Simulation of Pollution Load at Basin Scale Based on LSTM-BP Spatiotemporal Combination Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.2.1. Time-Series Data
2.2.2. Spatial Data
2.3. Data Preprocessing
2.4. Spatial Correlation Analysis
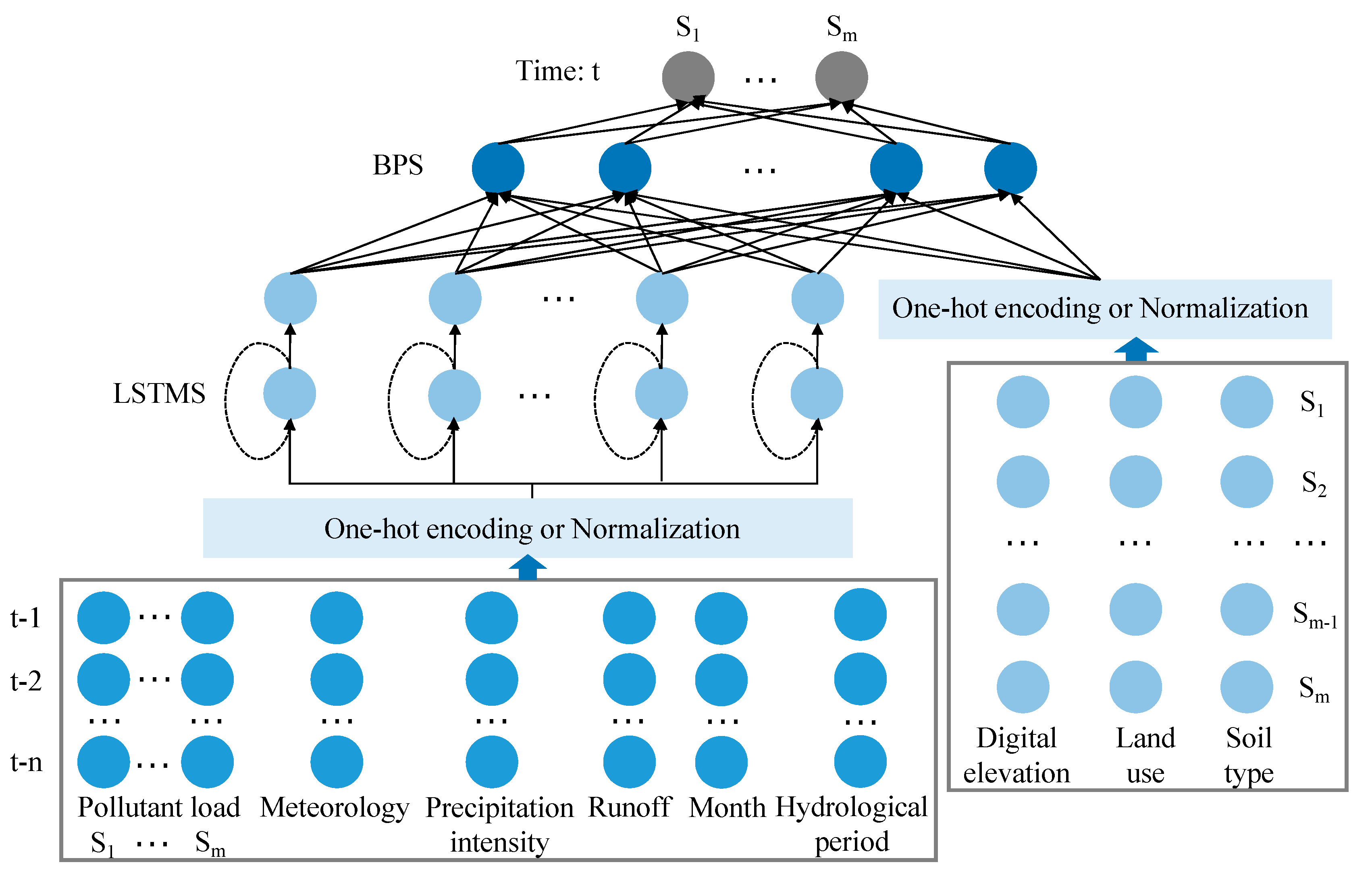
2.5. LSTM-BP Model Setup
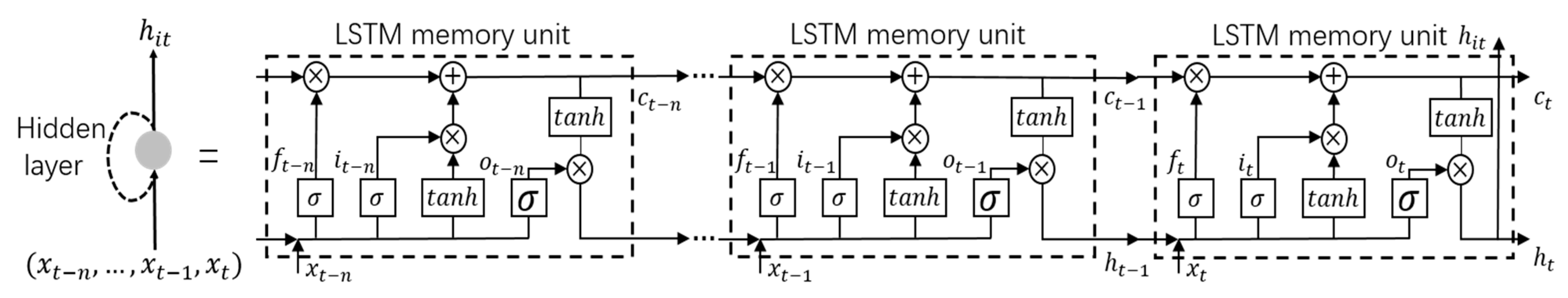
2.5.1. LSTM-Based Temporal Simulator
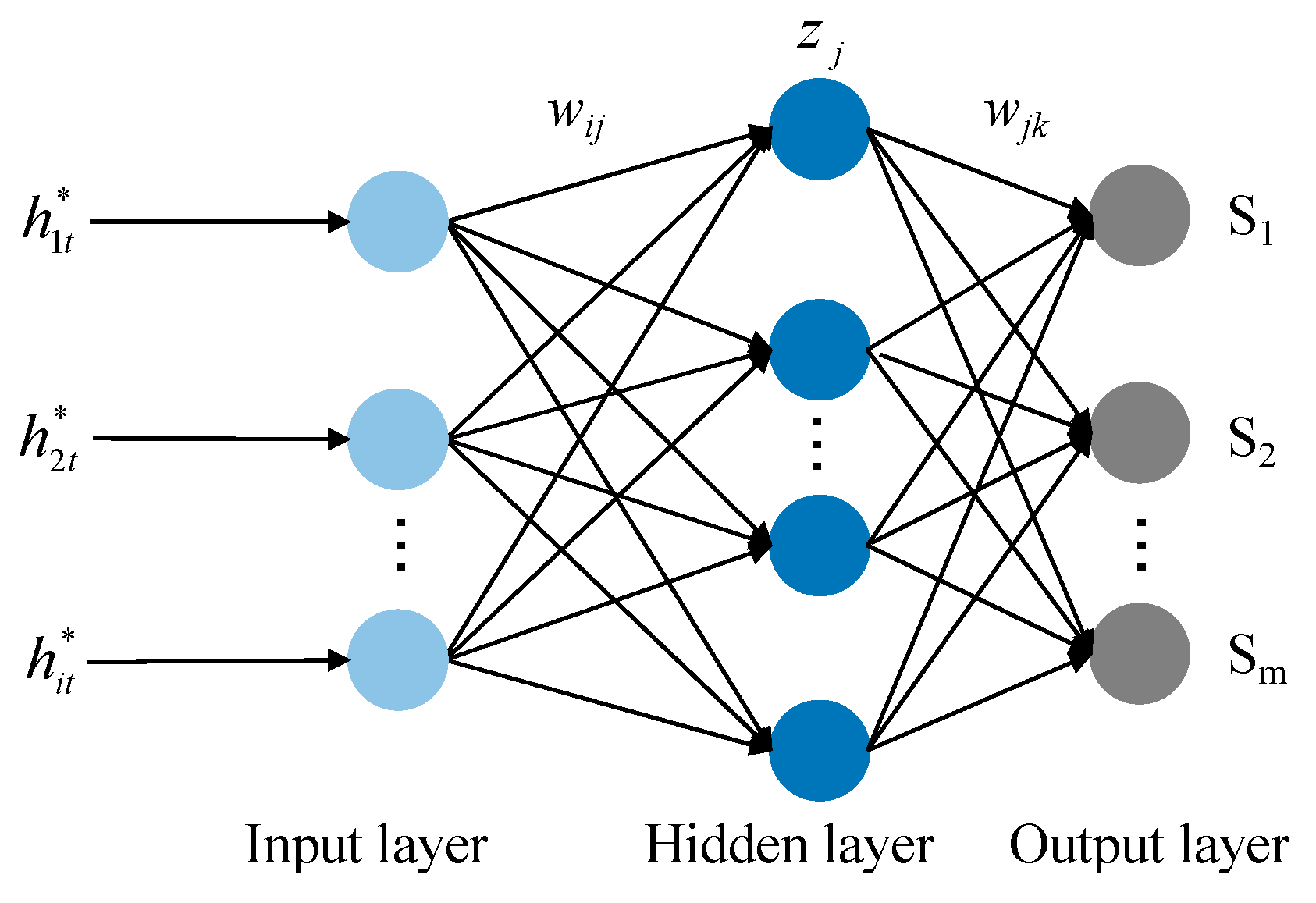
2.5.2. BP-Based Spatial Combinatory
2.5.3. LSTM-BP Model
2.5.4. Tuning for Hyper-Parameters
2.6. Contrast Model Setup
2.6.1. BP Model
2.6.2. LSTM Model
2.6.3. SWAT Model
2.7. Model Evaluation Indicators
Good: 0.65 < NSE ≤ 0.75, 25 ≤ |BIAS| < 40
Satisfactory: 0.5 < NSE ≤ 0.65, 40 ≤ |BIAS| < 70
Unsatisfactory: NSE ≤ 0.5, |BIAS| ≥ 70
3. Results and Discussion
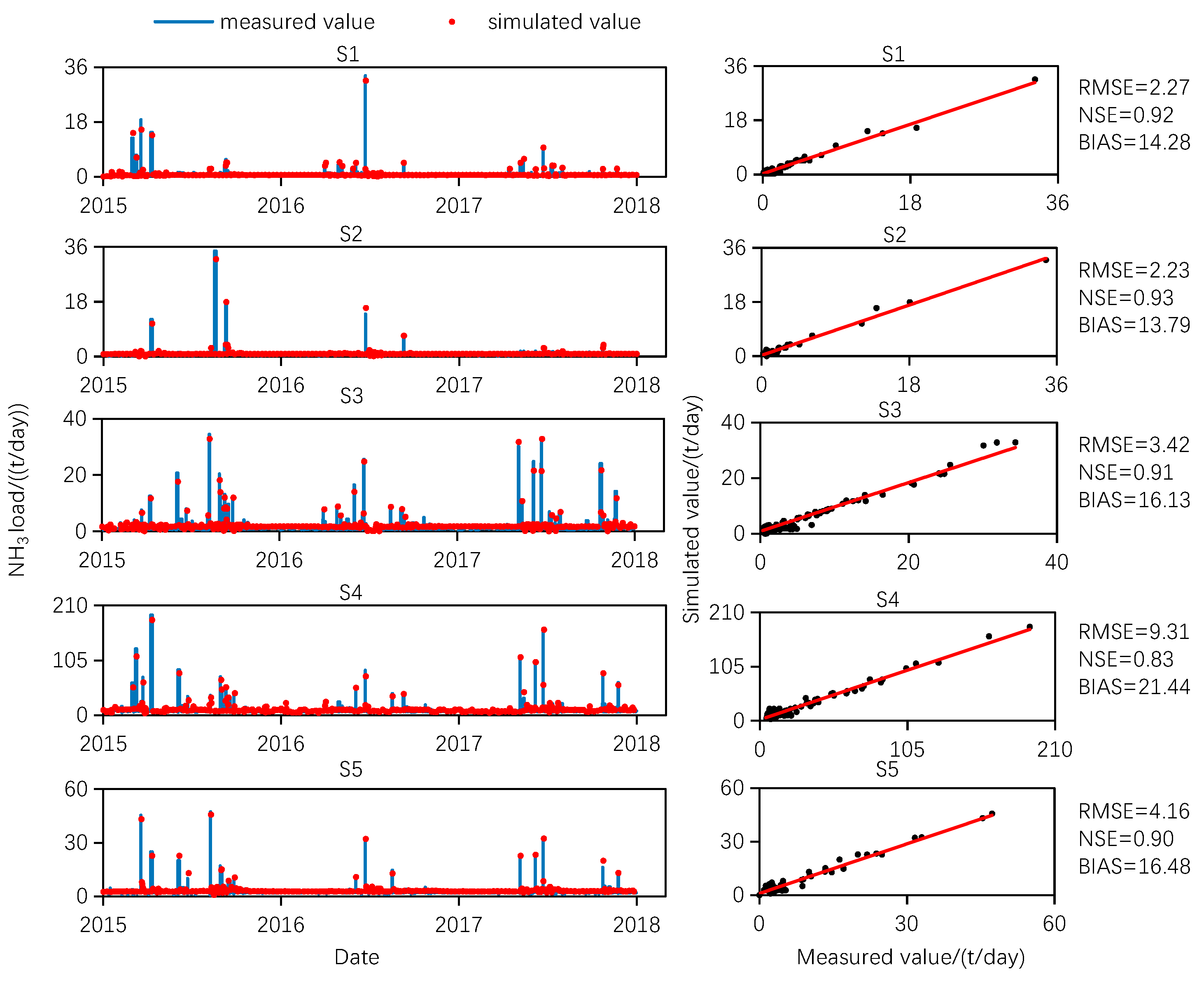
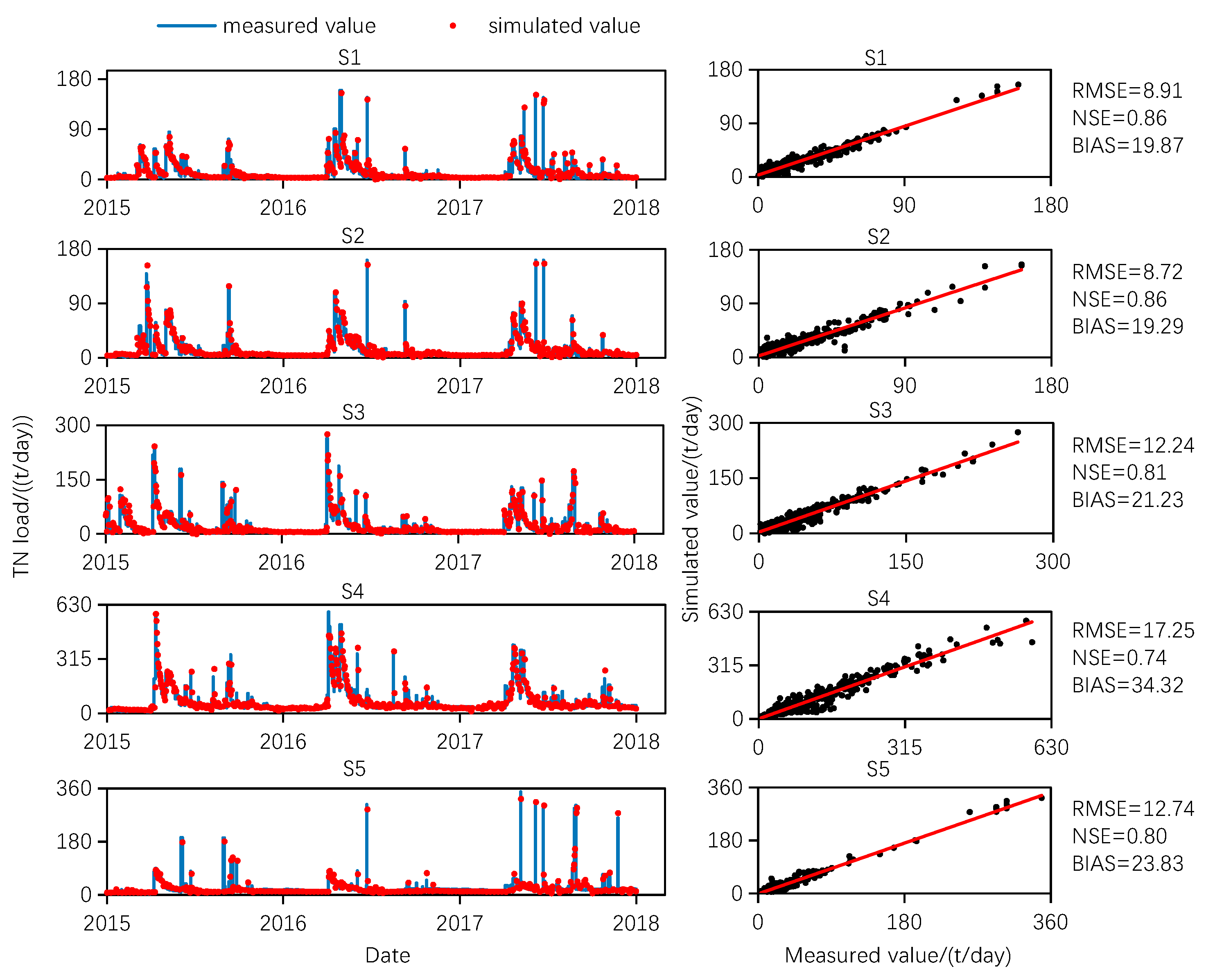
3.1. Comparison of Simulation Performance with Other Models
3.2. LSTM-BP Model’s Performance under Different Hydrological Periods and Precipitation Intensities
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, C.L.; Li, M.Y. Predictions of diffuse pollution by the HSPF model and the Back-Propagation neural network model. Water Environ. Res. 2017, 89, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albek, M.; Albek, E.A.; Göncü, S.; Uygun, B.S. Ensemble streamflow projections for a small watershed with HSPF model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 36023–36036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.G.; Choi, K.-S. A study on water quality change by land use change using HSPF. Environ. Eng. Res. 2019, 25, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouslihim, Y.; Rochdi, A.; Paaza, N.E.A.; Liuzzo, L. Understanding the effects of soil data quality on SWAT model performance and hydrological processes in Tamedroust watershed (Morocco). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2019, 160, 103616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J.Y.; Libera, D.A.; Wang, G.Q.; Li, Z.J.; Wang, D.B. Verification of a new spatial distribution function of soil water storage capacity using conceptual and SWAT models. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2020, 25, 04020001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Ma, J.; Nie, C.; Xue, L.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ni, F.Q.; Deng, Y.; Liu, J.S.; Zhou, D.K.; Li, L.H.; et al. Attribution analysis of runoff change in Min-Tuo River basin based on SWAT model simulations. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdelwahab, O.M.M.; Bingner, R.L.; Milillo, F.; Gentile, F. Evaluation of alternative management practices with the AnnAGNPS model in the Carapelle watershed. Soil Sci. 2016, 181, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, R.; Tagert, M.L.M.; Paz, J.O.; Bingner, R.L. Application of AnnAGNPS to model an agricultural watershed in East-Central Mississippi for the evaluation of an on-farm water storage (OFWS) system. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 192, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, P.; Pruski, L.O.S.; Kaleita, A.L.; Soupir, M.L. Evaluation of AnnAGNPS for simulating the inundation of drained and farmed potholes in the Prairie Pothole Region of Iowa. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 204, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, N.; Kalin, L.; Isik, S. Water quality prediction using SWAT-ANN coupled approach. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.-S.; Pyo, J.; Chun, J.A. Prediction of water level and water quality using a CNN-LSTM combined deep learning approach. Water 2020, 12, 3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Jiang, M.; Xu, L.; Zhu, H.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, J. Snowmelt-Driven Streamflow Prediction Using Machine Learning Techniques (LSTM, ARX, GPR and SVR). Water 2020, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behzad, M.; Asghari, K.; Eazi, M.; Palhang, M. Generalization performance of support vector machines and neural networks in runoff modeling. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 7624–7629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katimon, A.; Shahid, S.; Mohsenipour, M. Modeling water quality and hydrological variables using ARIMA: A case study of Johor River, Malaysia. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 4, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Kang, Y.B.; Wang, D.Y.; Lu, Z.Y.; Tian, W.; Wang, S.Q. Forecast of water quality along the Luanhe River line based on BP neural network. Iop Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 267, 032075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frate, F.D.; Ferrazzoli, P.; Schiavon, G. Retrieving soil moisture and agricultural variables by microwave radiometry using neural networks. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, G.; Birkinshaw, S.J.; Younger, P.L.; Rao, Z.; Kirk, S. A numerical modelling and neural network approach to estimate the impact of groundwater abstractions on river flows. J. Hydrol. 2007, 339, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R. Prediction of Runoff Series in Jiulong River Basin Based on LSTM Model. Master’s Thesis, Changan University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, B.; Fang, K.; Chen, Y.M.; Zhu, X.H.; He, X.P. Wavelet-Recurrent neural network (RNN): A real-time denoising technology for water quality sensor data. J. Nanoelectron. Optoelectron. 2019, 14, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, K.J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Liu, L.F. Water quality prediction method based on LSTM neural network. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Knowledge Engineering, Nanjing, China, 24–26 November 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, K.; Shen, C.P.; Kifer, D.; Yang, X. Prolongation of SMAP to spatiotemporally seamless coverage of continental U.S. using a deep learning neural network. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Xiao, F.; Wang, Y.Y.; Sun, L.J. Water quality prediction method based on IGRA and LSTM. Water 2018, 10, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Wu, Q.; Li, H.; Jian, S.; Li, N.; Lou, Z. Deep Learning with a Long Short-Term Memory Networks Approach for Rainfall-Runoff Simulation. Water 2018, 10, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kratzert, F.; Klotz, D.; Brenner, C.; Schulz, K.; Herrnegger, M. Rainfall-runoff modeling using long short-term memory (LSTM) networks. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 6005–6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, X.; Gong, Y.F.; Cen, S.X.; Tian, H.; Zhang, H. Impact of the westerly jet on rainfall/runoff in the source region of the Yangtze River during the flood season. Adv. Meteorol. 2020, 6726347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wrb, I.W.G. World reference base for soil resources 2014. In International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, S.; Reynders, E.; Magalhães, F.; Cunha, Á.; Gomes, J.P. The role of modal parameters uncertainty estimation in automated modal identification, modal tracking and data normalization. Eng. Struct. 2020, 224, 111208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, S.; Ohzeki, M.; Taguchi, S. Efficient partition of integer optimization problems with one-hot encoding. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Peng, L.; Yao, X.J.; Cui, S.L.; Hu, Y.; You, C.Z.; Chi, T.H. Long short-term memory neural network for air pollutant concentration predictions: Method development and evaluation. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Wu, H.; Wang, J.W.; Dede, T. Research on the prediction of the water demand of construction engineering based on the BP neural network. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 8868817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans. Asabe 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, P.; Zhang, R.; Lin, Z. Determination of spatiotemporal characteristics of agricultural non-point source pollution of river basins using the dynamic time warping distance. J. Hydrol. 2020, 583, 124303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, S.J.; Baker, L.A. Sources and transport of organic carbon in an Arizona river-reservoir system. Water Res. 1997, 31, 1751–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamdari, N.; Sample, D.J.; Steinberg, P.; Ross, A.C.; Easton, Z.M. Assessing the effects of climate change on water quantity and quality in an urban watershed using a calibrated stormwater model. Water 2017, 9, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlen, D.L.; Dinnes, D.L.; Jaynes, D.B.; Hurburgh, C.R.; Cambardella, C.A.; Colvin, T.S.; Rippke, G.R. Corn response to late-spring nitrogen management in the Walnut Creek watershed. Agron. J. 2005, 97, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, T.; Mu, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, C. Smiulated research on decreasing pollution loads in rainfall runoff with accelerating infiltration. Tech. Equip. Environ. Pollut. Control 2006, 7, 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Schrumpf, M.; Zech, W.; Lehmann, J.; Lyaruu, H.V. TOC, TON, TOS and TOP in rainfall, throughfall, litter percolate and soil solution of a montane rainforest succession at Mt. Kilimanjaro, Tanzania. Biogeochemistry 2006, 78, 361–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Choi, Y.S.; Shin, H.J.; Song, I.; Yoon, C.G.; Choi, J.D.; Yu, S.J. A comparison study of runoff characteristics of non-point source pollution from three watersheds in South Korea. Water 2019, 11, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Deng, F.; Cai, Y.; Chen, J. Long short-term memory-Fully connected (LSTM-FC) neural network for PM2.5 concentration prediction. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

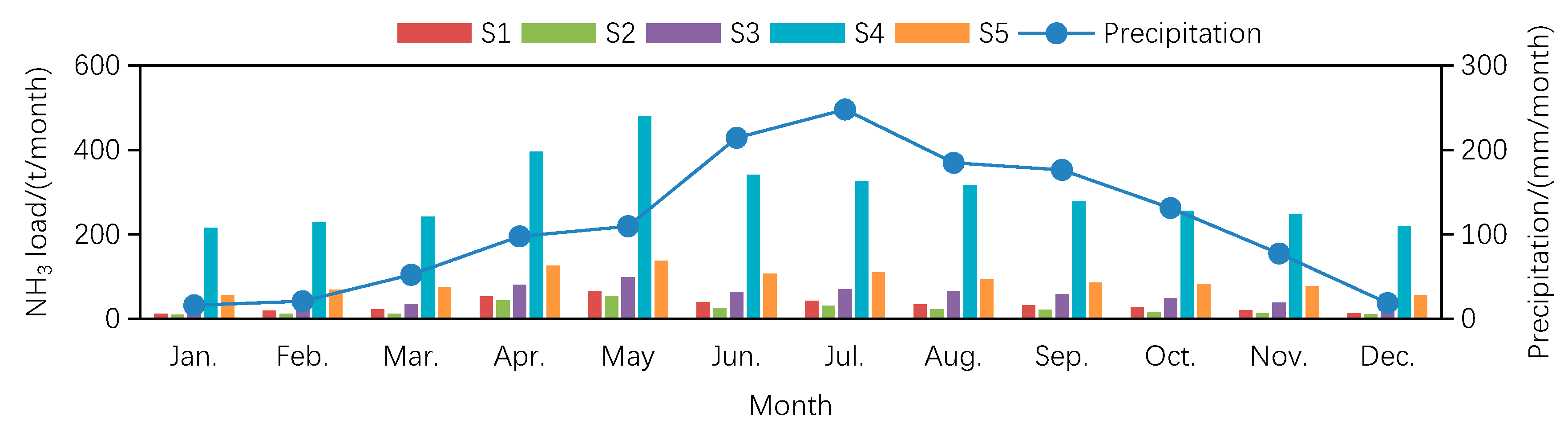
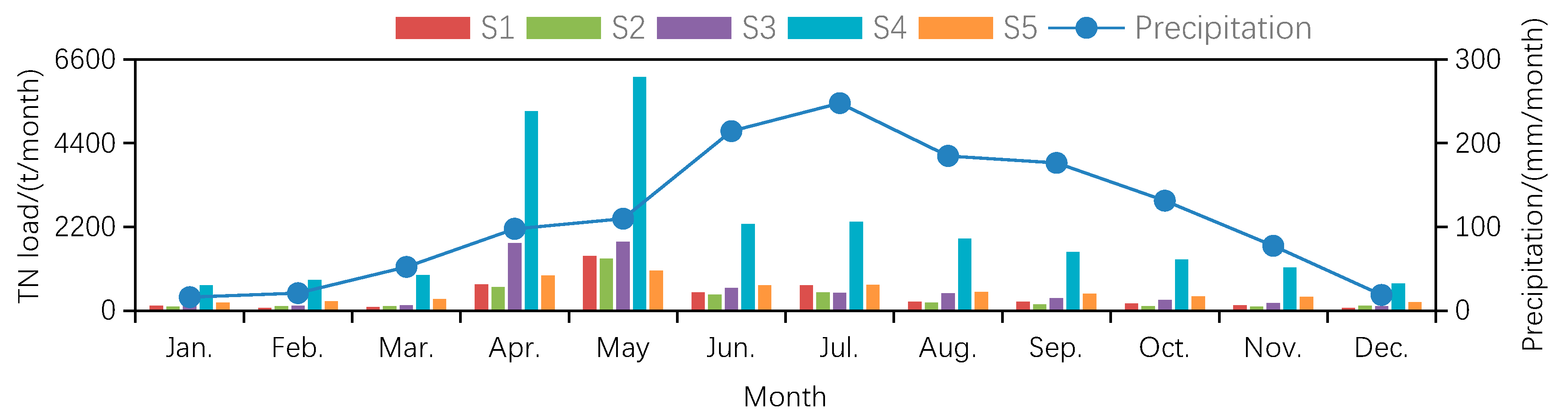
| Sub-Basin | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (km2) | 2040.1 | 816.0 | 2448.2 | 3019.4 | 2856.2 | |
| Mean slope (degree) | 12.2 | 8.4 | 16.8 | 13.5 | 11.4 | |
| Drainage density (km−1) | 0.174 | 0.201 | 0.165 | 0.164 | 0.157 | |
| Soil properties | Clay (%) | 21.56 ± 4.87 * | 22.74 ± 8.48 | 16.24 ± 5.80 | 19.04 ± 6.99 | 17.94 ± 10.27 |
| Silt (%) | 35.78 ± 12.04 | 31.18 ± 12.87 | 40.04 ± 18.12 | 30.17 ± 11.38 | 22.17 ± 15.84 | |
| Sand (%) | 41.16 ± 14.55 | 40.09 ± 19.72 | 44.26 ± 15.10 | 49.51 ± 15.07 | 59. 51 ± 18.40 | |
| Hydraulic conductivity (10−6 m·s−1) | 13.46 ± 8.71 | 12.41 ± 6.17 | 9.77 ± 8.54 | 10.24 ± 6.60 | 16.51 ± 8.31 | |
| Bulk density (g cm−³) | 1.38 ± 0.56 | 1.36 ± 0.44 | 1.37 ± 0.61 | 1.36 ± 0.52 | 1.33 ± 0.32 | |
| R2 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH3 | TN | NH3 | TN | NH3 | TN | NH3 | TN | NH3 | TN | |
| S1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.74 | 0.71 | 0.76 | 0.67 | 0.81 | 0.72 | 0.32 | 0.33 |
| S2 | 0.74 | 0.71 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.54 | 0.51 | 0.68 | 0.64 | 0.27 | 0.27 |
| S3 | 0.76 | 0.67 | 0.54 | 0.51 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.48 | 0.46 |
| S4 | 0.81 | 0.72 | 0.68 | 0.64 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.75 | 0.87 |
| S5 | 0.32 | 0.33 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.48 | 0.46 | 0.75 | 0.87 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Pollutant | Sub-Basin | BP | LSTM | LSTM-BP | SWAT | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | NSE | BIAS | RMSE | NSE | BIAS | RMSE | NSE | BIAS | RMSE | NSE | BIAS | ||
| NH3 (t/day) | S1 | 3.43 | 0.86 | 17.78 | 2.91 | 0.89 | 15.84 | 2.27 | 0.92 | 14.28 | 2.84 | 0.90 | 15.17 |
| S2 | 3.15 | 0.87 | 16.42 | 2.69 | 0.90 | 15.68 | 2.23 | 0.93 | 13.79 | 2.67 | 0.92 | 15.09 | |
| S3 | 5.32 | 0.84 | 19.09 | 4.13 | 0.89 | 17.98 | 3.42 | 0.91 | 16.13 | 4.53 | 0.89 | 18.25 | |
| S4 | 12.23 | 0.79 | 24.45 | 10.63 | 0.81 | 22.42 | 9.31 | 0.83 | 21.44 | 10.45 | 0.82 | 22.16 | |
| S5 | 7.28 | 0.82 | 22.43 | 5.23 | 0.89 | 18.34 | 4.16 | 0.90 | 16.48 | 5.18 | 0.89 | 19.53 | |
| TN (t/day) | S1 | 12.45 | 0.81 | 24.17 | 9.43 | 0.85 | 21.26 | 8.91 | 0.86 | 19.87 | 9.76 | 0.85 | 21.95 |
| S2 | 10.59 | 0.79 | 23.94 | 9.15 | 0.86 | 20.43 | 8.72 | 0.86 | 19.29 | 9.36 | 0.86 | 21.58 | |
| S3 | 17.45 | 0.75 | 29.64 | 13.66 | 0.78 | 21.83 | 12.24 | 0.81 | 21.23 | 13.82 | 0.79 | 22.47 | |
| S4 | 26.67 | 0.69 | 45.32 | 19.06 | 0.73 | 39.57 | 17.25 | 0.74 | 34.32 | 18.57 | 0.73 | 38.62 | |
| S5 | 19.52 | 0.74 | 32.37 | 13.76 | 0.79 | 25.77 | 12.74 | 0.80 | 23.83 | 14.98 | 0.79 | 25.13 | |
| Hydrological Periods | Dry Season | Flat Season | Flood Season | All Year | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH3 load (t/day) | RMSE | 3.98 | 9.31 | 8.97 | 6.27 |
| NSE | 0.88 | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.86 | |
| BIAS | 18.14 | 22.94 | 21.12 | 19.46 | |
| TN load (t/day) | RMSE | 13.75 | 32.31 | 28.24 | 20.27 |
| NSE | 0.78 | 0.64 | 0.68 | 0.71 | |
| BIAS | 24.43 | 41.28 | 39.03 | 36.87 | |
| Precipitation Intensity | No Rain | Light Rain | Moderate Rain | Heavy Rain | Torrential Rain | Severe Torrential Rain | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH3 load (t/day) | RMSE | 1.34 | 3.47 | 6.72 | 10.27 | 15.16 | 23.34 |
| NSE | 0.97 | 0.90 | 0.85 | 0.80 | 0.76 | 0.73 | |
| BIAS | 9.85 | 17.16 | 19.89 | 22.64 | 28.19 | 32.27 | |
| TN load (t/day) | RMSE | 8.71 | 12.84 | 17.23 | 22.34 | 27.75 | 36.49 |
| NSE | 0.84 | 0.80 | 0.75 | 0.74 | 0.69 | 0.63 | |
| BIAS | 20.99 | 22.98 | 29.71 | 31.85 | 37.63 | 45.57 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, D. Simulation of Pollution Load at Basin Scale Based on LSTM-BP Spatiotemporal Combination Model. Water 2021, 13, 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13040516
Li L, Liu Y, Wang K, Zhang D. Simulation of Pollution Load at Basin Scale Based on LSTM-BP Spatiotemporal Combination Model. Water. 2021; 13(4):516. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13040516
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Li, Yingjun Liu, Kang Wang, and Dan Zhang. 2021. "Simulation of Pollution Load at Basin Scale Based on LSTM-BP Spatiotemporal Combination Model" Water 13, no. 4: 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13040516






