The Influence of Precision Dripping Irrigation System on the Phenology and Yield Indices of Sweet Maize Hybrids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
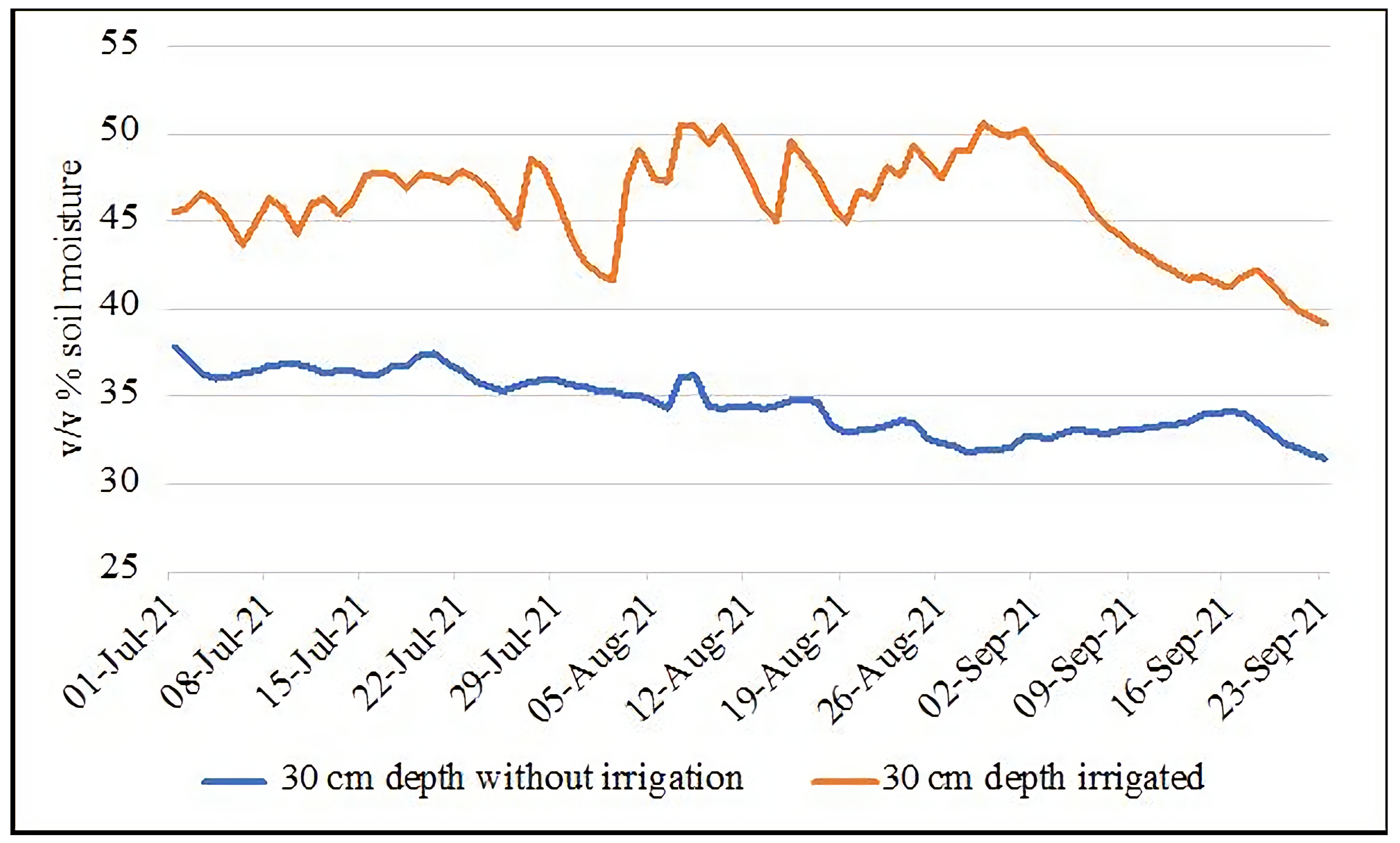
2.2. Irrigation Process
2.2.1. Irrigation Schedule
2.2.2. Analysis of the Irrigation Water
2.3. Determination of the Total Soluble Solids (TSS) of Kernels
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, M.M.; Masiunas, J.B. Functional relationships between giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida) interference and sweet corn yield and ear traits. Weed Sci. 2006, 54, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodossi, S.; Kovács, A.A. koraiság javításának jelentősége és lehetőségei a csemegekukorica termesztésben. Hajtatás Korai Termesztés. 1996, 27, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Gere, A.; Losó, V.; Radványi, D.; Juhász, R.; Kókai, Z.; Sipos, L. Csemegekukorica fajták komplex értékelése. Élelmiszervizsg.Közl. 2013, 59, 120–134. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, M. Relationships among phenotypic traits of sweet corn and tolerance to crowding stress. Field Crops Res. 2016, 185, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sönmez, K.; Özlem, A.L.A.N.; Kinaci, E.; Kinaci, G.; Kutlu, I.; Başçiftçi, Z.; Evrenosoğlu, Y. Bazı şeker mısır çeşitlerinin (Zea mays saccharata Sturt) bitki, koçan ve verim özellikleri. Ziraat Fakültesi Derg. 2013, 8, 28–40. [Google Scholar]
- Merry, R.E. “Dripping with success”: The challenges of an irrigation redevelopment project. Irrig. Drain. J. Int. Comm. Irrig. Drain. 2003, 52, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, G.C.; Paredes, P.; Gonçalves, J.M.; Alves, I.; Pereira, L.S. Comparing sprinkler and drip irrigation systems for full and deficit irrigated maize using multicriteria analysis and simulation modelling: Ranking for water saving vs. farm economic returns. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 126, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmeier, G.; Hofer, K.; Schmidhalter, U. Mid-season prediction of grain yield and protein content of spring barley cultivars using high-throughput spectral sensing. Eur. J. Agron. 2017, 90, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Shi, W.; Zhang, J. An improved water-use efficiency for maize grown under regulated deficit irrigation. Field Crop. Res. 2000, 67, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeskéri, E.; Molnár, K.; Rácz, C.; Dobos, A.C.; Helyes, L. Effect of water supply on spectral traits and their relationship with the productivity of sweet corns. Agronomy. 2019, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, R.; Kosterna-Kelle, E.; Franczuk, J.; Zaniewicz-Bajkowska, A. The influence of weather conditions of eastern Poland on sweet corn yields and length of growing season. J. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 17, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, J. Az optimális víz- és tápanyagellátás hatása a borsó és kukorica növények növekedésére, fejlődésére és termésmennyiségére. Doctoral Dissertation, DATE, Debrecen, Hungary, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Viswanatha, G.B.; Ramachandrappa, B.K.; Nanjappa, H.V. Soil–plant water status and yield of sweet corn (Zea mays L. cv. Saccharata) as influenced by drip irrigation and planting methods. Agric. Water Manag. 2002, 55, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktem, A. Effects of deficit irrigation on some yield characteristics of sweet corn. Bangladesh J. Bot. 2008, 37, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dağdelen, N.; Yılmaz, E.; Sezgin, F.; Gürbüz, T. Water-yield relation and water use efficiency of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) and second crop corn (Zea mays L.) in western Turkey. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 82, 63–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motazedian, A.; Kazemeini, S.A.; Bahrani, M.J. Sweet corn growth and GrainYield as influenced by irrigation and wheat residue management. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 224, 105748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, S.G. The effect of water deficit stress and nitrogen fertilizer levels on morphology traits, yield and leaf area index in maize. Pak. J. Bot. 2012, 44, 1351–1355. [Google Scholar]
- Kazemeini, S.A.; Bahrani, M.J.; Pirasteh-Anosheh, H.; Momeni, S.M.M. Maize growth and yield as affected by wheat residues and irrigation management in a no-tillage system. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2014, 60, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydinsakir, K.; Erdal, S.; Buyuktas, D.; Bastug, R.; Toker, R. The influence of regular deficit irrigation applications on water use, yield, and quality components of two corn (Zea mays L.) genotypes. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 128, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiani, P.; Saleh, G.; Osman, M.; Habibi, D. Sweet corn yield response to alternate furrow irrigation methods under different planting densities in a semi-arid climatic condition. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2011, 6, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera-Hernández, B.; Carrillo-Ávila, E.; Obrador-Olán, J.J.; Juárez-López, J.F.; Aceves-Navarro, L.A. Morphological quality of sweet corn (Zea mays L.) ears as response to soil moisture tension and phosphate fertilization in Campeche, Mexico. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazar, A.; Howell, T.A.; Dusek, D.A.; Copeland, K.S. Evaluation of crop water stress index for LEPA irrigated corn. Irrig. Sci. 1999, 18, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.B.; Patel, V.J.; Patel, J.R. Influence of different methods of irrigation and nitrogen levels on crop growth rate and yield of maize (Zea mays L.). Indian J. Crop Sci. 2006, 1, 175–177. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, R.K.; Maranville, J.W.; Admou, A. Deficit irrigation and nitrogen effects on maize in a Sahelian environment: I. Grain yield and yield components. Agric. Water Manag. 2000, 46, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertek, A.; Kara, B.U.R.H.A.N. Yield and quality of sweet corn under deficit irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 129, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadkhani, N.; Heidari, R. Drought-induced accumulation of soluble sugars and proline in two maize varieties. World Appl. Sci. J. 2008, 3, 448–453. [Google Scholar]
- Dickert, T.E.; Tracy, W.F. Irrigation and sugar in sweet corn. Wis. Crop Manag. Conf. 2001. Available online: http://www.soils.wisc.edu/extension/FAPM/2001.php (accessed on 23 February 2022).
- Karam, F.; Breidy, J.; Stephan, C.; Rouphael, J. Evapotranspiration, yield and water use efficiency of drip irrigated corn in the Bekaa Valley of Lebanon. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 63, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhumed, M.A.; Jusop, S.; Sung, C.T.B.; Wahab, P.E.M.; Panhwar, Q.A. Effects of drip irrigation frequency, fertilizer sources and their interaction on the dry matter and yield components of sweet corn. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2014, 8, 223–231. [Google Scholar]
- Farsiani, A.; Ghobadi, M.E.; Jalali-Honarm, S. The effect of water deficit and sowing date on yield components and seed sugar contents of sweet corn (Zea mays L.). Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2011, 6, 5769–5774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, G.M.B.; Pereira, M.G.; Ferreira Júnior, J.A.; Schwantes, I.A.; Durães, N.N.L.; Crevelari, J.A.; Amaral Junior, A.T.D. Development and selection of super-sweet corn genotypes (sh2) through multivariate approaches. Bragantia 2018, 77, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water quality for agriculture Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Irrig. Drain. Pap. 1985, 29, 174. [Google Scholar]
- Zsembeli, J.; Szűcs, L. Environmental friendly irrigation of vegetables with high salt content water. Acta Agrar. Debr. 2014, 61, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsembeli, J.; Czellér, K.; Tuba, G.; Szücs, L.; Sinka, L. Effect of Irrigation with Saline Water on the Soil and Legumes in Simple Drainage Lysimeter. In Brigitte, Marold (szerk.) 17. Gumpensteiner Lysimetertagung: Lysimeterforschung-Möglichtkeiten und Grenzen Lysimeter Research—Options and Limits; Raumberg-Gumpenstein, Höhere Bundeslehr- und Forschungsanstalt für Landwirtschaft Raumberg-Gumpenstein (HBLFA): Irdning, Ausztria, 2017; pp. 189–191. [Google Scholar]
- Zsembeli, J.; Sinka, L.; Rivera-García, A.; Czellér, K.; Tuba, G.; Krištof, K.; Findura, P. Effect of soil conditioning on the moisture content and the salt profile of the soil under irrigation with saline water. Agriculture 2019, 65, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FILEP, G. Az öntözővizek minősége és minősítése. Agrokémia És Talajt. 1999, 48, 49–66. [Google Scholar]
- Terbe, I.; Hodossi, S.; Kovács, A.; Glits, M. Zöldségtermesztés termesztőberendezésekben. Mezőgazda 2005, 211. [Google Scholar]
- ATAGO. Available online: https://www.atago.net/en/products-pal-top.php (accessed on 23 February 2022).
- Illes, A.; Bojtor, C.; Szeles, A.; Mousavi, S.M.N.; Toth, B.; Nagy, J. Analysing the effect of intensive and low-input agrotechnical support for the physiological, phenometric, and yield parameters of different maize hybrids using multivariate statistical methods. Int. J. Agron. 2021, 2021, 6682573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodadad, M.; Morteza, F.; Seyed, M.N.M. Effect of drought stress on yield and yield components of maize hybrids. Sci. Res. Essays. 2013, 8, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi, S.M.N.; Bojtor, C.; Illés, Á.; Nagy, J. Genotype by Trait Interaction (GT) in Maize Hybrids on Complete Fertilizer. Plants 2021, 10, 2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei, S.H.; Mostafavi, K.; Omrani, A.; Omrani, S.; Nasir Mousavi, S.M.; Illés, Á.; Bojtor, C.; Nagy, J. Yield stability analysis of maize (Zea mays L.) hybrids using parametric and ammi methods. Scientifica 2021, 2021, 5576691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, K.; Shiri, M.R.; Kazemi Azar, F. The effect of water in drip irrigation and planting on corn yield. J. Water Agric. 2014, 28, 97–105. [Google Scholar]
- Tagheian Aghdam, E.; Hashemi, S.R.; Khashei, A.; Shahidi, A. Effect of various irrigation treatments on qualitative and quantitative characteristics of sweet corn. International. Res. J. Appl. Basic Sci. 2014, 8, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar]
- Siadat, S.A.A.; Karmalachab, A.; Monjzi, H.; Fathi Gh., A.; Hamdi, H. The effect of filter cake on morphological traits and yield of sweet corn under drought stress. J. Crop Prod. Process. 2015, 5, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, F.H.; Sadras, V.O.; Vega, C.R.C.; Echarte, L. Physiological determinant crop growth and yield in maize, sunflower and soybean: Their application to crop management, modeling and breeding. J. Crop Improv. 2015, 14, 51–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noein, B.; Soleymani, A. Corn (Zea mays L.) physiology and yield affected by plant growth regulators under drought stress. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2022, 41, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.N.; Illés, Á.; Bojtor, C.; Nagy, J. The impact of different nutritional treatments on maize hybrids morphological traits based on stability statistical methods. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2020, 11, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalamian, S.; Modares, S.S.; Sepehri, A. Effect of water deficit at vegetative and reproductive growth stages in leafy and commercial hybrids of maize. Agric. Res. 2006, 5, 38–53. [Google Scholar]
- Clarck, W.M.; Wissman, S.; Albers, G.W.; Jhamandas, J.H.; Madden, K.P.; Hamilton, S. Recombinant tissue-typ plasminogen activator (alteplase) for ischemic stroke 3 to 5 hours after symptom onset. JAMA 1999, 282, 2019–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazian Tafrishi, S.; Ayenehband, A.; Tavakoli, H.; Khavari Khorasani, S.; Joleini, M. Effect of limited irrigation on yield and yield component of several sweet corn (Zea mays L. var Saccharata) Varieties. Iran. J. Field Crops Res. 2013, 11, 171–178. [Google Scholar]
- Hammad, H.M.; Ahmad, A.; Azhar, F.; Khaliq, T.; Wajid, A.; Nasim, W.; Farhad, W. Optimizing water and nitrogen requirement in maize (Zea mays L.) under semi arid conditions of Pakistan. Pak. J. Bot. 2011, 43, 2919–2923. [Google Scholar]
- Khalili, M.; Naghavi, M.R.; Aboughadareh, A.P.; Rad, H.N. Effects of drought stress on yield and yield components in maize cultivars (Zea mays L.). Int. J. Agron. Plant Prod. 2013, 4, 809–812. [Google Scholar]
| pH | EC | TDS | SAR | Na% | Mg% | HCO3− | Cl− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| µS cm−1 | mg L−1 | % | % | mgmol L−1 | mgmol L−1 | ||
| 7.42 | 0.51 | 326.40 | 0.67 | 18.30 | 30.34 | 3.67 | 0.10 |
| Source | DF | F-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ear length | Irrigation | 1 | 45.12 | 0.000 |
| Hybrid | 6 | 5.96 | 0.000 | |
| Irrigation x Hybrid | 6 | 3.52 | 0.007 | |
| Net ear length (covered with kernels) | Irrigation | 1 | 10.35 | 0.002 |
| Hybrid | 6 | 3.37 | 0.008 | |
| Irrigation x Hybrid | 6 | 2.72 | 0.026 | |
| Ear weight | Irrigation | 1 | 48.69 | 0.000 |
| Hybrid | 6 | 4.93 | 0.001 | |
| Irrigation x Hybrid | 6 | 3.42 | 0.008 | |
| Number of kernel rows | Irrigation | 1 | 1.23 | 0.273 |
| Hybrid | 6 | 7.20 | 0.000 | |
| Irrigation x Hybrid | 6 | 3.52 | 0.007 | |
| Brix/Atago Pal-1 | Irrigation | 1 | 16.96 | 0.000 |
| Hybrid | 6 | 5.64 | 0.000 | |
| Irrigation x Hybrid | 6 | 4.45 | 0.001 | |
| Brix/Abbe | Irrigation | 1 | 12.53 | 0.001 |
| Hybrid | 6 | 3.19 | 0.011 | |
| Irrigation x Hybrid | 6 | 3.90 | 0.003 | |
| MC | Irrigation | 1 | 11.19 | 0.002 |
| Hybrid | 6 | 28.47 | 0.000 | |
| Irrigation x Hybrid | 6 | 4.73 | 0.001 | |
| DMC | Irrigation | 1 | 1.42 | 0.239 |
| Hybrid | 6 | 114.45 | 0.000 | |
| Irrigation x Hybrid | 6 | 3.65 | 0.001 |
| LC | LCL | WC | NSR | Brix/Atago Pal-1 | Brix/Abbe | M | DM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCL | 0.635 * | |||||||
| WC | 0.470 | 0.409 | ||||||
| NSR | 0.220 | 0.217 | 0.415 | |||||
| Brix/Atago Pal-1 | −0.039 | −0.103 | 0.461 | 0.103 | ||||
| Brix/Abbe | −0.001 | −0.100 | 0.434 | 0.096 | 0.978 ** | |||
| M | −0.483 | −0.186 | 0.086 | −0.066 | 0.254 | 0.238 | ||
| DM | −0.493 | −0.252 | 0.271 | 0.027 | 0.469 | 0.422 | −0.897 ** | |
| MC | −0.450 | −0.149 | 0.006 | −0.100 | 0.153 | 0.150 | 0.984 ** | −0.803 ** |
| Source | df | SS | MS | F | % | F_prob |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 503 | 6052 | 12.03 | * | * | |
| Treatments | 62 | 5797 | 93.51 | 153.80 | 0.00000 | |
| Genotypes | 6 | 58 | 9.61 | 15.81 | 0.00000 | |
| Irrigation | 8 | 5647 | 705.84 | 6844.64 | 0.00000 | |
| Block | 27 | 3 | 0.10 | 0.17 | 1.00000 | |
| Interactions | 48 | 93 | 1.94 | 3.19 | 0.00000 | |
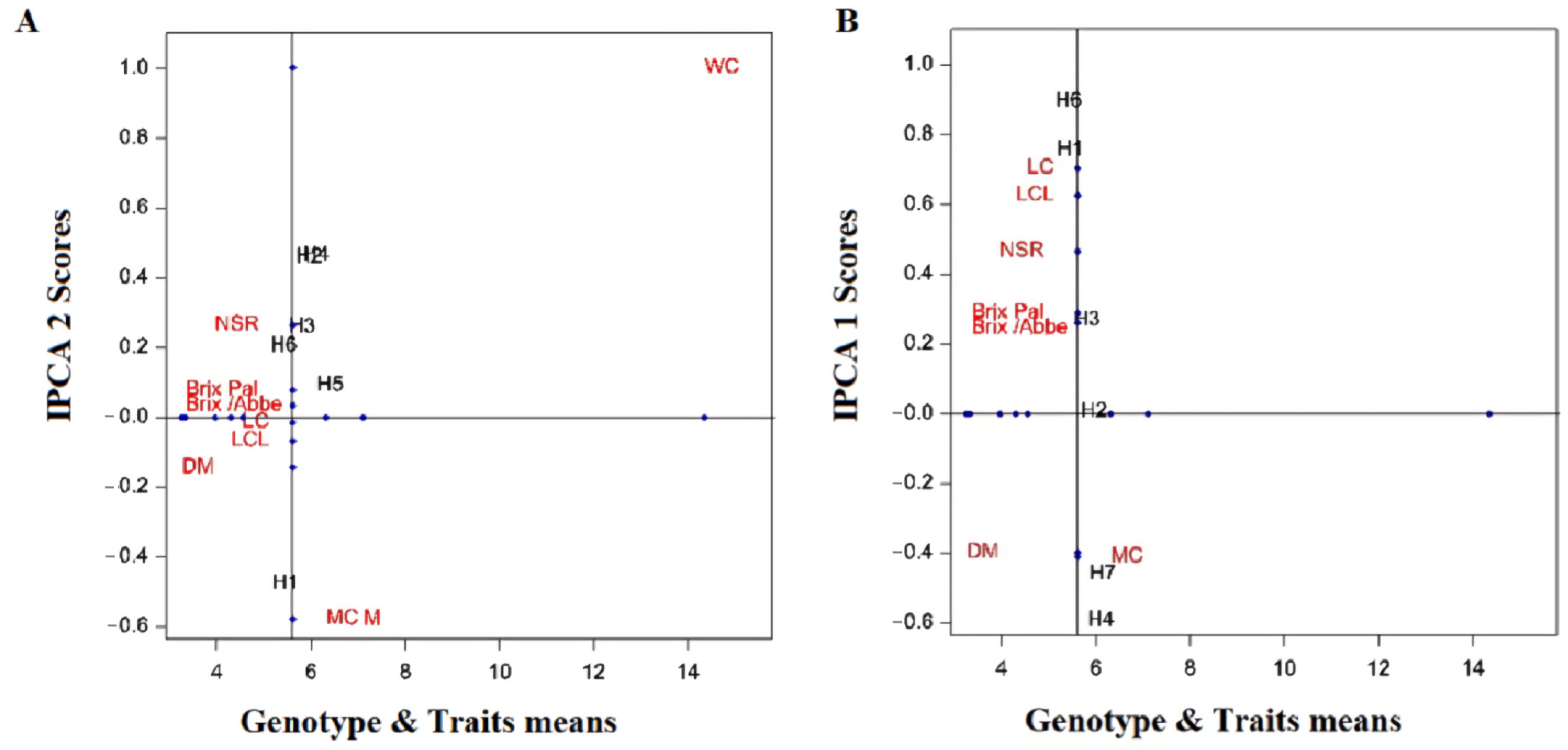
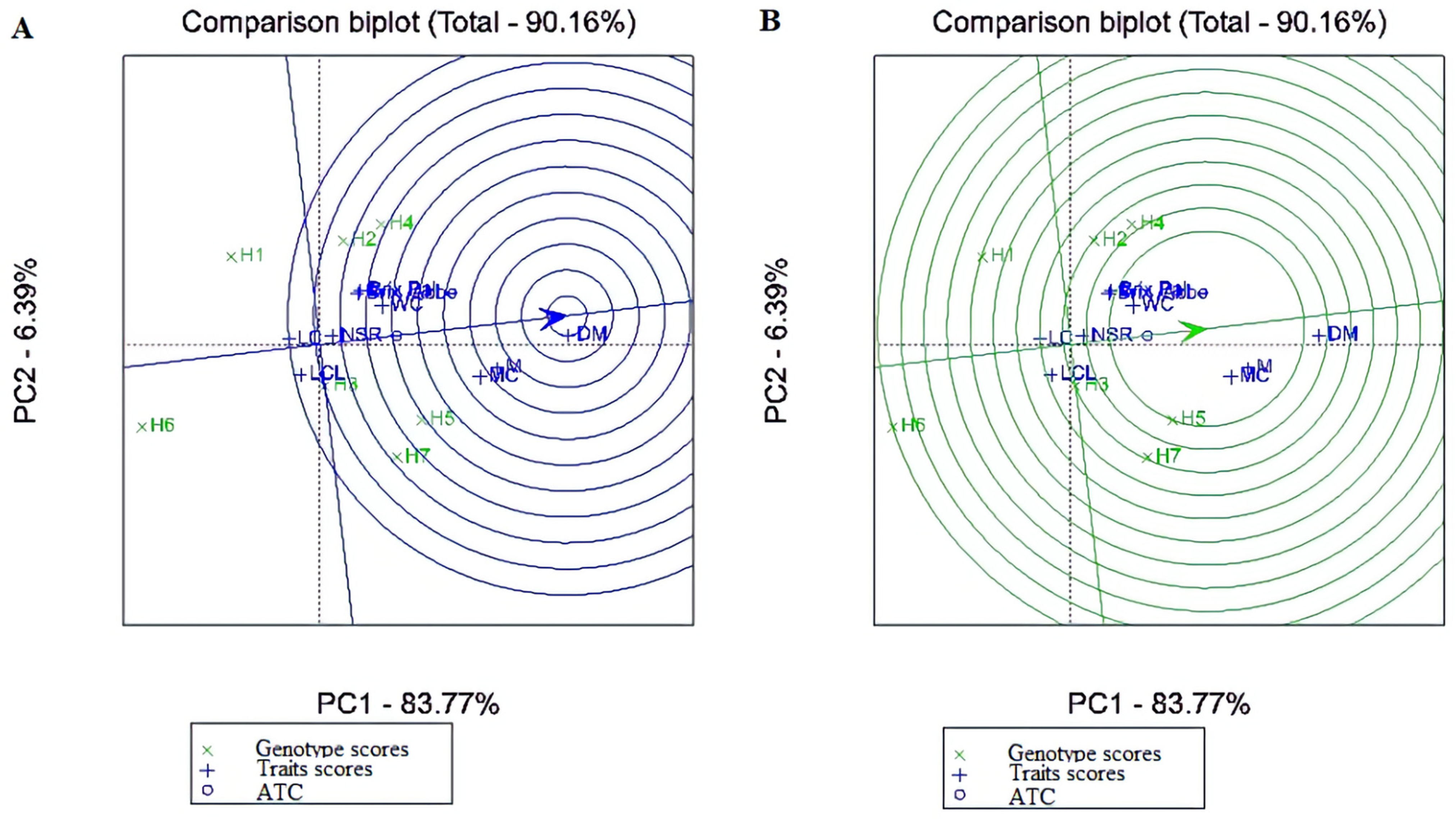
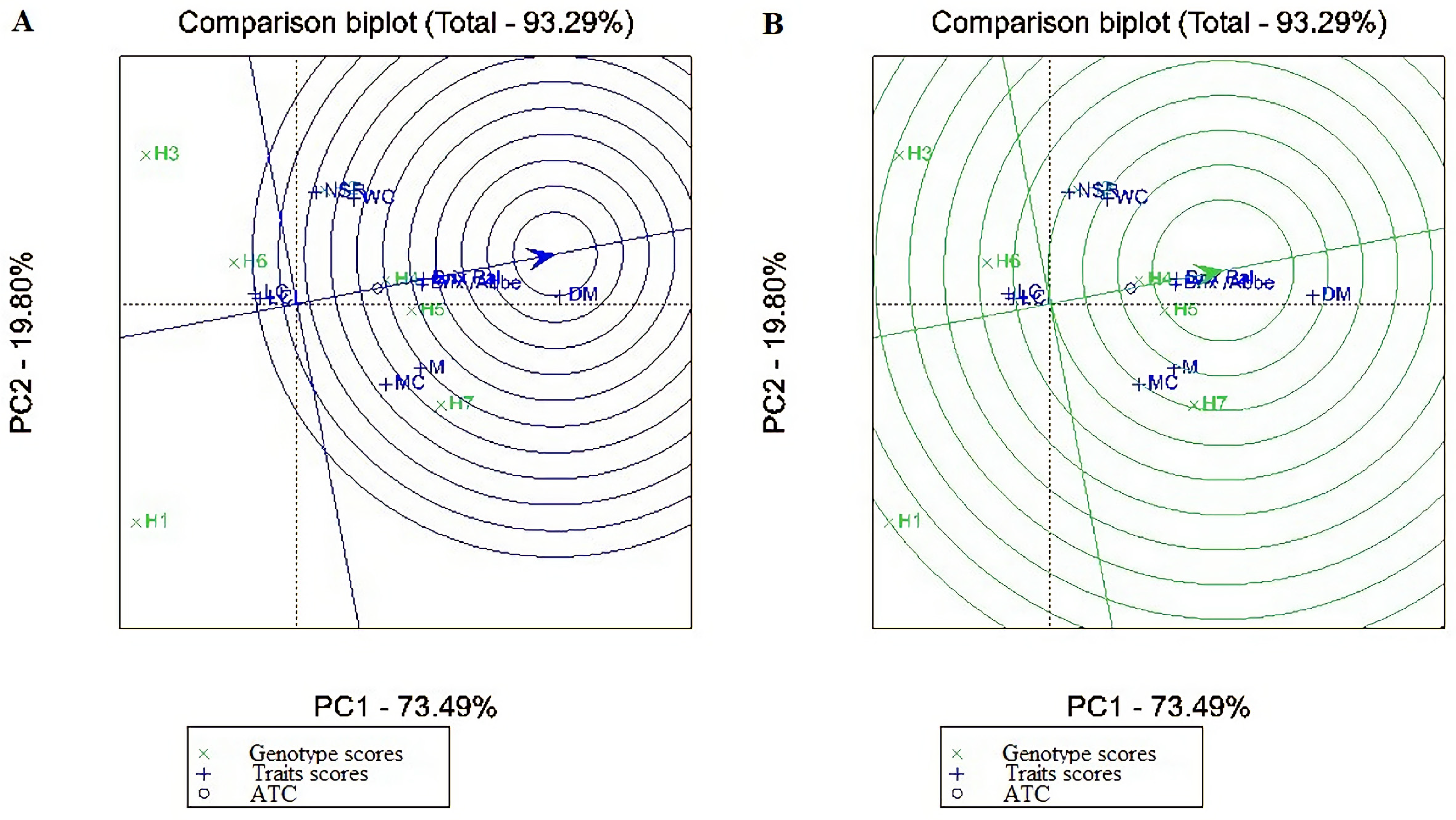
| IPCA1 | 13 | 61 | 4.73 | 7.77 | 65.60 | 0.00000 |
| IPCA2 | 11 | 25 | 2.29 | 3.77 | 26.88 | 0.00004 |
| Residuals | 24 | 6 | 0.27 | 0.44 | 0.99138 | |
| Error | 414 | 252 | 0.61 | * | * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Illés, Á.; Szabó, A.; Mousavi, S.M.N.; Bojtor, C.; Vad, A.; Harsányi, E.; Sinka, L. The Influence of Precision Dripping Irrigation System on the Phenology and Yield Indices of Sweet Maize Hybrids. Water 2022, 14, 2480. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162480
Illés Á, Szabó A, Mousavi SMN, Bojtor C, Vad A, Harsányi E, Sinka L. The Influence of Precision Dripping Irrigation System on the Phenology and Yield Indices of Sweet Maize Hybrids. Water. 2022; 14(16):2480. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162480
Chicago/Turabian StyleIllés, Árpád, Atala Szabó, Seyed Mohammad Nasir Mousavi, Csaba Bojtor, Attila Vad, Endre Harsányi, and Lúcia Sinka. 2022. "The Influence of Precision Dripping Irrigation System on the Phenology and Yield Indices of Sweet Maize Hybrids" Water 14, no. 16: 2480. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162480









