Sewage Irrigation Fields—From Relict Landscape to Blue-Green Urban Infrastructure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Motivation
- The article should contain information on ecosystem services based on the creation or restoration of wetlands.
- The article should provide information on how sewage irrigation fields are created; the history of their creation; and economic, social, ecological, cultural, environmental, climatic, landscape, spatial, ecological, educational, and tourist and recreational aspects.
- The article should refer to the determination of the location of sewage irrigation fields in a system of green and blue infrastructure and their importance in the urban fabric.
- The article should contain information on examples of the use of sewage irrigation fields in areas of various world cities and their impact on the environment and landscape.
- Analyses and studies on green and blue infrastructure in the urban fabric.
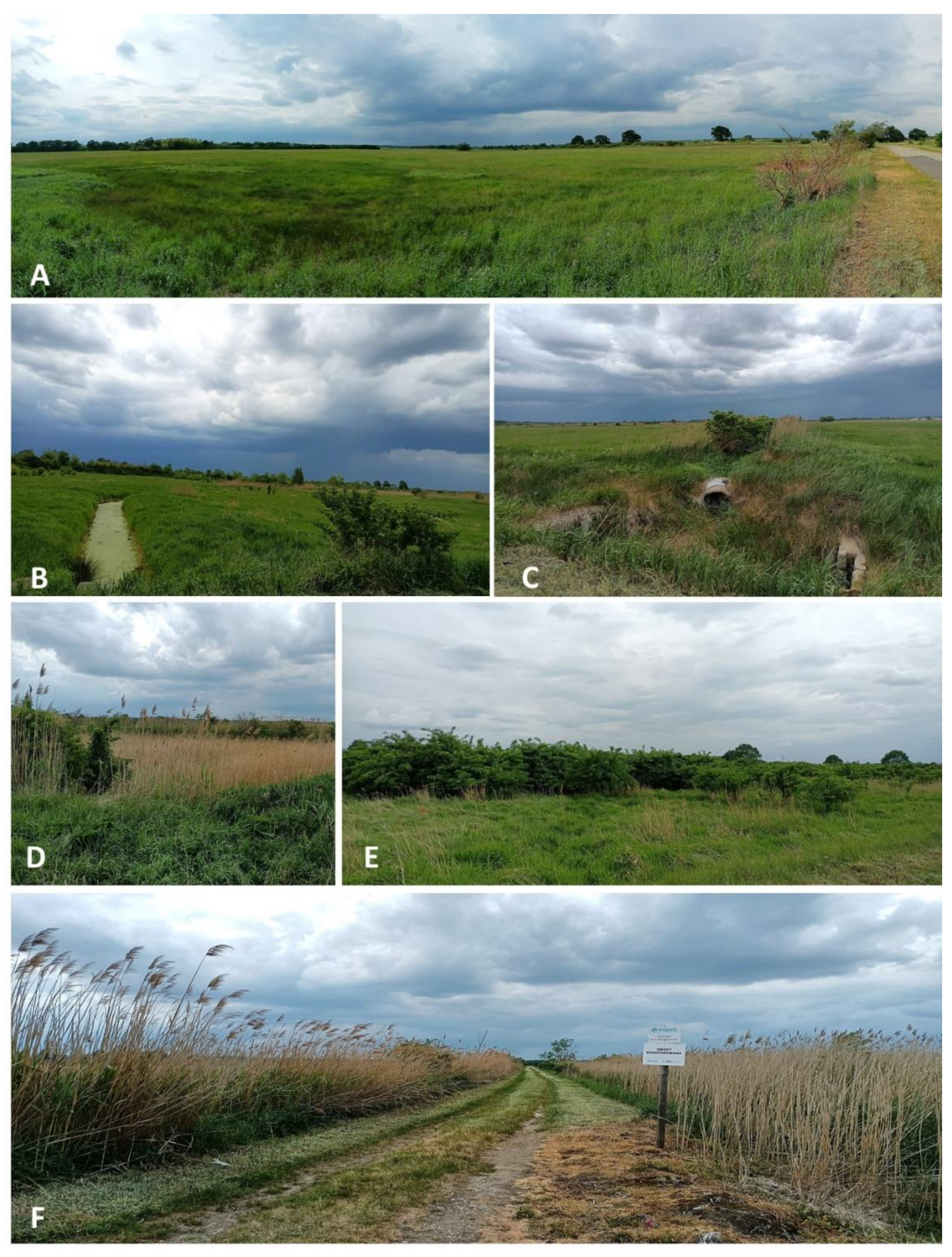
2.2. Sewage Irrigation Fields in Cities—History and Significance
3. Results
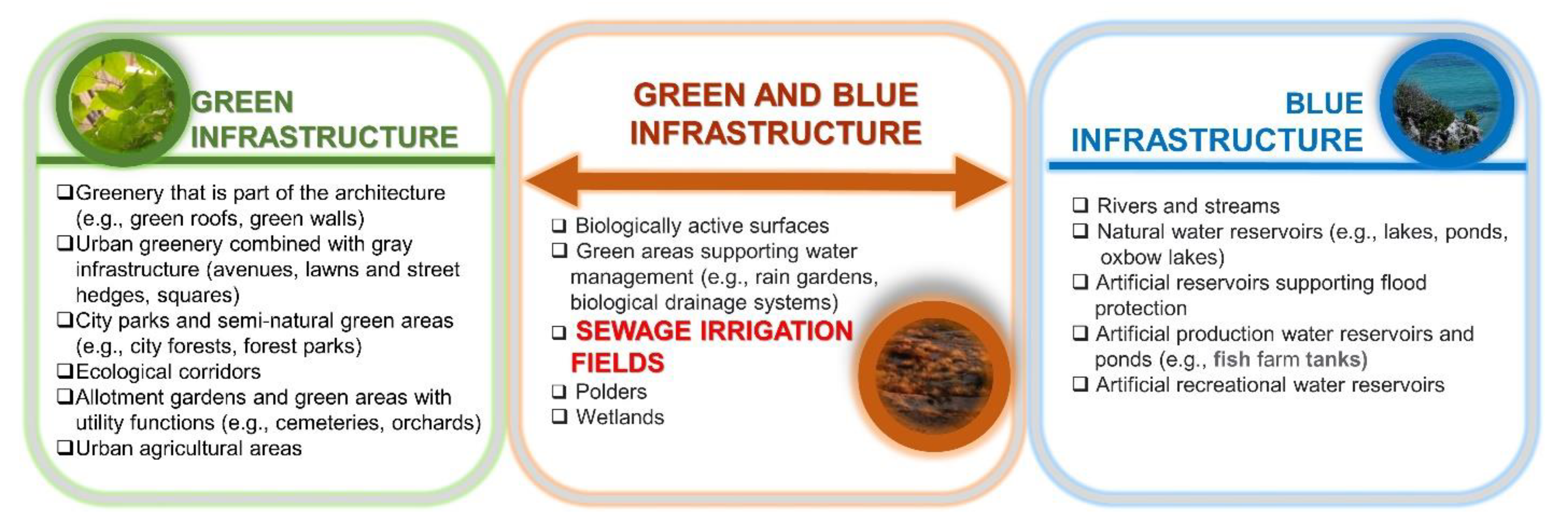
3.1. Location of Sewage Irrigation Fields in Blue-Green Infrastructure Systems
3.2. The Multifunctionality of Sewage Irrigation Fields in an Urban System
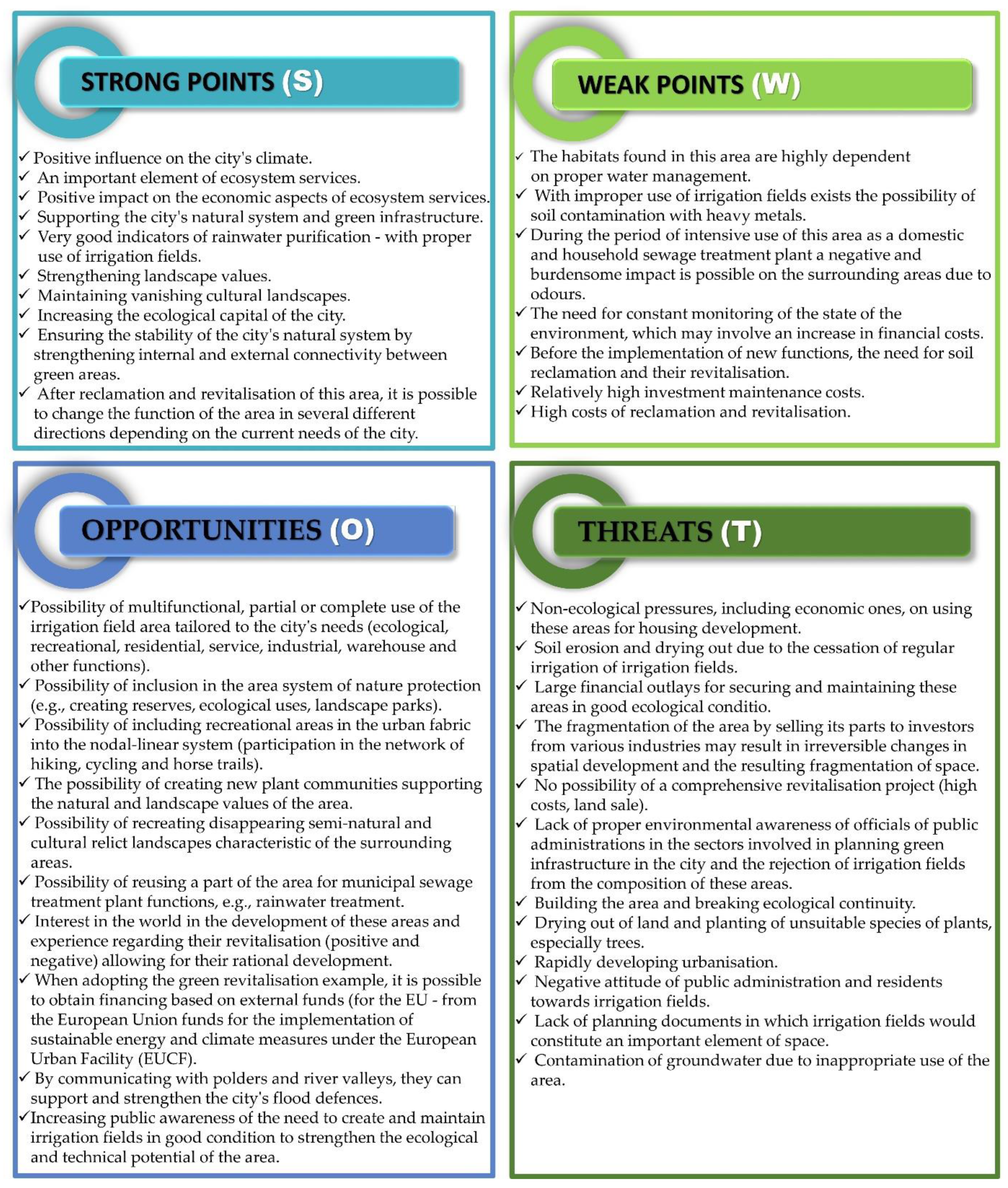
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benedict, M.A.; McMahon, E.T. Green Infrastructure: Smart Conservation for the 21st Century. Renew. Res. J. 2002, 20, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Wende, W. Ecosystem Services and Landscape Planning. How to lntegrate Two Different Worlds in a High-Density Urban Setting. In Urban Landscapes in High-Density Cities; Rinaldi, B.M., Tan, P.J., Eds.; Birkhäuser: Berlin, Germany; Basel, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 154–164. [Google Scholar]
- Bolund, P.; Hunhammer, S. Ecosystem Services in Urban Areas. Ecol. Econ. 1999, 29, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemelä, J.; Saarela, S.R.; Soderman, T.; Kopperoinen, L.; Yli-Pelkonen, V.; Vare, S.; Kotze, D.J. Using the Ecosystem Services Approach for Better Planning and Conservation of Urban Green Spaces. A Finland case study. Biodivers. Conserv. 2010, 19, 3225–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauleit, S.; Liu, L.; Ahern, J.; Kazmierczak, A. Multifunctional Green Infrastructure Planning to Promote Ecological Services in the City. In Handbook of Urban Ecology; Niemelä, J., Ed.; Oxford Univnversity Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 272–285. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Seto, K.C. Projecting Global Urban Land Expansion and Heat Island Intensification through 2050. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 114037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marando, F.; Salvatori, E.; Sebastiani, A.; Fusaro, L.; Manes, F. Regulating Ecosystem Services and Green Infrastructure: Assessment of Urban Heat Island E_ect Mitigation in the Municipality of Rome, Italy. Ecol. Model. 2019, 392, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demuzere, M.; Orru, K.; Heidrich, O.; Olazabal, E.; Geneletti, D.; Orru, H.; Bhave, A.G.; Mittal, N.; Feliu, E.; Faehnle, M. Mitigating and Adapting to Climate Change: Multi-functional and Mulit-Scale Assessment of Green Urban Infrastructure. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 146, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathey, J.; Rößler, S.; Banse, J.; Lehmann, I.; Bräuer, A. Brownfields as an Element of Green Infrastructure for Implementing Ecosystem Services into Urban Areas. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2015, 141, A4015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleszczuk, P.; Malara, A.; Jośko, I.; Lesiuk, A. The phytotoxicity changes of sewage sludge-amended soils. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 4937–4948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojanowska-Olichwer, A. Wstępna ocena ekotoksykologiczna gleb na obszarze Pól Irygacyjnych we Wrocławiu (Initial Ecotoxicological Assessment of Soils in the Area of Irrigation Fields in Wrocław). Prz. Geol. 2016, 64, 719–725. Available online: https://geojournals.pgi.gov.pl/pg/article/view/27439/19155 (accessed on 2 February 2021).
- Boćko, J. Gleba jako środowisko oczyszczania ścieków (Soil as an environment for wastewater treatment). Rocz. Glebozn. 1965, 15, 496–548. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. The Water Framework Directive (Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy). Off. J. Eur. Econ. L 2000, 327, 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.K.; Deshbhratar, P.B.; Ramteke, D.S. Effects of sewage wastewater irrigation on soil properties, crop yield and environment. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 103, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-J.; Wang, J.; Yu, X. Wastewater irrigation and crop yield: A meta-analysis. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra-Castro, C.; Lopes, A.R.; Vaz-Moreira, I.; Silva, E.F.; Manaia, C.M.; Nunes, O.C. Wastewater reuse in irrigation: A microbiological perspective on implications in soil fertility and human and environmental health. Environ. Int. 2015, 75, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kargol, A.K.; Cao, C.; James, C.A.; Gough, H.L. Wastewater reuse for tree irrigation: Influence on rhizosphere microbial communities, Resources. Environ. Sustain. 2022, 9, 100063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrover, M.; Farrús, E.; Moyà, G.; Vadell, J. Chemical properties and biological activity in soils of Mallorca following twenty years of treated wastewater irrigation. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 95, S188–S192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbaniak, M.; Wyrwicka, A.; Tołoczko, W.; Serwecińska, L.; Zieliński, M. The effect of sewage sludge application on soil properties and willow (Salix sp.) cultivation. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaoua, S.; Boussaa, S.; El Gharmali, A.; Boumezzough, A. Impact of irrigation with wastewater on accumulation of heavy metals in soil and crops in the region of Marrakech in Morocco. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2019, 18, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjami, K.; Ennaji, M.M.; Fouad, S.; Oubrim, N.; Cohen, N. Wastewater reuse for irrigation in Morocco: Helminth eggs contamination level of irrigated crops and sanitary risk (a case study of Settat and Soualem regions). J. Bacteriol. Parasitol. 2013, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slobodiuk, S.; Niven, C.; Arthur, G.; Thakur, S.; Ercumen, A. Does Irrigation with Treated and Untreated Wastewater Increase Antimicrobial Resistance in Soil and Water: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bougnom, B.P.; Thiele-Bruhn, S.; Ricci, V.; Zongo, C.; Piddock, L.J.V. Raw wastewater irrigation for urban agriculture in three African cities increases the abundance of transferable antibiotic resistance genes in soil, including those encoding extended spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Li, Y. Using Reclaimed Water for Agricultural and Landscape Irrigation in China: A Review. Irrig. Drain. 2017, 66, 672–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickin, S.K.; Schuster-Wallace, C.J.; Qadir, M.; Pizzacalla, K. A review of health risks and pathways for exposure to wastewater Use in Agriculture. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nnadozie, C.F.; Kumari, S.; Bux, F. Status of pathogens, antibiotic resistance genes and antibiotic residues in wastewater treatment systems. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2017, 16, 491–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatica, J.; Cytryn, E. Impact of treated wastewater irrigation on antibiotic resistance in the soil microbiome. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 3529–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, A.; Agüera, A.; Bayona, J.M.; Cytryn, E.; Fotopoulos, V.; Lambropoulou, D.; Manaia, C.M.; Michael, C.; Revitt, M.; Schröder, P.; et al. The potential implications of reclaimed wastewater reuse for irrigation on the agricultural environment: The knowns and unknowns of the fate of antibiotics and antibiotic resistant bacteria and resistance genes—A review. Water Res. 2017, 123, 448–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorinolu, A.J.; Tyagi, N.; Kumar, A.; Munir, M. Antibiotic resistance development and human health risks during wastewater reuse and biosolids application in agriculture. Chemosphere 2021, 265, 129032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oztekin, T.; Brown, L.C.; Holdsworth, P.M.; Kurunc, A.; Rector, D. Evaluating drainage design parameters forwastewater irrigation applications to minimize impact on surfacewaters. Appl. Eng. Agric. 1999, 99, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalkmann, P.; Broszat, M.; Siebe, C.; Willaschek, E.; Sakinc, T.; Huebner, J.; Amelung, W.; Grohmann, E.; Siemens, J. Accumulation of pharmaceuticals, enterococcus, and resistance genes in soils irrigated with wastewater for zero to 100 years in central Mexico. PLoS ONE. 2012, 7, e45397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broszat, M.; Nacke, H.; Blasi, R.; Siebe, C.; Huebner, J.; Daniel, R.; Grohmanna, E. Wastewater irrigation increases the abundance of potentially harmful Gammaproteobacteria in soils in Mezquital Valley, Mexico. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5282–5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleem, A.; Isar, J.; Malik, A. Impact of long-term application of industrial wastewater on the emergence of resistance traits in Azotobacter chroococcum isolated from rhizospheric soil. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 86, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiani, S.; Malik, A. Tolerance of pesticides and antibiotic resistance in bacteria isolated from wastewater-irrigated soil. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 19, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougnom, B.P.; Thiele-Bruhn, S.; Ricci, V.; Zongo, C.; Piddock, L.J.V. High-throughput sequencing data and antibiotic resistance mechanisms of soil microbial communities in non-irrigated and irrigated soils with raw sewage in African cities. Data Brief. 2019, 27, 104638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, J.; Chen, P.; Ding, R.; Zhang, P.; Li, X. Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistances in soils from wastewater irrigation areas in Beijing and Tianjin, China. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 193, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Zhang, S.; Xue, X.; Yang, J.; Hu, K.; Yu, X. Influence of the sewage irrigation on the agricultural soil properties in Tongliao City, China. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2013, 7, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibekwe, A.M.; Gonzalez-Rubio, A.; Suarez, D.L. Impact of treated wastewater for irrigation on soil microbial communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 1603–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerbi, A.; Nissim, W.G.; Fluet, R.; Labrecque, M. Willow Root Development and Morphology Changes Under Different Irrigation and Fertilization Regimes in a Vegetation Filter. Bioenerg. Res. 2015, 8, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolti, A.; Green, S.J.; Ben Mordechay, E.; Hadar, Y.; Minz, D. Root microbiome response to treated wastewater irrigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-H.; Zhao, J.-Z.; Ouyang, Z.-Y.; Söderlund, L.; Liu, G.-H. Impacts of sewage irrigation on heavy metal distribution and contamination in Beijing, China. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattan, R.K.; Datta, S.P.; Chhonkar, P.K.; Suribabu, K.; Singh, A.K. Long-term impact of irrigation with sewage effluents on heavy metal content in soils, crops and groundwater—A case study, Agriculture. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 109, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimkus, A.; Gudrā, D.; Dubova, L.; Fridmanis, D.; Alsiņa, I.; Muter, O. Stimulation of sewage sludge treatment by carbon sources and bioaugmentation with a sludge-derived microbial consortium. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 146989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmecke, M.; Fries, E.; Schulte, C. Regulating water reuse for agricultural irrigation: Risks related to organic micro-contaminants. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, P.F. Historical aspects of wastewater treatment. In Decentralised Sanitation and Reuse: Concepts, Systems and Implementation; Lens, P., Zeeman, G., Lettinga, G., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2001; pp. 11–38. Available online: https://sleigh-munoz.co.uk/wash/Mara/History/HistSewTreat.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2021).
- Łapczyńska-Pieprz, M. Badania nad potencjałem wymywania azotu oraz utleniania siarczków po zaprzestaniu nawadniania ściekami pól irygacyjnych, rozprawa doktorska (Research on the Potential of Nitrogen Leaching and Oxidation of Sulphides after Cessation of Irrigation with Wastewater of Irrigation Fields, Doctoral Dissertation). Ph.D. Thesis, Uniwersytet Przyrodniczy we Wrocławiu, Wrocław, Poland, 2012; pp. 1–315. Available online: https://www.dbc.wroc.pl/dlibra/publication/21421/edition/19121/content (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Ashton, J.; Ubido, J. The Healthy City and the Ecological Idea. Soc. Hist. Med. 1991, 4, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashton, J.; Seymour, H. The New Public Health; Open University Press: Milton Keynes, UK, 1988; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez, B.; Drechsel, P.; Koné, D.; Bahri, A.; Raschid-Sally, L.; Qadir, M. Wastewater, Sludge and Excreta Use in Developing Countries: An Overview. In Wastewater Irrigation and Health, Assessing and Mitigating Risk in Low-Income Countries; Drechsel, P., Scott, C.A., Raschid-Sally, L., Redwood, M., Bahri, A., Eds.; International Water Management Institute: Sri Lanka, India, 2010; pp. 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Tzanakakis, V.E.; Koo-Oshima, S.; Haddad, M.; Apostolidis, N.; Angelakis, A.N. The his tory of land application and hydroponic systems for wastewater treatment and reuse. In Evolution of Sanitation and Wastewater Management through the Centuries; Angelakis, A.N., Rose, J.B., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2014; pp. 459–482. [Google Scholar]
- Łyczko, W. Rola irygacyjne Osobowice—historia i teraźniejszość (Irrigation Role of Osobowice—History and Present). Inż. Ekol. (Ecol. Eng.) 2018, 19, 37–43. Available online: http://www.ecoeet.com/POLA-IRYGACYJNE-OSOBOWICE-HISTORIA-I-TERAZNIEJSZOSC,93488,0,2.html (accessed on 2 February 2021). [CrossRef]
- Łapczyńska-Pieprz, M.; Łomotowski, J. Wpływ zaprzestania eksploatacji pól irygowanych na zakwaszanie gleb organicznych (The effect of cessation of sewage farmsexploatation on organic soil acidification). Infrastrukt. Ekol. Teren. Wiej. (Infrastruct. Ecol. Rural Areas). 2010, 8, 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Obidoska, G.; Karaczun, Z.; Żarska, B. Phytotoxicity and phytogenotoxicity of municipal sewage sludge. Ann. Warsaw Univ. of Life Sci. SGGW, Horticult. Landsc. Architect. 2020, 41, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa Martins, M.N.; de Souza, V.V.; Souza, T.D.S. Genotoxic and mutagenic effects of sewage sludge on higher plants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2016, 124, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Singh, P.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Hashim, R. Land application of sewage sludge: Physicochemical and microbial response. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2011, 214, 41–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boćko, J. Usprawnianie gleb lekkich nawadnianych ściekami w wyniku gromadzenia substancji organicznej (Improvement of light soils irrigated with sewage as a result of the accumulation of organic matter). Rocz. Glebozn. 1980, 31, 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Licznar, M.; Drozd, J.; Licznar, S.E.; Weber, J.; Bekier, J.; Tyszka, R.; Walenczak, K.; Szadorski, J.; Pora, E. Wpływ wieloletniego stosowania ścieków komunalnych na wybrane właściwości gleb pól irygacyjnych (Influence of Many Years of Municipal Wastewater Use on Selected Soil Properties of Irrigation Fields). Woda-Śr.-Obsz. Wiej. (Water Environ. Rural Areas) 2010, 10, 129–137. Available online: https://www.itp.edu.pl/old/wydawnictwo/woda/zeszyt_31_2010/artykuly/Licznar%20i%20in.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2021).
- Tai, Y.; Li, Z.; Mcbride, M.B. Natural attenuation of toxic metal phytoavailability in 35-year-old sewage sludge-amended soil. Environ Monit Assess 2016, 188, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Wichelns, D.; Raschid-Sally, L.; Mccornick, P.G.; Drechsel, P.; Bahri, A.; Minhas, P.S. The challenges of wastewater irrigation in developing countries. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnaak, W.; Küchler, T.H.; Kujawa, M.; Henschel, K.-P.; Süssenbach, D.; Donau, R. Organic contaminants in sewage sludge and their ecotoxicological significance in the agricultural utilization of sewage sludge. Chemosphere 1997, 35, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, T.; Ge, Y.; Jia, Y. Studies on land application of sewage sludge and its limiting factors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 160, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleiman, M.F.; Al-Suhaibani, N.; El-Hendawy, N.S.; Abdella, K.; Alotaibi, M.; Alderfasi, A. Impacts of Long- and Short-Term of Irrigation with Treated Wastewater and Synthetic Fertilizers on the Growth, Biomass, Heavy Metal Content, and Energy Traits of Three Potential Bioenergy Crops in Arid Regions. Energies 2021, 14, 3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkhair, K.S.; Ashraf, M.A. Field Accumulation Risks of Heavy Metals in Soil and Vegetable Crop Irrigated with Sewage Waterin Western Region of Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, S32–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ociepa-Kubicka, A.; Ociepa, E. Toksyczne oddziaływanie metali ciężkich na rośliny, zwierzęta i ludzi (Toxic effect of heavy metals on plants, animals and people). Inż. Ochr. Śr. 2012, 12, 169–180. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti, C. Residual effects of long-term land application of domestic wastewater. Environ. Int. 1995, 21, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliwal, K.; Karunaichamy, K.S.T.K.; Ananthavalli, M. Effect of sewage water irrigation on growth performance, biomass and nutrient accumulation in hardwickia binate under conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 1998, 66, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, C. Schwermetallmobilität und Risikopotentiale der Rieselfeldböden Berlin Buch. Heft35. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universitat Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Angin, I.; Yaganoglu, A.V.; Turan, M. Effects of Long-Term Wastewater Irrigation on Soil Properties. J. Sustain. Agric. 2005, 26, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedler, E. Water reuse—an integral part of water resources management: Israel as a case study. Water Policy 2001, 3, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozos, E.; Makropoulos, C.; Maksimovic´, Č. Rethinking urban areas: An example of an integrated blue-green approach. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2013, 13, 1534–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.; Gersonius, B.; Kapelan, Z.; Vojinovic, Z.; Sanchez, A. Assessing the Co-Benefits of green-blue-grey infrastructure for sustainable urban flood risk management. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 239, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahern, J.; Cilliers, S.S.; Niemelä, J. The concept of ecosystem services in adaptive urban planning and design: A framework for supporting innovation. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 125, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapetas, L.; Fenner, R. Integrating blue-green and grey infrastructure through an adaptation pathways approach to surface water flooding. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2020, 378, 20190204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y. Wastewater irrigation: Past, present, and future. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2017, 6, e1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Z.-H. Optimizing urban irrigation schemes for the trade-off between energy and water consumption. Energy Build. 2015, 107, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Lin, H.; Niu, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, S.; Fan, L. Effects of irrigation on the ecological services in an intensive agricultural region in China: A trade-off perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 156, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahern, J. Greenways as a Planning Strategy. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1995, 33, 131–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Lang, W.; Tao, X.; Feng, J.; Liu, K. Exploring the Quality of Urban Green Spaces Based on Urban Neighborhood Green Index—A Case Study of Guangzhou City. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahriny, F.; Bell, S. Patterns of Urban Park Use and Their Relationship to Factors of Quality: A Case Study of Tehran, Iran. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolowitz, D.P.; Bell, S.; Keeley, M. Retrofitting urban drainage infrastructure: Green or grey? Urban Water J. 2018, 15, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, M.; Fenner, R. Spatial evaluation of the multiple benefits of sustainable drainage systems. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Water Manag. 2019, 172, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortinovis, C.; Geneletti, D. Ecosystem services in urban plans: What is there, and what is still needed for better decisions. Land Use Policy 2018, 70, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Song, C.; Chen, Y.; Finka, M.; La Rosa, D. Understanding the relationship between urban blue infrastructure and land surface temperature. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright Wendel, H.E.; Zarger, R.K.; Mihelcic, J.R. Accessibility and usability: Green space preferences, perceptions, and barriers in a rapidly urbanizing city in Latin America. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 107, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, R.; Pauleit, S. From Multifunctionality to Multiple Ecosystem Services? A Conceptual Framework for Multifunctionality in Green Infrastructure Planning for Urban Areas. Ambio 2014, 43, 516–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ncube, S.; Spray, C.; Geddes, A. Assessment of changes in ecosystem service delivery–A historical perspective on catchment landscapes. Int. J. Biodivers. Sci. Ecosyst. Serv. Manag. 2018, 14, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulczewska, B.; Giedych, R.; Maksymiuk, G. Can we face the challenge: How to implement a theoretical concept of green infrastructure into planning practice? Warsaw case study. Landsc. Res. 2017, 42, 176–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedźwiecka-Filipiak, I.; Rubaszek, J.; Potyrała, J.; Filipiak, P. The Method of Planning Green Infrastructure System with the Use of Landscape-Functional Units (Method LaFU) and its Implementation in the Wrocław Functional Area (Poland). Sustainability 2019, 11, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaręba, A. Multifunctional and Multiscale Aspects of Green Infrastructure in Contemporary Research (June 11, 2014). Probl. Ekorozw.—Probl. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 9, 149–156. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=2478640 (accessed on 2 January 2021).
- Zaręba, A.D.; Krzemińska, A.E.; Dzikowska, A. Urban Green Network—Synthesis of Environmental, Social and Economic Linkages in Urban Landscape. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 362, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, B.A.; Coutts, A.M.; Livesley, S.J.; Harris, R.J.; Hunter, A.M.; Nicholas, S.G.; Williams, N.S.G. Planning for cooler cities: A framework to prioritize green infrastructure to mitigate high temperatures in urban landscapes. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 134, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, S.T.; Taylor, J.R. Supplying urban ecosystem services through multifunctional green infrastructure in the United States. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 1447–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.B.; Meyers, J.; Beaty, R.M.; Barnett, G.B. Urban green infrastructure impacts on climate regulation services in Sydney, Australia. Sustainability 2016, 8, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, R.; Ferreira, J.C.; Antunes, P. Green Infrastructure Planning Principles: An Integrated Literature Review. Land 2020, 9, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brears, R.C. From Traditional Grey Infrastructure to Blue-Green Infrastructure. In Blue and Green Cities: The Role of Blue-Green Infrastructure in Managing Urban Water Resources; Brears, R.C., Ed.; Palgrave Macmillan UK: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ghofrani, Z.; Sposito, V.; Faggian, R. A comprehensive review of blue-green infrastructure concepts. Int. J. Environ. Sustain. 2017, 6, 15–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpera, E.B.; Dall’erbab, S.; Barkc, R.H.; Scottd, C.H.A.; Yool, S.R. Effects of irrigated parks on outdoor residential water use in a semi-arid city. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 134, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myriounis, C.; Tsirogiannis, I.; Malamos, N.; Barouchas, P.; Babilis, D.; Chalkidis, I. Agricultural and Urban Green Infrastructure Irrigation Systems Auditing—A case study for the Region of Epirus. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2015, 4, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, D.; Henderson, H.; Mazarro, A.D.; Rotbart, D.; Arada, R. Blue-Green Infrastructure (BGI) in Dense Urban Watersheds. The Case of the Medrano Stream Basin (MSB) in Buenos Aires. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bois, P.; Beisel, J.-N.; Heitz, C.; Katinka, L.; Laurent, J.; Pierrette, M.; Walaszek, M.; Wanko, A. Integrated Blue and Green Corridor Restoration in Strasbourg: Green Toads, Citizens, and Long-Term Issues. In Ecological Wisdom Inspired Restoration Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Depietri, Y.; McPhearson, T. Integrating the Grey, Green, and Blue in Cities: Nature-Based Solutions for Climate Change Adaptation and Risk Reduction. In Nature-Based Solutions to Climate Change Adaptation in Urban Areas: Linkages between Science, Policy and Practice; Kabisch, N., Korn, H., Stadler, J., Bonn, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 91–109. [Google Scholar]
- Dushkova, D.; Haase, D. Not Simply Green: Nature-Based Solutions as a Concept and Practical Approach for Sustainability Studies and Planning Agendas in Cities. Land 2020, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuste, J.; Artmann, M.; Li, J.X.; Xie, M.M. Special issue on green infrastructure for urban sustainability. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2015, 141, A2015001-1–A2015001-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, A. “Green Infrastructure” Concept as an Effective Medium to Manipulating Sustainable Urban Development. In Green and Ecological Technologies for Urban Planning: Creating Smart Cities (Volume in “Regional Development: Concepts, Methodologies, Tools and Applications”); Ercoskun, O.Y., Ed.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2011; pp. 234–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermaat, J.E.; Ellers, J.; Helmus, M.R. The role of biodiversity in the provision of ecosystem services. In Ecosystem Services: From Concept to Practice; Bouma, J.A., van Beukering, P.J.H., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 22–39. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Banzhaf, E. Towards a better understanding of Green Infrastructure: A critical review. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 85, 758–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, R.S.; Stuip, M.A.M.; Finlayson, C.M.; Davidson, N. Valuing Wet-Lands: Guidance for Valuing the Benefits Derived from Wetland Ecosystem Services; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2006; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/40110849_Valuing_Wetlands_Guidance_for_Valuing_the_Benefits_Derived_from_Wetland_Ecosystem_Services (accessed on 21 March 2021).
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Ecosystemsand Human Well-Being: Wetlandsand Water Synthesis; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; Available online: https://www.millenniumassessment.org/documents/document.358.aspx.pdf (accessed on 21 March 2021).
- Ramsar Convention Secretariat. The Ramsar Convention Manual: A guide to the Convention on Wetlands (Ramsar, Iran, 1971), 6th ed.; Ramsar Convention Secretariat: Gland, Switzerland, 2013; Available online: https://www.ramsar.org/sites/default/files/documents/library/manual6-2013-e.pdf (accessed on 21 March 2021).
- IPBES. Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services; Brondizio, E.S., Settele, J., Díaz, S., Ngo, H.T., Eds.; IPBES Secretariat: Bonn, Germany, 2019; Available online: https://ipbes.net/global-assessment (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Xu, T.; Weng, B.; Yan, D.; Wang, K.; Li, X.; Bi, W.; Li, M.; Cheng, X.; Liu, Y. Wetlands of International Importance: Status, Threats, and Future Protection. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, N.C. How much wetland has the world lost? Long-term and recent trends in global wetland area. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2014, 65, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šabić, D.; Vujadinović, S.; Stojković, S.; Snežana, D. Urban Development Consequences on the Wetland Ecosystems Transformations—Case Study: Pančevački Rit, Serbia. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2018, 11, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giner, M.E.; Córdova, A.; Vázquez-Gálvez, F.A.; Marruffo, J. Promoting Green Infrastructure in Mexico’s Northern Border: The Border Environment Cooperation Commission’s Experience and Lessons Learned. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 248, 109104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, D.T.; Walsh, T.C.; Burian, S.J. Ecosystem Services from Rainwater Harvesting in India. Urban Water J. 2017, 14, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endreny, T.; Santagata, R.; Perna, A.; De Stefano, C.; Rallo, R.F.; Ulgiati, S. Implementing and Managing Urban Forests: A Much Needed Conservation Strategy to Increase Ecosystem Services and Urban Wellbeing. Ecol. Model. 2017, 360, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhearson, T.; Kremer, P.; Hamstead, Z.A. Mapping Ecosystem Services in New York City: Applying a Social-Ecological Approach in Urban Vacant Land. Ecosyst. Serv. 2013, 5, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perini, K.; Sabbion, P. Green and Blue Infrastructure in Cities. In Urban Sustainability and River Restoration: Green and Blue Infrastructure; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Espinoza, L.; Gortáres-Moroyoqui, P.; Mondaca-Fernández, I.; Meza-Montenegro, M.; Balderas-Cortez, J.; López-Cervantes, J.; Lares-Villa, F. Patógenos emergentes como restricción para el reuso de las aguas residuals municipales tratadas en Ciudad Obregón, Sonora. Rev. Latinoam. Recur. Nat. 2009, 5, 9–21. Available online: https://revista.itson.edu.mx/index.php/rlrn/article/view/148 (accessed on 21 March 2021).
- Ochoa-Noriega, C.A.; Aznar-Sánchez, J.A.; Velasco-Muñoz, J.F.; Álvarez-Bejar, A. The Use of Water in Agriculture in Mexico and Its Sustainable Management: A Bibliometric Review. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twohig-Bennett, C.; Jones, A. The health benefits of the great outdoors: A systematic review and meta-analysis of greenspace exposure and health outcomes. Environ. Res. 2018, 166, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.P.; Alcock, I.; Grellier, J.; Wheeler, B.W.; Hartig, T.; Warber, S.L.; Bone, A.; Depledge, M.H.; Fleming, L.E. Spending at least 120 minutes a week in nature is associated with good health and wellbeing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, D.; Muñoz Meléndez, G.; Arteaga, A.; Ojeda-Revah, L.; Mladenov, N. Greening Urban Areas with Decentralized Wastewater Treatment and Reuse: A Case Study of Ecoparque in Tijuana, Mexico. Water 2022, 14, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valipour, M.; Singh, V.P. Global Experiences on Wastewater Irrigation: Challenges and Prospects. In Balanced Urban Development: Options and Strategies for Liveable Cities; Maheshwari, B., Thoradeniya, B., Singh, V.P., Eds.; Water Science and Technology Library; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Agrawal, M. Potential benefits and risks of land application of sewage sludge. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrafioti, E.; Diamadopoulos, E. A strategic plan for reuse of treated municipal wastewater for crop irrigation on the Island of Crete. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 105, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hamaiedeh, H.; Bino, M. Effect of treated grey water reuse in irrigation on soil and plants. Desalination 2010, 256, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.-J.; Yoon, C.G.; Jung, K.-W.; Ham, J.-H. Estimating the microbial risk of E. coli in reclaimed wastewater irrigation on paddy field. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 129, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, M.S.; Qi, X. Treated Wastewater Irrigation—A Review. Water 2021, 13, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Patel, N.; Gadedjisso-Tossou, A.; Patra, S.; Singh, N.; Singh, P.K. Incidence of Escherichia coli in Vegetable Crops and Soil Profile Drip Irrigated with Primarily Treated Municipal Wastewater in a Semi-Arid Peri Urban Area. Agriculture 2020, 10, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundin, M.; Bengtsson, M.; Molander, S. Life Cycle Assessment of Wastewater Systems: Influence of System Boundaries and Scale on Calculated Environmental Loads. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krzemińska, A.; Zaręba, A.; Adynkiewicz-Piragas, M.; Modelska, M.; Grijalva, F.J.; Monreal, R.; Horst, D.v.d. Sewage Irrigation Fields—From Relict Landscape to Blue-Green Urban Infrastructure. Water 2022, 14, 2505. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162505
Krzemińska A, Zaręba A, Adynkiewicz-Piragas M, Modelska M, Grijalva FJ, Monreal R, Horst Dvd. Sewage Irrigation Fields—From Relict Landscape to Blue-Green Urban Infrastructure. Water. 2022; 14(16):2505. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162505
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrzemińska, Alicja, Anna Zaręba, Mariusz Adynkiewicz-Piragas, Magdalena Modelska, Francisco Javier Grijalva, Rogelio Monreal, and Dan van der Horst. 2022. "Sewage Irrigation Fields—From Relict Landscape to Blue-Green Urban Infrastructure" Water 14, no. 16: 2505. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162505






