Improving Daily Streamflow Forecasting Using Deep Belief Net-Work Based on Flow Regime Recognition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
3. Methodology
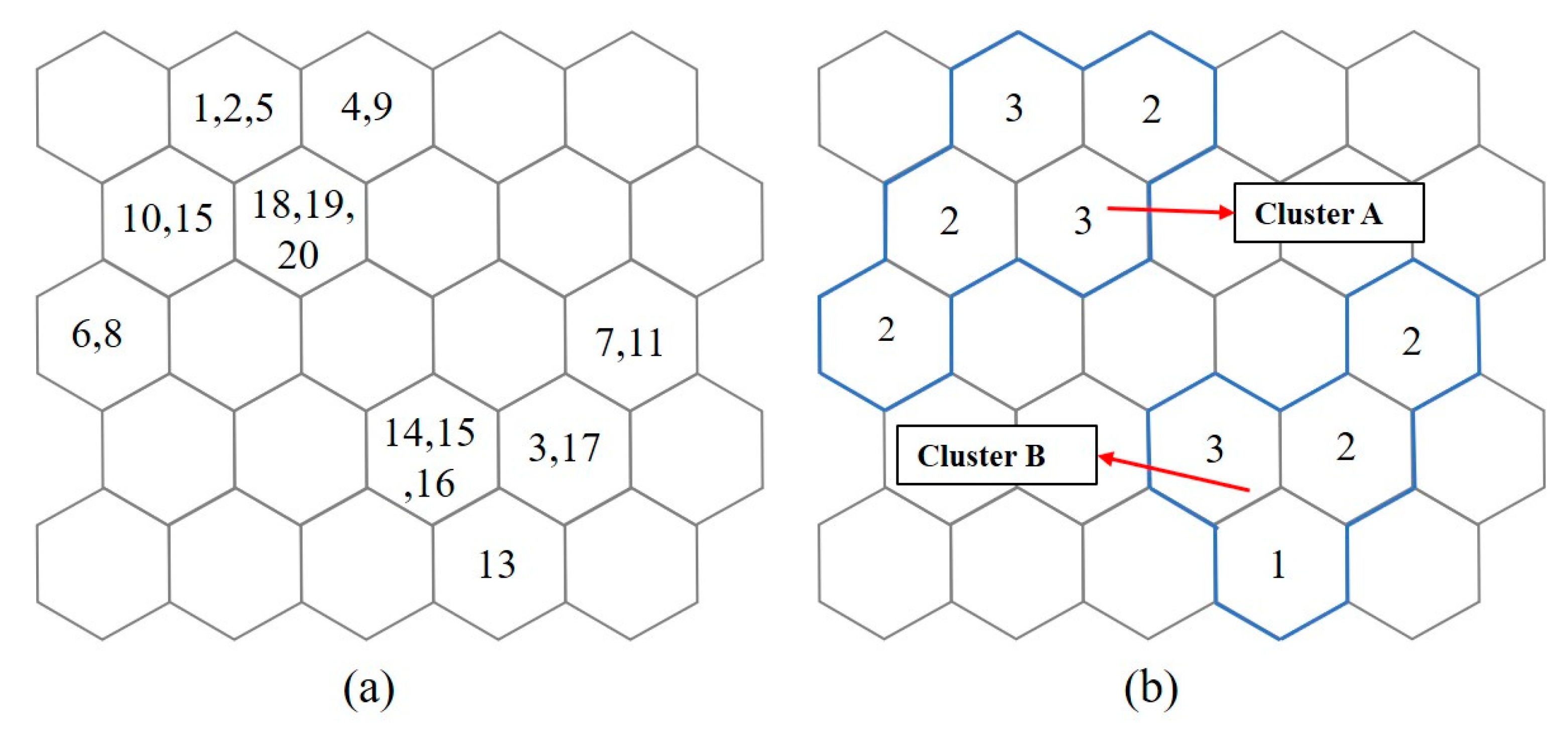
3.1. Streamflow Process Clusters Based on Hydro-Meteorological Conditions
3.2. Integrated Neural Network Framework (SOM-RF-DBN)
3.2.1. Self-Organizing Map (SOM)
3.2.2. Random Forests (RF)
3.2.3. Deep Belief Network (DBN)
3.3. Experiment Setup
3.4. Performance Evaluation Criteria
4. Results and Discussion
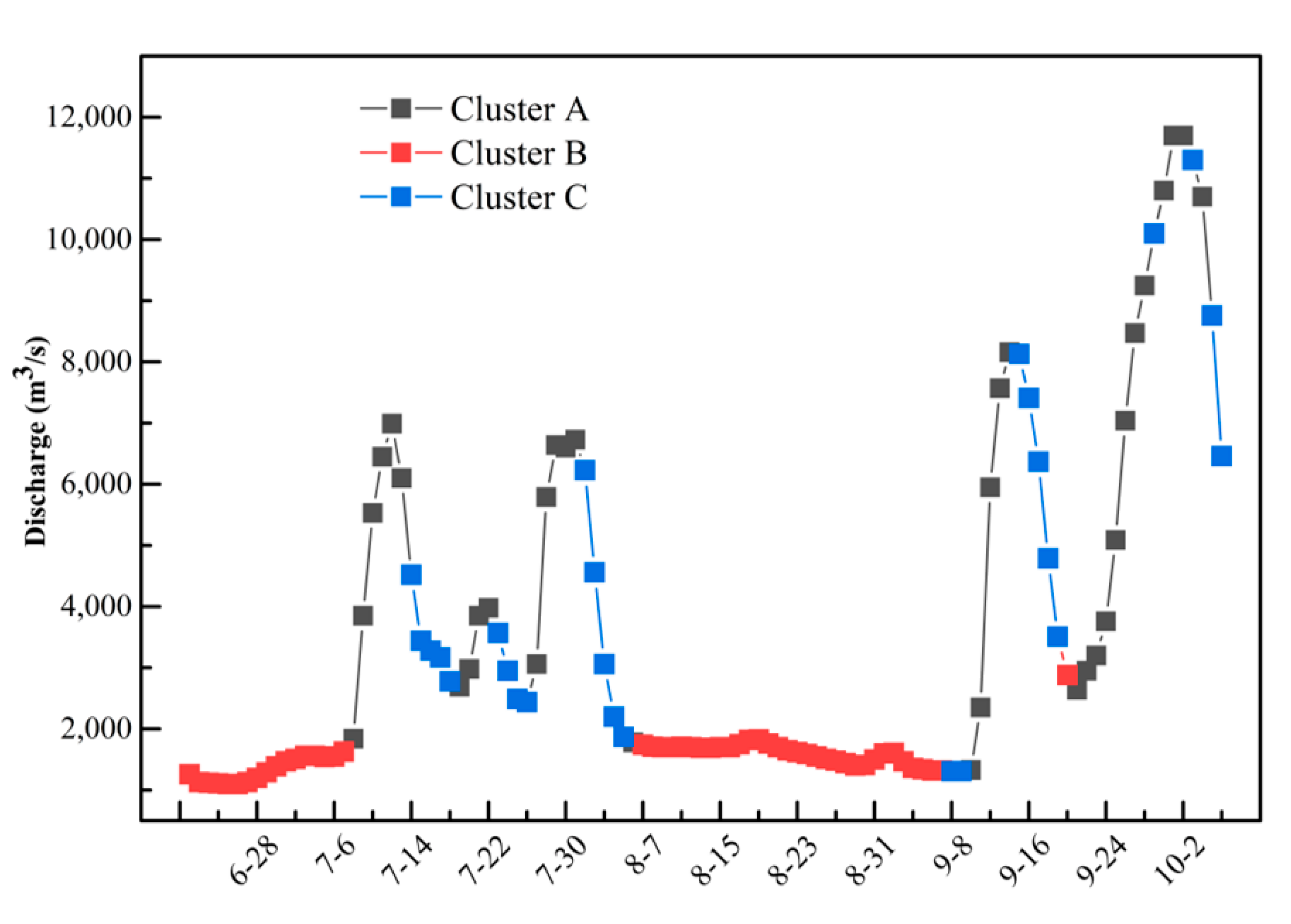
4.1. Data Clustering
4.2. Input Variable Selection
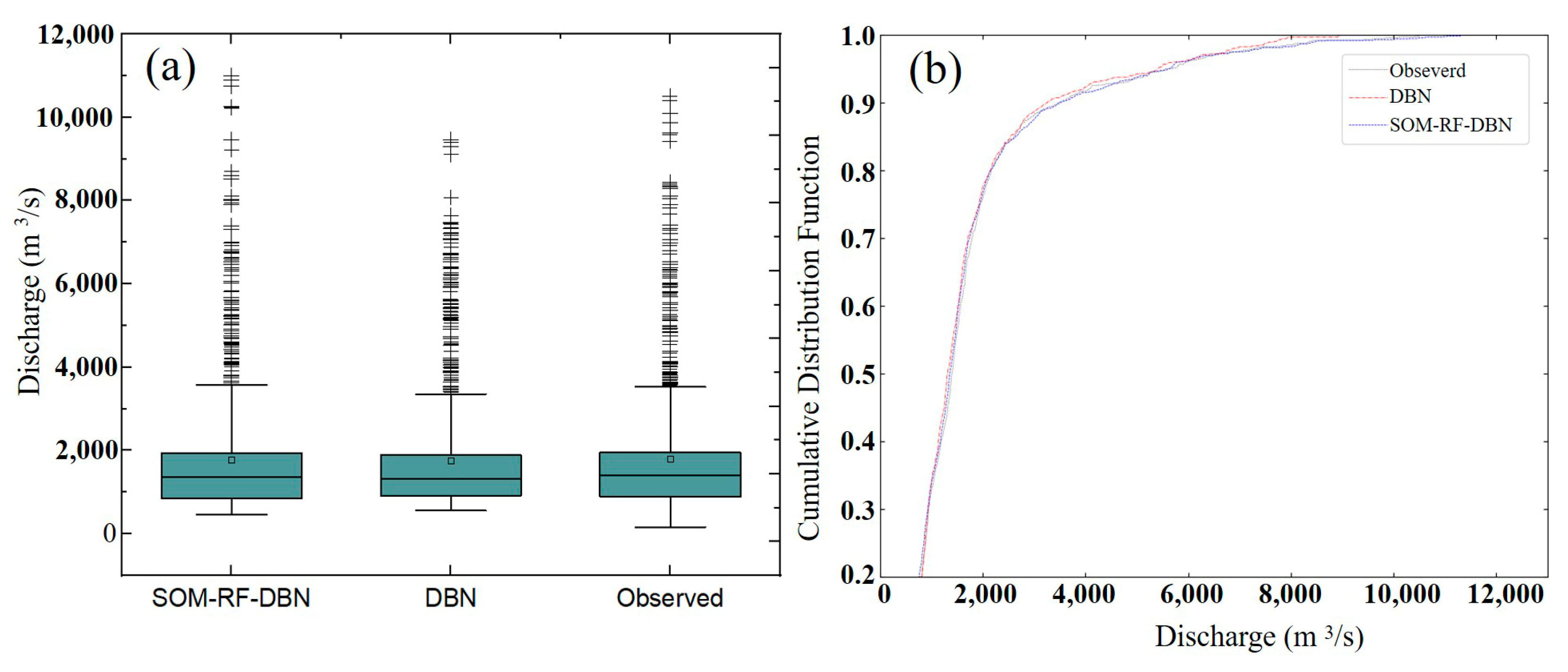
4.3. Performance Comparison between the Integrated Framework and Single DBN Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, M.; Fang, F.; Kinouchi, T.; Navon, I.M.; Pain, C.C. Long lead-time daily and monthly streamflow forecasting using machine learning methods. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilinc, H.C.; Yurtsever, A. Short-Term Streamflow Forecasting Using Hybrid Deep Learning Model Based on Grey Wolf Algorithm for Hydrological Time Series. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazid, T.; Doudja, S.G.; Ali, N.A.; Ozgur, K.; Ahmed, E.S. Improving artificial intelligence models accuracy for monthly streamflow forecasting using grey Wolf optimization (GWO) algorithm. J. Hydrol. 2020, 582, 124435. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, K.; Huang, Y.F.; Ahmed, A.N.; Koo, C.H.; El-Shafie, A. A review of the hybrid artificial intelligence and optimization modelling of hydrological streamflow forecasting. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 279–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, R.; Xu, B.; Zhong, P.A.; Zhu, F.; Huang, X.; Liu, W.F.; Xu, S.Y.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhang, J.Y. Dynamic long-term streamflow probabilistic forecasting model for a multisite system considering real-time forecast updating through spatio-temporal dependent error correction. J. Hydrol. 2021, 601, 126666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, E.H.; Huang, S.Z.; Huang, Q.; Fang, W.; Wu, L.Z.; Wang, L. A robust method for non-stationary streamflow prediction based on improved EMD-SVM model. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 462–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.Z.; Huang, Q.; Leng, G.Y.; Liu, S.Y. A nonparametric multivariate standardized drought index for characterizing socioeconomic drought: A case study in the Heihe River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2016, 542, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, M.A.; Quilty, J.; Adamowski, J. Data Assimilation for Streamflow Forecasting Using Extreme Learning Machines and Multilayer Perceptrons. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR026226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.B.; Wei, J.H.; Wu, W.Y.; Jiang, Y.; Chu, Q.; Meng, X.J. A classification-based deep belief networks model framework for daily streamflow forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2021, 595, 125967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johan, V.T.; Bieger, K.; Arnold, J.G. A hydropedological approach to simulate streamflow and soil water contents with SWAT+. Hydrol. Processes 2021, 35, e14242. [Google Scholar]
- Maza, M.; Srivastava, A.; Bisht, D.S.; Raghuwanshi, N.S.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Chatterjee, C.; Bhadra, A. Simulating hydrological response of a monsoon dominated reservoir catchment and command with heterogeneous cropping pattern using VIC model. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 129, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aredo, M.R.; Hatiye, S.D.; Pingale, S.M. Impact of land use/land cover change on stream flow in the Shaya catchment of Ethiopia using the MIKE SHE model. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Bao, W.M.; Gao, Q.Y.; Si, W.; Sun, Y.Q. Coupling the Xinanjiang model and wavelet-based random forests method for improved daily streamflow simulation. J. Hydroinform. 2021, 23, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, J.; Wahab, S.H. Heavy Rainfall Forecasting Model Using Artificial Neural Network for Flood Prone Area. In IT Convergence and Security; Springer: Singapore, 2017; Volume 2018, pp. 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Minocha, V.K. Discussion of “Comparative Analysis of Event-based Rainfall-runoff Modeling Techniques—Deterministic, Statistical, and Artificial Neural Networks” by Ashu Jain and S. K. V. Prasad Indurthy. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2004, 9, 550–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riad, S.; Mania, J.; Bouchaou, L.; Najjar, Y. Rainfall-runoff model using an artificial neural network approach. Math. Comput. Model. 2004, 40, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, D.B.D.; Lima, M.D.C.E.; Salgado, R.M. An Empirical Analysis of MLP Neural Networks Applied to Streamflow Forecasting. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2011, 9, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.R.; Cannon, A.J.; Hsieh, W.W. Forecasting daily streamflow using online sequential extreme learning machines. J. Hydrol. 2016, 537, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, Z.M.; Jaafar, O.; Deo, R.C.; Kisi, O.; Adamowski, J.; Quilty, J.; El-Shafie, A. Stream-flow forecasting using extreme learning machines: A case study in a semi-arid region in Iraq. J. Hydrol. 2016, 542, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.B.; Wei, J.H.; Qiu, J. Monthly Streamflow Forecasting Using EEMD-Lasso-DBN Method Based on Multi-Scale Predictors Selection. Water 2018, 10, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghaith, M.; Siam, A.; Li, Z.; El-Dakhakhni, W. Hybrid Hydrological Data-Driven Approach for Daily Streamflow Forecasting. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2020, 25, 04019063–04019071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Maier, H.R.; Zecchin, A.C. Improved PMI-based input variable selection approach for artificial neural network and other data driven environmental and water resource models. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 65, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.; Deo, R.C.; Li, Y.; Maraseni, T. Input selection and performance optimization of ANN-based streamflow forecasts in the drought-prone Murray Darling Basin region using IIS and MODWT algorithm. Atmos. Res. 2017, 197, 42–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
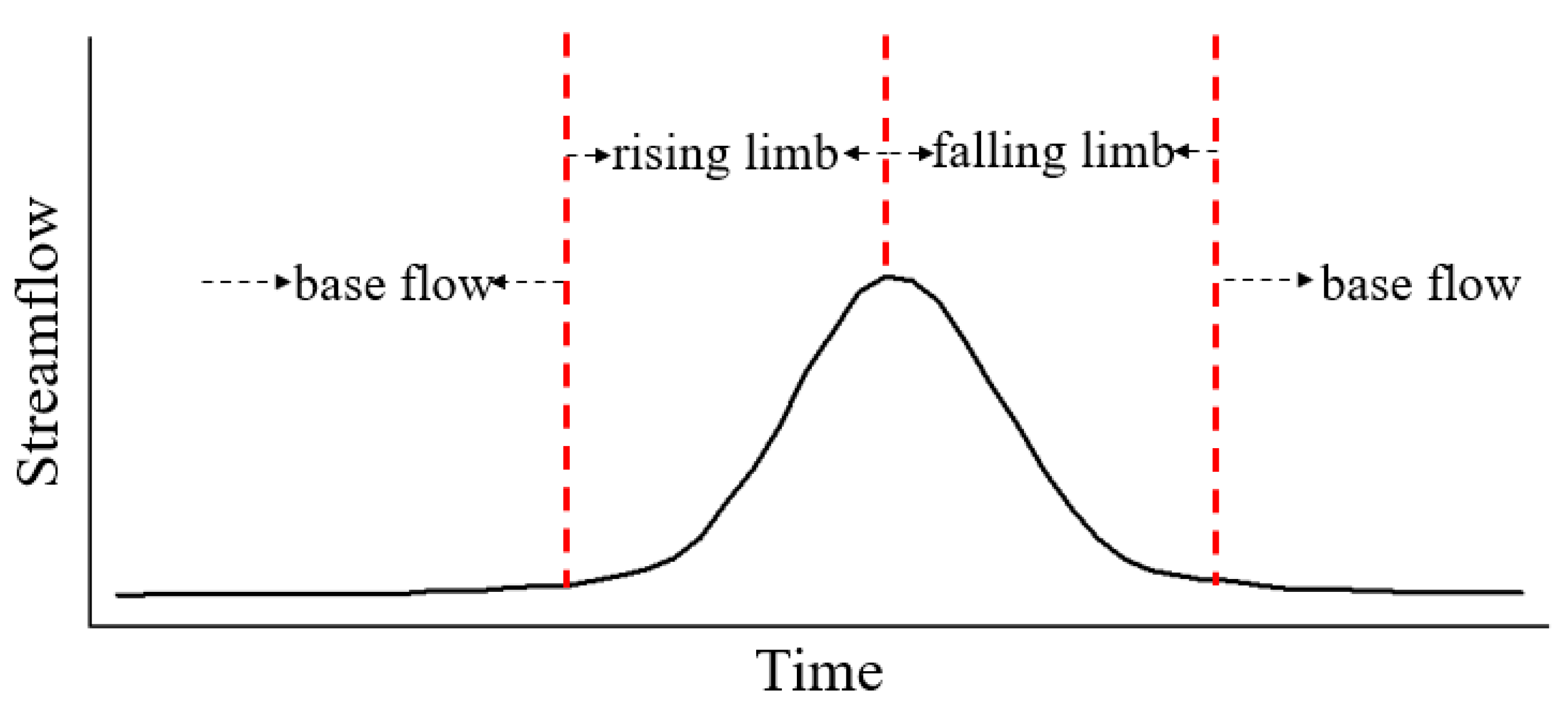
- Li, M.; Wang, Q.J.; Robertson, D.E.; Bennett, J.C. Improved error modelling for streamflow forecasting at hourly time steps by splitting hydrographs into rising and falling limbs. J. Hydrol. 2017, 555, 586–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.F.; Cao, H.; Hao, C.F.; Qiu, J. Daily Streamflow Forecasting Based on Flow Pattern Recognition. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 4601–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.l.; Gupta, H.V.; Gao, X.G.; Sorooshian, S.; Imam, B. Self-organizing linear output map (SOLO): An artificial neural network suitable for hydrologic modeling and analysis. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 1302–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, G.F.; Wang, C.M. Performing cluster analysis and discrimination analysis of hydrological factors in one step. Adv. Water Resour. 2006, 29, 1573–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Srinivasulu, S. Integrated approach to model decomposed flow hydrograph using artificial neural network and conceptual techniques. J. Hydrol. 2006, 317, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.F.; Wu, M.C. A hybrid neural network model for typhoon-rainfall forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2009, 375, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, E. Classification of hydro-meteorological conditions and multiple artificial neural networks for streamflow forecasting. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 1555–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaher, Y.M.; Isa, E.; Hossein, B.; Ravinesh, C.D.; Ali, D.M.; Wan, H.M.W.M.; Lamine, D.; Ahmed, E.; Singh, V.P. Novel approach for streamflow forecasting using a hybrid ANFIS-FFA model. J. Hydrol. 2017, 554, 263–276. [Google Scholar]
- Jhong, Y.D.; Chen, C.S.; Lin, H.P.; Chen, S.T. Physical Hybrid Neural Network Model to Forecast Typhoon Floods. Water 2018, 10, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Guo, J.; Xiong, W.; Guo, S.L.; Xu, C.Y. Downscaling GCMs using the Smooth Support Vector Machine method to predict daily precipitation in the Hanjiang Basin. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 27, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wu, D.; Xie, X.; Li, X. Study on Spatio-Temporal Variation of Runoff in Flood Season in Hanjiang River Basin. Pearl River 2020, 41, 30–39. [Google Scholar]
- Kohonen, T. Self-Organized Formation of Topologically Correct Feature Maps. Biol. Cybern. 1982, 43, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Genuer, R.; Poggi, J.-M.; Tuleau-Malot, C. Variable selection using random forests. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2010, 31, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hinton, G.E.; Salakhutdinov, R.R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science 2006, 313, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.H.; Song, G.J.; Hong, H.K.; Xie, K.Q. Deep Architecture for Traffic Flow Prediction: Deep Belief Networks with Multitask Learning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2014, 15, 2191–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzert, F.; Klotz, D.; Brenner, C.; Schulz, K.; Herrnegger, M. Rainfall-runoff modelling using Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 6005–6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, C.H.; Wu, Q.; Li, H.; Jian, S.Q.; Li, N.; Lou, Z.Z. Deep Learning with a Long Short-Term Memory Networks Approach for Rainfall-Runoff Simulation. Water 2018, 10, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Datasets | MEAN | CV | SKEW | KURT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Streamflow | 1260 | 0.85 | 2.79 | 9.94 |
| Rainfall | 4.2 | 1.51 | 2.41 | 7.22 |
| Soil moisture | 0.3 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.09 |
| Evaporation | 2.6 | 0.30 | −0.09 | −0.67 |
| Period | Dimension of SOM | NSE | R2 | RMSE | MAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | 5 × 5 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 262.79 | 140.45 |
| 7 × 7 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 256.12 | 111.71 | |
| 10 × 10 | 0.72 | 0.87 | 471.45 | 221.42 | |
| 15 × 1 5 | 0.63 | 0.82 | 612.35 | 361.87 | |
| Validation | 5 × 5 | 0.89 | 0.90 | 263.35 | 141.98 |
| 7 × 7 | 0.91 | 0.93 | 261.66 | 129.17 | |
| 10 × 10 | 0.73 | 0.86 | 442.13 | 241.67 | |
| 15 × 15 | 0.65 | 0.80 | 601.23 | 354.13 |
| Out Variable | Group | Input Variables and Importance Scores |
|---|---|---|
| Q (t) | Cluster A | Q (t − 1), 0.67; R (t − 3), 0.10; Q (t − 2), 0.07; R (t − 2), 0.04; Q (t − 3), 0.04; S (t − 3), 0.04; |
| Cluster B | Q (t − 1), 0.65; R (t − 3), 0.08; Q (t − 2), 0.08; S (t − 3), 0.05; R (t − 2), 0.04; E (t − 3), 0.04; R (t − 4), 0.03; | |
| Cluster C | Q (t − 1), 0.69; Q (t − 2), 0.12; S (t − 3), 0.07; R (t − 3), 0.05; R (t − 2), 0.02; |
| Datasets | Models | NSE | R2 | RMSE | MAE | EQp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | ||||||
| 1980–2004 | DBN | 0.85 | 0.89 | 446.20 | 194.83 | 9.95% |
| SOM-RF-DBN | 0.94 | 0.95 | 256.29 | 111.71 | 4.84% | |
| Validation | ||||||
| 2005–2014 | DBN | 0.81 | 0.89 | 404.77 | 197.53 | 10.34% |
| SOM-RF-DBN | 0.91 | 0.93 | 261.66 | 129.17 | 5.74% | |
| Time | Period | Models | NSE | R2 | RMSE | MAE | EQp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t + 1 | Calibration | DBN | 0.80 | 0.83 | 474.83 | 235.13 | 12.81% |
| SOM-RF-DBN | 0.86 | 0.88 | 332.54 | 154.67 | 8.42% | ||
| Validation | DBN | 0.77 | 0.81 | 464.30 | 228.22 | 12.05% | |
| SOM-RF-DBN | 0.87 | 0.89 | 324.45 | 139.27 | 7.89% | ||
| t + 2 | Calibration | DBN | 0.68 | 0.70 | 661.08 | 323.73 | 18.30% |
| SOM-RF-DBN | 0.72 | 0.74 | 578.45 | 291.78 | 15.64% | ||
| Validation | DBN | 0.64 | 0.64 | 658.06 | 317.03 | 18.36% | |
| SOM-RF-DBN | 0.70 | 0.71 | 610.76 | 301.21 | 16.81% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, J.; Zou, L.; Dong, Y.; Xiao, S.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, C. Improving Daily Streamflow Forecasting Using Deep Belief Net-Work Based on Flow Regime Recognition. Water 2022, 14, 2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142241
Shen J, Zou L, Dong Y, Xiao S, Zhao Y, Liu C. Improving Daily Streamflow Forecasting Using Deep Belief Net-Work Based on Flow Regime Recognition. Water. 2022; 14(14):2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142241
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Jianming, Lei Zou, Yi Dong, Shuai Xiao, Yanjun Zhao, and Chengjian Liu. 2022. "Improving Daily Streamflow Forecasting Using Deep Belief Net-Work Based on Flow Regime Recognition" Water 14, no. 14: 2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142241
APA StyleShen, J., Zou, L., Dong, Y., Xiao, S., Zhao, Y., & Liu, C. (2022). Improving Daily Streamflow Forecasting Using Deep Belief Net-Work Based on Flow Regime Recognition. Water, 14(14), 2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142241






