Active Biomonitoring of Heavy Metal Concentrations in Aquatic Environment Using Mosses and Algae
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
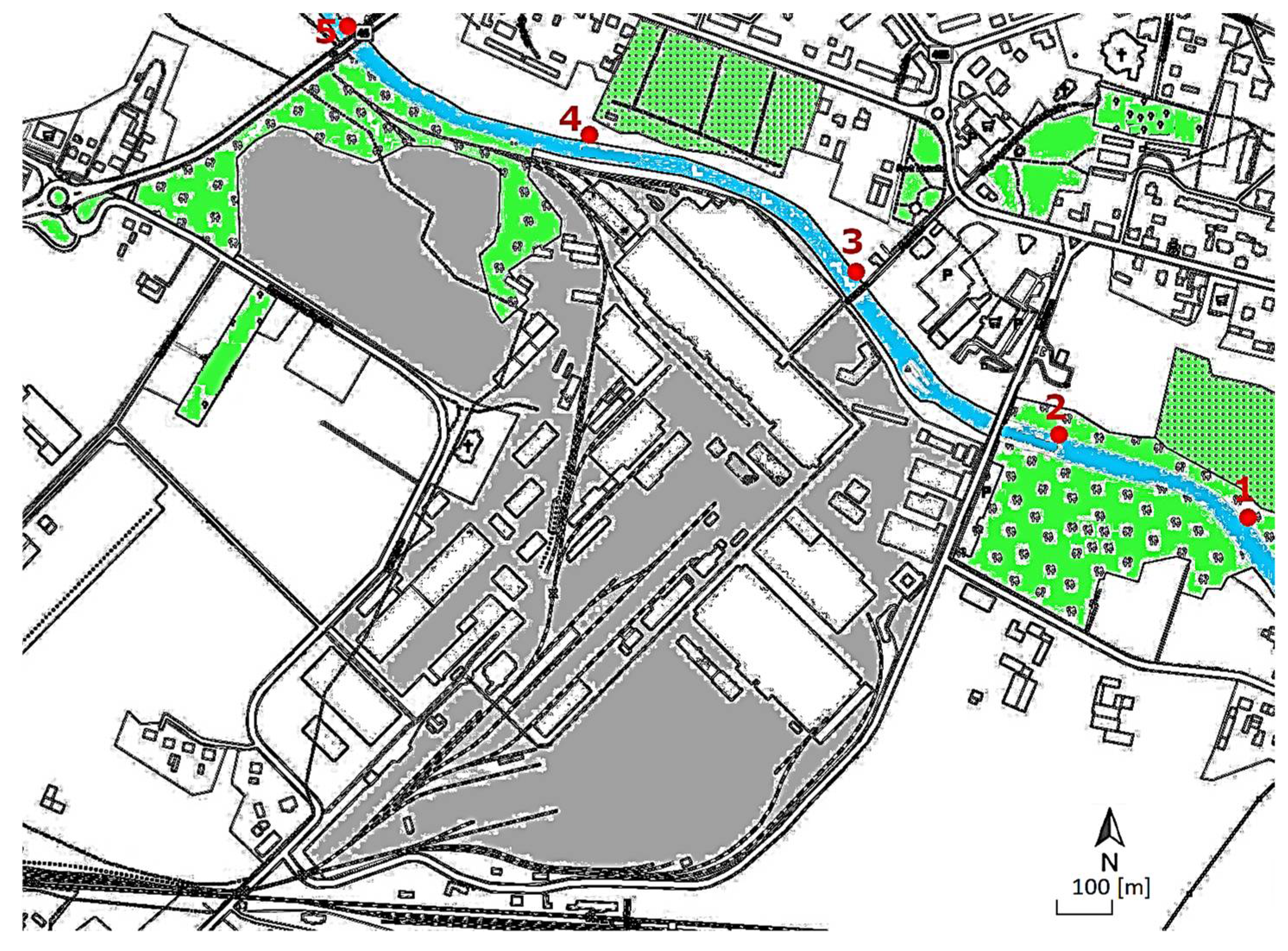
2.1. Characteristics of the Study Area
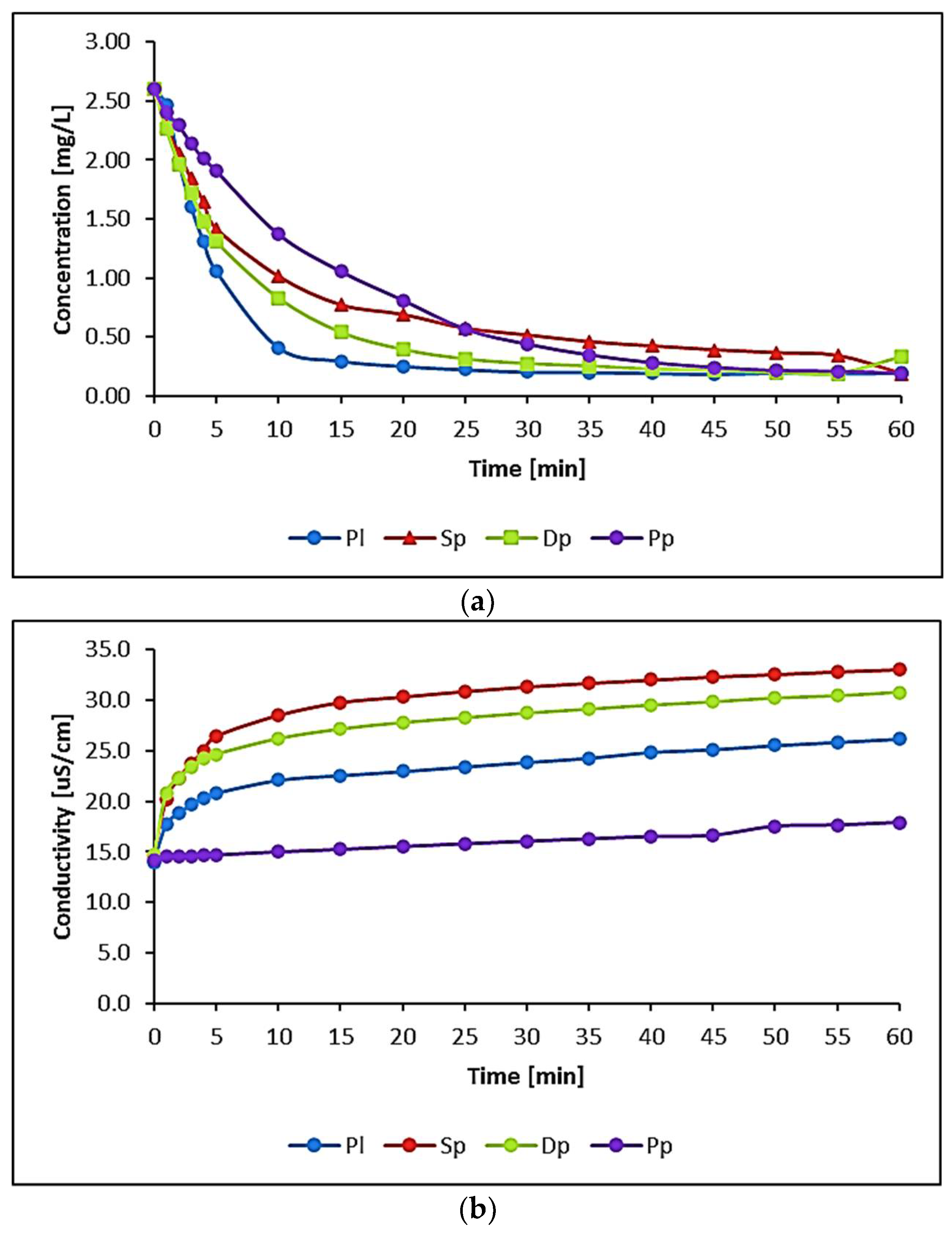
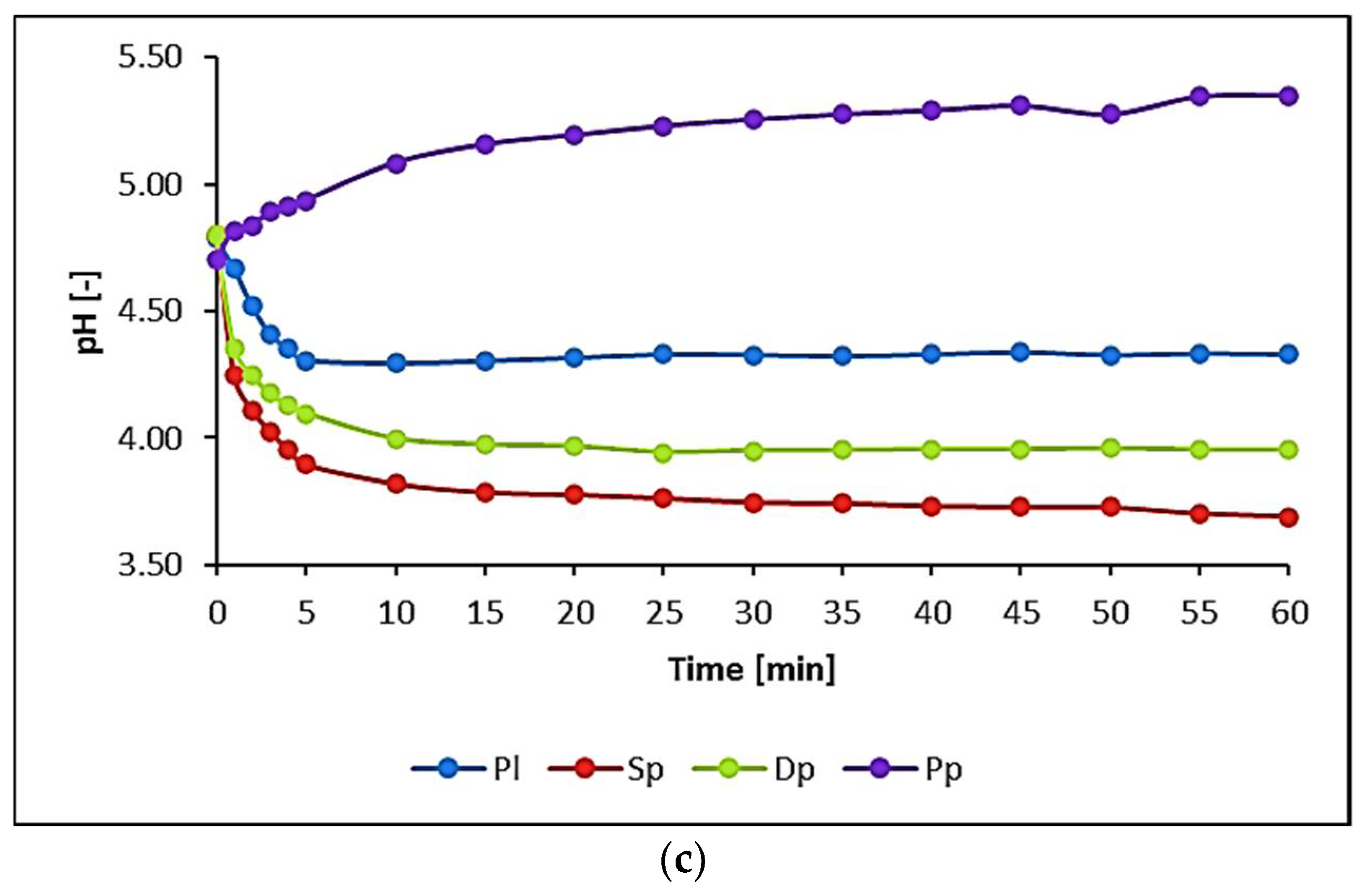
2.2. Method of Conducting Laboratory Experiment
Apparatus and Reagents
2.3. Method of Conducting Biomonitoring Study in the Field
Apparatus and Reagents
2.4. Quality Control
3. Results and Discussion
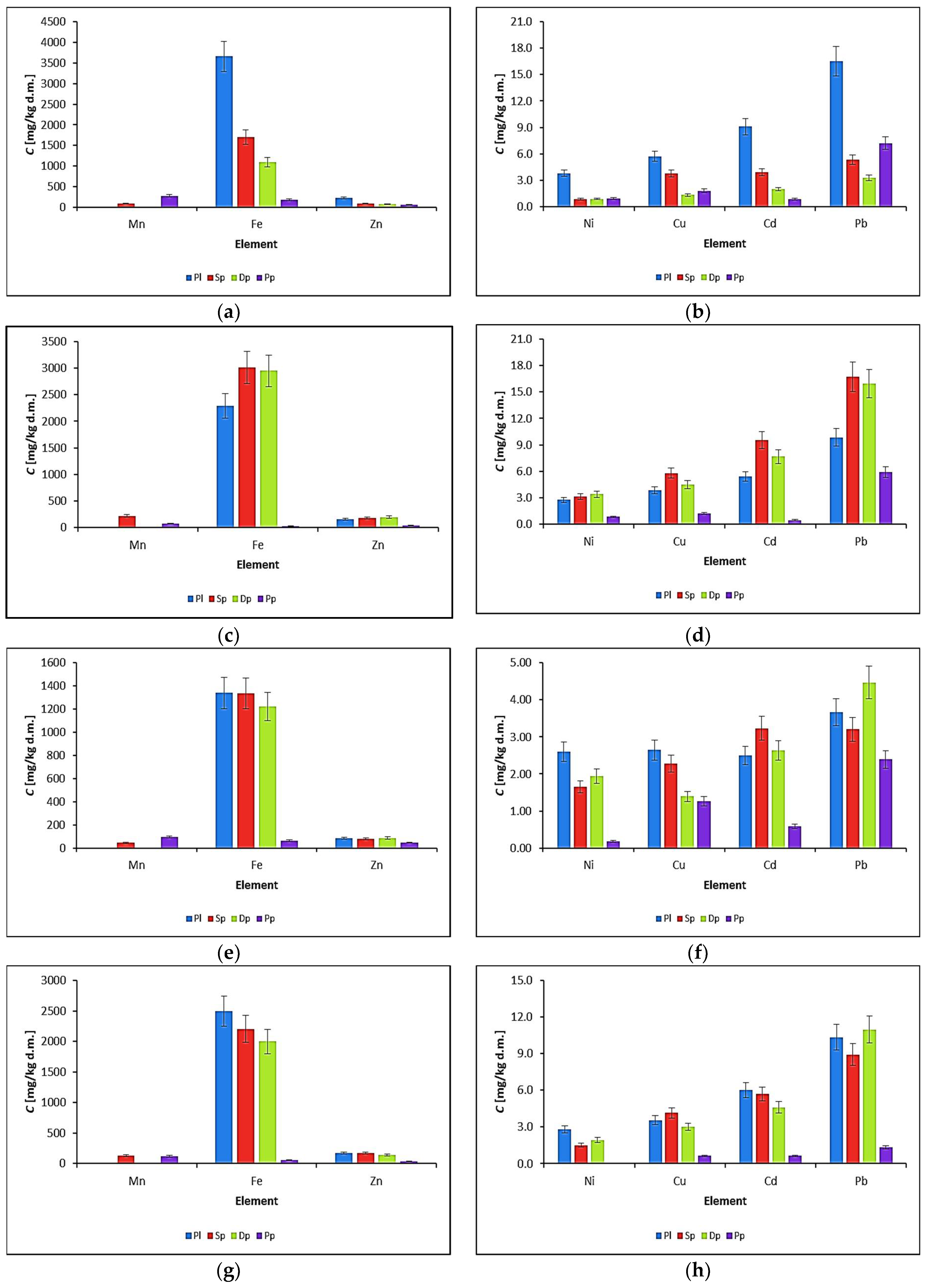
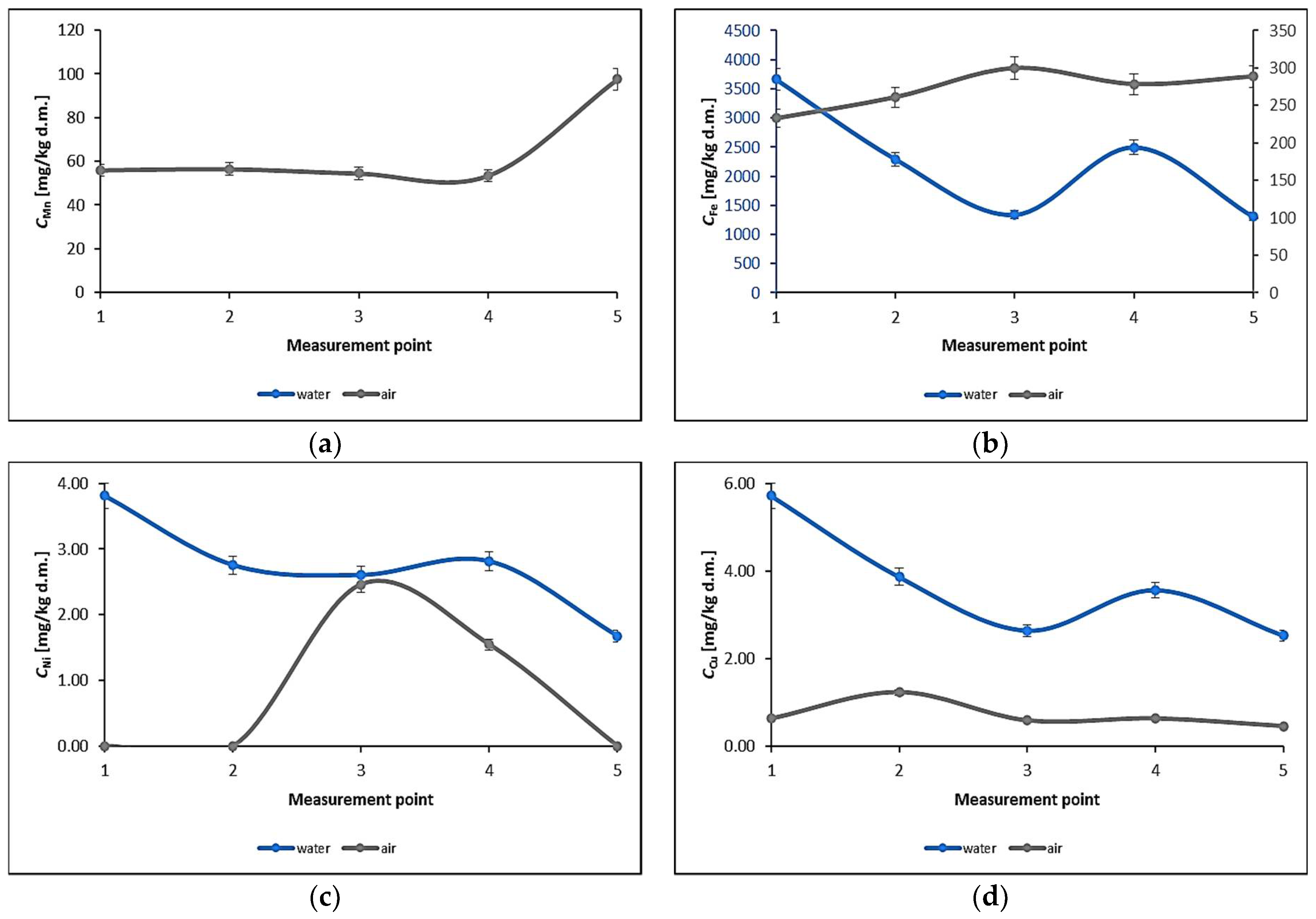
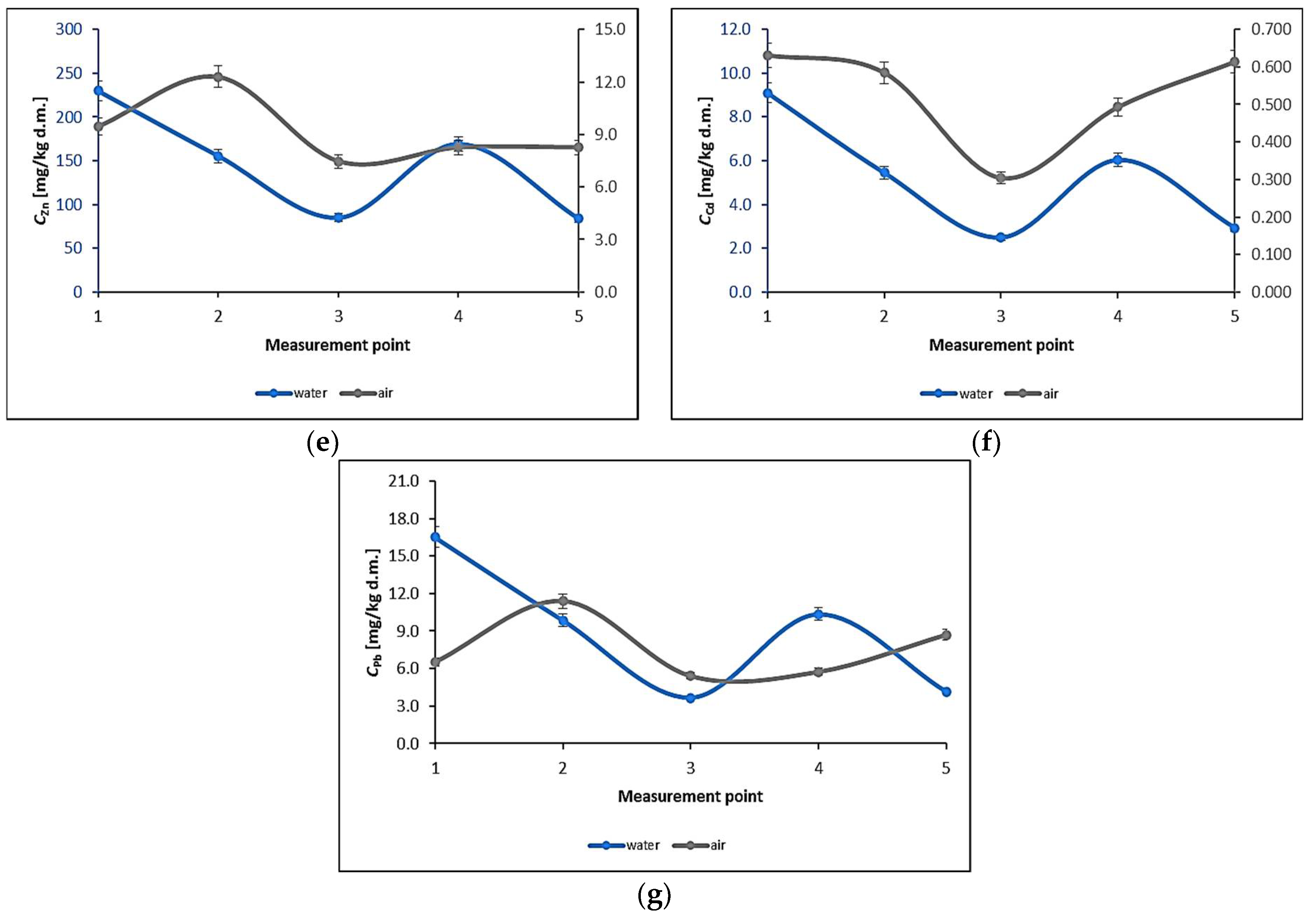
3.1. Water Biomonitoring Using Mosses and Algae
3.2. Biomonitoring of Atmospheric Aerosol Using P. schreberi Mosses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lawniczak, A.E.; Zbierska, J.; Nowak, B.; Achtenberg, K.; Grześkowiak, A.; Kanas, K. Impact of Agriculture and Land Use on Nitrate Contamination in Groundwater and Running Waters in Central-West Poland. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Izydorczyk, G.; Mikula, K.; Skrzypczak, D.; Moustakas, K.; Witek-Krowiak, A.; Chojnacka, K. Potential Environmental Pollution from Copper Metallurgy and Methods of Management. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohdálková, L.; Bohdálek, P.; Břízová, E.; Pacherová, P.; Kuběna, A.A. Atmospheric Metal Pollution Records in the Kovářská Bog (Czech Republic) as an Indicator of Anthropogenic Activities over the Last Three Millennia. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 857–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy Metal Pollution in the Environment and Their Toxicological Effects on Humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology of Hazardous Heavy Metals: Environmental Persistence, Toxicity, and Bioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 6730305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Fu, D.; Liu, S.; Zevenbergen, C.; Singh, R.P. Hydrologic and Pollutant Removal Performance of Media Layers in Bioretention. Water 2020, 12, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Castro, O.; Gianguzzi, L.; Colombo, P.; De Luca, P.; Marino, G.; Guida, M. Multivariate Analysis of Sites Using Water Invertebrates and Land Use as Indicators of the Quality of Biotopes of Mediterranean Relic Plant (Petagnaea Gussonei, Apiaceae). Environ. Bioindic. 2007, 2, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, J.L.; Resh, V.H.; Hannaford, M.J. Macroinvertebrates as Biotic Indicators of Environmental Quality; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 2, ISBN 9780128132692. [Google Scholar]
- Baby, J.; Raj, J.; Biby, E.; Sankarganesh, P.; Jeevitha, M.; Ajisha, S.; Rajan, S. Toxic Effect of Heavy Metals on Aquatic Environment. Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2011, 4, 939–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riani, E.; Cordova, M.R.; Arifin, Z. Heavy Metal Pollution and Its Relation to the Malformation of Green Mussels Cultured in Muara Kamal Waters, Jakarta Bay, Indonesia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Sharma, A.; Verma, R.K.; Chopade, R.L.; Pandit, P.P.; Nagar, V.; Aseri, V.; Choudhary, S.K.; Awasthi, G.; Awasthi, K.K.; et al. Heavy Metal Contamination of Water and Their Toxic Effect on Living Organisms. In The Toxicity of Environmental Pollutants; Dorta, D.D., De Oliveira, P.D.P., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Gao, Q.; Yuan, B. Analysis and Identification of Pollution Sources of Comprehensive River Water Quality: Evidence from Two River Basins in China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 135, 108561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Caro, F.; Corbett, C.J.; Ding, X. Estimating the Environmental and Economic Impacts of Widespread Adoption of Potential Technology Solutions to Reduce Water Use and Pollution: Application to China’s Textile Industry. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2019, 79, 106293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gunkel, G.; Kosmol, J.; Sobral, M.; Rohn, H.; Montenegro, S.; Aureliano, J. Sugar Cane Industry as a Source of Water Pollution—Case Study on the Situation in Ipojuca River, Pernambuco, Brazil. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2007, 180, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłońska-Czapla, M.; Nocoń, K.; Szopa, S.; Łyko, A. Impact of the Pb and Zn Ore Mining Industry on the Pollution of the Biała Przemsza River, Poland. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dobrzyński, J.; Kulkova, I.; Wierzchowski, P.S.; Wróbel, B. Response of Physicochemical and Microbiological Properties to the Application of Effective Microorganisms in the Water of the Turawa Reservoir. Water 2022, 14, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, P.; Wiatkowski, M.; Gruss, Ł. Application of Macrophytes to the Assessment and Classification of Ecological Status above and below the Barrage with Hydroelectric Buildings. Water 2019, 11, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bezuidenhout, J.; Nekhoroshkov, P.; Zinicovscaia, I.; Yushin, N.; Frontasyeva, M. Accumulation Features of Micro and Macroelements in Indigenous and Alien Molluscs in Saldanha Bay, South Africa. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2020, 27, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, J.; Fu, J.; Shi, J.; Jiang, G. Biomonitoring: An Appealing Tool for Assessment of Metal Pollution in the Aquatic Ecosystem. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 606, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zheng, B.; Liu, L. Biomonitoring and Bioindicators Used for River Ecosystems: Definitions, Approaches and Trends. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 1510–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iodice, P.; Adamo, P.; Capozzi, F.; Di Palma, A.; Senatorea, A.; Spagnuolo, V.; Giordano, S. Air Pollution Monitoring Using Emission Inventories Combined with the Moss Bag Approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 1410–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajfur, M. Algae as a Source of Information on Surface Waters Contamination with Heavy Metals. Ecol. Chem. Eng. A 2013, 20, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krems, P.; Rajfur, M.; Waclawek, M.; Klos, A. The Use of Water Plants in Biomonitoring and Phytoremediation of Waters Polluted with Heavy Metals. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2013, 20, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Traubenberg, C.R.; Ah-Peng, C. A Procedure to Purify and Culture A Clonal Strain of the Aquatic Moss Fontinalis Antipyretica for Use As A Bioindicator of Heavy Metals. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2004, 46, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favas, P.J.C.; Pratas, J.; Rodrigues, N.; D’Souza, R.; Varun, M.; Paul, M.S. Metal(Loid) Accumulation in Aquatic Plants of a Mining Area: Potential for Water Quality Biomonitoring and Biogeochemical Prospecting. Chemosphere 2018, 194, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajfur, M.; Kłos, A. Use of Algae in Active Biomonitoring of Surface Waters. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2014, 21, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajfur, M.; Krems, P.; Kłos, A.; Kozłowski, R.; Jóźwiak, M.A.; Kříž, J.; Wacławek, M. Application of Algae in Active Biomonitoring of the Selected Holding Reservoirs in Swietokrzyskie Province. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2016, 23, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baldantoni, D.; Bellino, A.; Lofrano, G.; Libralato, G.; Pucci, L.; Carotenuto, M. Biomonitoring of Nutrient and Toxic Element Concentrations in the Sarno River through Aquatic Plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, E.M.; Galal, T.M.; Shaltout, K.H.; El-Sheikh, M.A.; Asaeda, T.; Alatar, A.A.; Alfarhan, A.H.; Alharthi, A.; Alshehri, A.M.A.; Picó, Y.; et al. Biomonitoring Potential of the Native Aquatic Plant Typha Domingensis by Predicting Trace Metals Accumulation in the Egyptian Lake Burullus. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Arias, A.; Debén, S.; Casanova, A.; Pacín, C.; Aboal, J.R.; Fernández, J.A. Effect of Current Velocity on Cd Accumulation in the Aquatic Moss Fontinalis Antipyretica. Water 2021, 13, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, M.D.; Real, C.; Villares, R. Optimization of the Biomonitoring Technique with the Aquatic Moss Fontinalis Antipyretica Hedw.: Selection of Shoot Segment Length for Determining Trace Element Concentrations. Water 2020, 12, 2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gecheva, G.; Mollov, I.; Yahubyan, G.; Gozmanova, M.; Apostolova, E.; Nikolova, M.; Dimitrova-Dyulgerova, I.; Radoukova, T.; Vasileva, T. Can Biomarkers Respond upon Freshwater Pollution?—A Moss-Bag Approach. Biology 2021, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gecheva, G.; Yancheva, V.; Velcheva, I.; Georgieva, E.; Stoyanova, S.; Arnaudova, D.; Stefanova, V.; Georgieva, D.; Genina, V.; Todorova, B.; et al. Integrated Monitoring with Moss-Bag and Mussel Transplants in Reservoirs. Water 2020, 12, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debén, S.; Aboal, J.R.; Giráldez, P.; Varela, Z.; Fernández, J.A. Developing a Biotechnological Tool for Monitoring Water Quality: In Vitro Clone Culture of the Aquatic Moss Fontinalis Antipyretica. Water 2019, 11, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stojanowska, A.; Mach, T.; Olszowski, T.; Bihałowicz, J.S.; Górka, M.; Rybak, J.; Rajfur, M.; Świsłowski, P. Air Pollution Research Based on Spider Web and Parallel Continuous Particulate Monitoring—A Comparison Study Coupled with Identification of Sources. Minerals 2021, 11, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłos, A.; Rajfur, M. Influence of Hydrogen Cations on Kinetics and Equilibria of Heavy-Metal Sorption by Algae-Sorption of Copper Cations by the Alga Palmaria Palmata (Linnaeus) Weber & Mohr (Rhodophyta). J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Demková, L.; Bobul’ská, L.; Árvay, J.; Jezný, T.; Ducsay, L. Biomonitoring of Heavy Metals Contamination by Mosses and Lichens around Slovinky Tailing Pond (Slovakia). J. Environ. Sci. Health—Part A Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2017, 52, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmuchowski, W.; Gozdowski, D.; Baczewska, A.H.; Bragoszewska, P. Evaluation of Various Bioindication Methods of Measuring Zinc Environmental Pollution. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 51, 238–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. ICE 3000 Series AA Spectrometers Operator’s Manual; Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.: Waltham, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 1, 7–18. [Google Scholar]
- Świsłowski, P.; Kosior, G.; Rajfur, M. The Influence of Preparation Methodology on the Concentrations of Heavy Metals in Pleurozium Schreberi Moss Samples Prior to Use in Active Biomonitoring Studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 10068–10076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanković, J.D.; Sabovljević, A.D.; Sabovljević, M.S. Bryophytes and Heavy Metals: A Review. Acta Bot. Croat. 2018, 77, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz de Carvalho, R.; Bernardes da Silva, A.; Branquinho, C.; Marques da Silva, J. Influence of Dehydration Rate on Cell Sucrose and Water Relations Parameters in an Inducible Desiccation Tolerant Aquatic Bryophyte. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2015, 120, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, K.L.; Balsamo, R.A.; Espinoza, C.; Oliver, M.J. Desiccation Sensitivity and Tolerance in the Moss Physcomitrella Patens: Assessing Limits and Damage. Plant Growth Regul. 2010, 62, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćosić, M.; Vujičić, M.M.; Sabovljević, M.S.; Sabovljević, A.D. What Do We Know about Salt Stress in Bryophytes? Plant Biosyst. 2019, 153, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłos, A.; Rajfur, M.; Wacławek, M.; Wacławek, W. Ion Equilibrium in Lichen Surrounding. Bioelectrochemistry 2005, 66, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Chang, S.P. The Biosorption of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solution by Spirogyra and Cladophora Filamentous Macroalgae. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5297–5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadzki, K.; Samecka-Cymerman, A.; Kolon, K.; Wojtuń, B.; Mróz, L.; Kempers, A.J. Metals in Pleurozium Schreberi and Polytrichum Commune from Areas with Various Levels of Pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 11100–11108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sergeeva, A.; Zinicovscaia, I.; Vergel, K.; Yushin, N.; Urošević, M.A. The Effect of Heavy Industry on Air Pollution Studied by Active Moss Biomonitoring in Donetsk Region (Ukraine). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 80, 546–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demková, L.; Árvay, J.; Bobul’ská, L.; Obona, J. The Risk Elements Biomonitoring in the Ambient Air of an Underground Parking Lot. Polish J. Nat. Sci. 2018, 33, 545–559. [Google Scholar]
- Carrieri, V.; Varela, Z.; Aboal, J.R.; De Nicola, F.; Fernández, J.A. Suitability of Aquatic Mosses for Biomonitoring Micro/Meso Plastics in Freshwater Ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2022, 34, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debén, S.; Fernández, J.A.; Giráldez, P.; Vázquez Arias, A.; Aboal, J.R. Methodological Advances to Biomonitor Water Quality with Transplanted Aquatic Mosses. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 136082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debén, S.; Fernández, J.A.; Carballeira, A.; Kosior, G.; Aboal, J.R. Improving Active Biomonitoring in Aquatic Environments: The Optimal Number and Position of Moss Bags. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debén, S.; Fernández, J.A.; Carballeira, A.; Aboal, J.R. Using Devitalized Moss for Active Biomonitoring of Water Pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 210, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakovská, A.S.; Svozilík, V.; Zinicovscaia, I.; Vergel, K.; Jančík, P. Analysis of Spatial Data from Moss Biomonitoring in Czech-Polish Border. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaligava, O.; Nikolaev, I.; Khetagurov, K.; Lavrinenko, Y.; Bazaev, A.; Frontasyeva, M.; Vergel, K.; Grozdov, D. First Results on Moss Biomonitoring of Trace Elements in the Central Part of Georgia, Caucasus. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domańska, W. Ochrona Środowiska 2019; Główny Urząd Statystyczny, Departament Badań Przestrzennych i Środowiska: Warsaw, Poland, 2019; pp. 186–188. [Google Scholar]
- García-Seoane, R.; Fernández, J.A.; Chilà, A.; Aboal, J.R. Improving the Uptake of Pollutants in Moss Bags: The Wind Effect. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 107, 105577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, B.E.; White, H.M. Environmental Pollution by Wind Blown Lead Mine Waste: A Case Study in Wales, U.K. Sci. Total Environ. 1981, 20, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajfur, M.; Klos, A.; Waclawek, M. Algae Utilization in Assessment of the Large Turawa Lake (Poland) Pollution with Heavy Metals. J. Environ. Sci. Health—Part A Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2011, 46, 1401–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemčić-Jurec, J.; Jazbec, A. Point Source Pollution and Variability of Nitrate Concentrations in Water from Shallow Aquifers. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1337–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, N.; Yang, L.; Dai, J.; Pang, X. Heavy Metal Pollution in Surface Water of Linglong Gold Mining Area, China. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 10, 914–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Świsłowski, P.; Nowak, A.; Wacławek, S.; Ziembik, Z.; Rajfur, M. Is Active Moss Biomonitoring Comparable to Air Filter Standard Sampling? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Metal | IDL | IQL |
|---|---|---|
| Mn | 0.0016 | 0.020 |
| Fe | 0.0043 | 0.050 |
| Ni | 0.0043 | 0.050 |
| Cu | 0.0045 | 0.033 |
| Zn | 0.0033 | 0.010 |
| Cd | 0.0028 | 0.013 |
| Pb | 0.0130 | 0.070 |
| BCR-482 Lichen | AAS | Dev. ** | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metal | Concentration | ±Uncertainty | Mean | ±SD * | |
| [mg/kg d.m.] | [%] | ||||
| Mn | 33.0 | 0.5 | 31.7 | 0.68 | −3.9 |
| Fe | 804 | 160 | 771 | 154 | −4.1 |
| Ni | 2.47 | 0.07 | 2.16 | 0.32 | −13 |
| Cu | 7.03 | 0.19 | 6.63 | 0.17 | −5.7 |
| Zn | 100.6 | 2.2 | 95.1 | 2.3 | −5.5 |
| Cd | 0.56 | 0.02 | 0.53 | 0.03 | −5.3 |
| Pb | 40.9 | 1.4 | 38.2 | 1.0 | −6.6 |
| BCR-414 Plankton | AAS | Dev. ** | |||
| Mn | 299 | 12 | 284 | 13 | −5.0 |
| Fe | 1.85 | 0.19 | 1.79 | 0.20 | −3.2 |
| Ni | 18.8 | 0.8 | 18.2 | 0.9 | −3.2 |
| Cu | 29.5 | 1.3 | 28.4 | 1.6 | −3.7 |
| Zn | 112 | 3.0 | 107 | 3 | −4.5 |
| Cd | 0.383 | 0.014 | 0.371 | 0.018 | −3.1 |
| Pb | 3.97 | 0.19 | 3.75 | 0.21 | −5.5 |
| P. schreberi | S. fallax | D. polysetum | P. palmata | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cs,Cu(0) | cs,Cu(1) | cM,1 | cs,Cu(0) | cs,Cu(1) | cM,1 | cs,Cu(0) | cs,Cu(1) | cM,1 | cs,Cu(0) | cs,Cu(1) | cA,1 |
| 2.60 | 0.20 | 2.40 | 2.60 | 0.33 | 2.30 | 2.60 | 0.19 | 2.40 | 2.60 | 0.19 | 2.41 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Respondek, Z.; Jerz, D.; Świsłowski, P.; Rajfur, M. Active Biomonitoring of Heavy Metal Concentrations in Aquatic Environment Using Mosses and Algae. Water 2022, 14, 3335. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203335
Respondek Z, Jerz D, Świsłowski P, Rajfur M. Active Biomonitoring of Heavy Metal Concentrations in Aquatic Environment Using Mosses and Algae. Water. 2022; 14(20):3335. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203335
Chicago/Turabian StyleRespondek, Zuzanna, Dominik Jerz, Paweł Świsłowski, and Małgorzata Rajfur. 2022. "Active Biomonitoring of Heavy Metal Concentrations in Aquatic Environment Using Mosses and Algae" Water 14, no. 20: 3335. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203335
APA StyleRespondek, Z., Jerz, D., Świsłowski, P., & Rajfur, M. (2022). Active Biomonitoring of Heavy Metal Concentrations in Aquatic Environment Using Mosses and Algae. Water, 14(20), 3335. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203335








