Understanding the Mechanism of Urbanization Affect Agricultural Water Efficiency: Evidence from China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
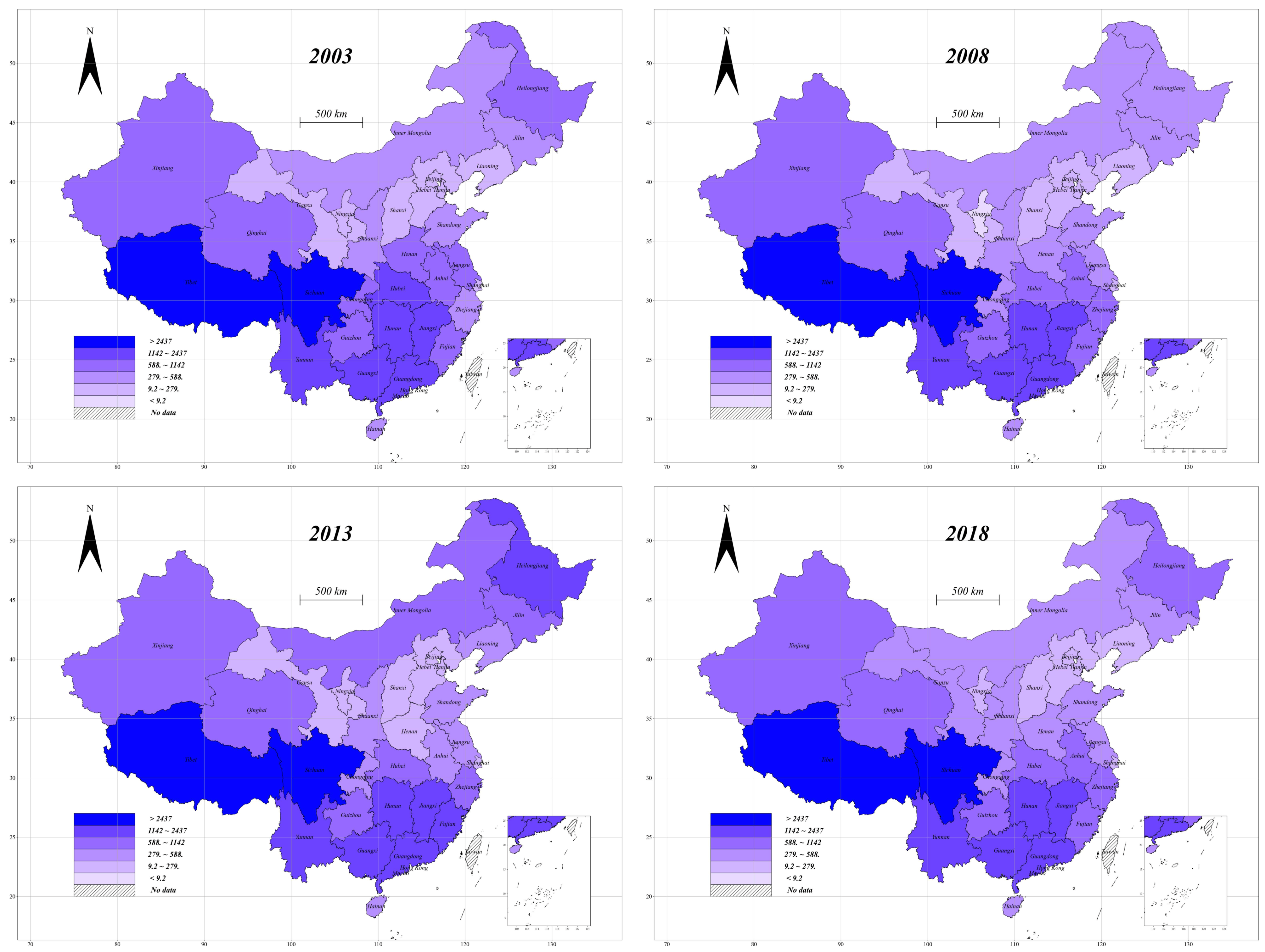
2.1. Measuring Agricultural Water Efficiency
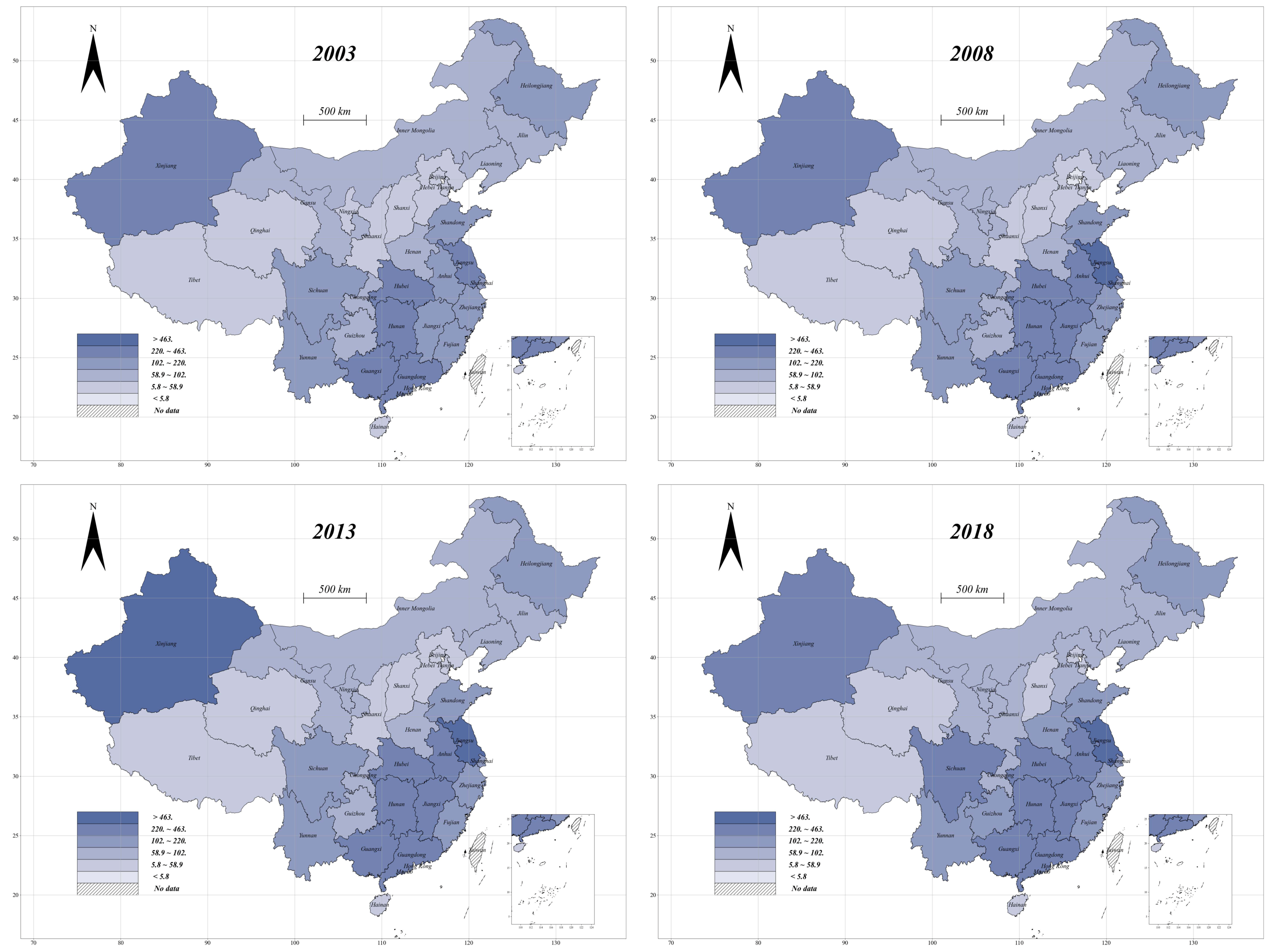
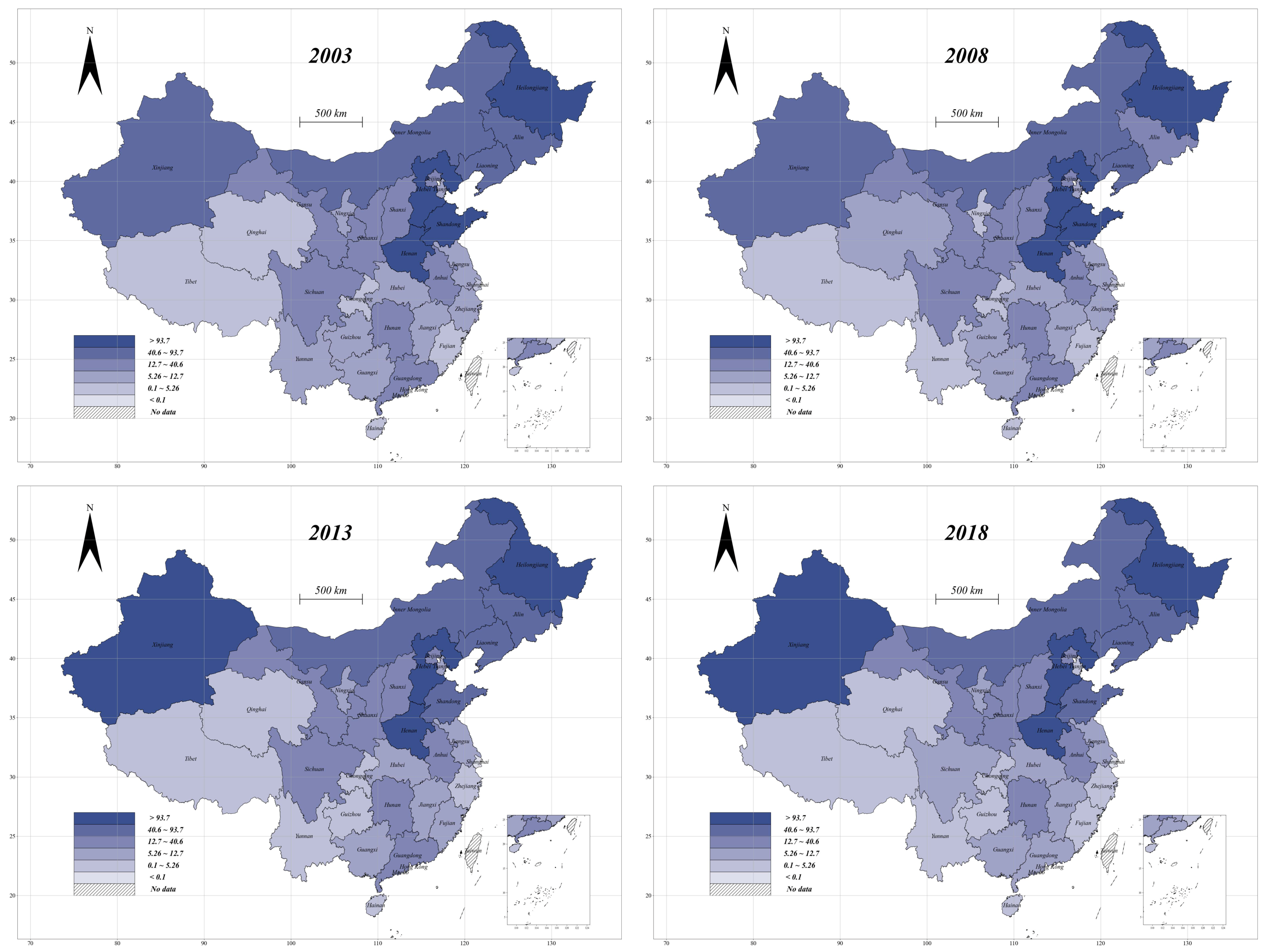
2.2. Measuring Urbanization
2.3. Control Variables
2.4. Empirical Strategy
2.4.1. Two-Way Fixed Effects Model (FE)
2.4.2. Instrumental Variable Estimation
2.4.3. Structural Equation Modeling
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
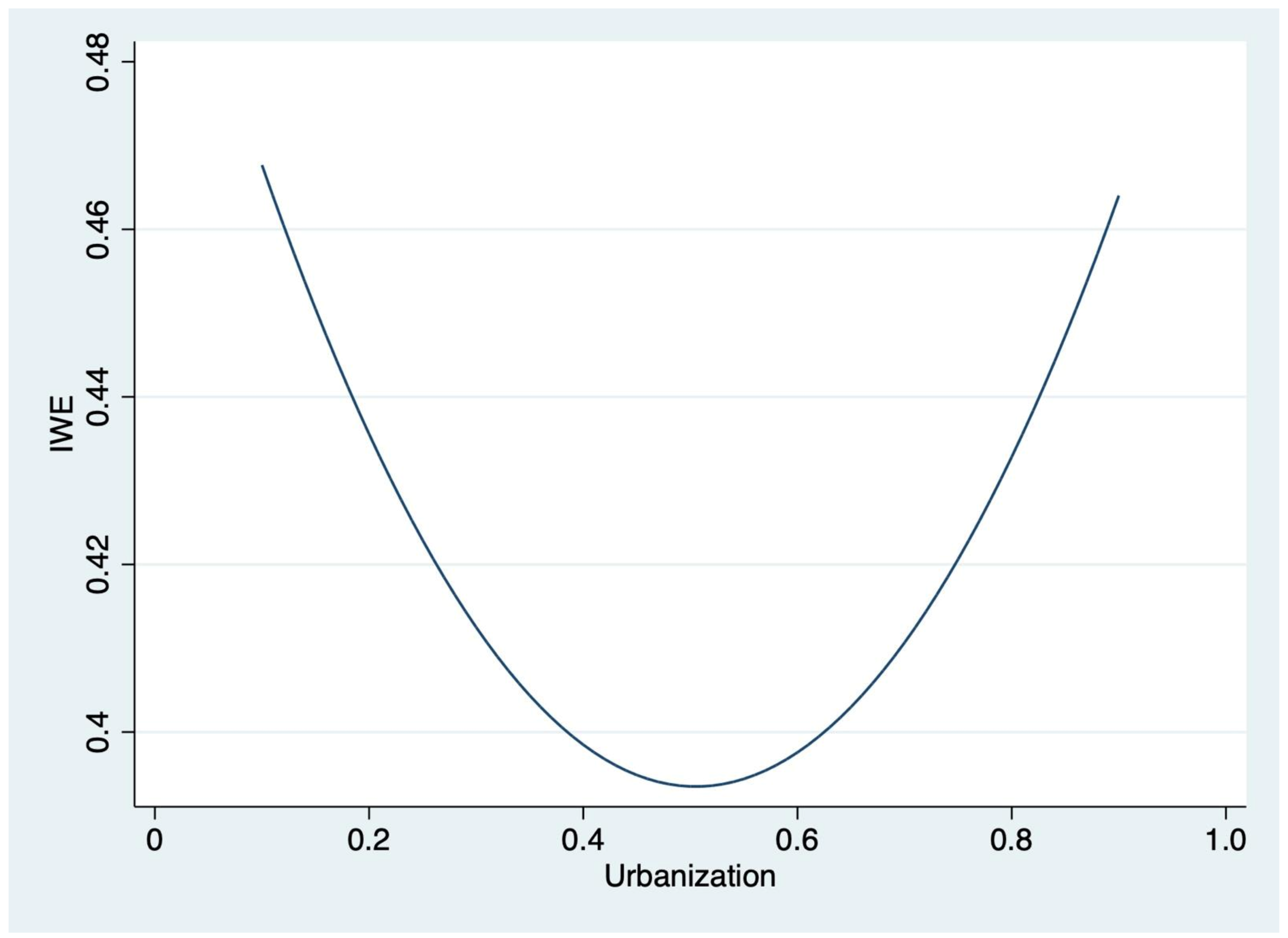
3.2. Impact of Urbanization on AWE: Fixed Effect Estimates
3.3. Two-Stage Least Squares Estimates
3.4. Potential Mechanisms
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Bank. Urban China: Toward Efficient, Inclusive, and Sustainable Urbanization; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-1-4648-0206-5. [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann, J. Four Theses in the Study of China’s Urbanization. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2006, 30, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Wang, J.; Huang, J. Urbanization, Agricultural Water Use, and Regional and National Crop Production in China. Ecol. Model. 2015, 318, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Phillips, M.A. The Influence of the Regulatory Environment on Chinese Urban Water Utilities. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hou, B.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, W.; Lu, F. Research on Scale Demonstration Technology of Inter Basin Water Transfer Project in Agricultural Irrigation. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 5243–5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Mollá, M.; Puertas, R.; Sanchis-Ibor, C. Application of Data Envelopment Analysis to Evaluate Investments in the Modernization of Collective Management Irrigation Systems in Valencia (Spain). Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 5011–5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Liu, Z.; Su, M.; Xu, M.; Rong, Q.; Xu, C.; Tan, Z.; Jiang, X.; Su, Z.; Cai, Y. Inclusion of Ecological Water Requirements in Optimization of Water Resource Allocation Under Changing Climatic Conditions. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 36, 551–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H. Performance of Community-Based Water-Saving Technology under Land Fragmentation: Evidence from Groundwater Overexploitation in the North China Plain. Water Policy 2021, 23, 1542–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, J.; Yang, G.; Wang, J.; Xiang, C.; Cao, X.; Liu, H. Changing Mechanisms of Agricultural Water Use in the Urbanization and Industrialization of China. Water Policy 2017, 19, 908–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oueslati, W.; Salanié, J.; Wu, J. Urbanization and Agricultural Productivity: Some Lessons from European Cities. J. Econ. Geogr. 2019, 19, 225–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Yang, L.; Rahman, S.; Sriboonchitta, S. Agricultural Productivity Growth and Its Determinants in South and Southeast Asian Countries. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Engel, B.A.; Sun, S.; Zhao, X.; Wu, P.; Wang, Y. The Impact of Urbanization and Aging on Food Security in Developing Countries: The View from Northwest China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 292, 126067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, H. Sustainable Agricultural Total Factor Productivity and Its Spatial Relationship with Urbanization in China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Bao, H.X.H. The Impact of Urbanization on Farmland Productivity: Implications for China’s Requisition–Compensation Balance of Farmland Policy. SSRN J. 2020, 9, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aneseyee, A.B.; Soromessa, T.; Elias, E.; Noszczyk, T.; Feyisa, G.L. Evaluation of Water Provision Ecosystem Services Associated with Land Use/Cover and Climate Variability in the Winike Watershed, Omo Gibe Basin of Ethiopia. Environ. Manag. 2022, 69, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, Y. Influence Measurement of Rapid Urbanization on Agricultural Production Factors Based on Provincial Panel Data. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2019, 67, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2021; The Department of Economic and Social Affairs, United Nations Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2021.
- Wang, Y.; Zang, L.; Araral, E. The Impacts of Land Fragmentation on Irrigation Collective Action: Empirical Test of the Social-Ecological System Framework in China. J. Rural Stud. 2020, 78, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, T.; Huang, J.; Zhang, L.; Guan, B.; Huang, Q. Forty Years of Irrigation Development and Reform in China. Aust. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 2020, 64, 126–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Ling, Y.; Shen, T.; Yang, L. How Does Rural Homestead Influence the Hukou Transfer Intention of Rural-Urban Migrants in China? Habitat Int. 2020, 105, 102267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, X.; Xiong, X. Urbanization’s Effects on the Urban-Rural Income Gap in China: A Meta-Regression Analysis. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 104995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Araral, E. The Effects of Migration on Collective Action in the Commons: Evidence from Rural China. World Dev. 2016, 88, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Kong, Y.; Ding, X. How High-Quality Urbanization Affects Utilization Efficiency of Agricultural Water Resources in the Yellow River Basin under Double Control Action? Sustainability 2020, 12, 2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, W.; Liu, W.; Hou, M.; Deng, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, K. Spatial—Temporal Evolution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Agricultural Water Use Efficiency in Northwest China—Based on a Super-DEA Model and a Spatial Panel Econometric Model. Water 2021, 13, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.S.; Qiu, L.F.; Wang, K.; Yang, H.; Shi, Y.Y. An Integrated Analysis of Urbanization-Triggered Cropland Loss Trajectory and Implications for Sustainable Land Management. Cities 2011, 28, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, X.; Ye, C. The Integration of New-Type Urbanization and Rural Revitalization Strategies in China: Origin, Reality and Future Trends. Land 2021, 10, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, J.T.H.; Lok, J.; Gietel-Basten, S.; Koh, K. The Food Environments of Fruit and Vegetable Consumption in East and Southeast Asia: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putra, A.S.; Tong, G.; Pribadi, D.O. Food Security Challenges in Rapidly Urbanizing Developing Countries: Insight from Indonesia. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Meki, M.N.; Kim, S.; Kiniry, J.R. Crop Modeling Application to Improve Irrigation Efficiency in Year-Round Vegetable Production in the Texas Winter Garden Region. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, R.; Kumar, A.; Sandal, S.K.; Sharma, A.; Raina, R.; Thakur, K.S. Water and Nutrient Economy in Vegetable Crops through Drip Fertigation and Mulching Techniques: A Review. J. Plant Nutr. 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi-Pelesaraei, A.; Abdi, R.; Rafiee, S.; Bagheri, I. Determination of Efficient and Inefficient Units for Watermelon Production-a Case Study: Guilan Province of Iran. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2016, 15, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersen, P.; Petersen, N.C. A Procedure for Ranking Efficient Units in Data Envelopment Analysis. Manag. Sci. 1993, 39, 1261–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Ma, P.; Zeng, Y.; Sheng, J. Understanding the Interaction between Regulatory Focus and Message Framing in Determining Chinese Consumers’ Attitudes toward Artificial Meat. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, X.; Sui, B.; Gao, S.; Liu, G.; Wang, T.; Wang, B.; Ning, D.; Bi, W. Regions and Their Typical Paradigms for Soil and Water Conservation in China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 643–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, P.; Tang, J.; Wang, S.; Niu, X.; Zong, P.; Dong, X. Climate Change Projections over China Using Regional Climate Models Forced by Two CMIP5 Global Models. Part II: Projections of Future Climate: Projections of Climate Over China with Multi-RCM Driven by CMIP5 GCM. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, e78–e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jin, J.; Niu, G. Effects of Irrigation on Seasonal and Annual Temperature and Precipitation over China Simulated by the WRF Model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD034222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; McVicar, T.R.; Yang, D. An Analytical Solution for the Impact of Vegetation Changes on Hydrological Partitioning Within the Budyko Framework. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 519–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Miao, C. Urbanization Level in Chinese Counties: Imbalance Pattern and Driving Force. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
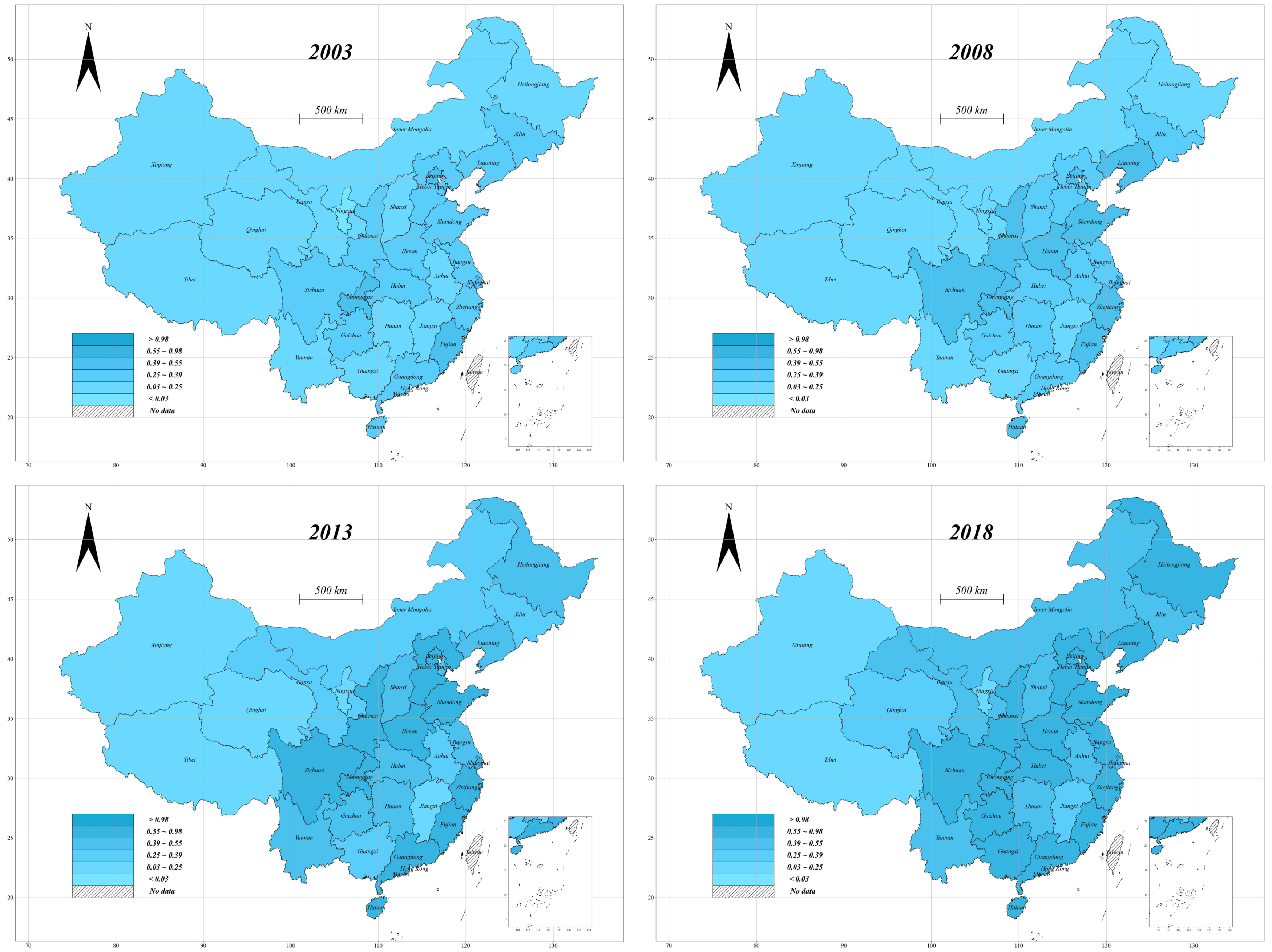
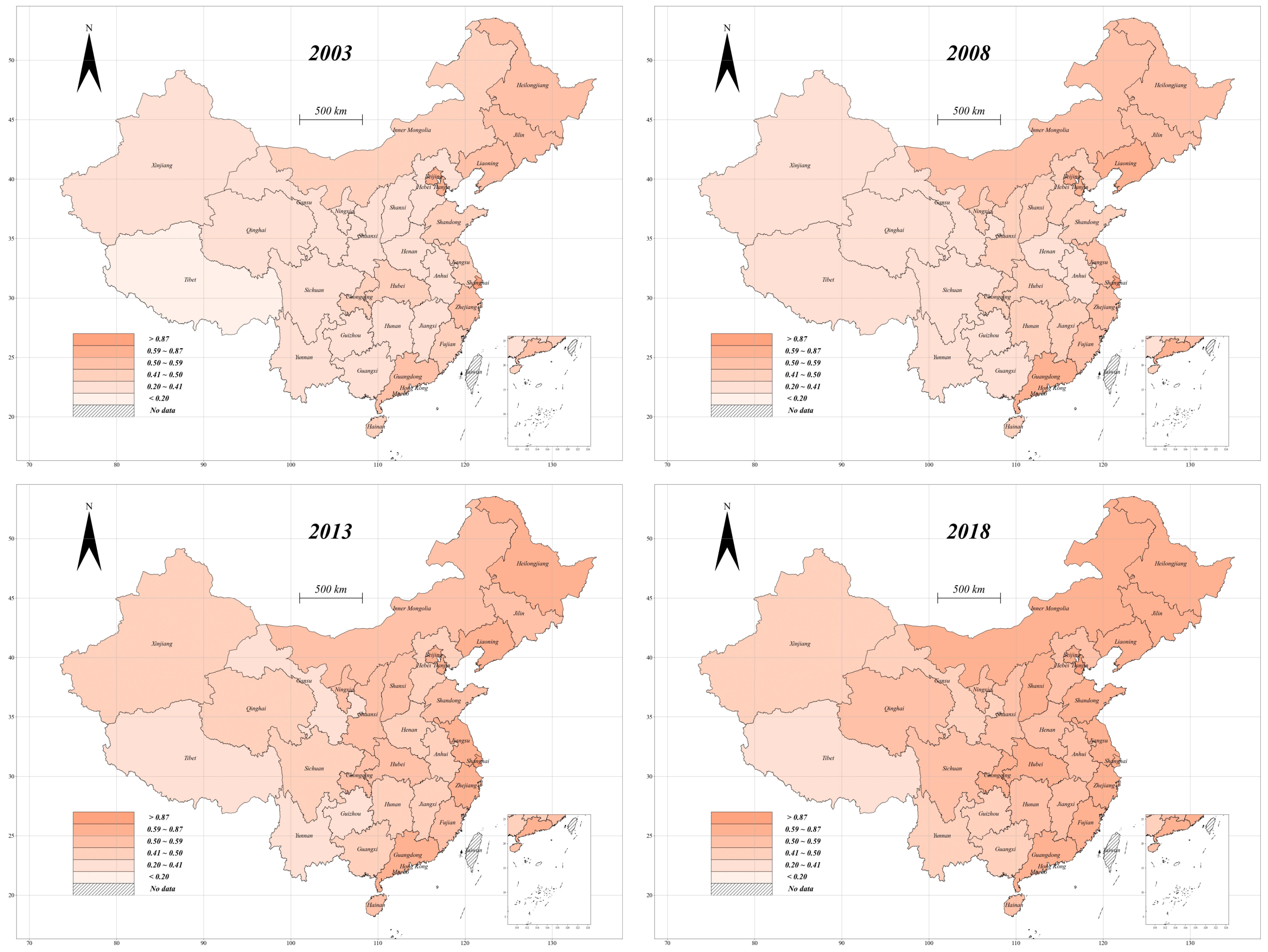
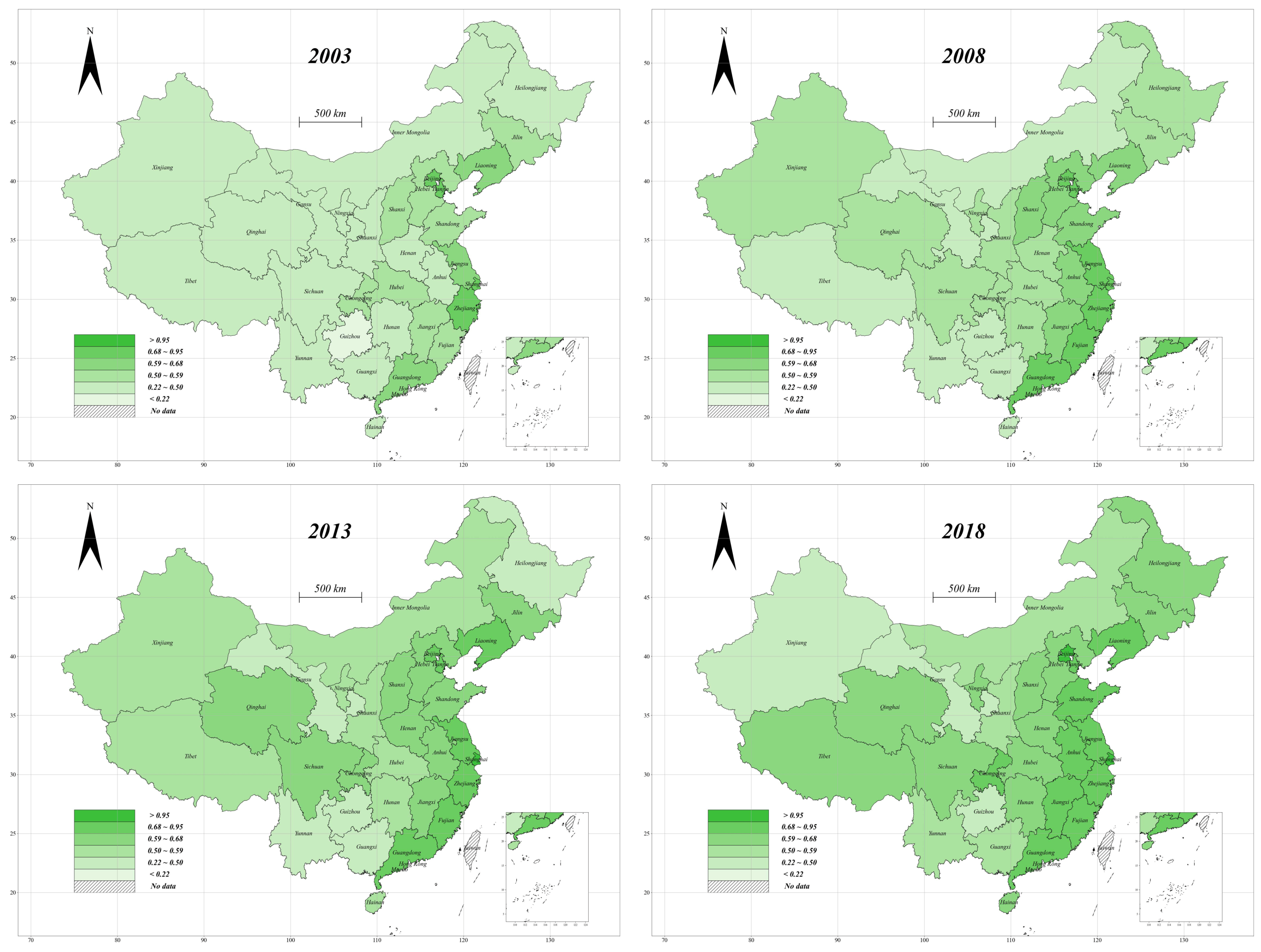
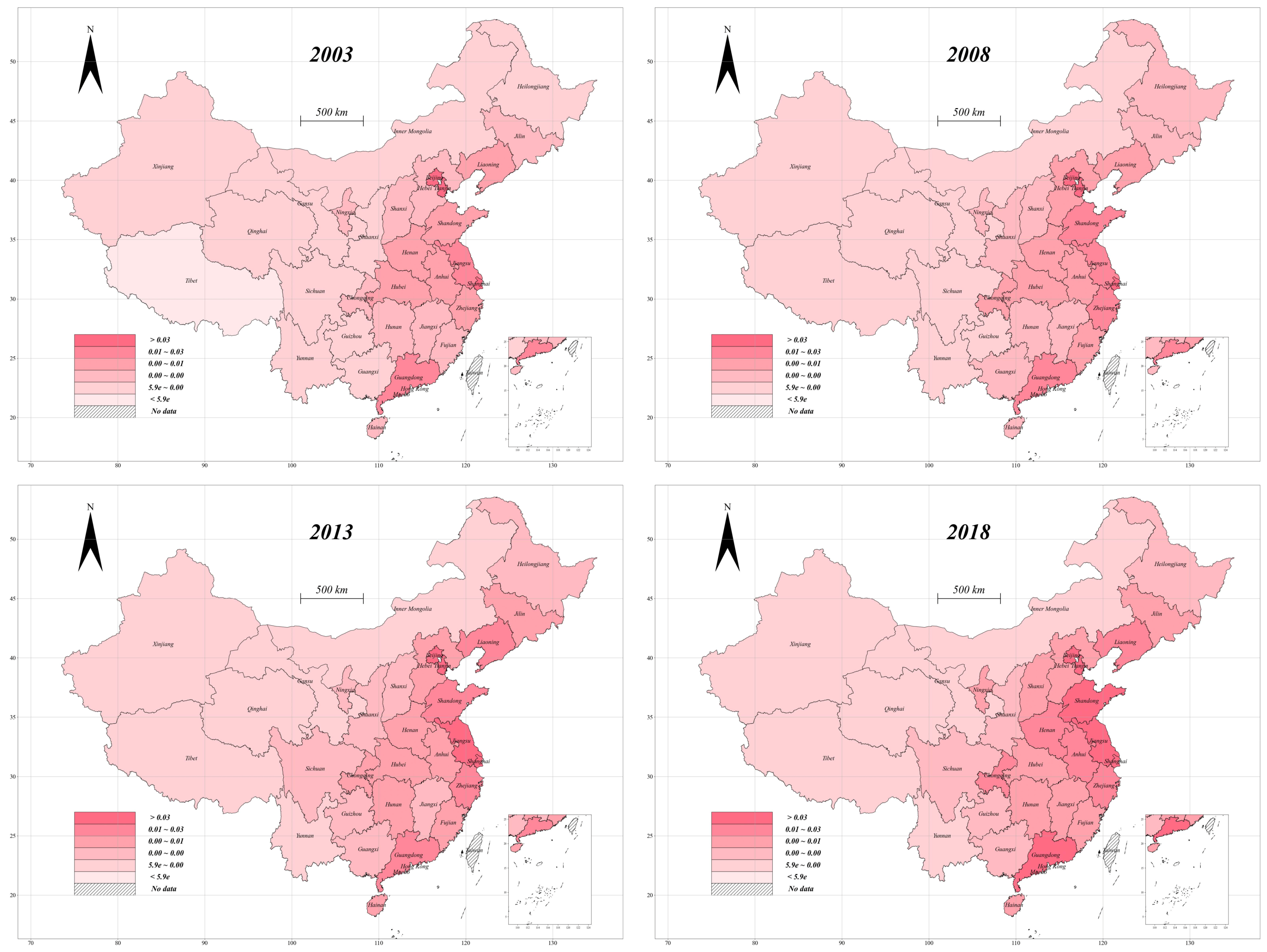
| VarName | Unit/Measure | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent Variable | |||
| AWE | The results of DEA | 0.420 | 0.243 |
| Agricultural Production Input and Output | |||
| Pesticide input | 10 thousand ton | 5.165 | 4.264 |
| Fertilizer input | 10 thousand ton | 173.443 | 140.696 |
| Energy input | 10 thousand ton | 63.562 | 65.914 |
| Water input | 100 million m3 | 119.801 | 101.188 |
| Land input | thousand hectare | 4201.223 | 3038.830 |
| Output Value | 100 million CNY | 899.265 | 787.222 |
| Indicator of Urbanization | |||
| Population Urbanization | Proportion of permanent urban population in the total population | 0.447 | 0.238 |
| Employment Urbanization | Proportion of people employed in the secondary and tertiary industries | 0.610 | 0.160 |
| Land Urbanization | Proportion of urban built-up area to provincial administrative area | 0.017 | 0.030 |
| Control Variable | |||
| Natural disaster | Proportion of the affected area to the cultivated area | 0.221 | 0.151 |
| Industry Output Value | 100 million CNY | 5232.700 | 5303.610 |
| Grain size per capital | Thousand hectare/10 thousand people | 5.931 | 3.222 |
| Water Resource Adequacy | 100 million m3/Thousand hectare | 0.601 | 1.897 |
| Rural income | Log (CNY per Person) | 8.761 | 0.700 |
| Traffic | km3/ Thousand hectare | 3.702 | 3.502 |
| Human Capital | proportion of people with a high school education or above | 0.111 | 0.052 |
| Channel Variable | |||
| Irrigation Facility | Number of irrigation equipment per capita per unit of land | 3.531 | 9.723 |
| Planting Structure | Proportion of vegetable sown area | 0.148 | 0.123 |
| Population Urbanization | Employment Urbanization | Land Urbanization | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) Without Controls | (2) With Controls | (3) Without Controls | (4) With Controls | (5) Without Controls | (6) With Controls | |
| Urban | −0.213 ** | −0.456 ** | −0.174 | −1.419 *** | −23.34 *** | −9.974 *** |
| (0.0888) | (0.180) | (0.347) | (0.351) | (1.467) | (2.005) | |
| Urban2 | 1.121 *** | 0.452 ** | 1.333 *** | 1.168 *** | 90.30 *** | 45.18 *** |
| (0.137) | (0.178) | (0.298) | (0.342) | (7.514) | (8.064) | |
| Natural disaster | −0.0239 | −0.0333 | −0.0131 | |||
| (0.0351) | (0.0347) | (0.0344) | ||||
| Water Resource Adequacy | −0.0938 | −0.245 *** | −0.101 | |||
| (0.0852) | (0.0876) | (0.0829) | ||||
| Industrial Output | 9.75 × 10−6 *** | 1.30 × 10−5 *** | 3.69 × 10−6 | |||
| (2.27 × 10−6) | (2.60 × 10−6) | (2.54 × 10−6) | ||||
| Traffic | −0.0139 *** | −0.00569 | −0.00200 | |||
| (0.00422) | (0.00401) | (0.00466) | ||||
| Grain size per capita | 0.00740 * | 0.0110 *** | 0.0102 ** | |||
| (0.00419) | (0.00408) | (0.00399) | ||||
| Rural income | 0.0567 *** | 0.0563 *** | 0.0510 *** | |||
| (0.0167) | (0.0162) | (0.0160) | ||||
| Rural Human Capital | 0.131 | 0.302 | −0.128 | |||
| −0.366 ** | (0.230) | (0.234) | ||||
| Constant | 0.227 *** | 1.275 * | −0.216 ** | 2.191 *** | 0.130 *** | 0.818 |
| (0.0324) | (0.740) | (0.104) | (0.745) | (0.0371) | (0.740) | |
| Individual FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Time FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R-squared | 0.288 | 0.887 | 0.262 | 0.889 | 0.224 | 0.893 |
| Population Urbanization | Employment Urbanization | Land Urbanization | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
| Urban | −0.548 ** | −1.820 *** | −17.20 *** |
| (0.260) | (0.461) | (2.380) | |
| Urban2 (squared) | 0.722 *** | 1.262 *** | 56.00 *** |
| (0.244) | (0.407) | (7.457) | |
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| F statistic | 61.21 *** | 60.59 *** | 64.09 *** |
| Urbanization | AWE | Planting Structure | Irrigation Facilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Population Urbanization | |||
| Panel A: High urbanization | |||
| Urbanization | 0.283 *** | 0.361 *** | 0.481 *** |
| (0.0766) | (0.0459) | (0.0395) | |
| Planting Structure | 0.122 ** | ||
| (0.0527) | |||
| Irrigation Facilities | 0.129 ** | ||
| (0.0564) | |||
| Panel B: Low urbanization | |||
| Urbanization | −0.0982 * | 0.0551 | −0.0259 |
| (0.0551) | (0.0677) | (0.0679) | |
| Planting Structure | 0.143 ** | ||
| (0.0642) | |||
| Irrigation Facilities | −0.112 ** | ||
| (0.050) | |||
| Employment Urbanization | |||
| Panel C: High urbanization | |||
| Urbanization | 0.0485 | 0.461 *** | 0.420 *** |
| (0.0764) | (0.0401) | (0.0430) | |
| Planting Structure | 0.174 ** | ||
| (0.0522) | |||
| Irrigation Facilities | 0.107 * | ||
| (0.0581) | |||
| Panel D: Low urbanization | |||
| Urbanization | −0.378 *** | 0.0301 | 0.0182 |
| (0.0702) | (0.0604) | (0.0679) | |
| Planting Structure | 0.178 ** | ||
| (0.0627) | |||
| Irrigation Facilities | −0.125 ** | ||
| (0.0517) | |||
| Land Urbanization | |||
| Panel E: High urbanization | |||
| Urbanization | 0.240 ** | 0.409 *** | 0.749 *** |
| (0.104) | (0.0408) | (0.0191) | |
| Planting Structure | 0.152 *** | ||
| (0.0484) | |||
| Irrigation Facilities | 0.572 *** | ||
| (0.0621) | |||
| Panel F: Low urbanization | |||
| Urbanization | −0.344 *** | 0.0478 | 0.0509 |
| (0.0614) | (0.0556) | (0.0764) | |
| Planting Structure | 0.376 *** | ||
| (0.0657) | |||
| Irrigation Facilities | −0.103 * | ||
| (0.0547) | |||
| Population Urbanization | Employment Urbanization | Land Urbanization | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panel A | Panel B | Panel A | Panel B | Panel A | Panel B | |
| RMSEA | 0.022 | 0.025 | 0.022 | 0.021 | 0.018 | 0.021 |
| SRMR | 0.009 | 0.013 | 0.075 | 0.012 | 0.080 | 0.0102 |
| CFI | 0.957 | 0.953 | 0.956 | 0.961 | 0.978 | 0.971 |
| Population Urbanization | Employment Urbanization | Land Urbanization | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High | Low | High | Low | High | Low | |
| Direct effects | 0.283 *** | −0.0982 * | 0.0485 | −0.378 *** | 0.240 ** | −0.344 *** |
| (0.0766) | (0.0551) | (0.0764) | (0.0702) | (0.104) | (0.0614) | |
| Indirect effects | 0.106 *** | 0.0109 | 0.125 ** | 0.0031 | 0.490 * | −0.003 |
| (0.0315) | (0.0132) | (0.0321) | (0.0025) | (0.259) | (0.009) | |
| Total effects | 0.388 *** | −0.0982 * | 0.125 ** | −0.378 *** | 0.730 ** | −0.344 *** |
| (0.0788) | (0.0551) | (0.0321) | (0.0702) | (0.410) | (0.0614) | |
| Indirect effects/ Total effects | 0.273 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.671 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Shi, H.; Ma, P.; Zhu, S.; Xu, H. Understanding the Mechanism of Urbanization Affect Agricultural Water Efficiency: Evidence from China. Water 2022, 14, 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142176
Li D, Shi H, Ma P, Zhu S, Xu H. Understanding the Mechanism of Urbanization Affect Agricultural Water Efficiency: Evidence from China. Water. 2022; 14(14):2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142176
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Deyang, Hongxu Shi, Peihua Ma, Shuning Zhu, and Hao Xu. 2022. "Understanding the Mechanism of Urbanization Affect Agricultural Water Efficiency: Evidence from China" Water 14, no. 14: 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142176






