Abstract
The current knowledge of the spatial variability of precipitation in High Mountain Asia is based on the remotely-sensed estimates (coarse spatial and temporal resolution) or data from sparsely-distributed rain gauges. However, as precipitation is strongly affected by topography in mountainous terrain, the spatially varying precipitation and the resulting water balances are currently poorly understood. To fill this gap in knowledge, we studied the spatial variation of the precipitation and its impact on water balance in a small headwater basin located in the foothills of the Himalaya, Nepal. We deployed ten rain gauges and climate stations, spanning the whole elevation range 700–4500 m above sea level (masl) for a period of four years. Our results show a quadratic polynomial relationship between annual precipitation and station elevation, which are used to produce annual precipitation maps. The performance of the elevation-based precipitation estimates is adequate in closing the water balance while the performances of average precipitation and Thiessen polygon method are poor and inconsistent in closing the water balance. We also demonstrate that precipitation estimates from one or two gauges at the lowest basin elevation substantially underestimate the water balance. However, the precipitation from one or two rain gauges at 2000–3000 masl provide a significantly better estimate of the water balance of a small headwater basin.
1. Introduction
High Mountain Asia (HMA) supplies the water for human consumption, power generation, and irrigation and supports ~3 billion people in southeast Asia, e.g., [1,2,3]. As the global climate is changing, the global mean air temperatures are forecasted to increase by about 1 °C and precipitation (mountainous landscape) is forecasted to increase by 5–25% based on outputs from several general circulation models over the 2046–2065 period in the HMA region [4]. The glaciers contribute a sizable fraction of the current river discharge in HMA, but the glacial meltwater contribution is expected to decrease due to regional warming and subsequent shrinking of the snowpack [3]. Both the glacier mass balance analyses and the general stream discharge prediction at the headwater scale depend on the adequate spatiotemporal representation of precipitation regime. However, spatial variability of precipitation at the headwater basin scale in HMA is poorly understood.
The significance of realistic characterization of the spatially distributed precipitation regimes is critical as it (i) influences the shape of topography through erosion at sub–mountain-range scale [5]; (ii) causes spatially variable ecohydrological responses (e.g., interception and ET), e.g., [6]); (iii) forces a distributed hydrologic and land surface models using spatially variable precipitation surfaces [6]; (iv) triggers extreme hydroclimatic events such as flooding and drought, e.g., [7,8]; (v) sets initial conditions in global climate models by exerting controls on soil moisture [9]; (vi) controls catastrophic surface processes such as landslides, e.g., [10]; and (vii) is useful for investigating both ecohydrological and biogeochemical processes such as nutrient exports from watersheds, e.g., [11]. However, accurately characterizing the precipitation regimes in HMA is challenging due to the extreme topography and lack of observational data.
The spatial variability of precipitation regime and its association with Himalayan topography are poorly defined and need a robust quantitative framework to describe spatial variability of precipitation with input from direct precipitation measurements and watershed characteristics such as topography. In addition, in HMA, precipitation in higher elevations falls as snow during winter season resulting in a lag in the stream discharge.
Our current knowledge of the spatial variability of precipitation in HMA is based on the large scale (4 km pixel size or larger) remotely sensed estimates at coarse temporal resolution (~every 12 h instantaneous rain rate), e.g., [12,13,14,15,16]. While the availability with broad spatial coverage of satellite-borne remotely sensed data (e.g., Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission, TRMM) provides invaluable regional precipitation estimates, particularly over the complex terrain having high altitudes and relief, the evaluations against ground observations are not satisfactory and often systematically biased toward topography [7] and seasonality [17]. Over last two decades, extensive accuracy studies of remotely sensed precipitation (TRMM) products have been conducted over the different continents in the world [7]. In the Himalayan mountains, detailed evaluations of several operational precipitation estimates have been conducted by Andermann et al. [16] and Bookhagen [13]. In the meantime, other studies [17] tested the performance of satellite estimates (TRMM) at the high mountain complex terrains in the Himalaya region in southeast Asia and Tibetan Plateau in China. Although significant progress has been made over the last few years in the accuracy of satellite products and downscaling algorithms, there are still serious concerns and evidence of a positive bias toward estimating winter and high-altitude precipitation [7,17].
To date, perhaps the best knowledge of HMA hydrology is based on outlet gauge streamflow, which is an integrated response of many hydrological processes. More comprehensive hydrologic modeling studies are conducted at the mesoscale or even larger continental scale where hydroclimatic responses of headwater basins are often ignored or not adequately represented, e.g., [12,18,19]. In addition, in these studies, precipitation inputs are from remotely sensed data that are characterized by many shortcomings such as coarse spatial and temporal resolution resulting in inaccurate estimates of summer monsoon rainfall. Other hydrologic studies, e.g., [20,21], only utilize precipitation data from the limited number of rain gauges. For example, various studies involving hydrologic and climate change and hydrologic modeling [1,22,23] utilized 16 rainfall gauges to study 8220 km2 of Koshi River Basin (1 rain gauge/516 km2). Note that, in these studies, only one gauge is located in higher elevation (>6000 m altitude) while others are from mid-to-lower elevation. Authors in [24] used only one rainfall station to simulate 4274 km2 watershed (Tamor River Basin) while Nepal et al., (2014) used only five stations to simulate 3712 km2 (Dudh Kosi Basin). All five stations are located below 4000 m elevation, while a substantial portion of the watershed is located above 4000 m [25]. We realize that the density of rain gauge networks is often dictated by economic and logistical barriers, and share the common sentiment that studies like these would greatly benefit of the larger number of distributed rain gauges across the respective watersheds.
Extreme hydrologic events such as flooding in southeast Asia are often triggered by the summer monsoon rainfall at the HMA or the combined response of snowmelt runoff and monsoon rain. Currently, there are not enough rain gauges in the area to have a representative understanding of the HMA monsoon rainfall, and most of the existing gauges are located in the valley bottoms. As mentioned above, remotely sensed precipitation products render high uncertainty and often are unable to capture spatial variability within a headwater catchment. Thus, to better understand headwater hydrology in HMA, there is a need for a comprehensive water balance study using robust data representing three major fluxes: precipitation, streamflow, and evapotranspiration. Such a study requires a high-resolution precipitation gauge network for adequate representation of spatial variability of precipitation, field-based streamflow observations, and realistic estimates of evapotranspiration.
In this study, we conduct a comprehensive water balance study of a headwater basin in HMA using high-resolution precipitation measurements from a dense network of rain gauges covering several elevation bands, daily streamflow observations at basin outlet and modeled evapotranspiration using daily climatic data from a dense network of weather stations at distributed elevation bands. Specifically, we inspect the impacts of elevation-based spatially distributed annual precipitation on basin-scale water balance. The weather stations were installed and maintained in the field for a limited time period as part of a large research campaign [26].
To prepare the elevation-based annual precipitation maps, we derive a series of equations estimating annual precipitation as a function of elevation. We further investigate how the calculated water balance is affected by the following scenarios: (1) only one rain gauge in the watershed, (2) rain gauges only at lower altitude, (3) arithmetic averages of rain gauges at all elevation bands, and (4) basin-scale rainfall estimate using traditional Thiessen polygon approach. Such investigations provide useful knowledge on the optimum design of rain gauge networks involving the number of rain gauges and installation locations and elevations. This study will also provide valuable information on potential errors when only a small number of low-altitude rain gauges are used to estimate total rainfall of a mountainous headwater basin.
Our study area is Khudi Khola Watershed (KKW) in central Nepal. The climate, topography, and land use and cover of the KKW are representative of numerous watersheds along the E–W transect of the mid-altitude elevation band (600–3100 masl) of HMA. Thus, we expect the findings of this study to be widely applicable to the greater HMA region. Investigating the water balance and its sensitivity to elevation-based precipitation variability in HMA is of particular hydroclimatic and societal importance since these areas are vulnerable to climate change through shifts in temperature and precipitation regimes, heavily cultivated, and increasingly used for hydropower production at many scales. Our investigation is expected to illuminate the effects of elevation-based annual precipitation variability on water balance in KKW and provide guidance to future field-based and process-based studies in this region.
2. Study Area
The study area is the KKW (central Nepal) located at the southern fringe of Annapurna Mountain Range, spanning an area of 125 km2. The elevation of the KKW ranges from 500 to 4500 masl with the mean elevation of 2566 masl (Figure 1b); [10]. The precipitation in the watershed exhibits high seasonality with most of the rainfall in monsoon season (June–September) and little precipitation during the dry season (November–May). During the dry season, precipitation primarily occurs as snow in elevations greater than 3000 masl, while rainfall during monsoon season across the KKW contributes ~95% of annual precipitation [26]. There is no or very little snowfall contribution to annual precipitation and 0% glacierized area [10] in KKW.
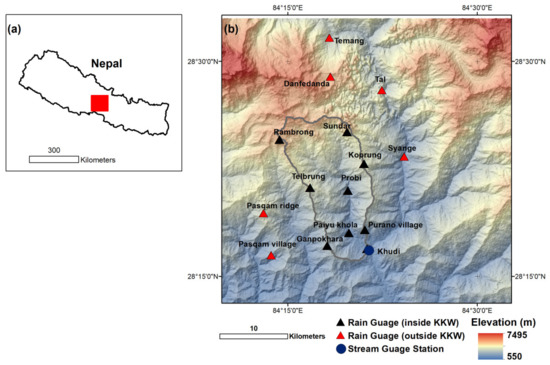
Figure 1.
Location map of the study site (Khudi Khola Watershed, KKW) and hydroclimatological observatories: (a) Location of the study site in the southeast Asia, (b) topography derived from Shuttle RADAR Topography Mission (SRTM) digital elevation model (DEM) and locations of rain gauges and a streamflow gauge. The grey outline shows the KKW boundary.
The summer monsoon is created by warm, humid air originating from the Bay of Bengal traveling to the northwest until it encounters the southern edge of the Himalayan Mountains. This leads to the uplifting of the air mass, cooling, and precipitation. This process is known as orographic precipitation and is the partial cause of the monsoon rainfall in the study area. The KKW is located in the heavy rainfall zone with a pronounced precipitation gradient resulting in substantial difference (~4–5 times increase) in annual precipitation between lowest and highest points in the basin [26]. The streamflow at the KKW outlet is highly seasonal with the largest annual discharge during monsoon season due to heavy monsoon rainfall and low base flow due to slow groundwater seepage during the dry season [10].
The KKW has two primary geological sequences, the Lesser Himalayan Sequence and the Greater Himalayan Sequence. The Lesser Himalayan Sequence is composed of schist, limestone, and quartzite, while the Greater Himalayan Sequence is composed of gneisses [10]. The Khudi River is a non-alluvial (bedrock) channel, with little to no storage of alluvium. The study area is heavily cultivated in elevations below 2000 m and livestock graze the slopes in the summer in elevations up to 4500 m. A rhododendron forest grows in this region, but not above elevations of 3700 m, above which only grasses and small bushes grow [26].
Figure 2 shows the cumulative outlet streamflow (mm) and spatially averaged precipitation (mm) during 2001, 2002, 2003, and 2004 water years. Overall, precipitation dynamics are strongly controlled by monsoon rainfall and subsequently generates large streamflow volume during monsoon season. During wet years like 2001 and 2003, cumulative streamflow is substantially higher than cumulative precipitation. This can be attributed to orographic precipitation across KKW and illustrates how traditional, mean precipitation averaged over all climate stations is unable to capture representative KKW precipitation. However, during dry years like 2002 and 2004, the spatially averaged precipitation is very close to streamflow volume.
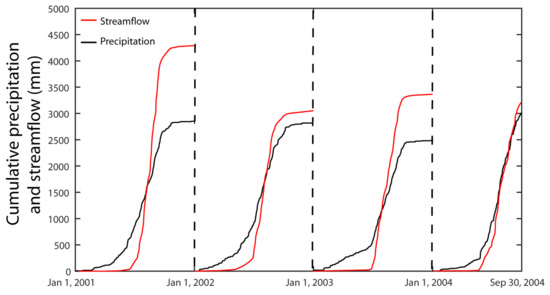
Figure 2.
Cumulative annual precipitation (mm) and outlet streamflow (mm) during 2001–2004 period in the Khudi Khola Watershed (KKW). Note that precipitation is the arithmetic mean of precipitation estimates of all rain gauges in the KKW.
3. Methods
3.1. Data Collections
In this study, we utilize the climatic data such as precipitation at multiple rain gauges, streamflow data collected at KKW outlet, and Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) digital elevation model (DEM) at 15 m resolution (Table S1). While Putkonen [26] and Gabet et al. [10] collected climatic data, and streamflow data, respectively, Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) DEM was procured from NASA’s EARTHEXPLORER web viewer.
3.1.1. Climatic Data Collection
The site characteristics of these stations are highly variable in terms of elevation (altitude above mean sea level), geomorphic locations (e.g., valleys and ridge), and geographic locations (north and south side of the general Himalayan east–west trending crest). The stations located at the north side of the general Himalayan east–west trending crest are in the rainshadow zone. Putkonen [26] selected these sites based on even spatial and elevation coverage of the watershed. Each climate station includes rain gauge (rainfall measurement; Texas Instrument and Hobo), thermometers (air temperature measurement), hygrometers (relative humidity measurement). In addition, some stations also included anemometers (wind speed measurement) and snow depth and water content instrumentation. All rain gauges were calibrated, inspected, and serviced every six months.
3.1.2. Streamflow Measurement
In KKW outlet, a streamflow monitoring station was deployed in 2000 (Figure 1). The installation of streamflow gauge comprises the deployment of stage measurement gauges and cross-sectional surveys. In addition, Gabet et al. [10] deployed turbidity sensors and pressure transducers that recorded measurements to dataloggers every 30 min. Gabet et al. [10] estimated streamflow velocities along a cross-section using a floating boat method. Here, they dropped a series of small plastic balls partially filled with water in the stream and timed starting and endpoints of travel downriver across a known distance. The surface velocity of flow for each ball was obtained by multiplying the ball’s velocity with 0.8 to obtain the mean cross-sectional velocity [10]. To develop a stage–discharge relationship, Gabet et al. [10] measured mean flow velocities at a range of discharges at the KKW outlet.
3.2. Evapotranspiration (ET) Simulation Using the Penman–Monteith Approach
We simulated daily evapotranspiration using the Penman–Monteith approach for each climate station. Monteith [27] demonstrated that the modified Penman [28] equation can be used to estimate evapotranspiration (ET) using the following:
where K = net shortwave input, L = net longwave radiation, ɣ = psychrometric constant,
= density of air, = density of water, = density of air, = atmospheric conductance for water vapor, = canopy conductance, = density of air, = saturated vapor pressure, = latent heat of vaporization, = saturated vapor pressure gradient. Most of these parameters are taken from the literature [29], previous scientific studies [30] and field and remotely sensed observations. ET is simulated daily for each station for each water year using mean daily temperature and relative humidity. Later, daily ET is integrated over time during a specific water year (1 October–30 September) to estimate the annual ET.
3.3. Interpolation of Precipitation and ET Flux
The terrain properties such as elevation, slope, and topographic exposure are found to exert strong control on precipitation in a topographically variable terrain, e.g., [26]. Therefore, to interpolate our precipitation record between the stations, we initially considered elevation, slope, and topographic exposure index as input functions for developing our interpolation equation. Our approach to select an interpolation equation is based on statistical metrics and the effectiveness to interpolate the precipitation in 2000–3000 m elevation band. First, we utilize a best-fit approach using linear and quadratic functions (using Minitab software, [31]) to estimate annual precipitation while considering elevation, slope, and topographic exposure index separately and collectively.
While the performances of linear equations are poor, the quadratic equations yield better R2 for all three input variables (elevation, slope and topographic exposure) (Table S2 and Figure S2). However, even when using quadratic equations, the relationships of slope and topographic exposure with annual precipitation are weak (Table S2). Table S1 clearly shows the considerable strength of elevation over the other two terrain variables while estimating annual precipitation. In addition, a multivariate quadratic equation by incorporating all three terrain variables (elevation, slope, and topographic exposure) substantially improves R2 in Table S2. However, we believe that the predictions are less accurate at the most critical elevation band (2000–3000 masl) where most of the precipitation falls. In addition, the multivariate quadratic equation results in a numerical instability by predicting very low and often negative precipitation in the low-altitude, low-slope (flatter) areas and the areas that have less topographic exposure. The quadratic function using three variables also produced unrealistic annual precipitation values in other critical areas of the watershed. We expect the complications with the multivariate equation to rise from the following facts: (1) [26] only considered elevation and spatial distribution (while deploying rain gauges) and installed the gauges in unobstructed and level areas following World Meteorological Organization guidance, (2) the considerable topographic complexity of the Himalayan terrain, and (3) the generally low winds in the field area [26].
As a result of the above-listed reasons and given the high topographic complexity of the terrain, and the lack of small scale topographic and wind patterns to support more sophisticated analyses, we have chosen to use an interpolation method that is based on elevation only. Our approach to derive a precipitation model is based on statistical metrics (Table 1) and visual inspection (how effective the model is to capture the precipitation in the 2000–3000 m elevation band). We derived a separate quadratic polynomial equation for each water year using precipitation–elevation (Pr−Z) relationship of the stations inside KKW (Figure 3). Note that black circles in Figure 3 show the stations inside the watershed while rec circles represent stations outside or at the periphery of the watershed. The equations shown in Figure 3 are used to prepare annual precipitation maps (Figure 4) for 2001, 2002, 2003, and 2004 water years. These quadratic equations are effective in estimating the Pr of the 2000–3000 m elevation band as well as other elevation bands. Note that R2, NSE, and RMSE for the quadratic polynomial function are also reasonable considering the level of inherent topographic complexity in the KKW (Table 1). Putkonen [26] deployed 8 climate stations at the periphery and inside of the KKW and 6 climate stations at the neighboring watersheds of the KKW (Figure 1b). The data record of these gauges spans from 2000 to 2004. However, 4 of these climate stations are very far away from the KKW and the data are not available for some climate stations due to malfunction of equipment in some years. It is not uncommon to have one or two station’s equipment to malfunction and incomplete dataset amid such a large-scale field operation like Putkonen [26]. As a result, we utilize 11, 11, 10, and 9 stations in Figure 3 for 2001, 2002, 2003, and 2004, respectively.

Table 1.
Nash Sutcliff efficiency (NSE), root mean squared error (RMSE), and correlation coefficient (R2) for predicted annual precipitation (using quadratic polynomial) and evapotranspiration (ET). The statistical metric for predicted ET is shown inside the parenthesis.
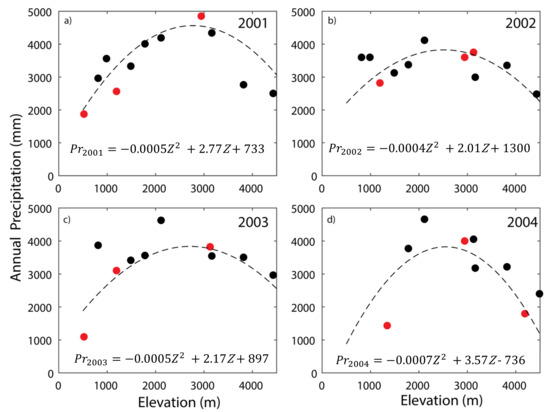
Figure 3.
Function for interpolation of the precipitation based on the relationship between elevation and annual precipitation during each year of the 2001–2004 period in the study area. The red circles are rain gauges just outside the watershed and black circles are within the KKW. Note that equations are shown at the bottom of each subplot and derived using the data corresponding to black circles (within the KKW). Figure (a–d) represents the relationship between elevation and annual precipitation during 2001, 2002, 2003 and 2004 respectively.
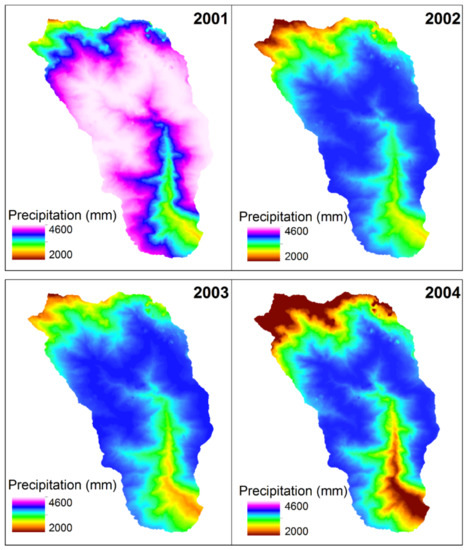
Figure 4.
Interpolated precipitation surface based on the equations developed and shown in Figure 3 for each year.
The elevation (Z) variable in these equations is derived from ASTER DEM. In addition to the Pr–Z-based precipitation map, we also produced precipitation maps using the traditional Thiessen polygon approach [32]. The Thiessen method uses the assumption that estimated rainfall amounts at any point can be applied midway to the next point in any direction, which indicates that rainfall is equal to the observed rainfall at the closest gauge for any point. The weighting factors of the rain gauges in the watershed are determined by their relative areas, that are calculated using the Thiessen polygon network.
Generally, the polygons are created by the perpendicular bisectors of the lines connecting neighboring stations. The precipitation amount is measured in the center of the polygon, not estimated by its area. However, in case of missing rainfall data at any station, the polygon must be changed. Thiessen Pr estimates are generated with the same data used for the Pr–Z model in Figure 3. The number of stations used for 2001, 2002, and 2003 are 12, 10, and 10, respectively. All the stations are inside or at the periphery of the KKW except two stations in adjacent watersheds (Figure S2).
Figure 5 shows the plots between annual simulated ET and station elevations (Z) in the KKW during 2001, 2002, and 2003 water year. Unfortunately, adequate temperature and relative humidity data are not available for some climate stations during 2004 water year; thus, ET–Z is not possible to derive. Figure 5 shows a robust ET–Z relationship for water years with R2 around 0.9 (Table 1). We have utilized the strong ET–Z relationship of Figure 5 to produce annual ET maps (Figure 6) for 2001, 2002, and 2003 water years using ASTER DEM as the source for elevation data (Z).
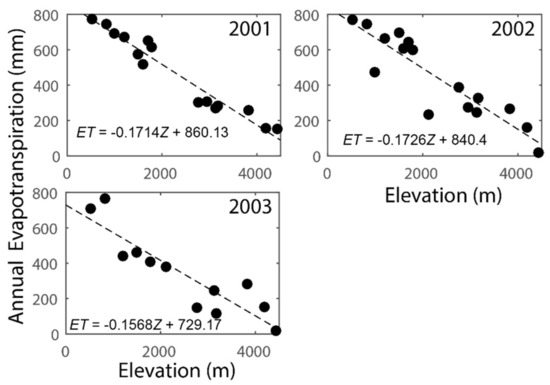
Figure 5.
Plots of annual evapotranspiration (ET) using Pennman-Monteith approach vs. elevation. Figure 5 represents the relationship between elevation and annual ET during 2001, 2002, and 2003 respectively. Note that a complete meteorological dataset was not available for Pennman-Monteith approach to calculate ET during 2004. Note that the equations for the best fit lines are shown at the bottom of each panel.
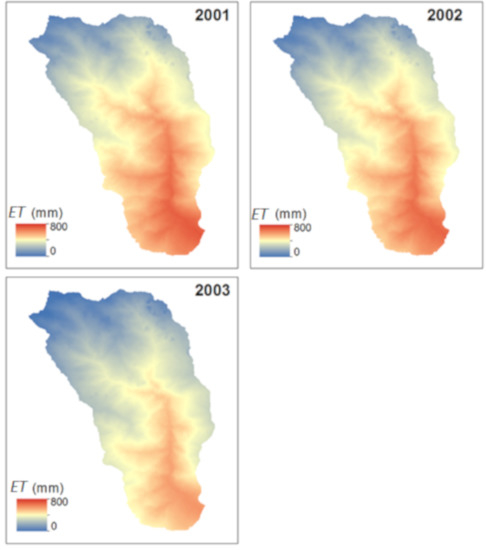
Figure 6.
Distributed ET as a function of elevation based on the ET-elevation relationships detected in Figure 5.
3.4. Water Balance
We estimated the water balance () using input (precipitation) and output fluxes (streamflow and ET). The comparison between estimated water balances using three annual basin-scale precipitation depths is conducted. They are Pr–Z-based precipitation depth (), arithmetically averaged precipitation depth overall climatic stations and basin-scale precipitation depth () derived interpolated maps using the Thiessen polygon method. The purpose of this comparison to investigate how efficient Pr–Z-based precipitation interpolation (Prelev) is to close the water balance of the KKW. Equation (2) estimates the water balance (ΔSelev) using Pr–Z-based precipitation.
Equation (3) quantifies the water balance using arithmetically averaged precipitation (ΔSavg) over all climate stations.
We utilize Equation (4) to quantify the water balance (ΔSThiessen) using interpolated precipitation using the Thiessen polygons approach.
In these equations, streamflows are derived from field-based observation and ET is simulated at a daily scale using Equation (1) and integrated over each year. Using ET–Z relationship, Figure 6 is constructed and subsequently, we derived basin-scale ET from Figure 6. Note that ET for 2004 is calculated using data from only two stations distributed across elevation. Since ET is less than 10% of the annual water balance, we believe such limited data availability will have a minor influence on the scientific findings of our study.
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Interpolated Precipitation Surface
Figure 3 shows the impacts of Z on Pr for 2001, 2002, 2003, and 2004 water years. Clearly, monsoon rainfall is the major contributor to annual precipitation (Figure 2 and Figure S3). The stations located at ridges or higher elevations receive substantially more rainfall than the stations located at the valley bottom in KKW. Overall, Figure 3 shows inconclusive Pr–Z relationship (both positive and negative correlation). Instead, it exhibits three zones of distinct Pr–Z relationships; zone 1 (outlet elevation-2000 m band): the Pr sharply increases with Z; zone 2 (2000–3000 m elevation band): the Pr varies slightly and increases sluggishly with Z; zone 3 (Z > 3000 m): the Pr decreases with Z. A maximum of ~5000 mm Pr at an altitude of 3000 m is observed while the Pr subsides northward to 1100 mm water/yr at the most northerly station in KKW. Clearly, Figure 3 shows the reversal of Pr–Z relationship at the 2000–3000 m elevation band (zone 2); thus, we name this as a critical elevation band (Zcr). Such a reversal of Pr–Z relationship around Zcr can be attributed to continued dewatering of the monsoon system via rainfall as the system gradually rises to Zcr during their northward migration. During the rise of the monsoon system below Zcr the system experiences cooler temperatures which induce condensation and subsequent rainfall. However, the rainfall amount decreases with Z above Zcr, possibly due to lack of moisture (because of substantial rainfall below Zcr), and/or lack of moisture-holding capacity due to the colder temperature at the higher altitude.
In order to decipher the impacts of seasonality on the annual Pr–Z relationship, we also investigated the Pr–Z relationships during monsoon (Figure S3) and winter (Figure S4) seasons. Overall, the Pr–Z relationship for the monsoon season (Figure S3) is similar to the annual Pr–Z relationship and shows a strong dependency on the elevation. However, the Pr–Z relationships for the winter season are highly variable and show little dependency on the elevation (Figure S4). Thus, we believe the annual Pr–Z relationship is highly influenced by the monsoon season’s rainfall as the monsoon rain is a significant contributor to annual precipitation.
We believe that the monsoon system loses a significant amount of moisture via rainfall as it approaches Zcr resulting in dry conditions in the elevation above Zcr. We have experimented with various functional equations (e.g., linear, multi-order polynomial) as a function of Z to capture such Pr–Z relationships. Our analyses suggest that such a reversal of Pr–Z relationship around Zcr band can be captured by using the quadratic polynomial equations. Figure 3 shows the quadratic polynomial equations exhibiting strong predictive capability based on NSE, R2, and RMSE for each water year (Table 1). The rising limb of the fitted line shows the rapid increase of Pr with Z in the 820–2000 elevation band while the recession limb exhibits inverse Pr–Z relationship in the 3000–4400 elevation band. The zone between both limbs shows mild convex upward curvature in 2000–3000 elevation representing areas of heavy Pr in the KKW.
The quadratic polynomial equations for four years indicate that the Pr–Z relationships vary from year to year due to small scale spatial variability in Pr. Figure 3a shows the Pr–Z relationship for the 2001 water year during which the fitted quadratic polynomial equation captures the Pr well for the elevations lower than 3100 m while it overestimates Pr in the altitude higher than 3100 m. The R for the Pr–Z relationship below 3000 m is 0.79 while R2 for the Pr–Z relationship above 3000 m is -0.8, which can be attributed to the rainshadow part of Figure 3a [26]. However, the curvature of the quadratic polynomial for the water year 2002 is much smoother than 2001 but still shows Pr−Z relationship reversal around 3000 m altitude. A strong positive Pr−Z relationship (R = 0.68) is below 3000 m elevation band while the Pr−Z relationship is inversely proportional (R = −0.72) above 3000 during 2002. Note that the Pr at stations of 820 and 993 m are quite high and deviated from the Pr−Z relationship. This can be attributed to heavy localized precipitation due to early summer convective storm systems. The Pr−Z relationship and fitted line from the quadratic polynomial equation during 2003 water year is very similar to that of the 2002 water year. However, the fitted line is unable to capture the maximum precipitation at 2900 m altitude and underestimates it by ~1000 mm. Figure 4 shows the interpolated precipitation surfaces using quadratic polynomial equations shown in Figure 3. The Pr increases with Z in the areas between outlet elevation and Zcr elevation band while above Zcr band, the Pr gradually declines as the Z increases. Figure 7 shows elevation distribution across the KKW. The area below Zcr is ~70% of the KKW area while the area above Zcr contributes to 30% of the KKW. Overall, during the study period, we have detected three zones of low Pr: the flat valleys near the outlet of KKW and the mountains located above Zcr. The Pr in valleys (Z < 2100 m) varies between 2000 mm and 3100 mm while in high-elevation mountains (Z> Zcr) the Pr fluctuates from 2000 mm to 4000 mm. In the flat valleys, low precipitation can be attributed to lack of condensation inside the monsoon system due to warmer temperature while lack of precipitation in the high mountains is due to lack of moisture as the system experience moisture depletion due to heavy rainfall at the lower elevation band (Z< Zcr). The mean Pr values in this elevation band (40% area of the KKW) are 4598 (mean KKW Pr = 4167 mm), 3796 (mean KKW Pr = 3486), 3793 (mean KKW Pr = 3593), and 3769 (mean KKW Pr = 3651) mm for 2001, 2002, 2003, and 2004 water years, respectively. This elevation contributes 45%, 42%, 41%, and 41% of Pr for 2001, 2002, 2003, and 2004 water years, respectively.
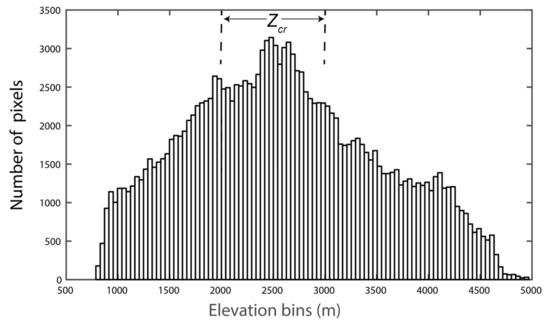
Figure 7.
Histogram of Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) digital elevation model (DEM) surface.
The Pr sharply increases with an elevation between outlet elevation (787 m) and 2000 m altitude. The rapid rise of Pr with Z in this elevation band contributes 29% of the KKW area. The Pr in this elevation band also accounts for 26%, 29%, 27%, and 24% for 2001, 2002, 2003, and 2004 water years, respectively. The elevation over Zcr is 31% of the study area and contributes 29%, 29%, 32%, and 35% of Pr for 2001, 2002, 2003, and 2004 water years, respectively. Our findings on the Pr−Z relationships are not comparable with Pr−Z relationships from other mountain ranges such as the Alps. Frei and Schar [33] reported a weak and insignificant Pr−Z relationship in the Alps. Several studies [34,35] attributed such weak height dependence to other physiographical factors (slope, topographic exposure, broad-scale topographic environment). Note that the findings from the Alps are based on observations from a dense local network while rain gauges in the HMA are sparse.
Our current knowledge of the spatial variability of KKW Pr is based on coarse resolution (~ 4 km pixel size) remotely sensed estimate, e.g., [12,13,36] lacking orographic influences. Our findings improve the current understanding of spatial variability of Pr in KKW by producing maps and reporting zones of high and low atmospheric accumulation. The interpolations of precipitation at a larger scale are recently conducted using the geostatistical approach with elevation variation, e.g., [37], and clustering coefficient, e.g., [38]. However, in KKW, we have a unique Pr−Z relationship that transitions from strong positive to strong negative around Zcr. Such reversal of the Pr−Z relationship makes it difficult to fit any model to semi-variogram. In addition, the number of climate stations is not adequate to conduct other interpolation methods.
In addition to Pr−Z- based elevation, we have interpolated the precipitation based on the conventional Thiessen polygon-based method for 2001, 2002, and 2003 water years (Figure 8). Due to data availability and the limited number of climate stations, this study is unable to derive Thiessen polygons for the 2004 water year. Overall, the results capture the wide spatial variability of Pr across KKW. A total of 10 polygons with a mean polygon area of 14 km2 are drawn in this analysis (Figure S2). Like the Pr−Z relationship-based approach, lower precipitation is shown at the outlet and higher elevation area while higher precipitation is observed mid-altitude area. The spatial variability shown in Figure 8 is very coarse and unable to capture the level of detailed spatial variability detected by the Pr−Z relationship-based approach. Table 2 reports the KKW scale Pr using both Thiessen polygon (Prthiessen) and Pr–Z relationship-based approach (Prelev). The comparison indicates that Prelev is consistently higher than Prthiessen, suggesting poor estimation of by Prthiessen around high precipitation elevation band (in Zcr).
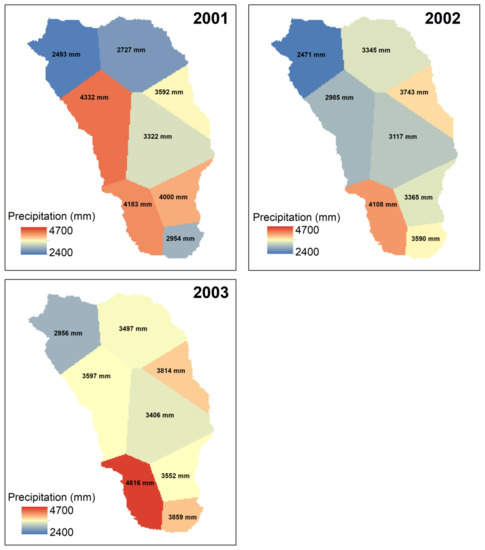
Figure 8.
Interpolated precipitation surface using traditional Thiessen polygons approaches [32].

Table 2.
Water balance (ΔS in mm) to distributed precipitation based on elevation (Prelev), arithmetically averaged precipitation over rain gauges (Pravg), and precipitation surface using Thiessen polygons (PrThiessen) in the Khudi River Basin. Note that the percentage of water balance (ΔS) of total water is shown inside the parenthesis.
4.2. Interpolated ET Surface
Figure 5 shows the impacts of Z on simulated ET using the Penman–Monteith approach (described in Section 3.2) for 2001, 2002, and 2003 water years. Clearly, the ET increases as the Z decreases, suggesting an inversely proportional ET–Z relationship. Annual ET is 414, 319, and 322 mm for 2001, 2002, and 2003 water years, respectively. High annual ET (~800 mm) is observed near outlet of KKW while the ET is low (<50 mm) in the very high mountains. Our diagnosis of ET simulations suggests that the inverse ET–Z relationship emerges from an inverse T–Z (mean annual temperature-elevation) relationship with a 0.99 R2 for T–Z relationship. At the outlet (Z = 820 m) of KKW, the annual Tmean is 20 °C while the Tmean is 6 °C at the high altitude (Z = 3160 m). However, like Pr, the relative humidity is low (mean annual is 80%) at the outlet and higher altitude while just below Zcr elevation band the relative humidity is quite high (mean annual is 91%). This is expectedly consistent with Pr−Z relationship and previous studies [36]. Nevertheless, T exerts a firm control on annual ET as it is one of the influential input parameters estimating ρa, , λv, and Δ for Equation (1), which simulates ET. We believe the detected influence of T on ET is mainly important in the context of a warming climate as the watershed like KKW in HMA are highly vulnerable to climate change. Our simulated annual ET values and their variability are consistent with a previous study in mid-altitude mountains of Nepal [39] where Baral, [39] sap flow and other modeling approaches to estimate the ET.
The ET maps in Figure 6 are constructed using the inverse linear relationships derived in Figure 5 for 2001, 2002, and 2003 water years. Figure 6 shows the spatial variation of ET across the KKW, exhibiting strong controls of Z on ET. The land covers near the outlet or elevation band (<2000 m) evapotranspire 43%, 43%, and 45% of KKW ET for 2001, 2002, and 2003 water year, respectively. Note that this elevation band is only 29% of the KKW. The elevation having heavy annual precipitation (zone 2, 40% of KKW) contribute 40%, of the KKW annual ET during 2001, 2002, and 2003 water years. In contrast, the high elevation band (>3000 m) contributes only 17% (2001), 17% (2002), and 15% (2003) of KKW annual ET despite occupying 31% of the KKW. Note that KKW ET for 2003 is lower than the ET of 2001 and 2002. This can be attributed cold conditions at high altitudes. The Tmean is 20.1, 19.8, and 19.8 for 2001, 2002, and 2003 water years at the low altitude station (Z = 820). In contrast, at the high altitude elevation the Tmean during 2001 and 2002 are 6.6 and 6.7, which are substantially higher than Tmean of 2003 (4.5). The Tmean in the mid-altitude station also remains invariable during the study period.
4.3. Water Balance
In this section, we examine the impacts of Z-based distributed precipitation on water balance. Table 2 shows calculated the KKW water balance using Z-based distributed precipitation (Prelev), arithmetically averaged precipitation (Pravg), and interpolated precipitation using the Thiessen polygons approach (PrThiessen). ΔSelev, ΔSavg, and ΔSThiessen are calculated using Equations (2)–(4), respectively. The Prelev derived from Pr–Z-based approach (Figure 4) is higher than both Pravg and PrThiessen as the Pr–Z based approach considers Pr−Z variability across the KKW. In contrast, both Pravg and PrThiessen calculations are biased by stations having low Pr due to lack of stations in 2000–3000 m elevation. Note that the installation of a climate station in this elevation is challenging due to steeper slopes, rugged topography and total lack of infrastructure. The maximum difference between Prelev and the other two approaches is observed in a wetter year (2001) while the difference is small during a dry year (2002). Figure 4 may include some uncertainty in the 2003 Pr estimate as the quadratic equation is unable to capture P at 2100 m altitude and underestimates Pr by about 1000 mm (Figure 3).
Table 2 shows that the performance of Prelev is adequate and consistent (<4% of total water budget except 2004) in closing the water balance (ΔSelev) of the KKW during four years of the study period. During the 2001 water year, the water balance is closed using Prelev, while the other two approaches show the depletion of 821 mm water from KKW storage. It is unlikely that such an amount of depletion is possible via ET as it contributes less than 10% of water balance. Both methods (Prelev and Pravg) are not able to close the water balance (>15% error) in a very wet year like 2001 (Table 2). However, during a dry year like 2002, the water balances using Prelev, Pravg, and PrThiessen are within 5% of the annual water budget. However, during 2003, the Pravg is clearly not able to close the water balance. Since, our rain gauges are located in most of the elevation bands; it is anticipated that Pravg, and PrThiessen methods can be effective in a dry year like 2002 and a moderately wet year like 2003. Both Prelev and Pravg are adequate to close the water balance during 2004 considering the availability of data from a limited number of climate stations.
Figure 9 shows the influences on ΔS if we consider precipitation data from the individual rain gauge. Note that streamflow and ET are taken from Table 2 while calculating ΔS for Figure 9 during 2001, 2002, 2003, and 2004 water years. The solid red line shows the ΔS using Z-based Pr maps from Figure 4. The low elevation (Z < 2000 m) rain gauges are not able to close the ΔS during 2001 and 2004, while the failure to close ΔS is prominent using high elevation (Z > 3000 m) rain gauges for all water years. We believe, during 2002 and 2003, precipitation at low elevation rain gauges are higher due to localized convective systems resulting in improved ΔS. The rain gauges located at 2000-3000 m elevation band adequately close ΔS with few exceptions. However, our dataset has a limited number of rain gauges in this band while there are some around 2000 m and 3000 m elevation. Clearly, Figure 9 shows the effectiveness of rain gauges around 2000 m and 3000 m elevation in closing the ΔS for all water years. We believe these zones around 2000 m and 3000 m elevation band receive representative precipitation for the KKW. Thus, populating these zones with rain gauges will be helpful to close ΔS for hydrologic studies in similar watersheds in HMA.
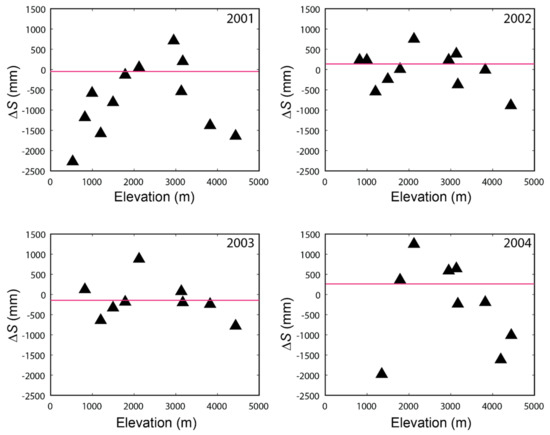
Figure 9.
Water balance (ΔS) of the KKW while considering precipitation input from the individual rain gauge. Note that the red lines represent the ΔSelev using elevation-based distributed precipitation.
Since most of the hydrologic studies in HMA [22,24] utilize only rain gauges from lower altitude (due to inaccessibility and thick forest cover at high altitude), in Figure 10, we examine the optimum elevation up to which the rain gauges should be installed. This provides an interesting perspective in a way that it is useful to install rain gauge up to certain elevation to improve ΔS and the installation beyond this critical elevation will not improve the ΔS. Figure 10 shows the dynamics of ΔS with the number of rain gauges from the lowest altitude. As the elevation increases, we consider the mean of multiple rain gauges and at the highest altitude, the mean of all rain gauges is considered to calculate water balance. The ΔS changes clearly show that the ΔS approaches zero as the number of rain gauges increases with elevation during 2001, 2003, and 2004 water years. However, beyond ~2100 m altitude, the ΔS no longer improves and fluctuates very little during 2001, 2003, and 2004 water years, suggesting the importance of deploying rain gauges at the 528–2100 m elevation band. Unfortunately, since there is no rain gauge between 2100 and 3000 m altitude, we cannot conclusively recommend the upper limit of this elevation band. We believe more rain gauge installations at the 2100–3000 m elevation band in future studies will improve our knowledge and subsequently close ΔS.
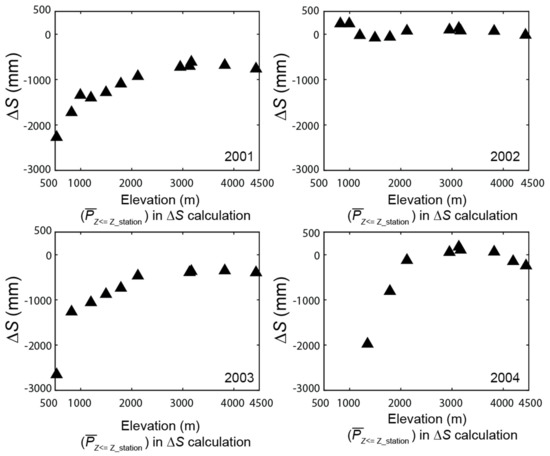
Figure 10.
Water balance (ΔS) of the KKW. Note that mean precipitation (Z ≤ Z_station) calculated for all the stations located at or lower than the respective station. As the plot approach higher elevation, data from more stations are considered for mean calculation.
Our analyses clearly reveal the usefulness of elevation-based Pr interpolation in closing water balance in a headwater basin of HMA. Previous hydrologic studies, e.g., [20,23], only used a limited number of gauges from downstream areas. For example, Devoka and Gyawali [40] utilized 16 rainfall gauges to simulate hydrology of 8220 km2 (1 gauge/514 km2) of the Koshi River Basin. In our study, we utilized 11 gauges to capture the spatial variability in 125 km2 basin (1 gauge/13 km2). Other studies, e.g., [12], conducted water balance study at broader HMA scale lacking representation of small headwater basins like KKW in terms of precipitation and streamflow. Our studies improve the current understanding of the impacts of elevation-based basin-scale precipitation on closing the water balance and provide guidance in designing future observation networks. We believe peak Pr elevation varies between mountain ranges or climate regions and that the same Pr−Z relationship may or may not be found elsewhere. However, future studies should consider precipitation measurements from all the elevation bands.
Our study period is limited to four years due to lack of continued funding to support data collection. Note that we utilized an exceptional dataset which were collected during 2001–2004 [26]. The climate stations were deployed in remote areas having very rugged topography and thick forest cover. Our study period also includes two relatively dry years (2002, 2004) and two wet years (2001,2003). We believe that the availability of data for additional years would really bolster our findings and provide more robust understandings on Pr−Z relationship in the HMA region. It is not uncommon to have limited dataset (due to lack of support for the operation of the stations) to investigate atmospheric processes [6,26,41,42]. In addition, we utilize the Pr–Z relationship to investigate the effectiveness of spatially variable precipitation on closing the water balance.
5. Conclusions
We studied the spatial variation of the precipitation in a small (125 km2) headwater basin in the KKW, located in the foothills of the Himalaya, Nepal. We deployed ten rain gauges in elevations ranging 700–4500 masl for a period of four years, with a density of 1 rain gauge/13 km2. This density is orders of magnitudes higher than typical watershed-level studies in the Himalaya [16]. In addition to precipitation data, we collected other climatic variables such as air temperature, wind speed, and relative humidity which were used to simulate ET at each station. Using precipitation data, simulated ET and outlet gauge streamflow [10], we conducted a detailed basin-scale water balance study and investigated the impacts of elevation-based precipitation variability on closing water balance in KKW. We further examined how the use of just one rain gauge or a combination of multiple rain gauges affects the accuracy of the estimated KKW water balance.
Collectively this research shows that the small mountainous watersheds in the Himalaya have highly variable spatial precipitation patterns. Our results show that the amount of annual precipitation is strongly dependent on the altitude, revealing maximum precipitation at middle elevation and lower precipitation both at higher and lower elevations. This variation is not captured by space-born satellite products such as (TRRM) due to their relatively large pixel size. In addition, the rain gauges employed in such areas are sparse and typically found at the lowest elevation of the given basins due to logistical limitations. Therefore, even the best precipitation estimates for these watersheds based on satellite data or single rain gauge can be offset by a significant fraction.
Our results show three zones based on distinctive precipitation–elevation relationships; zone 1 (outlet elevation-2000 masl band): the precipitation sharply increases with elevation; zone 2 (2000–3000 masl elevation band): the precipitation varies slightly and increases minimally with elevation; zone 3 (Z > 3000 m): the precipitation decreases with elevation. Due to the variable nature of the elevation–precipitation relationship, the quadratic polynomial relationship was found to be the best fit for the precipitation–elevation plot. Interestingly, zone 2 also represents the basin-scale precipitation and we called the critical precipitation zone. In addition, simulated ET at multiple stations also shows an inverse and strong correlation with elevation. Putkonen [26] qualitatively described the orographic precipitation in the southern flank of the Annapurna range. Our results add new knowledge by detecting a quantitative framework of Pr−Z relationships for four water years and provide a useful platform to interpolate precipitation as a function elevation. Since recent technologies such as LiDAR and RADAR, advance DEM construction substantially, our quantitative framework will be a timely contribution to analyze annual precipitation for a mid-altitude headwater basin in HMA.
Our water balance clearly shows that the elevation-based precipitation yields the best performance in closing the KKW water balance for all water years. While considering only one rain gauge for the watershed, the rain gauges at zone 2 (critical zone) perform much better than the rain gauges from other altitudes (zone 1 and zone 3). While considering average rainfall from the lowest altitude, it is adequate only to deploy rain gauges until zone 2. A single low altitude rain gauge leads to underestimations of the watershed level precipitation, which make it impossible to close the water balance, or calculate other derivatives needed for infrastructure and agriculture (such as stream discharge, soil saturation, crop irrigation, water power management, dam operation).
We recognize that every watershed is unique, and every mountain range is unique in terms of precipitation and topography, and how the precipitation is distributed in the given watershed. However, based on the existing sparse ground level and satellite data, the orographic precipitation effect is well established [43]. It is also a reasonable first-order expectation that the peak of the orographic precipitation in adjacent and maybe even regional watersheds is found at approximately similar elevations. Therefore, we suggest that by making use of these results it will be possible to estimate watershed-wide precipitation in mountainous watersheds with higher accuracy even when sparse rain gauge data are available.
Our data clearly show that a single low altitude precipitation gauge will always underestimate the total watershed precipitation. We recognize that rain gauge placement is usually sparse due to logistical and economic constraints. However, based on our analyses (Figure 9 and Figure 10), a remarkable improvement in capturing a representative total precipitation for a given watershed can be achieved by having two rain gauges instead of just one. Our sample case suggests that those gauges should be located at the lowest elevation (usually the easiest to access), and a secondary gauge at the elevation of the peak precipitation at 2000–3000 masl. Armed with these data and the basin hypsometry, a significantly improved estimate of the total basin precipitation can be calculated, by assuming a simple parabolic relationship with elevation that intersects the low altitude total and the maximum at the 2000–3000 m altitude total, with monotonic decrease with the elevation above 3000 masl.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4441/13/3/254/s1, Table S1. Hydro-climatic data and DEM used in this study, Table S2. Best fit equation performance in predicting annual precipitation. Note that Table S1 contains the performance of quadratic equations as linear equations yield very poor performance. The column elevation shows the R2 of the quadratic equations (only elevation as function) while predicting annual precipitation. The slope and exposure columns also show their respective quadratic equation’s performance, Figure S1. Relationship between slope (degree) and annual precipitation. Note that a linear fit would produce R2 of 0.12, 0.07, 0.11, and 0.049 for 2001, 2002, 2003, and 2004, respectively, Figure S2. Distribution of Thiessen polygons and rain gauges for the year 2002, Figure S3. The plots between elevation and annual monsoon (June-September) precipitation during each year of the 2001–2004 period in the study area. The red circles are rain gauges just outside the watershed and black circles are within the KKW. Note that equations are shown at the bottom of each subplot and derived using the data corresponding to black circles (within the KKW), Figure S4. The plots between elevation and annual winter (Oct–May) precipitation during each year of 2001–2004 period in the study area. The red circles are rain gauges just outside the watershed and black circles are within the KKW. Note that equations are shown at the bottom of each subplot and derived using the data corresponding to black circles (within the KKW).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.H.M. and J.P.; methodology, T.H.M., J.P. and A.S.; software, T.H.M. and A.S.; formal analysis, T.H.M. and J.P.; investigation, T.H.M., J.P. and A.S.; resources, T.H.M. and J.P.; data collection, T.H.M. and J.P.; writing, T.H.M., J.P. and A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
NSF funded ND EPSCoR (NSF grant #IIA-135466).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We want to thank NSF funded ND EPSCoR (NSF grant #IIA-135466) and the Harold Hamm School of Geology and Geological Engineering for partially funding this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Devkota, M.P. Environmental Impacts of Khudi Small Hydropower Project on the Fishery of the Khudi River during Operation Phase. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Small Hydropower-Hydro Sri Lanka, Kandy, Sri Lanka, 22–24 October 2007; Volume 22, p. 24. [Google Scholar]
- Bajracharya, T.R.; Acharya, S.; Ale, B.B. Changing climatic parameters and its possible impacts in hydropower generation in Nepal (a case study on Gandaki River Basin). J. Inst. Eng. 2011, 8, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppes, M.; Hallet, B.; Rignot, E.; Mouginot, J.; Wellner, J.S.; Boldt, K. Observed latitudinal variations in erosion as a function of glacier dynamics. Nature 2015, 526, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Bierkens, M.F. Asian water towers: More on monsoons-response. Science 2010, 330, 585. [Google Scholar]
- Andres, A.M.; Roe, G.H.; Hallet, B.; Montgomery, D.R.; Finnegan, N.J.; Putkonen, J. Spatial patterns of precipitation and topography in the Himalaya. Spec. Pap. Geol. Soc. Am. 2006, 398, 39. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, T.H.; Vivoni, E.R. Evaluation of distributed soil moisture simulations through field observations during the North American monsoon in Redondo Creek, New Mexico. Ecohydrology 2008, 1, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.I.; Hong, Y.; Gourley, J.J.; Khattak, M.U.K.; Yong, B.; Vergara, H.J. Evaluation of three high-resolution satellite precipitation estimates: Potential for monsoon monitoring over Pakistan. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 54, 670–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.D.; Wigington, P.J., Jr.; Leibowitz, S.G.; Sproles, E.A.; Comeleo, R.L. How does spatial variability of climate affect catchment streamflow predictions? J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Essery, R. Boreal forests and snow in climate models. Hydrol. Process. 1998, 12, 1561–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabet, E.J.; Burbank, D.W.; Pratt-Sitaula, B.; Putkonen, J.; Bookhagen, B. Modern erosion rates in the High Himalayas of Nepal. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2008, 267, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeannotte, T.L.; Mahmood, T.H.; Vandeberg, G.S.; Matheney, R.K.; Hou, X.; Van Hoy, D.F. Impacts of cold region hydroclimatic variability on phosphorus exports: Insights from concentration-discharge relationship. J. Hydrol. 2020, 591, 125312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bookhagen, B.; Burbank, D.W. Topography, relief, and TRMM-derived rainfall variations along the Himalaya. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bookhagen, B.; Burbank, D.W. Toward a complete Himalayan hydrological budget: Spatiotemporal distribution of snowmelt and rainfall and their impact on river discharge. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigdel, M.; Ma, Y. Variability and trends in daily precipitation extremes on the northern and southern slopes of the central Himalaya. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 130, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.K.; Ojha, C.S.P.; Singh, R.P.; Pal, L.; Fu, D. Evaluation of TRMM Precipitation Dataset over Himalayan Catchment: The Upper Ganga Basin, India. Water 2019, 11, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Khadka, N.; Hamal, K.; Shrestha, D.; Talchabhadel, R.; Chen, Y. How accurately can satellite products (TMPA and IMERG) detect precipitation patterns, extremities, and drought across the Nepalese Himalaya? Earth Space Sci. 2020, 7, e2020EA001315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, B.; Hong, Y.; Ren, L.L.; Gourley, J.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Khan, S.I. Assessment of evolving TRMM-based multisatellite real-time precipitation estimation methods and their impacts on hydrologic prediction in a high latitude basin. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andermann, C.; Bonnet, S.; Gloaguen, R. Evaluation of precipitation data sets along the Himalayan front. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2011, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaini, S.; Nepal, S.; Pradhananga, S.; Gardner, T.; Sharma, A.K. Impacts of climate change on the flow of the transboundary Koshi River, with implications for local irrigation. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2020, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.H.; Shakya, N.M. Hydrological changes and its impact on water resources of Bagmati watershed, Nepal. J. Hydrol. 2006, 327, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.; Gupta, A.; Mishra, K.; Tripathi, S.; Nepal, S.; Wahid, S.M.; Swarnkar, S. Basin-scale hydrology and sediment dynamics of the Kosi river in the Himalayan foreland. J. Hydrol. 2019, 570, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, S. Impacts of climate change on the hydrological regime of the Koshi river basin in the Himalayan region. J. Hydro Environ. Res. 2016, 10, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.P.; Moore, B.; Vorosmarty, C.J. Anthropogenic, climatic, and hydrologic trends in the Kosi Basin, Himalaya. Clim. Change 2000, 47, 141–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panday, P.K.; Williams, C.A.; Frey, K.E.; Brown, M.E. Application and evaluation of a snowmelt runoff model in the Tamor River basin, Eastern Himalaya using a Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) data assimilation approach. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 5337–5353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, S.; Flügel, W.A.; Shrestha, A.B. Upstream-downstream linkages of hydrological processes in the Himalayan region. Ecol. Process. 2014, 3, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putkonen, J.K. Continuous snow and rain data at 500 to 4400 m altitude near Annapurna, Nepal, 1999–2001. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2004, 36, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteith, J.L. Evaporation and environment. In Symposia of the Society for Experimental Biology; Cambridge University Press (CUP): Cambridge, UK, 1965; Volume 19, pp. 205–234. [Google Scholar]
- Penman, H.L. Natural evaporation from open water, bare soil and grass. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1948, 193, 120–145. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, T.H.; Vivoni, E.R. A climate-induced threshold in hydrologic response in a semiarid ponderosa pine hillslope. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsawa, M.; Shakya, P.R.; Numata, M. Distribution and succession of west Himalayan forest types in the eastern part of the Nepal Himalaya. Mt. Res. Dev. 1986, 6, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arend, D.N. Choices (Version 4.0) [Computer Software]; CERL Report No. CH7-22510; US Army Corps of Engineers Research Laboratory: Champaign, IL, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Thiessen, A.H. Precipitation averages for large areas. Mon. Weather Rev. 1911, 39, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, C.; Schär, C. A precipitation climatology of the Alps from high-resolution rain-gauge observations. Int. J. Climatol. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 18, 873–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desurosne, I.; Ribot-Bruno, J.; Watremez, S.; Oberlin, G. Interactions Pluies:Rélief à L’échelle Temporelle des Intensités, Guide Pratique des Données Pluivographiques et des Résultats d’un Réseau Préalpin, Le TGP; Report CP 220; Cemagref, Dision Hydrologie-Hydraulique: Lyon, France, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wastl, C.; Zängl, G. Analysis of mountain-valley precipitation differences in the Alps. Meteorol. Z. 2008, 17, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Haugen, J.E.; Xu, C.Y. Precipitation pattern in the Western Himalayas revealed by four datasets. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 5097–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistical approaches for incorporating elevation into the spatial interpolation of rainfall. J. Hydrol. 2000, 228, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.K.; Zhao, H.; Woldemeskel, F.M.; Sivakumar, B. Network theory and spatial rainfall connections: An interpretation. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baral, T. Evapotransiration from Natural and Planted Forest in the Middle Mountain of Nepal; University of Twente Faculty of Geo-Information and Earth Observation (ITC): Enschede, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Devkota, L.P.; Gyawali, D.R. Impacts of climate change on hydrological regime and water resources management of the Koshi River Basin, Nepal. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2015, 4, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, A.P.; Chiao, S.; Lang, T.J.; Burbank, D.; Putkonen, J. From weather to climate-seasonal and interannual variability of storms and implications for erosion processes in the Himalaya. Spec. Pap. Geol. Soc. Am. 2006, 398, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Barros, A.P.; Joshi, M.; Putkonen, J.; Burbank, D.W. A study of the 1999 monsoon rainfall in a mountainous region in central Nepal using TRMM products and rain gauge observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 3683–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, G.H. Orographic Precipitation. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2005, 33, 645–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).