Organic Contamination Distribution Constrained with Induced Polarization at a Waste Disposal Site
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
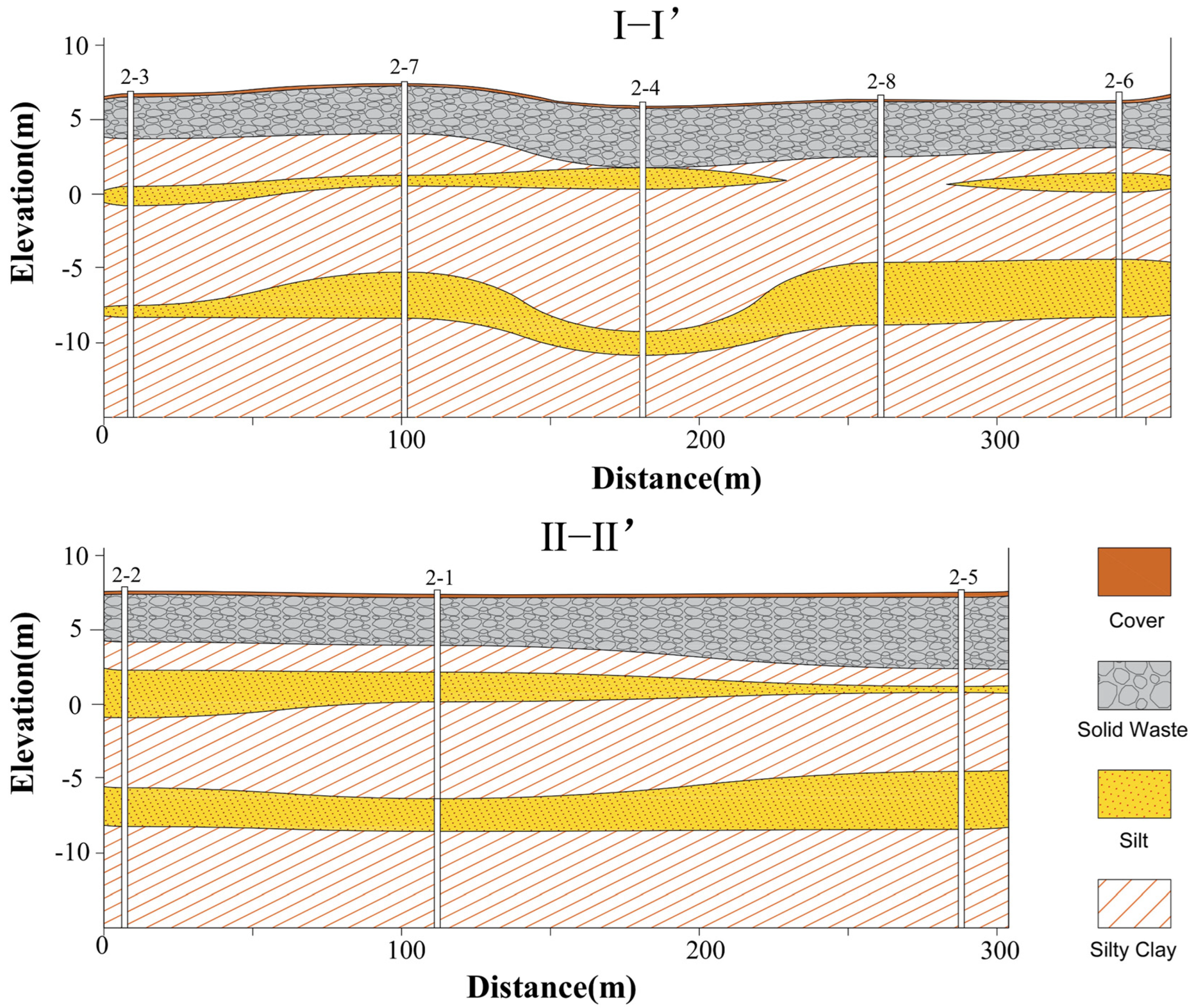
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Field Time-Domain Induced Polarization Survey
2.3. Soil Sampling and Processing
2.4. Laboratory Frequency-Domain Induced Polarization Measurement
3. Results
3.1. Data Quality Analysis of Field IP Data
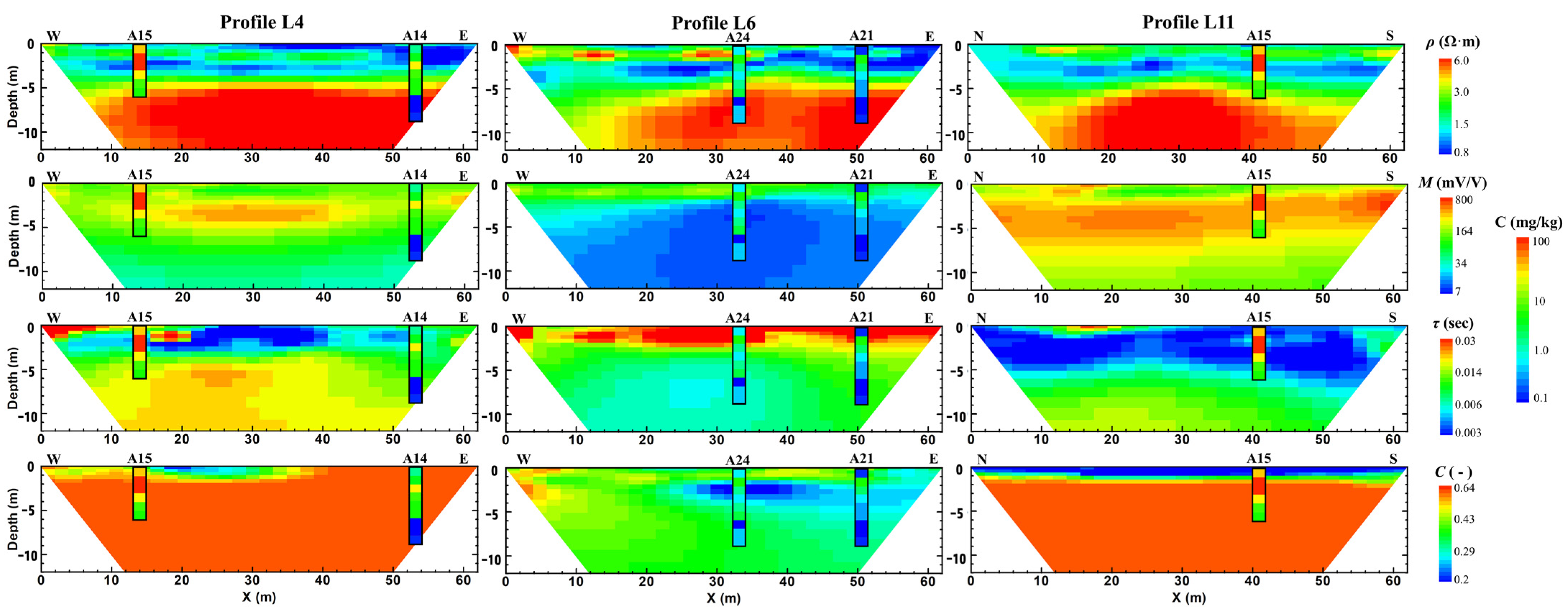
3.2. Inversion Results of Field IP Investigation
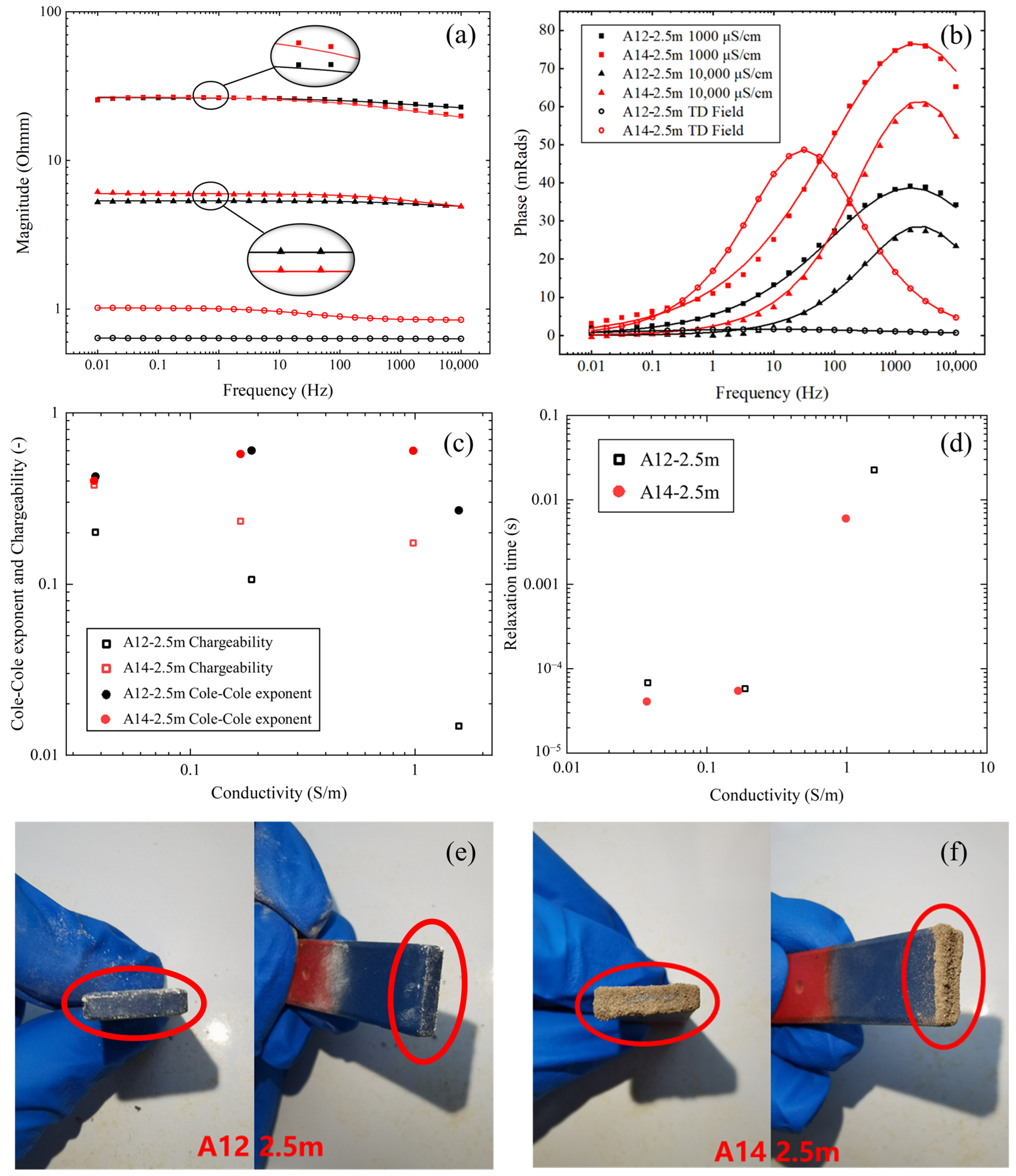
3.3. FDIP Experiment Results
3.4. Contaminant Concentration from Sampling
4. Discussion
4.1. Verification with Laboratory Soil Samples and IP Field Survey
4.2. TDIP Parameters versus Benzene Concentration
4.3. Organic Contamination Constrained with Chargeability
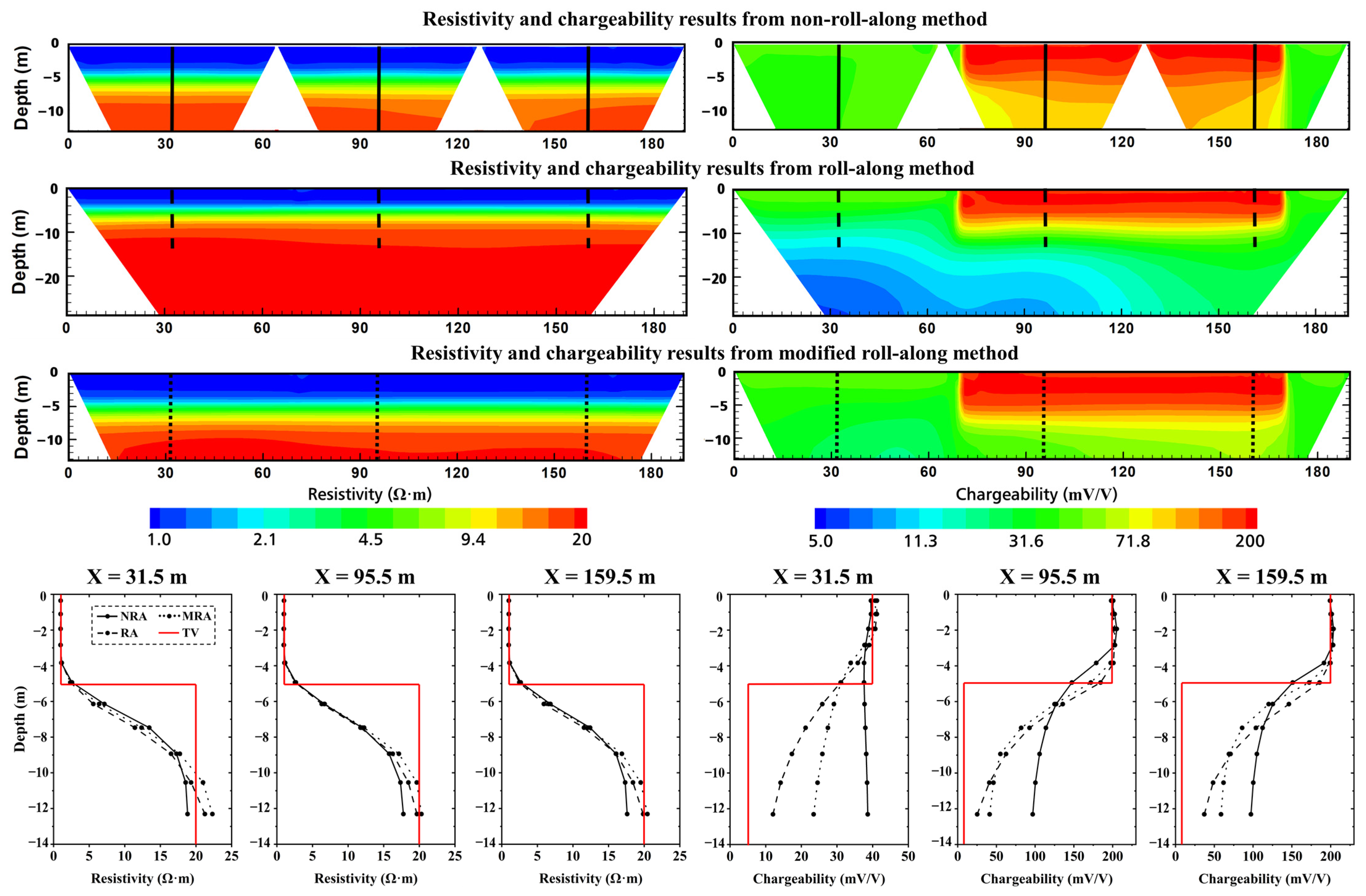
4.4. Improvement of Roll-Along Measurement Protocol
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ustra, A.T.; Elis, V.R.; Mondelli, G.; Zuquette, L.V.; Giacheti, H.L. Case study: A 3D resistivity and induced polarization imaging from downstream a waste disposal site in Brazil. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 66, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kjeldsen, P.; Bjerg, P.L.; Rügge, K.; Christensen, T.H.; Pedersen, J.K. Characterization of an old municipal landfill (Grindsted, Denmark) as a groundwater pollution source: Landfill hydrology and leachate migration. Waste Manag. Res. 1998, 16, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, T.H.; Kjeldsen, P.; Bjerg, P.L.; Jensen, D.L.; Christensen, J.B.; Baun, A. Review: Biogeochemistry of landfill leachate plumes. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 659–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, T.G.; Moldroup, P.; Sørensen, K.; Hansen, J.A. Linking landfill hydrology and leachate chemical composition at a controlled municipal landfill (Kåstrup, Denmark) using state-space analysis. Waste Manag. Res. 2002, 20, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wemegah, D.D.; Finadaca, G.; Auken, E.; Menyeh, A.; Danuor, S.K. Spectral time-domain induced polarisation and magnetic surveying—An efficient tool for characterisation of solid waste deposits in developing countries. Near Surf. Geophys. 2017, 15, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Umar, U.M.; Naibbi, A.I. Analysis and suitability modeling of solid waste disposal sites in Kano metropolis, Nigeria. Geocarto Int. 2021, 36, 1409–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerg, P.L.; Tuxen, N.; Reitzel, L.A.; Albrechtsen, H.-J.; Kjeldsen, P. Natural attenuation processes in landfill leachate plumes at three Danish sites. Groundwater 2011, 49, 688–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baderna, D.; Caloni, F.; Benfenati, E. Investigating landfill leachate toxicity In Vitro: A review of cell models and endpoints. Environ. Int. 2019, 122, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Shahid, M. Metal−Organic Frameworks for Environmental Remediation; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2021; pp. 171–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, S.; Khalid, M.; Khan, M.S.; Shahid, M. Metal organic frameworks and their composites as effective tools for sensing environmental hazards: An up to date tale of mechanism, current trends and future prospects. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 474, 214859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Khalid, M.; Shahid, M. What triggers dye adsorption by metal organic frameworks? The current perspectives. Mater. Adv. 2020, 1, 1575–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinne, J.; Pihlatie, M.; Lohila, A.; Thum, T.; Aurela, M.; Tuovinen, J.; Laurila, T.; Vesala, T. Nitrous Oxide Emissions from a Municipal Landfill. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7790–7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milosevic, N.; Thomsen, N.I.; Juhler, R.K.; Albrechtsen, H.-J.; Bjerg, P.L. Identification of discharge zones and quantification of contaminant mass discharges into a local stream from a landfill in a heterogeneous geologic setting. J. Hydrol. 2012, 446–447, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Reguyal, F.; Zhuang, T. Risk assessment and investigation of landfill leachate as a source of emerging organic contaminants to the surrounding environment: A case study of the largest landfill in Jinan City, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 28, 18368–18381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenhard, R.J.; Parker, J.C. Estimation of free hydrocarbon volume from fluid levels in monitoring wells. Groundwater 1990, 28, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, J.E.; Wilkinson, P.B.; Wealthall, G.P.; Loke, M.H.; Dearden, R.; Wilson, R.; Allen, D.; Ogilvy, R.D. Hydrogeophysical imaging of deposit heterogeneity and groundwater chemistry changes during DNAPL source zone bioremediation. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2010, 118, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, Q.; Deng, Y.; Shi, X.; Sun, Y.; Duan, W.; Wu, J. Delineation of contaminant plume for an inorganic contaminated site using electrical resistivity tomography: Comparison with direct-push technique. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revil, A.; Karaoulis, M.; Johnson, T.; Kemna, A. Review: Some low-frequency electrical methods for subsurface characterization and monitoring in hydrogeology. Hydrogeol. J. 2012, 20, 617–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Lu, L.; Revil, A.; Zuo, Y.; Hinton, J.; Ren, Z.J. Geophysical Monitoring of Hydrocarbon-Contaminated Soils Remediated with a Bioelectrochemical System. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8205–8213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Dong, Y.H.; Xia, T.; Ma, X.M.; Gao, C.L.; Mao, D.Q. Detailed LNAPL plume mapping using electrical resistivity tomography inside an industrial building. Acta Geophys. 2022, 70, 1651–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux, V.; Dahlin, T. Dense resistivity and induced polarization profiling for a landfill restoration project at Härlöv, Southern Sweden. Waste Manag. Res. 2007, 25, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donno, G.D.; Cardarelli, E. Tomographic inversion of time-domain resistivity and chargeability data for the investigation of landfills using a priori information. Waste Manag. 2017, 59, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flores-Orozco, A.; Gallistl, J.; Steiner, M.; Brandstätter, C.; Fellner, J. Mapping biogeochemically active zones in landfills with induced polarization imaging: The Heferlbach landfill. Waste Manag. 2020, 107, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sogade, J.A.; Scira-Scappuzzon, F.; Vichabian, Y.; Shi, W.; Rodi William Lesmes, D.P.; Morgan, F.D. Induced-polarization detection and mapping of contaminant plumes. Geophysics 2006, 71, B75–B84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, S.; Fiandaca, G.; Dahlin, T. Influence of non-aqueous phase liquid configuration on induced polarization parameters: Conceptual models applied to a time-domain field case study. J. Appl. Geophys. 2015, 123, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sparrenbom, C.J.; Åkesson, S.; Johansson, S.; Hagerberg, D.; Dahlin, T. Investigation of chlorinated solvent pollution with resistivity and induced polarization. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-González, A.E.; Tejero-Andrade, A.; Hernández-Martínez, J.L.; Prado, B.; Chávez, R.E. Induced Polarization and Resistivity of Second Potential Differences (SPD) with Focused Sources Applied to Environmental Problems. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2019, 24, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wemegah, D.D.; Fiandaca, G.; Auken, E.; Menyeh, A.; Danuor, S.K. Spectral time-domain induced polarilation and magnetic for mapping municipal solid waste deposits in Ghana. In Proceedings of the 20th European Meeting of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics, Athens, Greece, 14–18 September 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frid, V.; Sharabi, I.; Frid, M.; Averbakh, A. Leachate detection via statistical analysis of electrical resistivity and induced polarization data at a waste disposal site (Northern Israel). Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux, V.; Dahlin, T.; Rosqvist, H. Time-domain IP and resistivity sections measured at four landfills with different contents. In Proceedings of the Near Surface 2010—16th EAGE European Meeting of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–8 September 2010; p. 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazoty, A.; Fiandaca, G.; Pedersen, E.; Auken, E.; Christiansen, A.V. Mapping of landfills using time-domain spectral induced polarization data: The Eskelund case study. Near Surf. Geophys. 2012, 10, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elis, V.R.; Ustra, A.T.; Hidalgo-Gato, M.C.; Pejon, O.J.; Hiodo, F.Y. Application of induced polarization and resistivity to the environmental investigation of an old waste disposal area. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazoty, A.; Fiandaca, G.; Pedersen, E.; Auken, E.; Christiansen, A.V.; Pedersen, J.K. Application of time domain induced polarization to the mapping of lithotypes in a landfill site. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 1793–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, T.I. The effect of electrode contact resistance and capacitive coupling on Complex Resistivity measurements. SEG Tech. Program Expand. Abstr. 2006, 25, 1376–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlin, T. Short note on electrode charge-up effects in DC resistivity data acquisition using multi-electrode arrays. Geophys. Prospect. 2000, 48, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarif, F.; Kessouri, P.; Slater, L. Recommendations for Field-Scale Induced Polarization (IP) Data Acquisition and Interpretation. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2017, 22, 395–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlin, T.; Leroux, V.; Nissen, J. Measuring techniques in induced polarisation imaging. J. Appl. Geophys. 2002, 50, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dahlin, T.; Leroux, V. Improvement in time-domain induced polarization data quality with multi-electrode systems by separating current and potential cables. Near Surf. Geophys. 2012, 10, 545–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gündoğdu, N.Y.; Demirci, İ.; Özyildirim, Ö.; Aktarakçi, H.; Candansayar, H.E. Investigating the Use of Stainless Steel Electrodes with the IP Method: A Metallic Ore Deposit Example. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2022, 179, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, P.I.; Fiandaca, G.; Larsen, J.J.; Dahlin, T.; Auken, E. Doubling the spectrum of time-domain induced polarization by harmonic de-noising, drift correction, spike removal, tapered gating and data uncertainty estimation. Geophys. J. Int. 2016, 207, 774–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barfod, A.S.; Lévy, L.; Larsen, J.J. Automatic Processing of Time Domain Induced Polarisation Data using Supervised Artificial Neural Networks. Geophys. J. Int. 2020, 224, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiandaca, G.; Ramm, J.; Binley, A.; Gazoty, A.; Christiansen, A.; Auken, E. Resolving spectral information from time domain induced polarization data through 2-D inversion. Geophys. J. Int. 2013, 192, 631–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, P.K.; Fiandaca, G.; Christiansen, A.V.; Auken, E. Field-scale comparison of frequency- and time-domain spectral induced polarization. Geophys. J. Int. 2018, 214, 1441–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johansson, S.; Lindskog, A.; Fiandaca, G.; Dahlin, T. Spectral Induced Polarization of limestones: Time domain field data, frequency domain laboratory data and physicochemical rock properties. Geophys. J. Int. 2020, 220, 928–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auken, E.; Viezzoli, A.; Christensen, A. A single software for processing, inversion, and presentation of AEM data of different systems: The Aarhus Workbench. ASEG Ext. Abstr. 2009, 2009, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Slater, L.D. Extending Accurate Spectral Induced Polarization Measurements into the kHz Range: Modeling and Removal of Errors from Interactions between the Parasitic Capacitive Coupling and the Sample Holder. Geophys. J. Int. 2019, 218, 895–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, K.S.; Cole, R.H. Dispersion and absorption in dielectrics I. Alternating current characteristics. J. Chem. Phys. 1941, 9, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelton, W.H.; Ward, S.H.; Hallof, P.G.; Sill, W.R.; Nelson, P.H. Mineral Discrimination and Removal of Inductive Coupling with Multifrequency IP. Geophysics 1978, 43, 588–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revil, A.; Florsch, N.; Mao, D. Induced polarization response of porous media with metallic particles—Part 1: A theory for disseminated semiconductors. Geophysics 2015, 80, D525–D538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Revil, A.; Hinton, J. Induced polarization response of porous media with metallic particles—Part 4: Detection of metallic and nonmetallic targets in time-domain induced polarization tomography. Geophysics 2016, 81, D359–D375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revil, A.; Sleevi, M.F.; Mao, D. Induced polarization response of porous media with metallic particles—Part 5: Influence of the background polarization. Geophysics 2017, 82, E77–E96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasov, A.; Titov, K. On the use of the Cole–Cole equations in spectral induced polarization. Geophys. J. Int. 2013, 195, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, L.; Lesmes, D.P. Electrical-hydraulic relationships observed for unconsolidated sediments. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revil, A.; Coperey, A.; Mao, D.; Abdulsamad, F.; Ghorbani, A.; Rossi, M.; Gasquet, D. Induced polarization response of porous media with metallic particles—Part 8. Influence of temperature and salinity. Geophysics 2018, 83, E435–E456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maineult, A.; Revil, A.; Camerlynck, C.; Florsch, N.; Titov, K. Upscaling of spectral induced polarization response using random tube networks. Geophys. J. Int. 2017, 209, 948–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johansson, S.; Hedblom, P.; Dahlin, T. Spectral analysis of time domain induced polarization waveforms. J. Appl. Geophys. 2020, 177, 104077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auken, E.; Christiansen, A.V. Layered and laterally constrained 2D inversion of resistivity data. Geophysics 2004, 69, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, M.H.; Barker, R.D. Rapid least-squares inversion of apparent resistivity pseudosections by a quasi-Newton method. Geophys. Prospect. 1996, 44, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Dong, Y.; Mao, D.; Meng, J. Delineation of LNAPL contaminant plumes at a former perfumery plant using electrical resistivity tomography. Hydrogeol. J. 2021, 29, 1189–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| IP Gate | Off Time (ms) | Separating Current and Potential Cables | Single Cable | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel Current Electrodes and Non-Polarized Potential Electrodes | Stainless Steel Current and Potential Electrodes | |||
| Gate 1 | 20 | 204 | 21 | 39 |
| Gate 2 | 60 | 280 | 91 | 88 |
| Gate 3 | 120 | 289 | 146 | 152 |
| Gate 4 | 200 | 293 | 151 | 165 |
| Gate 5 | 300 | 293 | 161 | 173 |
| Gate 6 | 440 | 293 | 162 | 178 |
| Gate 7 | 620 | 293 | 165 | 175 |
| Gate 8 | 880 | 293 | 162 | 175 |
| Gate 9 | 1280 | 289 | 162 | 172 |
| Gate 10 | 1880 | 284 | 151 | 168 |
| Gate 11 | 2760 | 270 | 143 | 157 |
| Gate 12 | 3960 | 75 | 85 | 52 |
| Total | 3156 | 1600 | 1694 | |
| Borehole and Depth | Cr | K | Ca | Sc | Mn | Fe | Cu | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A12-2.5m | 123.59 | 2506 | 215,621 | 1588 | 280 | 9576 | 58 | 152 |
| A14-2.5m | 139.56 | 4135 | 106,089 | 811 | 449 | 31,683 | 56 | 150 |
| Borehole | 0.5 m | 1.5 m | 2.5 m | 3.5 m | 4.5 m | 5.5 m | 6.5 m | 8 m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 0.07 | 1.28 | 0.50 | 0.39 * | 0.11 | — | ||
| A2 | — | 0.10 | 0.3 * | 0.33 | 0.12 | — | ||
| A3 | 3.12 | 0.37 | 0.43 * | 0.28 | 0.07 | 0.08 | — | — |
| A4 | 1.60 | 1.90 | 2.853 * | 1.08 | 0.22 | 0.30 | ||
| A5 | 23.90 | 19.60 | 15.75 * | 0.71 | 0.13 | — | — | — |
| A6 | 0.43 | 0.89 | 0.99 * | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.05 | — | — |
| A7 | 0.46 | 0.31 | 0.08 * | — | — | — | — | — |
| A9 | 1.35 | 5.10 | 2.12 * | 0.79 | 0.17 | — | — | — |
| A10 | 2.41 | 1.95 | 1.23 * | 0.09 | 0.14 | — | ||
| A11 | — | 2.37 | 0.37 * | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.10 | ||
| A12 | 0.00 | 0.19 | 1.88 * | 0.39 | 0.17 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.03 |
| A13 | 0.12 | 1.77 | 1.70 | 0.59 * | 0.26 | 0.18 | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| A14 | 1.51 | 2.33 * | 15.90 | 7.84 | 2.91 | 3.06 | 0.05 | 0.00 |
| A15 | 24.80 | 2460.00 | 183.00 * | 12.50 | 7.21 | 3.46 | ||
| A16 | 0.55 | 5.30 | 3.65 * | 0.33 | 0.16 | 0.07 | ||
| A17 | 0.34 | 1.78 | 1.74 | 1.38 * | 0.52 | 0.44 | ||
| A18 | 0.26 | 292.00 | 48.30 * | 7.15 | 1.77 | 1.33 | — | — |
| A19 | 45.50 | 6.99 | 16.80 | 4.11 * | 2.57 | 1.20 | ||
| A20 | 38.70 | 15.60 | 4.21 | 3.60 * | 0.54 | 0.06 | ||
| A21 | 0.12 | 3.30 | 1.51 * | 0.29 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| A23 | 1.06 | 3.32 | 3.63 * | 0.34 | 0.99 | 0.76 | — | — |
| A24 | 0.51 | 3.20 | 1.30 * | 0.57 | 1.10 | 1.72 | 0.01 | 0.26 |
| A25 | 2.77 | 1.07 | 1.25 * | 0.43 | 0.28 | 0.01 | — | — |
| A26 | 0.03 | |||||||
| A27 | 0.35 | 0.89 * | 1.78 | 0.52 | 0.30 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 0.01 |
| A28 | — | 0.70 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.37 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.85 |
| A29 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.1 * | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, J.; Zhang, J.; Mao, D.; Han, C.; Guo, L.; Li, S.; Chao, C. Organic Contamination Distribution Constrained with Induced Polarization at a Waste Disposal Site. Water 2022, 14, 3630. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223630
Meng J, Zhang J, Mao D, Han C, Guo L, Li S, Chao C. Organic Contamination Distribution Constrained with Induced Polarization at a Waste Disposal Site. Water. 2022; 14(22):3630. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223630
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Jian, Jiaming Zhang, Deqiang Mao, Chunmei Han, Lili Guo, Shupeng Li, and Chen Chao. 2022. "Organic Contamination Distribution Constrained with Induced Polarization at a Waste Disposal Site" Water 14, no. 22: 3630. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223630






