Assessment of Diffuse Pollution Loads in Peri-Urban Rivers—Analysis of the Accuracy of Estimation Based on Monthly Monitoring Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
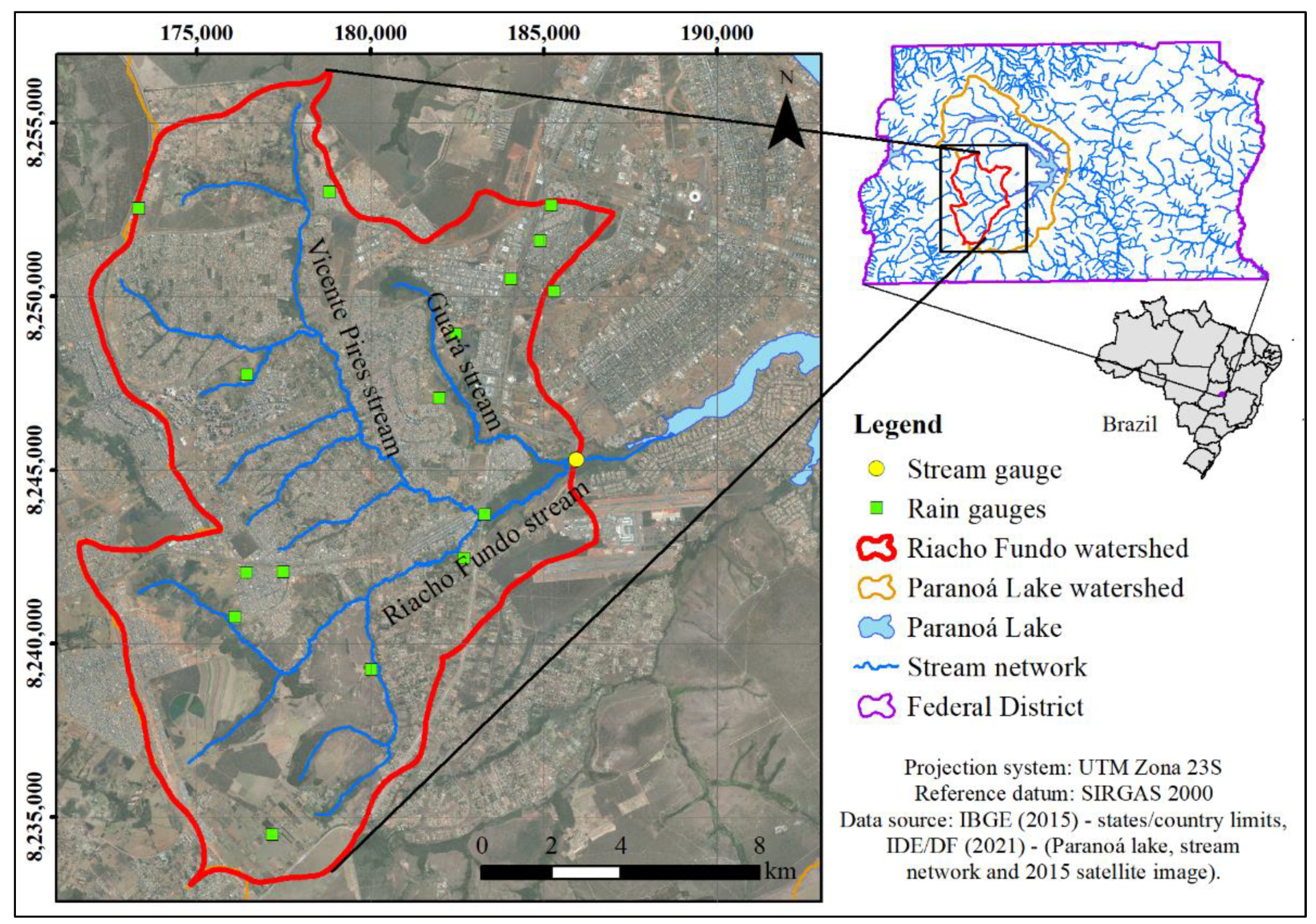
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Diffuse Pollution Monitoring
2.3. Water Quality Assessment
2.4. Comparison of Methodologies for Estimating Long-Term Pollutant Loads
3. Results and Discussion
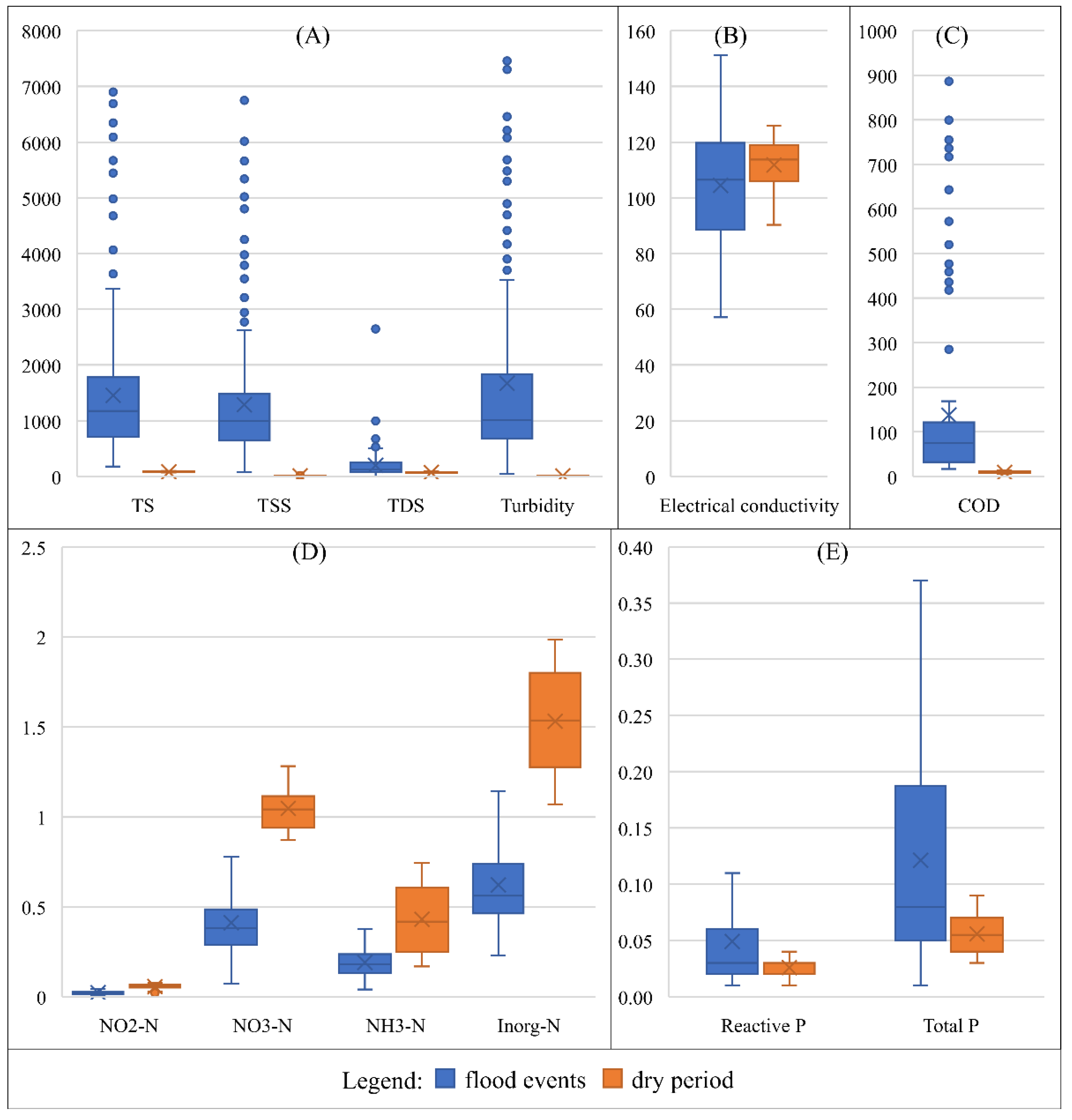
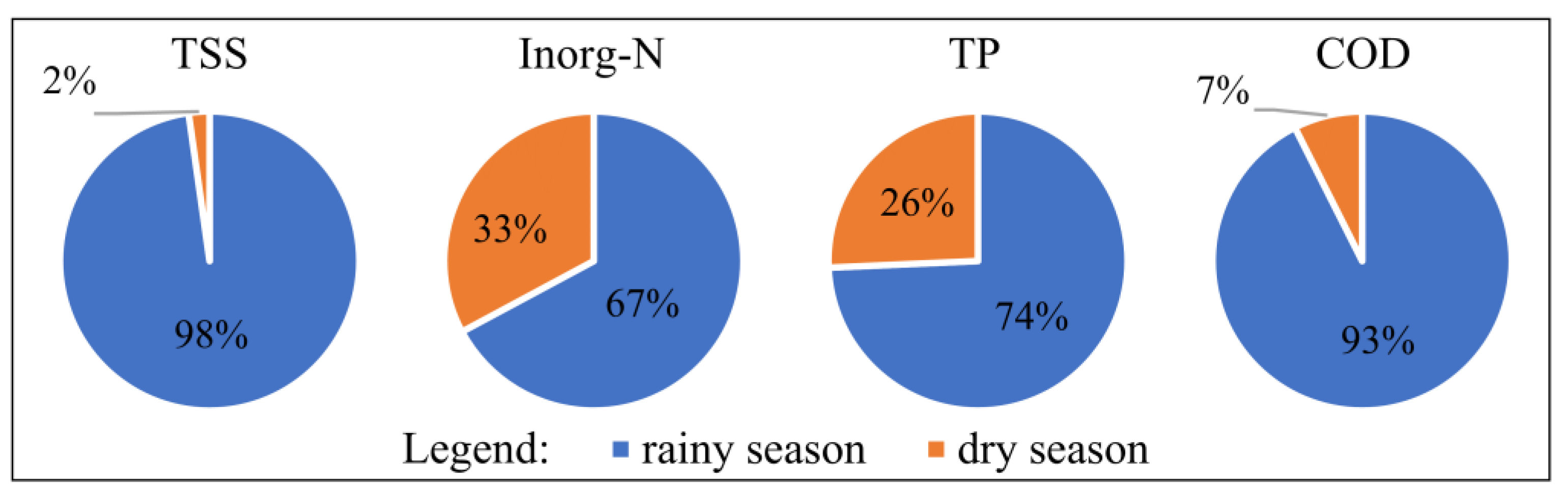
3.1. Collected Data and the Effects of Diffuse Pollution on Water Quality
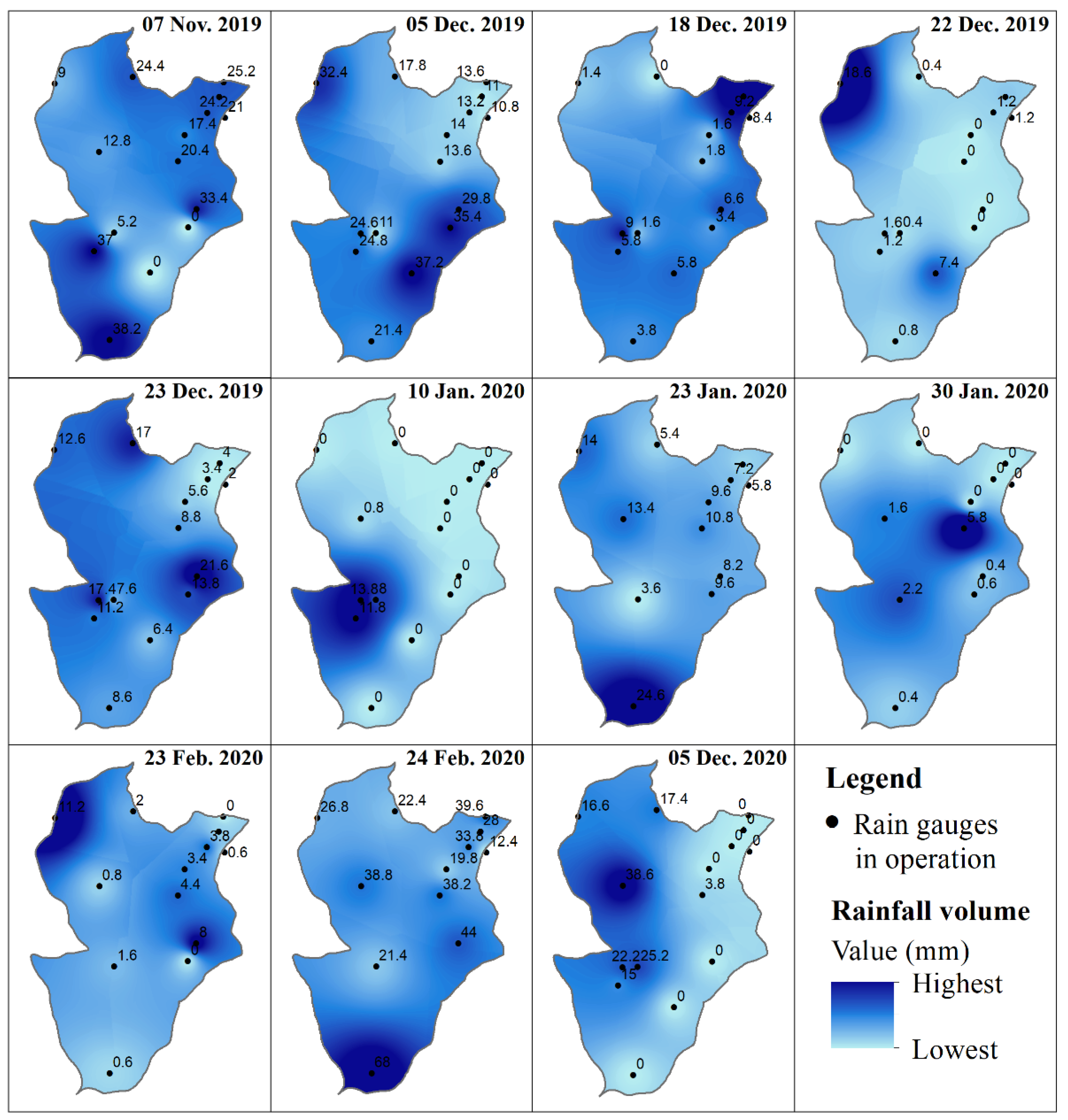
3.2. Water Quality Correlation with Hydrological Characteristics and Rainfall Spatial Distribution
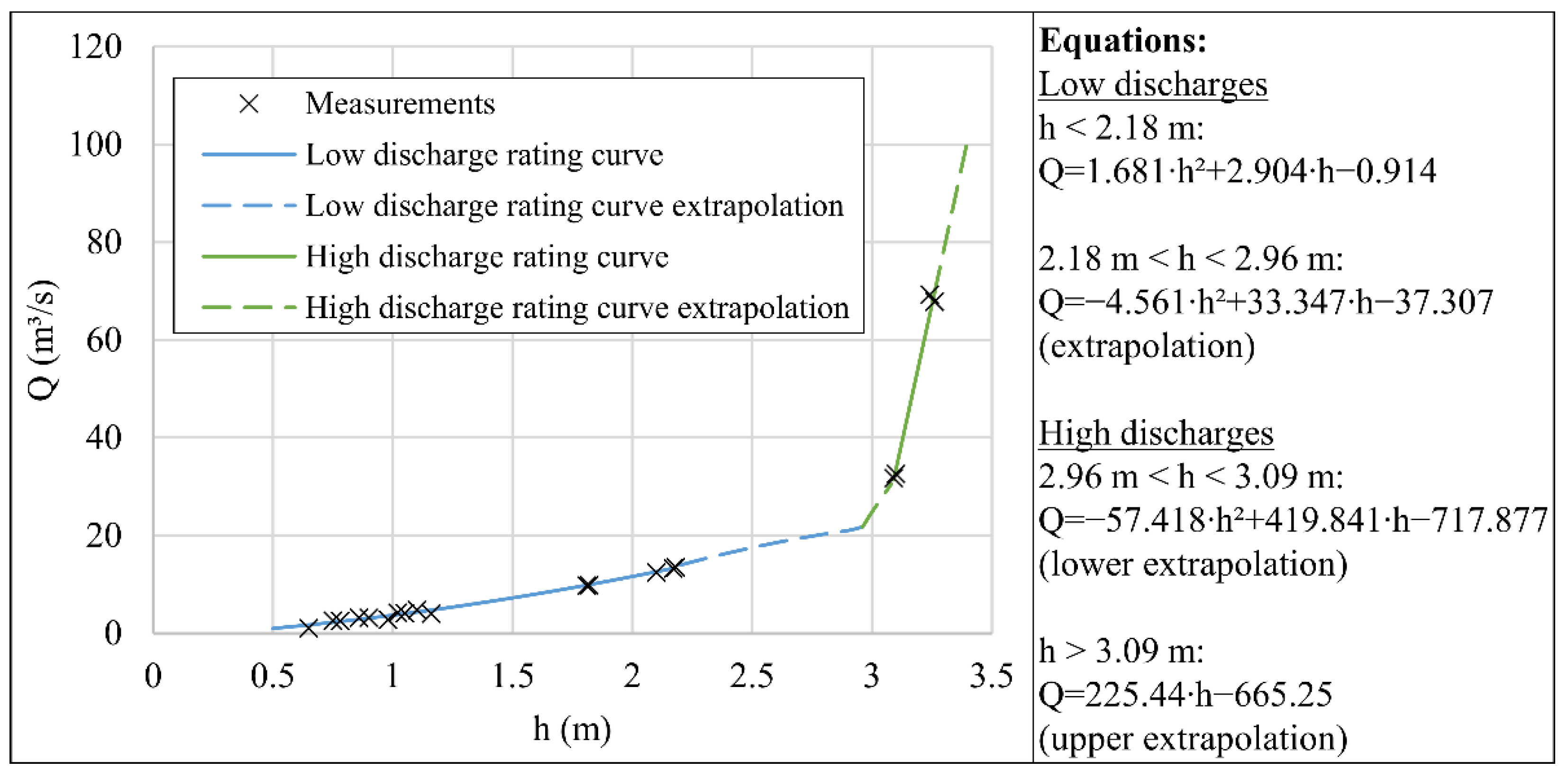
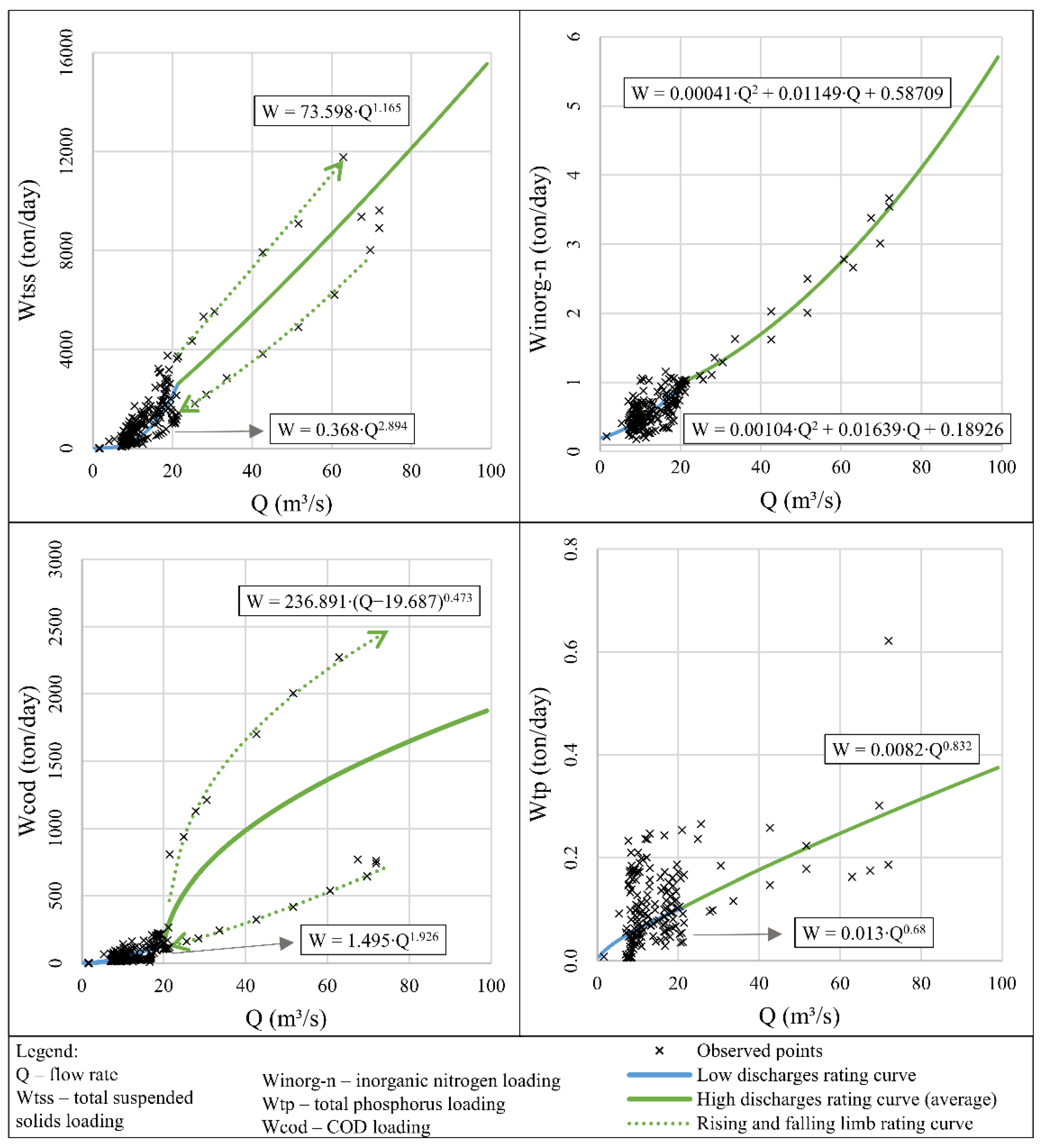
3.3. Pollutant Rating Curves
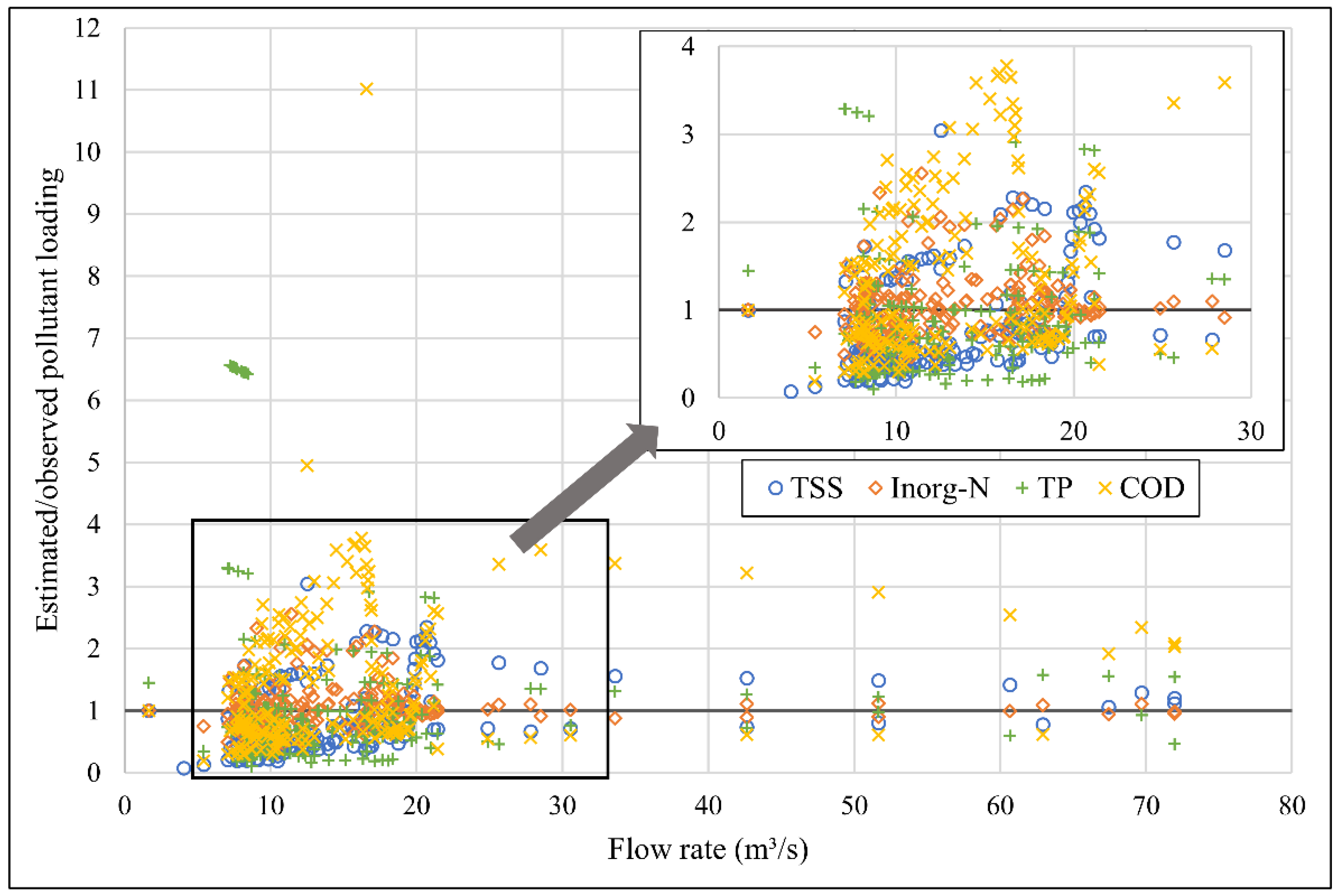
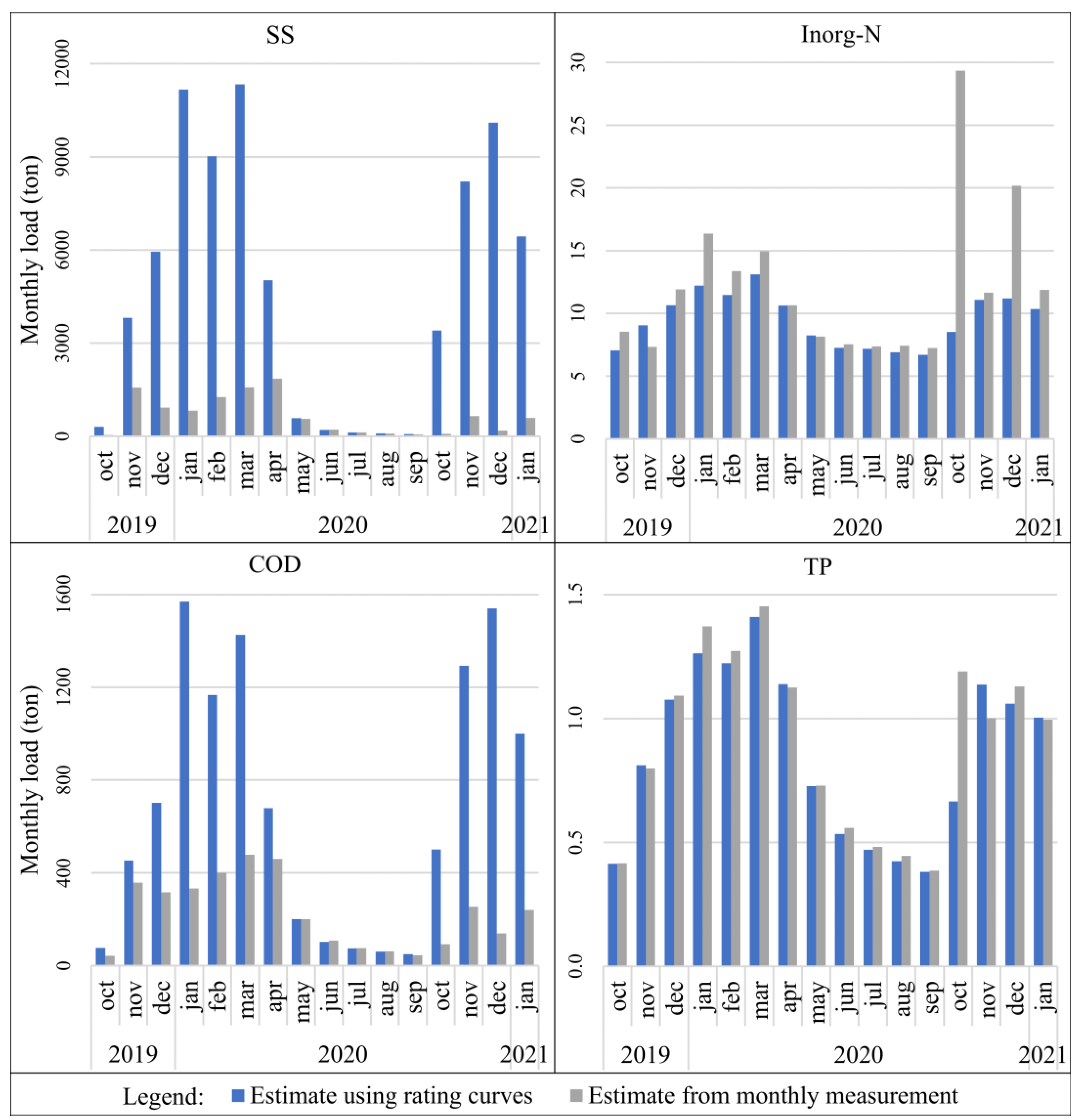
3.4. Estimation of Monthly Pollutant Loads
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yazdanfar, Z.; Sharma, A. Urban drainage system planning and design—Challenges with climate change and urbanization: A review. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 72, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S. Water Challenges of an Urbanizing World. In Management of Cities and Regions; Bobek, V., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017; pp. 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novotny, V.; Goodrich-Mahoney, J. Comparative assessment of pollution loadings from non-point sources in urban land use. Prog. Water Technol. 1978, 10, 775–785. [Google Scholar]
- Goonetilleke, A.; Thomas, E.; Ginn, S.; Gilbert, D. Understanding the role of land use in urban stormwater quality management. J. Environ. Manag. 2005, 74, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Novotny, V. The next step—Incorporating diffuse pollution abatement into watershed management. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 51, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinelt, L.E.; Horner, R.R.; Castensson, R. Non-point source water pollution management: Improving decision-making information through water quality monitoring. J. Environ. Manag. 1992, 34, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrier, R.C.; D’Arcy, B.J.; MacDonald, J.; Aitken, M. Diffuse pollution—What is the nature of the problem? Water Environ. J. 2005, 19, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meals, D.W.; Richards, R.P.; Dressing, S.A. Pollutant Load Estimation for Water Quality Monitoring Projects; Tech Notes 8, Developed for U.S. Environmental Protection Agency; Tetra Tech, Inc.: Fairfax, VA, USA, 2013. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/polluted-runoff-nonpoint-source-pollution/nonpoint-source-monitoring-technical-notes (accessed on 11 May 2022).
- Yazdi, M.N.; Sample, D.J.; Scott, D.; Wang, X.; Ketabchy, M. The effects of land use characteristics on urban stormwater quality and watershed pollutant loads. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righetto, A.M.; Gomes, K.M.; Freitas, F.R.S. Poluição difusa nas águas pluviais de uma bacia de drenagem urbana. Eng. Sanit. E Ambient. 2017, 22, 1109–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsuji, T.M.; Costa, M.E.L.; Koide, S. Diffuse pollution monitoring and modelling of small urban watershed in Brazil Cerrado. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 79, 1912–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brites, A.P.Z.; Gastaldini, M.d.C.C. Avaliação da Carga Poluente no Sistema de Drenagem de Duas Bacias Hidrográficas Urbanas. Rev. Bras. Recur. Hídricos 2007, 12, 211–221. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, P.C.; Seidl, M.; Nascimento, N.O.; Sperling, M.V. Avaliação de Fluxo de poluentes em Tempo seco e Durante Eventos de Chuva em uma Microbacia Urbanizada no Município de belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais. In Manejo de águas pluviais urbanas; Righetto, A.M., Ed.; ABES: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2009; pp. 346–366. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Dai, Y.; Zhi, X.; Xie, H.; Shen, Z. Quantifying nonpoint source emissions and their water quality responses in a complex catchment: A case study of a typical urban-rural mixed catchment. J. Hydrol. 2018, 559, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, C.; Fernandes, C.V.S.; Braga, S.M.; Prado, L.L.; Froehner, S.; Hilgert, S. Water quality dynamic during rainfall episodes: Integrated approach to assess diffuse pollution using automatic sampling. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, H.; Shen, B.; Li, Y. Effect of non-point source pollution on water quality of the Weihe River. Int. J. Sediment. Res. 2011, 26, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, R.; Bonifácio, C.M.; de Freitas, F.H.; Schneider, R.M.; Tavares, C.R.G. Formas nitrogenadas e fósforo total em cursos d’água: Estudo de caso do ribeirão Maringá, Estado do Paraná. Acta Sci. Technol. 2013, 35, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girardi, R.; Pinheiro, A.; Garbossa, L.H.P.; Torres, E. Water quality change of rivers during rainy events in a watershed with different land uses in Southern Brazil. Rev. Bras. Recur. Hídricos 2016, 21, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medeiros, W.M.V.; Silva, C.E.; Lins, R.P.M. Avaliação sazonal e espacial da qualidade das águas superficiais da bacia hidrográfica do rio Longá, Piauí, Brasil. Rev. Ambient. Água 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, M.E.L.; Koide, S.; Carvalho, D.J.; Garnier, J. Qualidade das águas urbanas no córrego Vicente Pires—Distrito Federal. Rev. Eletrônica De Gestão E Tecnol. Ambient. (GESTA) 2021, 9, 47–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donigian, A.S.; Huber, W.C. Modeling of Non Point Sources Water Quality in Urban and Non-Urban Areas; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Technical Report; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1991. Available online: https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyPURL.cgi?Dockey=30000OTC.txt%0A (accessed on 11 May 2022).
- Lin, J.P. Review of Published Export Coefficient and Event Mean Concentration (EMC); Technical Note; Wetlands Regulatory Assistance Program; U.S. Army Engineer Research and Development Center: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 2004. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/11681/3547 (accessed on 11 May 2022).
- Richards, R.P. Estimation of Pollutant Loads in Rivers and Streams: A Guidance Document for NPS Programs; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Tiffin, OH, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Vaze, J.; Chiew, F.H.S. Comparative evaluation of urban storm water quality models. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsihrintzis, V.A.; Hamid, R. Modeling and management of urban stormwater runoff quality: A review. Water Resour. Manag. 1997, 11, 136–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, D.K.; Bera, M. Watershed-Scale Hydrologic and Nonpoint-Source Pollution Models: Review of Applications. Trans. ASAE 2013, 47, 789–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, Y.S.; Engel, B.A. Use of Pollutant Load Regression Models with Various Sampling Frequencies for Annual Load Estimation. Water 2014, 6, 1685–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crawford, C.G. Estimation of suspended-sediment rating curves and mean suspended-sediment loads. J. Hydrol. 1991, 129, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapong, E.; Fujihara, M.; Izumi, T.; Kobayashi, N.; Kakihara, T. Suspended Load Estimation in Rivers in Agricultural Areas Using Regression Analyses with Data Stratification. J. Water Environ. Technol. 2012, 10, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stenback, G.A.; Crumpton, W.G.; Schilling, K.E.; Helmers, M.J. Rating curve estimation of nutrient loads in Iowa rivers. J. Hydrol. 2011, 396, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, J.; Chiwa, M.; Higashi, N.; Maruno, R.; Mori, Y.; Otsuki, K.; Mori, Y. Determining storm sampling requirements for improving precision of annual load estimates of nutrients from a small forested watershed. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 4747–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, A.J. Determining annual suspended sediment and sediment-associated trace element and nutrient fluxes. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 400, 315–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellerin, B.A.; Bergamaschi, B.A.; Gilliom, R.J.; Crawford, C.G.; Saraceno, J.; Frederick, C.P.; Murphy, J.C. Mississippi River Nitrate Loads from High Frequency Sensor Measurements and Regression-Based Load Estimation Terms of Use. Environ. Sci. Technol 2014, 48, 12612–12619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, A. Simulação da eutrofização do Lago Paranoá. Revista DAE 1985, 45, 386–389. [Google Scholar]
- Menezes, P.H.B.J. Avaliação do efeito das ações antrópicas no Processo de Escoamento Superficial e Assoreamento na bacia do Lago Paranoá. Master’s Thesis, University of Brasília, Brasília, Brazil, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Franz, C.; Makeschin, F.; Weiß, H.; Lorz, C. Sediments in urban river basins: Identification of sediment sources within the Lago Paranoá catchment, Brasilia DF, Brazil—Using the fingerprint approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 466–467, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, E.S. Qualidade dos Sedimentos e Análise Multi-temporal do Assoreamento do Lago Paranoá—DF. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Brasília, Brasília, Brazil, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, G. Aplicação do Modelo SWAT no Estudo Hidrológico e de Qualidade da água da Bacia do lago Paranoá—DF. Master’s Thesis, University of Brasília, Brasília, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, G.; Minoti, R.T.; Koide, S. Mathematical Modeling of Watersheds as a Subsidy for Reservoir Water Balance Determination: The Case of Paranoá Lake, Federal District, Brazil. Hydrology 2020, 7, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paula, A.C.V. Estudo Experimental e Modelagem da Lagoa de Detenção do Guará-DF: Comportamento no Amortecimento de Cheias e na Alteração da Qualidade da água. Master’s Thesis, University of Brasília, Brasília, Brazil, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, M.E.L.; Carvalho, D.J.; Koide, S. Assessment of Pollutants from Diffuse Pollution through the Correlation between Rainfall and Runoff Characteristics Using EMC and First Flush Analysis. Water 2021, 13, 2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Nacional de Meteorologia (INMET). 2021. Normais Climatológicas. Available online: https://portal.inmet.gov.br/servicos/normais-climatológicas (accessed on 11 May 2022).
- Ribeiro, J.F.; Walter, B.M.T. Fitofisionomias do bioma cerrado. In Cerrado: Ambiente e flora; Sano, S.N., Almeida, S.P., Eds.; EMBRAPA-CPAC: Planaltina, Brazil, 1998; pp. 89–166. Available online: http://www.alice.cnptia.embrapa.br/handle/doc/554094 (accessed on 11 May 2022).
- Infraestrutura de Dados Espaciais do Distrito Federal—IDE/DF. 2021. Cobertura do Solo 2019; Geoportal/DF. Available online: https://www.geoportal.seduh.df.gov.br/geoportal/ (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Reatto, A.; Martins, E.S.; Farias, M.F.R.; Silva, A.V.; Carvalho, O.A., Jr. Mapa pedológico digital—SIG atualizado do Distrito Federal Escala 1:100.000 e uma síntese do texto explicativo; Documentos/Embrapa Cerrados n. 120; Embrapa Cerrados: Planaltina, Brazil, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araújo Pedron, F.; Dalmolin, R.S.D.; Azevedo, A.C.; Kaminski, J. Solos urbanos. Ciência Rural 2004, 34, 1647–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secretaria Nacional de Saneamento (SNS). 2021. Diagnósticos SNIS 2021/2022. Available online: http://www.snis.gov.br/diagnosticos (accessed on 11 May 2022).
- American Public Health Association (APHA); American Water Works Association (AWWA); Water Environment Federation (WEF). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; Baird, R.B., Eaton, A.D., Rice, E.W., Eds.; APHA: Washington, DC, USA; AWWA: Denver, CO, USA; WEF: Alexandria VA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Bang, K.W.; Ketchum, J.H.; Choe, J.S.; Yu, M.J. First flush analysis of urban storm runoff. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 293, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotny, V. Unit Pollutant Loads. Water Environ. Technol. 1992, 4, 40–43. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/24661272 (accessed on 11 May 2022).
- Peng, H.-Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.-W.; Gao, X.-L.; Ma, L.-M. Event mean concentration and first flush effect from different drainage systems and functional areas during storms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 5390–5398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Park, B.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Ryu, J.; Kim, K.; Kim, Y. Determination of NPS Pollutant Unit Loads from Different Landuses. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, T.; Mcgree, J.; Egodawatta, P.; Jinadasa, K.B.S.N.; Goonetilleke, A. Catchment based estimation of pollutant event mean concentration (EMC) and implications for first flush assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 279, 111737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, C. Water Quality Assessment and its Effects on Diffuse Pollution Considering a New Water Quality and Quantity Approach. Master’s Thesis, Federal University of Paraná, Curitiba, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira, F.F. Métodos para monitoramento e estimativa de cargas poluidoras difusas em bacias hidrográficas. Master’s Thesis, University of São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Menezes, D.; Marcuzzo, F.F.N.; Pedrollo, M.C.R. Estimativa da produção de sedimentos utilizando a curva-chave de sedimentos. Ci. e Nat. 2021, 43, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Governo do Distrito Federal (GDF). Relatório Final—Volume I—Diagnóstico; Plano de Gerenciamento Integrado de Recursos Hídricos do Distrito Federal; GDF: Brasília, Brazil, 2012.
- Barbosa, J.S.B.; Bellotto, V.R.; Silva, D.B.; Lima, T.B. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Budget for a Deep Tropical Reservoir of the Brazilian Savannah. Water 2019, 11, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aquino, I.G.; Roig, H.L.; Oliveira, E.S.; Garnier, J.; Guimarães, E.M.; Koide, S. Variação temporal da descarga sólida em suspensão e identificação de minerais a partir de aperfeiçoamento de método de amostragem automática no Córrego Riacho Fundo, Brasília, Distrito Federal. Geol. USP Série Científica 2018, 18, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De França Lopes, L.L.; De Sousa Diniz, L.A.; Costa, M.E.L.; Koide, S. Análise do comportamento qualitativo de uma lagoa de detenção no Distrito Federal. In Proceedings of the XIII Encontro Nacional de Águas Urbanas, Porto Alegre, Brazil, 19–20 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Távora, B.E. Zona Ripária De Cerrado: Processos Hidrossedimentológicos. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Brasília, Brasília, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, G.R. Estudos hidrológicos e hidrossedimentológicos na bacia do córrego do Capão Comprido, DF. Master’s Thesis, University of Brasília, Brasília, Brazil, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fim, B.M. Análises quantitativa e qualitativa das águas superficiais da bacia hidrográfica do ribeirão Rodeador/DF para avaliação das cargas de poluição. Master’s Thesis, University of Brasília, Brasília, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Quinatto, J.; De Nale Zambelli, N.L.; Souza, D.H.; Neto, S.L.R.; Cardoso, J.T.; Skoronski, E. Using the pollutant load concept to assess water quality in an urban river: The case of Carahá River (Lages, Brazil). Rev. Ambiente Água 2019, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, C.; Fernandes, C.V.S. A influência dos eventos de chuva na contribuição da poluição não pontual para a qualidade da água dos rios. In Proceedings of the XXIV Simpósio Brasileiro de Recursos Hídricos, Belo Horizonte, Brazil, November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Park, M.; Choi, Y.S.; Shin, H.J.; Song, I.; Yoon, C.G.; Choi, J.D.; Yu, S.J. A comparison study of runoff characteristics of non-point source pollution from three watersheds in South Korea. Water 2019, 11, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mallin, M.A.; Johnson, V.L.; Ensign, S.H.; Johnson, V.L.; Ensign, S.H. Comparative impacts of stormwater runoff on water quality of an urban, a suburban; a rural stream. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 159, 475–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Gitau, M.W.; Pai, N.; Daggupati, P. Hydrologic and water quality models: Performance measures and evaluation criteria. Trans. ASABE 2015, 58, 1763–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aguiar, M.R.F. Análise da Descarga Sólida em Suspensão na Bacia do Córrego Riacho Fundo, Brasília-DF. Master’s Thesis, University of Brasília, Brasília, Brazil, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Marsalek, J. Pollution Due to Urban Runoff: Unit Loads and Abatement Measures; Environmental Hydraulics Section, Hydraulics Research Division, National Water Research Institute, Canada Centre for Inland Waters: Burlington, ON, Canada, 1978. [Google Scholar]

| Parameter | Method | Stand. Met. Reference | Equipment | Measuring Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TS | Gravimetric determination | 2540 B | Analytical scale | 0.01–210 g |
| TSS | Gravimetric determination | 2540 D | Analytical scale | 0.01–210 g |
| TDS | Differential | - | - | - |
| Turbidity | Nephelometric | 2130 B | Turbidimeter | 0–10,000 NTU |
| Conductivity | Direct measurement | 2510 B | Conductivity meter | 0.01 μS–200 mS/cm |
| COD | Reactor digestion, Colorimetric | 5220 D | Spectrophotometer, reactor | 0–150 mg/L COD (LR) 20–1500 mg/L COD (HR) |
| NO2− | Diazotization, Colorimetric | 4500-NO2 B | Spectrophotometer | 0–0.3 mg/L NO2-N |
| NO3− | Cadmium reduction, Colorimetric | 4500-NO3 E | Spectrophotometer | 0–0.5 mg/L NO2 + NO3-N (LR) 0–5 mg/L NO2 + NO3-N (MR) |
| NH3 | Nesslerization, Colorimetric | 4500-NH3 C (1995) | Spectrophotometer | 0–2.5 mg/L NH3-N |
| RP | Ascorbic acid, Colorimetric | 4500-P E | Spectrophotometer | 0–2.5 mg/L PO43− |
| TP | Acid persulfate digestion, Colorimetric | 4500-P B 4500-P E | Spectrophotometer, reactor | 0–3.5 mg/L PO43− 0–1.1 mg/L P |
| Event | COD | TS | TSS | NO2-N | NO3-N | NH3-N | Inorg-N | RP | TP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 November 2019 | 95 | 932 | 806 | 0.02 | 0.28 | 0.26 | 0.56 | 0.05 | 0.28 |
| 5 December 2019 * | 98 | 1664 | 1258 | 0.01 | 0.25 | 0.15 | 0.41 | 0.03 | 0.07 |
| 18 December 2019 | 35 | 1130 | 989 | 0.02 | 0.34 | 0.18 | 0.54 | 0.03 | 0.09 |
| 22 December 2019 | 23 | 1040 | 899 | 0.02 | 0.63 | 0.09 | 0.73 | 0.05 | 0.07 |
| 23 December 2019 | 25 | 1681 | 1363 | 0.03 | 0.35 | 0.17 | 0.54 | 0.03 | 0.07 |
| 10 January 2020 | 96 | 1053 | 1053 | 0.05 | 0.70 | 0.19 | 0.94 | 0.02 | 0.09 |
| 23 January 2020 | 58 | 515 | 413 | 0.04 | 0.18 | 0.23 | 0.46 | 0.08 | 0.01 |
| 30 January 2020 | 29 | 267 | 178 | 0.02 | 0.57 | 0.16 | 0.75 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| 23 February 2020 | 51 | 451 | 120 | 0.02 | 0.45 | 0.09 | 0.56 | 0.07 | 0.05 |
| 24 February 2020 | 171 | 1472 | 1360 | 0.01 | 0.35 | 0.17 | 0.53 | 0.07 | 0.06 |
| 5 December 2020 * | 534 | 3775 | 3530 | 0.03 | 0.62 | 0.27 | 0.91 | 0.07 | 0.21 |
| Mean | 110 | 1271 | 1088 | 0.02 | 0.43 | 0.18 | 0.63 | 0.05 | 0.09 |
| Median | 58 | 1053 | 989 | 0.02 | 0.35 | 0.17 | 0.56 | 0.05 | 0.06 |
| Minimum | 23 | 267 | 120 | 0.01 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 0.41 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| Maximum | 534 | 3775 | 3530 | 0.05 | 0.70 | 0.27 | 0.94 | 0.08 | 0.21 |
| Dry period | 9 | 82 | 11 | 0.06 | 1.04 | 0.43 | 1.53 | 0.03 | 0.06 |
| Event | Mean * Cumulative Volume (mm) | Mean * Duration (min) | Mean * Intensity (mm/h) | Mean * ADD (Days) | Mean Flow Rate (m3/s) | Max Flow Rate (m3/s) | Flood Duration (Hours) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 November 2019 | 22.5 | 105 | 13.7 | 0.5 | 11.5 | 19.3 | 14.7 |
| 5 December 2019 | 20.7 | 575 | 2.2 | 0.6 | 11.7 | 18.8 | 22.7 |
| 18 December 2019 | 5.8 | 98 | 7.8 | 2.3 | 8.3 | 14.0 | 8 |
| 22 December 2019 | 3.5 | 19 | 11.1 | 2 | 6.3 | 9.9 | 7.3 |
| 23 December 2019 | 10 | 95 | 8.4 | 1.5 | 11.0 | 16.9 | 10.7 |
| 10 January 2020 | 8.6 | 11 | 42.4 | 0 | 8.4 | 11.0 | 5.5 |
| 23 January 2020 | 9.8 | 462 | 1.3 | 0.4 | 6.2 | 8.3 | 14.5 |
| 30 January 2020 | 1.8 | 56 | 6.9 | 0.7 | 7.2 | 8.5 | 5.8 |
| 23 February 2020 | 3.4 | 59 | 4.4 | 0.9 | 8.1 | 10.6 | 4.3 |
| 24 February 2020 | 32.8 | 375 | 5.6 | 0.3 | 25.0 | 71.9 | 20.5 |
| 5 December 2020 | 17.6 | 42 | 32.3 | 10.8 | 21.0 | 32.1 | 10.5 |
| Pollutant Rating Curve | R2 | S (ton/Day) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TSS | Low discharges | 0.51 | 482.37 |
| High discharges | 0.68 | 1760.36 | |
| Inorganic N | Low discharges | 0.38 | 0.15 |
| High discharges | 0.97 | 0.18 | |
| Total P | Low discharges | 0.06 | 0.02 |
| High discharges | 0.28 | 0.06 | |
| COD | Low discharges | 0.43 | 31.47 |
| High discharges | 0.3 | 430.7 | |
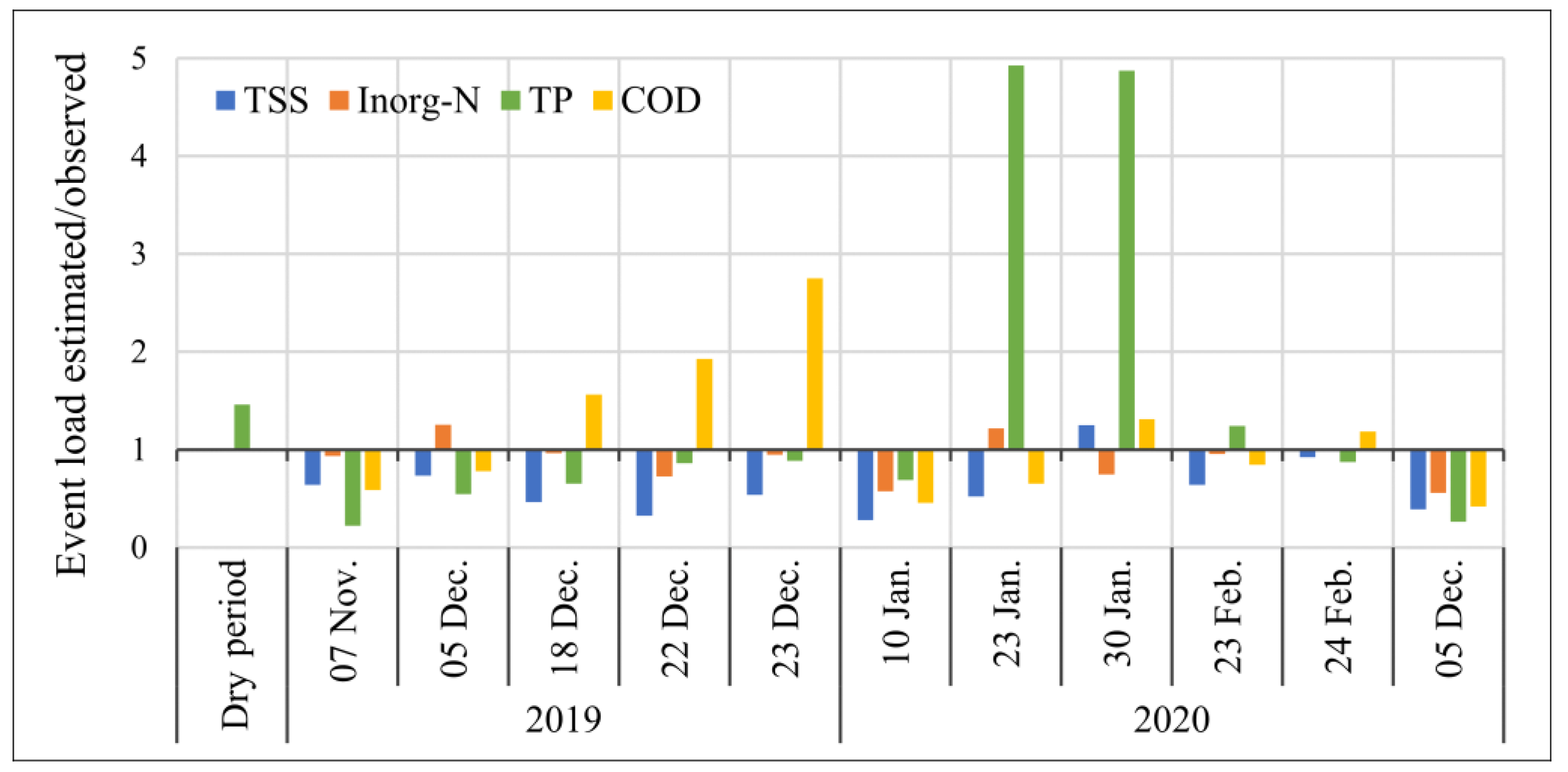
| Event’s Total Pollutant Load | TSS (ton/Event) | Inorg N (kg/Event) | Total P (kg/Event) | COD (ton/Event) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obs. | Estim. | Obs. | Estim. | Obs. | Estim. | Obs. | Estim. | |
| 7 November 2019 | 165.8 | 106 | 116 | 108.5 | 57.2 | 12.7 | 19.5 | 11.5 |
| 5 December 2019 | 236.8 | 174.3 | 77.9 | 97.7 | 20.1 | 11 | 18.4 | 14.3 |
| 18 December 2019 | 151.8 | 70.2 | 82.4 | 79.5 | 14.4 | 9.4 | 5.3 | 8.3 |
| 22 December 2019 | 52.6 | 17.1 | 42.9 | 31.2 | 4.3 | 3.7 | 1.3 | 2.6 |
| 23 December 2019 | 427.2 | 229.1 | 170.2 | 161.1 | 21 | 18.6 | 7.7 | 21.3 |
| 10 January 2020 | 134.4 | 37.8 | 117.1 | 67.4 | 11.6 | 8 | 12.2 | 5.6 |
| 23 January 2020 | 25.5 | 13.3 | 28.4 | 34.7 | 0.8 | 4 | 3.6 | 2.4 |
| 30 January 2020 | 15.3 | 19.2 | 64 | 47.7 | 1.1 | 5.6 | 2.5 | 3.3 |
| 23 February 2020 | 43.5 | 27.8 | 54.5 | 52 | 4.9 | 6.1 | 5 | 4.2 |
| 24 February 2020 | 2192.8 | 2027.2 | 793.8 | 790.8 | 89.4 | 78.2 | 254.2 | 301.8 |
| 5 December 2020 | 1362.4 | 530.7 | 351.8 | 196.3 | 80.3 | 21.2 | 206 | 86.2 |
| Total Event Pollutant Load Estimate | R2 | NSE | S |
|---|---|---|---|
| TSS | 0.89 | 0.84 | 194.9 ton/event |
| Inorganic N | 0.95 | 0.95 | 46.9 kg/event |
| Total P | 0.6 | 0.47 | 13.6 kg/event |
| COD | 0.81 | 0.8 | 39.3 ton/event |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carvalho, D.J.; Costa, M.E.L.; Koide, S. Assessment of Diffuse Pollution Loads in Peri-Urban Rivers—Analysis of the Accuracy of Estimation Based on Monthly Monitoring Data. Water 2022, 14, 2354. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14152354
Carvalho DJ, Costa MEL, Koide S. Assessment of Diffuse Pollution Loads in Peri-Urban Rivers—Analysis of the Accuracy of Estimation Based on Monthly Monitoring Data. Water. 2022; 14(15):2354. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14152354
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarvalho, Daniela Junqueira, Maria Elisa Leite Costa, and Sergio Koide. 2022. "Assessment of Diffuse Pollution Loads in Peri-Urban Rivers—Analysis of the Accuracy of Estimation Based on Monthly Monitoring Data" Water 14, no. 15: 2354. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14152354






