Using Electrochemical Oxidation to Remove PFAS in Simulated Investigation-Derived Waste (IDW): Laboratory and Pilot-Scale Experiments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Chemical Analysis
2.3. Electrochemical Experiments
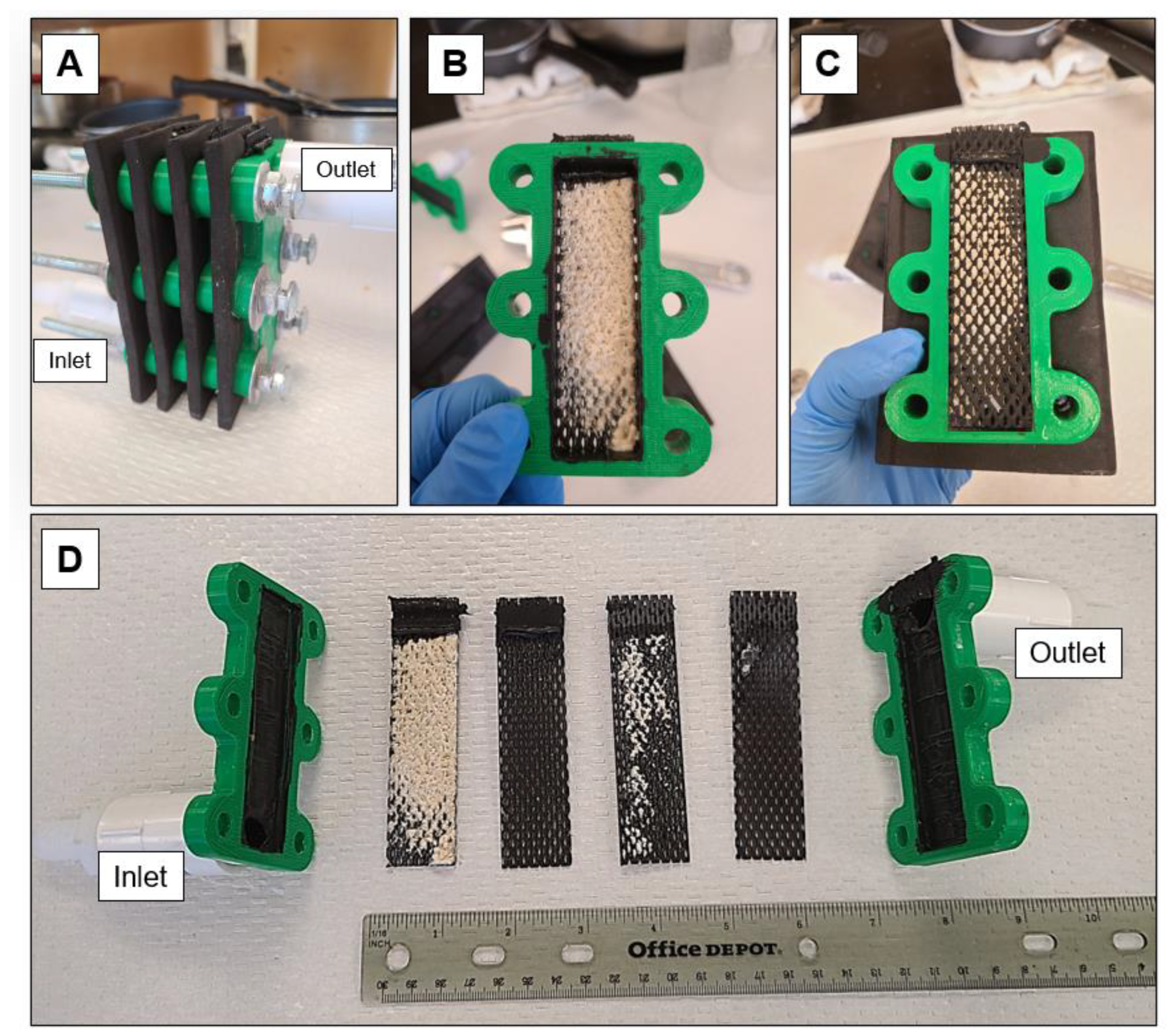
2.3.1. Generalized Setup of Electrochemical Experiments
2.3.2. Effect of Electrical Current
2.3.3. Effect of Acid Addition (pH)
2.3.4. Effect of Electrolyte
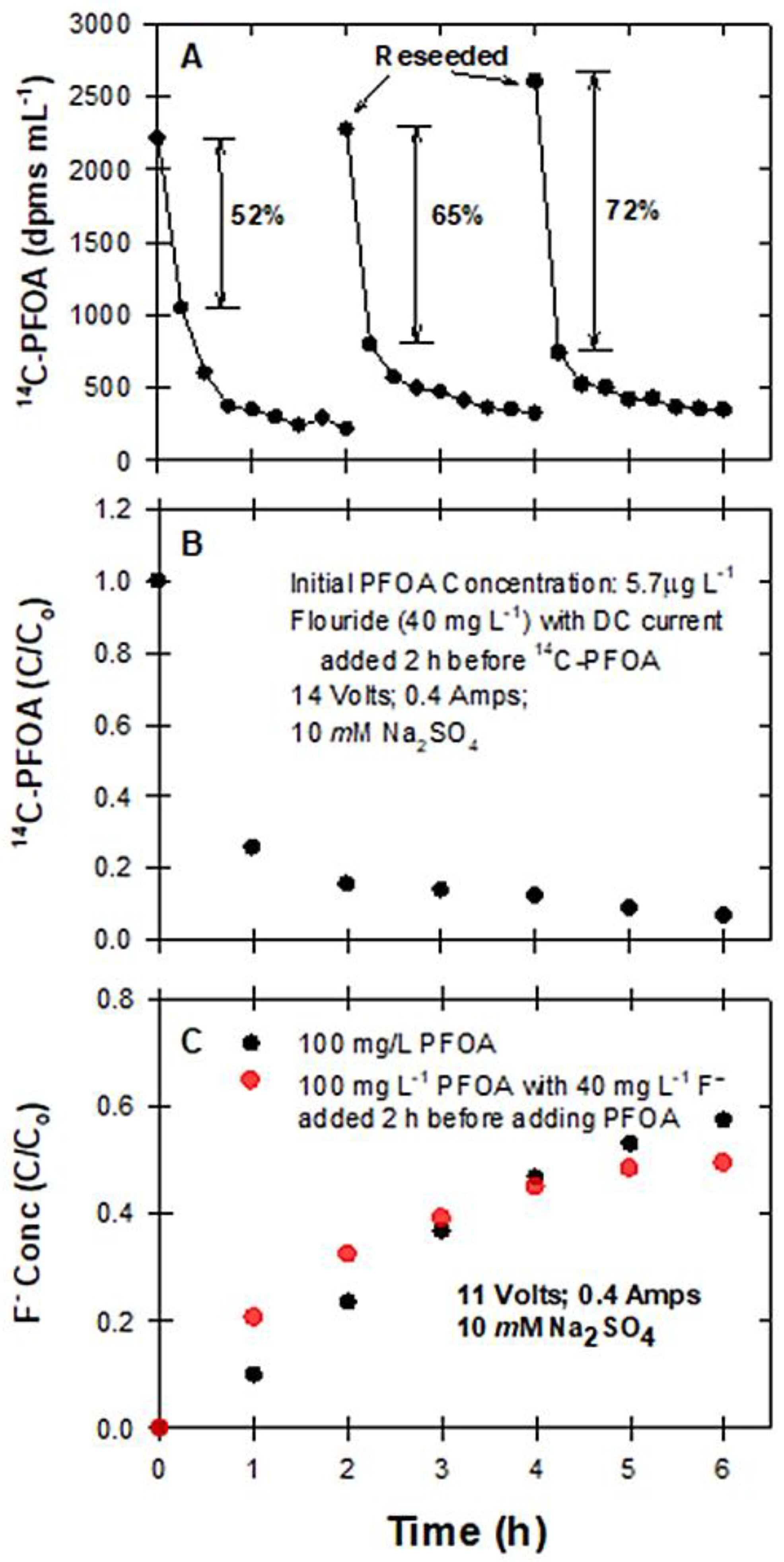
2.3.5. The Effects of Reseeding PFOA and Fluoride on Degradation
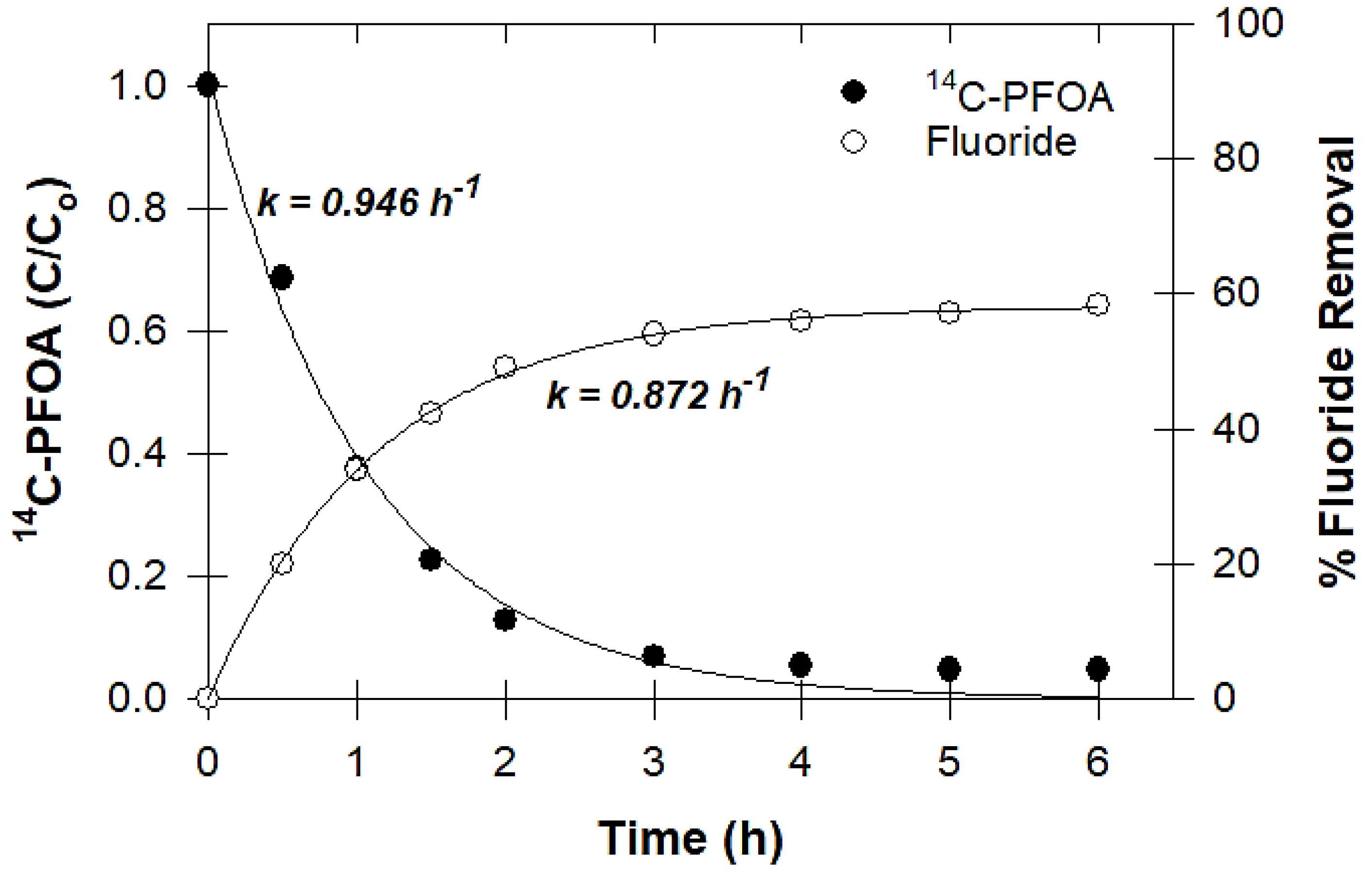
2.3.6. Measuring Defluorination
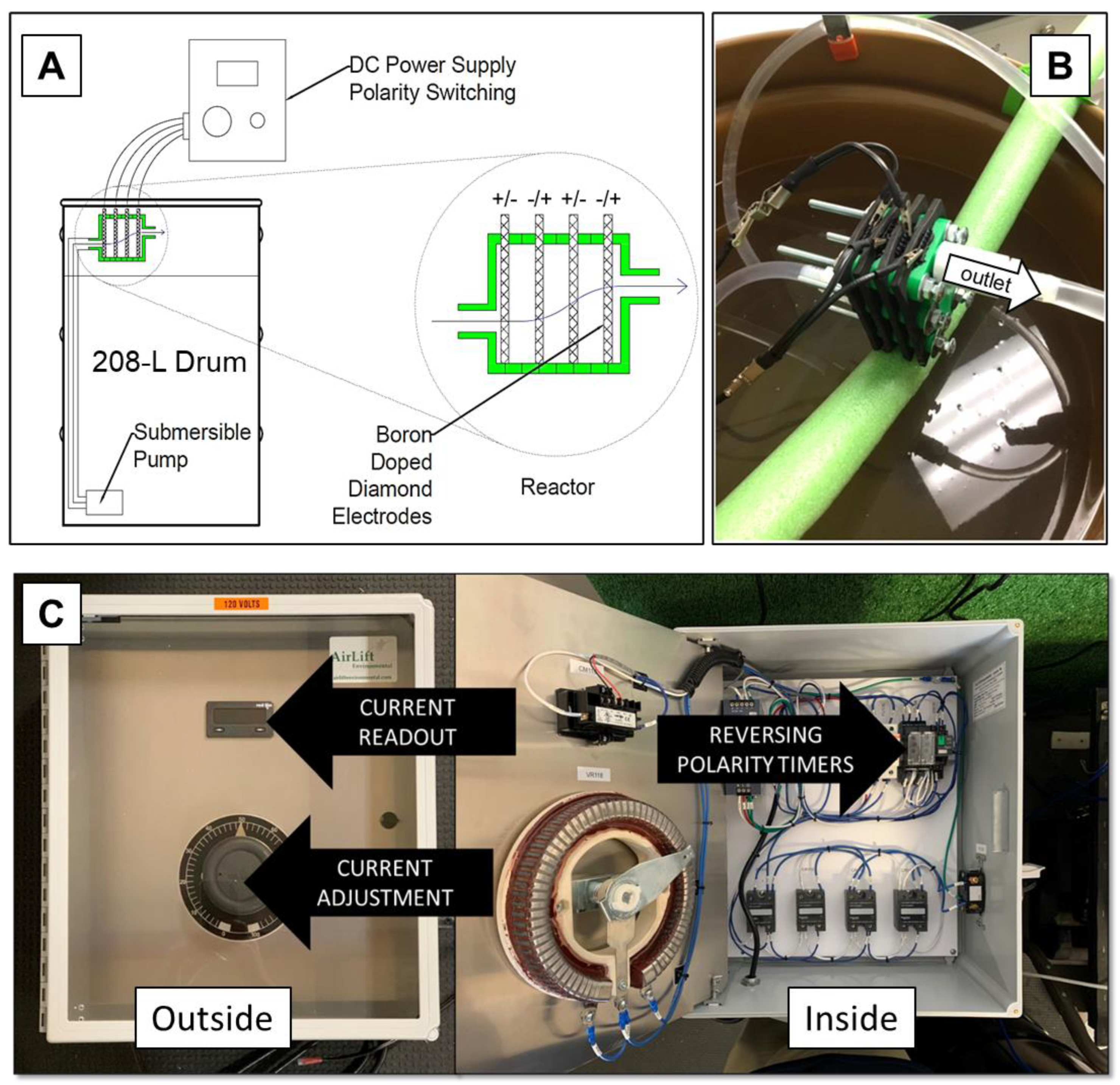
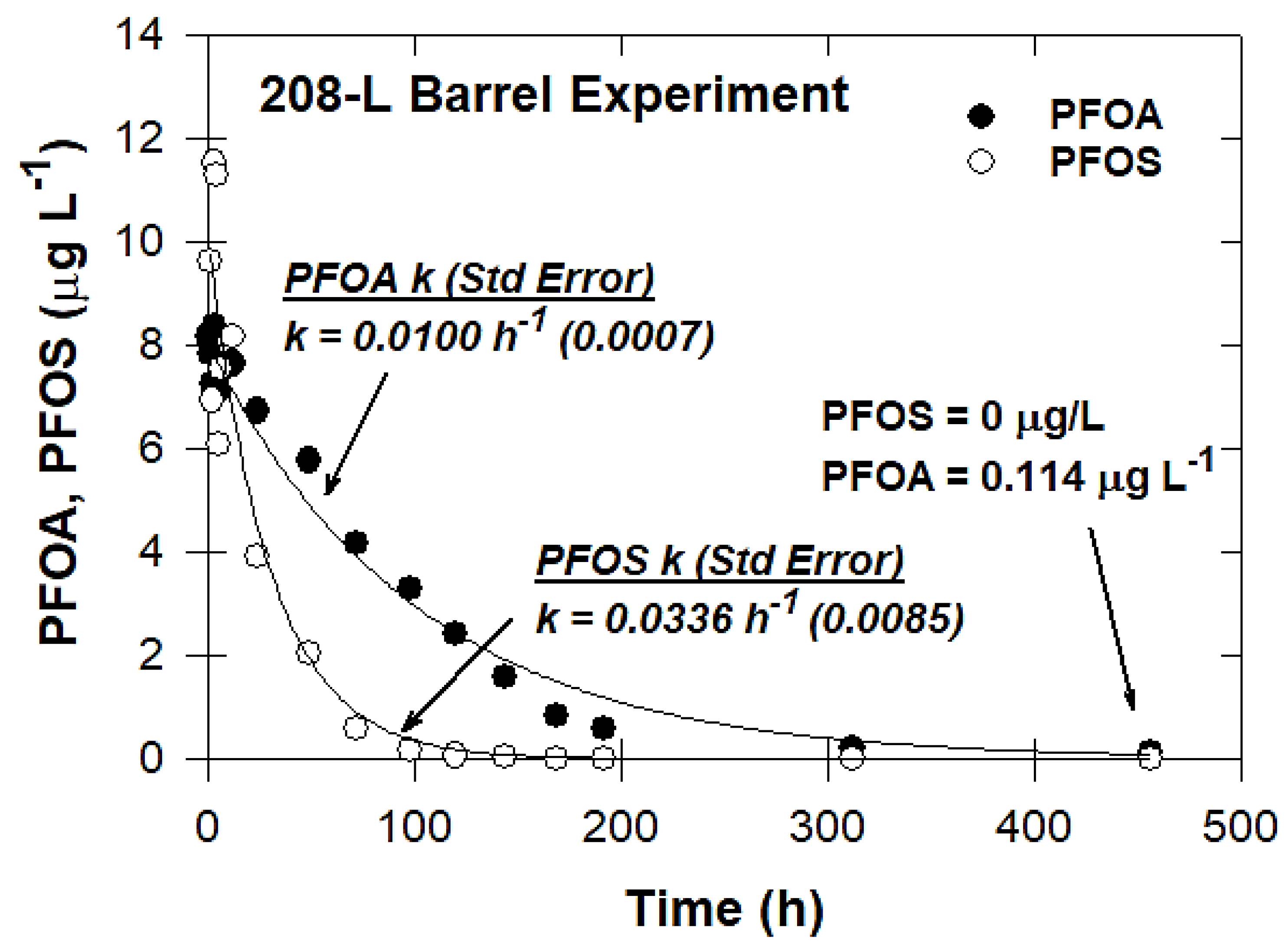
2.3.7. Pilot-Scale Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
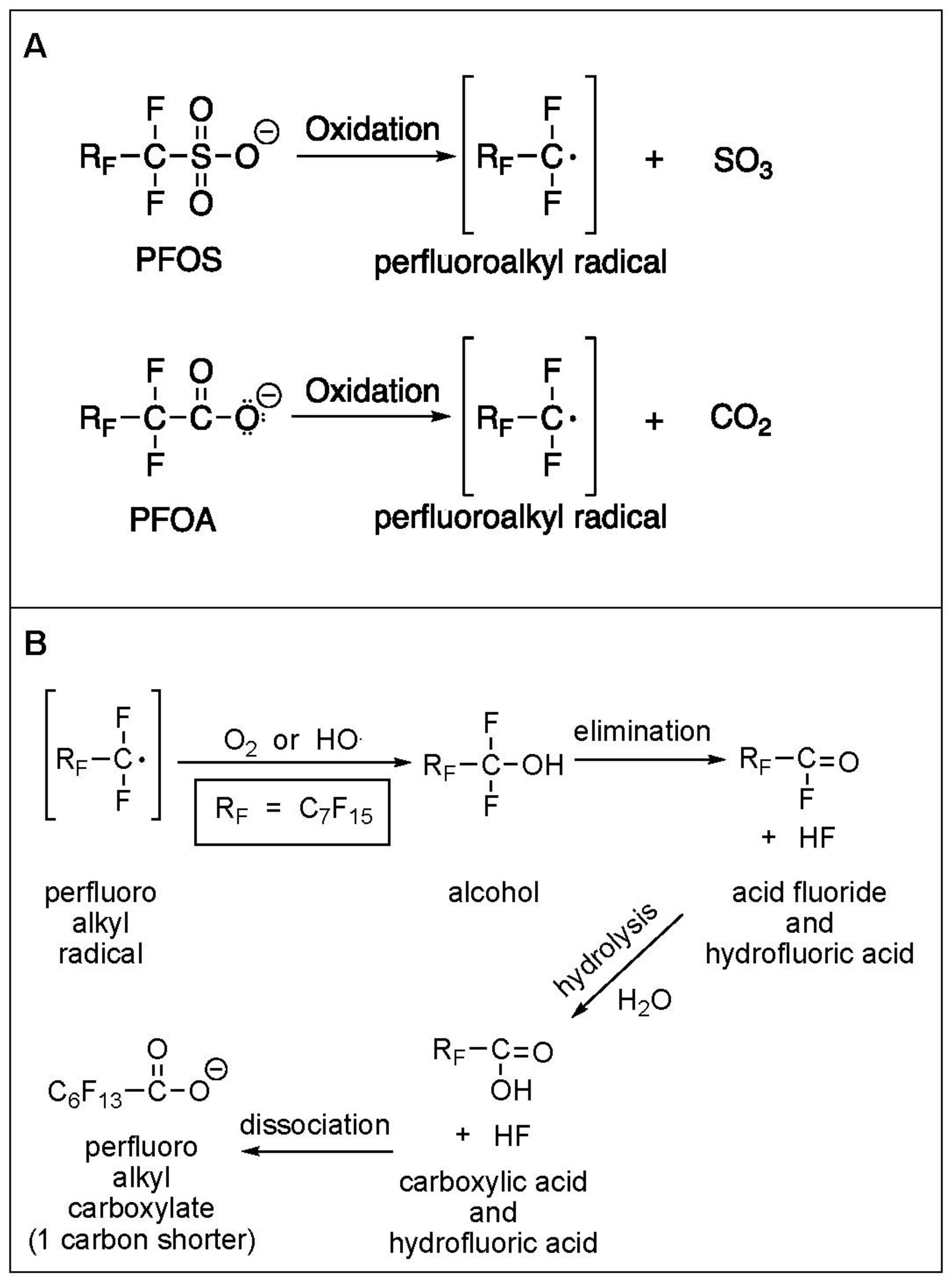
3.1. Electrochemical Oxidation of PFAS
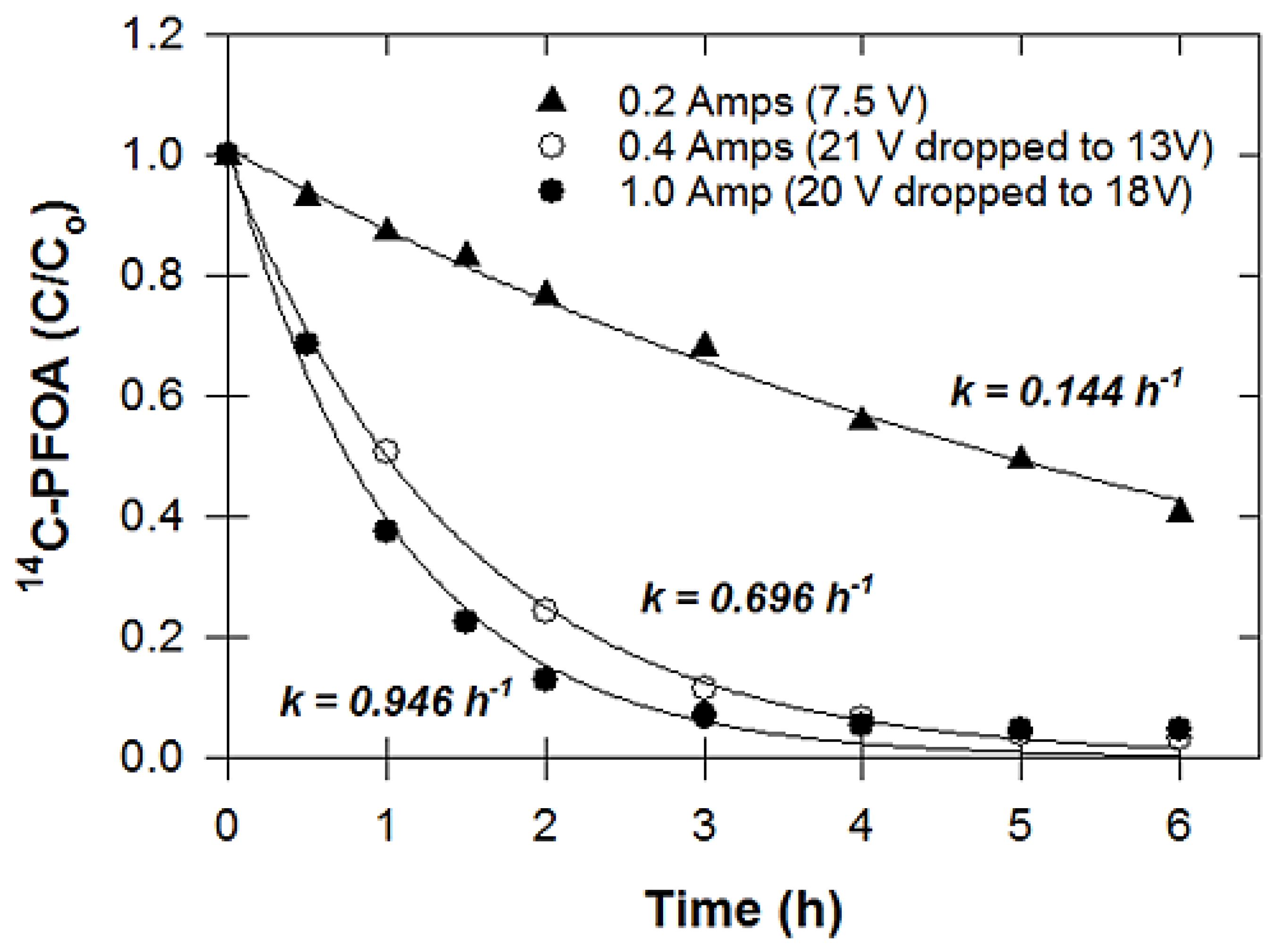
3.2. Effect of Electrical Current
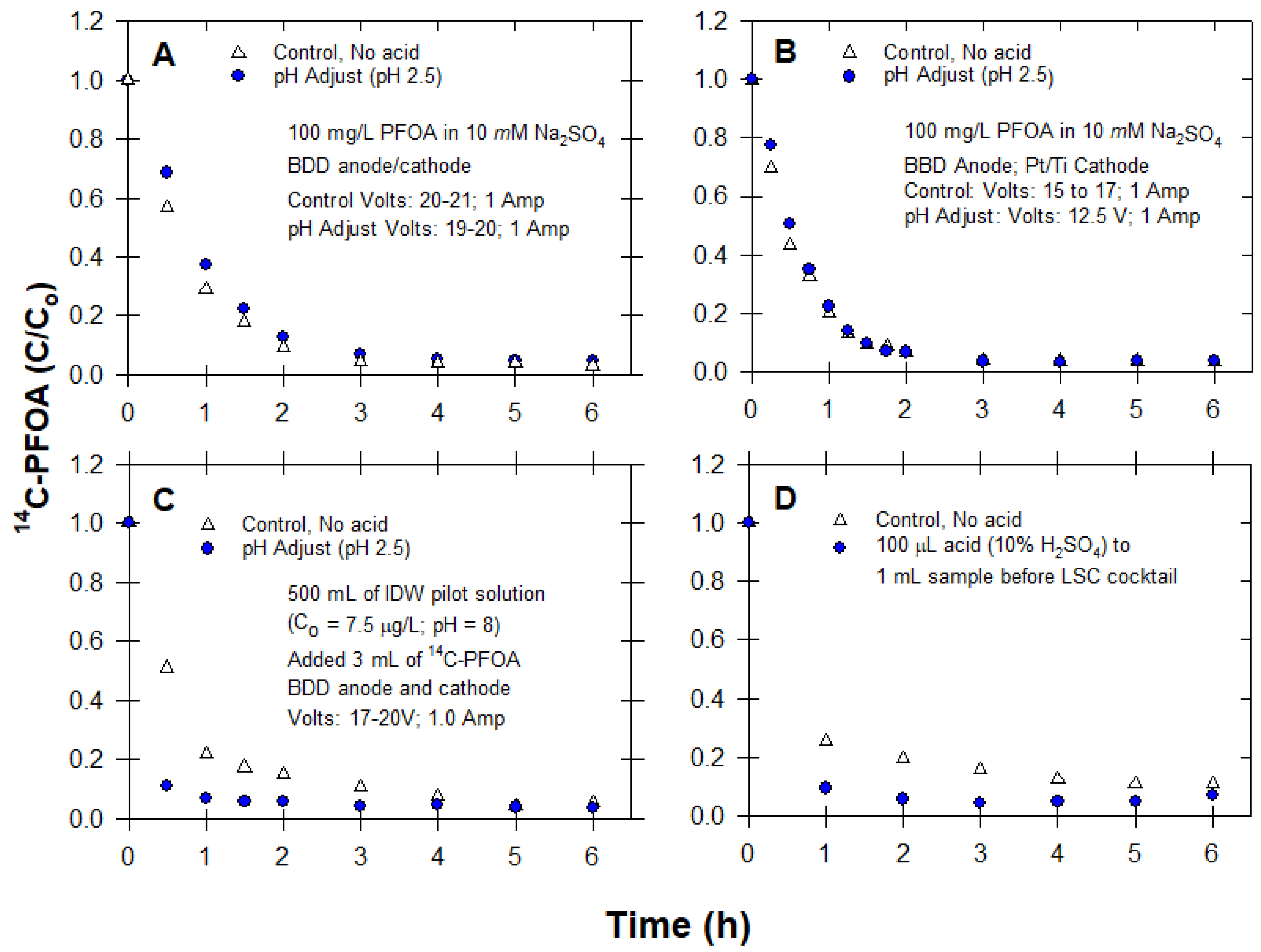
3.3. pH Adjustment
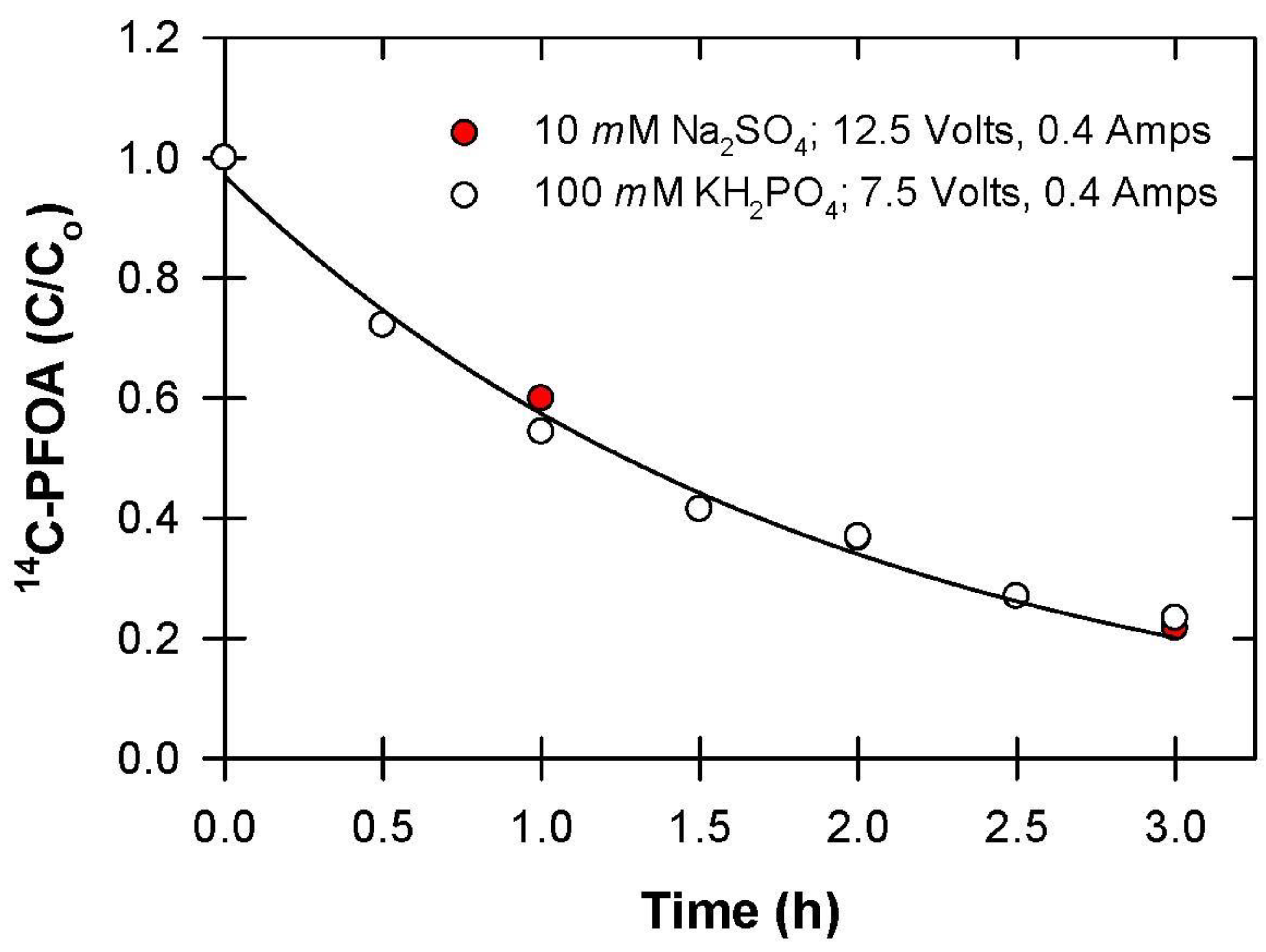
3.4. Electrolyte
3.5. Reseeding PFAS to BDD Electrodes
3.6. Defluorination and Fluoride Mass Balance
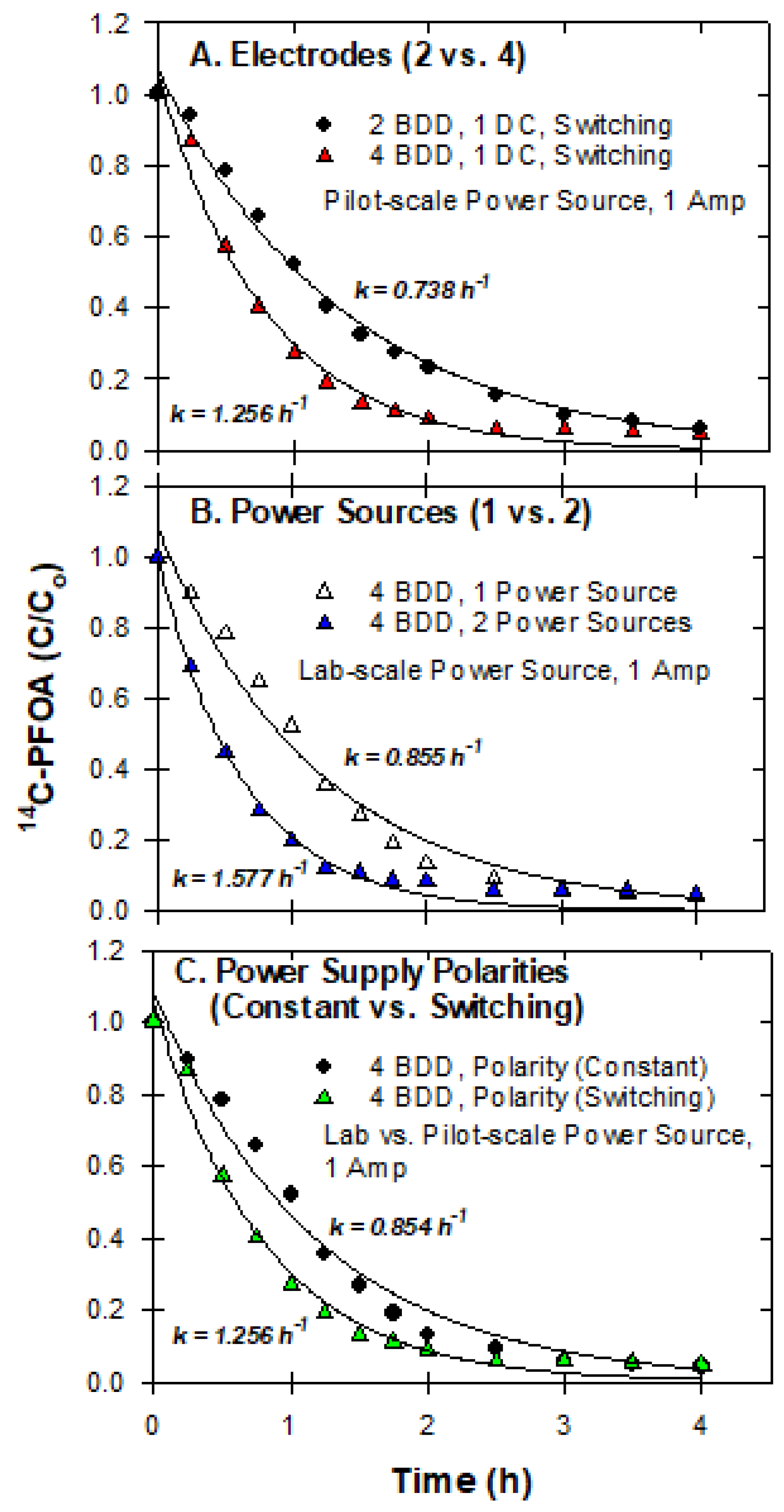
3.7. Pilot-Scale Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Copp, T. DoD: At least 126 bases report water contaminants linked to cancer, birth defects. Military Times, 26 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Moody, C.A.; Field, J.A. Determination of perfluorocarboxylates in groundwater impacted by fire-fighting activity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 2800–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, C.A.; Hebert, G.N.; Strauss, S.H.; Field, J.A. Occurrence and persistence of perfluorooctanesulfonate and other perfluorinated surfactants in groundwater at a fire-training area at Wurtsmith Air Force Base, Michigan, USA. J. Environ. Monit. 2003, 5, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, M.M.; Barofsky, D.F.; Field, J.A. Quantitative determination of fluorotelomer sulfonates in groundwater by LC MS/MS. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1828–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suthersan, S.S.; Horst, J.; Ross, I.; Kalve, E.; Quinnan, J.; Houtz, E.; Burdick, J. Responding to emerging contaminant impacts: Situational management. Groundw. Monit. Remediat. 2016, 36, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, B.L.; Howell, R.D.; Criddle, C.S. Fluorinated organics in the biosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 2445–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hagan, D. Understanding organofluorine chemistry. An introduction to the C-F bond. Chem Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conder, J.M.; Hoke, R.A.; Wolf, W.D.; Russell, M.H.; Buck, R.C. Are PFCAs Bioaccumulative? A critical review and comparison with regulatory criteria and persistent lipophilic compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.; Anitole, K.; Hodes, C.; Lai, D.; Pfahles-Hutchens, A.; Seed, J. Perfluoroalkyl acids: A review of monitoring and toxicological findings. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 99, 366–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, N.; Eriksson, P.; Viberg, H. Neonatal exposure to PFOS and PFOA in mice results in changes in proteins which are important for neuronal growth and synaptogenesis in the developing brain. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 108, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xu, X.L.; Li, X.; Jin, Y.H.; Sasaki, K.; Saito, N.; Sato, I.; Tsuda, S. Human nails analysis as biomarker of exposure to perfluoroalkyl compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8144–8150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. EPA Announces New Drinking Water Health Advisories for PFAS Chemicals, $1 Billion in Bipartisan Infrastructure Law Funding to Strengthen Health Protections|US EPA. 2022. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/newsreleases/epa-announces-new-drinking-water-health-advisories-pfas-chemicals-1-billion-bipartisan (accessed on 30 July 2022).
- Crunden, E.A. Defense department hits the brakes on PFAS incineration. E&E PM News. 2022. Available online: https://www.eenews.net/articles/defense-department-hits-the-brakes-on-pfas-incineration/ (accessed on 30 July 2022).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. PFAS Innovative Treatment Team (PITT). 2020. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/chemical-research/pfas-innovative-treatment-team-pitt (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- Zhuo, Q.; Deng, S.; Yang, B.; Huang, J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, T.; Yu, G. Degradation of perfluorinated compounds on a boron-doped diamond electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 77, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjenovic, J.; Duinslaeger, N.; Avvl, S.S.; Chaplin, B.P. Facing the challenge of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances in water: Is electrochemical oxidation the answer? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14815–14829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Method 533: Determination of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Drinking Water by Isotope Dilution Anion Exchange Solid Phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry|US EPA. 2019. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/dwanalyticalmethods/method-533-determination-and-polyfluoroalkyl-substances-drinking-water-isotope (accessed on 30 July 2022).
- Carter, K.E.; Farrel, J. Oxidative destruction of perfluorooctane sulfate using boron-doped diamond film electrodes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 42, 6111–6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Farrell, J. Electrochemical oxidation of perfluorobutane sulfonate using boron-doped diamond film electrodes. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2009, 39, 1993–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzek, L.W.; Tipton, M.J.; Farmer, A.T.; Steen, A.D.; Carter, K.E. Understanding electrochemically activated persulfate and its application to Ciprofloxacin abatement. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 5875–5883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, C.E.; Andaya, C.; Urtiaga, A.; McKenzie, E.R.; Higgins, C.P. Electrochemical treatment of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) in groundwater impacted by aqueous film forming foams (AFFFs). J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 295, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, C.E.; Andaya, C.; Burant, A.; Condee, C.W.; Urtiagad, A.; Strathmann, T.J.; Higgins, C.P. Electrochemical treatment of perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctane sulfonate: Insights into mechanisms and application to groundwater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapalka, A.; Fóti, G.; Comninellis, C. Kinetic modelling of electrochemical mineralization of organic pollutants for wastewater treatment. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2008, 38, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, T.; Iizuka, Y.; Nakata, K.; Murakami, T.; Tryk, D.A.; Fujishima, A.; Koide, Y.; Morito, Y. Efficient electrochemical decomposition of perfluorocarboxylic acids by the use of a boron-doped diamond electrode. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2011, 20, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Li, Y.; Shang, E.; Xu, Z.; Liu, J. Electrochemical oxidation of perfluorinated compounds in water. Chemosphere 2016, 146, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Niu, J.; Ding, S.; Zhang, L. Electrochemical degradation of per-fluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) by Ti/SnO2-Sb, Ti/SnO2-Sb/PbO2 and Ti/SnO2-Sb/MnO2 anodes. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2281–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nienhauser, A.B.; Ersan, M.S.; Lin, Z.; Perreault, F.; Westerhoff, P. Boron-doped diamond electrodes degrade short- and long-chain per- and polyfluorinated alkyl substances in real industrial wastewaters. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Q.; Li, X.; Yan, F.; Yang, B.; Deng, S.; Huang, J.; Yu, G. Electrochemical oxidation of 1H, 1H, 2H, 2H-perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (6:2 FTS) on DSA electrode: Operating parameters and mechanism. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 1733–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, B.; Zhi, J.; Zhang, X.; Murakami, T.; Fujishima, A. Electrochemical route for fluorinated modification of boron-doped diamond surface with perfluorooctanoic acid. Electrochem. Commun. 2007, 9, 2817–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Abad, J.; Perez-Herranz, V.; Urtiaga, A. Electrochemical oxidation of 6:2 fluorotelomer sulfonic acid (6:2 FTSA) on BDD: Electrode characterization and mechanistic investigation. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2018, 48, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin, B.P.; Wylie, I.; Zheng, H.; Carlisle, J.A.; Farrell, J. Characterization of the performance and failure mechanisms of boron-doped diamond ultrananocrystalline diamond electrodes. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2011, 41, 1329–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin, B.P.; Hubler, D.K.; Farrell, J. Understanding anodic wear at boron doped diamond film electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 89, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duo, I.; Levy-Clement, C.; Fujishima, A.; Comninellis, C. Electron transfer kinetics on boron-doped diamond Part I: Influence of anodic treatment. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2004, 34, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uwayezu, J.N.; Carabante, I.; Lejon, T.; van Hees, P.; Karlsson, P.; Hollman, P.; Kumpiene, J. Electrochemical degradation of per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances using boron-doped diamond electrodes. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 290, 112573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barisci, S.; Suri, R. Electrooxidation of short and long chain perfluorocarboxylic acids using boron doped diamond electrodes. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pierce, R.D.; Shi, H.; Li, C.; Huang, Q. Electrochemical degradation of perfluoroalkyl acids by titanium suboxides anodes. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, Y.; Landi, G.M.; Ensch, M.; Becker, M.F.; Witt, S.E.; Rusinek, C.A. A flow-through cell for the electrochemical oxidation of perfluoroalkyl substances in landfill leachates. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 43, 102210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Pierce, R.D., Jr.; Lin, H.; Chiang, S.-Y.D.; Huang, Q.J. Electrochemical oxidation of PFOA and PFOS in concentrated waste streams. Remediation 2018, 28, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenti, A.; Jin, Y.; Rhoades, A.J.H.; Dooley, G.P.; Iovino, P.; Salvestrini, S.; Musmarra, D.; Mahendra, S.; Peaslee, G.F.; Blotevogel, J. Performance testing of mesh anodes for in situ electrochemical oxidation of PFAS. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 9, 100205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, Y.; Becker, M.F.; Nickelsen, M.G.; Witt, S.E. Laboratory and semi-pilot scale study on the electrochemical treatment of perfluoroalkyl acids from ion exchange still bottoms. Water 2021, 13, 2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, S.; Rancis, N.; Ensch, M.; Maldonado, V. Electrochemical destruction of “Forever Chemicals”: The right solution at the right time. Electrochem. Soc. Interface 2020, 29, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compound (C#) | Acronym | Formula | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Perfluorooctanoic Acid (C8) | PFOA | F(CF2)7COOH | 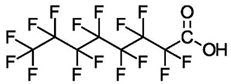 |
| Perfluorohexanoic Acid (C6) | PFHxA | F(CF2)5COOH | 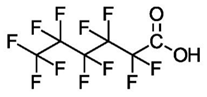 |
| Perfluorobutyric Acid (C4) | PFBA | F(CF2)3COOH | 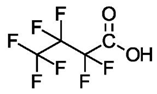 |
| Perfluoropropionic Acid (C3) | PFPrA | F(CF2)2COOH | 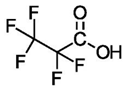 |
| Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid (C8) | PFOS | F(CF2)8SO3H | 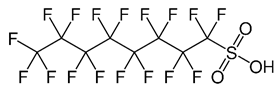 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yanagida, A.; Webb, E.; Harris, C.E.; Christenson, M.; Comfort, S. Using Electrochemical Oxidation to Remove PFAS in Simulated Investigation-Derived Waste (IDW): Laboratory and Pilot-Scale Experiments. Water 2022, 14, 2708. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14172708
Yanagida A, Webb E, Harris CE, Christenson M, Comfort S. Using Electrochemical Oxidation to Remove PFAS in Simulated Investigation-Derived Waste (IDW): Laboratory and Pilot-Scale Experiments. Water. 2022; 14(17):2708. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14172708
Chicago/Turabian StyleYanagida, Amy, Elise Webb, Clifford E. Harris, Mark Christenson, and Steve Comfort. 2022. "Using Electrochemical Oxidation to Remove PFAS in Simulated Investigation-Derived Waste (IDW): Laboratory and Pilot-Scale Experiments" Water 14, no. 17: 2708. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14172708
APA StyleYanagida, A., Webb, E., Harris, C. E., Christenson, M., & Comfort, S. (2022). Using Electrochemical Oxidation to Remove PFAS in Simulated Investigation-Derived Waste (IDW): Laboratory and Pilot-Scale Experiments. Water, 14(17), 2708. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14172708



_Dionysiou.jpg)




