Algae Bloom and Decomposition Changes the Phosphorus Cycle Pattern in Taihu Lake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Measurement Methods
2.3. Deployment of the HR-Peeper and DGT
2.4. DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Gene High Throughput Sequencing
3. Result
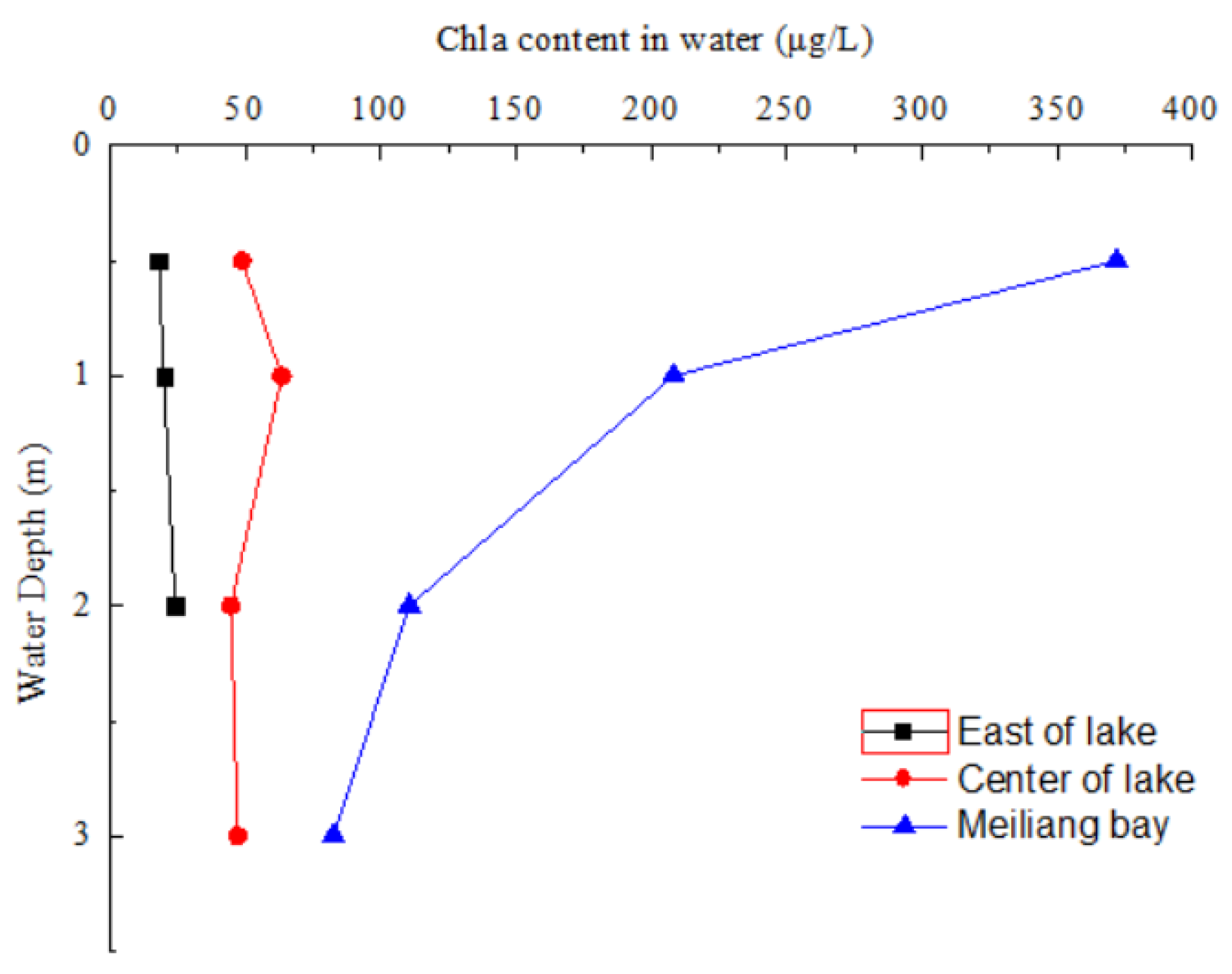
3.1. Chla Content and Water Quality Parameter in Water of Taihu Lake
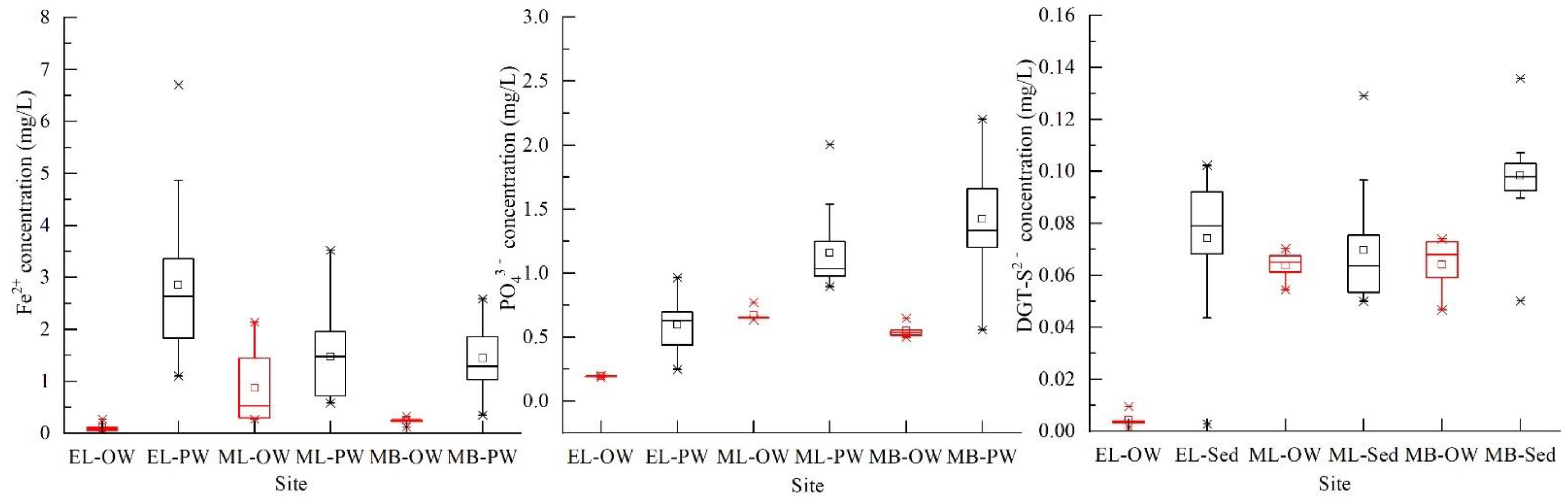
3.2. P Forms in Water, Suspended Particles and Sediments of Taihu Lake
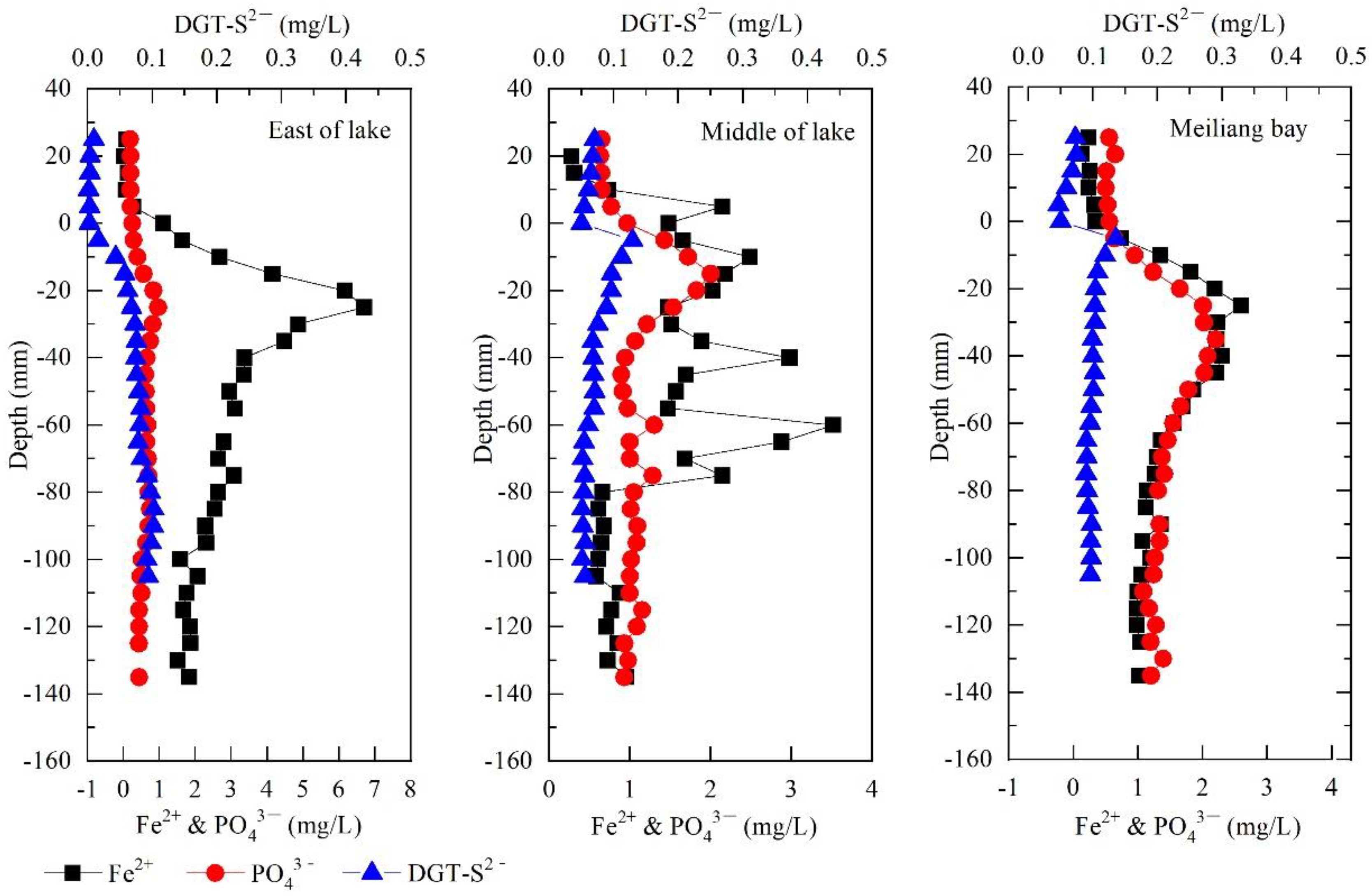
3.3. High-Resolution Profiles of PO43−, Fe2+, DGT-S2− in the Interface between Pore Water and Overlying Water
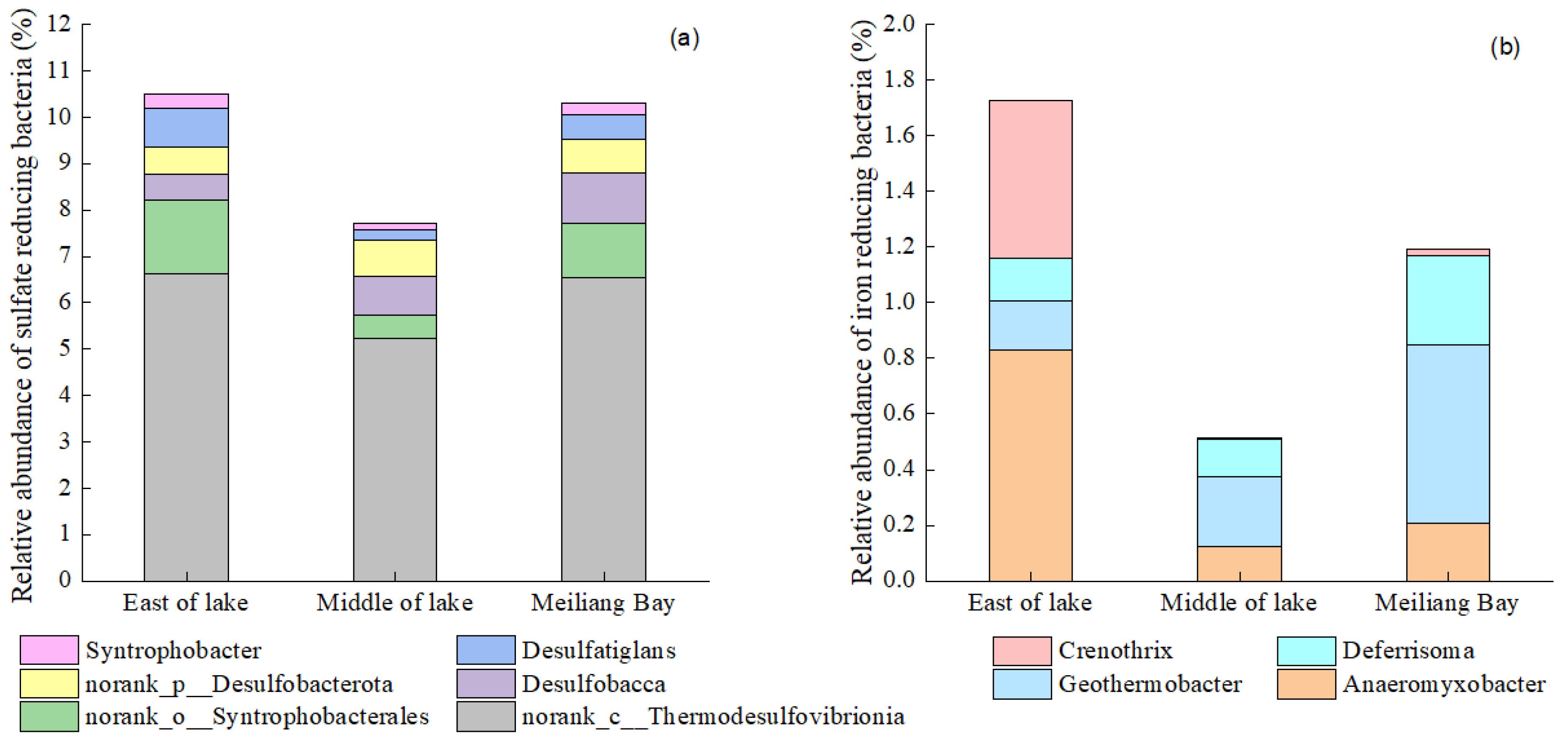
3.4. Bacteria Community Structure of Taihu Lake
4. Discussion
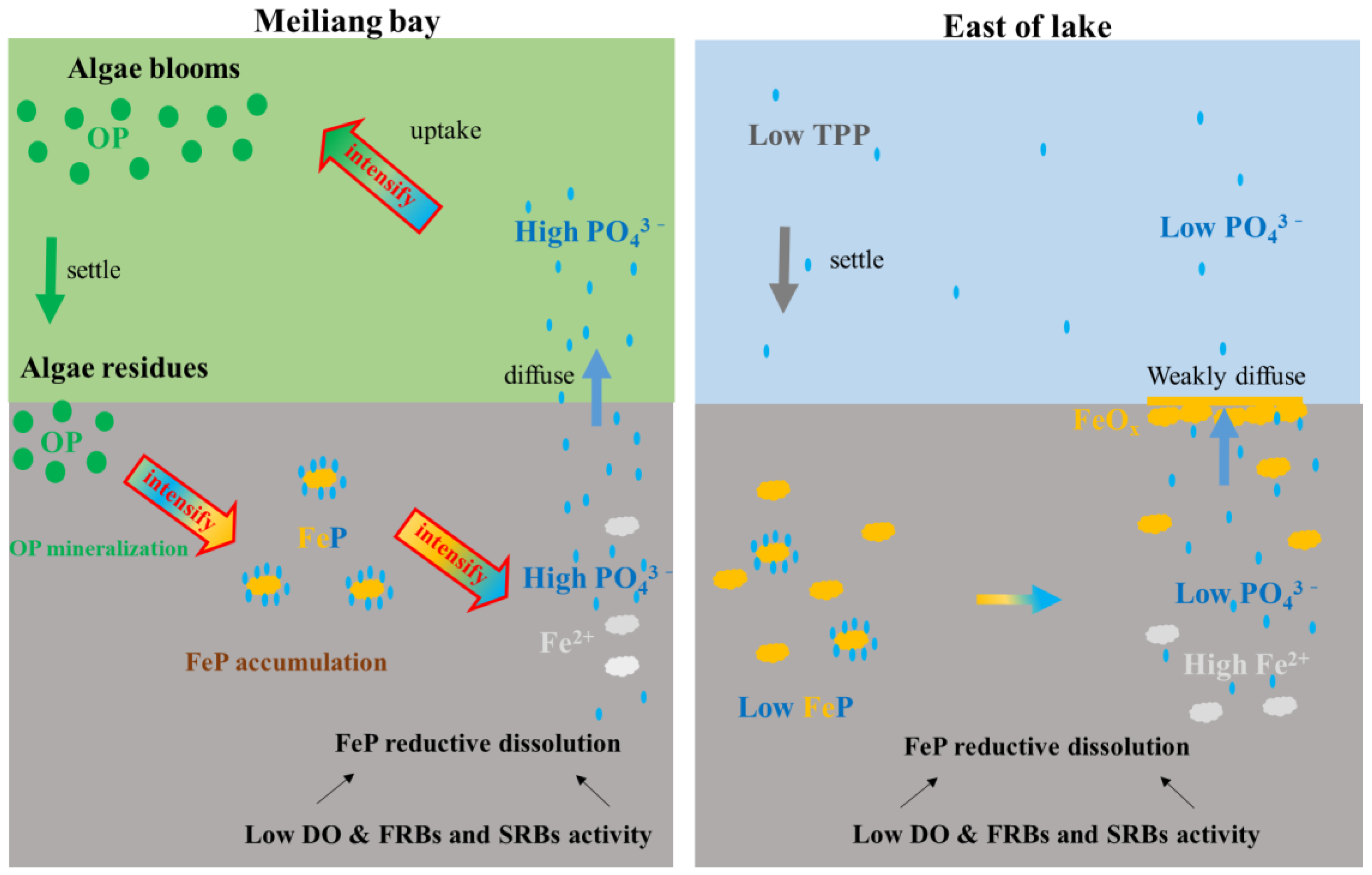
4.1. Sediment OP Mineralization and FeP Accumulation Promoted by Algae Bloom and Decomposition
4.2. Sediment P Remobilization Driven by FeP Reductive Dissolution
4.3. Reason about Algae Bloom in Eutrophic Lakes Endless for a Long Time
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lean, D.R.S. Phosphorus dynamics in lake water. Science 1973, 179, 678–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, D.M. Aquatic ecology: Phosphorus, the staff of life. Nature 2000, 406, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.T.; Michalak, A.M.; Beletsky, D.; Rao, Y.R.; Richards, R.P. Record-Breaking Lake Erie Hypoxia during 2012 Drought. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QIN, B.; Zhu, G.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Paerl, H.W.; Carmichael, W.W. A Drinking Water Crisis in Lake Taihu, China: Linkage to Climatic Variability and Lake Management. Env. Manag. 2010, 45, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisler, J.; Glibert, P.M.; Burkholder, J.M.; Anderson, D.M.; Cochlan, W.; Dennison, W.C.; Dortch, Q.; Gobler, C.J.; Heil, C.A.; Humphries, E.; et al. Eutrophication and harmful algal blooms: A scientific consensus. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nemery, J.; Gratiot, N.; Doan, P.T.K.; Duvert, C.; Villanueva, R.A.; Duwig, C. Carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and sediment sources and retention in a small eutrophic tropical reservoir. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 78, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondergaard, M.; Bjerring, R.; Jeppesen, E. Persistent internal phosphorus loading during summer in shallow eutrophic lakes. Hydrobiologia 2013, 710, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Ding, S.; Liu, L.; Xu, D.; Han, C.; Zhang, C. Iron-coupled inactivation of phosphorus in sediments by macrozoobenthos (chironomid larvae) bioturbation: Evidences from high-resolution dynamic measurements. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 204, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Ding, S.; Chen, X.; Sun, Q.; Fan, X.; Lin, J.; Ren, M.; Yang, L.; Zhang, C. Mechanisms driving phosphorus release during algal blooms based on hourly changes in iron and phosphorus concentrations in sediments. Water Res. 2018, 133, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liang, T.; Tian, S.; Wang, L.; Holm, P.E.; Hansen, H.C.B. High-resolution imaging of labile phosphorus and its relationship with iron redox state in lake sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Liu, H.; Tong, M.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, P.; Liu, D.; Yuan, S. Impact of Fe(II) oxidation in the presence of iron-reducing bacteria on subsequent Fe(III) bio-reduction. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, D.; Fleming, E.J.; McBeth, J.M. Iron-Oxidizing Bacteria: An Environmental and Genomic Perspective. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 64, 561–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Liu, H.; Guo, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Cai, Y.; Gao, A. Effects of tide and season changes on the iron-sulfur-phosphorus biogeochemistry in sediment porewater of a mangrove coast. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 686–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Jiang, H.L. Relative contribution of iron reduction to sediments organic matter mineralization in contrasting habitats of a shallow eutrophic freshwater lake. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 213, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Pan, F.; Santos, I.R.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, C.M.; Chen, N.W.; Lu, Z.Y.; Wang, F.F.; Li, Z.Y.; Li, H.L. Crab bioturbation drives coupled iron-phosphate-sulfide cycling in mangrove and salt marsh soils. Geoderma 2022, 424, 115990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozan, T.F.; Taillefert, M.; Trouwborst, R.E. Iron-sulfure-phosphorus cycling in the sediments of a shallow coastal bay: Implications for sediment nutrient release and benthic macro algal bloom. Limnol Ocean. 2002, 47, 1346–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, H.Y. Study on Nitrogen and Carbon Cycles in Lakes in the Middle and Late Period of Algal Bloom Outbreak; Yangzhou University: Yangzhou, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.M.; Chen, M.S.; Gong, M.D.; Fan, X.F.; Qin, B.Q.; Xu, H.; Gao, S.S.; Jin, Z.F.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Zhang, C.S. Internal phosphorus loading from sediments causes seasonal nitrogen limitation for harmful algal blooms. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 872–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, S.; Li, D. Decomposition of cyanobacterial bloom contributes to the formation and distribution of iron-bound phosphorus (Fe-P): Insight for cycling mechanism of internal phosphorus loading. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 696–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, G.; Li, X.; Ma, J.; Chen, S.; Deng, H.; Annalisa, O.-H. High sulfide production induced by algae decomposition and its potential stimulation to phosphorus mobility in sediment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.L.; Qian, P.Q.; Ye, L.; Song, T. Changes in nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations in Lake Taihu, 1985–2015. J. Lake Sci. 2016, 28, 935–943. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.J.; Li, J.; Chen, G.X. The current situation of cyanobacteria outbreak in Lake Taihu and innovative control measures. World Trop. Agric. Inf. 2021, 04, 58–59. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.F.; Ding, S.M.; Gong, M.D.; Chen, M.S.; Gao, S.S.; Jin, Z.F.; Tsang, D.C.W. Different Influences of Bacterial Communities on Fe (III) Reduction and Phosphorus Availability in Sediments of the Cyanobacteria- and Macrophyte-Dominated Zones. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Editorial board of Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analysis Methods. Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analysis Methods; (In Chinese). China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 670–671. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ruban, V.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.F.; Pardo, P.; Rauret, G.; Muntau, H.; Quevauviller, P. Selection and evaluation of sequential extraction procedures for the determination of phosphorus forms in lake sediment. J. Environ. Monit. 1999, 1, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wu, W.; Ding, S.M.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, C. A high-resolution dialysis technique for rapid determination of dissolved reactive phosphate and ferrous iron in pore water of sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 1, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Chen, Y.; Ding, S.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C. Diffusive Gradients in Thin Films Technique Equipped with a Mixed Binding Gel for Simultaneous Measurements of Dissolved Reactive Phosphorus and Dissolved Iron. Env. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10477–10484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.M.; Sun, Q.; Xu, D.; Jia, F.; He, X.; Zhang, C. High-resolution simultaneous measurements of dissolved reactive phosphorus and dissolved sulfide: The first observation of their simultaneous release in sediments. Env. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 8297–8304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ding, S.M.; Shi, L.; Gong, M.D.; Xu, S.W.; Zhang, C.S. Simultaneous measurements of cations and anions using diffusive gradients in thin films with a ZrO-Chelex mixed binding layer. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 972, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.M.; Xu, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Gong, M.; Zhang, C. Simultaneous Measurements of Eight Oxyanions Using High-Capacity Diffusive Gradients in Thin Films (Zr-Oxide DGT) with a High-Efficiency Elution Procedure. Env. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 7572–7580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, M.P.; Davison, W.; Zhang, H.; Tych, W. Kinetics of metal exchange between solids and solutions in sediments and soils interpreted from DGT measured fluxes. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 2757–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Gregory, S. Diffusion of ions in sea warer and in deep-sea sediments. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 1974, 38, 703–714. [Google Scholar]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dai, Z.M.; Liu, G.F.; Chen, H.H.; Chen, C.R.; Wang, J.K.; Ai, S.Y.; Wei, D.; Li, D.M.; Ma, B.; Tang, C.X.; et al. Long-term nutrient inputs shift soil microbial functional profiles of phosphorus cycling in diverse agroecosystems. ISME J. 2020, 14, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, M.; Lu, Z.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Qian, X. Pollution characteristics of phosphorus in different media in Taihu Lake and its treatment enlightenment. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 2575–2585. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Fang, H.W.; Reible, D. Mathematical model for interactions and transport of phosphorus and sediment in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Water Res. 2015, 85, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarczynska, M.; Romanowska-Duda, Z.; Jurczak, T.; Zalewski, M. Toxic cyanobacterial blooms in a drinking water reservoir-causes, consequences and management strategy. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2001, 1, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codd, G.A.; Lindsay, J.; Young, F.M.; Morrison, L.F.; Metcalf, J.S. Harmful Cyanobacteria; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, S.; Peng, X.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X.; Ge, F.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, Z. Potential ecological implication of Cladophora oligoclora decomposition: Characteristics of nutrient migration, transformation, and response of bacterial community structure. Water Res. 2021, 190, 116741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, E. Decomposition of macroalgae, vascular plants and sediment detritus in seawater: Use of stepwise thermogravimetry. Biogeochemistry 1994, 26, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Huang, D.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, S. Novel insights into molecular composition of organic phosphorus in lake sediments. Water Res. 2022, 214, 118197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Guo, Z.; Cai, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, X. Remobilization and hypoxia-dependent migration of phosphorus at the coastal sediment-water interface. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 125078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, J.; Berelson, W.M.; Coale, K.H.; Johnson, K.S.; Kilgore, T.E. Phosphorus regeneration in continental margin sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 2891–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Xu, N.; Jia, Y.; Gao, S.; Tian, T.; Shen, W. Degradation of tetracycline by activated peroxodisulfate using Cufe2o4-Loaded biochar. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 368, 120622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, C.; Liang, X. Biogeochemical cycling of iron at lake water-sediment interface and its influence on trace metals. Geol. Geochem. 2003, 31, 63–69. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- van de Velde, S.J.; Hidalgo-Martinez, S.; Callebaut, I.; Antler, G.; James, R.K.; Leermakers, M.; Meysman, F.J.R. Burrowing fauna mediate alternative stable states in the redox cycling of salt marsh sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2020, 276, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, F.; Guo, Z.R.; Cai, Y.; Fu, Y.Y.; Wu, J.Y.; Wang, B.; Liu, H.T.; Gao, A.G. Cyclical patterns and (im)mobilization mechanisms of phosphorus in sediments from a small creek estuary: Evidence from in situ monthly sampling and indoor experiments. Water Res. 2020, 171, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.R.; Pellerin, A.; Antler, G.; Kasten, S.; Findlay, A.J.; Dohrmann, I.; Roy, H.; Turchyn, A.V.; Jorgensen, B.B. Early diagenesis of iron and sulfur in Bornholm Basin sediments: The role of near-surface pyrite formation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2020, 284, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, I.R.; Burdige, D.J.; Jennerjahn, T.C.; Bouillon, S.; Cabral, A.; Serrano, O.; Wernberg, T.; Filbee-Dexter, K.; Guimond, J.A.; Tamborski, J.J. The renaissance of Odum’s outwelling hypothesis in ‘Blue Carbon’ science. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 255, 107361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijs, S.K.; Jonkers, H.M.; van Gemerden, H.; Schaub, B.E.M.; Stal, L.J. The Buffering Capacity Towards Free Sulphide in Sediments of a Coastal Lagoon (Bassin d’Arcachon, France)—The Relative Importance of Chemical and Biological Processes. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1999, 49, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibault, P.-J.; Rancourt, D.G.; Evans, R.J.; Dutrizac, J.E. Mineralogical confirmation of a near-P:Fe=1:2 limiting stoichiometric ratio in colloidal P-bearing ferrihydrite-like hydrous ferric oxide. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomqvist, S.; Gunnars, A.; Elmgren, R.; Blomqvist, S.; Gunnars, A.; Elmgren, R. Why the limiting nutrient differs between temperate coastal seas and freshwater lakes: A matter of salt. Limnol Oceanogr. Limnol. Oceanogr. Am. Soc. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2004, 49, 2236–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, B.; Huang, R.; Diaz, J.M.; Tang, Y. Rethinking the biotic and abiotic remineralization of complex phosphate molecules in soils and sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Shang, J.; Lu, X.; Fan, C. Effects of sludge dredging on the prevention and control of algae-caused black bloom in Taihu Lake, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Y. Study on the In-Situ Emergency Treatment of Algae and Resource Utilization; Tianjin University of Science & Technology: Tianjin, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Zhao, D.; Hu, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, D.; Yuan, X.; Xie, B. Trichloromethane Formation Potential in Killing Algae with Chlorine Dioxide. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2013, 18, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Guo, M.; Wang, Y.; Ye, B.; Chen, Y.; Yang, X. Preparation of biological sustained-release nanocapsules and explore on algae-killing properties. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 31, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Weitzel, K.A.; Duan, X.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Dionysiou, D.D. A comprehensive review on algae removal and control by coagulation-based processes: Mechanism, material, and application. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 293, 121106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, C.; Dai, Y.; Sun, N.; Wu, H.; Tang, Y.; Dai, T. Algae Bloom and Decomposition Changes the Phosphorus Cycle Pattern in Taihu Lake. Water 2022, 14, 3607. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223607
Han C, Dai Y, Sun N, Wu H, Tang Y, Dai T. Algae Bloom and Decomposition Changes the Phosphorus Cycle Pattern in Taihu Lake. Water. 2022; 14(22):3607. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223607
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Chaonan, Yan Dai, Ningning Sun, Hao Wu, Yu Tang, and Tianhao Dai. 2022. "Algae Bloom and Decomposition Changes the Phosphorus Cycle Pattern in Taihu Lake" Water 14, no. 22: 3607. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223607





