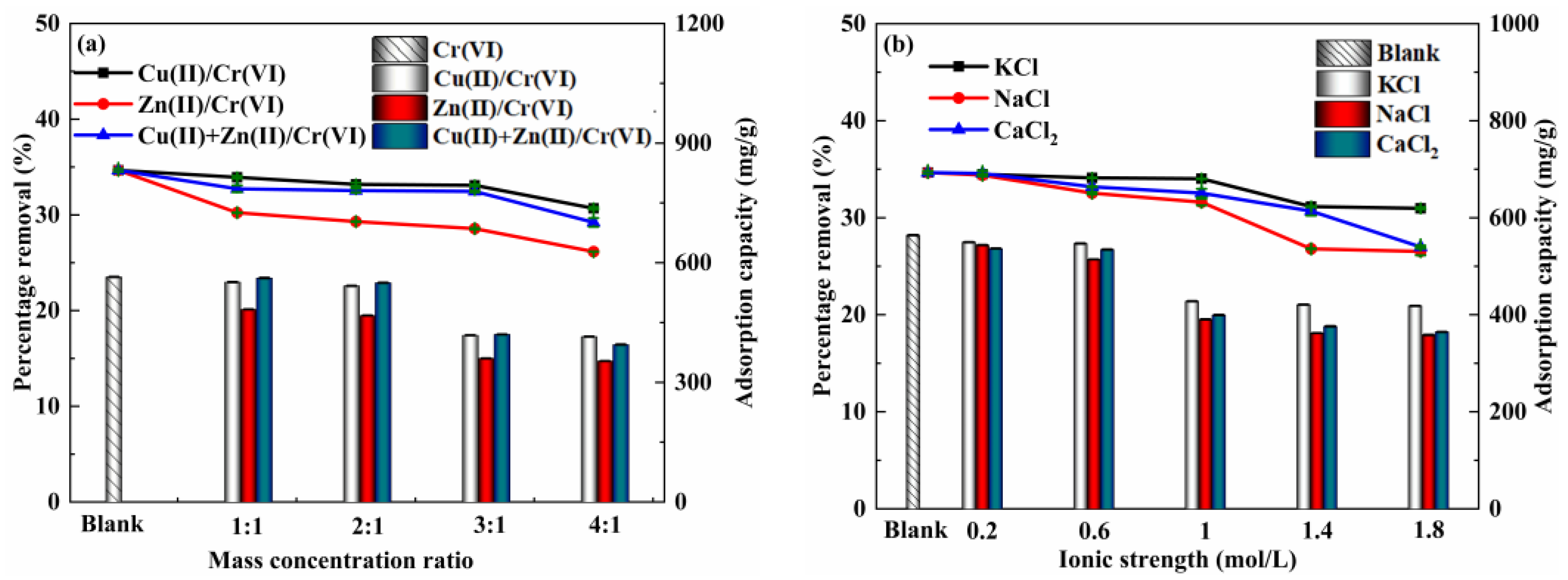
3.5. Influence of Co-Existing Heavy Metal Ions
3.6. Influence of Inorganic Ions
3.7. Practical Application and Reusability Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, H.; Gao, M.; Hu, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, R.; Yang, X.; Tang, C.; Hu, X. A novel preparation of S-NZVI and its high efficient removal of Cr(VI) in aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Xu, X.M.; Yue, C.L.; Song, L.; Lv, Y.Z.; Liu, F.Q.; Li, A.M. Insight into the efficient co-removal of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) by positively charged UiO-66-NH2 decorated ultrafiltration membrane. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 404, 126546–126555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.Q.; Lin, J.; Liang, J.; Li, M.H.; Fu, Y.W.; Wang, H.T.; Tu, S.; Li, J. Hypercrosslinked mesoporous poly(ionic liquid)s with high density of ion pairs: Efficient adsorbents for Cr(VI) removal via ion-exchange. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122107–122116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.D.; Wan, Y.S.; Zheng, Y.L.; He, F.; Yu, Z.B.; Huang, J.; Wang, H.L.; Ok, Y.S.; Jiang, Y.S.; Gao, B. Surface functional groups of carbon-based adsorbents and their roles in the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions: A critical review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 366, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.J.; Yu, W.C.; Qie, Y.; Zhao, L.X.; Zhang, H.; Guo, L.H. Enhanced photocatalytic removal of hexavalent chromium through localized electrons in polydopamine-modified TiO2 under visible irradiation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 373, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.C.; Liu, X.N.; Lv, X.T.; Wang, T.T.; Xue, B.L. Synthesis of novel lignosulfonate-modified graphene hydrogel for ultrahigh adsorption capacity of Cr(VI) from wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126406–126418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.T.; Yang, L.R.; Li, Q.; Liu, Z.N.; Dong, T.T.; Liu, H.Z. Polyethylenimine-functionalized poly(vinyl alcohol) magnetic microspheres as a novel adsorbent for rapid removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Othman, Z.A.; Ali, R.; Naushad, M. Hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous medium by activated carbon prepared from peanut shell: Adsorption kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 184, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.F.; Shi, X.X.; Wu, W.D.; An, X.X.; Tian, Y.Y.; Qiao, Y.Y. Facile preparation of lignosulfonate/N-methylaniline composite and its application in efficient removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 1194–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.F.; Wang, X.L.; Yuan, T.Q.; Sun, R.C. Lignosulfonate-modified graphene hydrogel with ultrahigh adsorption capacity for Pb(II) removal. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 11888–11896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Gu, F.; Chang, J.M. Fabrication of magnetic lignosulfonate using ultrasonic-assisted in situ synthesis for efficient removal of Cr(VI) and Rhodamine B from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 375, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myglovets, M.; Poddubnaya, O.I.; Sevastyanova, O.; Lindström, M.E.; Gawdzik, B.; Sobiesiak, M.; Tsyba, M.M.; Sapsay, V.I.; Klymchuk, D.O.; Puziy, A.M. Preparation of carbon adsorbents from lignosulfonate by phosphoric acid activation for the adsorption of metal ions. Carbon 2014, 80, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.Y.; Xing, J.C.; Xu, P.P.; Chang, J.M.; Zhang, Q.F.; Usman, K.M. Activated carbon microsphere from sodium lignosulfonate for Cr(VI) adsorption evaluation in wastewater treatment. Polymers 2020, 12, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Z.Q.; Liao, T.; Li, W.X.; Qiao, Y.X.; Ostrikov, K. Beyond seashells: Bioinspired 2D photonic and photoelectronic devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1901460–1901484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, L.; Liu, J.S.; Liu, X.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Li, G.Y.; Meng, Y.F. Graphene oxides cross-linked with hyperbranched polyethylenimines: Preparation, characterization and their potential as recyclable and highly efficient adsorption materials for lead(II) ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 285, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, J.Q.; Fan, C.J.; Xiao, Z.; Sun, T.S.; Zhou, X.D. Novel graphene oxide/carboxymethyl chitosan aerogels via vacuum-assisted self-assembly for heavy metal adsorption capacity. Colloid. Surface. A. 2019, 578, 123584–123594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.Y.; Yang, W.W.; Wang, Y.J.; Yu, Y.S.; Sun, Y.Y.; Li, K.F. PEI grafted amino-functionalized graphene oxide nanosheets for ultrafast and high selectivity removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions by adsorption combined with reduction: Behaviors and mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 399, 125762–125772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Chen, F.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, L. Synthesis of three-dimensional graphene oxide foam for the removal of heavy metal ions. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2014, 593, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, A.K.; Abdel Aal, M.M.; Abd El-Rahem, K.A.; Allam, E.M.; Abdel Dayem, S.M.; Elshehy, E.A.; Hanfi, M.Y.; Alqahtani, M.S.; Cheira, M.F. Characteristic Aspects of Uranium(VI) Adsorption Utilizing Nano-Silica/Chitosan from Wastewater Solution. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Gao, J.; Jia, L.; Wang, S.; Ning, P. Green synthesis of a novel functionalized chitosan adsorbent for Cu(II) adsorption from aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczajowska-Zadrożna, M.; Filipkowska, U.; Jóźwiak, T. Adsorption of Cu (II) and Cd (II) from aqueous solutions by chitosan immobilized in alginate beads. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, L.N.; Petrović, P.V.; Gonzalez, I.S.; Stavitski, E.; Fishman, Z.S.; Rudel, H.E.; Anastas, P.T.; Zimmerman, J.B. Selective adsorption of arsenic over phosphate by transition metal cross-linked chitosan. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 412, 128582–128592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.F.; Huang, W.X.; Li, Z.L. Chitosan cross-linked graphene oxide/lignosulfonate composite aerogel for enhanced adsorption of methylene blue in water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.L.; Ge, Y.Y.; Wan, L. Fabrication of a green porous lignin-based sphere for the removal of lead ions from aqueous media. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 285, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musico, Y.L.F.; Santos, C.M.; Dalida, M.L.P.; Rodrigues, D.F. Improved removal of lead(II) from water using a polymer-based graphene oxide nanocomposite. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 3789–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.X.; Xie, J.J.; Liu, J.X.; Kang, H.M.; Liu, Y. Adsorption of lead ions using a modified lignin hydrogel. J. Polym. Res. 2014, 21, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragan, E.S.; Cocarta, A.I.; Dinu, M.V. Facile fabrication of chitosan/poly(vinyl amine) composite beads with enhanced sorption of Cu2+. Equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamics. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 255, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Lingamdinne, L.P.; Yang, J.K.; Chang, Y.Y.; Koduru, J.R. Fabrication of chitosan/graphene oxide-gadolinium nanorods as a novel nanocomposite for arsenic removal from aqueous solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 320, 114410–114420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y.; Lai, C.; Li, B.S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.M.; Huang, D.L.; Qin, L.; Yi, H.; Liu, X.G.; Huang, F.L.; et al. Role of radical and non-radical pathway in activating persulfate for degradation of p-nitrophenol by sulfur-doped ordered mesoporous carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123304–123313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, H.W.; Shin, M.; Yun, H.; Lee, K.H. Preparation of silk sericin/lignin blend beads for the removal of hexavalent chromium ions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.L.; Yan, L.F.; Chen, W.F. Preparation of chitosan/graphene oxide composite film with enhanced mechanical strength in the wet state. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, T.L.; Meng, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Lu, J.; Wang, H.S. Novel graphene oxide/aminated lignin aerogels for enhanced adsorption of malachite green in wastewater. Colloid. Surface. A 2020, 603, 125281–125289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.P.; Wang, Q.; Wang, A.Q. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan-g-poly(acrylic acid)/attapulgite superabsorbent composites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 68, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.J.; Shan, X.Y.; Li, Z.L. Preparation of a porous graphene oxide/alkali lignin aerogel composite and its adsorption properties for methylene blue. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 143, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, G.H.; Wang, X.R.; Li, S.P.; Liu, Y.; Yang, G.H. Removal of hexavalent chromium by bentonite supported organosolv lignin-stabilized zero-valent iron nanoparticles from wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 267, 122009–122019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.B.; Rapole, S.B.; Huang, Y.D.; Cao, D.M.; Luo, Z.P.; Wei, S.Y.; Guo, Z.H. Synergistic interactions between multi-walled carbon nanotubes and toxic hexavalent chromium. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 2011–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, H.W.; Kim, M.K.; Lee, J.Y.; Yun, H.; Kim, M.H.; Park, Y.H.; Lee, K.H. Preparation of bead-type biosorbent from water-soluble Spirulina platensis extracts for chromium (VI) removal. Algal. Res. 2015, 7, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.Q.; Lu, C.H.; He, X.; Zhang, X.F.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.M. Polyethylenimine-grafted cellulose nanofibril aerogels as versatile vehicles for drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 2607–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, P.M.; Vinarta, S.C.; Bernal, A.R.; Cruz, E.L.; Figueroa, L.I.C. Bioremediation strategies for chromium removal: Current research, scale-up approach and future perspectives. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.A.; Hameed, B.H.; Aziz, N. Adsorption of direct dye on palm ash: Kinetic and equilibrium modeling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, R.L.; Wu, F.C.; Juang, R.S. Characteristics and applications of the Lagergren’s first-order equation for adsorption kinetics. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. E. 2010, 41, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process. Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangiri, M.; Kiani, F.; Tahermansouri, H.; Rajabalinezhad, A. The removal of lead ions from aqueous solutions by modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes with 1-isatin-3-thiosemicarbazone. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 212, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Comparative sorption kinetic studies of dye and aromatic compounds onto fly ash. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 1999, 34, 1179–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rusmirovic, J.D.; Obradovic, N.; Perendija, J.; Umicevic, A.; Kapidzic, A.; Vlahovic, B.; Pavlovic, V.; Marinkovic, A.D.; Pavlovic, V.B. Controllable synthesis of Fe3O4-wollastonite adsorbents for efficient heavy metal ions/oxyanions removal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 12379–12398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehlivan, E.; Altun, T. The study of various parameters affecting the ion exchange of Cu2+, Zn2+, Ni2+, Cd2+, and Pb2+ from aqueous solution on Dowex 50 W synthetic resin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 134, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. Adsorption of gases on glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarin, V.; Singh, T.S.; Pant, K.K. Thermodynamic and breakthrough column studies for the selective sorption of chromium from industrial effluent on activated eucalyptus bark. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1986–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.W.; Chen, Z.H.; Wang, M.H.; Liu, S.J.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhang, J.A.; Han, R.P.; Xu, Q. Adsorption of methylene blue by a high-efficiency adsorbent (polydopamine microspheres): Kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamics and mechanism analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gereli, G.; Seki, Y.; Murat Kusoglu, I.; Yurdakoc, K. Equilibrium and kinetics for the sorption of promethazine hydrochloride onto K10 montmorillonite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 299, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, P.D.; Subramanian, S. Thermodynamics of protein association reactions: Forces contributing to stability. Biochemistry 1981, 20, 3096–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.X.; Chen, W.; Li, Z.L.; Liu, Z.Z.; Xu, A. Synthesis of cationic biomass lignosulfonate hydrogel for the efficient adsorption of Cr(VI) in wastewater with low pH. Environ. Technol. 2021, 1–14, ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.J.; Liang, Q.W.; Yu, W.Y.; Chen, W.; Lu, G.N.; Luo, H.J. Enhanced removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions by polymer-mediated nitrogen-rich reduced graphene oxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ko, Y.G.; Choi, U.S.; Kim, T.Y.; Ahn, D.J.; Chun, Y.J. FT-IR and isotherm study on anion adsorption onto novel chelating fibers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2002, 23, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatehi, M.; Shayegan, J.; Zabihi, M.; Goodarznia, I. Functionalized magnetic nanoparticles supported on activated carbon for adsorption of Pb(II) and Cr(VI) ions from saline solutions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1754–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.Q.; Yue, Q.Y.; Gao, B.Y.; Li, Q.; Xu, X. A novel amphoteric adsorbent derived from biomass materials: Synthesis and adsorption for Cu(II)/Cr(VI) in single and binary systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 229, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.Y.; Liang, J.S.; Li, Y.; Hunang, S.Q.; Wei, Y.N.; Bai, X.; Jin, Z.H.; Zhang, M.; Qu, J.J. Effect of coexisting ions on Cr(VI) adsorption onto surfactant modified Auricularia auricula spent substrate in aqueous solution. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 166, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, R.H. H2O2 treatment enhanced the heavy metals removal by manure biochar in aqueous solutions. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 1139–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.X.; Tang, S.Y.; He, F.X.; Liu, Y.; Mao, W.; Guan, Y.T. Highly efficient and selective capture of heavy metals by poly(acrylic acid) grafted chitosan and biochar composite for wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122215–122231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Xue, H.X.; Lv, C.W.; Fan, Q.Y.; Liang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Shen, L.L.; Bai, S. The impacts of common ions on the adsorption of heavy metal. Environ. Geol. 2009, 58, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.D.; Zhao, C.; Zeng, W.G.; Wang, X.M.; Liu, C.F.; Yu, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, Z.M. Ultra-high selective removal of CR and Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using polyethyleneimine functionalized magnetic hydrochar: Application strategy and mechanisms insight. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 448, 137464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Isotherm Model | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order model | Qe (mg/g) | 129.12 |
| K1 × 10−2 (min−1) | 0.343 | |
| R2 | 0.9645 | |
| Pseudo-second-order model | Qe (mg/g) | 495.050 |
| h (mg/(g·mg)) | 22.6552 | |
| K2 × 10−4 [g·(mg·min)−1] | 0.9244 | |
| R2 | 0.9716 | |
| Intraparticle diffusion model | Kint1 (mg/(g·min0.5)) | 21.4413 |
| C1 | 167.8161 | |
| R12 | 0.9692 | |
| Kint2 (mg/(g·min0.5)) | 47.3354 | |
| C2 | −89.3949 | |
| R22 | 0.9448 | |
| Kint3 (mg/(g·min0.5)) | 3.1494 | |
| C3 | 521.9974 | |
| R32 | 0.9998 |
| Concentration (mg/L) | Temp. | Ke | ΔG (kJ/mol) | ΔH (kJ/mol) | ΔS (kJ/(mol·K)) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 298 K | 193.4111 | −5.8550 | 36.1735 | 0.1407 | 0.9929 |
| 308 K | 683.8367 | −7.4952 | ||||
| 318 K | 1752.6599 | −8.8455 | ||||
| 10 | 298 K | 59.1725 | −4.5379 | 44.1209 | 0.1635 | 0.9603 |
| 308 K | 364.3415 | −6.7722 | ||||
| 318 K | 870.2609 | −8.0164 | ||||
| 25 | 298 K | 29.0520 | −3.7468 | 35.2438 | 0.1297 | 0.8762 |
| 308 K | 42.2562 | −4.2986 | ||||
| 318 K | 248.7869 | −6.5334 | ||||
| 50 | 298 K | 17.2718 | −3.1685 | 17.1003 | 0.06776 | 0.9998 |
| 308 K | 29.4458 | −3.8839 | ||||
| 318 K | 48.9530 | −4.6080 | ||||
| 75 | 298 K | 9.8444 | −2.5433 | 13.2117 | 0.05267 | 0.9995 |
| 308 K | 14.9613 | −3.1064 | ||||
| 318 K | 22.0170 | −3.6617 | ||||
| 100 | 298 K | 7.6527 | −2.2632 | 12.1384 | 0.04814 | 0.9999 |
| 308 K | 11.1510 | −2.7689 | ||||
| 318 K | 16.0341 | −3.2861 |
| Adsorbent | Pollutants | Adsorption Capacity(mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| MLS | Cr(VI) | 57.1 | [11] |
| SLACM | Cr(VI) | 227.7 | [13] |
| LS-g-P (AM-co-DAC) | Cr(VI) | 58.86 | [52] |
| N-LEGO | Cr(VI) | 416.97 | [53] |
| Lignosulfonate-modified graphene hydrogel (LCGH) | Cr(VI) | 564.2 | This work |
| Composition | Simulated Electroplating Wastewater (mg/L) |
|---|---|
| Cr(VI) | 100.0 |
| Cu2+ | 12.4 |
| Ni2+ | 5.3 |
| Fe3+ | 5.5 |
| Al3+ | 3.4 |
| Zn2+ | 6.7 |
| Ca2+ | 15.0 |
| Cl− | 53.9 |
| SO42− | 126.5 |
| COD | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, T.; Sun, X.; Bai, L.; Sun, Y. The Preparation of a Lignosulfonate/Chitosan–Graphene Oxide Hydrogel Biosorbent to Effectively Remove Cr(VI) from Wastewater: Adsorption Performance and Mechanisms. Water 2022, 14, 3684. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223684
Han C, Liu X, Wang T, Sun X, Bai L, Sun Y. The Preparation of a Lignosulfonate/Chitosan–Graphene Oxide Hydrogel Biosorbent to Effectively Remove Cr(VI) from Wastewater: Adsorption Performance and Mechanisms. Water. 2022; 14(22):3684. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223684
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Caohui, Xiaonan Liu, Tingting Wang, Xiaoyin Sun, Lu Bai, and Yongchang Sun. 2022. "The Preparation of a Lignosulfonate/Chitosan–Graphene Oxide Hydrogel Biosorbent to Effectively Remove Cr(VI) from Wastewater: Adsorption Performance and Mechanisms" Water 14, no. 22: 3684. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223684
APA StyleHan, C., Liu, X., Wang, T., Sun, X., Bai, L., & Sun, Y. (2022). The Preparation of a Lignosulfonate/Chitosan–Graphene Oxide Hydrogel Biosorbent to Effectively Remove Cr(VI) from Wastewater: Adsorption Performance and Mechanisms. Water, 14(22), 3684. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223684







