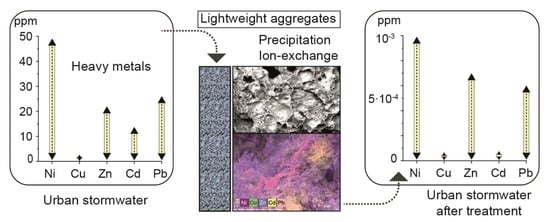
Recovery of Polluted Urban Stormwater Containing Heavy Metals: Laboratory-Based Experiments with Arlita and Filtralite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterization of Filter Materials
2.2. Aqueous Contaminated Solutions
2.3. Batch Experiments
2.4. Heavy-Metal Concentration in the Synthetic Water under Different pH Values
2.5. Geochemical Modeling
3. Results and Discussion
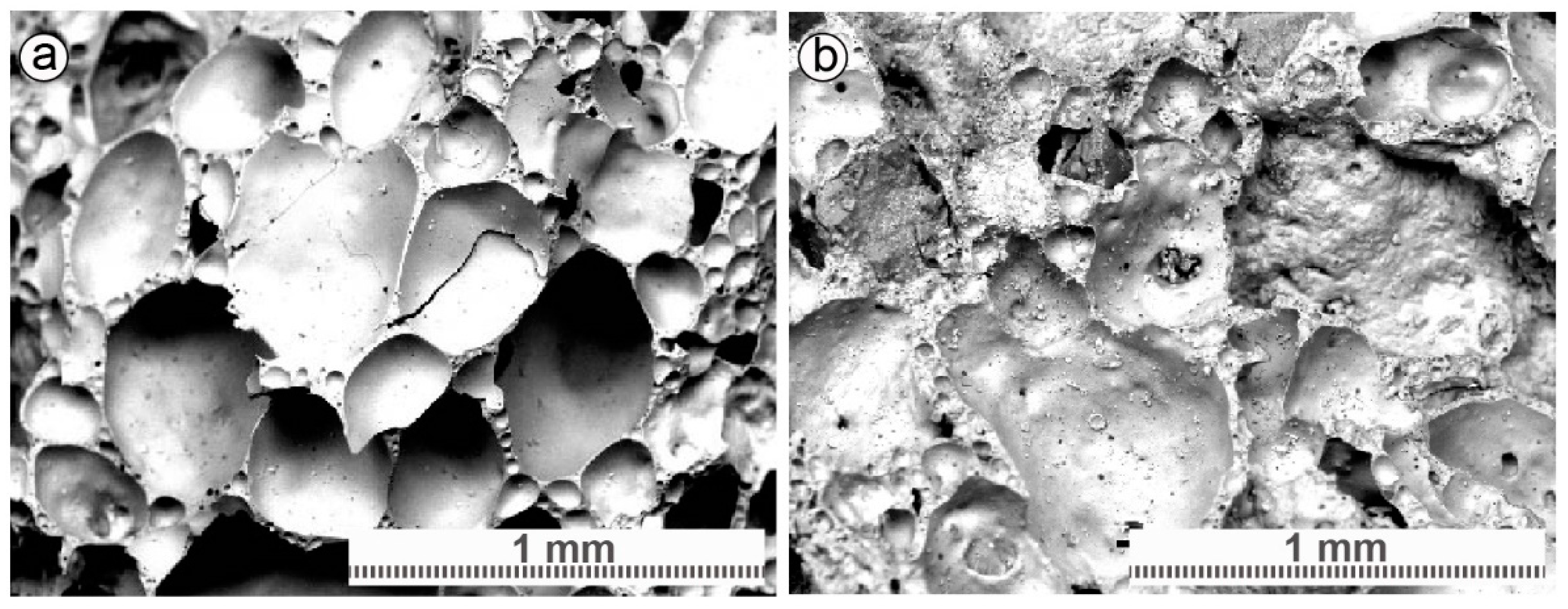
3.1. Filter Material Characterization
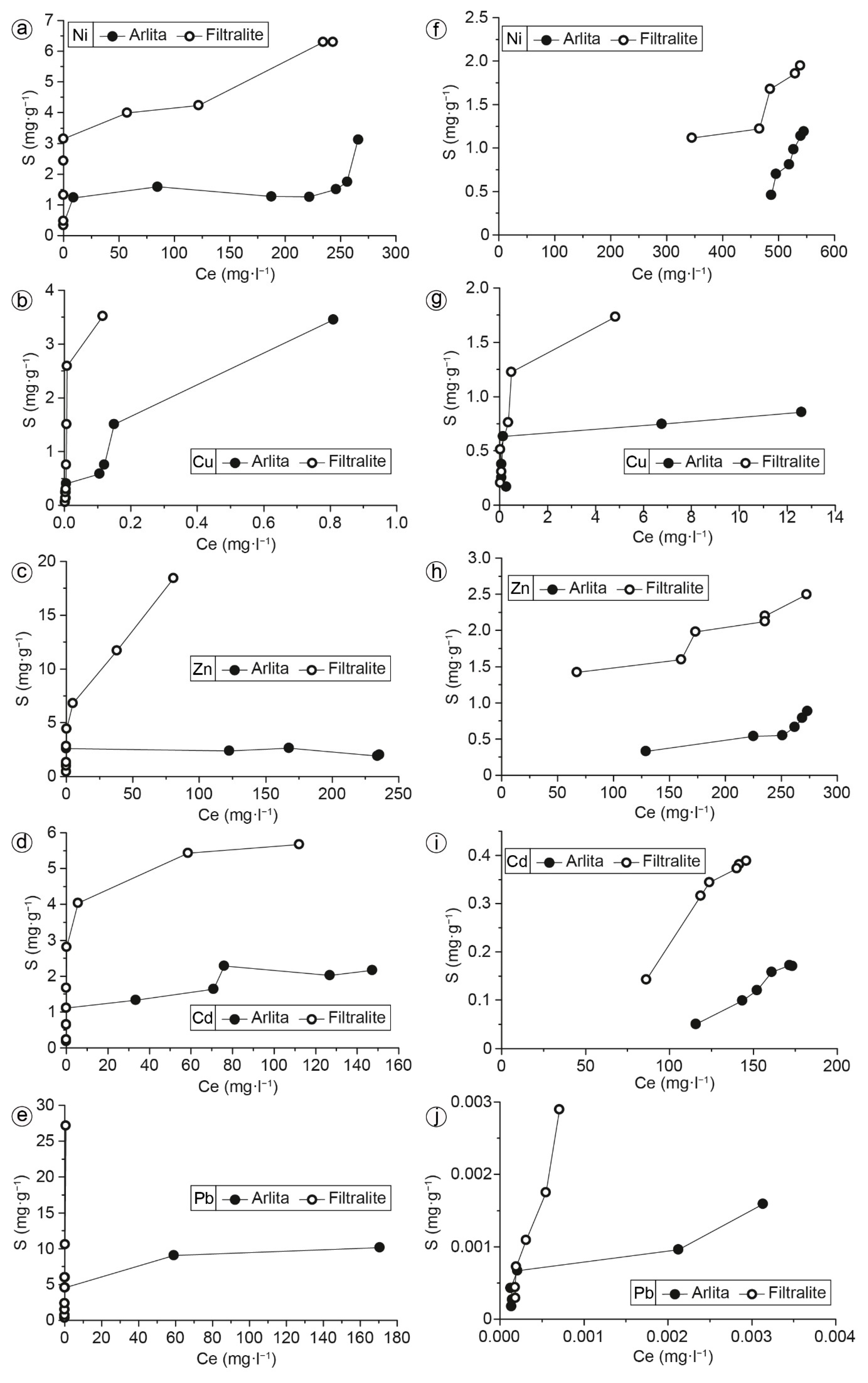
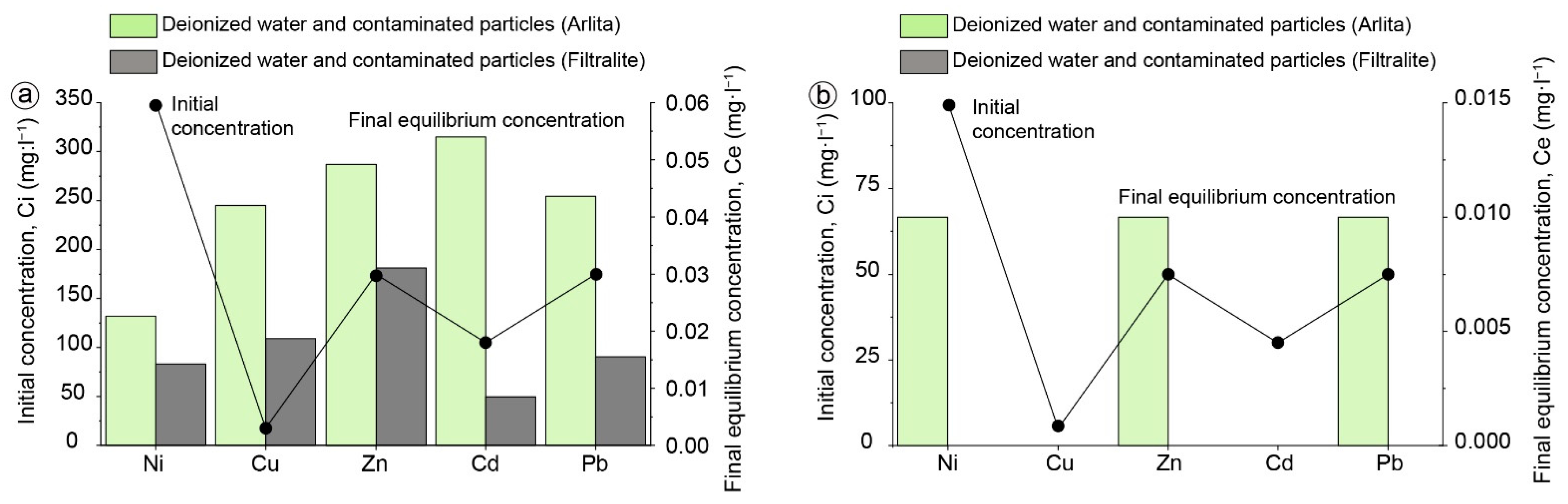
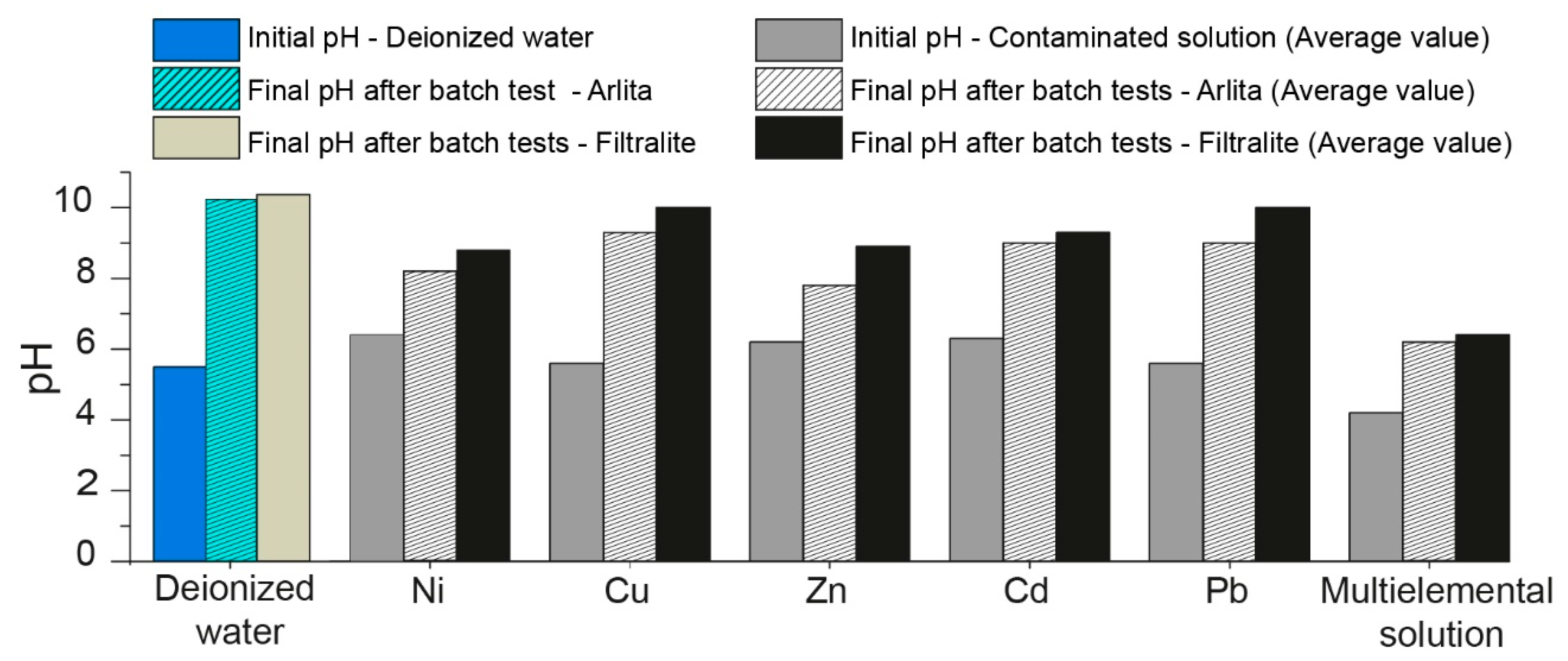
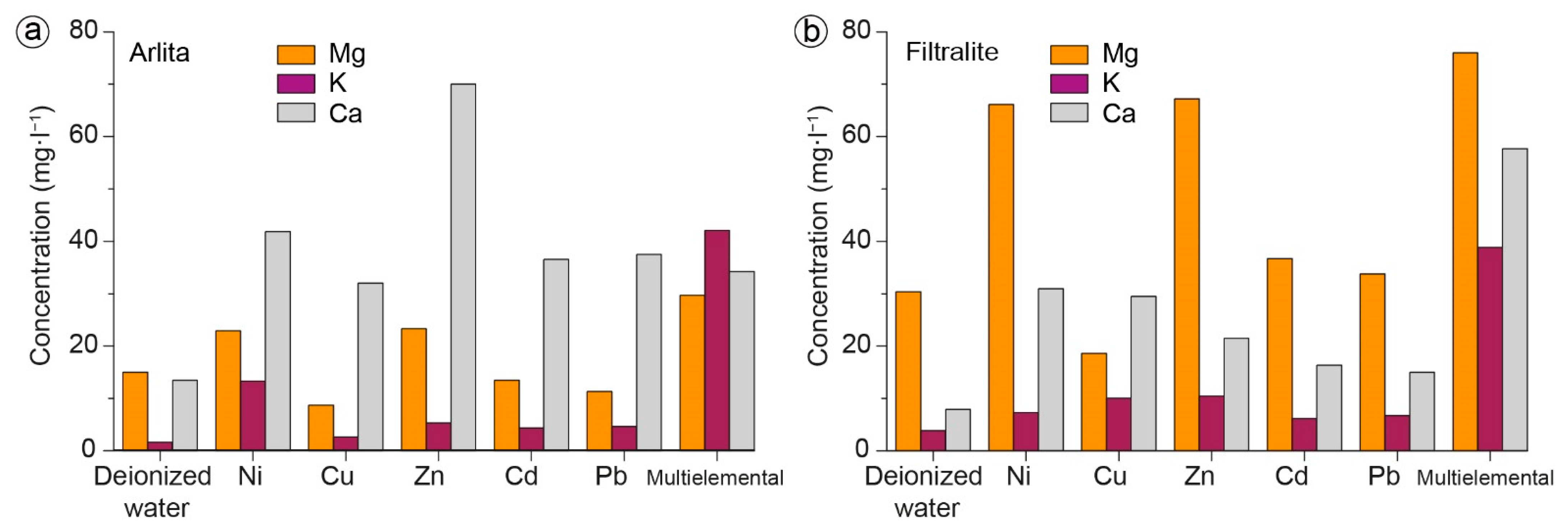
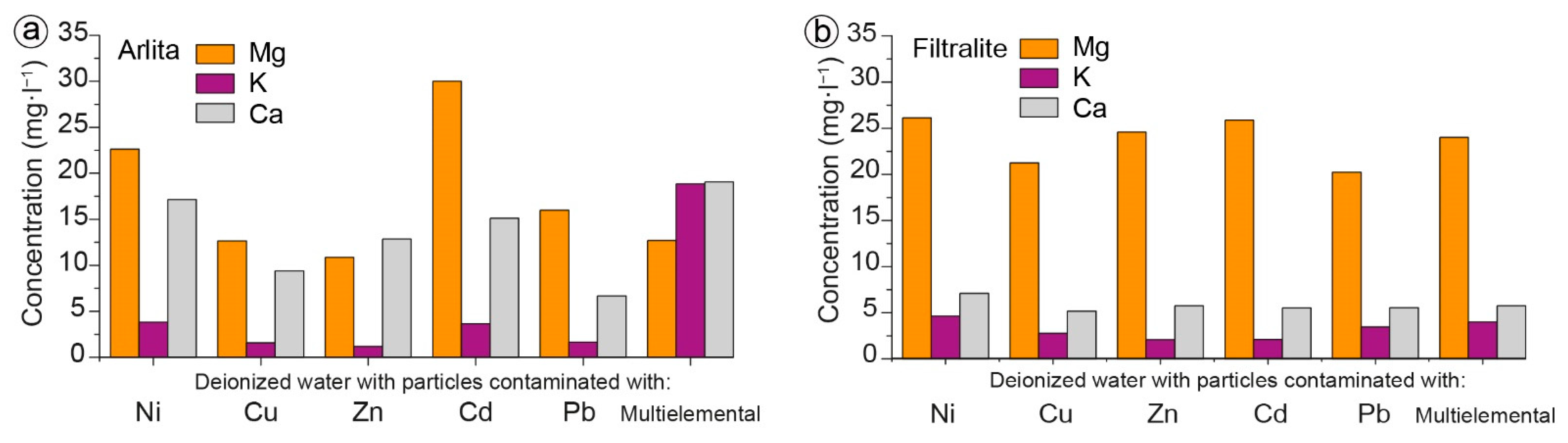
3.2. Batch Experiments
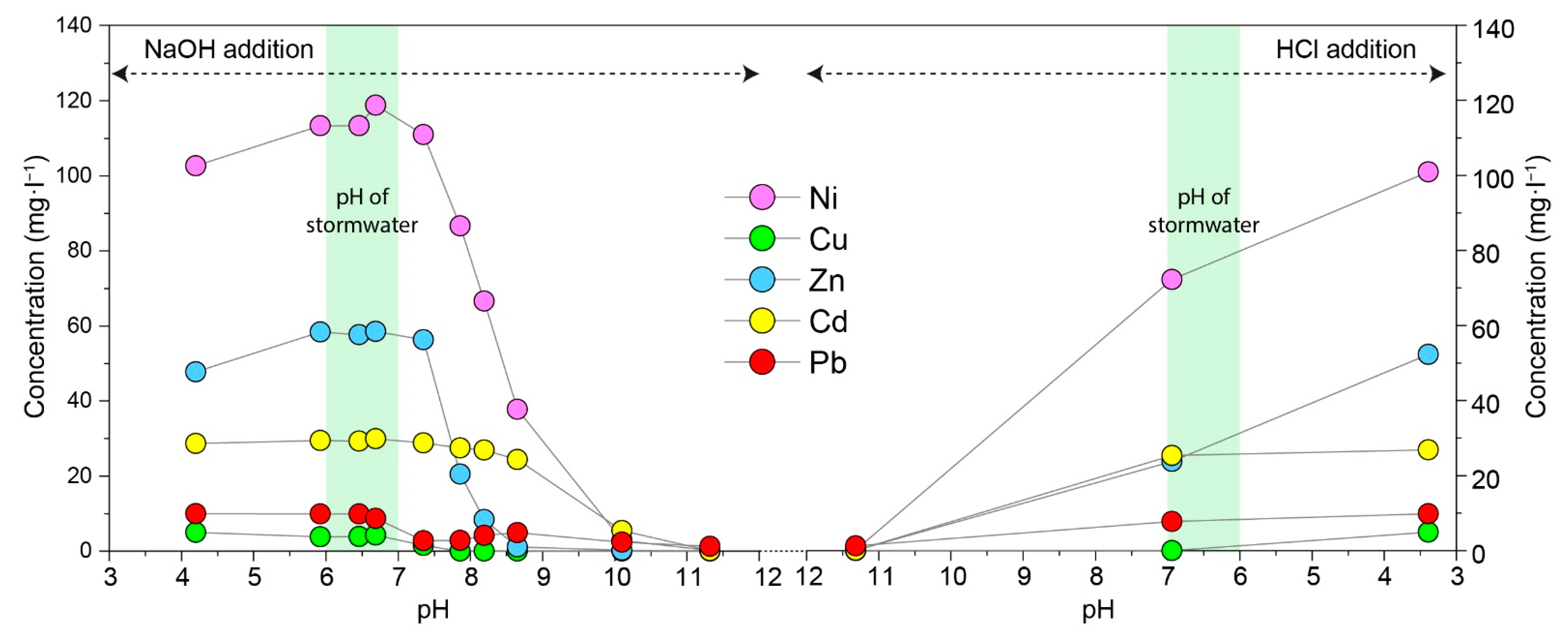
3.3. Influence of pH on Heavy-Metal Removal
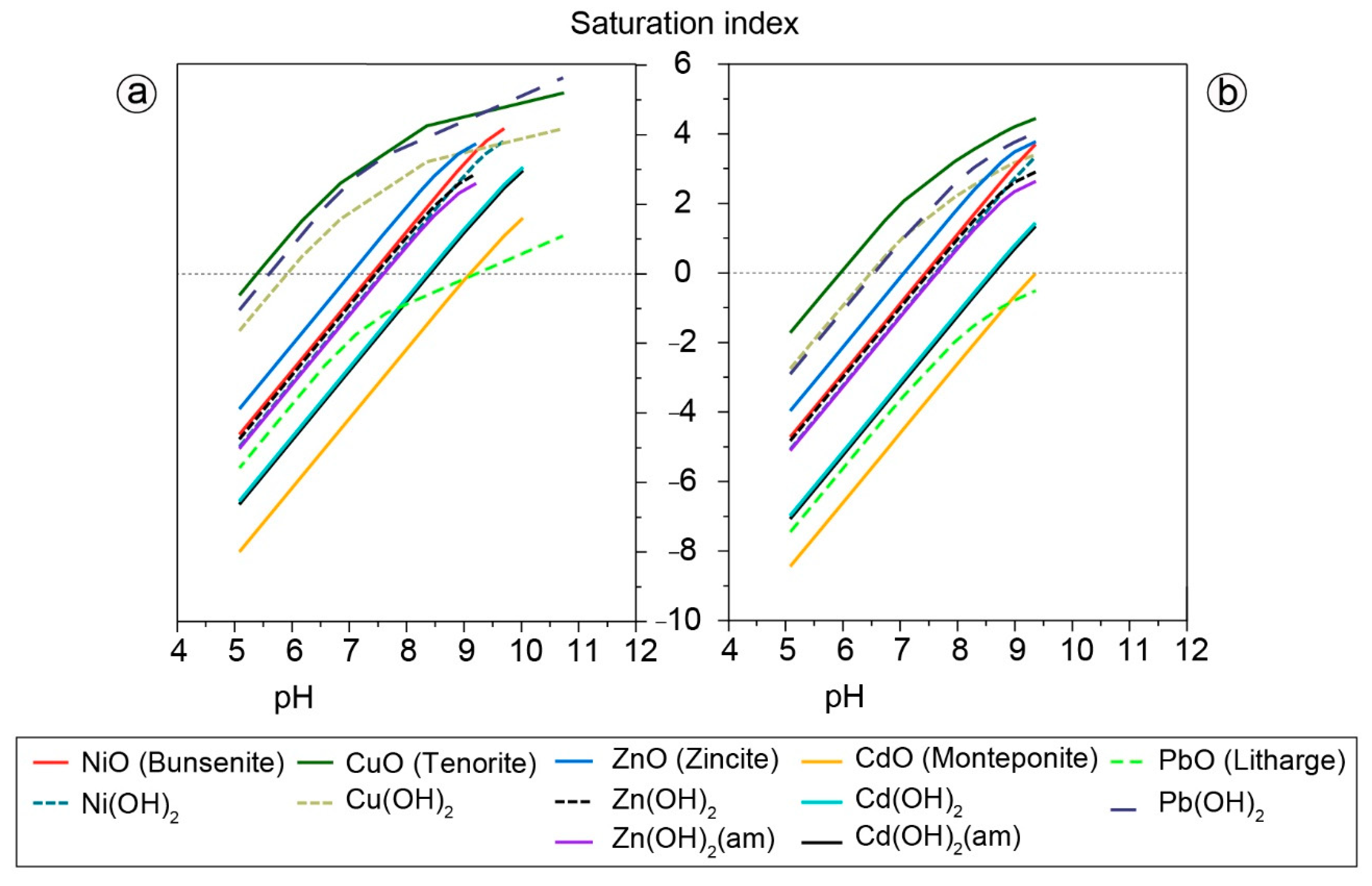
3.4. Geochemical Modeling
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kharin, V.V.; Zwiers, F.W.; Zhang, X.; Wehner, M. Changes in temperature and precipitation extremes in the CMIP5 ensemble. Clim. Chang. 2013, 119, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, R.; Dussaillant, A. Predicting infiltration pollutant retention in bioretention sustainable drainage systems: Model development and validation. Hydrol. Res. 2014, 45, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sounthararajah, D.P.; Loganathan, P.; Kandasamy, J.; Vigneswaran, S. Adsorptive removal of heavy metals from water using sodium titanate nanofibres loaded onto GAC in fixed-bed columns. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 287, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spahr, S.; Teixidó, M.; Sedlak, D.L.; Luthy, R.G. Hydrophilic trace organic contaminants in urban stormwater: Occurrence, toxicological relevance, and the need to enhance green stormwater infrastructure. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 15–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulos, P.F. Smart water network modeling for sustainable and resilient infrastructure. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 3177–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, N.; Wanko, A.; Laurent, J.; Bois, P.; Molle, P.; Mosé, R. Constructed wetlands treating stormwater from separate sewer networks in a residential Strasbourg urban catchment area: Micropollutant removal and fate. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2816–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, L.; Tu, N.; Xi, G.; Fang, X. Removal of heavy metals from urban stormwater runoff using bioretention media mix. Water 2017, 9, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharin, V.; Zwiers, F.; Zhang, X.; Hegerl, G. Changes in temperature and precipitation extremes in the IPCC ensemble of global coupled model simulations. J. Climate 2007, 20, 1419–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Gorman, P.A. Sensitivity of tropical precipitation extremes to climate change. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallman, S.; Spongberg, M. Expanding local water supplies: Assessing the impacts of stormwater infiltration on groundwater quality. Prof. Geogr. 2012, 64, 232–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwer, H. Artificial recharge of groundwater: Hydrogeology and engineering. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 121–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipolla, S.S.; Maglionico, M.; Stojkov, I. Experimental infiltration tests on existing permeable pavement surfaces. Clean Soil Air Water 2016, 44, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeimi, G.; Safavi, H.R. Integrated stormwater and groundwater management in urban areas, a case study. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 17, 1281–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodar-Abellan, A.; Valdes-Abellan, J.; Pla, C.; Gomariz-Castillo, F. Impact of land use changes on flash flood prediction using a sub-daily SWAT model in five Mediterranean ungauged watersheds (SE Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 1578–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Z.; Zhang, L.; Pan, S.-Y.; Chiang, P.-C.; Pei, S.; Zhang, S. Performance evaluation of modified bioretention systems with alkaline solid wastes for enhanced nutrient removal from stormwater runoff. Water Res. 2019, 161, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, A.; Foti, R.; Montalto, F. Green infrastructure implementation in urban parks for stormwater management. J. Sustain. Water Built. Environ. 2019, 5, 05019003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miskewitz, R.; Uchrin, C. In-stream dissolved oxygen impacts and sediment oxygen demand resulting from combined sewer overflow discharges. J. Environ. Eng. 2013, 139, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekanayake, D.; Aryal, R.; Hasan Johir, M.A.; Loganathan, P.; Bush, C.; Kandasamy, J.; Vigneswaran, S. Interrelationship among the pollutants in stormwater in an urban catchment and first flush identification using UV spectroscopy. Chemosphere 2019, 233, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryal, R.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kandasamy, J.; Naidu, R. Urban stormwater quality and treatment. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 27, 1343–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierkes, C.; Lohmann, M.; Becker, M.; Raasch, U. Pollution retention of different permeable pavements with reservoir structure at high hydraulic loads. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Urban Drainage, Copenhagen, Denmark, 21–26 August 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Vu, C.T.; Wu, T. Engineered multifunctional sand for enhanced removal of stormwater runoff contaminants in fixed-bed column systems. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 852–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Bai, Y.; Fan, G.; Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Su, Y.; et al. The influence of heavy metals in road dust on the surface runoff quality: Kinetic, isotherm, and sequential extraction investigations. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2019, 176, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taka, M.; Aalto, J.; Virkanen, J.; Luoto, M. The direct and indirect effects of watershed land use and soil type on stream water metal concentrations. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 7711–7725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveh-Rubin, S.; Edery, Y.; Dror, I.; Berkowitz, B. Nickel migration and retention dynamics in natural soil columns. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 7702–7722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.P.; Shokouhian, M.; Sharma, H.; Minami, C.; Winogradoff, D. Water quality improvement through bioretention: Lead, copper, and zinc removal. Water Environ. Res. 2003, 75, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.R.; Xie, T.; Dastgheibi, S. Removal of heavy metals from urban stormwater runoff using different filter materials. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh kumar, K.; Anbazhagan, V. Analysis and assessment of heavy metals in soils around the industrial areas in Mettur, Tamilnadu, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniquiz-Redillas, M.C.; Kim, L.H. Evaluation of the capability of low-impact development practices for the removal of heavy metal from urban stormwater runoff. Environ. Technol. 2016, 37, 2265–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, R.; Field, R.; Lalor, M.; Brown, M. Urban stormwater toxic pollutants: Assessment, sources, and treatability. Water Environ. Res. 1995, 67, 260–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haile, T.M.; Fuerhacker, M. Simultaneous adsorption of heavy metals from roadway stormwater runoff using different filter media in column studies. Water 2018, 10, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, T.N.; Burian, S.J.; Stenstrom, M.K.; Turin, H.J.; Brown, M.J.; Suffet, I.H. Trace metal pollutant load in urban runoff from a southern california watershed. J. Environ. Eng. 2005, 131, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, N.; Yusof, N.; Lau, W.J.; Jaafar, J.; Ismail, A.F. Recent trends of heavy metal removal from water/wastewater by membrane technologies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 76, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, M.A. New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2011, 4, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, M.; Zhang, S.; Pan, B.; Zhang, W.; Lv, L.; Zhang, Q. Heavy metal removal from water/wastewater by nanosized metal oxides: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 211–212, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Manage. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carolin, C.F.; Kumar, P.S.; Saravanan, A.; Joshiba, G.J.; Naushad, M. Efficient techniques for the removal of toxic heavy metals from aquatic environment: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2782–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaba, P.A.; Oladoja, N.A.; Sani, Y.M.; Ayodele, O.B.; Mohammed, I.Y.; Olupinla, S.F.; Daud, W.M.W. Insight into wastewater decontamination using polymeric adsorbents. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1651–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, T.D.; Shuster, W.; Hunt, W.F.; Ashley, R.; Butler, D.; Arthur, S.; Trowsdale, S.; Barraud, S.; Semadeni-Davies, A.; Bertrand-Krajewski, J.-L.; et al. SUDS, LID, BMPs, WSUD and more—The evolution and application of terminology surrounding urban drainage. Urban Water J. 2015, 12, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockhorn, B.; Klint, K.E.S.; Locatelli, L.; Park, Y.-J.; Binning, P.J.; Sudicky, E.; Bergen Jensen, M. Factors affecting the hydraulic performance of infiltration based SUDS in clay. Urban Water J. 2017, 14, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods-Ballard, B.; Wilson, S.; Udale-Clarke, H.; Illman, S.; Scott, T.; Ashley, R.; Kellager, R. The SuDS manual; CIRIA: London, UK, 2015; p. 937. [Google Scholar]
- Soleimanifar, H.; Deng, Y.; Wu, L.; Sarkar, D. Water treatment residual (WTR)-coated wood mulch for alleviation of toxic metals and phosphorus from polluted urban stormwater runoff. Chemosphere 2016, 154, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlesworth, S.M.; Nnadi, E.; Oyelola, O.; Bennett, J.; Warwick, F.; Jackson, R.; Lawson, D. Laboratory based experiments to assess the use of green and food based compost to improve water quality in a Sustainable Drainage (SUDS) device such as a swale. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 424, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öövel, M.; Tooming, A.; Mauring, T.; Mander, Ü. Schoolhouse wastewater purification in a LWA-filled hybrid constructed wetland in Estonia. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 29, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, C.M.; Labrincha, J.A. Removal of contaminants from aqueous solutions by beds made of rejects of the lightweight aggregates production. Ceram. Int. 2008, 34, 1735–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RD 506/2013, 2013. Real Decreto 506/2013, de 28 de Junio, Sobre Productos Fertilizantes. Available online: https://www.boe.es/boe/dias/2013/07/10/pdfs/BOE-A-2013-7540.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2021).
- RD 865/2010, 2010. Real Decreto 865/2010, de 2 de Julio, Sobre Sustratos de Cultivo. Available online: https://www.boe.es/buscar/pdf/2010/BOE-A-2010-11153-consolidado.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2021).
- RD 1310/1990, 1990. Real Decreto 1310/1990, de 29 de Octubre, por el que se Regula la Utilización de los Lodos de Depuración en el Sector Agrario. Available online: https://www.boe.es/eli/es/rd/1990/10/29/1310/dof/spa/pdf (accessed on 12 March 2021).
- UE 2015/2099, 2015. Decisión (UE) 2015/2099 de la Comisión, de 18 de Noviembre de 2015, por la que se Establecen los Criterios Ecológicos Para la Concesión de la Etiqueta Ecológica de la UE a Sustratos de Cultivo, Enmiendas del Suelo y Cubiertas del Suelo. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/ES/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32015D2099&from=ES (accessed on 12 March 2021).
- Davis, A.P.; Burns, M. Evaluation of lead concentration in runoff from painted structures. Water Res. 1999, 33, 2949–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.P.; Shokouhian, M.; Ni, S. Loading estimates of lead, copper, cadmium, and zinc in urban runoff from specific sources. Chemosphere 2001, 44, 997–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.D. Using XPowder: A software package for Powder X-Ray diffraction analysis. D.L. GR 1001/04, 2004. Available online: http://www.xpowder.com/download/QuickUserGuideForXPowderX.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2021).
- Rouquerol, J.; Avnir, D.; Fairbridge, C.; Everett, D.; Haynes, J.; Pernicone, N.; Ramsay, J.; Sing, K.; Unger, K. Recommendations for the characterization of porous solids (Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 1994, 66, 1739–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.H.; Dzakpasu, M.; Chang, N.N.; Wang, X.C. Transferral of HMs pollution from road-deposited sediments to stormwater runoff during transport processes. Front. Env. Sci. Eng. 2019, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R.; Kumar, G. Permeable reactive filter systems for the treatment of urban stormwater runoff with mixed pollutants. In Geotechnical Frontiers 2017: Waste Containment, Barriers, Remediation, and Sustainable Geoengineering; Brandon, T.L., Valentine, R.J., Eds.; American Society of Civil Engineers: Orlando, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 508–517. [Google Scholar]
- Pla, C.; Benavente, D.; Valdes-Abellan, J.; Kovacova, Z. Effectiveness of two lightweight aggregates for the removal of heavy metals from contaminated urban stormwater. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2021, 239, 103778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNE-ISO10390:2012. Soil Quality. Determination of pH. 2012. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/40879.html (accessed on 12 March 2021).
- Parkhurst, D.L.; Appelo, C.A.J. Description of Input and Examples for PHREEQC, Version 3. A Computer Program for Speciation, Batch-Reaction, One-Dimensional Transport, and Inverse Geochemical Calculations; Techniques and Methods, Book 6; U.S. Geological Survey: Denver, CO, USA, 2013; Chapter A43; p. 497. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/tm/06/a43/ (accessed on 12 March 2021).
- Benavente, D.; Brimblecome, P.; Grossi, C. Thermodynamic calculations for the salt crystallisation damage in porous built heritage using PHREEQC. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 2297–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerolli-Mustafa, M.; Bačić, I.; Ćurković, L. Investigation of jarosite process tailing waste by means of raman and infrared spectroscopy. Materialwiss. Werkst. 2013, 44, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez, G.E.; Ribeiro, M.J.P.; Ventura, J.M.; Labrincha, J.A. Removal of nickel from aqueous solutions by clay-based beds. Ceram. Int. 2004, 30, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sounthararajah, D.; Loganathan, P.; Kandasamy, J.; Vigneswaran, S. Removing heavy metals using permeable pavement system with a titanate nano-fibrous adsorbent column as a post treatment. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuong, D.V.; Liu, N.-L.; Nguyen, V.A.; Hou, C.-H. Meso/micropore-controlled hierarchical porous carbon derived from activated biochar as a high-performance adsorbent for copper removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsi, A.; Aghasi, M.; Esmaeili, A.; Eslami, H. Efficient removal of Cu(II) and Zn(II) from aqueous solution and real acid mine drainage by natural vermiculite and kaolinite. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 204, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, A.; Mobini, M.; Eslami, H. Removal of heavy metals from acid mine drainage by native natural clay minerals, batch and continuous studies. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irannajad, M.; Kamran Haghighi, H. Removal of heavy metals from polluted solutions by zeolitic adsorbents: A review. Environ. Process. 2021, 8, 7–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brink, I.; Kamish, W. Associations between stormwater retention pond parameters and pollutant (suspended solids and metals) removal efficiencies. Water SA 2018, 44, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, D. Aqueous Environmental Geochemistry; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
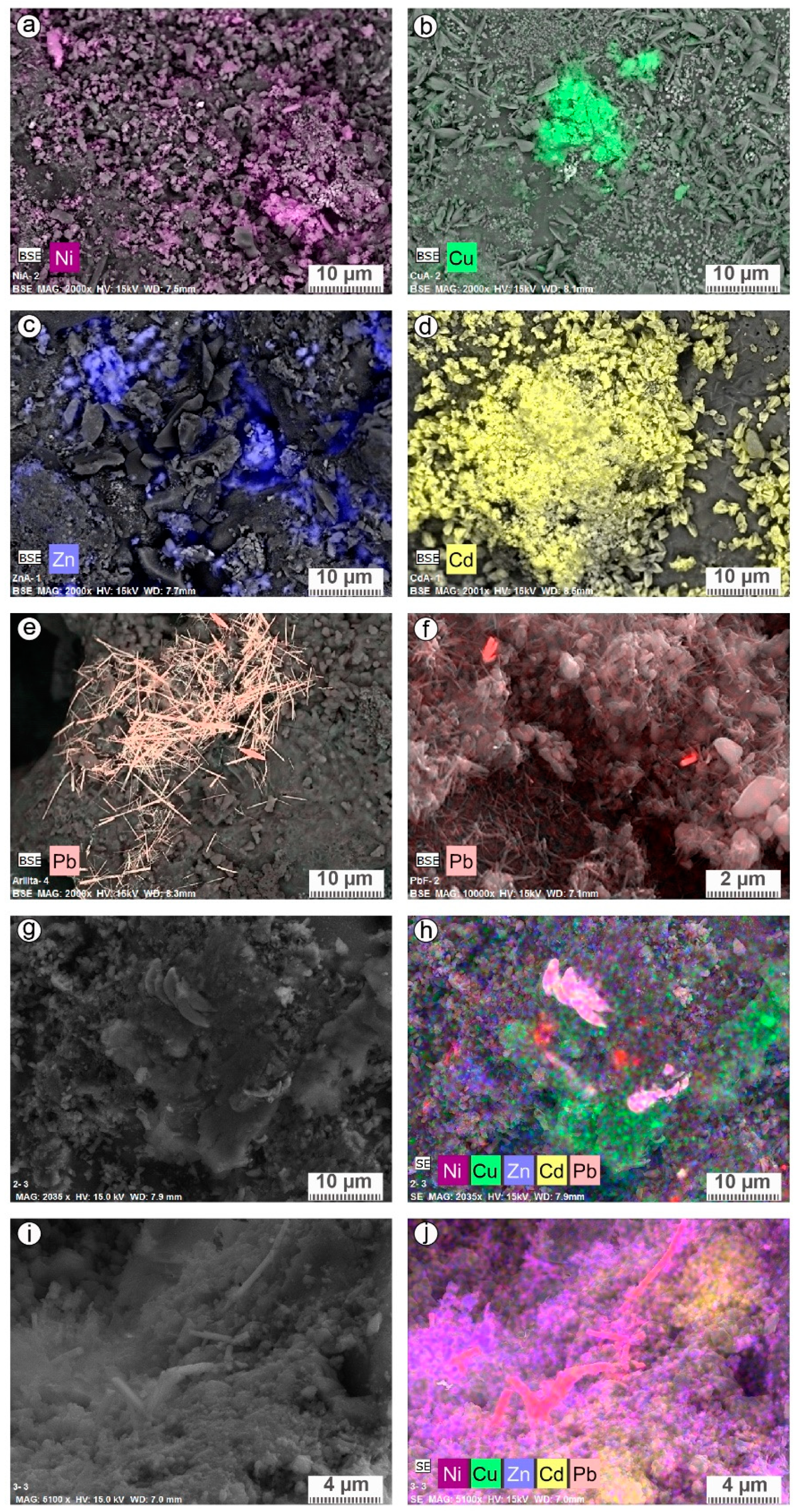
| % | Quartz SiO2 | Anorthite (Ca,Na)Al2Si2O8 | K-Feldspart (K,Na)(Si,Al)4O8 | Wadsleyite (Mg,Fe)2SiO4 | Calcite CaCO3 | Amorphous Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arlita | 31.5 | 18.7 | 11.2 | 28.9 | - | 9.7 |
| Filtralite | 20.4 | 22.8 | 18.7 | 18.7 | 5.9 | 13.5 |
| % | Na2O | MgO | Al2O3 | SiO2 | P2O5 | SO3 | K2O | CaO | TiO2 | MnO | Fe2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arlita | 0.29 | 4.25 | 18.86 | 60.13 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 3.92 | 3.39 | 0.92 | 0.09 | 7.82 |
| Filtralite | 1.94 | 4.78 | 16.21 | 59.12 | 0.23 | 0.17 | 4.09 | 4.51 | 0.79 | 0.12 | 8.04 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pla, C.; Benavente, D.; Valdes-Abellan, J.; Jodar-Abellan, A. Recovery of Polluted Urban Stormwater Containing Heavy Metals: Laboratory-Based Experiments with Arlita and Filtralite. Water 2021, 13, 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13060780
Pla C, Benavente D, Valdes-Abellan J, Jodar-Abellan A. Recovery of Polluted Urban Stormwater Containing Heavy Metals: Laboratory-Based Experiments with Arlita and Filtralite. Water. 2021; 13(6):780. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13060780
Chicago/Turabian StylePla, Concepcion, David Benavente, Javier Valdes-Abellan, and Antonio Jodar-Abellan. 2021. "Recovery of Polluted Urban Stormwater Containing Heavy Metals: Laboratory-Based Experiments with Arlita and Filtralite" Water 13, no. 6: 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13060780
APA StylePla, C., Benavente, D., Valdes-Abellan, J., & Jodar-Abellan, A. (2021). Recovery of Polluted Urban Stormwater Containing Heavy Metals: Laboratory-Based Experiments with Arlita and Filtralite. Water, 13(6), 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13060780