Effects of Rice Husk Biochar on Nitrogen Leaching from Vegetable Soils by 15N Tracing Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil, Biochar and Nitrogen Fertilizer
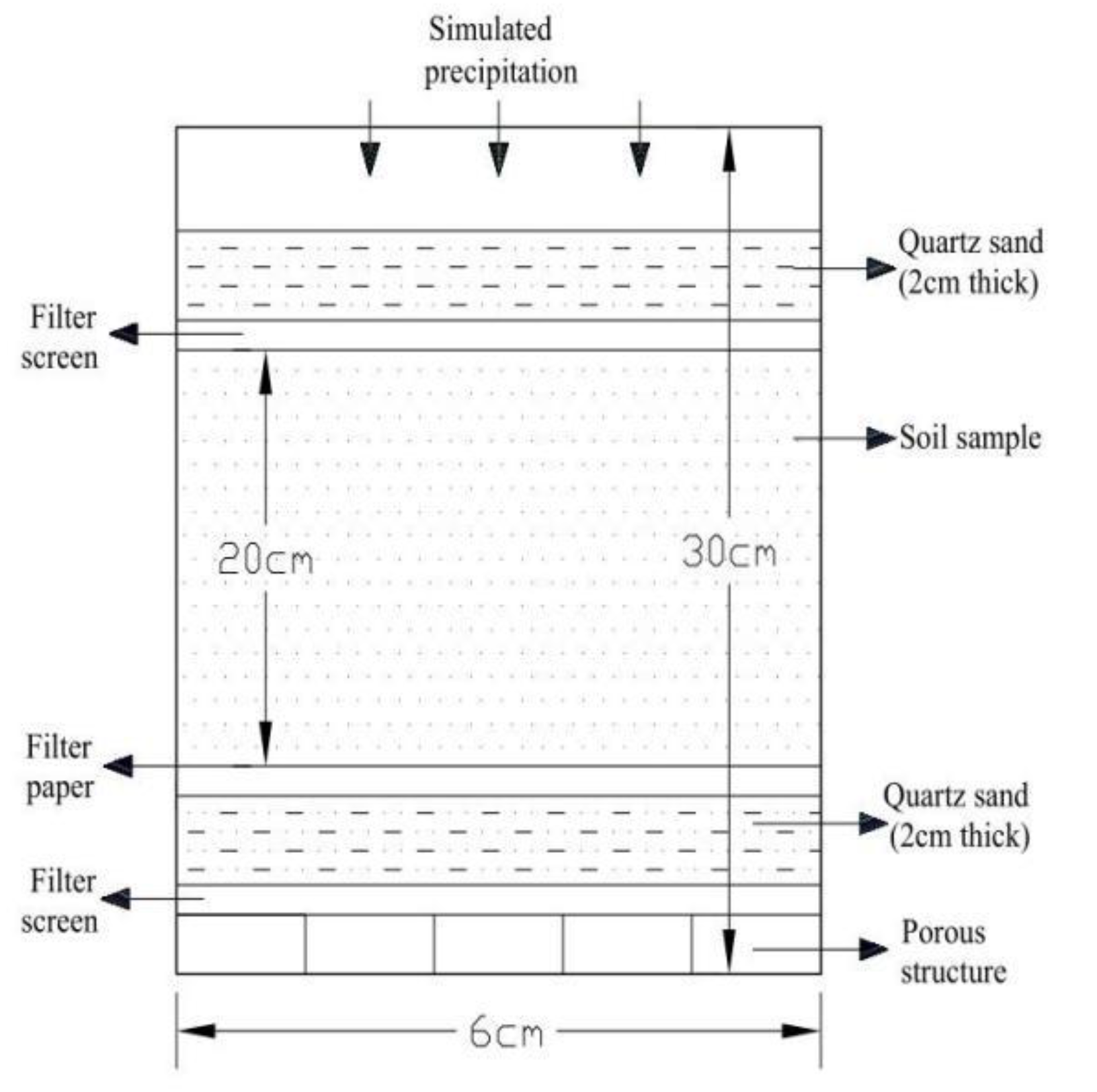
2.2. Preparation of Soil Columns
2.3. Incubation and Leaching of Soil Columns
2.4. Chemical Analysis
2.5. Calculation and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Properties of Tested Soils and Biochar Materials
3.2. Effects of Different Treatments on Soil Chemical Properties
3.3. Nitrogen Concentration and Loss in Leachate
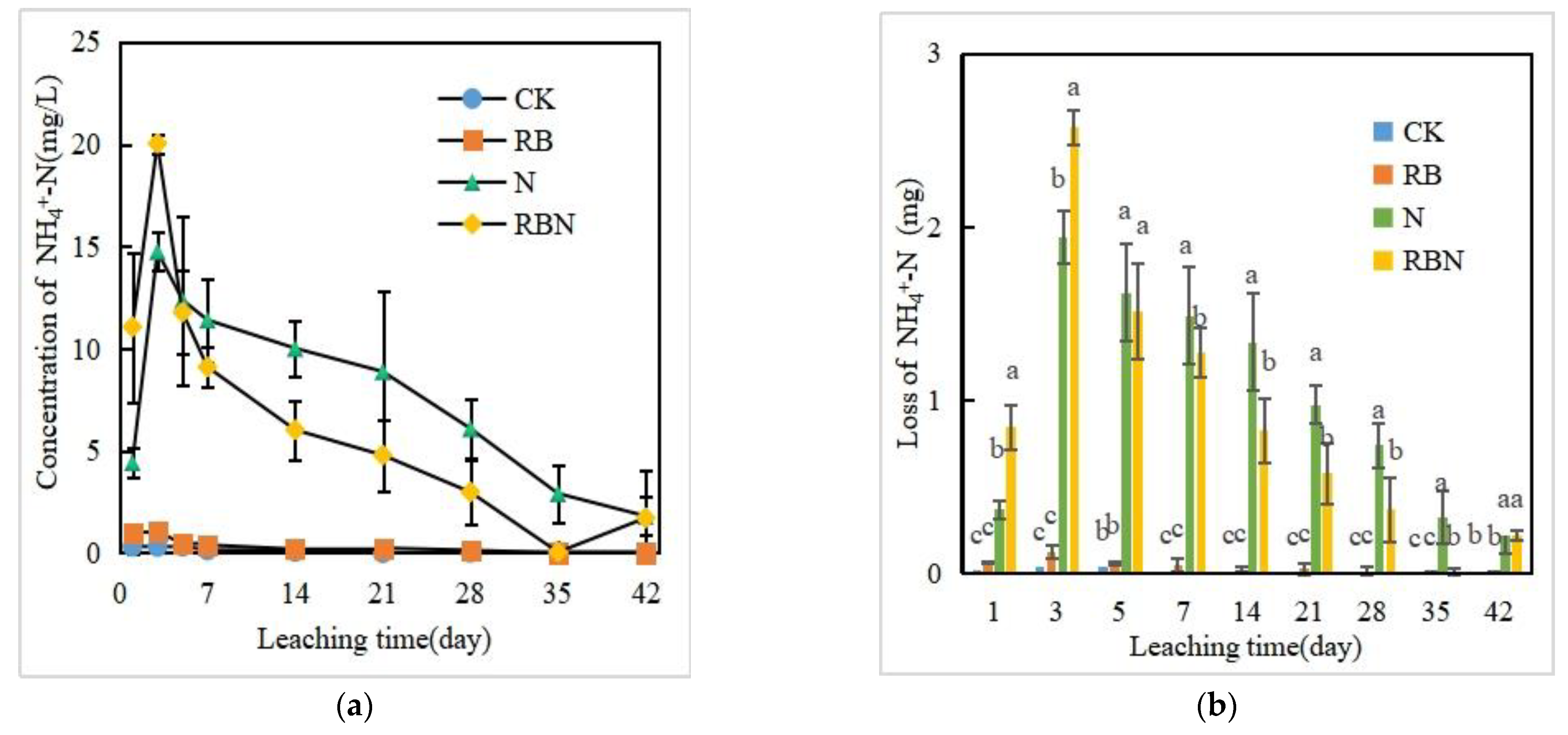
3.3.1. NH4+-N Concentration and Loss in Leachate
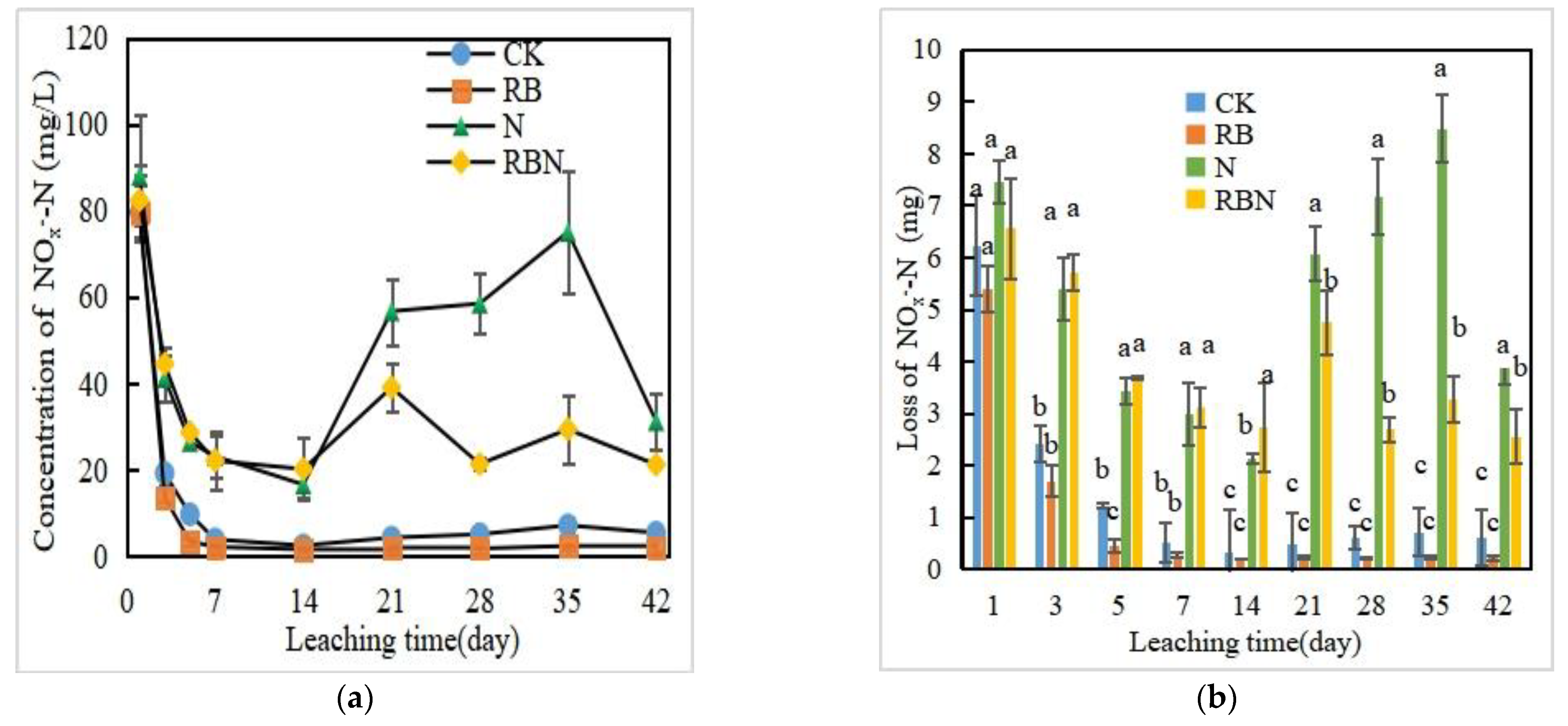
3.3.2. NOx−-N Concentration and Loss in Leachate
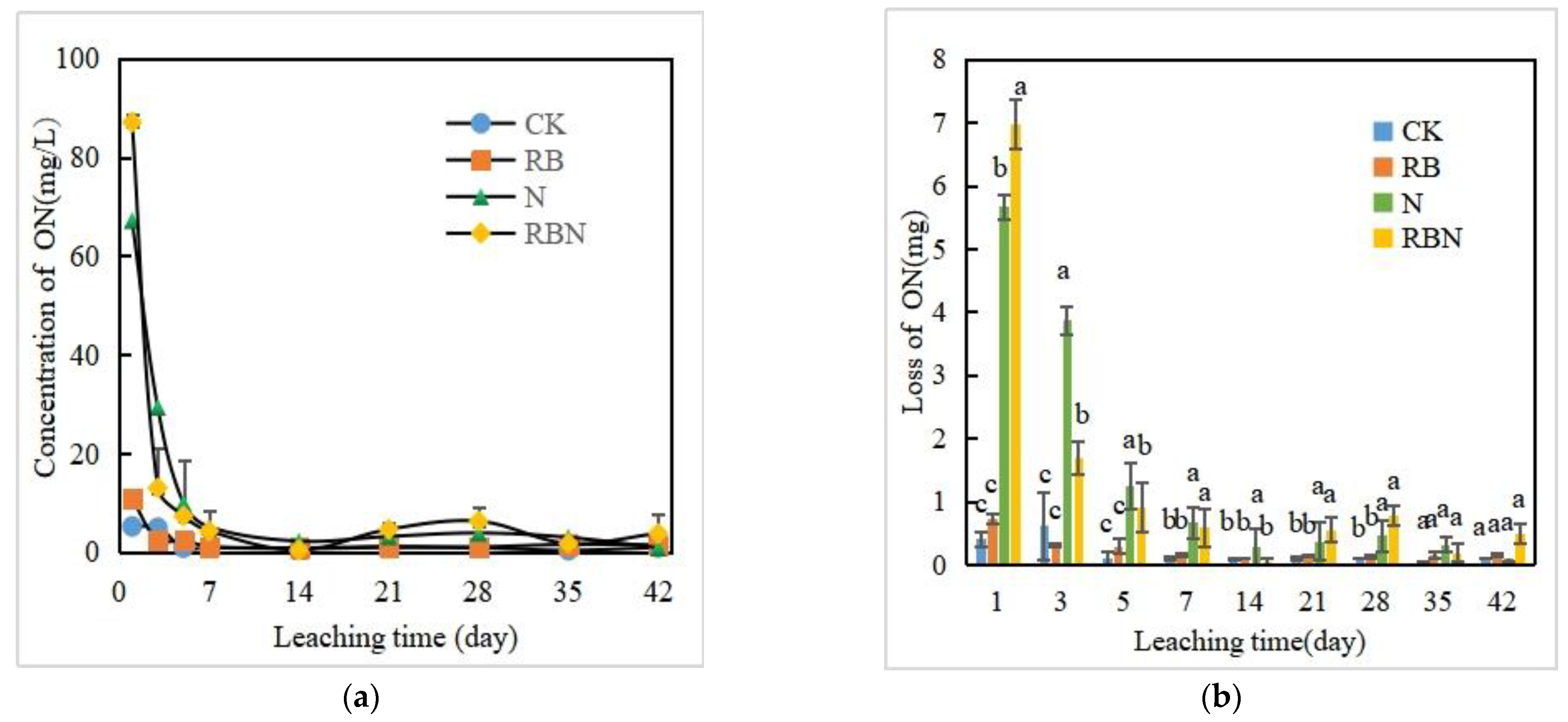
3.3.3. ON Concentration and Loss in Leachate
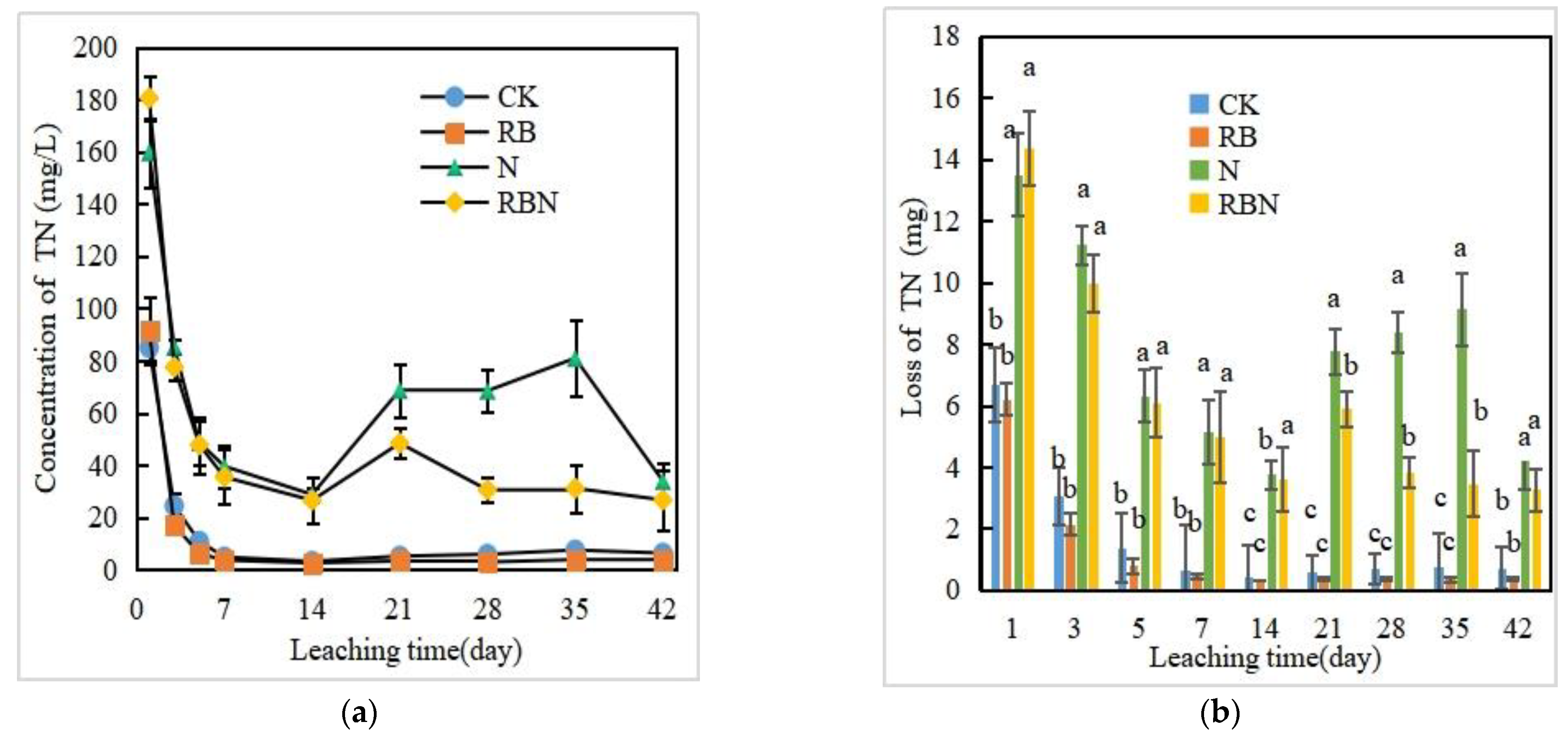
3.3.4. TN Concentration and Loss in Leachate
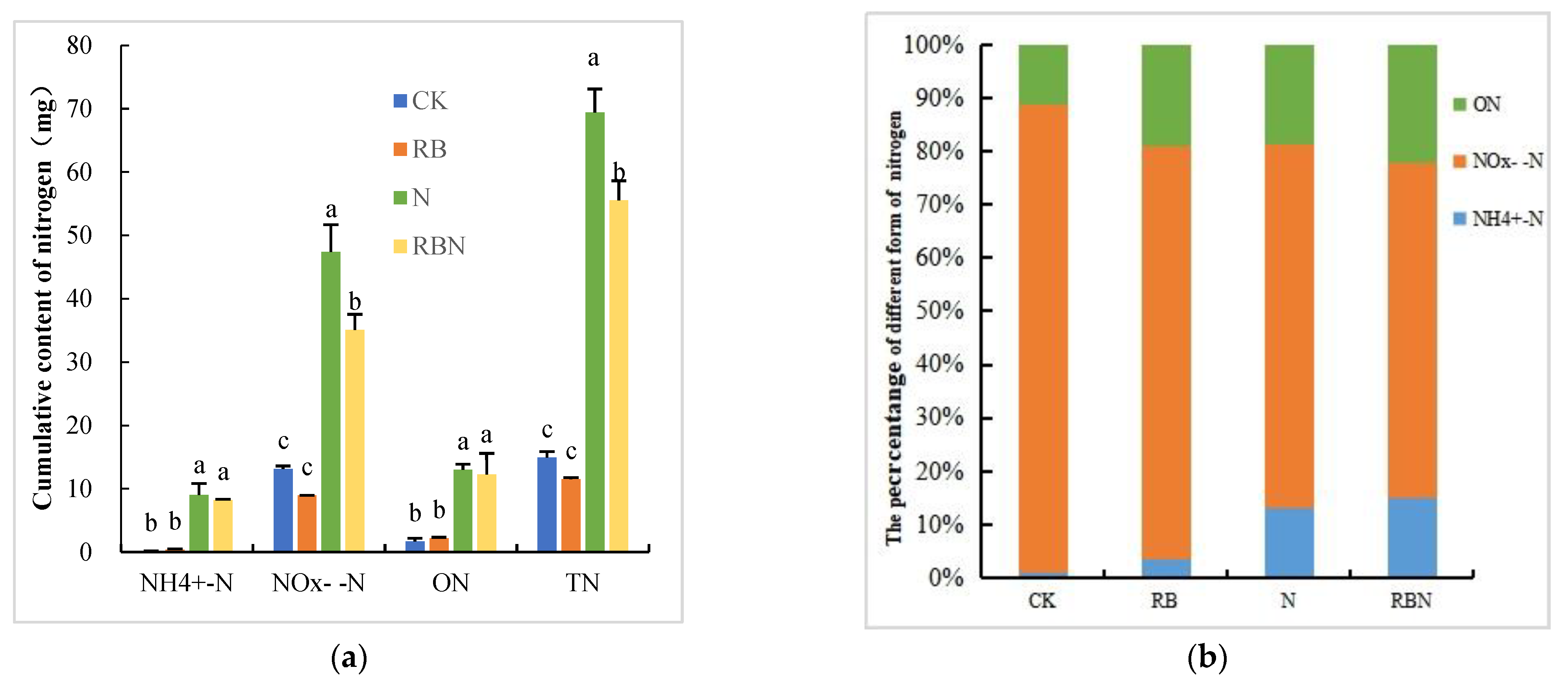
3.4. Cumulative Content of Nitrogen Loss in Leachate
3.5. Losses and Residues of 15N-Labeled Urea Applied to the Soil
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Biochar on Soil Chemical Properties
4.2. Effects of Biochar on Soil Nitrogen Transformation and Leaching
4.3. Effects of Biochar on the Leaching and Retention of Urea Fertilizer
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thompson, R.B.; Martinez-Gaitan, C.; Gallardo, M.; Gimenez, C.; Fernandez, M. Identification of irrigation and N management practices that contribute to nitrate leaching loss from an intensive vegetable production system by use of a comprehensive survey. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 89, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.L.; Sakoda, A.; Shibasaki, R.; Suzuki, M. A Modelling Approach to Global Nitrate Leaching Caused by Anthropogenic Fertilisation. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1961–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Entz, T. Nitrate Leaching Losses Under Repeated Cattle Feedlot Manure Applications in Southern Alberta. J. Environ. Qual. 1996, 25, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, D.; Mather, P.; Russell, S.; Rajapakse, J. Dynamics of Nitrate-Nitrogen Removal in Experimental Stormwater Biofilters under Intermittent Wetting and Drying. J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 142, 04015090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, R.; Leo, M.; Tim, J.; Mark, F.; Alison, S.; Robert, A.; Robert, R. Biochar induced soil microbial community change: Implications for biogeochemical cycling of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus. Pedobiologia 2011, 54, 309–320. [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann, I.; Martens, R.; Rillig, M.; Kruse, A.; Nutrition, M.K.; Bodenkunde, S.S. Hydrochar amendment promotes microbial immobilization of mineral nitrogen. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2014, 177, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, S.; Whalen, J.K.; Thomas, B.W.; Sachdeva, V.; Deng, H. Environment Physico-chemical properties and microbial responses in biochar-amended soils: Mechanisms and future directions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 206, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liao, F.; Huang, M.; Yang, L.; Li, Y. Biochar Improves Sugarcane Seedling Root and Soil Properties Under a Pot Experiment. Sugar Tech. 2015, 17, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Wu, W.X.; Shi, D.Z.; Yang, M.; Zhong, Z. Evaluation of Biochar Effects on Nitrogen Retention and Leaching in Multi-Layered Soil Columns. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 213, 1961–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi, A.E.; Horn, R.J. Biochar-Induced Changes in Soil Resilience: Effects of Soil Texture and Biochar Dosage. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.; Hoang, S.A.; Beiyuan, J.; Gupta, S.; Hou, D.; Karakoti, A.; Joseph, S.; Jung, S.; Kim, K.-H.; Kirkham, M.B.; et al. Multifunctional applications of biochar beyond carbon storage. Int. Mater. Rev. 2021, 67, 150–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harter, J.; Weigold, P.; El-Hadidi, M.; Huson, D.H.; Kappler, A.; Behrens, T.E. Soil biochar amendment shapes the composition of N2O-reducing microbial communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Hu, S.; Chen, J.; Müller, K.; Li, Y.; Fu, W.; Lin, Z.; Wang, H.J. Sediments Effects of biochar application in forest ecosystems on soil properties and greenhouse gas emissions: A review. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 546–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Xu, C.Y.; Tahmasbian, I.; Che, R.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wallace, H.M.; Bai, S.H.J.G. Effects of biochar on soil available inorganic nitrogen: A review and meta-analysis. Geoderma 2017, 288, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, D.; Fleming, P.; Wang, B.; Horton, R.; Karlen, D. Biochar impact on nutrient leaching from a Midwestern agricultural soil. Geoderma 2010, 158, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sika, M.; Hardie, A. Effect of pine wood biochar on ammonium nitrate leaching and availability in a South African sandy soil. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 65, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameyama, K.; Miyamoto, T.; Shiono, T.; Shinogi, Y. Influence of Sugarcane Bagasse-derived Biochar Application on Nitrate Leaching in Calcaric Dark Red Soil. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 41, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, Z.; Deng, X.; Herbert, S.; Xing, B. Impacts of adding biochar on nitrogen retention and bioavailability in agricultural soil. Geoderma 2013, 206, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Gao, B.; Zhang, M.; Inyang, M.; Zimmerman, A.R. Effect of biochar amendment on sorption and leaching of nitrate, ammonium, and phosphate in a sandy soil. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 1467–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, J.; Rondon, M.; Molina, D.; Riha, S.J.; Lehmann, J. Maize yield and nutrition during 4years after biochar application to a Colombian savanna oxisol. Plant Soil 2010, 333, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruun, E.W.; Petersen, C.; Strobel, B.W.; Hauggaard-Nielsen, H. Nitrogen and Carbon Leaching in Repacked Sandy Soil with Added Fine Particulate Biochar. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Cai, Z.; Müller, C.; Zhang, J. Short-term effects of nitrapyrin, rice straw and its biochar application on N transformation in soils of humid subtropical China. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B—Soil Plant Sci. 2018, 68, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvořáčková, H.; Dvořáček, J.; Záhora, J.; Šimečková, J. Biochar Alone Did Not Increase Microbial Activity in Soils from a Temperate Climate That Had Long-Term Acidity Stress. Agriculture 2022, 12, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratiwi, E.; Hillary, A.K.; Fukuda, T.; Shinogi, Y. The effects of rice husk char on ammonium, nitrate and phosphate retention and leaching in loamy soil. Geoderma 2016, 277, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakongkep, N.; Gilkes, R.J.; Wiriyakitnateekul, W.; Duangchan, A.; Darunsontaya, T. The Effects of Pyrolysis Conditions on the Chemical and Physical Properties of Rice Husk Biochar. Int. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 3, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, S.; Knowles, T.; Middelink, E.; Haefele, S.; Sohi, S.; Cross, A.; Haszeldine], S. Sustainable gasification–biochar systems? A case-study of rice-husk gasification in Cambodia, Part I: Context, chemical properties, environmental and health and safety issues. Energy Policy 2012, 42, 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, G.; Kim, H.; Chen, J.; Kim, Y. Effects of Biochar Addition on Nitrogen Leaching and Soil Structure following Fertilizer Application to Rice Paddy Soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shizhengyuan, L. Degradation of soil Nutrients in southeast China. Pedosphere 2000, 10, 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.; Song, X.; Ju, X.; Zhang, J.; Muller, C.; Sylvester, B.; Thorman, R.; Bingham, I.; Rees, R. Gross N transformation rates and related N2 O emissions in Chinese and UK agricultural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.; Bu, J.; Ren, G.; Zhang, Z.; Li, K.; Ding, A. Mechanism of Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Aqueous Solution by Fe-Modified Biochar and Its Application. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, S.D.; Camps-Arbestain, M.; Lin, Y.; Munroe, P.; Chiaa, C.H. An investigation into the reactions of biochar in soil. Soil Res. 2010, 48, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Sima, J.; Zhao, L.; Mak, O.; Cao, X. Indispensable role of biochar-inherent mineral constituents in its environmental applications: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.Y.; Hong, Z.; Li, J.; Jiang, J.; Baquy, A.A.; Xu, R.; Qian, W. Mechanisms for Increasing the pH Buffering Capacity of an Acidic Ultisol by Crop Residue-Derived Biochars. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 8111–8119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruun, S.; Harmer, S.L.; Bekiaris, G.; Christel, W.; Zuin, L.; Hu, Y.; Jensen, L.S.; Lombi, E. The effect of different pyrolysis temperatures on the speciation and availability in soil of P in biochar produced from the solid fraction of manure. Chemosphere 2017, 169, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limwikran, T.; Kheoruenromne, I.; Suddhiprakarn, A.; Prakongkep, N.; Gilkes, R.J. Dissolution of K, Ca, and P from biochar grains in tropical soils. Geoderma 2018, 312, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, X.; Tan, G.; Wang, H.; Gai, X. Effect of biochar additions to soil on nitrogen leaching, microbial biomass and bacterial community structure. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2016, 74, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.; Meng, J.; Yu, L.; Su, W.; Afzal, M.; Li, Y.; Brookes, P.C.; Redmile-Gordon, M.; Luo, Y.; Xu, J. Changes in nitrogen related functional genes along soil pH, C and nutrient gradients in the charosphere. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 650, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, R.; Yong, S.; Sarkar, B.; Mandal, S.; Khan, N. Biochar-induced concomitant decrease in ammonia volatilization and increase in nitrogen use efficiency by wheat. Chemosphere Environ. Toxicol. Risk Assess. 2016, 142, 120–127. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.; Ding, W.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Luo, J.; Bolan, N.; Xie, Z. Biochar suppressed the decomposition of organic carbon in a cultivated sandy loam soil: A negative priming effect. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 76, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.L.; Murphy, D.V.; Khalid, M.; Ahmad, W.; Edwards-Jones, G.; Deluca, T.H. Short-term biochar-induced increase in soil CO2 release is both biotically and abiotically mediated. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1723–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodor, D.E.; Amanor, Y.J.; Attor, F.T.; Adjadeh, T.A.; Neina, D.; Miyittah, M. Co-application of biochar and cattle manure counteract positive priming of carbon mineralization in a sandy soil. Environ. Syst. Res. 2018, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Zhang, R.; Shaun, N.; Joseph, S.D.; Huang, D.; Torsten, T. A Combination of Biochar–Mineral Complexes and Compost Improves Soil Bacterial Processes, Soil Quality, and Plant Properties. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Wang, A.; Hou, C.; Han, S.; Chen, W. The limited effects of carbonaceous material amendments on nitrite-oxidizing bacteria in an Alfisol. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 139398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, B.; Chang, S.X.; Gong, J. Biochar addition affected the dynamics of ammonia oxidizers and nitrification in microcosms of a coastal alkaline soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2014, 50, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelissen, R.; Huygens, S.; Ruysschaert, B. Maize biochars accelerate short-term soil nitrogen dynamics in a loamy sand soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 55, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daims, H.; Luecker, S.; Wagner, M. A New Perspective on Microbes Formerly Known as Nitrite-Oxidizing Bacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster, D.N.; Jones, D.L.; Murphy, D.V. Organic nitrogen mineralisation in soil is unchanged by biochar addition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 48, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Luo, Y.; Deng, X.; Xing, B. Characterization and influence of biochars on nitrous oxide emission from agricultural soil. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 174, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.W.; Zhang, L.M.; Dai, Y.; Di, H.J.; He, J.Z. pH-dependent distribution of soil ammonia oxidizers across a large geographical scale as revealed by high-throughput pyrosequencing. J. Soils Sediments 2013, 13, 1439–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Shan, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Yan, X. Variable responses of nitrification and denitrification in a paddy soil to long-term biochar amendment and short-term biochar addition. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangarajan, R.; Bolan, N.S.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; Wijesekara, H.; Xu, Y.; Tsang, D.; Hou, D. The potential value of biochar in the mitigation of gaseous emission of nitrogen. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D. The Impact of Agricultural Extension on Farmer Nutrient Management Behavior in Chinese Rice Production: A Household-Level Analysis. Sustainability 2014, 6, 6644–6665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.P.; Hatton, B.J.; Singh, B.; Cowie, A.L.; Kathuria, A. Influence of biochars on nitrous oxide emission and nitrogen leaching from two contrasting soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 1224–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Lu, H.; Chu, L.; Shao, H.; Shi, W. Biochar applied with appropriate rates can reduce N leaching, keep N retention and not increase NH3 volatilization in a coastal saline soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, H.; Zhou, S.; Bai, N.; Zheng, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Lv, W. Effect of Straw and Straw Biochar on the Community Structure and Diversity of Ammonia-oxidizing Bacteria and Archaea in Rice-wheat Rotation Ecosystems. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9367–9678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Properties | Soil | Rice Rusk Biochar (RB) |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.26 | 9.85 |
| CEC (cmol(+)/kg) | 20.60 | 31.70 |
| TOC (g/kg) | 8.60 | 260 |
| DOC (mg kg−1) | 11.0 | 4450 |
| TN (g/kg) | 1.23 | 4.29 |
| NH4+-N (mg kg−1) | 6.90 | 1.16 |
| NOx−-N (mg kg−1) | 16.63 | 3.00 |
| Ava. P (mg kg−1) | 22.40 | 195.8 |
| SSA (m2 g−1) | - | 11.08 |
| Properties | CK | RB | N | RBN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 5.59 ± 0.02 b | 5.93 ± 0.068 a | 5.27 ± 0.02 c | 5.58 ± 0.03 b |
| TOC (g kg−1) | 8.51 ± 0.053 b | 18.23 ± 0.30 a | 8.49 ± 0.02 b | 18.17 ± 0.14 a |
| TN (g kg−1) | 1.22 ± 0.01 d | 1.43 ± 0.01 b | 1.28 ± 0.01 c | 1.49 ± 0.05 a |
| NH4+-N (mg kg−1) | 1.66 ± 0.06 a | 1.47 ± 0.01 a | 1.77 ± 0.16 a | 1.54 ± 0.21 a |
| NOx−-N (mg kg−1) | 1.91 ± 0.38 b | 1.65 ± 0.08 c | 2.46 ± 0.12 a | 1.99 ± 0.09 b |
| Ava. P (mg kg−1) | 15.16 ± 0.71 b | 22.06 ± 0.98 a | 14.95 ± 0.35 b | 23.49 ± 0.97 a |
| Treatments | NH4+-N Leached | NOx−-N Leached | Other N Loss | Retained N in the Soil |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 7.75 ± 1.70 a | 31.79 ± 4.23 a | 29.01 ± 3.96 a | 28.96 ± 0.27 b |
| RBN | 6.97 ± 0.22 a | 22.30 ± 1.37 b | 35.31 ± 1.83 a | 32.92 ± 0.28 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, Y.; Zhu, S.; Pan, R.; Bu, J.; Liu, Y.; Ding, A. Effects of Rice Husk Biochar on Nitrogen Leaching from Vegetable Soils by 15N Tracing Approach. Water 2022, 14, 3563. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14213563
Ding Y, Zhu S, Pan R, Bu J, Liu Y, Ding A. Effects of Rice Husk Biochar on Nitrogen Leaching from Vegetable Soils by 15N Tracing Approach. Water. 2022; 14(21):3563. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14213563
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Ying, Siyu Zhu, Run Pan, Jiangping Bu, Yong Liu, and Aifang Ding. 2022. "Effects of Rice Husk Biochar on Nitrogen Leaching from Vegetable Soils by 15N Tracing Approach" Water 14, no. 21: 3563. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14213563
APA StyleDing, Y., Zhu, S., Pan, R., Bu, J., Liu, Y., & Ding, A. (2022). Effects of Rice Husk Biochar on Nitrogen Leaching from Vegetable Soils by 15N Tracing Approach. Water, 14(21), 3563. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14213563







