Evaluating the Performance of Sentinel-1A and Sentinel-2 in Small Waterbody Mapping over Urban and Mountainous Regions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- Cloud/cloud shadows: SAR images are free of cloud-related contamination. However, the optical images are easily affected by clouds and cloud shadows. Thus, it is necessary to select cloudless images through visual or automatic methods [18].
- (2)
- Mountain/built-up shadows: The mountain/skyscraper shadow is caused by similar factors as optical and SAR images: An object blocks the path of direct radiation in optical imaging and the radar beam in the case of SAR. However, unlike optical imagery, in which objects in shadows can be seen because of atmospheric scattering, there is no information in a SAR shadow because there is no return signal. Theoretically, the mountain shadow can be identified by simulating hill-shading with Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) and the solar azimuth and elevation at the time of image acquisition. However, owing to the limitation of DEM resolution and the influence of land cover, using DEM alone is often not enough to eliminate mountain shadows in practice. Thus, ancillary data other than DEM are required.
- (3)
- Flat surfaces: Noises like those made by asphalt, cement surfaces, and roads mainly appear in SAR images rather than in optical images. Generally, the rough surfaces scatter the energy and return a significant amount back to the antenna, resulting in a bright feature. In contrast, the flat surfaces reflect the signal away, resulting in a dark feature. As waterbodies absorb radar energy, they also exhibit a dark feature. Flat surfaces are often misidentified as waterbodies by using images of SAR backscatter coefficients. However, these noises are usually different from waterbodies in infrared bands of optical data.
- (4)
- Ships: The ships have a high reflectivity or backscatter coefficient that may cause “holes” in the waterbody extraction results.
2. Materials and Methods
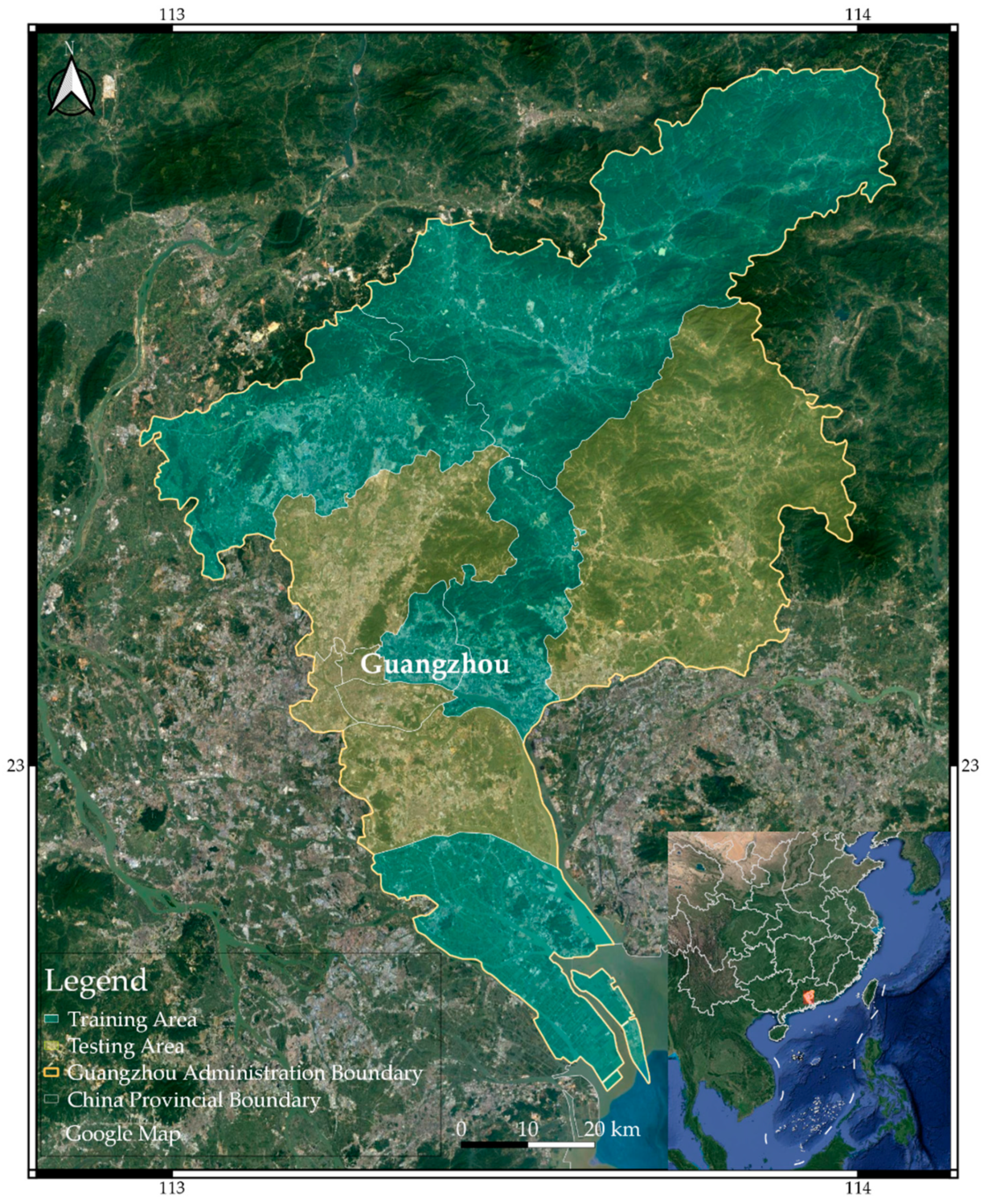
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Sentinel-1A Data and Pre-Processing
2.2.2. Sentinel-2 Data and Pre-Processing
2.2.3. Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) Digital Elevation Model (DEM)
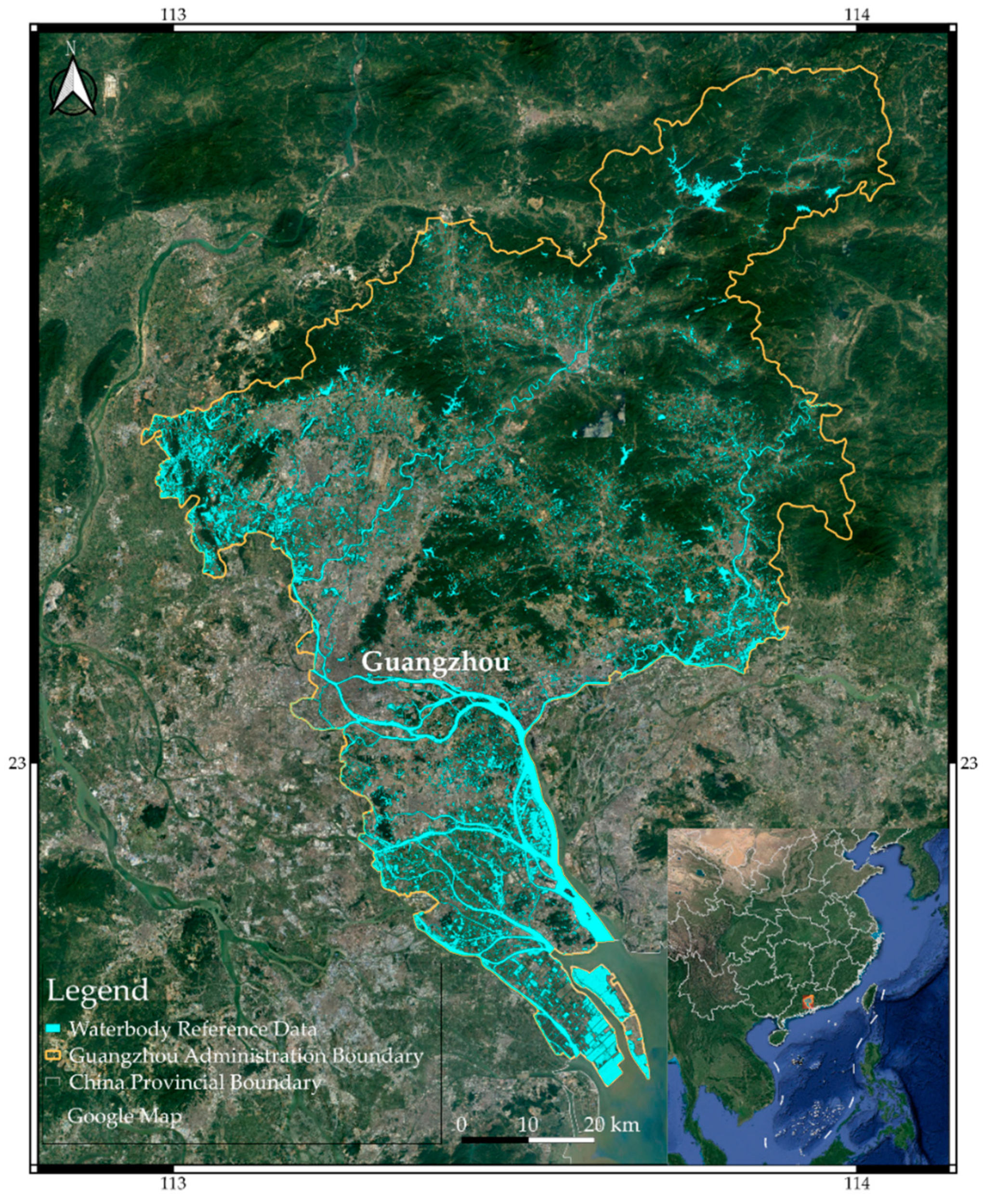
2.2.4. Waterbody Reference Data
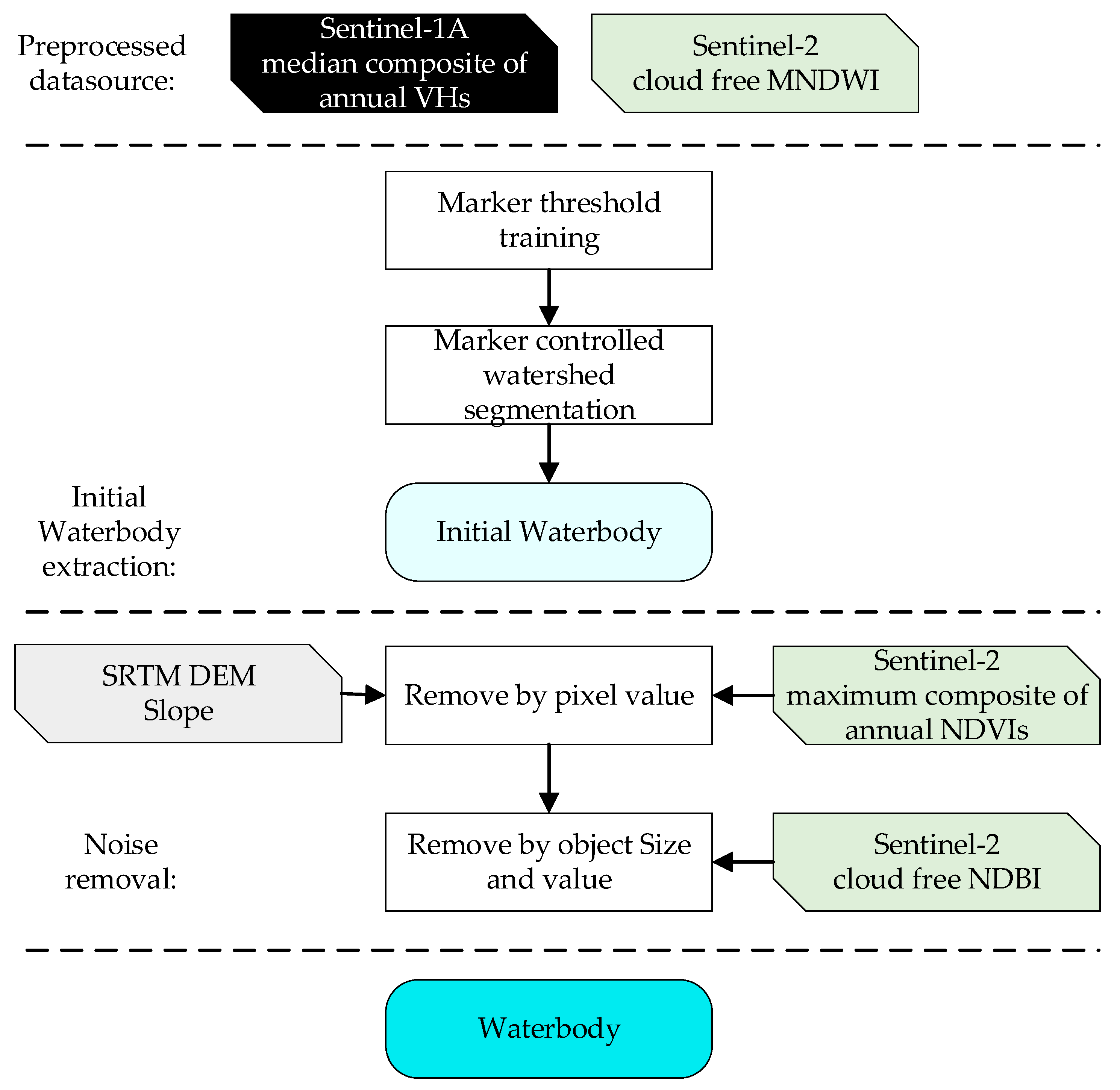
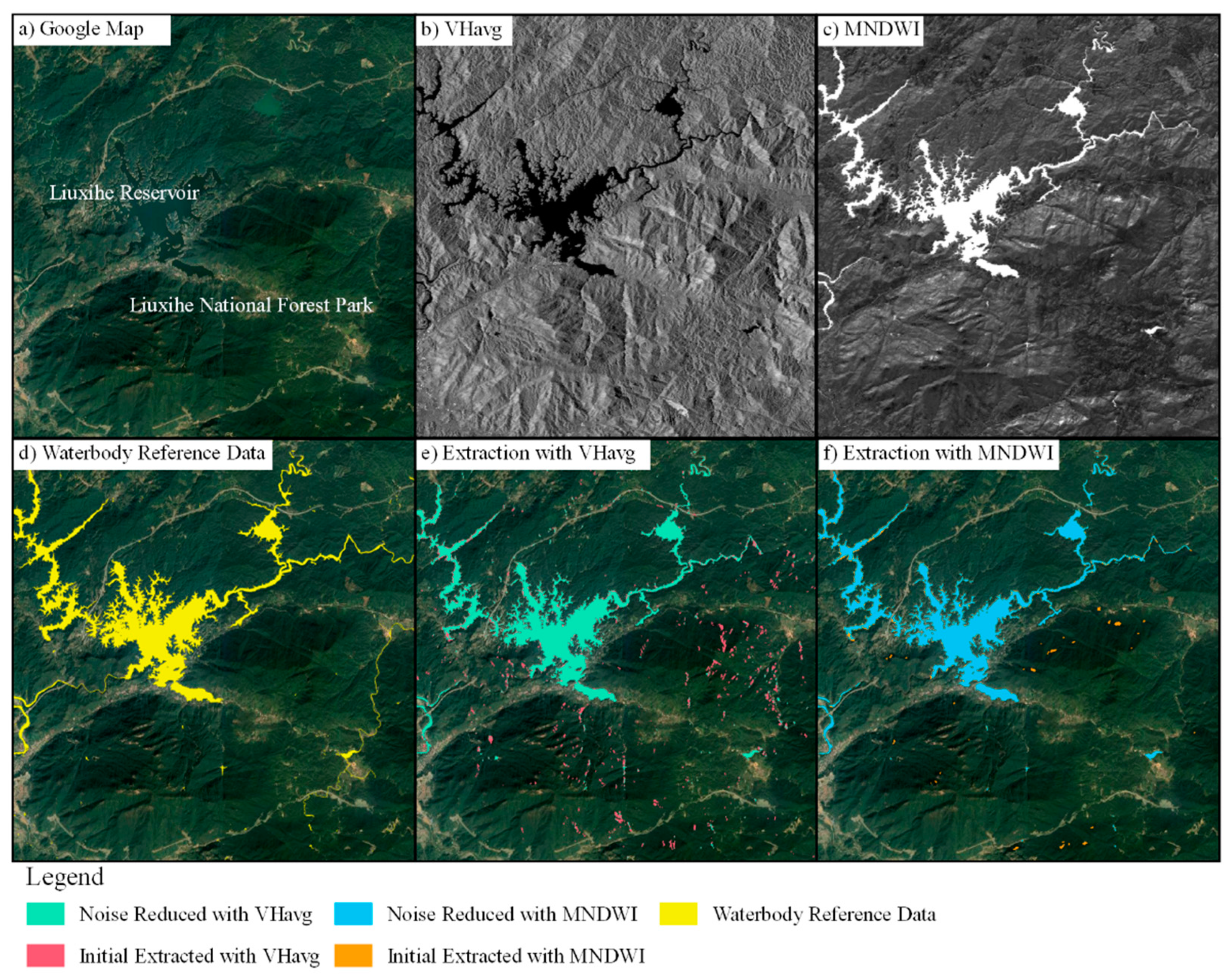
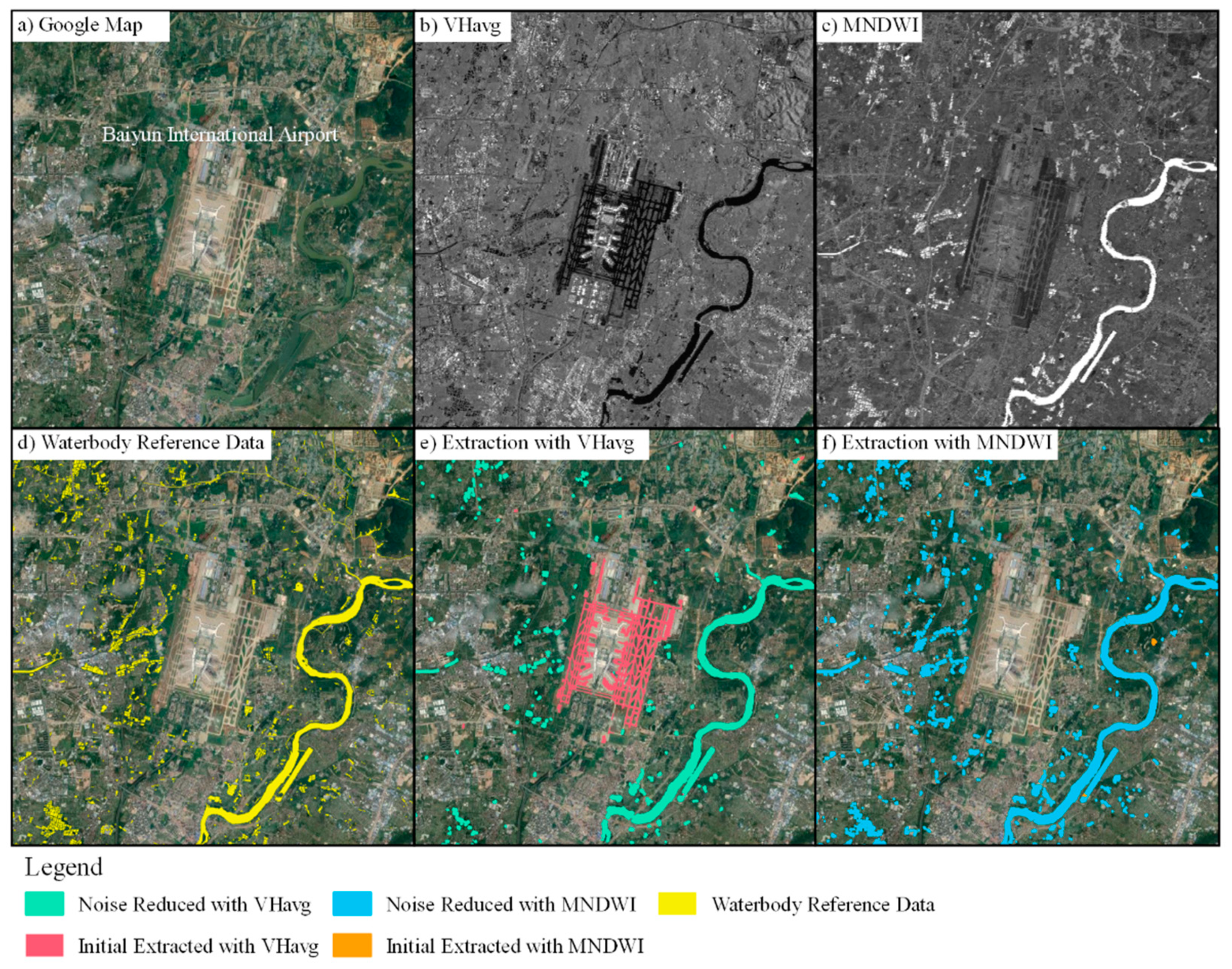
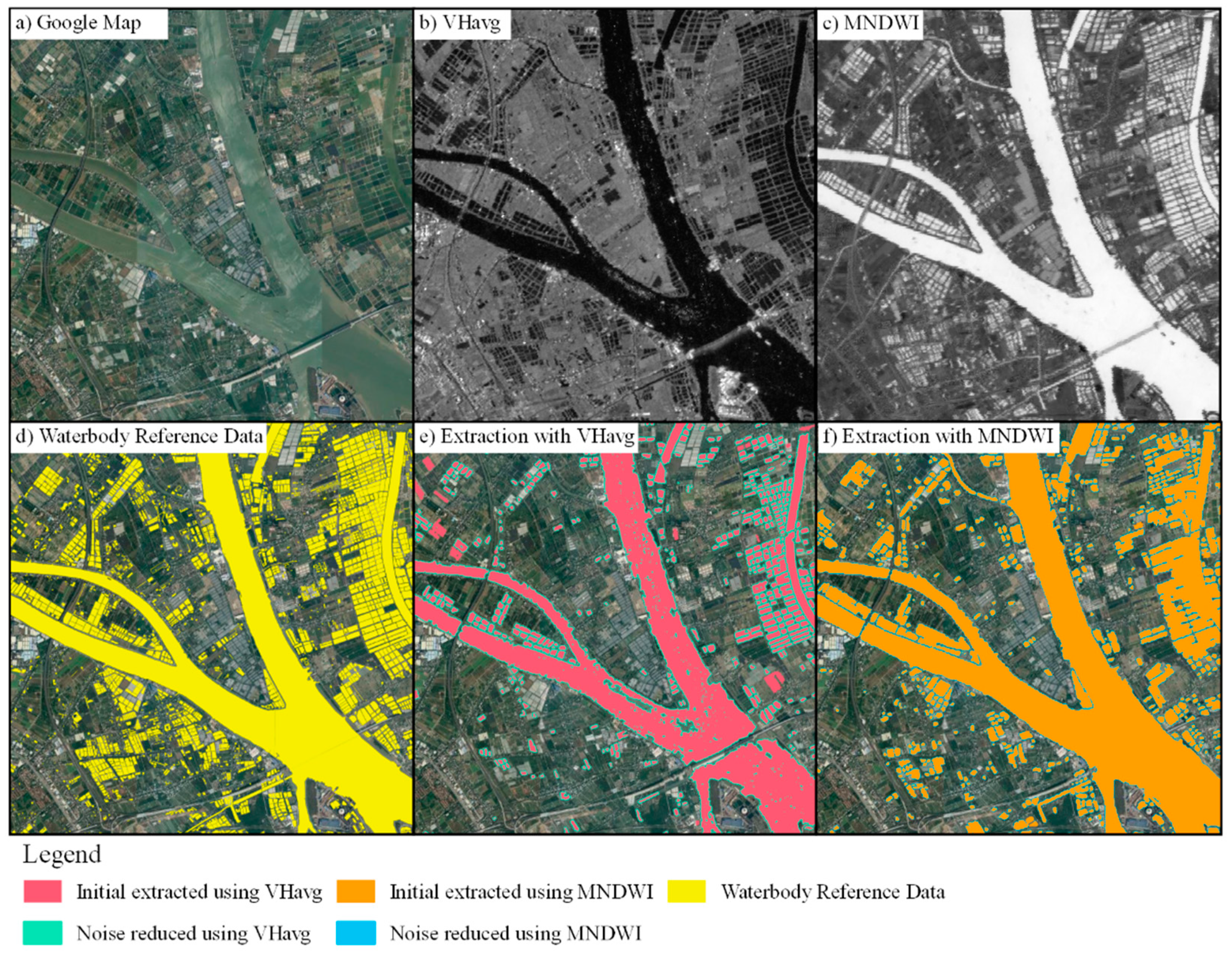
2.3. Framework of Waterbody Mapping
2.3.1. Initial Waterbody Extraction
- (1)
- Generate the non-water polygons: The non-water (NW) polygons were generated using Equation (8).where PWRD and PNW are the polygons of WRD and NW, respectively. The Buffering3 and Buffering1 are buffers of the WRD data with 3 or 1 pixels, respectively.
- (2)
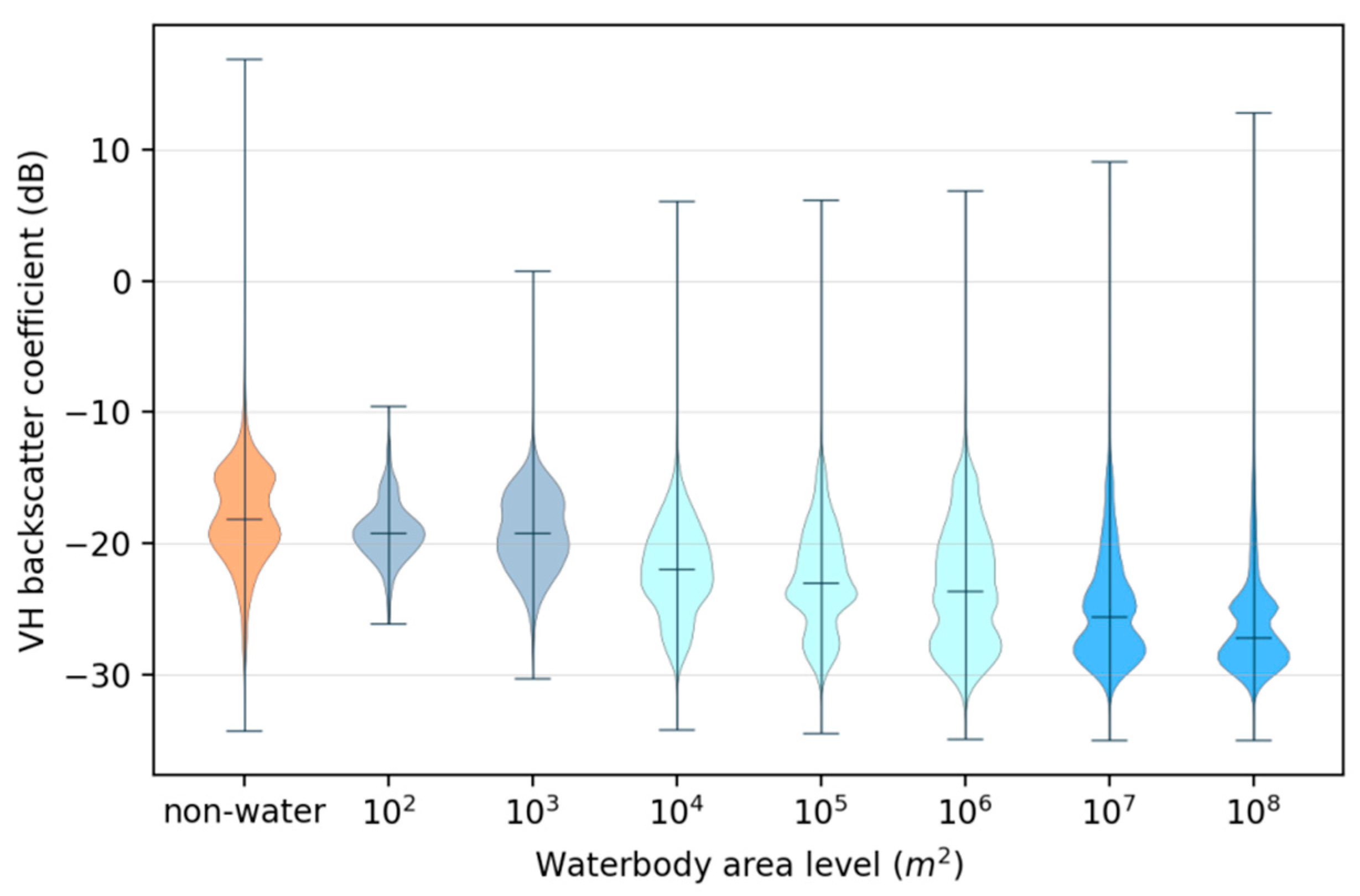
- Statistics on pixel values of waterbodies by each area level and non-water: For VHavg and MNDWI, we calculated the median of pixel values associated with NW data and WRD for each waterbody area level.
- (3)
- Determine the thresholds: We analyzed the statistical pixel values of WRD under different area levels and NW through a violin chart. Then, the values of , , , and were determined by those levels where the pixel values were changing rapidly. The details and results are described in Section 3.
2.3.2. Noise Reduction
- (1)
- Mountain shadow removal by SLOPE: The SLOPE was first applied with the thresholding method to remove pixels in IWM that satisfied Equation (9). However, the use of slope data alone could not wholly exclude mountain shadows as the spatial resolution of SRTM DEM data was lower than that of the Sentinel data.
- (2)
- Mountain shadow removal by NDVImax: Mountain shadows are significant noise in waterbody identification. However, the mountains are usually covered by dense vegetation in southern China. Thus, it was possible to use the NDVImax that satisfied Equation (10) to eliminate mountain shadows.
- (3)
- Flat surface removal by NDBI: Waterbodies and flat surfaces have a similar SAR backscattering coefficient value. For optical data, these two types exhibit significant differences in the near-infrared and short-wave infrared bands. The NDBI was designed to identify built-up areas and barren land. Thus, Equation (11) was applied to distinguish between a waterbody and a flat surface.
- (4)
- Hole removal by binary image morphology: The waterbody extraction results may contain some “holes” caused by ships or islands. A binary image morphology method was thus applied to remove the holes. Additionally, a threshold satisfying Equation (12) was set on the maximum pixels of the holes to avoid holes caused by islands.
2.4. Accuracy Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Statistics on the Waterbody Value in Images
3.2. Accuracy of Waterbody Identification
4. Discussion
4.1. Noise Reduction
4.2. Comparison of Sentinel-1A & 2 in Waterbody Mapping
4.3. The Smallest Identifiable Area of Waterbody
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pekel, J.-F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehner, B.; Döll, P. Development and validation of a global database of lakes, reservoirs and wetlands. J. Hydrol. 2004, 296, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Nunziata, F.; Li, X.; Migliaccio, M. Performance Analysis and Validation of Waterline Extraction Approaches Using Single- and Dual-Polarimetric SAR Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 8, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Feng, M.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, N.; Huang, J.; Xiao, T. An Automated Method for Extracting Rivers and Lakes from Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 5067–5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiucheng, Y.; Shanshan, Z.; Xuebin, Q.; Na, Z.; Ligang, L. Mapping of Urban Surface Water Bodies from Sentinel-2 MSI Imagery at 10 m Resolution via NDWI-Based Image Sharpening. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 596. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Zheng, G.; Gao, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Lei, Y.; Li, J. Automated Water Classification in the Tibetan Plateau Using Chinese GF-1 WFV Data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2017, 83, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; He, H.; Yu, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, L. Using the modified two-mode method to identify surface water in Gaofen-1 images. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2018, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanqiu, X.U. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenzer, C.; Guo, H.; Huth, J.; Leinenkugel, P.; Li, X.; Dech, S. Flood Mapping and Flood Dynamics of the Mekong Delta: ENVISAT-ASAR-WSM Based Time Series Analyses. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 687–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanguy, M.; Chokmani, K.; Bernier, M.; Poulin, J.; Raymond, S. River flood mapping in urban areas combining Radarsat-2 data and flood return period data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 442–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bioresita, F.; Puissant, A.; Stumpf, A.; Malet, J. A Method for Automatic and Rapid Mapping of Water Surfaces from Sentinel-1 Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Nguyen, B.D.; Zhang, S.; Cao, S.; Wagner, W. A Comparison of Terrain Indices toward Their Ability in Assisting Surface Water Mapping from Sentinel-1 Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, D.; Weng, Q. A survey of image classification methods and techniques for improving classification performance. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 823–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, P.S.; Page, K.J. Water Body Detection and Delineation with Landsat TM Data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2000, 66, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar]
- Bonafilia, D.; Tellman, B.; Anderson, T.; Issenberg, E. Sen1Floods11: A Georeferenced Dataset to Train and Test Deep Learning Flood Algorithms for Sentinel-1. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Qin, Q.; Grussenmeyer, P.; Koehl, M. Urban surface water body detection with suppressed built-up noise based on water indices from Sentinel-2 MSI imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 219, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhe, Z.; Shixiong, W.; Woodcock, C.E. Improvement and expansion of the Fmask algorithm: Cloud, cloud shadow, and snow detection for Landsats 4–7, 8, and Sentinel 2 images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Introduction of Guangdong Province. Available online: http://www.gd.gov.cn/zjgd/sqgk/zrdl/index.html (accessed on 25 March 2021).
- Topography of Guangzhou City. Available online: http://nyncj.gz.gov.cn/sj/sn/dxdm/ (accessed on 24 November 2020).
- Guangzhou Water Resources Bulletin. 2018. Available online: http://swj.gz.gov.cn/attachment/0/45/45140/5298825.pdf (accessed on 24 November 2020).
- Sentinel-1 SAR User Guide. Available online: https://sentinel.esa.int/web/sentinel/user-guides/sentinel-1-sar (accessed on 25 March 2021).
- Sentinel-2 User Handbook. Available online: https://sentinel.esa.int/documents/247904/685211/Sentinel-2_User_Handbook (accessed on 25 March 2021).
- Ubukawa, T. An Evaluation of the Horizontal Positional Accuracy of Google and Bing Satellite Imagery and Three Roads Data Sets Based on High Resolution Satellite Imagery; Center for International Earth Science Information Network (CIESIN) The Earth Institute at Columbia University: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, X.; Xin, Q.; Ao, Z.; Zuo, Q.; Chen, L. Automated Surface Water Extraction Combining Sentinel-2 Imagery and OpenStreetMap Using Presence and Background Learning (PBL) Algorithm. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. IEEE J. 2019, 12, 3784–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Shi, W.; Miao, Z.; Hao, M. Accuracy Assessment Measures for Object Extraction from Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Waterbody Type | Description | Number of Polygons | Total Area (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rivers | The main stream and tributaries of the Pearl River | 652 | 335.23 |
| Channels | Drainage channels in urban areas or ditches for drainage and irrigation in rural areas. | 221 | 1.85 |
| Reservoirs | Mainly distributed in northern Guangzhou | 255 | 38.70 |
| Lakes | Lakes for tourism in urban areas | 28 | 1.46 |
| Ponds | Mainly ponds for aquaculture | 74,212 | 279.39 |
| Method | Dataset | Precisiona | Recalla | F-Measurea |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial extracted | VHavg | 0.835 | 0.547 | 0.661 |
| MNDWI | 0.818 | 0.705 | 0.757 | |
| Noise reduced | VHavg | 0.878 | 0.532 | 0.662 |
| MNDWI | 0. 824 | 0.692 | 0.752 |
| Method | Dataset | Precisionn | Recalln | F-Measuren |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial extracted | VHavg | 0.703 | 0.151 | 0.249 |
| MNDWI | 0.853 | 0.269 | 0.409 | |
| Noise reduced | VHavg | 0.707 | 0.144 | 0.239 |
| MNDWI | 0.842 | 0.262 | 0.400 |
| Waterbody Area (m2) | Waterbody Number | Recalln | |
|---|---|---|---|
| VHavg | MNDWI | ||
| 102 | 340 | 0 | 0.009 |
| 103 | 15015 | 0.005 | 0.028 |
| 104 | 22854 | 0.167 | 0.334 |
| 105 | 3235 | 0.621 | 0.847 |
| 106 | 109 | 0.661 | 0.770 |
| 107 | 20 | 0.750 | 0.800 |
| 108 | 4 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, H.; Wang, M.; Hu, H.; Xu, J. Evaluating the Performance of Sentinel-1A and Sentinel-2 in Small Waterbody Mapping over Urban and Mountainous Regions. Water 2021, 13, 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13070945
Jiang H, Wang M, Hu H, Xu J. Evaluating the Performance of Sentinel-1A and Sentinel-2 in Small Waterbody Mapping over Urban and Mountainous Regions. Water. 2021; 13(7):945. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13070945
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Hao, Mo Wang, Hongda Hu, and Jianhui Xu. 2021. "Evaluating the Performance of Sentinel-1A and Sentinel-2 in Small Waterbody Mapping over Urban and Mountainous Regions" Water 13, no. 7: 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13070945







