Framework for the Integrated Sustainability Assessment of Irrigation with Marginal Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Contaminant Balance
2.2. Sustainability Indices
2.2.1. Critical Sustainability Factor
2.2.2. Critical Sustainability Time
2.2.3. Discrepancy Factor
3. Example: The Sustainability of Onion Farming in the Netherlands Using Irrigation with Marginal Water
3.1. Input Parameters
| Parameter | Diuron | Isoproturon | Naphthalene | Phosphate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [µg/cm] | [57] | [57] | [57] | [19] |
| [µg/cm] | [61] | [61] | [61] | 10 [65] |
| [µg/cm/y] | [61] | [61] | [61] | [61] |
| [µg/cm/y] | [61] | [61] | [61] | [62] |
| [µg/cm/y] | - | - | [61] | - |
| [µg/cm/y] | [64] | [64] | * | - |
| k [cm/g] | 33 [66] | 5 [44] | [67] | [68] |
| [1/y] | [69] | [70] | [71] | 0 |
| [-] | [72] | [72] | [72] | 0 |
| [-] | 2.68 [60] | 2.87 [60] | 3.30 [60] | - |
| Parameter | Cadmium | Lead | Diclofenac | Metoprolol |
| [µg/cm] | [57] | [57] | [57] | [57] |
| [µg/cm] | [61] | 65 [61] | [61] | [61] |
| [µg/cm/y] | [61] | [61] | [61] | [61] |
| [µg/cm/y] | [61] | [61] | [62] | [61] |
| [µg/cm/y] | - | - | - | - |
| [µg/cm/y] | [73] | [73] | * | * |
| k [cm/g] | 810 [74] | 230 [75] | 1.03 [76] | 17.2 [45] |
| [1/y] | 0 | 0 | [76] | [77] |
| [-] | 0 | 0 | [60] | [72] |
| [-] | −0.07 [78] | −0.57 [78] | 4.51 [60] | 1.88 [60] |
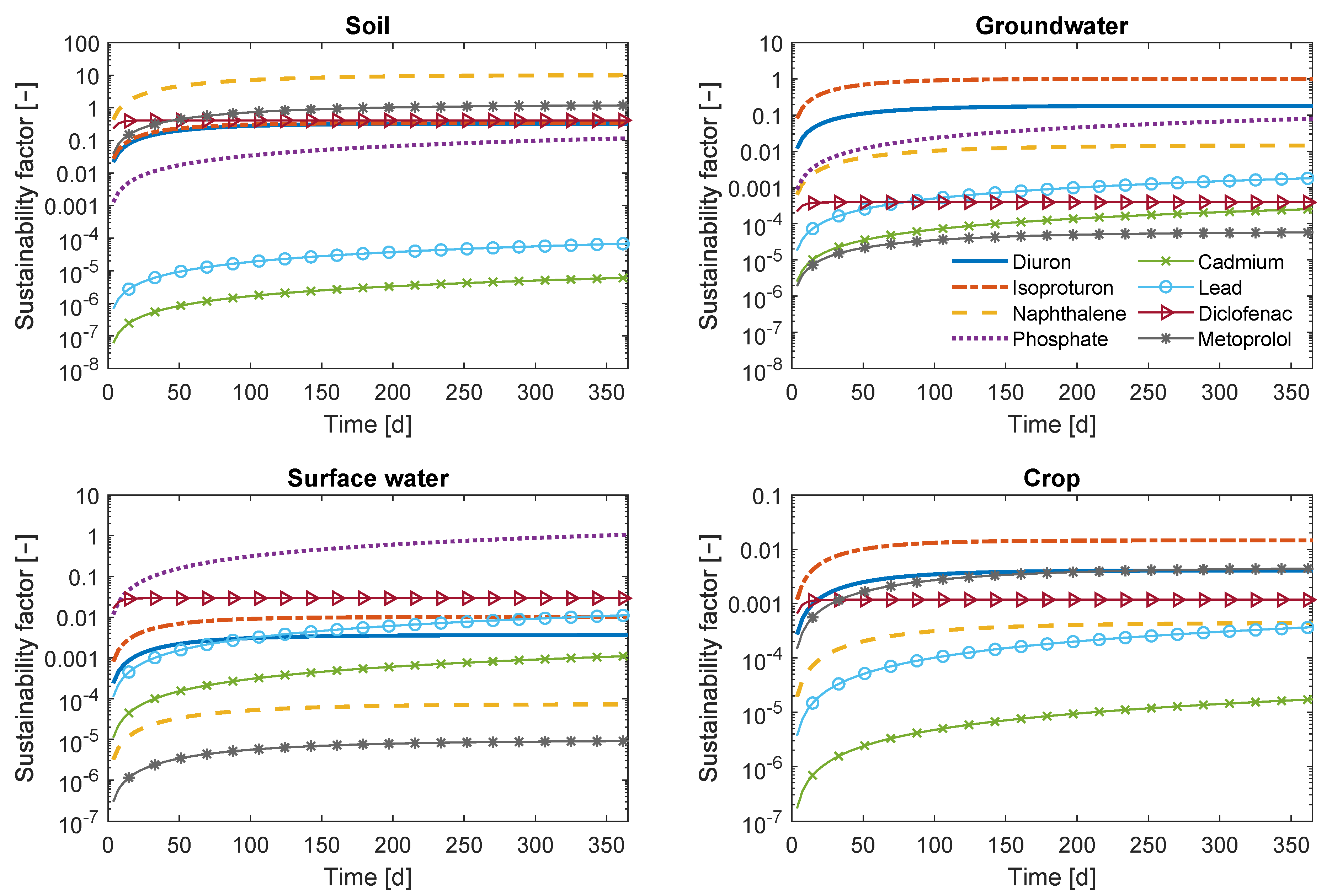
3.2. Results
3.2.1. Sustainability Indices
3.2.2. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CECs | Contaminants of emerging concern |
References
- Sarhadi, A.; Burn, D.H.; Johnson, F.; Mehrotra, R.; Sharma, A. Water resources climate change projections using supervised nonlinear and multivariate soft computing techniques. J. Hydrol. 2016, 536, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Shafiee, M.E.; Berglund, E.Z. Agent-based modeling to simulate the dynamics of urban water supply: Climate, population growth, and water shortages. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 28, 420–434. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). Beyond Scarcity: Power, Poverty and the Global Water Crisis; Human Development Report; Palgrave Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Available online: https://www.undp.org/content/undp/en/home/librarypage/hdr/human-development-report-2006.html (accessed on 22 April 2021).
- UNESCO-WWAP. 1st UN World Water Development Report: Water for People, Water for Life; UNESCO and Berghahn Books: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, A.J.; Stagnitti, F.; Xiong, X.; Kreidl, S.L.; Benke, K.K.; Maher, P. Wastewater Irrigation: The State of Play. Vadose Zone J. 2007, 6, 823–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bixio, D.; Thoeye, C.; De Koning, J.; Joksimovic, D.; Savic, D.; Wintgens, T.; Melin, T. Wastewater reuse in Europe. Desalination 2006, 187, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toze, S. Reuse of effluent water—benefits and risks. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 80, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nakshabandi, G.; Saqqar, M.; Shatanawi, M.; Fayyad, M.; Al-Horani, H. Some environmental problems associated with the use of treated wastewater for irrigation in Jordan. Agric. Water Manag. 1997, 34, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, L.; Harrison, P.E.; Tchobanoglous, G. Wastewater Engineering: Treatment, Disposal, and Reuse; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2004; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Petrović, M.; Gonzalez, S.; Barceló, D. Analysis and removal of emerging contaminants in wastewater and drinking water. Trends Anal. Chem. 2003, 22, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chu, K.H.; Al-Hamadani, Y.A.; Park, C.M.; Jang, M.; Kim, D.H.; Yu, M.; Heo, J.; Yoon, Y. Removal of contaminants of emerging concern by membranes in water and wastewater: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 896–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapanda, F.; Mangwayana, E.; Nyamangara, J.; Giller, K. The effect of long-term irrigation using wastewater on heavy metal contents of soils under vegetables in Harare, Zimbabwe. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 107, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezapour, S.; Samadi, A.; Khodaverdiloo, H. An Investigation of the Soil Property Changes and Heavy Metal Accumulation in Relation to Long-term Wastewater Irrigation in the Semi-arid Region of Iran. Soil Sediment Contam. 2011, 20, 841–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahat, E.; Linderholm, H.W. The effect of long-term wastewater irrigation on accumulation and transfer of heavy metals in Cupressus sempervirens leaves and adjacent soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalali, M.; Merikhpour, H.; Kaledhonkar, M.; Van Der Zee, S.E.A.T.M. Effects of wastewater irrigation on soil sodicity and nutrient leaching in calcareous soils. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyen, Z.; Moore, G.A.; Wrigley, R.J. Soil salinity and sodicity effects of wastewater irrigation in South East Australia. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 99, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunc, T.; Sahin, U. The changes in the physical and hydraulic properties of a loamy soil under irrigation with simpler-reclaimed wastewaters. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 158, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Chen, J.; Shindo, S.; Sakura, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shen, Y. Assessment of groundwater contamination by nitrates associated with wastewater irrigation: A case study in Shijiazhuang region, China. Hydrol. Process. 2004, 18, 2303–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, B.F.F.; He, Z.; Stoffella, P.J.; Montes, C.R.; Melfi, A.J.; Baligar, V.C. Nutrients and Nonessential Elements in Soil after 11 Years of Wastewater Irrigation. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 41, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paruch, A.M. The impact of wastewater irrigation on the chemical quality of groundwater. Water Environ. J. 2014, 28, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, J.; Chen, P.; Ding, R.; Zhang, P.; Li, X. Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistances in soils from wastewater irrigation areas in Beijing and Tianjin, China. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 193, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, E.E.; Andrews, D.M.; Williams, C.F.; Watson, J.E. Vadose Zone Transport of Natural and Synthetic Estrogen Hormones at Penn State’s “Living Filter” Wastewater Irrigation Site. J. Environ. Qual. 2014, 43, 1933–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Wu, W.; Liu, F.; Yin, S.; Bao, Z.; Liu, H. Spatial distribution and migration of nonylphenol in groundwater following long-term wastewater irrigation. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2015, 177–178, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for the Safe Use of Wastewater, Excreta and Greywater; Technical Report; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; Volume 4, Available online: https://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/publications/gsuweg4/en/ (accessed on 22 April 2021).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). Guidelines for Water Reuse; Technical Report EPA/600/R-12/618; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- European Council. Regulation of the European Parliament and of the Council on Minimum Requirements for Water Reuse. 2019. Available online: https://www.consilium.europa.eu/en/press/press-releases/2020/04/07/water-reuse-for-agricultural-irrigation-council-adopts-new-rules/ (accessed on 22 April 2021).
- Rizzo, L.; Krätke, R.; Linders, J.; Scott, M.; Vighi, M.; de Voogt, P. Proposed EU minimum quality requirements for water reuse in agricultural irrigation and aquifer recharge: SCHEER scientific advice. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 2, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, S.; Khan, S.; Hollender, J. Human risk assessment of organic contaminants in reclaimed wastewater used for irrigation. Desalination 2006, 187, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troldborg, M.; Duckett, D.; Allan, R.; Hastings, E.; Hough, R.L. A risk-based approach for developing standards for irrigation with reclaimed water. Water Res. 2017, 126, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.L.; Mecham, B. Long-Term Effects of Recycled Wastewater Irrigation on Soil Chemical Properties on Golf Course Fairways. Agron. J. 2005, 97, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virto, I.; Bescansa, P.; Imaz, M.; Enrique, A. Soil quality under food-processing wastewater irrigation in semi-arid land, northern Spain: Aggregation and organic matter fractions. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2006, 61, 398–407. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Wu, L.; Chang, A.C.; Zhang, Y. Impact of long-term reclaimed wastewater irrigation on agricultural soils: A preliminary assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezapour, S.; Samadi, A. Soil quality response to long-term wastewater irrigation in Inceptisols from a semi-arid environment. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2011, 91, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaghi, S.; Khodaverdiloo, H.; Dashtaki, S.G. Effects of long-term wastewater irrigation on soil physical properties and performance of selected infiltration models in a semi-arid region. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 1778–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, C.T.; Sheng, G.; Manes, M. A Partition-Limited Model for the Plant Uptake of Organic Contaminants from Soil and Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jjemba, P.K. The effect of chloroquine, quinacrine, and metronidazole on both soybean plants and soil microbiota. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrero, F.; Alarcón, J.J. Effects of treated wastewater irrigation on lemon trees. Desalination 2009, 246, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallegos, E.; Warren, A.; Robles, E.; Campoy, E.; Calderon, A.; Sainz, M.G.; Bonilla, P.; Escolero, O. The effects of wastewater irrigation on groundwater quality in Mexico. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candela, L.; Fabregat, S.; Josa, A.; Suriol, J.; Vigués, N.; Mas, J. Assessment of soil and groundwater impacts by treated urban wastewater reuse. A case study: Application in a golf course (Girona, Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 374, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, J.A.; Soliman, M.; Suffet, I.H.M. Human Pharmaceuticals, Hormones, and Personal Care Product Ingredients in Runoff from Agricultural Fields Irrigated with Treated Wastewater. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1625–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jury, W.A.; Russo, D.; Streile, G.; El Abd, H. Evaluation of volatilization by organic chemicals residing below the soil surface. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildenschild, D.; Jensen, K.H. Numerical modeling of observed effective flow behavior in unsaturated heterogeneous sands. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, P.; Van der Zee, S.E.A.T.M.; Leijnse, A. Role of degradation concepts for adsorbing contaminants in context of wastewater irrigation. Vadose Zone J. 2020, 19, e20064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boivin, A.; Cherrier, R.; Schiavon, M. A comparison of five pesticides adsorption and desorption processes in thirteen contrasting field soils. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodešová, R.; Grabic, R.; Kočárek, M.; Klement, A.; Golovko, O.; Fér, M.; Nikodem, A.; Jakšík, O. Pharmaceuticals’ sorptions relative to properties of thirteen different soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moolenaar, S.W.; Van Der Zee, S.E.A.T.M.; Lexmond, T.M. Indicators of the sustainability of heavy-metal management in agro-ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 1997, 201, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Council. Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council. 2006. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A02006R1907-20140410 (accessed on 22 April 2021).
- Van De Craats, D.; Van Der Zee, S.E.A.T.M.; Sui, C.; Van Asten, P.J.A.; Cornelissen, P.; Leijnse, A. Soil sodicity originating from marginal groundwater. Vadose Zone J. 2020, 19, e20010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boekhold, A.E.; Van Der Zee, S.E.A.T.M. Long-term effects of soil heterogeneity on cadmium behaviour in soil. J. Contam. Hydrol. 1991, 7, 371–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, M.F.; Restrepo, I. Wastewater reuse in agriculture: A review about its limitations and benefits. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop evapotranspiration—Guidelines for computing crop water requirements. FAO Irr. Drain. Pap. 1998, 56, 110. [Google Scholar]
- Minasny, B.; McBratney, A.B. The efficiency of various approaches to obtaining estimates of soil hydraulic properties. Geoderma 2002, 107, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service (USDA NRCS). 2014; Soil Bulk Density/Moisture/Aeration. Available online: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_DOCUMENTS/nrcs142p2_053260.pdf (accessed on 22 April 2021).
- Van Der Meer, R.W. Watergebruik in de Land- en Tuinbouw 2017 en 2018; Technical Report Nota 2020-030, Wageningen Economic Research; Wageningen: Gelderland, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Royal Dutch Meteorological Institute (KNMI). Overzicht van de Neerslag en Verdamping in Nederland. 2020. Available online: https://www.knmi.nl/nederland-nu/klimatologie/gegevens/monv (accessed on 22 April 2021).
- Kwaad, F.J.P.M. Summer and winter regimes of runoff generation and soil erosion on cultivated loess soils (The Netherlands). Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1991, 16, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, I.; Gómez-Ramos, M.J.; Agüera, A.; Fernández-Alba, A.R.; García-Reyes, J.F.; Molina-Díaz, A. Chemical evaluation of contaminants in wastewater effluents and the environmental risk of reusing effluents in agriculture. Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 676–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Technical Guidance Document on Risk Assessment, Part II; Report EUR 20418 EN/2; European Chemicals Bureau, Institute for Health and Consumer Protection: Ispra, Italy, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Briggs, G.G.; Bromilow, R.H.; Evans, A.A. Relationships between lipophilicity and root uptake and translocation of non-ionised chemicals by barley. Pestic. Sci. 1982, 13, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q. and Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; Zaslavsky, L.; Zhang, J.; Bolton, E.E. PubChem 2019 update: Improved access to chemical data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D1102–D1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute for Public Health and the Environment (RIVM). Zoeksysteem Risico’s van Stoffen. Available online: https://rvszoeksysteem.rivm.nl/stoffen (accessed on 22 April 2021).
- European Commission. Proposal for a Directive of the European Parliament and of the Council amending Directives 2000/60/EC and 2008/105/EC as Regards Priority Substances in the Field of Water Policy. 2011. Available online: https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/859825c3-d7c7-424b-96dd-84eb700ef0bf (accessed on 22 April 2021).
- Verenigde Telers Akkerbouw (VTA). Opbrengst uien. 2019. Available online: https://www.vtanederland.nl/opbrengst-uien-ongeveer-op-langjarig-gemiddelde (accessed on 22 April 2021).
- European Council. On Maximum Residue Levels of Pesticides in or on Food and Feed of Plant and Animal Origin and Amending Council Directive 91/414/EEC. 2005. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A32005R0396 (accessed on 22 April 2021).
- Bouwer, H.; Idelovitch, E. Quality requirements for irrigation with sewage water. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1987, 113, 516–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wu, X.; Gui, W.; Zhu, G. Adsorption and desorption behavior of herbicide diuron on various Chinese cultivated soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 178, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmo, A.M.; Hundal, L.S.; Thompson, M.L. Sorption of Hydrophobic Organic Compounds by Soil Materials: Application of Unit Equivalent Freundlich Coefficients. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 4363–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debicka, M.; Kocowicz, A.; Weber, J.; Jamroz, E. Organic matter effects on phosphorus sorption in sandy soils. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2016, 62, 840–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouchaud, J.; Neus, O.; Bulcke, R.; Cools, K.; Eelen, H.; Dekkers, T. Soil Dissipation of Diuron, Chlorotoluron, Simazine, Propyzamide, and Diflufenican Herbicides After Repeated Applications in Fruit Tree Orchards. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 39, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.; Jurado-Exposito, M.; Bending, G.; Smith, V. Spatial variability in the degradation rate of isoproturon in soil. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 111, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele-Bruhn, S.; Brümmer, G.W. Kinetics of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon (PAH) Degradation in Long-term Polluted Soils during Bioremediation. Plant Soil 2005, 275, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, R. Compilation of Henry’s law constants (version 4.0) for water as solvent. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 4399–4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutch Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport. Warenwetregeling Verontreinigingen in levensmiddelen. Staatscourant 1999, 30, 11. Available online: https://zoek.officielebekendmakingen.nl/stcrt-1998-61-p8-SC13207.pdf (accessed on 22 April 2021).
- Lee, S.Z.; Allen, H.E.; Huang, C.P.; Sparks, D.L.; Sanders, P.F.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M. Predicting soil-water partition coefficients for cadmium. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 3418–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Z.; Chang, L.; Yang, H.H.; Chen, C.M.; Liu, M.C. Adsorption characteristics of lead onto soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 1998, 63, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wu, L.; Chang, A.C. Degradation and adsorption of selected pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in agricultural soils. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 1299–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodešová, R.; Kočárek, M.; Klement, A.; Golovko, O.; Koba, O.; Fér, M.; Nikodem, A.; Vondráčková, L.; Jakšík, O.; Grabic, R. An analysis of the dissipation of pharmaceuticals under thirteen different soil conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Technical Appendix B, Physico-chemical Properties for TRI Chemicals and Chemical Categories. 2014. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2014-03/documents/tech_app_b_v215.pdf (accessed on 22 April 2021).
- Dubus, I.G.; Brown, C.D.; Beulke, S. Sensitivity analyses for four pesticide leaching models. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2003, 59, 962–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammoglia, S.K.; Brun, F.; Quemar, T.; Moeys, J.; Barriuso, E.; Gabrielle, B.; Mamy, L. Modelling pesticides leaching in cropping systems: Effect of uncertainties in climate, agricultural practices, soil and pesticide properties. Environ. Model. Softw. 2018, 109, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Longuevergne, L.; Scanlon, B.R. Uncertainty in evapotranspiration from land surface modeling, remote sensing, and GRACE satellites. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 1131–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapworth, D.; Baran, N.; Stuart, M.; Ward, R. Emerging organic contaminants in groundwater: A review of sources, fate and occurrence. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 163, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapworth, D.J.; Lopez, B.; Laabs, V.; Kozel, R.; Wolter, R.; Ward, R.; Amelin, E.V.; Besien, T.; Claessens, J.; Delloy, F. Developing a groundwater watch list for substances of emerging concern. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 035004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, L.B.; Keefe, S.H.; Brown, G.K.; Furlong, E.T.; Gray, J.L.; Kolpin, D.W.; Meyer, M.T.; Sandstrom, M.W.; Zaugg, S.D. Persistence and potential effects of complex organic contaminant mixtures in wastewater-impacted streams. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2177–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
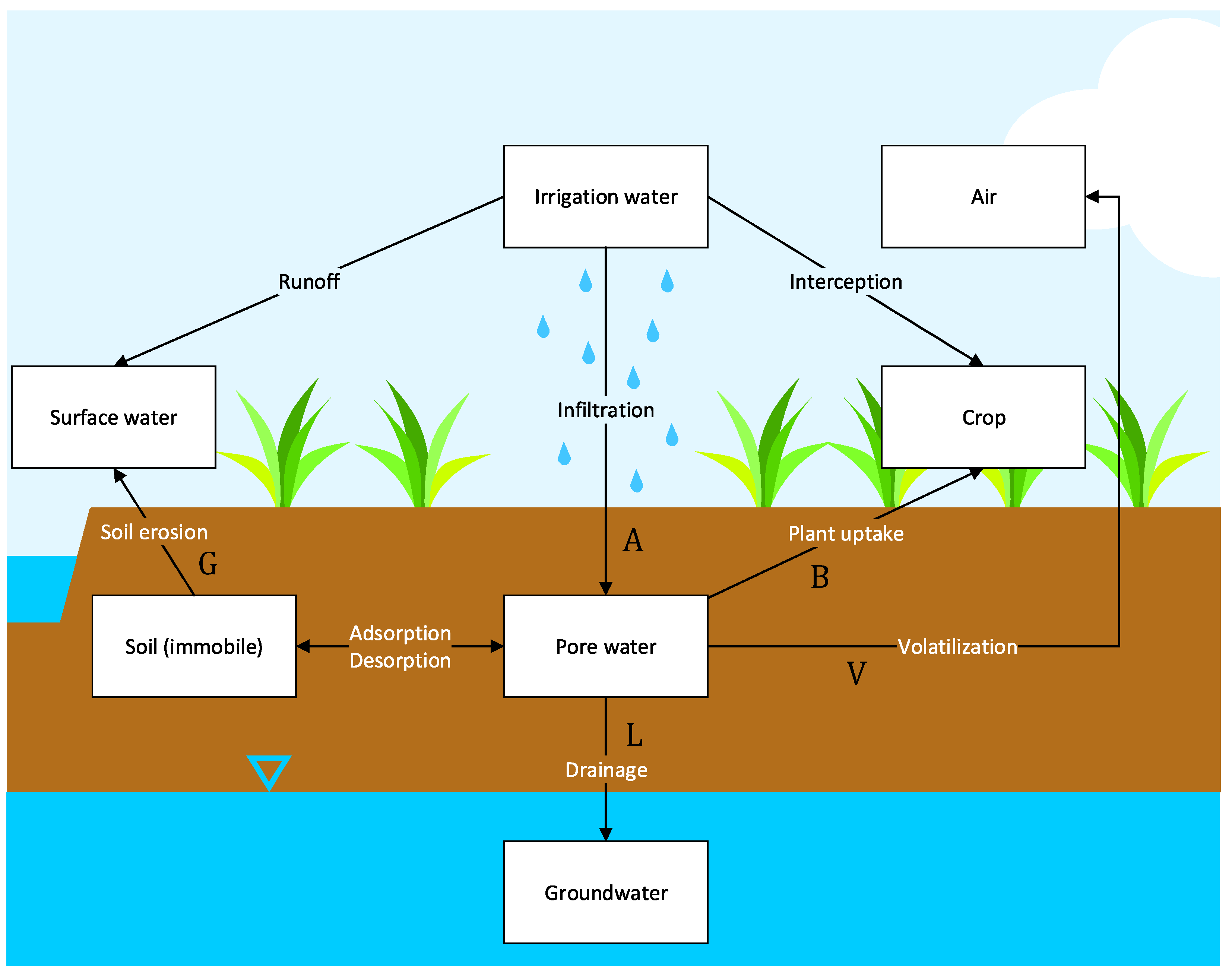

| Parameter | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Field area [cm] | 10 | |
| Irrigation [cm/y] | I | 26.5 [54] |
| Crop evapotranspiration [cm/y] | T | 60.1 [55] |
| Drainage [cm/y] | q | 7.95 |
| Soil erosion [g/cm/y] | E | 0.2031 [56] |
| Root zone depth [cm] | Z | 45 [51] |
| Soil porosity [-] | 0.367 [52] | |
| Soil moisture content [-] | 0.18 | |
| Soil dry bulk density [g/cm] | 1.3 |
| [-] | [-] | [d] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diuron | 0.33 | n/a | |
| Isoproturon | 1.10 | 101 | |
| Naphthalene | 10.17 | 8 | |
| Phosphate | 3.63 | 5.63 | 312 |
| Cadmium | 0.31 | n/a | |
| Lead | 0.68 | 2.79 | 36,556 |
| Diclofenac | 0.41 | n/a | |
| Metoprolol | 1.24 | 185 |
| k | q | T | I | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −10% | +10% | −10% | +10% | −10% | +10% | −10% | +10% | −10% | +10% | |
| Diuron | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.37 | 0.30 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.30 | 0.36 |
| Isoproturon | 1.22 | 1.01 | 1.23 | 1.01 | 1.10 | 1.10 | 1.11 | 1.10 | 0.99 | 1.22 |
| Naphthalene | 10.17 | 10.18 | 11.30 | 9.25 | 10.17 | 10.17 | 10.18 | 10.17 | 9.16 | 11.19 |
| Phosphate | 5.64 | 5.63 | 5.64 | 5.64 | 5.70 | 5.57 | 6.17 | 5.18 | 5.07 | 6.20 |
| Cadmium | 0.35 | 0.29 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 0.32 | 0.31 | 0.32 | 0.31 | 0.28 | 0.35 |
| Lead | 3.03 | 2.59 | 2.80 | 2.80 | 2.83 | 2.76 | 2.82 | 2.77 | 2.52 | 3.08 |
| Diclofenac | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.46 | 0.38 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.37 | 0.46 |
| Metoprolol | 1.24 | 1.24 | 1.38 | 1.13 | 1.24 | 1.24 | 1.24 | 1.24 | 1.12 | 1.36 |
| −10% | +10% | −10% | +10% | −10% | +10% | −10% | +10% | −10% | +10% | |
| Isoproturon | 73 | 208 | 81 | 204 | 101 | 101 | 101 | 102 | n/a | 74 |
| Naphthalene | 8 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 8 |
| Phosphate | 281 | 342 | 312 | 312 | 311 | 312 | 309 | 315 | 350 | 281 |
| Lead | 32,255 | 41,046 | 36,556 | 36,556 | 36,431 | 36,682 | 36,479 | 36,633 | 41,830 | 32,478 |
| Metoprolol | 185 | 184 | 162 | 222 | 185 | 185 | 184 | 185 | 254 | 149 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cornelissen, P.; van der Zee, S.E.A.T.M.; Leijnse, A. Framework for the Integrated Sustainability Assessment of Irrigation with Marginal Water. Water 2021, 13, 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13091168
Cornelissen P, van der Zee SEATM, Leijnse A. Framework for the Integrated Sustainability Assessment of Irrigation with Marginal Water. Water. 2021; 13(9):1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13091168
Chicago/Turabian StyleCornelissen, Pavan, Sjoerd E. A. T. M. van der Zee, and Anton Leijnse. 2021. "Framework for the Integrated Sustainability Assessment of Irrigation with Marginal Water" Water 13, no. 9: 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13091168
APA StyleCornelissen, P., van der Zee, S. E. A. T. M., & Leijnse, A. (2021). Framework for the Integrated Sustainability Assessment of Irrigation with Marginal Water. Water, 13(9), 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13091168






