Interannual and Spatial Variability of Cyanotoxins in the Prespa Lake Area, Greece
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
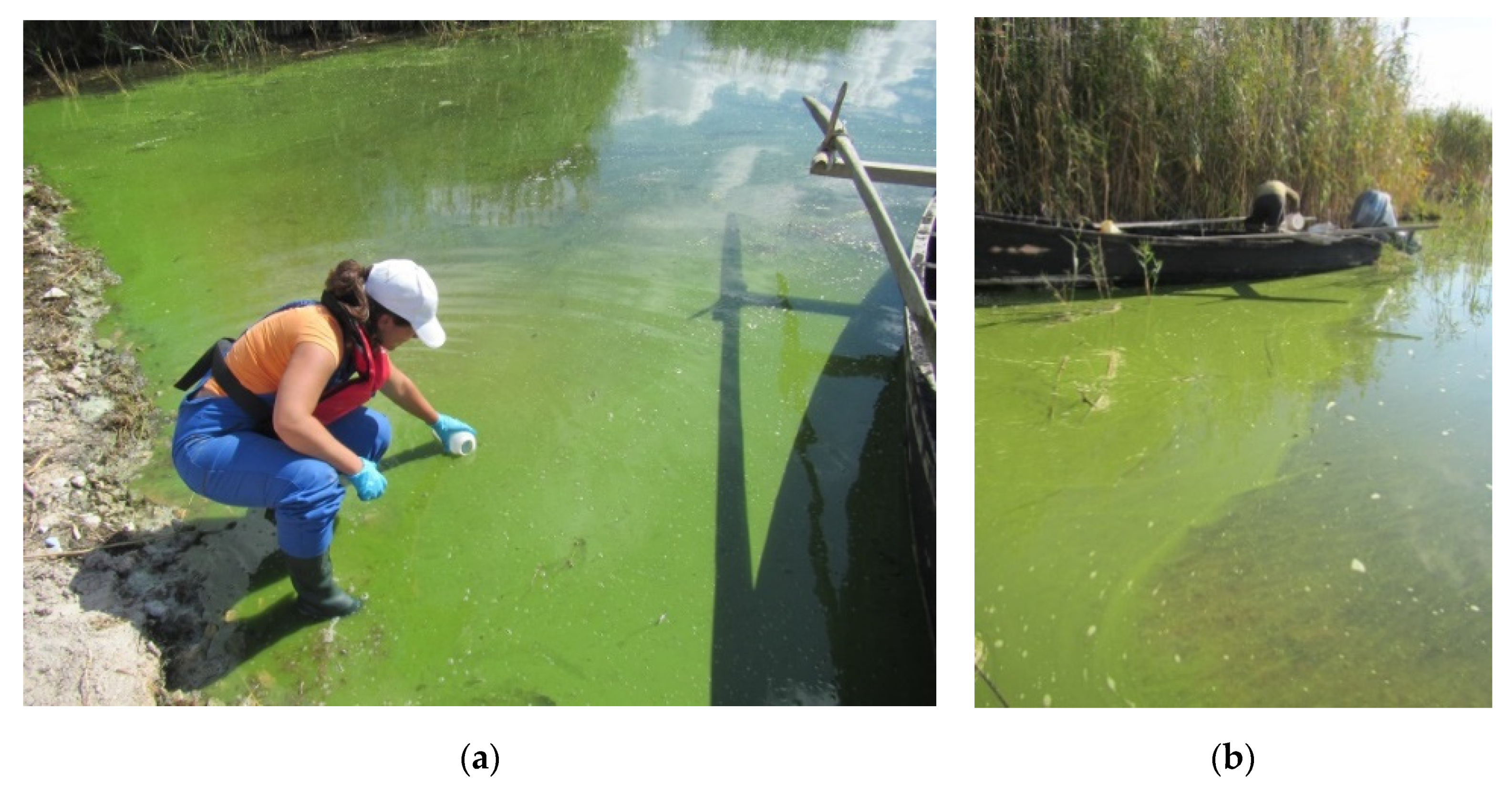
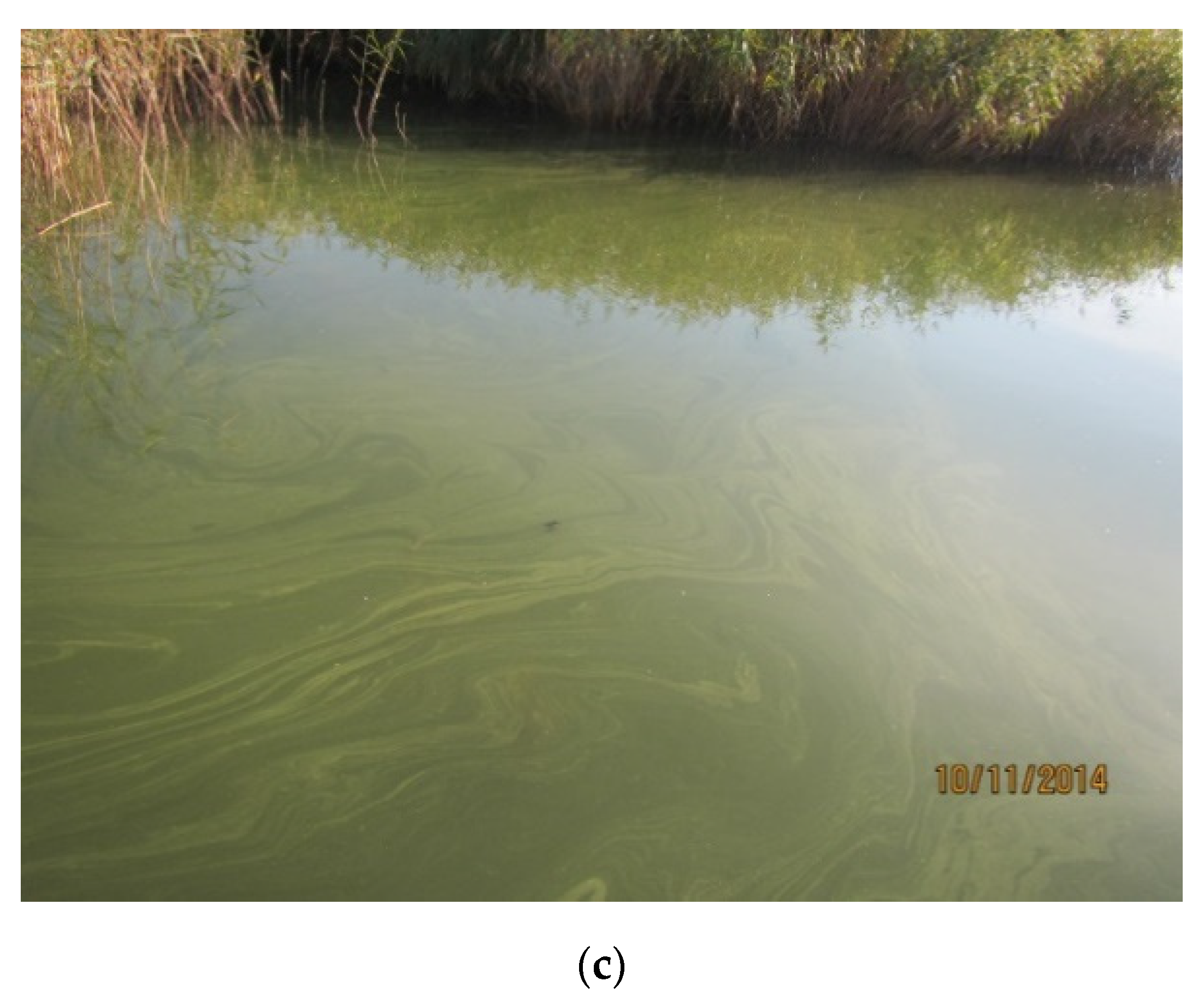
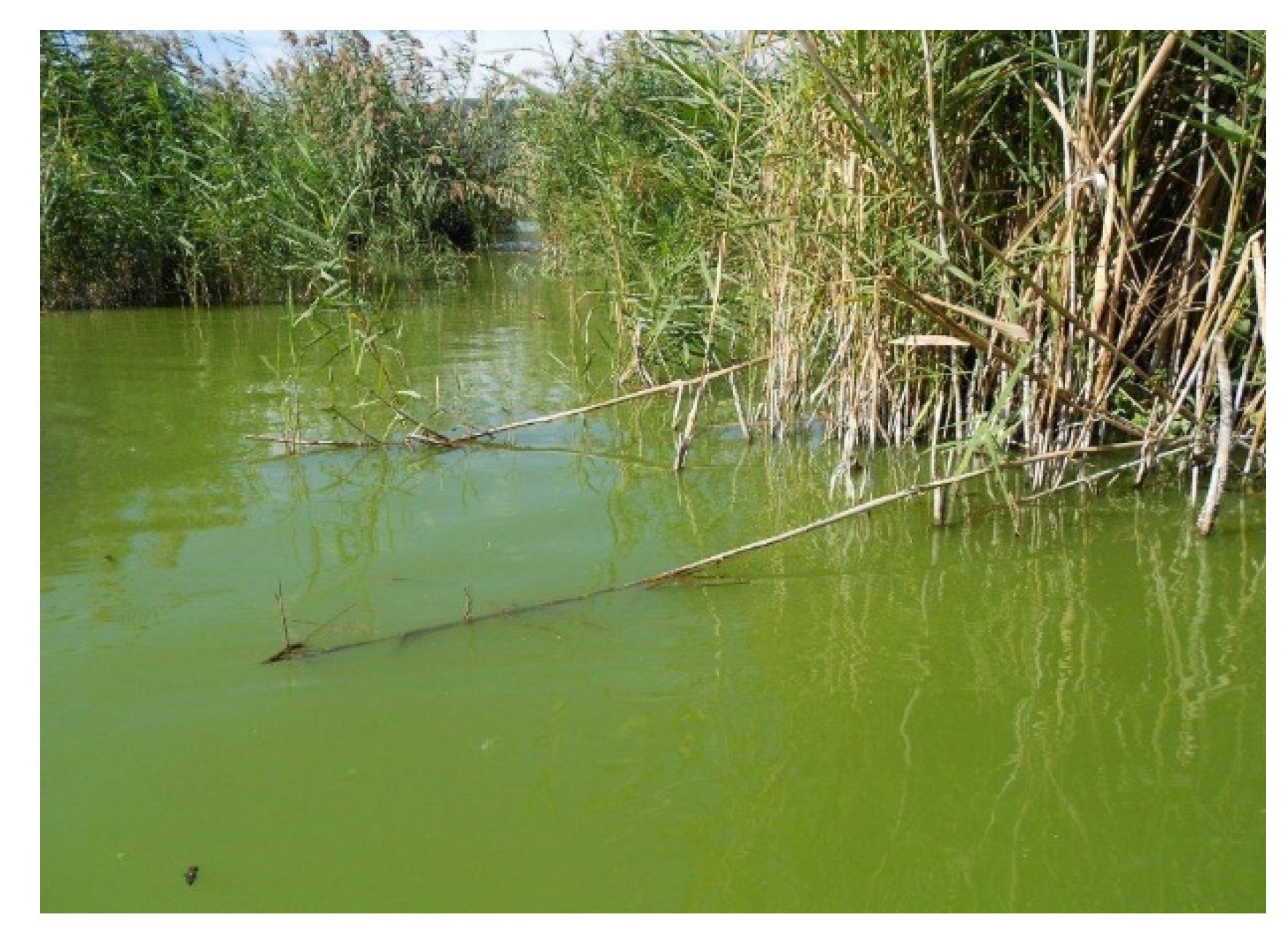
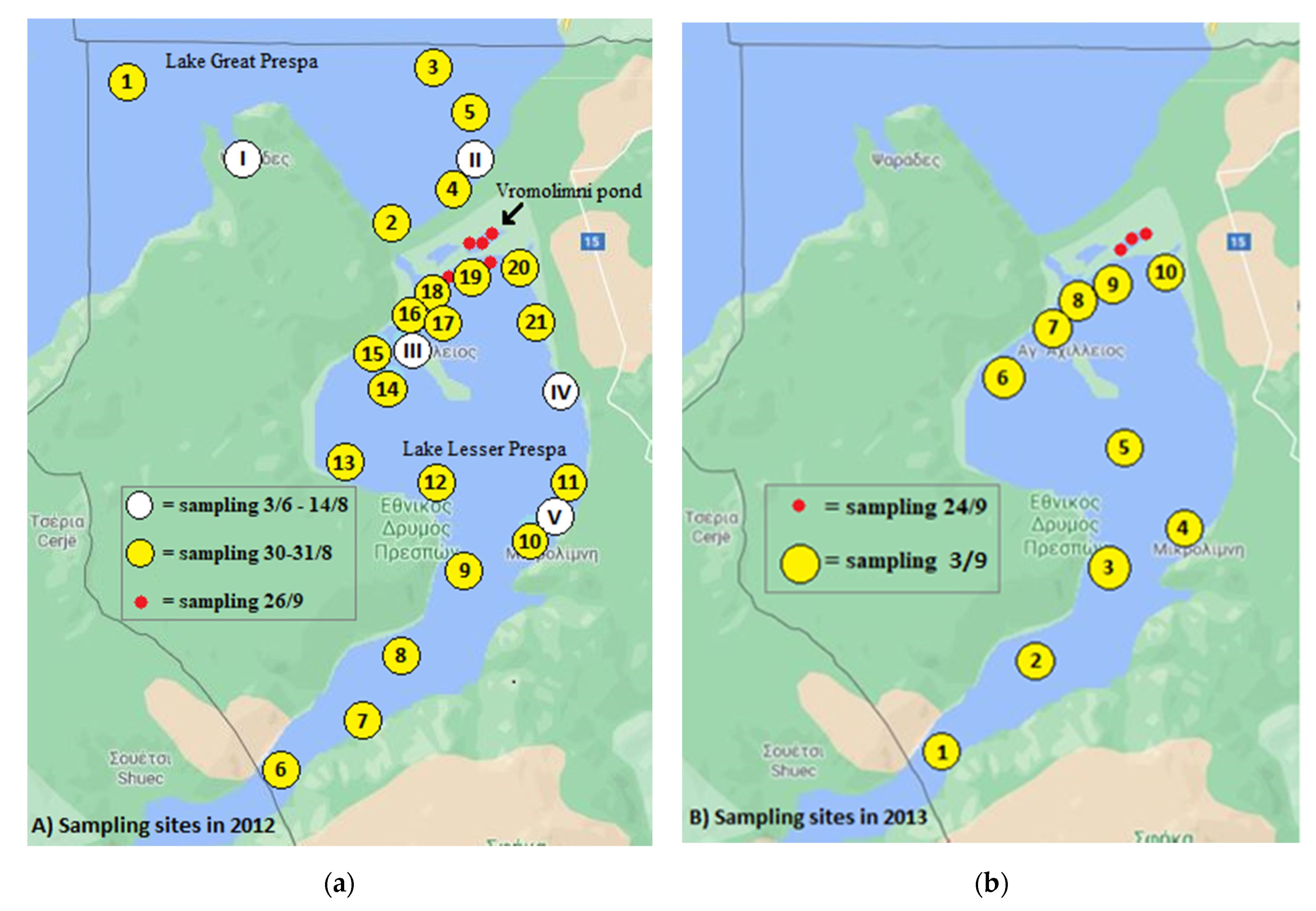
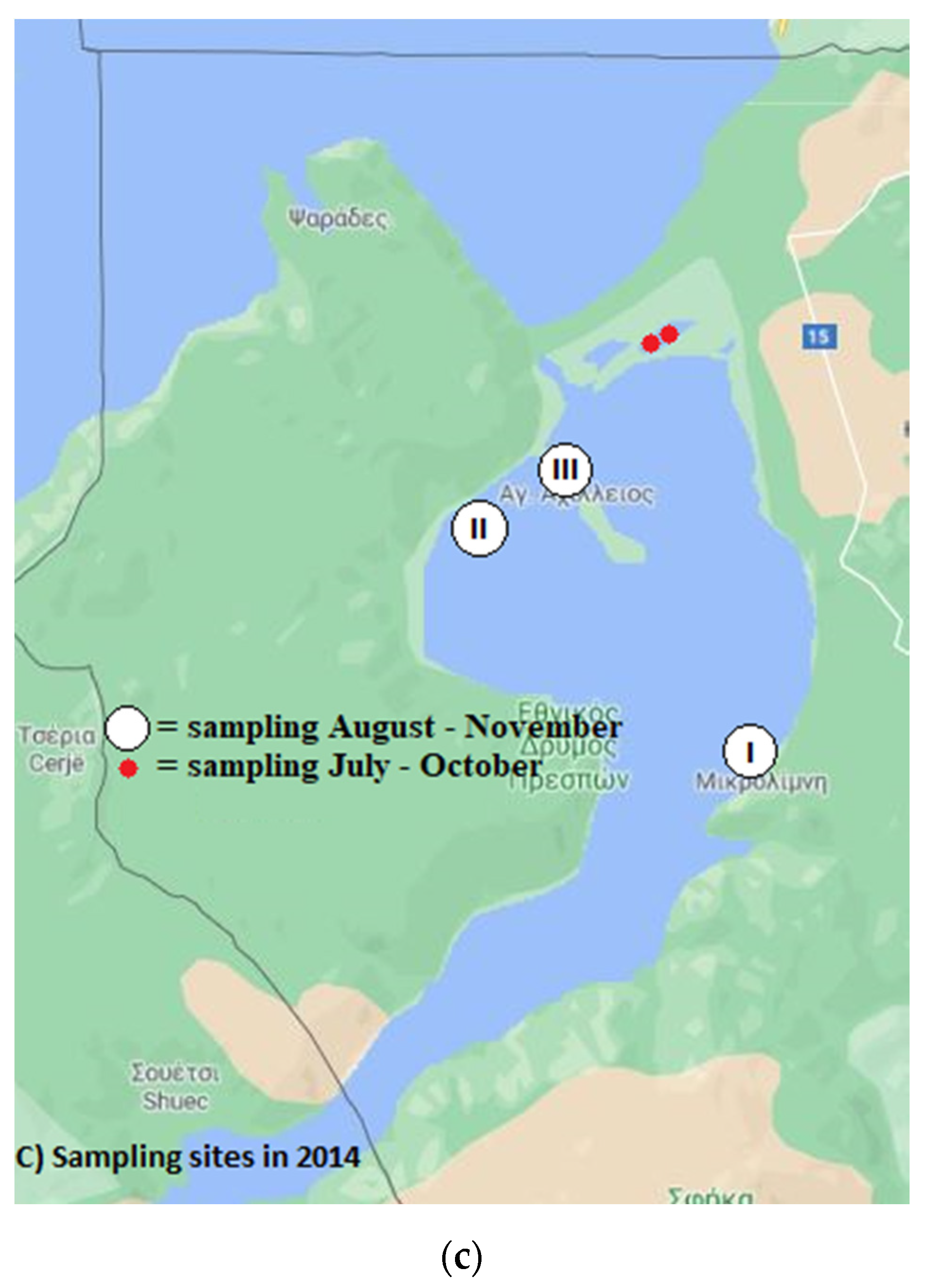
2.1. Sample Origin
2.1.1. Water Sampling
2.1.2. Animal Tissue Samples
2.2. Sample Extraction
2.2.1. Cyanobacteria Samples
2.2.2. Animal Tissue Samples
2.3. LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.3.1. Microcystins and Nodularin
2.3.2. Anatoxins and Cylindrospermopsins
2.3.3. Saxitoxins
3. Results
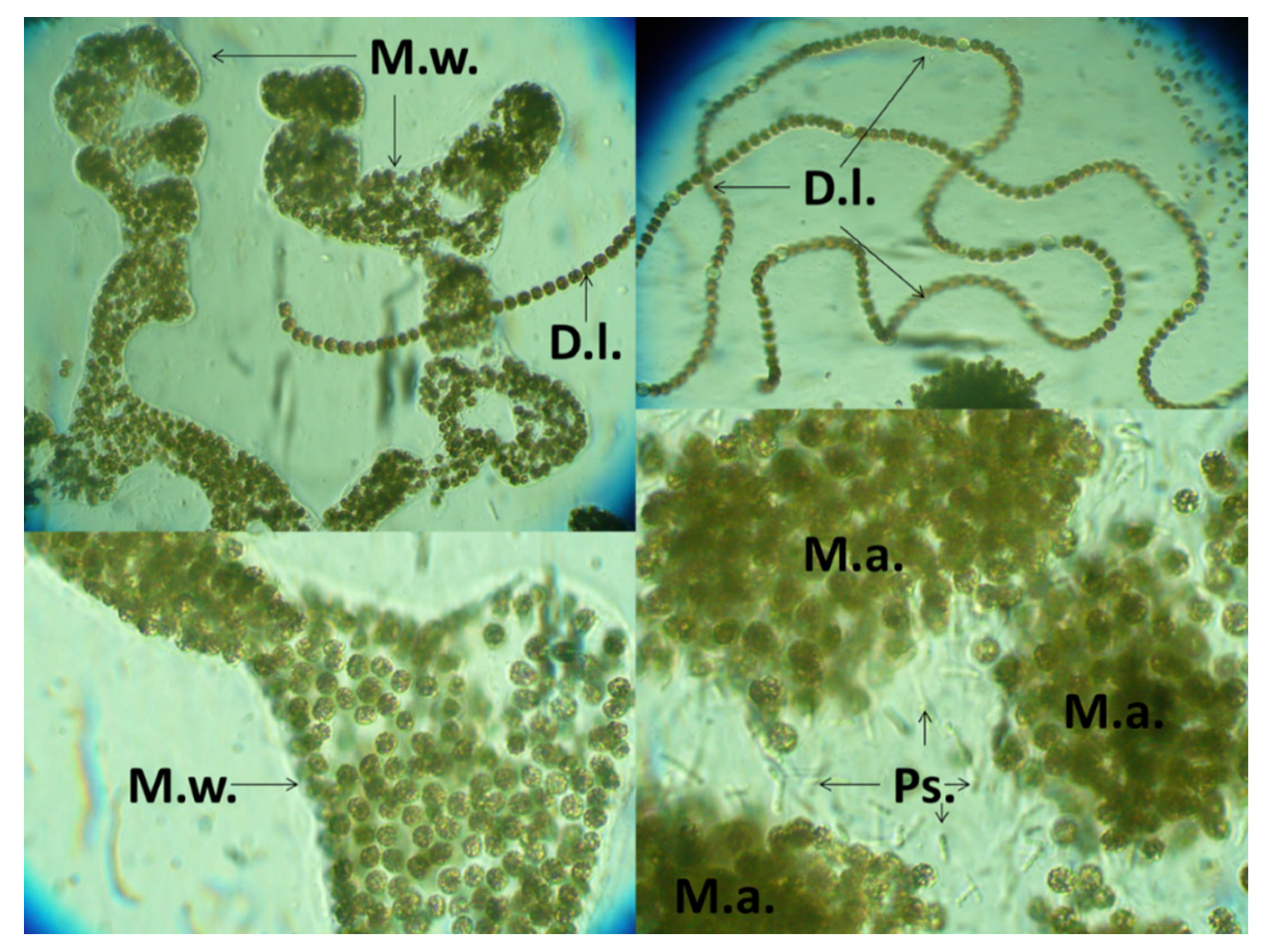
3.1. Lake Great Prespa
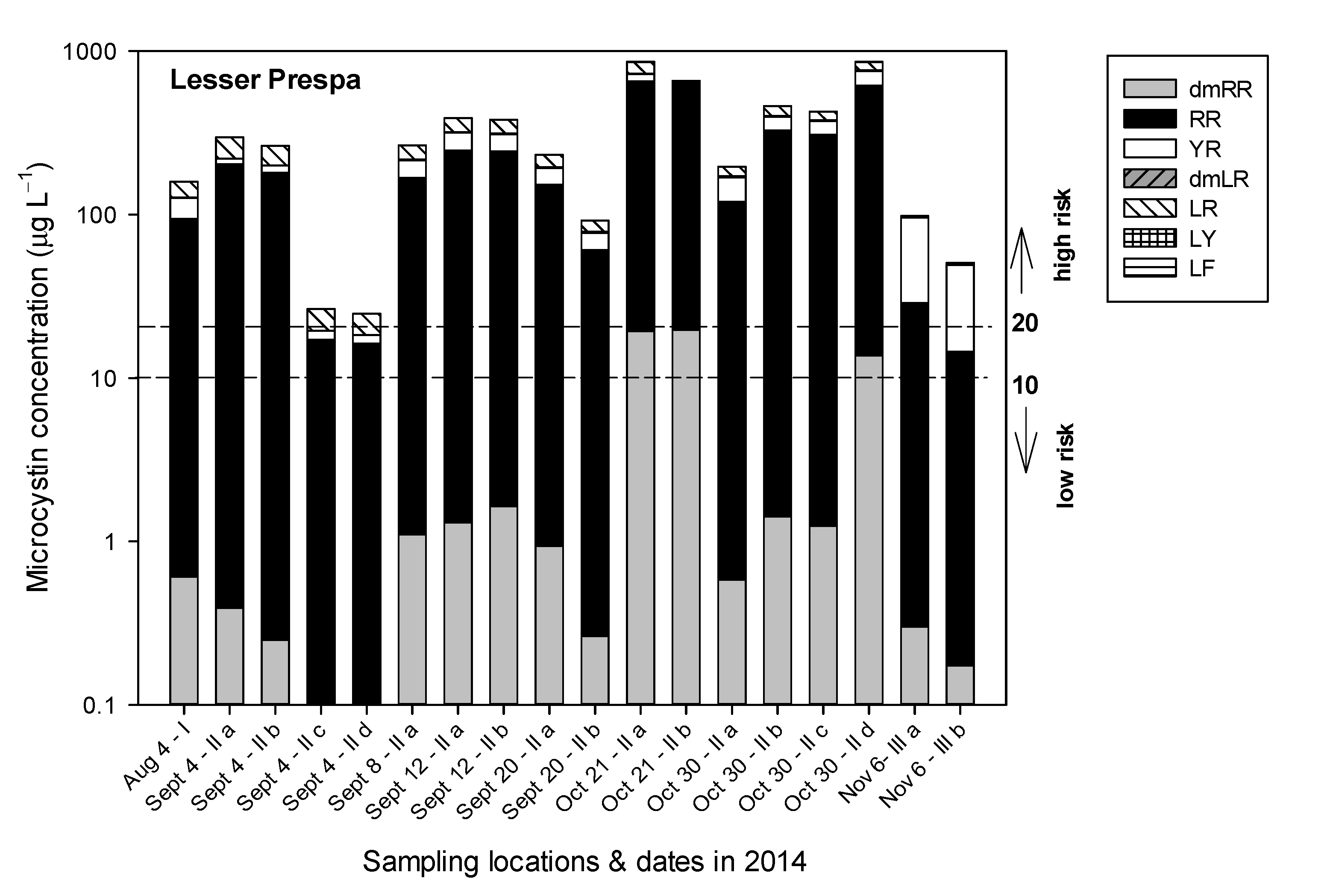
3.2. Lake Lesser Prespa
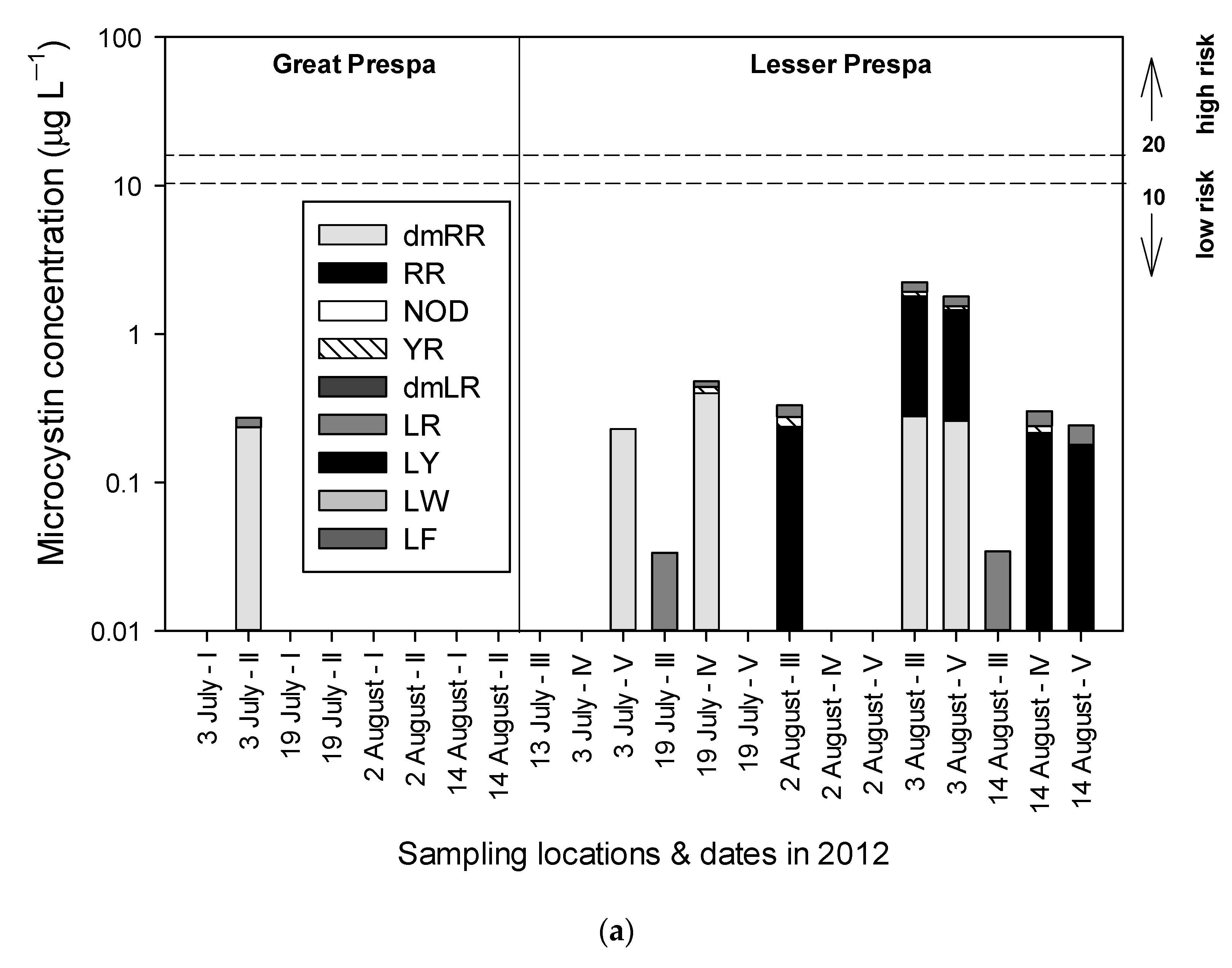
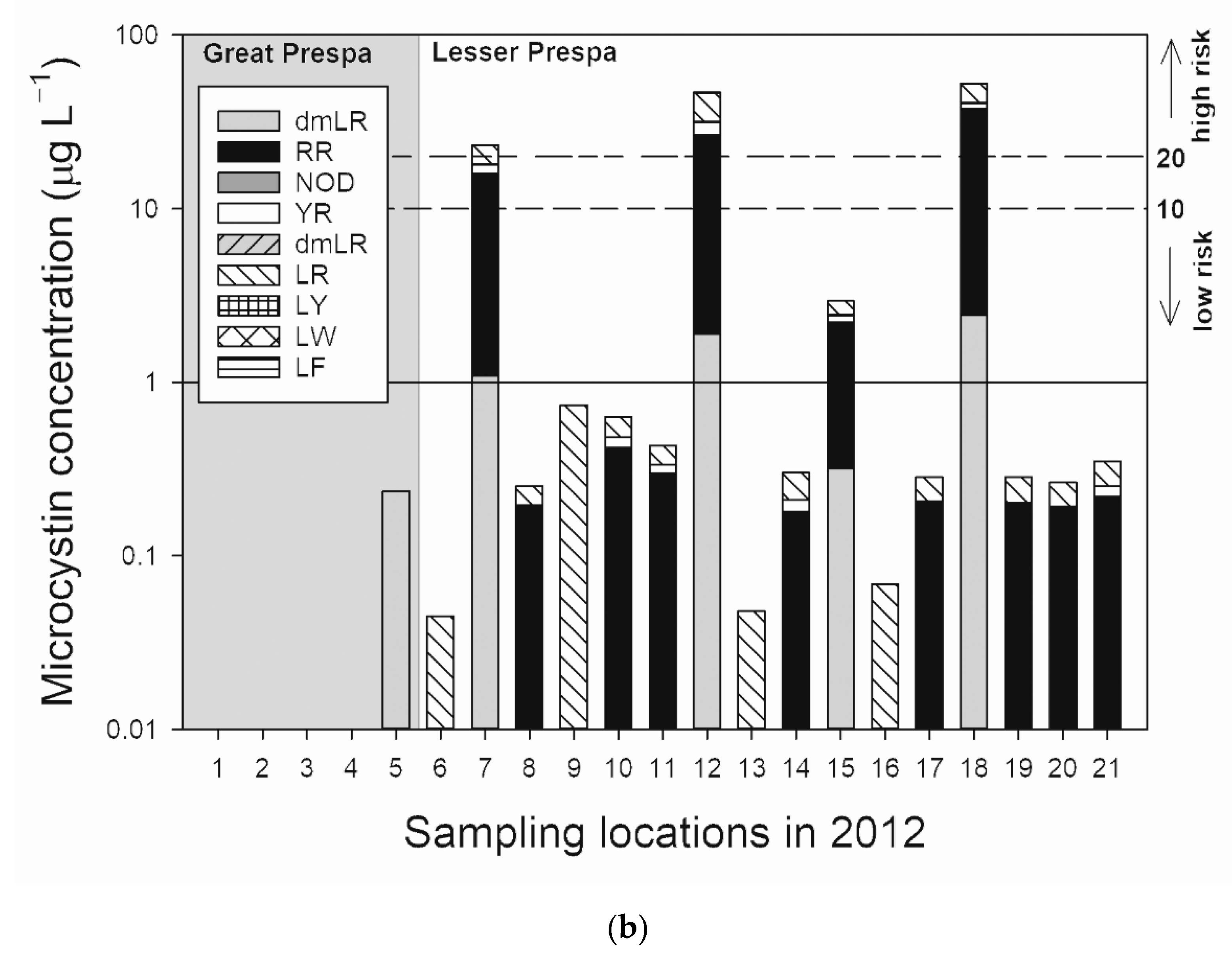
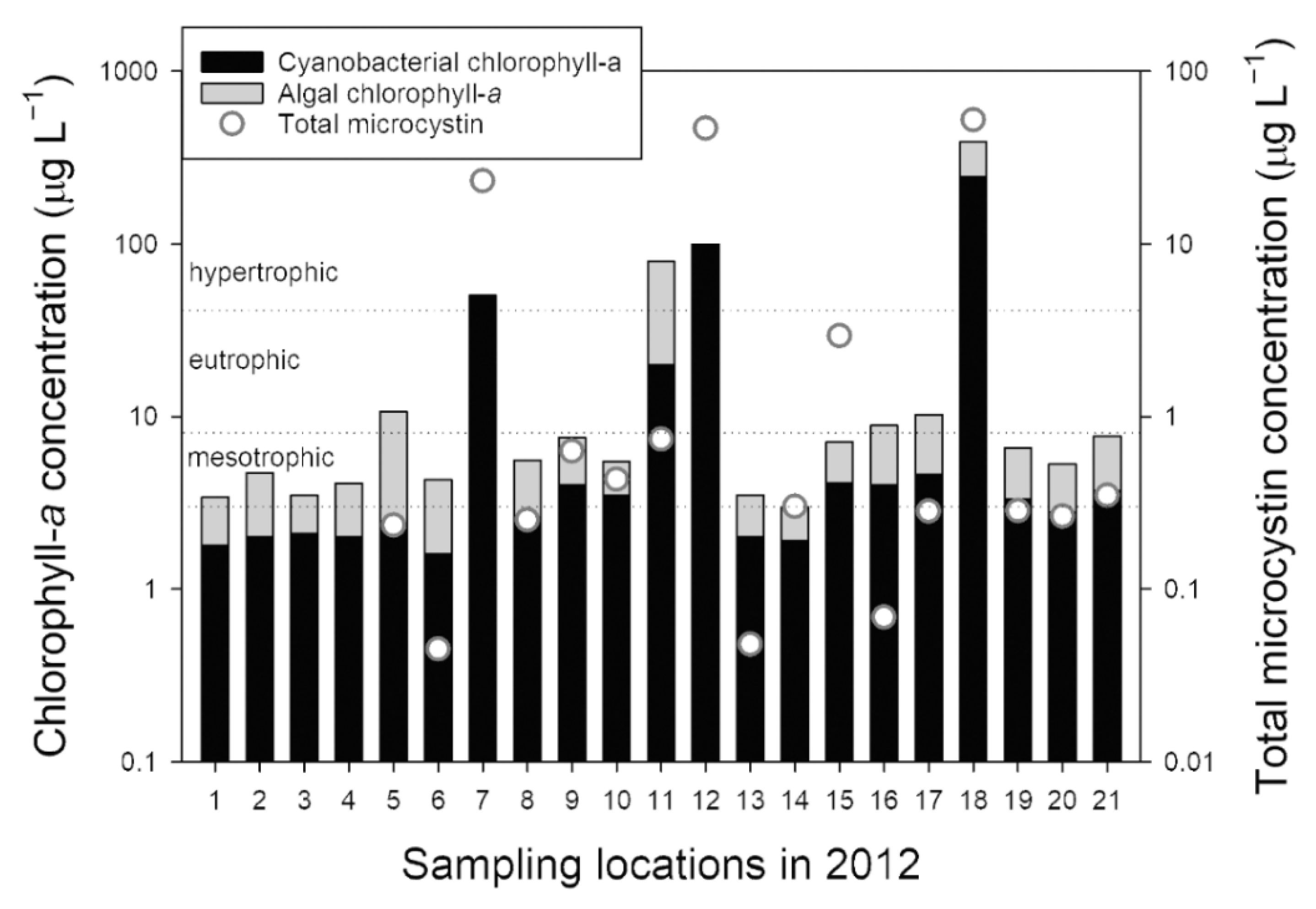
3.2.1. Sampling in 2012
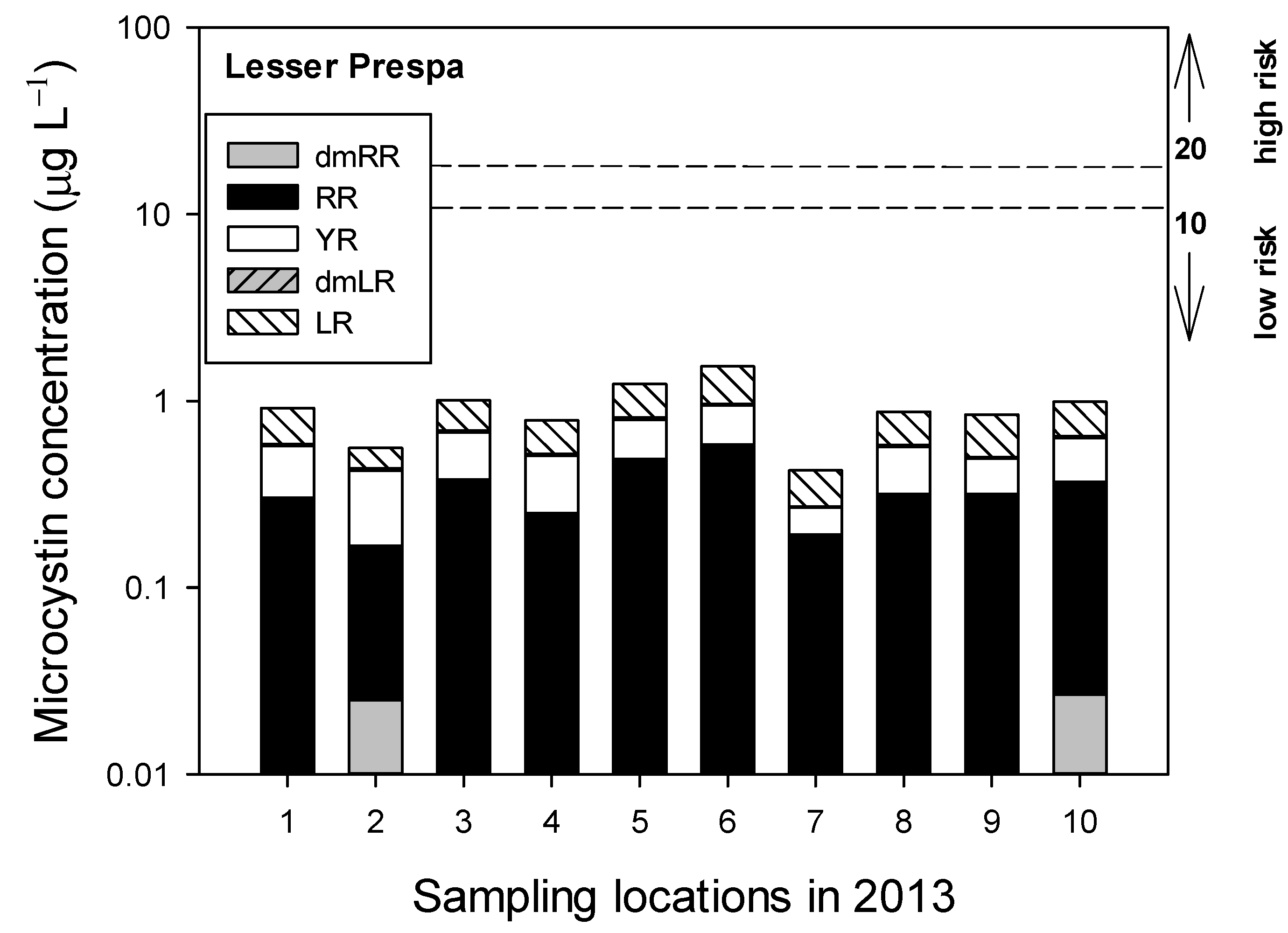
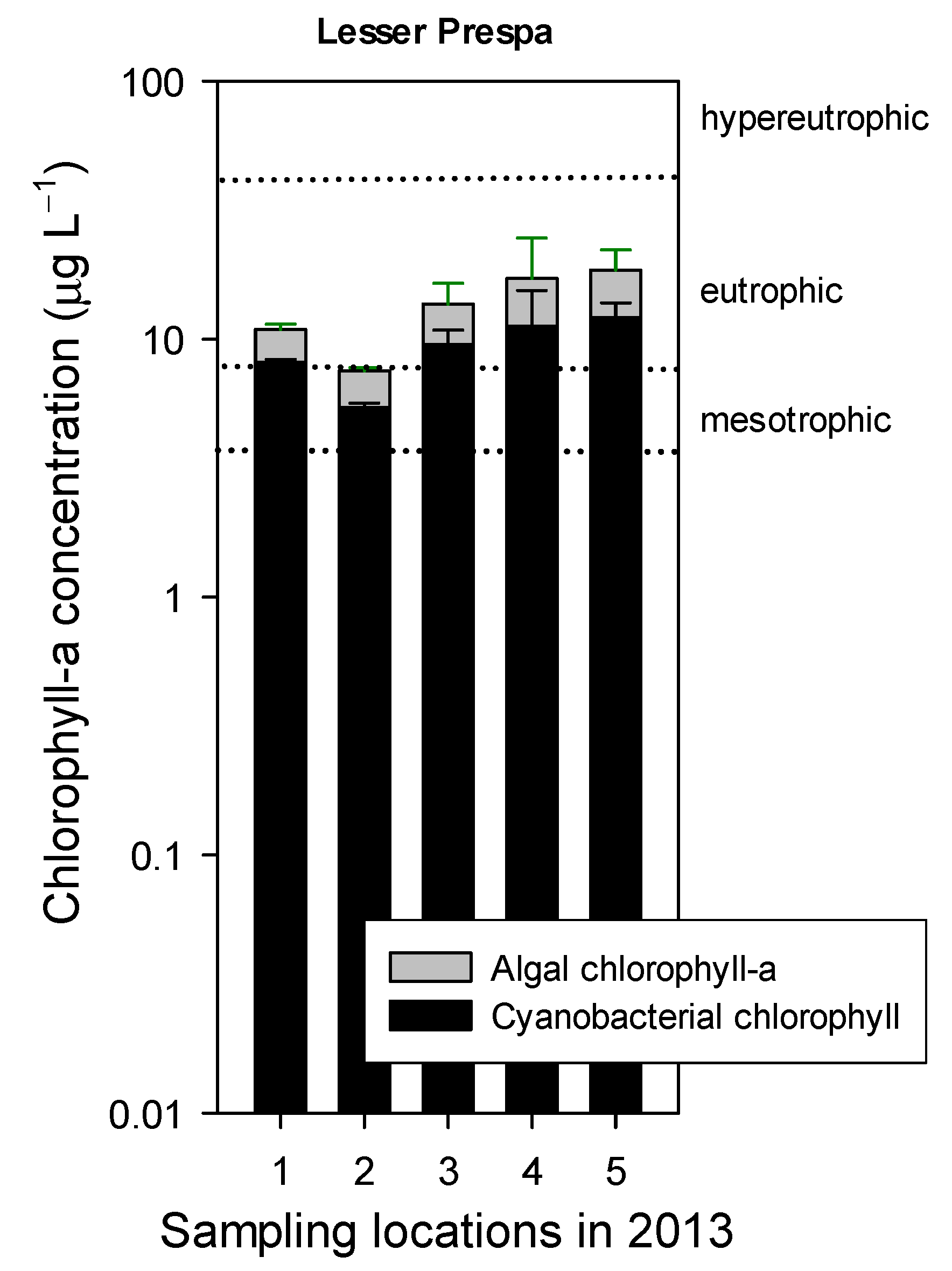
3.2.2. Sampling in 2013
3.2.3. Sampling in 2014
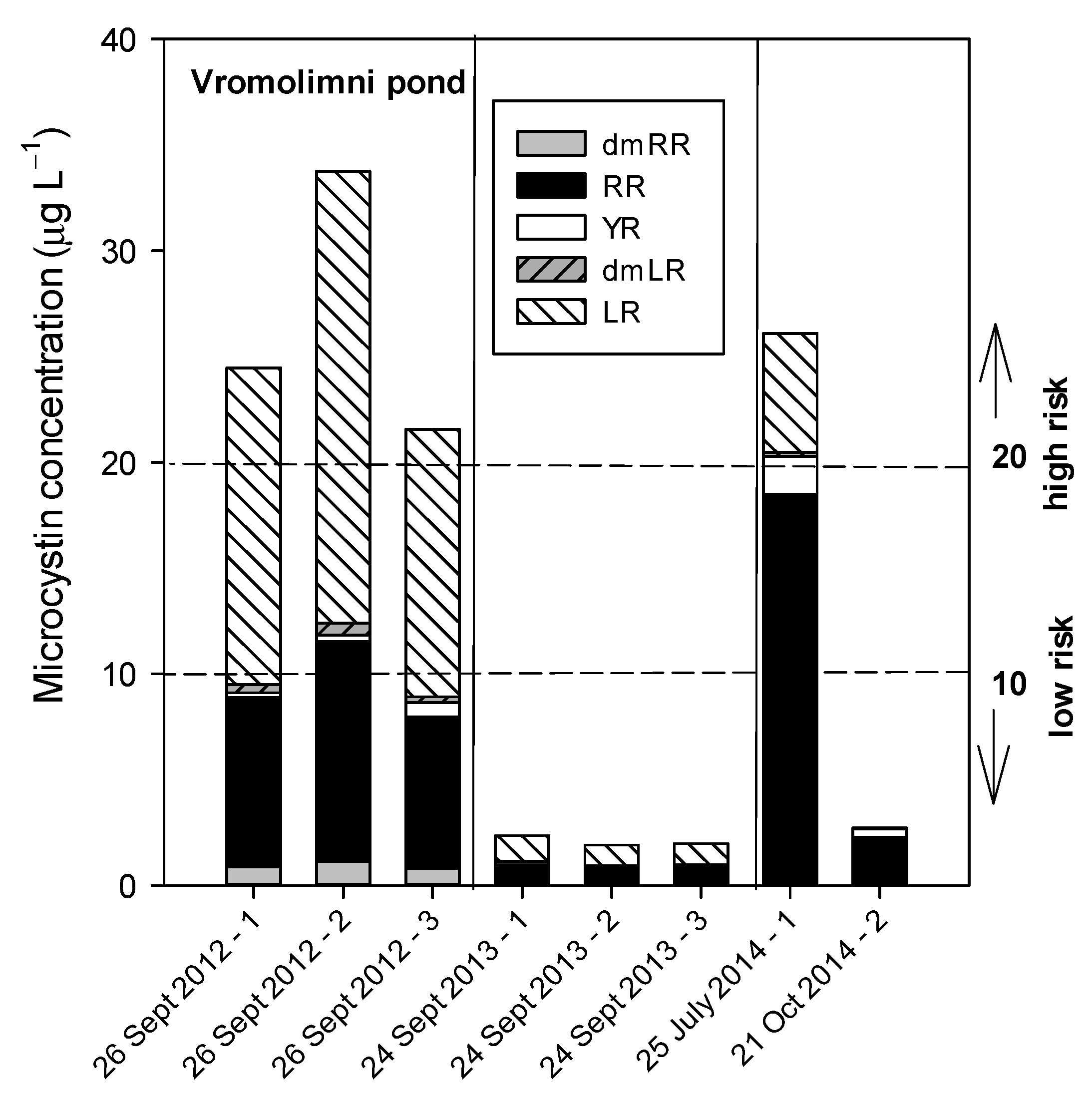
3.3. Pond Vromolimni
3.3.1. Sampling in 2012
3.3.2. Sampling in 2013
3.3.3. Sampling in 2014
3.4. Animal Tissue Samples
4. Discussion
4.1. Cyanotoxins in Prespa Waters
4.1.1. Lake Great Prespa
4.1.2. Lake Lesser Prespa
4.1.3. Vromolimni Pond
4.2. Cyanotoxins in Biota at Prespa Area
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A



References
- De Figueiredo, D.R.; Azeiteiro, U.M.; Esteves, S.M.; Gonçalves, F.J.; Pereira, M.J. Microcystin-producing blooms—a serious global public health issue. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 59, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neil, J.M.; Davis, T.W.; Burford, M.A.; Gobler, C.J. The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: The potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.B.; McCauley, E.; Downing, J.A. Patterns in phytoplankton taxonomic composition across temperate lakes of differing nutrient status. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H.; Tilman, G.D.; Nekola, J.C. Eutrophication: Impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 1999, 100, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Blooms Like It Hot. Science 2008, 320, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmann, E.; Wiegand, C. Cyanobacterial toxins--occurrence, biosynthesis and impact on human affairs. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2006, 50, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funari, E.; Testai, E. Human health risk assessment related to cyanotoxins exposure. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2008, 38, 97–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H. Nutrient and other environmental controls of harmful cyanobacterial blooms along the freshwater–marine continuum. In Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms: State of the Science and Research Needs; Hudnell, H.K., Ed.; Springer New York: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 217–237. [Google Scholar]
- Crivelli, A.J.; Catsadorakis, G. Lake Prespa, Northwestern Greece: A Unique Balkan Wetland; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 1997; Volume 351. [Google Scholar]
- Data from Ronald B. Mitchell. 2002–2021. International Environmental Agreements Database Project (Version 2020.1). Available online: http://iea.uoregon.edu/Date (accessed on 29 January 2021).
- Ramsar Site Information Service. Available online: https://rsis.ramsar.org/ris/60 (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- BirdLife International (2021) Species factsheet: Pelecanus crispus. Available online: http://www.birdlife.org (accessed on 29 January 2021).
- Malacou, M. Traditional ecological knowledge, conservation and socio-ecological perspectives in the Prespa transboundary Park. In Culture and Wetlands in the Mediterranean: An Evolving Story; Papayannis, T., Pritchard, D.E., Eds.; Med-INA: Athens, Greece, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Matzinger, A.; Jordanoski, M.; Veljanoska-Sarafiloska, E.; Sturm, M.; Müller, B.; Wüest, A. Is Lake Prespa Jeopardizing the Ecosystem of Ancient Lake Ohrid? Hydrobiologia 2006, 553, 89–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstić, S. Environmental Changes in Lakes Catchments as a Trigger for Rapid EutrophicationA Prespa Lake Case Study. In Studies on Environmental and Applied Geomorphology; Piacentini, T., Miccadei, E., Eds.; InTech: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Löffler, H.; Schiller, E.; Kusel, E.; Kraill, H. Lake Prespa, a European natural monument, endangered by irrigation and eutrophication? Hydrobiologia 1998, 384, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidis, K. Ecological Assessment of Lake of NW Greece with Emphasis on the Associations between Aquatic Macrophytes, Zooplankton and Water Quality; Department of Biology, University of Patras: Patras, Greece, 2012; 272p. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Schriek, T.; Giannakopoulos, C. Determining the causes for the dramatic recent fall of Lake Prespa (southwest Balkans). Hydrol. Sci. J. 2017, 62, 1131–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tryfon, E.; Moustaka-Gouni, M.; Nikolaidis, G. Planktic cyanophytes and their ecology in the shallow Lake Mikri Prespa, Greece. Nord. J. Bot. 1997, 17, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardaka, E.; Moustaka-Gouni, M.; Cook, M.C.; Lanaras, T. Cyanobacterial blooms and water quality in Greek waterbodies. J. Appl. Phycol. 2005, 17, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onen, K.; Jones, G.J. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management. In Cyanobacterial Toxins; Chorus, I., Bartram, J., Eds.; WHO: London, UK, 1999; pp. 41–111. [Google Scholar]
- Doekel, S.; Marahiel, M.A. Biosynthesis of Natural Products on Modular Peptide Synthetases. Metab. Eng. 2001, 3, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuiper-Goodman, T.; Falconer, I.R.; Fitzgerald, J. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management. In Human Health Aspects; Chorus, I., Bartram, J., Eds.; WHO: London, UK, 1999; pp. 41–110. [Google Scholar]
- Zurawell, R.W.; Chen, H.; Burke, J.M.; Prepas, E.E. Hepatotoxic cyanobacteria: A review of the biological importance of microcystins in freshwater environments. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2005, 8, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouria, S.; de Andrade, A.; Barbosa, J.; Cavalcanti, R.L.; Barreto, V.T.; Ward, C.J.; Preiser, W.; Poon, G.K.; Neild, G.H.; Codd, G.A. Fatal microcystin intoxication in haemodialysis unit in Caruaru, Brazil. Lancet 1998, 352, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Kudela, R.M.; Mekebri, A.; Crane, D.; Oates, S.C.; Tinker, M.T.; Staedler, M.; Miller, W.A.; Toy-Choutka, S.; Dominik, C.; et al. Evidence for a Novel Marine Harmful Algal Bloom: Cyanotoxin (Microcystin) Transfer from Land to Sea Otters. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhove, M.P.M.; Kovačić, M.; Koutsikos, N.E.; Zogaris, S.; Vardakas, L.E.; Huyse, T.; Economou, A.N. First record of a landlocked population of marine Millerigobius macrocephalus (Perciformes: Gobiidae): Observations from a unique spring-fed karstic lake (Lake Vouliagmeni, Greece) and phylogenetic positioning. Zool. Anz. J. Comp. Zool. 2011, 250, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lürling, M.; Faassen, E. Dog Poisonings Associated with a Microcystis aeruginosa Bloom in the Netherlands. Toxins 2013, 5, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, H.; Harada, K.I.; Senma, M.; Ito, Y.; Yasuda, N.; Ushida, S.; Kimura, Y. Possible cause of unnatural mass death of wild birds in a pond in Nishinomiya, Japan: Sudden appearance of toxic cyanobacteria. Nat. Toxins 1999, 7, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, C.M.; Vardaka, E.; Lanaras, T. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Greek Freshwaters, 1987—2000: Occurrence, Toxicity, and Impacts in the Mediterranean Region. Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 2004, 32, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkelis, S.; Harjunpää, V.; Lanaras, T.; Sivonen, K. Diversity of hepatotoxic microcystins and bioactive anabaenopeptins in cyanobacterial blooms from Greek freshwaters. Environ. Toxicol. 2005, 20, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitriou, T.; Kagalou, I.; Bacopoulos, V.; Leonardos, I.D. Accumulation of microcystins in water and fish tissues: An estimation of risks associated with microcystins in most of the Greek Lakes. Environ. Toxicol. 2010, 25, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkelis, S.; Lanaras, T.; Sivonen, K. Cyanobacterial Toxic and Bioactive Peptides in Freshwater Bodies of Greece: Concentrations, Occurrence Patterns, and Implications for Human Health. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6319–6335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christophoridis, C.; Zervou, S.; Manolidi, K.; Katsiapi, M.; Moustaka-Gouni, M.; Kaloudis, T.; Triantis, T.M.; Hiskia, A. Occurrence and diversity of cyanotoxins in Greek lakes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otten, T.G.; Xu, H.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Paerl, H.W. Spatiotemporal Patterns and Ecophysiology of Toxigenic Microcystis Blooms in Lake Taihu, China: Implications for Water Quality Management. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3480–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pobel, D.; Robin, L.; Humbert, J.-F. Influence of sampling strategies on the monitoring of cyanobacteria in shallow lakes: Lessons from a case study in France. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepistö, L.; Rapala, J.; Lyra, C.; Berg, K.A.; Erkomaa, K.; Issakainen, J. Occurrence and toxicity of cyanobacterial blooms dominated by Anabaena lemmermannii P. Richter and Aphanizomenon spp. in boreal lakes in 2003. Algol. Stud. 2005, 117, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koussouris, T.S.; Diapoulis, A.C.; Balopoulos, E.T. Assessing the trophic status of Lake Mikri Prespa, Greece. Ann. Limnol. Int. J. Limnol. 1989, 25, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faassen, E.J.; Harkema, L.; Begeman, L.; Lurling, M. First report of (homo)anatoxin-a and dog neurotoxicosis after ingestion of benthic cyanobacteria in The Netherlands. Toxicon 2012, 60, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, L.M.; Ger, K.A.; Silva, L.H.S.; Soares, M.C.S.; Faassen, E.J.; Lürling, M. Toxicity overrides morphology on Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii grazing resistance to the calanoid copepod Eudiaptomus gracilis. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 71, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorus, I.; Falconer, I.R.; Salas, H.J.; Bartram, J. Health risks caused by freshwater cyanobacteria in recreational waters. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2000, 3, 323–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nürnberg, G.K. Trophic State of Clear and Colored, Soft- and Hardwater Lakes with Special Consideration of Nutrients, Anoxia, Phytoplankton and Fish. Lake Reserv. Manag. 1996, 12, 432–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspers, H. OECD: Eutrophication of Waters. Monitoring, Assessment and Control; Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development: Paris, France, 1982; p. 154. [Google Scholar]
- Tryfon, E.; Moustaka-Gouni, M. Species composition and seasonal cycles of phytoplankton with special reference to the nanoplankton of Lake Mikri Prespa. Hydrobiologia 1997, 351, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsiapi, M.; Genitsaris, S.; Stefanidou, N.; Tsavdaridou, A.; Giannopoulou, I.; Stamou, G.; Michaloudi, E.; Mazaris, A.D.; Moustaka-Gouni, M. Ecological Connectivity in Two Ancient Lakes: Impact upon Planktonic Cyanobacteria and Water Quality. Water 2020, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivonen, K.; Namikoshi, M.; Evans, W.R.; Carmichael, W.W.; Sun, F.; Rouhiainen, L.; Luukkainen, R.; Rinehart, K.L. Isolation and characterization of a variety of microcystins from seven strains of the cyanobacterial genus Anabaena. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 2495–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapala, J.; Rapala, J.; Sivonen, K.; Lyra, C.; Niemelä, S.I. Variation of microcystins, cyanobacterial hepatotoxins, in Anabaena spp. as a function of growth stimuli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 2206–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tryfon, E. Chlorophyll-a distribution in the shallow lake Mikri Prespa, Greece. Biologia 2001, 56, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Tryfon, E.; Moustaka-Gouni, M.; Nikolaidis, G.; Tsekos, I. Phytoplankton and physical-chemical features of the shallow Lake Mikri Prespa, Macedonia, Greece. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1994, 131, 477–494. [Google Scholar]
- Boopathi, T.; Ki, J.-S. Impact of Environmental Factors on the Regulation of Cyanotoxin Production. Toxins 2014, 6, 1951–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliaka, V.; Verstijnen, Y.J.M.; Faassen, E.J.; Smolders, A.J.P.; Lurling, M. Effects of guanotrophication and warming on the abundance of green algae, cyanobacteria and microcystins in Lake Lesser Prespa, Greece. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittencourt-Oliveira, M.; Oliveira, M.; Pinto, E. Diversity of microcystin-producing genotypes in Brazilian strains of Microcystis (Cyanobacteria). Braz. J. Biol. 2011, 71, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstijnen, Y.J.M.; Maliaka, V.; Catsadorakis, G.; Lürling, M.; Smolders, A.J.P. Colonial nesting waterbirds as vectors of nutrients to Lake Lesser Prespa (Greece). Inland Waters 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agha, R.; Cirés, S.; Wörmer, L.; Quesada, A. Limited stability of microcystins in oligopeptide compositions of Microcystis aeruginosa (Cyanobacteria): Implications in the definition of chemotypes. Toxins 2013, 5, 1089–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Xue, Q.; Steinman, A.D.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, L. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Microcystin Variants and Relationships with Environmental Parameters in Lake Taihu, China. Toxins 2015, 7, 3224–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Waal, D.B.; Smith, V.H.; Declerck, S.A.J.; Stam, E.C.M.; Elser, J.J. Stoichiometric regulation of phytoplankton toxins. Ecol. Lett. 2014, 17, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Waal, D.B.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Lürling, M.; Van Donk, E.; Visser, P.M.; Huisman, J. The ecological stoichiometry of toxins produced by harmful cyanobacteria: An experimental test of the carbon-nutrient balance hypothesis. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 1326–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Xie, P.; Guo, L.; Li, L.; Miyabara, Y.; Park, H.D. Organ distribution and bioaccumulation of microcystins in freshwater fish at different trophic levels from the eutrophic Lake Chaohu, China. Environ. Toxicol. 2005, 20, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Asthana, R.K. Assessment of microcystin concentration in carp and catfish: A case study from Lakshmikund pond, Varanasi, India. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 92, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, T.; Katsiapi, M.; Kormas, K.A.; Moustaka-Gouni, M.; Kagalou, I. Artificially-born “killer” lake: Phytoplankton based water quality and microcystin affected fish in a reconstructed lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 452–453, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, J.P.; Lee, E.; Walton, K.; Wilson, A.E.; Bernal-Brooks, F. Bioaccumulation of microcystins by fish associated with a persistent cyanobacterial bloom in Lago de Patzcuaro (Michoacan, Mexico). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 1621–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Luo, W.; Lu, Y.; Giesy, J.P. Bioaccumulation of microcystins (MCs) in four fish species from Lake Taihu, China: Assessment of risks to humans. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 487, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Xie, P.; Liu, Y.; Qiou, T. Transfer, distribution and bioaccumulation of microcystins in the aquatic food web in Lake Taihu, China, with potential risks to human health. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2191–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, J.R.; Shaskus, M.; Estenik, J.F.; Oesch, C.; Khidekel, R.; Boyer, G.L. Variations in the microcystin content of different fish species collected from a eutrophic lake. Toxins 2013, 5, 992–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, W.; Zhang, J.; Luo, Y. Microcystin accumulation in bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis) during a Microcystis-dominated bloom and risk assessment of the dietary intake in a fish pond in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 8894–8902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Xie, P.; Ozawa, K.; Honma, T.; Yokoyama, A.; Park, H.-D. Dynamics of microcystins-LR and -RR in the phytoplanktivorous silver carp in a sub-chronic toxicity experiment. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 127, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamovský, O.; Kopp, R.; Hilscherová, K.; Babica, P.; Palíková, M.; Pasková, V.; Navrátil, S.; Marsálek, B.; Bláha, L. Microcystin kinetics (bioaccumulation and elimination) and biochemical responses in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) and silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) exposed to toxic cyanobacterial blooms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2007, 26, 2687–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, Q.; Zhang, X. Are fish fed with cyanobacteria safe, nutritious and delicious? A laboratory study. Sci Rep. 2015, 5, 15166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crivelli, A.J. Action Plan for the Dalmatian Pelican (Pelecanus crispus) in Europe; Station Biologique de la Tour du Valat: Arles, France, 1996; 29p. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, J. Toxic cyanobacteria in Florida waters. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2008, 619, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, T.; Katsiapi, M.; Vlachopoulos, K.; Christopoulos, A.; Laspidou, C.; Moustaka-Gouni, M.; Kormas, K. Cyanotoxins as the “common suspects” for the Dalmatian pelican (Pelecanus crispus) deaths in a Mediterranean reconstructed reservoir. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliaka, V.; Faassen, E.J.; Smolders, A.J.; Lürling, M. The Impact of Warming and Nutrients on Algae Production and Microcystins in Seston from the Iconic Lake Lesser Prespa, Greece. Toxins 2018, 10, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maliaka, V.; Lürling, M.; Fritz, C.; Verstijnen, Y.J.M.; Faassen, E.J.; van Oosterhout, F.; Smolders, A.J.P. Interannual and Spatial Variability of Cyanotoxins in the Prespa Lake Area, Greece. Water 2021, 13, 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030357
Maliaka V, Lürling M, Fritz C, Verstijnen YJM, Faassen EJ, van Oosterhout F, Smolders AJP. Interannual and Spatial Variability of Cyanotoxins in the Prespa Lake Area, Greece. Water. 2021; 13(3):357. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030357
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaliaka, Valentini, Miquel Lürling, Christian Fritz, Yvon J.M. Verstijnen, Elisabeth J. Faassen, Frank van Oosterhout, and Alfons J.P. Smolders. 2021. "Interannual and Spatial Variability of Cyanotoxins in the Prespa Lake Area, Greece" Water 13, no. 3: 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030357
APA StyleMaliaka, V., Lürling, M., Fritz, C., Verstijnen, Y. J. M., Faassen, E. J., van Oosterhout, F., & Smolders, A. J. P. (2021). Interannual and Spatial Variability of Cyanotoxins in the Prespa Lake Area, Greece. Water, 13(3), 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030357






