Abstract
Watershed management must take into account both the quantity and quality of water. Therefore, many hydrological models have been developed for hydrological and water quality prediction for various purposes. The Spreadsheet Tool for Estimating Pollutant Loads (STEPL), which was developed in the United States for water quality regulation, can predict both the quantity and quality of water, and has the advantage of including information on livestock. However, complex characteristics of the watershed must be generated by users for use as input data, and simulations only yield annual average values. Therefore, in this study, we developed a model that overcomes these limitations using geographic information data and enabling monthly predictions. The model developed in the study estimates monthly direct runoff and baseflow using daily rainfall data, while the STEPL model employs average annual approaches that are limited to consider seasonal variances of hydrological behaviors. It was developed for use within the QGIS software, and was applied to a watershed covering an area of 128.71 km2, considering information on livestock, soil, and land use. The model exhibited good predictive accuracy for four nonpoint source (NPS) pollutant loads and river flow, displaying acceptable criteria greater than 0.83 for river flow rates and 0.71 for all NPS pollutant load rates during calibration and validation.
1. Introduction
Urbanization and industrialization increase the impervious area, and thus limit water flow into groundwater and increase direct runoff. Because these changes can increase the loads of nonpoint source (NPS) pollutants, watershed management is necessary to secure water resources and manage pollutants. Various watershed-scale hydrological models have been developed for watershed management [1,2,3,4,5].
The Hydrological Simulation Program—FORTRAN (HSPF) is a watershed model for modeling the hydraulics and water quality of stormwater runoff; it was developed in the early 1960s as the Stanford Watershed Model. It has been continuously improved and supported by the US Environmental Protection Agency and United States Geological Survey, and thus has attracted many users [6,7,8]. The HSPF model is a physics-based semi-distributed model that consists of multiple modules for modeling hydraulics, hydrology, and water quality. In addition, it can apply various watershed spatial characteristics and meteorological data to subwatersheds and rivers constructed within the model [9]. The Soil Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) model [10] is a semi-distributed stormwater runoff model that can predict the long-term runoff of complex watersheds with multiple land use types. Hydrological response units (HRUs), which reflect land use type and hydrological soil group (HSG), are the fundamental unit of hydrological modeling using the SWAT model; they are used to simulate the initial abstraction, evapotranspiration, surface flow, baseflow, and soil moisture using the water balance equation [11]. The Long-Term Hydrologic Impact Assessment (L-THIA) model [12] was developed to assess the long-term effect of changes in land use. It was initially developed in a spreadsheet format and was later improved to predict river water and NPS pollutant loads using geographical information [13]. The Spreadsheet Tool for Estimating Pollutant Loads (STEPL) [14] is a spreadsheet-based model developed to model the annual average NPS pollutant loads. It can predict NPS pollutant loads for various land use types. Furthermore, it can estimate the NPS pollutant load reduction resulting from low impact development and best management practices. The STEPL calculates annual direct runoff using the annual average precipitation and National Resource Conservation Service curve number (NRCS-CN) method.
Hydrological models are used for hydrological behavior analyses; For example, Bieger et al. [15] analyzed the land use change impacts using the SWAT model for three land use scenarios. In their study, they reported that cropland, forest, and orchard area changes of +265.32%, −34.48%, and 204.51% led to 46.1% increases in surface flow. Guse et al. [16] estimated the impacts of five crop rotations, and reported that nitrate loads could be reduced by dynamic changes using the crop rotations. Martin et al. [17] employed the regional hydro-ecological simulation system model [18], and discovered that land use changes led to 37–88% increases in high flows and 23–37% increases in low flows. Kibii et al. [19] used the SWAT model and reported that terrace implementations on steep agricultural areas decreased direct runoff and increased groundwater recharges significantly. Hou et al. [20] used the HSPF model, revealing that controlling via a rural domestic lifestyle can reduce total nitrogen (T-N) by 37.86% and total phosphorus (T-P) by 66.95%, while fertilizer control can reduce T-N and T-P by only 5.07% and 2.01%, respectively.
Although these hydrological models differ in methods and complexity, they can all be used to analyze watershed flow rates and NPS pollutant loads. However, because a watershed consists of multiple types of land cover with various soil properties, the spatial properties based on geographical information must be considered [13]. In addition to these watershed properties, NPS pollutants discharged by livestock have a non-negligible impact on watershed quality [20,21]. In addition, to increase the probability that a hydrological model is used by practitioners (for example, construction companies) or policymakers, it is necessary to simplify the models used to construct the input data and simulations [13,22].
A comprehensive review of the above models suggests that it is nontrivial to apply livestock conditions in the SWAT and HSPF, which are less simple than the STEPL model. Although livestock-based conditions can be applied in the STEPL, it is based on Microsoft Excel, which does not use geographical information and is capable of predicting only annual average values. The L-THIA model uses geographic information, and is similar in simplicity to the STEPL, but livestock conditions cannot be implemented. Consequently, removing the limitations of the STEPL (that users manually generate input data, and that it models only annual average values, which makes it impossible to include the seasonal characteristics of watersheds) will enable better prediction of watershed conditions compared to other models.
Therefore, this study applies the STEPL and aims to improve it to automatically extract spatial information on watersheds using geographical information, and to facilitate monthly prediction in order to better reflect the seasonal characteristics of watersheds.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Addressing the Limitations of the STEPL
The STEPL was developed to determine the total maximum daily load (TMDL), which is the standard used in US water quality regulation. It can be used to predict flows such as annual average direct runoff and baseflow, as well as the annual average loads of nitrogen, phosphorus, suspended solids (SS), biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), and Escherichia coli [14]. This study focuses on this model because it facilitates the inclusion of livestock conditions, which is not commonly supported in other models.
However, this model has two main limitations. First, spatial information on the watershed must be input by users. Second, it supports only the prediction of annual averages.
To address the first limitation, the spatial characteristics of a watershed, namely, the land use and soil types, can be reclassified into a few to tens of subcategories. However, to predict the quantity and quality of water, both types of information must be used [23,24,25]. HRUs in which two conditions are combined may exhibit significant variation, which may be further complicated if spatial information is also considered. Thus, it is very difficult to manually generate information for each HRU. Therefore, the land use types and HSG map must be used to automatically generate HRUs that are spatially distributed across watersheds to facilitate the prediction of water quantity and quality for each HRU.
Regarding the second limitation, this model was developed to determine the TMDL, and can only predict the annual average load. Predictions of the annual average water quantity and quality cannot reflect seasonal changes in precipitation, which are a significant factor in predicting NPS pollutants [26,27]. The advantage of this model, in which the regional annual average precipitation database is stored for immediate access during simulation, is, simultaneously, a limitation, as daily precipitation data cannot be used [5].
Therefore, this study seeks to exploit the advantage of this model, which allows livestock information to be considered when calculating NPS pollutant loads, while further reducing the limitations of this model using the geographical information system and facilitating monthly predictions.
2.2. Predicting Direct Runoff and Baseflow
Direct runoff can be computed using the NRCS-CN method (formerly the Soil Conservation Service curve number method) [28]. The STEPL model applies this method to predict annual direct runoff on the basis of annual precipitation. However, the results obtained by this method show a non-negligible discrepancy from those of calculations based on the NRCS-CN method [5]. Therefore, this study follows the computational method of the STEPL, but takes the approach of the NRCS-CN method.
The NRCS-CN method uses the CN defined by HSG and land use type to determine the potential maximum retention after runoff begins (S, mm) and the initial abstraction (Ia, mm). In addition, the direct runoff depth (Q, mm) only occurs when the precipitation (P, mm) is greater than Ia (Equations (1)–(4)).
The direct runoff depth Q is calculated for each HRU defined by a combination of land use types and HSG. The area of each HRU is multiplied by the direct runoff depth to obtain the runoff volume (m3).
Because river flow consists of direct runoff and baseflow, these parameters must be estimated to predict the flow rate. The baseflow consists of stormwater that moves toward rivers after penetrating the ground surface; therefore, it may not be as simple to predict direct runoff. To address this difficulty, Lee et al. [29] classified 20 watersheds, ranging in area from 5695 to 155,806 ha, into seven categories based on land use: urban (URBN), agriculture (AGRL), forest (FRST), pasture (PAST), wetland (WTLD), bare (BARE), and water (WATR). The baseflow (m3) for month i is predicted from the land use area (ha), coefficient for each land use type, and monthly precipitation (Equation (5)).
In this equation, C is the coefficient for each land use type, which can vary between watersheds, and A is the land use area (ha).
In Equation (5), the land use coefficient C is a model parameter that can be calibrated for each land use type in the model area. Lee et al. [23] proposed default values of CURBN = 0.04, CAGRL = 0.40, CFRST = 0.20, CPAST = 0.18, CWTLD = 0.48, CBARE = 0.15, and CWATR = 0.22. In an extension of this study, Lee et al. [13] predicted the direct runoff using the NRCS-CN method and the baseflow using Equation (5). They compared the predicted values to the measured flow rate in 15 watersheds with areas between 5841 and 81,107 ha. The Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency (NSE) and coefficient of determination (R2) during model calibration were 0.601–0.868 and 0.743–0.917, respectively. In addition, for model validation, the NSE and R2 were 0.611–0.917 and 0.676–0.946, respectively, which suggests that the NRCS-CN method and Equation (5) can be used to predict the flow rate.
Therefore, the hydrological model developed in this study calculates the direct runoff and baseflow using the NRCS-CN method and Equation (5), respectively.
2.3. NPS Pollutant Prediction
The goal of this study is to develop a model that can take into account various nutrients produced by livestock and predict the quantity of NPS pollutants according to the land use and soil types in the watershed. The method used in the STEPL model was applied.
The STEPL model can simulate the average annual nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), BOD, and SS. In this model, the SS load is predicted using the universal soil loss equation (USLE) [30,31]. In addition, for the N, P, BOD, and E. coli loads, the direct runoff (m3) and pollutant coefficients (mg/L) are used to determine the nutrient loads from land. These loads are determined by multiplying the sediment values and amount of lost soil that reaches a river by the corresponding coefficients for nutrients. Then, the nutrient loads from livestock are determined using the type of livestock, nutrient emission for each type, and number of livestock [14].
The nutrient loads from land, sediment, and livestock are summed to determine the NPS pollutant loads. Here, the nutrient loads from land can be calculated as monthly loads based on monthly direct runoff, and the nutrient loads from sediment can be calculated on a monthly basis if the monthly soil loss is provided. Additionally, because the number of livestock has low monthly variability, the monthly nutrient loads from livestock were calculated by assuming the same type of livestock, nutrient emissions by livestock, and number of livestock. That is, the nutrient loads from land and sediment, which change by month, and nutrient loads from livestock, which have the same value for each month, are summed to yield the monthly NPS pollutant loads.
2.4. Developing Software to Predict Flow Rate and NPS Pollutant Load
Direct runoff is predicted using the NRCS-CN method, which is based on a combination of land use type and HSG and yields the direct runoff (m3) according to precipitation and area. In addition, the baseflow can be calculated using Equation (5), which requires knowledge of the land use type and area. Therefore, it is prohibitive to manually provide the information for a large number of HRUs based on the land use type and HSG of watersheds. To address this problem, this study uses geographical information to perform this procedure in the QGIS software Version 3.10 [32].
HSG and land use maps, which contain spatial information on soil and land use, respectively, are needed to compute the direct runoff. A CN table that lists the CN values according to the HSG and land use maps is also needed. The CN table is a CSV file that contains CN values specified by users. It superposes the HSG and land use maps spatially and generates a CN map by retrieving the appropriate value from the CN table (Figure 1).
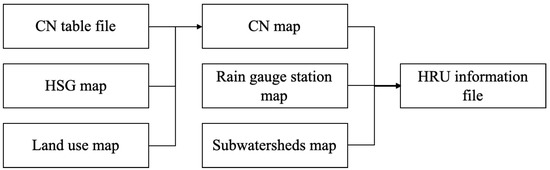
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of HRU information file.
After the CNs for HRUs distributed across watersheds are obtained, precipitation data can be used to calculate the direct runoff. The precipitation data may include measurement data for multiple sites within or near the watershed. If precipitation was measured at a single site, the precipitation must be uniform across the watershed. However, if the precipitation was measured at multiple sites, all the data must be used. To this end, a rain gauge station map and subwatershed map are used, and the precipitation data from the closest measuring site within or near the subwatershed are used (Figure 1). This process generates the HRU information file, which contains information on HSG, land use, CN, rain gauge station number, and subwatershed number for all the HRUs (Figure 2). This information helps predict not only the direct runoff, but also the baseflow, because it contains information about the area occupied by each land use type. This operation requires the land use map, soil map, CN table, subwatershed map, and rain gauge station map, which can be submitted as input in the interface (Figure 3).
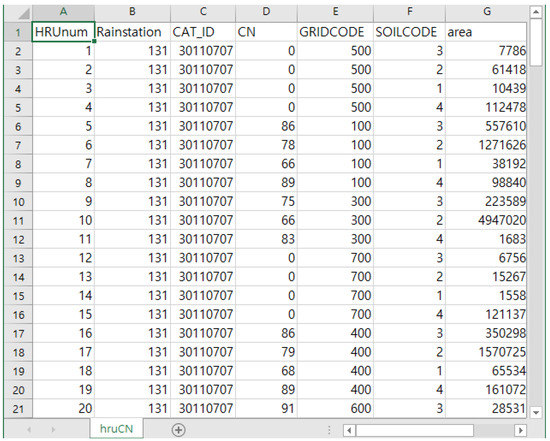
Figure 2.
Example of HRU information file.
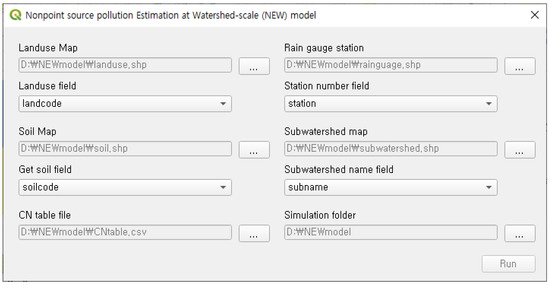
Figure 3.
Interface for generating HRU information file.
After the HRU information file is obtained, the direct runoff, baseflow, and NPS pollutant loads can be computed. Using the HRU information file and precipitation data from one or more sites, the direct runoff and baseflow are first calculated. Then, using the nutrient loads from livestock and pollutant coefficients, the nutrient loads from land for direct runoff and baseflow are calculated. In addition, the nutrient loads from sediment are calculated using the monthly soil loss data. Next, these three nutrient loads are summed to define the monthly NPS pollutant loads (Figure 4).
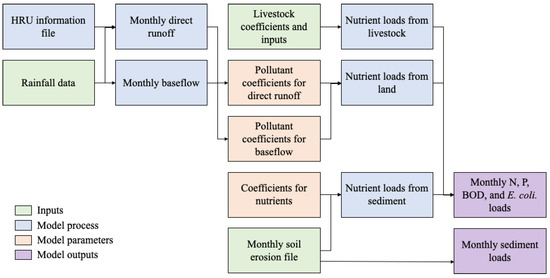
Figure 4.
Schematic illustration of streamflow and NPS pollutant load estimation.
A graphical user interface (GUI) was developed for the computation of the direct runoff, baseflow, and NPS pollutant loads using the HRU information file (Figure 5). This GUI displays information regarding the HRU information file, and requires precipitation data and monthly soil loss data as input from users. The CN and baseflow coefficients in Equation (5) for each land use type can be modified in this GUI.
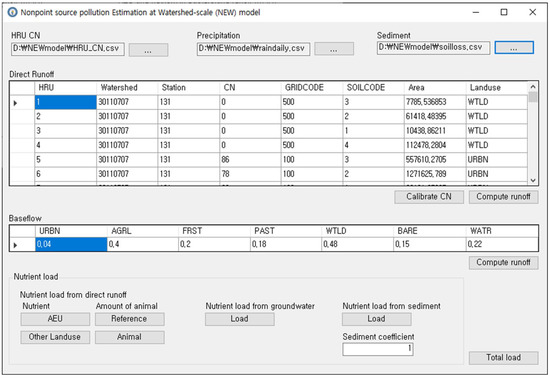
Figure 5.
Graphical user interface (GUI) for estimating monthly streamflow and NPS pollutant loads.
The STEPL model first calculates the direct runoff and baseflow, and then uses the pollutant coefficients to compute the NPS pollutant loads. The pollutant coefficients can vary between watersheds. In addition, the type, number, and unit loads for each livestock animal (kg) must be defined for each watershed. Inputting this information into a single interface can be extremely complicated. Thus, supplementary GUIs are accessible from the main GUI in Figure 5, so that this information can be entered or modified (Figure 6). These supplementary GUIs can be used to modify the model parameters of the STEPL: the nutrient concentration of direct runoff from agriculture and pastureland (Figure 6a), nutrient concentration of direct runoff from other land use types (Figure 6b), nutrient concentration of baseflow (Figure 6c), nutrient concentration of sediment (Figure 6d), and number of animals and daily BOD per animal (Figure 6e). Additionally, the number of livestock can be entered (Figure 6f).
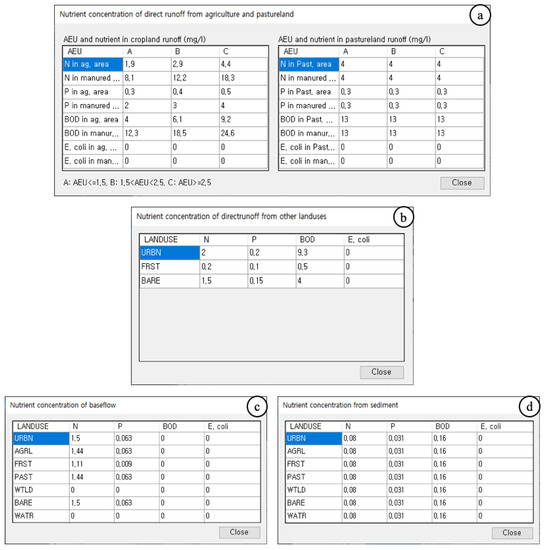
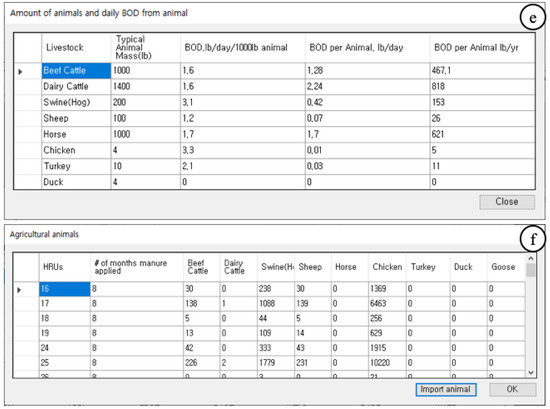
Figure 6.
Supplementary GUIs for nutrient and livestock inputs for editing (a) nutrient concentration of direct runoff from agriculture and pastureland, (b) nutrient concentration of direct runoff from other land use types, (c) nutrient concentration of baseflow, (d) nutrient concentration of sediment, and (e) number of animals and daily BOD per animal, and (f) for entering number of months during which manured is applied and number of animals for each HRU.
2.5. Applying the Developed Model
To assess the applicability of the Nonpoint source pollution Estimation at Watershed-scale (NEW) model developed in this study, the model was applied in designated areas. The input data consisted of land use data from the Environmental Geographic Information Service (1:5000 scale) [33], daily precipitation data from the Korea Meteorological Administration [34], daily flow data, and water quality data measured every 8 days by the Water Resources Management Information System (WAMIS) [35]. In addition, monthly soil loss data from the USLE-based monthly soil loss map data provided by the Nonpoint Source Pollution Modeling Research Group [36] were used. Regional agricultural animal data provided by the National Pollutant Survey System [37] of the National Institute of Environmental Research were collected to calculate the pollution from direct runoff, specifically, nutrients produced by agricultural animals. The model was applied to watersheds in which the outlets coincide with WAMIS measuring sites for flow and water quality. The watershed consists of seven subwatersheds with areas ranging from 39 to 2995 ha (Figure 7 and Table 1). The number and types of agricultural animals were also used for modeling. The number was largest for chicken (598,133) and smallest for dairy cattle (172) (Table 2).
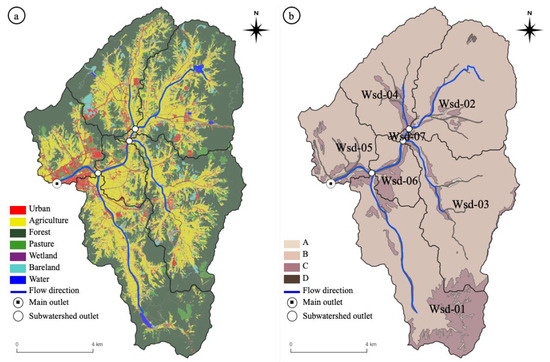
Figure 7.
Watersheds where model was applied: (a) land use map; (b) HSG map.

Table 1.
Land use area of subwatersheds where model was applied.

Table 2.
Number of agricultural animals in subwatersheds where model was applied.
The model was applied from January 2016 to December 2020; the monthly flows in the watersheds ranged from 0.08 × 106 m3 to 49.71 × 106 m3. Because the proposed model produces monthly predictions of the NPS pollutant loads, water quality data measured by the Load Estimator [38] every 8 days were converted to monthly loads for comparison with the model prediction.
3. Results
3.1. Model Calibration
Various values have been suggested for comparing measured river flow to the values estimated by hydrological models. The credibility criteria proposed by Duda et al. [39] are R2 > 0.65 and a difference of <45%, whereas Skaggs et al. [40] suggested an NSE value of >0.50. The criteria of Wang et al. [41] are NSE > 0.50, R2 > 0.60, and a percent bias (PBIAS) of ±15%, whereas Engel et al. [42] and Moriasi et al. [43] proposed criteria of R2 > 0.60, NSE > 0.50, and PBIAS < 15%. That is, although metrics such as NSE and R2 are often used, various standards are used to evaluate the credibility of a model. This study assessed the model credibility using scatter plots along with the NSE and R2.
The NEW model was calibrated using data from January 2016 to December 2017 for the monthly flow rate and NPS pollutant loads. The NSE and R2 values for river flow were 0.8903 and 0.9327, respectively; the NSE for the NPS pollutant loads was 0.7376–0.9527, whereas R2 was 0.9187–0.9906 (Table 3 and Figure 8).

Table 3.
NSE and R2 for measured and estimated monthly streamflow and NPS pollutant loads in model calibration.
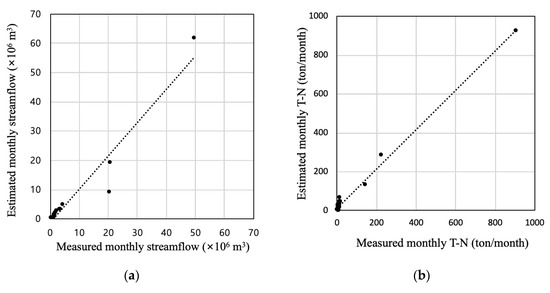
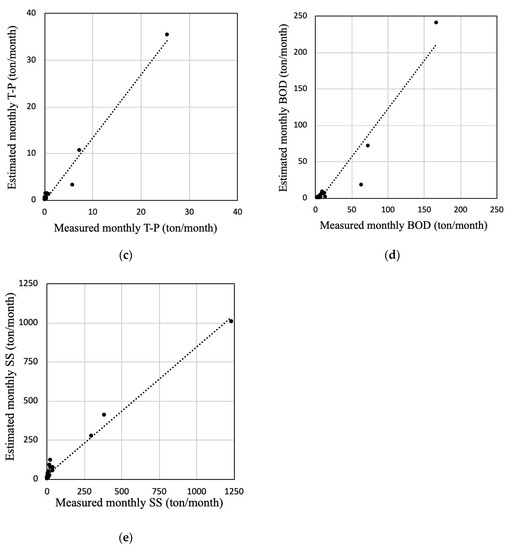
Figure 8.
Scatter plots of measured and estimated monthly streamflow and nutrients in model calibration: (a) streamflow; (b) T-N; (c) T-P; (d) BOD; (e) SS.
Therefore, model calibration was successful for the designated areas, and the predicted streamflow can be considered to be credible.
3.2. Model Validation
The model was validated for the period of January 2018 to December 2020. The NSE and R2 values for river flow were 0.8329 and 0.8633, respectively. The NSE for the NPS pollutant loads was 0.7111–0.7981, and R2 was 0.7546–0.9032 (Table 4). In the scatter plots for both calibration and validation, the estimated and measured values showed a close linear relationship for all values (Table 3 and Figure 9). Thus, as in the calibration step, the model showed credible performance in the validation procedure.

Table 4.
NSE and R2 for measured and estimated monthly streamflow in model validation.
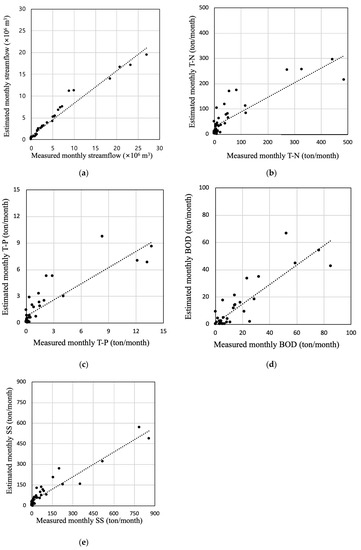
Figure 9.
Scatter plots of measured and estimated monthly streamflow and nutrients in model validation: (a) streamflow; (b) T-N; (c) T-P; (d) BOD; (e) SS.
4. Discussion
Various hydrological models have been developed and used for watershed management. Analyses or simulations for watershed management must include land use and rainfall pattern changes such as urbanization, industrialization, and climate changes. This indicates that it is required for the models to consider the watershed properties of land use and rainfall variances. The watershed management scenarios by watershed-scale hydrological models displayed that direct runoff, baseflow, groundwater, and NPS loads varied by land use [1,2,3,4,5]. Additionally, predictions of the annual average water quantity and quality cannot reflect seasonal changes in precipitation, which are a significant factor in predicting NPS pollutants [26,27]. In addition to land use and rainfall in the watershed, rural domestic animals, including livestock, are also influential components in NPS estimations [20,21]. Therefore, there is a need to consider land use and domestic animals in NPS load estimations in watershed-scale analyses. In addition, to increase the probability that a hydrological model is used by practitioners or policymakers, it is necessary to simplify the models used to construct the input data and simulations [13,22].
Thus, a GIS-based model was developed in the present study, improving the STEPL model. The STEPL model can be used to estimate direct runoff, baseflow, nitrogen, phosphorus, suspended solids, and biochemical oxygen demand, and it facilitates the inclusion of livestock. However, the model has two main limitations; one is that spatial information on the watershed must be input by the users, and the other is that it only enables the prediction of annual averages. To address these two limitations, this study developed a model that can extract spatial information on watersheds from geographical information and use daily rainfall data. This model was applied to a watershed with an area of 128.71 km2 for the period between January 2016 and December 2020. The land use types, HSG maps, and types and numbers of livestock were used. The NSE and R2 were used to assess the prediction accuracy of the model. For river flow, both criteria were greater than 0.8 in model validation and calibration. In addition, for the four NPS pollutant loads, both criteria were calculated to be greater than 0.7. Thus, the model showed credible performance in analyzing the hydrological and water quality characteristics of the watershed.
Therefore, it was concluded that the NEW model can be used to estimate monthly streamflow and NPS loads at watershed, facilitating the inclusion of livestock.
5. Conclusions
Watershed management must take into account both the water quantity and quality of watersheds. Additionally, it is important to consider various watershed conditions to understand how they affect water quantity and quality. Thus, multiple hydrological models have been developed using various software packages (e.g., ArcGIS, QGIS, and Microsoft Excel) to use different methods of hydrological and hydraulic prediction for various purposes.
The STEPL model was developed as a tool for evaluating the TMDL, a standard used in US water quality regulation, and is based on Microsoft Excel. Although it has the advantage of including livestock information when NPS pollutant loads are computed, it has two limitations: geographical information cannot be used, and thus, users must manually specify the spatial characteristics of watersheds, and the seasonal characteristics of precipitation cannot be considered because its approach is based on annual averages. This study developed a model to resolve these limitations; the proposed NEW model has the following advantages.
- It provides user convenience by applying a graphical user interface.
- HRUs are determined by land use and HSG maps in the QGIS software.
- It facilitates the inclusion of livestock.
- Seasonal variances are provided in direct runoff, baseflow, and NPS load estimations.
One of reasons for using the STEPL model is that the model provides the opportunity to estimate the effects of best management practices and low impact developments by applying NPS reduction coefficients for various practices. The NPS loads reduction estimations can be implemented by the users, manually selecting the practices for HRUs in the STEPL model. Thus, it is challenging to develop the optimum practice scenario to meet target loads. Thus, there is a need to improve the NEW model to provide optimized practice scenarios so that the model can be used as decision support model for watershed management policy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.S.P.; methodology, J.-Y.P.; investigation, J.-Y.P.; data curation, H.L.; writing—original draft preparation, H.L.; writing—review and editing, Y.S.P.; visualization, H.L.; supervision, Y.S.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This subject is supported by Korea Ministry of Environment as “The SS (Surface Soil conservation and management) projects; 2019~(2019002820001)”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors send special thanks to the Korea Environmental Industry & Technology Institute for continuous research project support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Atkins, J.T.; Wiley, J.B.; Paybins, K.S. Calibration Parameters Used to Simulate Streamflow from Application of the Hydrologic Simulation Program-FORTRAN Model (HSPF) to Mountainous Basins Containing Coal Mines in West Virginia; Scientific Investigations Report 2005-5099; US Geological Survey: McDowell County, WV, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, P.V.; Kennen, J.G.; Sun, G.; Kiang, J.E.; Butcher, J.B.; Eddy, M.C.; Hay, L.E.; LaFontaine, J.H.; Hain, E.F.; Nelson, S.A. A comparison of hydrologic models for ecological flows and water availability. Ecohydrology 2015, 8, 1525–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Jang, W.S.; Kim, J.; Choi, J.D.; Engel, B.A.; Yang, J.E.; Lim, K.J. Development of a watershed-scale long-term hydrologic impact assessment model with the asymptotic curve number regression equation. Water 2016, 8, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherkauer, D.S. Quantifying ground water recharge at multiple scales using PRMS and GIS. Groundwater 2004, 42, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.S.; Engel, B.A.; Harbor, J. A web-based model to estimate the impact of best management practices. Water 2014, 6, 455–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Knapp, H.V.; Arnold, J.; Demissie, M. Hydrological modeling of the Iroquois River watershed using HSPF and SWAT1. J. Am. Water. Resour. Assoc. 2005, 41, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.; Du, B. Evaluation of SWAT and HSPF within BASINS program for the upper North Bosque River watershed in central Texas. Trans. ASAE 2004, 47, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobel, R.; Rifai, H.; Petersen, T. Refinement and application of a coupled tidal prism model with HSPF for managing bacterial water quality impairment in a coastal watershed. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2015, 197, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicknell, B.R.; Imhoff, J.C.; Kittle, J.L., Jr.; Jobes, T.H.; Donigian, A.S., Jr. Hydrological Simulation Program-Fortran, User’s Manual for Version 12. National Exposure Research Laboratory, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Athens, GA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, J.G.; Allen, P.M. Automated methods for estimating baseflow and ground water recharge from streamflow records. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1999, 35, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neitsch, S.; Arnold, J.; Kiniry, J.; Srinivasan, R.; Williams, J. Soil and Water Assessment Tool. User’s Manual, Version 2009; Technical Report; Texas Water Resources Institute: College Station, TX, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Harbor, J. A practical method for estimating the impact of land-use change on surface runoff, groundwater recharge, and wetland hydrology. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1994, 60, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Chae, M.S.; Park, J.Y.; Lim, K.J.; Park, Y.S. Development and application of a QGIS-based model to estimate monthly streamflow. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetra Tech, Inc. User’s Guide. Spreadsheet Tool for the Estimation of Pollutant Load (STEPL) Version 4.1; Tetra Tech, Inc.: Fairfax, VA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bieger, K.; Hörmann, G.; Fohrer, N. The impact of land use change in the Xiangxi Catchment (China) on water balance and sediment transport. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2013, 15, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guse, B.; Pfannerstill, M.; Fohrer, N. Dynamic modelling of land use change impacts on nitrate loads in rivers. Environ. Process. 2015, 2, 575–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K.L.; Hwang, T.; Vose, J.M.; Coulston, J.W.; Wear, D.N.; Miles, B.; Band, L.E. Watershed impacts of climate and land use changes depend on magnitude and land use context. Ecohydrology 2017, 10, e1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tague, C.L.; Band, L.E. RHESSys: Regional Hydro-Ecologic Simulation System-An object-oriented approach to spatially distributed modeling of carbon, water, and nutrient cycling. Earth Interact. 2004, 8, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibii, J.; Kipkorir, E.C.; Kosgei, J.R. Application of Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) to evaluate the impact of land use and climate variability on the Kaptagat Catchment River discharge. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, R.; Li, J.; Dong, F.; Kiu, J. Research on the non-point source pollution characteristics of important drinking water sources. Water 2022, 14, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Ouyang, W.; Hao, F.; Ren, X.; Yang, S. The non-point source pollution in livestock-breeding areas of the Heihe River basin in Yellow River. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2007, 21, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Woo, W.; Park, Y.S. A user-friendly software package to develop storm water management model (SWMM) inputs and suggest low impact development scenario. Water 2020, 12, 2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Mishra, A. Critical erosion area identification based on hydrological response unit level for effective sediment control in a river basin. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 1749–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savvidou, E.; Efstratiadis, A.; Koussis, A.D.; Koukouvinos, A.; Skarlatos, D. The curve number concept as a driver for delineating hydrological response units. Water 2018, 10, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Xu, D. The application of a modified version of the SWAT model at the daily temporal scale and the hydrological response unit spatial scale: A case study covering an irrigation district in the Hei River Basin. Water 2018, 10, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zheng, B.; Chu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Huang, M. Seasonal variations of performance and operation in field-scale storing multipond constructed wetlands for nonpoint source pollution mitigation in a plateau lake basin. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 280, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencha, S.M.; Ulsido, M.D.; Muluneh, A. Evaluation of seasonal and spatial variations in water quality and identification of potential sources of pollution using multivariate statistical techniques for Lake Hawassa watershed, Ethiopia. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. Urban Hydrology for Small Watersheds; National Resources Conservation Service, United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1986.
- Lee, H.; Choi, H.S.; Chae, M.S.; Park, Y.S. A study to suggest monthly baseflow estimation approach for the Long-Term Hydrologic Impact Analysis models: A case study in South Korea. Water 2021, 13, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses from Cropland East of the Rocky Mountains: A Guide for Selection of Practices for Soil and Water Conservation; Handbook No. 282; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1965.
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; Handbook No. 537; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- QGIS Development Team. QGIS Geographic Information System, Open Source Geospatial Foundation Project. 2009. Available online: http://qgis.osgeo.org (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Environmental Geographic Information Service. Available online: https://egis.me.go.kr/main.do (accessed on 2 February 2021).
- Korea Meteorological Administration. Available online: https://www.weather.go.kr/w/index.do (accessed on 7 February 2021).
- Water Resources Management Information System. Available online: http://water.nier.go.kr/main/mainContent.do (accessed on 11 February 2021).
- Nonpoint Source Pollution Modeling Research Group. Available online: http://npslab.kongju.ac.kr (accessed on 11 February 2021).
- National Pollutant Survey System. Available online: https://wems.nier.go.kr/ (accessed on 7 February 2021).
- Runkel, R.L.; Crawford, C.G.; Cohn, T.A. Load Estimator (LOADEST): A Fortran Program for Estimating Constituent Loads in Streams and Rivers; U.S. Geological Survey Techniques and Methods: Reston, VA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Duda, P.B.; Hummel, P.R.; Donigian, A.S.; Imhoff, J.C. BASINS/HSPF: Model use, calibration, and validation. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1523–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaggs, R.W.; Youssef, M.A.; Chescheir, G.M. DRAINMOD: Model use, calibration, and validation. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1509–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Williams, J.; Gassman, P.; Baffaut, C.; Izaurralde, R.; Jeong, J.; Kiniry, J. EPIC and APEX: Model use, calibration, and validation. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1447–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, B.; Storm, D.; White, M.; Arnold, J.; Arabi, M. A hydrologic/water quality model application protocol. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2007, 43, 1223–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Gitau, M.W.; Pai, N.; Daggupati, P. Hydrologic and water quality models: Performance measures and evaluation criteria. Trans. ASABE 2015, 58, 1763–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).