The Assessment of External and Internal Nutrient Loading as a Basis for Lake Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Watercourses and Stormwater Runoff
2.2.2. Bottom Sediments
2.2.3. Computational Works
3. Results
3.1. Quality of Water Flowing into and out of Raczyńskie Lake
3.2. External Loading
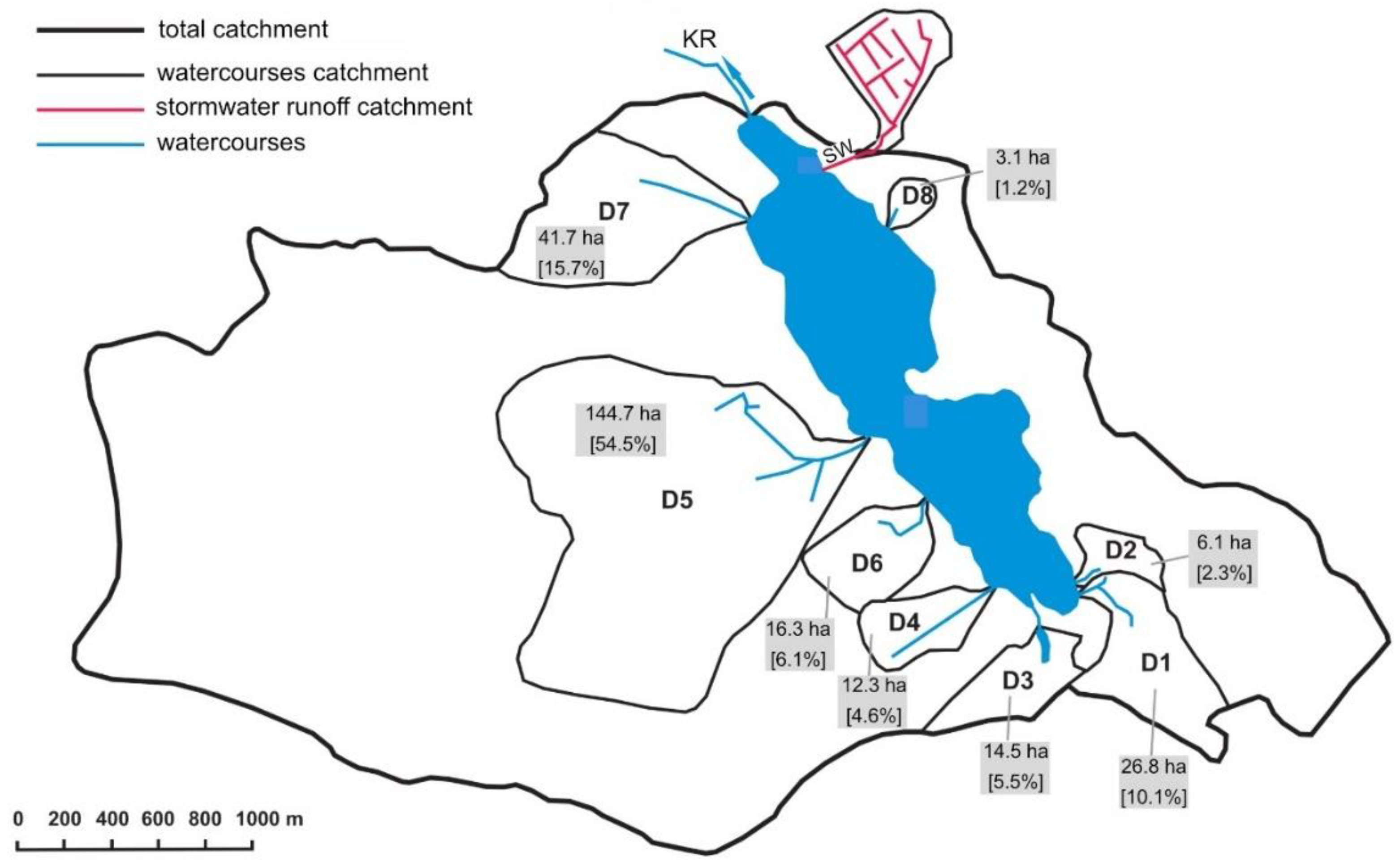
3.2.1. The Catchment of Raczyńskie Lake
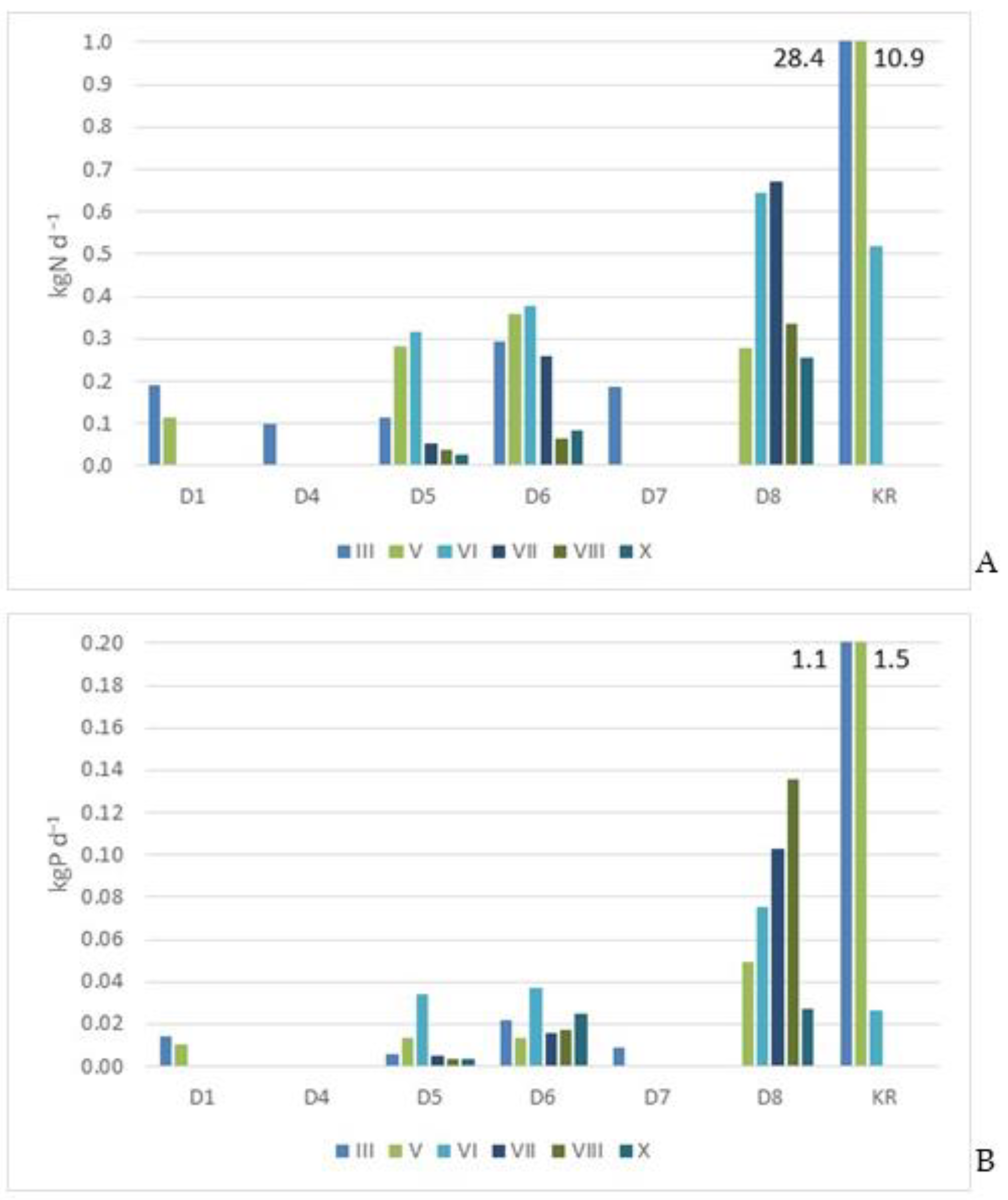
3.2.2. Loads of Nutrients and TSS in Natural Watercourses (D1–D8 and KR)
3.2.3. Loads of Nutrients and TSS in the Stormwater Runoff
3.2.4. Loads of Nutrients Supplied from Direct Catchment
3.2.5. Total External Loading
3.3. Bottom Sediments
3.3.1. Sediment Composition
3.3.2. Internal Loading of Phosphorus from Bottom Sediments
3.4. External vs. Internal Phosphorus Loading
4. Discussion
4.1. External Loading from the Catchment Area
4.2. Internal Phosphorus Loading from Bottom Sediments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dokulil, M.T.; Teubner, K. Eutrophication and restoration of shallow lakes—The concept of stable equilibria revisited. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padisak, J.; Reynolds, C.S. Shallow lakes: The absolute, the relative, the functional and the pragmatic. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammeorg, O.; Nürnberg, G.; Tõnno, I.; Kisand, A.; Tuvikene, L.; Nõges, T.; Nõges, P. Sediment phosphorus mobility in Vortysjarv, a large shallow lake: Insights from phosphorus sorption experiments and long-term monitoring. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jonge, V.N.; Elliott, M.; Orive, E. Causes, historical development, effects and future challenges of a common environmental problem: Eutrophication. Hydrobiologia 2002, 475, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xu, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Sun, P.; Wen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lu, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Seasonal Pattern of Nutrient Limitation in a Eutrophic Lake and Quantitative Analysis of the Impacts from Internal Nutrient Cycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 13675–13686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M. Ecology of Shallow Lakes; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1998; 357p. [Google Scholar]
- Janssen, A.B.G.; Hilt, S.; Kosten, S.; de Klein, J.J.M.; Paerl, H.W.; Van de Waal, D.B. Shifting states, shifting services: Linking regime shifts to changes in ecosystem services of shallow lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2021, 66, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerhoff, M.; de los Ángeles González Sagrario, M. Habitat complexity in shallow lakes and ponds: Importance, threats, and potential for restoration. Hydrobiologia 2021, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriata-Potasznik, A.; Szymczyk, S.; Skwierawski, A. Influence of cascading river systems on the dynamics of nutrient circulation in catchment areas. Water 2020, 12, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, L.M.V.; Calijuri, M.C. Restoration from eutrophication in interconnected reservoirs: Using a model approach to assess the propagation of water quality improvements downstream along a cascade system. Environ. Model. Softw. 2022, 149, 105308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djihouessi, M.B.; Tigo, B.A.; Aina, M.P. The use of nutrient budget approach for informing eutrophication management in urbanized shallow coastal lakes: A case study from Lake Nokoué in Benin. Int. J. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2021, 21, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, S.; Kang, J.; Lee, Y.; Cho, K.; An, K.; Kim, J. Advancing assessment and design of stormwater monitoring programs using a self-organizing map: Characterization of trace metal concentration profiles in stormwater runoff. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4183–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirasuna, H.; Fukushima, T.; Matsushige, K.; Imai, A.; Ozaki, N. Runoff and loads of nutrients and heavy metals from and urbanized area. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 53, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barałkiewicz, D.; Chudzińska, M.; Szpakowska, B.; Świerk, D.; Gołdyn, R.; Dondajewska, R. Stormwater contamination and its effect on the quality of urban surface waters. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 6789–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-Y.; Asal, S.; Toor, G.S. Residential catchments to coastal waters: Forms, fluxes, and mechanisms of phosphorus transport. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 142767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gołdyn, R.; Szpakowska, B.; Świerk, D.; Domek, P.; Buxakowski, J.; Dondajewska, R.; Barałkiewicz, D.; Sajnóg, A. Influence of stormwater runoff on macroinvertebrates in a small urban river and a reservoir. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Soulignac, F.; Roguet, A.; Li, C.; Melaire, B.; Martins, R.S.; Lucas, F.; Vincon-Leite, B. Impact of Escherichia coli from stormwater drainage on recreational water quality: An integrated monitoring and modelling of urban catchment, pipes and lake. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 2245–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napieralska, A.; Gołdyn, R. Sanitary analyses of runoff waters a river. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2013, 22, 481–486. [Google Scholar]
- Bowes, M.J.; Hilton, J.; Irons, G.P.; Hornby, D.D. The relative contribution of sewage and diffuse phosphorus sources in the River Avon catchment, southern England: Implications for nutrient management. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 344, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heathwaite, A.L.; Dils, R.M. Characterizing phosphorus loss in surface and subsurface hydrological pathways. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 251, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, A.; Trolle, D.; Sondergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Bjerring, R.; Olesen, J.E.; Jeppesen, E. Watersehd land use effects on lake water quality in Denmark. Ecol. Appl. 2012, 22, 1187–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Schmidt, J.P.; Bryant, R.B. Hot moments and hot spots of nutrient losses from a mixed land use watershed. J. Hydrol. 2012, 414–415, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gołdyn, R.; Kowalczewska-Madura, K. Chlorophyll-a and other water quality variables in lentic and lotic sections of the Cybina River. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2005, 34, 87–98. [Google Scholar]
- Räty, M.; Järvenranta, K.; Saarijärvi, E.; Koskiaho, J.; Virkajärvi, P. Losses of phosphorus, nitrogen, dissolved organic carbon and soil from a small agricultural and forested catchment in east-central Finland. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 302, 107075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmala, E.; Saikku, L.; Vienonen, S. Import-export balance of nitrogen and phosphorus in food, fodder and fertilizers in the Baltic Sea drainage area. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 4917–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, K.W.; Willimas, M.R.; Macrae, M.L.; Fausey, N.R.; Frankenberger, J.; Smith, D.R.; Kleinman, P.J.A.; Brown, L.C. Phosphorus transport in agricultural subsurface drainage: A review. J. Enviorn. Qual. 2015, 44, 467–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Havens, K.E.; Xu, H.; Zhu, G.; McCarthy, M.J.; Newell, S.E.; Scott, J.T.; Hall, N.S.; Otten, T.G.; Qin, B. Mitigating eutrophication and toxic cyanobacterial blooms in large lakes: The evolution of a dual nutrient (N and P) reduction paradigm. Hydrobiologia 2019, 847, 4359–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boström, B.; Andersen, J.M.; Fleischer, S.; Jansson, M. Exchange of phosphorus across the sediment-water interface. Hydrobiologia 1988, 170, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Jeppesen, E. Role of sediment and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Kristensen, P.; Jensen, J.P.; Sondergaard, M.; Mortensen, E.; Lauridsen, T. Recovery resilience following a reduction in external phosphorus loading of shallow, eutrophic Danish lakes: Duration, regulating factors and methods for overcoming resilience. Mem. Dell’istituto Ital. Di Idrobiol. 1991, 48, 127–148. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Kozak, A.; Kuczyńska-Kippen, N.; Dondajewska-Pielka, R.; Gołdyn, R. Sustainable restoration as a tool for the improvement of water quality in a shallow, hypetrophic lake. Water 2022, 14, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosińska, J.; Gołdyn, R. Response of vegetation to growing recreational pressure in the shallow Raczyńskie Lake. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2018, 419, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbanowska, H.; Zerbe, J.; Siepak, J. Physicochemical Water Analyses; UAM University Press: Poznań, Poland, 1999. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Psenner, R.; Boström, B.; Dinka, M.; Pettersson, K.; Pucsko, R.; Sager, M. Fractionation of phosphorus in suspended matter and sediment. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. Ergebn. Limnol. 1988, 30, 83–112. [Google Scholar]
- American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Gieruszkiewicz-Bajtlik, M. Prognozowanie Jakości Wód Stojących; Inspekcja Ochrony Środowiska: Warsaw, Poland, 1990. (In Polish)
- Pułyk, M.; Buczyńska, E. Surface Water Quality in the Kopla River Catchment based on Monitoring Studies; Biblioteka Monitoringu Środowiska: Poznań, Poland, 1997. (In Polish)
- Carpenter, S.R.; Caraco, N.F.; Correll, D.L.; Howarth, R.W.; Sharpley, A.N.; Smith, V.H. Nonpoint pollution of Surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecol. Appl. 1998, 8, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, B.; Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Liu, Z. Nitrogen, macrophytes, shallow lakes and nutrient limitation: Resolution of a current controversy? Hydrobiologia 2013, 710, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilampooranan, I.; Van Meter, K.J.; Basu, N.B. Intensive agriculture, nitrogen legacies, and water quality: Intersections and implications. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 035006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisboa, M.S.; Schneider, R.L.; Sullivan, P.J.; Walter, M.T. Drought and post-drought rain effect on stream phosphorus and other nutrient losses in the Northeastern USA. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 28, 100672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurczak, T.; Wagner, I.; Kaczkowski, Z.; Szklarek, S.; Zalewski, M. Hybrid system for the purification of street stormwater runoff supplying urban recreation reservoirs. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 110, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpakowska, B.; Świerk, D.; Dudzińska, A.; Pajchrowska, M.; Gołdyn, R. The influence of land use in the catchment area of small waterbodies on the quality of water and plant composition. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudzińska, A.; Szpakowska, B.; Pajchrowska, M. Influence of land development on the ecological status of small water bodies. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2020, 49, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpakowska, B. Occurrence and Role of Organic Compounds Dissolved in Surface and Ground Waters of Agricultural Landscape; Nicolai Copernicus University Publishing: Torun, Poland, 1999. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Drizo, A. Phosphorus Pollution Controls: Policies and Strategies; Willey-Blackwell: London, UK, 2019; p. 176. [Google Scholar]
- Randall, N.P.; Donnison, L.M.; Lewis, P.J.; James, K.L. How effective are on-fram mitigation measures for delivering and improved water environment? A systematic map. Environ. Evid. 2015, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kill, K.; Grinberga, L.; Koskiaho, J.; Mander, U.; Wahlroos, O.; Lauva, D.; Parn, J.; Kasak, K. Phosphorus removal efficiency by in-stream constructed wetlands treating agricultural runoff: Influence of vegetation and design. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 180, 106664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Reis Oliveira, P.C.; van der Geest, H.G.; Kraak, M.H.S.; Verdonschot, P.F.M. Land use affects lowland stream ecosystem through dissolved oxygen regimes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puustinen, M.; Koskiaho, J.; Peltonen, K. Influence of cultivation methods on suspended solids and phosphorus concentrations in surface runoff on clayey sloped fields in boreal climate. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 105, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Zhu, J.G.; Zhu, J.Y.; Gao, X.; Dou, Y.J.; Hosen, Y. Nitrogen export from an agriculture watershed in the Taihu Lake area, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2004, 26, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimaszyk, P.; Rzymski, P.; Piotrowicz, R.; Joniak, T. Contribution of Surface runoff from forested areas to the chemistry of a trough-flow lake. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 73, 3963–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, T.J. Agricultural best management practices for water pollution control: Current issues. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1993, 46, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvie, H.P.; Sharpley, A.N.; Withers, P.J.A.; Scott, T.; Haggard, B.E.; Neal, C. Phosphorus mitigation to control river eutrophication: Murky Waters, Inconvenient Truths and “Postnormal” Science. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Eutrophication of Waters. Monitoring, Assessment and Control; Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development: Paris, France, 1982; 154p.
- Sønderuup, M.J.; Egemose, S.; Hansen, A.S.; Grudinina, A.; Madsen, M.H.; Flindt, M.R. Factors affecting retention of nutrients and organic matter in stormwater ponds. Ecohydrology 2015, 9, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondajewska, R.; Kozak, A.; Budzyńska, A.; Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Gołdyn, R. Nature-based solutions for protection and restoration of degraded Bielsko Lake. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2018, 18, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragh, T.; Kolath, T.; Kolath, A.S.; Reitzel, K.; Martinsen, K.T.; Sondergaard, M.; Hoffmann, C.C.; Bastrup-Spohr, L.; Egemose, S. External phosphorus loading in new lakes. Water 2022, 14, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, M.; Wolter, K.D.; Ripl, E. Chemical treatment water and sediments with special references to lakes. In Handbook of Ecological Restoration. Vol. 1. Principles of Restoration; Perrow, M.R., Davy, A.J., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Granéli, W. Internal phosphorus loading in Lake Ringsjön. Hydrobiologia 1999, 404, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P. Biological mechanisms driving the seasonal changes in the internal loading of phosphorus in shallow lakes. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2006, 49, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golosov, S.D.; Ignatieva, N. Hydrothermodynamic features of mass exchange across the sediment-water interface in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 1999, 408, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Gołdyn, R.; Dera, M. Spatial and seasonal changes of phosphorus internal loading in two lakes with different trophy. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 74, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Dondajewska, R.; Gołdyn, R.; Podsiadłowski, S. The influence of restoration measures on phosphorus internal loading from the sediments of a hypereutrophic lake. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 14417–14429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleeberg, A.; Dudel, G.E. Changes in extent of phosphorus release in a shallow lake (Lake Grosser Muggelsee; Germany, Berlin) due to climatic factors and load. Mar. Geol. 1997, 139, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsev, S.; Dittrich, M. Modelling of decadal scale phosphorus retention in lake sediment under varying redox conditions. Ecol. Modell. 2013, 251, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noges, P.; Kisand, A. Horizontal distribution of sediment phosphorus in shallow eutrophic Lake Vortsjarv (Estonia). Hydrobiologia 1999, 408–409, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kentzer, A. Fosfor i Jego Biologicznie Dostępne Frakcje w Osadach Jezior Różnej Trofii; Rozprawy; Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Mikołaja Kopernika: Toruń, Poland, 2001. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Dondajewska, R.; Gołdyn, R.; Rosińska, J.; Podsiadłowski, S. Internal phosphorus loading as the response to complete and then limited susutainable restoration of a shallow lake. Ann. Limnol. Int. J. Lim. 2019, 55, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, E.; Fukushima, T.; Shiraishi, H. Modeling of P-dynamics and algal growth in a stratified reservoir-mechanisms of P-cycle in water and interaction between overlying water and sediment. Ecol. Model. 2006, 197, 331–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Dondajewska-Pielka, R.; Gołdyn, R. Wymiana fosforu w interfazie osad-woda w badaniach eksperymentalnych ex-situ. In Ekosystemy Wodne: Funkcjonowanie, Znaczenie, Ochrona i Rekultywacja; Budzyńska, A., Dondajewska-Pielka, R., Rosińska, J., Kozak, A., Kowalczewska-Madura, K., Eds.; Bogucki Wyd. Naukowe: Poznań, Poland, 2019; pp. 85–103. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Klapper, H. Technologies for lake restoration. J. Limnol. 2003, 62 (Suppl. 1), 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, G.; Haghseresht, F.; Cloete, T.E. The effect of pH and anoxia on the performance of Phoslock, a phosphorus binding clay. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wei, Z.; Shen, X.; Bai, L.; Jiang, H. Particle size-related vertical redistribution of phosphorus (P)-inactivating materials induced by resuspension shaped P immobilization in lake sediment profile. Water Res. 2022, 213, 118150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huser, B.J.; Futter, M.; Lee, J.T.; Perniel, M. In-lake measures for phosphorus control: The kost feasible and cost-effective solution for long-term management of water quality in urban lakes. Water Res. 2016, 97, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abell, J.M.; Ozkundaci, D.; Hamilton, D.P.; Reeves, P. Restoring shallow lakes impaired by eutrophication: Approaches, outcomes, and challenges. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 52, 1199–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondajewska, R.; Kozak, A.; Budzyńska, A.; Gołdyn, R.; Podsiadłowski, S.; Tomkowiak, A. The response of a shallow hypertrophic lake to innovative restoration measures—Uzarzewskie Lake case study. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 121, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondajewska, R.; Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Gołdyn, R.; Kozak, A.; Messyasz, B.; Cerbin, S. Long-term water quality changes as a result of a sustainable restoration—a case study of dimictic Durowskie Lake. Water 2019, 11, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosińska, J.; Kozak, A.; Dondajewska, R.; Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Gołdyn, R. Water quality response to sustainable restoration measures—case study of urban Swarzędzkie Lake. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 84, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Dondajewska, R.; Gołdyn, R.; Kozak, A.; Messyasz, B. Internal phosphorus loading from the bottom sediments of a dimictic lake during its sustainable restoration. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gołdyn, R.; Messyasz, B.; Domek, P.; Windhorst, W.; Hugenschmidt, C.; Nicoara, M.; Plavan, G. The response of Lake Durowskie ecosystem to restoration measures. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2013, 8, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Dondajewska, R.; Gołdyn, R.; Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Kozak, A.; Romanowicz-Brzozowska, W.; Rosińska, J.; Budzyńska, A.; Podsiadłowski, S. Hypertrophic lakes and the results of their restoration in Western Poland. In The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry. Polish River Basins and Lakes—Part II: Biological Status of Water Management; Korzeniewska, E., Harnisz, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 373–399. [Google Scholar]
- Dondajewska-Pielka, R.; Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Kozak, A.; Budzyńska, A.; Gołdyn, R.; Messyasz, B.; Podsiadłowski, S. Sustainable lake restoration as a long-term strategy for water quality improvement. In Water Ecosystems: Functioning, Importance, Protection and Restoration; Budzyńska, A., Dondajewska-Pielka, R., Rosińska, J., Kozak, A., Kowalczewska-Madura, K., Eds.; Bogucki Press: Poznań, Poland, 2019; pp. 105–117. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
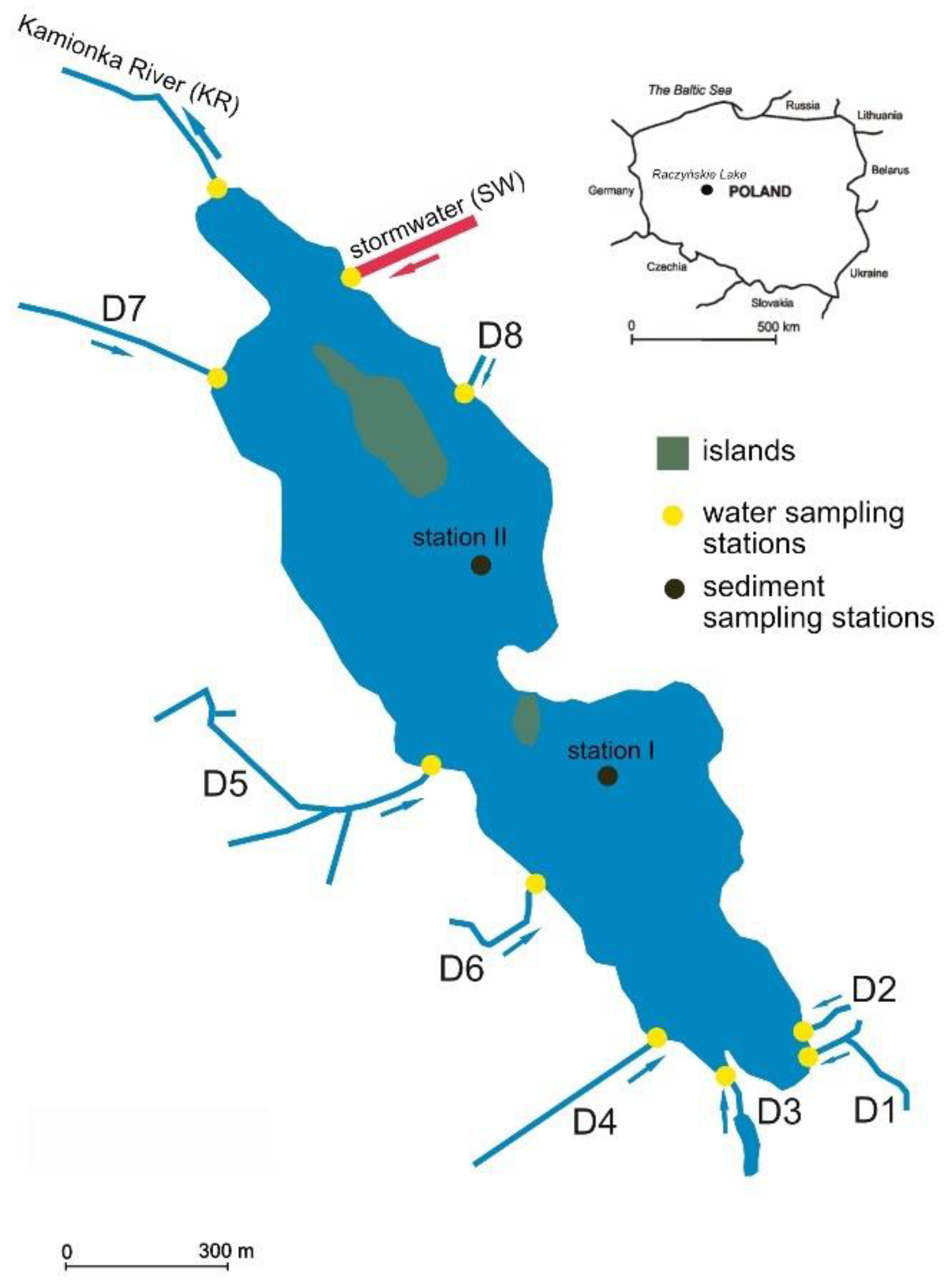

| Sampling Station | Tributary Characteristic | Catchment Characteristic | Sampling (n = Number of Samples) |
|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | tributary from the southeast, extension of the underground drainage line | meadows and croplands | only in spring and summer (n = 4) |
| D4 | tributary from southwest | forest and croplands | only in early spring (n = 1) |
| D5 | tributary from west, collecting waters from many small streams | forest and croplands | permanent water flow, n = 6 |
| D6 | tributary from west | forest and build-up areas | permanent water flow, n = 6 |
| D7 | tributary from northwest | meadows, forest and build-up areas | only in spring, n = 2 |
| D8 | tributary from east from Zaniemyśl village | green areas | permanent water flow, n = 6 |
| SW | outflow from collector of stormwater from the impermeable areas of Zaniemyśl village | built-up area | sampling after heavy rainfall, n = 6 |
| KR | outflow from the lake, decreasing water flow since March, no outflow since July | lake catchment covered by forest, croplands and built-up areas | only in spring and early summer, n = 3 |
| D1 | D4 * | D5 | D6 | D7 | D8 | KR | SW | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | 5.0–16.2 (11.8) | 7.2 | 9.1–18.1 (14.4) | 7.6–14.5 (12.1) | 6.8–15.6 (11.2) | 6.1–18 (13.3) | 7.4–19.5 (4.1) | 9.5–21.0 (15.1) |
| EC (µS cm−1) | 540–637 (589) | 697 | 695–871 (789) | 540–651 (589) | 837–870 (853) | 692–724 (707) | 457–488 (472) | 103–134 (113) |
| pH | 6.32–8.25 | 6.94 | 6.28–8.07 | 7.60–7.90 | 7.35–7.77 | 7.08–7.96 | 7.43–8.19 | 6.82–7.38 |
| DO (mgO2L−1) | 5.54–8.40 (6.32) | 7.25 | 3.27–5.56 (4.17) | 4.29–5.98 (5.21) | 2.13–6.16 (4.15) | 3.67–6.12 (4.82) | 1.55–10.13 (4.71) | 1.94–4.04 (3.21) |
| TSS (mgL−1) | 2.9–30.8 (11.4) | 12.9 | 9.8–28.0 (19.1) | 8.8–36.5 (19.3) | 12.7–30.0 (21.3) | 7.0–35.3 (13.7) | 11.0–12.3 (11.5) | 3.6–182 (47.3) |
| Ammonium N (mg N-NH4 L−1) | 0.85–1.39 (1.08) | 0.67 | 0.58–1.20 (0.84) | 0.58–1.55 (0.96) | 1.72–1.89 (1.81) | 0.50–0.82 (0.66) | 1.25–2.54 (1.86) | 1.40–2.43 (1.68) |
| Nitrate N (mgN-NO3 L−1) | 7.30–19.1 (12.7) | 2.30 | 0.23–0.48 (0.32) | 0.13–0.39 (0.27) | 0.16–0.30 (0.23) | 1.88–7.67 (4.42) | 0.20–0.31 (0.25) | 0.34–5.89 (1.75) |
| Mineral N (mgN L−1) | 8.50–19.9 (13.9) | 2.95 | 0.99–1.51 (1.18) | 0.77–1.93 (1.24) | 2.02–2.09 (2.05) | 2.72–8.35 (5.14) | 1.51–2.85 (2.14) | 1.95–7.48 (3.56) |
| Organic N (mgNL−1) | 0.99–1.91 (1.53) | 2.25 | 0.13–1.28 (0.79) | 0.11–1.46 (0.79) | 0.26–2.05 (1.15) | 0.41–1.33 (0.82) | 1.65–2.49 (2.09) | 0.03–2.41 (0.85) |
| TN (mgNL−1) | 10.3–21.6 (15.4) | 5.20 | 1.22–2.49 (1.97) | 1.08–2.85 (2.03) | 2.28–4.14 (3.21) | 3.22–8.89 (5.96) | 4.01–4.51 (4.23) | 2.37–8.23 (4.42) |
| SRP (mgPL−1) | 0.65–1.31 (1.04) | 0.004 | 0.02–0.15 (0.07) | 0.04–0.15 (0.09) | 0.04–0.06 (0.05) | 0.54–1.24 (0.79) | 0.08–0.12 (0.10) | 0.03–0.23 (0.11) |
| TP (mgPL−1) | 0.82–1.88 (1.26) | 0.037 | 0.09–0.26 (0.17) | 0.09–0.32 (0.22) | 0.11–0.17 (0.14) | 0.57–1.31 (0.88) | 0.18–0.58 (0.32) | 0.13–0.35 (0.230 |
| Daily Loading [kg d−1] | Annual Loading [kg y−1] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P | TSS | N | P | TSS | |
| D1 | 0.052 | 0.004 | 0.100 | 18.91 | 1.49 | 36.65 |
| D4 | 0.017 | 0.000 | 0.014 | 6.13 | 0.04 | 4.95 |
| D5 | 0.139 | 0.011 | 1.247 | 50.91 | 3.92 | 455.02 |
| D6 | 0.242 | 0.022 | 2.063 | 88.49 | 7.96 | 752.90 |
| D7 | 0.031 | 0.002 | 0.414 | 11.49 | 0.55 | 151.06 |
| D8 | 0.439 | 0.078 | 1.122 | 160.07 | 28.56 | 409.41 |
| Total | 0.920 | 0.117 | 4.960 | 336.00 | 42.52 | 1810.00 |
| Inflow | Mean Concentration [kg d−1] | Annual Load [kg y−1] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P | TSS | N | P | TSS | |
| D1 | 15.37 | 1.26 | 11.4 | 260.23 | 21.32 | 193.69 |
| D2 | 3.33 | 0.17 | 34.5 | 12.71 | 0.64 | 131.65 |
| D3 | 3.55 | 0.36 | 9.5 | 32.44 | 3.31 | 87.08 |
| D4 | 5.20 | 0.04 | 12.9 | 40.19 | 0.29 | 99.93 |
| D5 | 1.97 | 0.17 | 19.1 | 179.81 | 15.30 | 1740.47 |
| D6 | 2.02 | 0.22 | 19.3 | 20.82 | 2.23 | 198.08 |
| D7 | 3.21 | 0.14 | 21.3 | 84.31 | 3.68 | 560.42 |
| D8 | 5.96 | 0.88 | 13.7 | 11.65 | 1.73 | 26.81 |
| Total | 642.16 | 48.50 | 3038.13 | |||
| Inflow | Annual Load [kg y−1] | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| N | P | TSS | |
| D1 | 260.23 | 21.32 | 193.69 |
| D2 | 12.71 | 0.64 | 131.65 |
| D3 | 32.44 | 3.31 | 87.08 |
| D4 | 40.19 | 0.29 | 99.93 |
| D5 | 179.81 | 15.30 | 1740.47 |
| D6 | 88.49 | 7.96 | 752.90 |
| D7 | 84.31 | 3.68 | 560.42 |
| D8 | 160.07 | 28.56 | 409.41 |
| Total | 858.25 | 81.06 | 3975.55 |
| Parameter | Mean Concentration in Storm Water (III-X 2015) [mg L−1] | Annual Loading [kg y−1] | Maximum Concentration in Stormwater (III-X 2015) [mg L−1] | Load in Heavy Rainfall [kg d−1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 4.42 | 102.1 | 8.24 | 20.6 |
| P | 0.23 | 5.3 | 0.35 | 0.87 |
| TSS | 47.3 | 1092 | 182 | 454 |
| Catchment Cover | Area [ha] | Standard Unit Load (after Giercuszkiewicz-Bajtlik [36]) | Annual Loading | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [kgN y−1 ha−1] | [kgP y−1 ha−1] | [kgN y−1] | [kgP y−1] | ||
| Croplands | 286.8 | 10 | 0.4 | 2868 | 114.7 |
| Forests | 313.4 | 5 | 0.1 | 1567 | 31.3 |
| Meadows | 20.0 | 8 | 0.3 | 160 | 6.0 |
| Built-up areas | 46.7 | 6 | 0.9 | 280 | 42.0 |
| Total | 666.9 | 4875 | 194 | ||
| Source | N [kgN y−1] | P [kgP y−1] | TSS [kg y−1] |
|---|---|---|---|
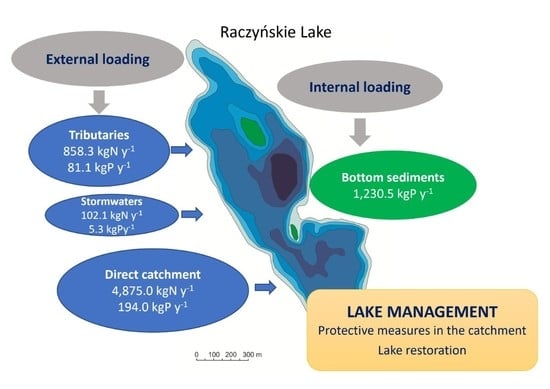
| Tributaries (D1-D8) | 858.3 | 81.1 | 3976 |
| Stormwater runoff | 102.1 | 5.3 | 1092 |
| Direct catchment | 4875.0 | 194.0 | - |
| Total | 5835.4 | 280.4 | 6115.8 |
| Parameter | Unit | Station I | Station II | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min-Max | Mean | SD | Min-Max | Mean | SD | |||
| Total phosphorus | mgPg−1 DW | 1.71–2.83 | 2.32 | 0.47 | 1.54–2.56 | 1.96 | 0.39 | |
| Fractions of TP | NH4Cl-P | % | 2.50–2.97 | 2.81 | 0.21 | 2.94–10.7 | 4.69 | 2.96 |
| BD-P | % | 0.07–0.88 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 0.23–1.56 | 0.79 | 0.51 | |
| NaOH-P | % | 3.08–7.12 | 4.46 | 1.83 | 1.56–5.74 | 3.59 | 1.74 | |
| NaOH-NRP | % | 18.6–28.3 | 25.1 | 4.53 | 12.7–30.5 | 18.8 | 7.38 | |
| HCl-P | % | 5.19–8.71 | 7.36 | 1.61 | 4.17–15.3 | 10.22 | 4.36 | |
| Res-P | % | 55.9–69.1 | 60.1 | 6.09 | 54.5–76.1 | 61.9 | 7.94 | |
| Organic matter | % | 34.2–37.4 | 36.3 | 1.48 | 33.4–38.9 | 37.4 | 2.11 | |
| Interstitial water | SRP | mgPL−1 | 0.50–2.63 | 1.28 | 0.94 | 0.44–4.74 | 2.98 | 1.47 |
| TP | mgPL−1 | 0.68–2.91 | 1.62 | 0.94 | 0.56–5.28 | 3.23 | 1.62 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Dondajewska-Pielka, R.; Gołdyn, R. The Assessment of External and Internal Nutrient Loading as a Basis for Lake Management. Water 2022, 14, 2844. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182844
Kowalczewska-Madura K, Dondajewska-Pielka R, Gołdyn R. The Assessment of External and Internal Nutrient Loading as a Basis for Lake Management. Water. 2022; 14(18):2844. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182844
Chicago/Turabian StyleKowalczewska-Madura, Katarzyna, Renata Dondajewska-Pielka, and Ryszard Gołdyn. 2022. "The Assessment of External and Internal Nutrient Loading as a Basis for Lake Management" Water 14, no. 18: 2844. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182844
APA StyleKowalczewska-Madura, K., Dondajewska-Pielka, R., & Gołdyn, R. (2022). The Assessment of External and Internal Nutrient Loading as a Basis for Lake Management. Water, 14(18), 2844. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182844