Economic Assessment of Energy Consumption in Wastewater Treatment Plants: Applicability of Alternative Nature-Based Technologies in Portugal
Abstract
1. Introduction
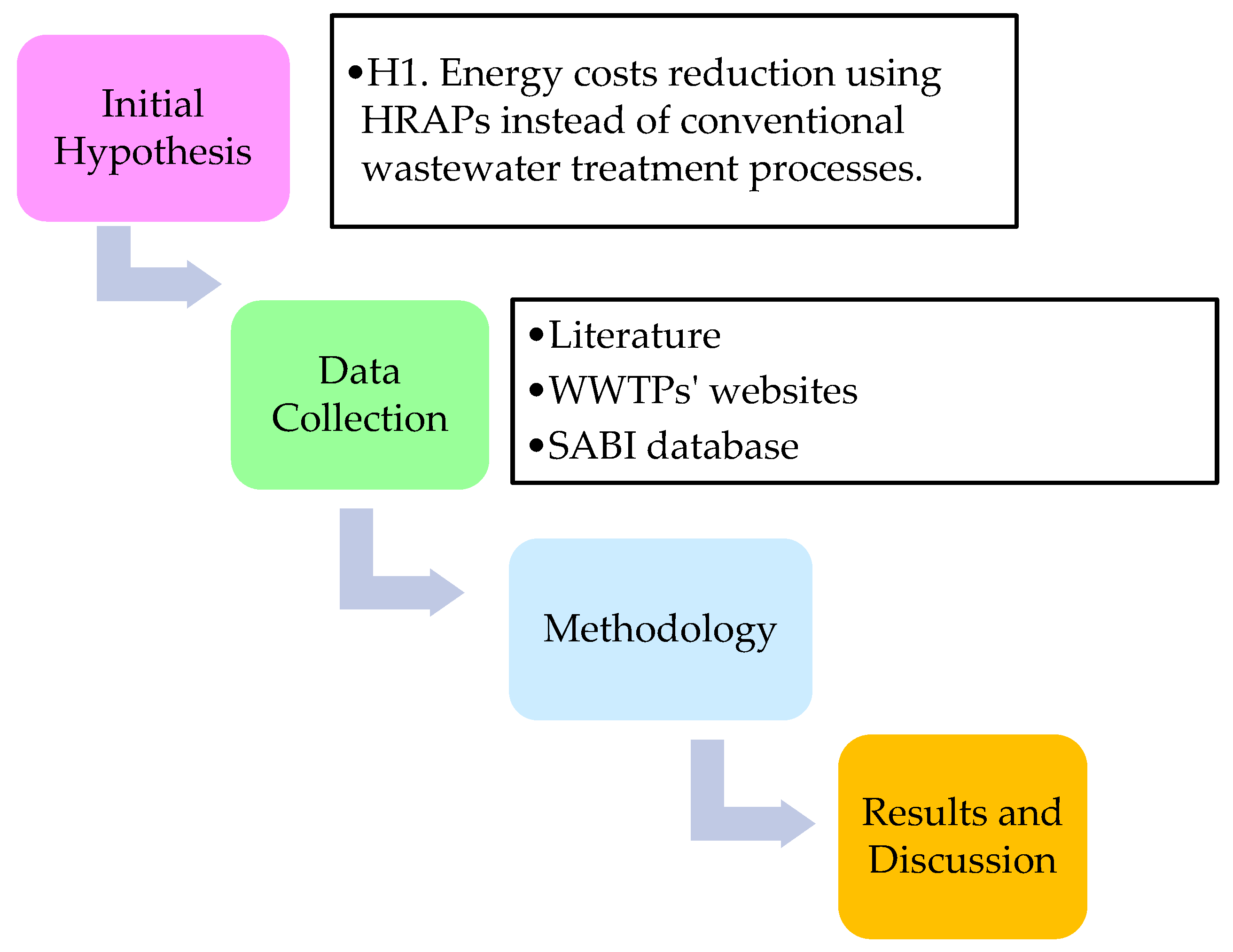
2. Material and Methods
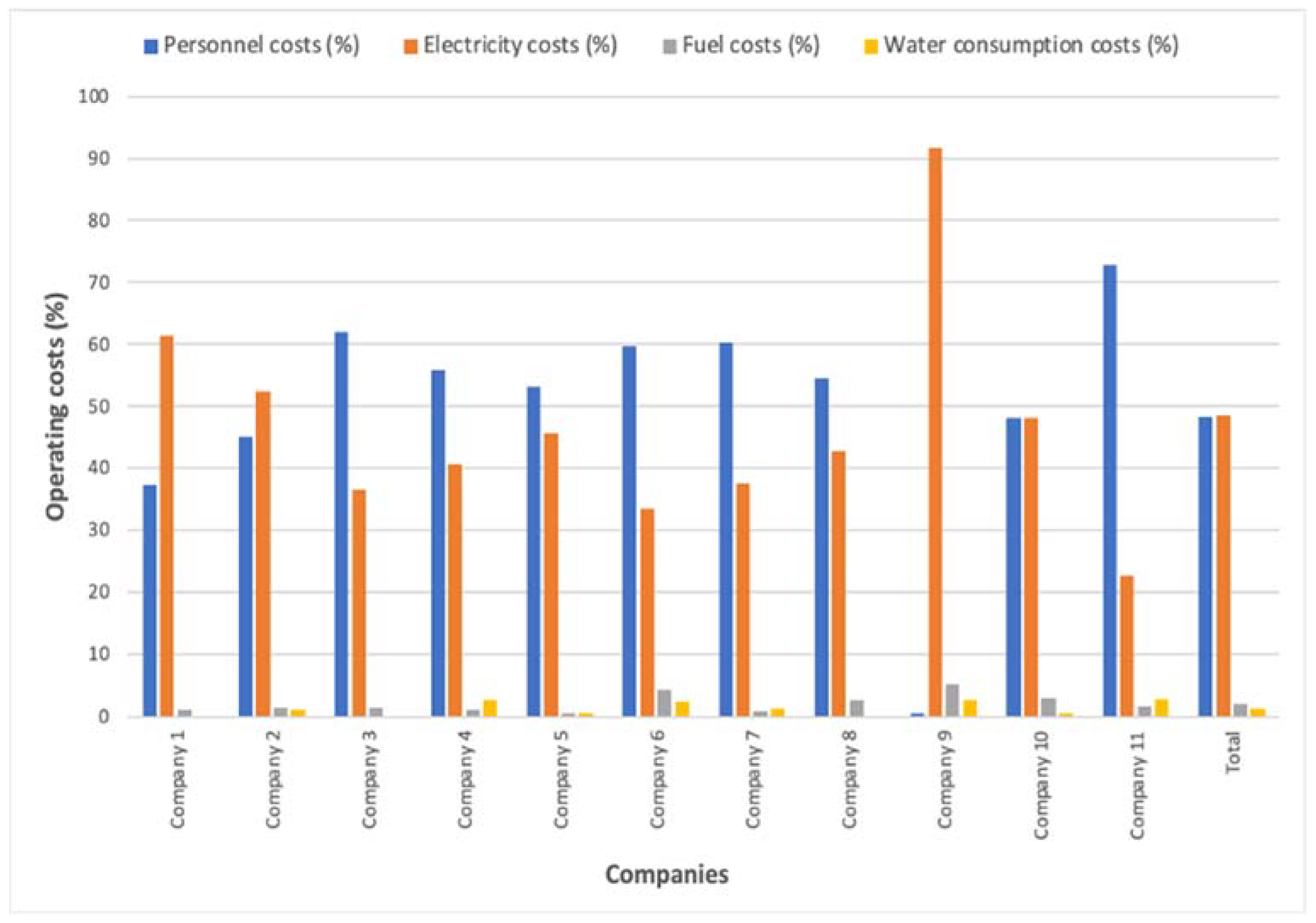
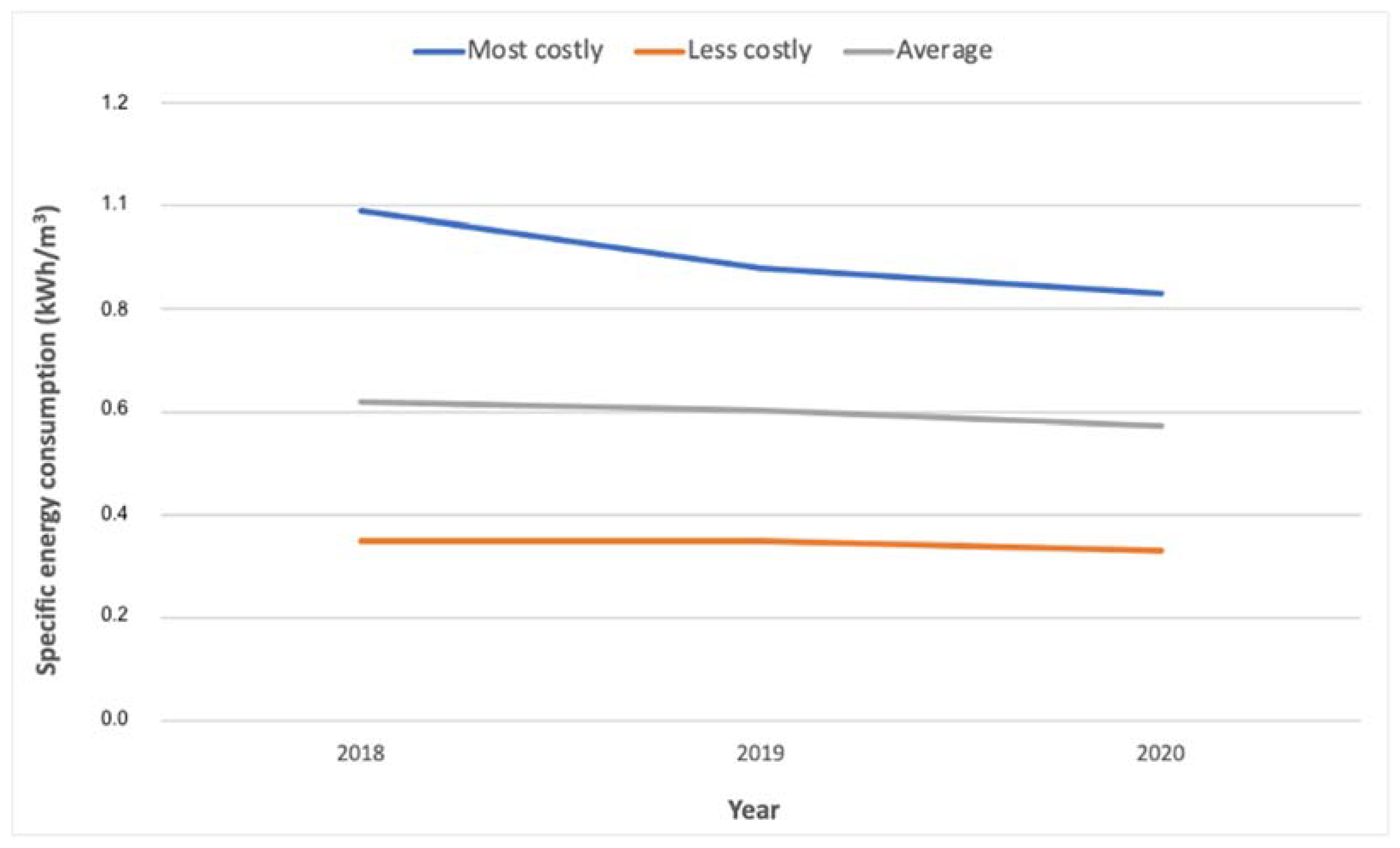
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gandiglio, M.; Lanzini, A.; Soto, A.; Leone, P.; Santarelli, M. Enhancing the Energy Efficiency of Wastewater Treatment Plants through Co-digestion and Fuel Cell Systems. Front. Environ. Sci. 2017, 5, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, P.E.; Mainardis, M.; Moretti, A.; Cottes, M. 100% renewable wastewater treatment plants: Techno-economic assement using a modelling and optimization approach. Energy Convers. Manage. 2021, 239, 114214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqualitrans Project. Available online: http://www.inega.gal/informacion/proxectos_europeos/aqualitrans.html (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Nogueira, R.; Brito, A.; Machado, A.; Janknecht, P.; Salas, J.; Vera, L.; Martel, G. Economic and environmental assessment of small and decentralized wastewater treatment systems. Desalin. Water Treat. 2009, 4, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, M.; Wang, P.; Wang, G.; Zou, W.; Zhou, G. Assessment of energy consumption of municipal wastewater treatment plants in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, D.L.; Howard-Williams, C.; Turnbull, M.H.; Broady, P.A.; Craggs, R.J. Seasonal variation in light utilisation, biomass production and nutrient removal by wastewater microalgae in a full-scale high-rate algal pond. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 1317–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Białowiec, A.; Albuquerque, A.; Randerson, P.F. The influence of evapotranspiration on vertical flow subsurface constructed wetland performance. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 67, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, C.; Albuquerque, A.; Amaral, L.; Nogueira, R. Effectiveness and Temporal Variation of a Full-Scale Horizontal Constructed Wetland in Reducing Nitrogen and Phosphorus from Domestic Wastewater. ChemEngineering 2018, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sátiro, J.; Cunha, A.; Gomes, A.P.; Simões, R.; Albuquerque, A. Optimization of Microalgae–Bacteria Consortium in the Treatment of Paper Pulp Wastewater. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanaathan, S.; Perumal, P.K.; Sundaram, S. Integrated Approach for Carbon Sequestration and Wastewater Treatment Using Algal–Bacterial Consortia: Opportunities and Challenges. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, A.; Malik, S.; Zhu, H.; Xu, J.; Nawaz, M.Z.; Nawaz, S.; Alam, A.; Mehmood, M.A. Cultivating microalgae in wastewater for biomass production, pollutant removal, and atmospheric carbon mitigation; a review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, D.L.; Park, J.; Ralph, P.J.; Craggs, R.J. Improved microalgal productivity and nutrient removal through operating wastewater high rate algal ponds in series. Algal Res. 2019, 47, 101850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbib, Z.; Ruiz, J.; Álvarez-Díaz, P.; Garrido-Pérez, M.D.C.; Perales, J.A. Capability of different microalgae species for phytoremediation processes: Wastewater tertiary treatment, CO2 bio-fixation and low cost biofuels production. Water Res. 2014, 49, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arashiro, L.T.; Montero, N.; Ferrer, I.; Acién, F.G.; Gómez, C.; Garfí, M. Life cycle assessment of high rate algal ponds for wastewater treatment and resource recovery. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 1118–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baena-Moreno, F.M.; Rodríguez-Galán, M.; Vega, F.; Reina, T.R.; Vilches, L.; Navarrete, B. Understanding the influence of the alkaline cation K + or Na + in the regeneration efficiency of a biogas upgrading unit. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 1578–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.N.; Kumar, J.; Vu, M.T.; Mohammed, J.A.; Pathak, N.; Commault, A.S.; Sutherland, D.; Zdarta, J.; Tyagi, V.K.; Nghiem, L.D. Biomethane production from anaerobic co-digestion at wastewater treatment plants: A critical review on development and innovations in biogas upgrading techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 765, 142753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon, C.; Colla, M.; Jossart, J.-M.; Hemelleers, N.; Martin, A.; Aveni, N.; Caferri, C. European Bioenergy Outlook 2019; Biogas: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Prussi, M.; Padella, M.; Conton, M.; Postma, E.D.; Lonza, L. Review of technologies for bio methane production and assessment of EU transport share in 2030. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 222, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baena-Moreno, F.M.; Reina, T.; Rodríguez-Galán, M.; Navarrete, B.; Vilches, L.F. Synergizing carbon capture and utilization in a biogas upgrading plant based on calcium chloride: Scaling-up and profitability analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 758, 143645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baena-Moreno, F.M.; Rodríguez-Galán, M.; Reina, T.R.; Zhang, Z.; Vilches, L.F.; Navarrete, B. Understanding the effect of Ca and Mg ions from wastes in the solvent regeneration stage of a biogas upgrading unit. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 691, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfí, M.; Flores, L.; Ferrer, I. Life Cycle Assessment of wastewater treatment systems for small communities: Activated sludge, constructed wetlands and high rate algal ponds. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 161, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.L.; Pérez, B.V.; Damgaard, A.; Plósz, B.G.; Rygaard, M. Life cycle assessment as development and decision support tool for wastewater resource recovery technology. Water Res. 2016, 88, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maga, D. Life cycle assessment of bio methane produced from microalgae grown in municipal wastewater. Biomass Convers. Bioref. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlheb, N.; van Afferden, M.; Lara, E.; Arbib, Z.; Conthe, M.; Poitzsch, C.; Becker, M.Y. Assessing the life-cycle sustainability of algae and bacteria-based wastewater treatment systems: High-rate algae pond and sequencing batch reactor. J. Environ. Manage. 2020, 264, 110459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, S.; Coutinho, L.; Brito, A.; Nogueira, R.; Machado, A.; Salas, J.; Póvoa, C. Cost-effectiveness analysis for sustainable wastewater engineering and water resources management: A case study at Minho-Lima river basins (Portugal). Desalin. Water Treat. 2009, 4, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mesquita, M.C.; Albuquerque, A.; Amaral, L.; Nogueira, R. Effect of vegetation on the performance of horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands with lightweight expanded clay aggregates. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 10, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.; Lisboa, I.; Eugénio, T. Economic Sustainability in Wastewater Treatment Companies: A Regional Analysis for the Iberian Peninsula. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rego, R. Performance Analysis of the Wastewater Treatment Plants Using a Metabolism Model. Master’s Thesis, IST, University of Lisbon, Lisbon, Portugal, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno, R.; Correia, M.; Martins, F. Energy and environmental performance of wastewater treatment plants: A statistical approach. Procedia 2017, 136, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkmenler, H. Investigation of energy efficiency in Gebze Wastewater Treatment Plant. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 6557–6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siatou, A.; Manali, A.; Gikas, P. Energy Consumption and Internal Distribution in Activated Sludge Wastewater Treatment Plants of Greece. Water 2020, 12, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, S.; Hospido, A.; Lema, J.; Mauricio-Iglesias, M. A systematic methodology for the robust quantification of energy efficiency at wastewater treatment plants featuring Data Envelopment Analysis. Water Res. 2018, 141, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, B.J.; Rodrigues, E.; Gaspar, A.R.; Gomes, A. Energy performance factors in wastewater treatment plants: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 322, 129107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamais, D.; Noutsopoulos, C.; Dimopoulou, A.; Stasinakis, A.; Lekkas, T.D. Wastewater treatment process impact on energy savings and greenhouse gas emissions. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 71, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Dzakpasu, M.; Yang, B.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.C. A novel index of total oxygen demand for the comprehensive evaluation of energy consumption for urban wastewater treatment. Appl. Energy 2019, 236, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslinger, J.; Lindtner, S.; Krampe, J. Operating costs and energy demand of wastewater treatment plants in Austria: Benchmarking results of the last 10 years. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 2620–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schopf, K.; Judex, J.; Schmid, B.; Kienberger, T. Modelling the bioenergy potential of municipal wastewater treatment plants. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 2613–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, N.; Pearce, P.; Farrow, J.; Thorpe, R.B.; Kirkby, N.F. Environmental & economic life cycle assessment of current & future sewage sludge to energy technologies. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasco-Correa, J.; Khanal, S.; Manandhar, A.; Shah, A. Anaerobic digestion for bioenergy production: Global status, environmental and techno-economic implications, and government policies. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baena-Moreno, F.; Malico, I.; Marques, I. Promoting sustainability: Wastewater treatment plants as a source of bio methane in regions far from a high-pressure grid. the real portuguese case study. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo, P.K.; Zhang, Q.; Mihelcic, J.R. Quantifying benefits of resource recovery from sanitation provision in a developing world setting. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 131, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldırım, M.; Topkaya, B. Assessing Environmental Impacts of Wastewater Treatment Alternatives for Small-Scale Communities. CLEAN Soil Air Water 2011, 40, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozkošný, M.; Kriška, M.; Šálek, J.; Bodík, I.; Istenič, D. Natural Technologies of Wastewater Treatment; Global Water Partnership Central and Eastern Europe: Stockholm, Sweden, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, A.; Simon, M.; Burkitt, T. Assessing the environmental impact of two options for small-scale wastewater treatment: Comparing a reedbed and an aerated biological filter using a life cycle approach. Ecol. Eng. 2003, 20, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Toja, Y.; Alfonsín, C.; Amores, M.J.; Aldea, X.; Marín, D.; Moreira, M.T.; Feijoo, G. Beyond the conventional life cycle inventory in wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 553, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Webber, M.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, W. Alternative water supply solutions: China’s South-to-North-water-diversion in Jinan. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 276, 111337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Source | Technology | SEC (kWh/m3) |
|---|---|---|
| Garfi et al. [21] | HRAP | 0.25 |
| Activated sludge | 1.26 | |
| Arashiro et al. [14] | HRAP + biogas production | 0.06 |
| HRAP + biofertilizer production | 0.08 | |
| Activated sludge | 0.89 | |
| Kohlheb et al. [24] | HRAP | 0.17–0.25 |
| Activated sludge | 0.45 | |
| Rego [28] 1) | Activated sludge | 0.68–0.98 |
| Moreno et al. [29] 1) | Activated sludge aeration with turbines | 0.73 |
| Activated sludge aeration with air bubble | 0.80 | |
| Turkmenler [30] | Activated sludge | 0.38–0.43 |
| Siatou et al. [31] | Activated sludge | 0.90 |
| This study 1) | Activated sludge | 0.57 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos, E.; Albuquerque, A.; Lisboa, I.; Murray, P.; Ermis, H. Economic Assessment of Energy Consumption in Wastewater Treatment Plants: Applicability of Alternative Nature-Based Technologies in Portugal. Water 2022, 14, 2042. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14132042
Santos E, Albuquerque A, Lisboa I, Murray P, Ermis H. Economic Assessment of Energy Consumption in Wastewater Treatment Plants: Applicability of Alternative Nature-Based Technologies in Portugal. Water. 2022; 14(13):2042. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14132042
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos, Eleonora, António Albuquerque, Inês Lisboa, Patrick Murray, and Hande Ermis. 2022. "Economic Assessment of Energy Consumption in Wastewater Treatment Plants: Applicability of Alternative Nature-Based Technologies in Portugal" Water 14, no. 13: 2042. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14132042
APA StyleSantos, E., Albuquerque, A., Lisboa, I., Murray, P., & Ermis, H. (2022). Economic Assessment of Energy Consumption in Wastewater Treatment Plants: Applicability of Alternative Nature-Based Technologies in Portugal. Water, 14(13), 2042. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14132042










