Numerical Canal Seepage Loss Evaluation for Different Lining and Crack Techniques in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions: A Case Study of the River Nile, Egypt
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
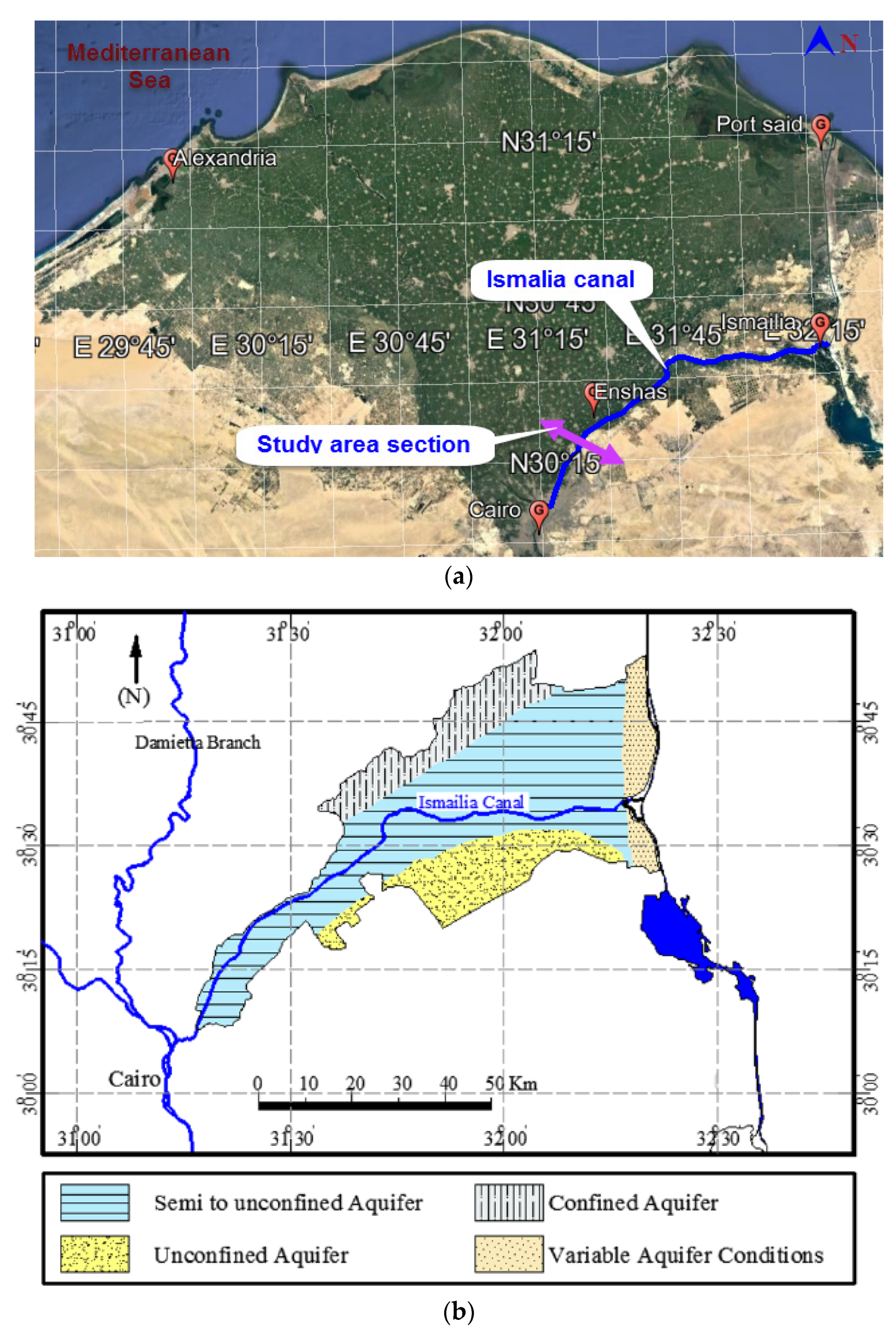
2.1. Case study and Site Investigation
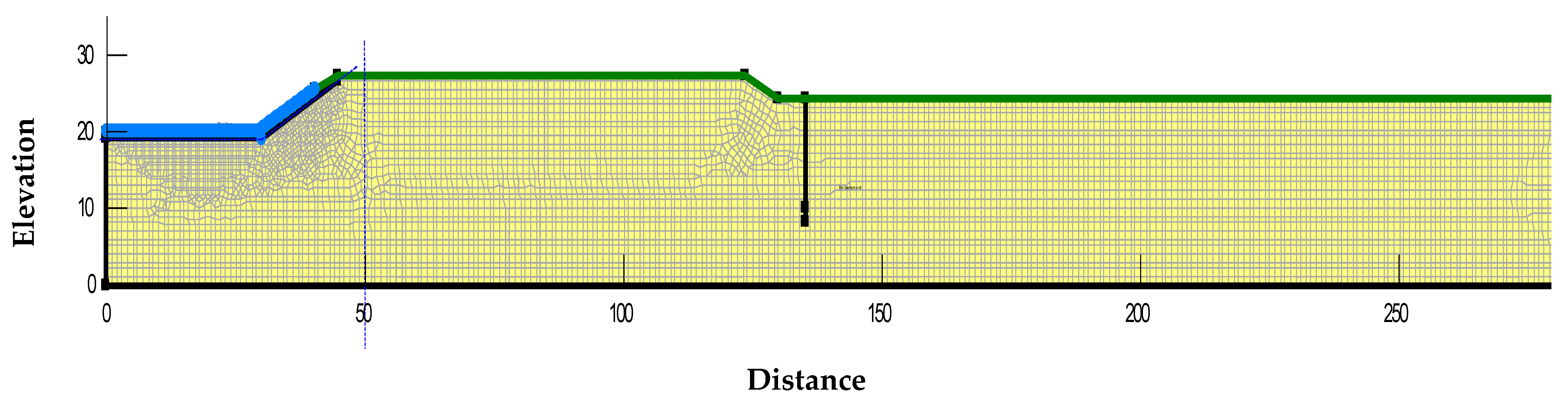
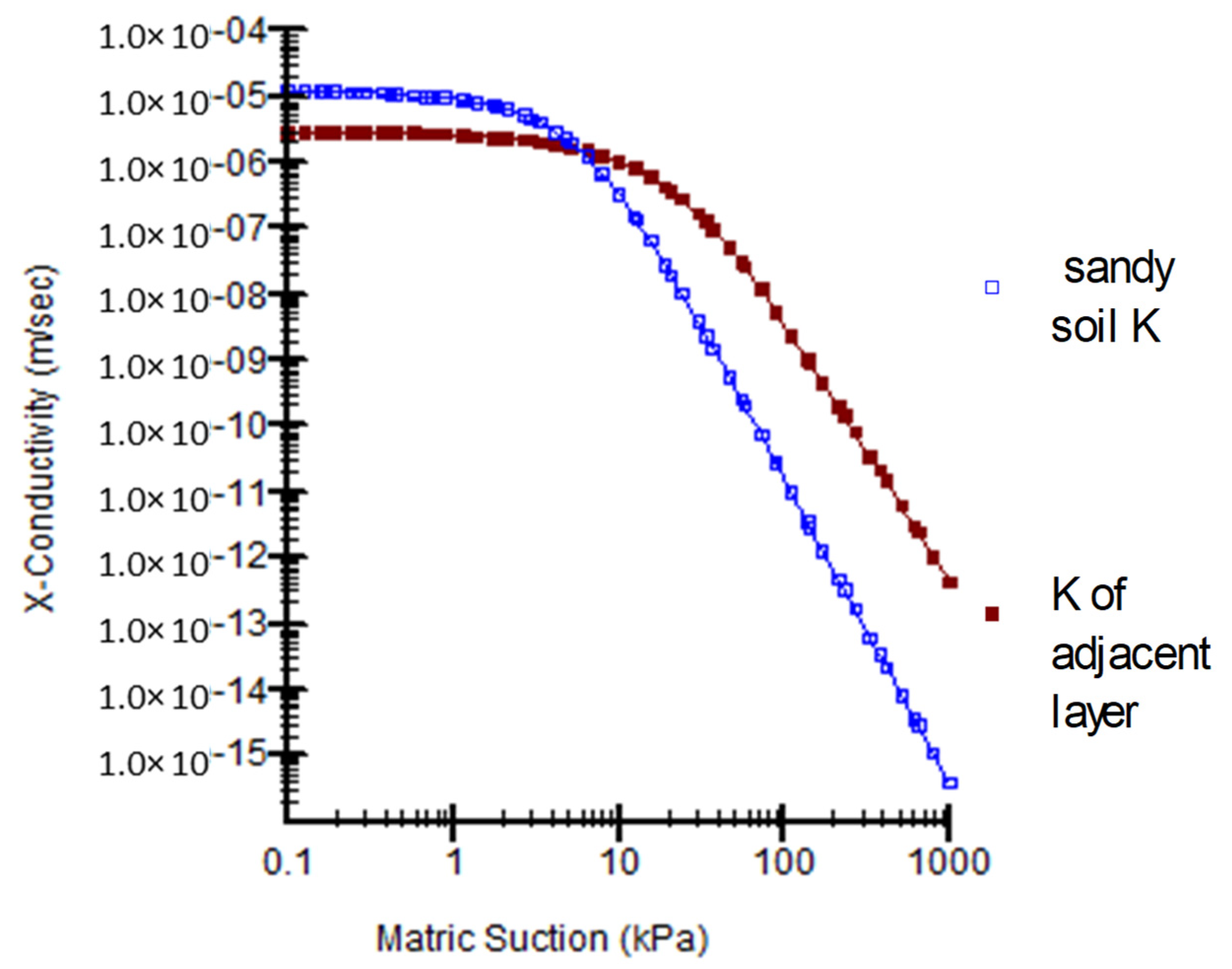
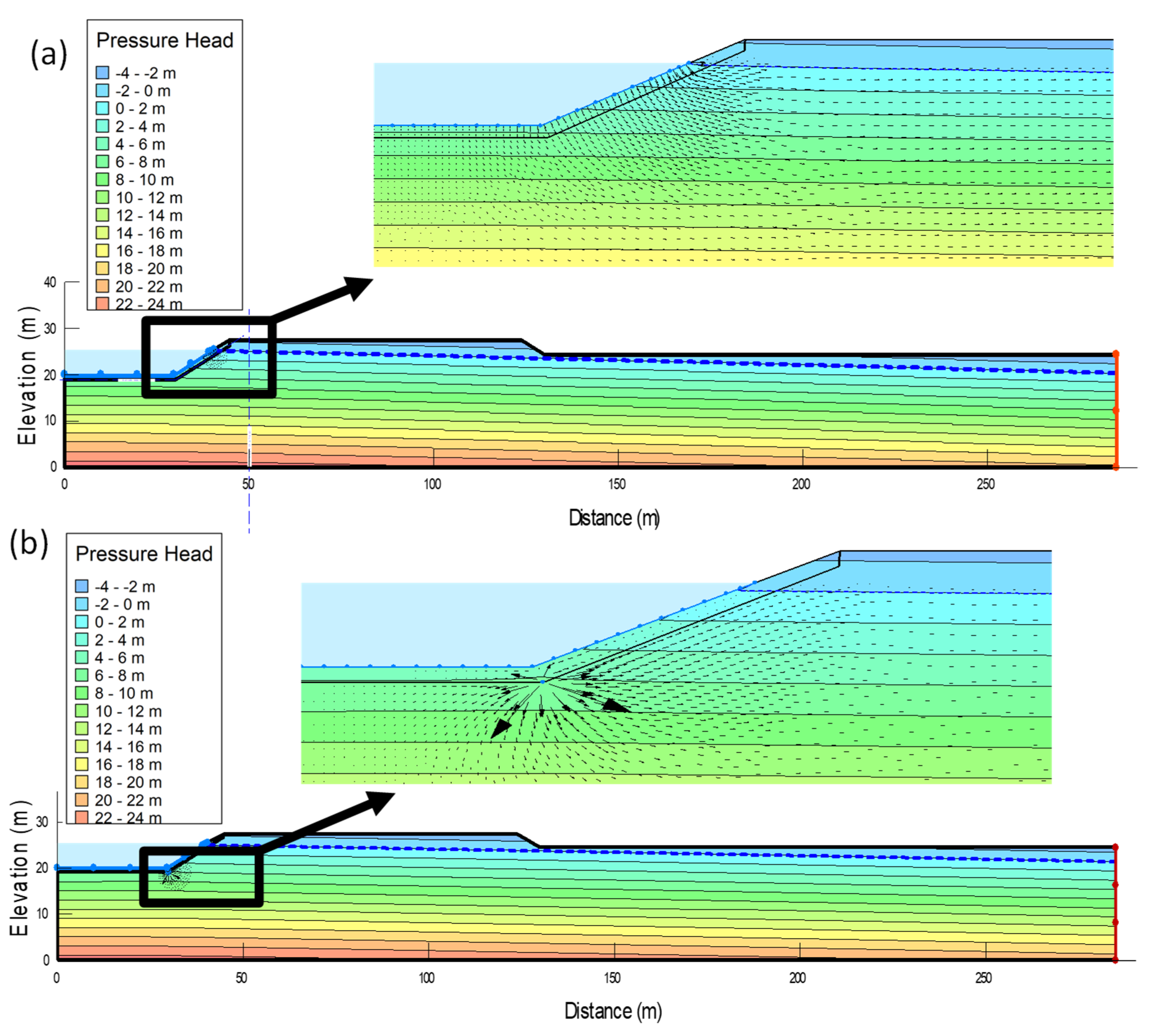
2.2. Numerical Modelling
3. Results and Discussion
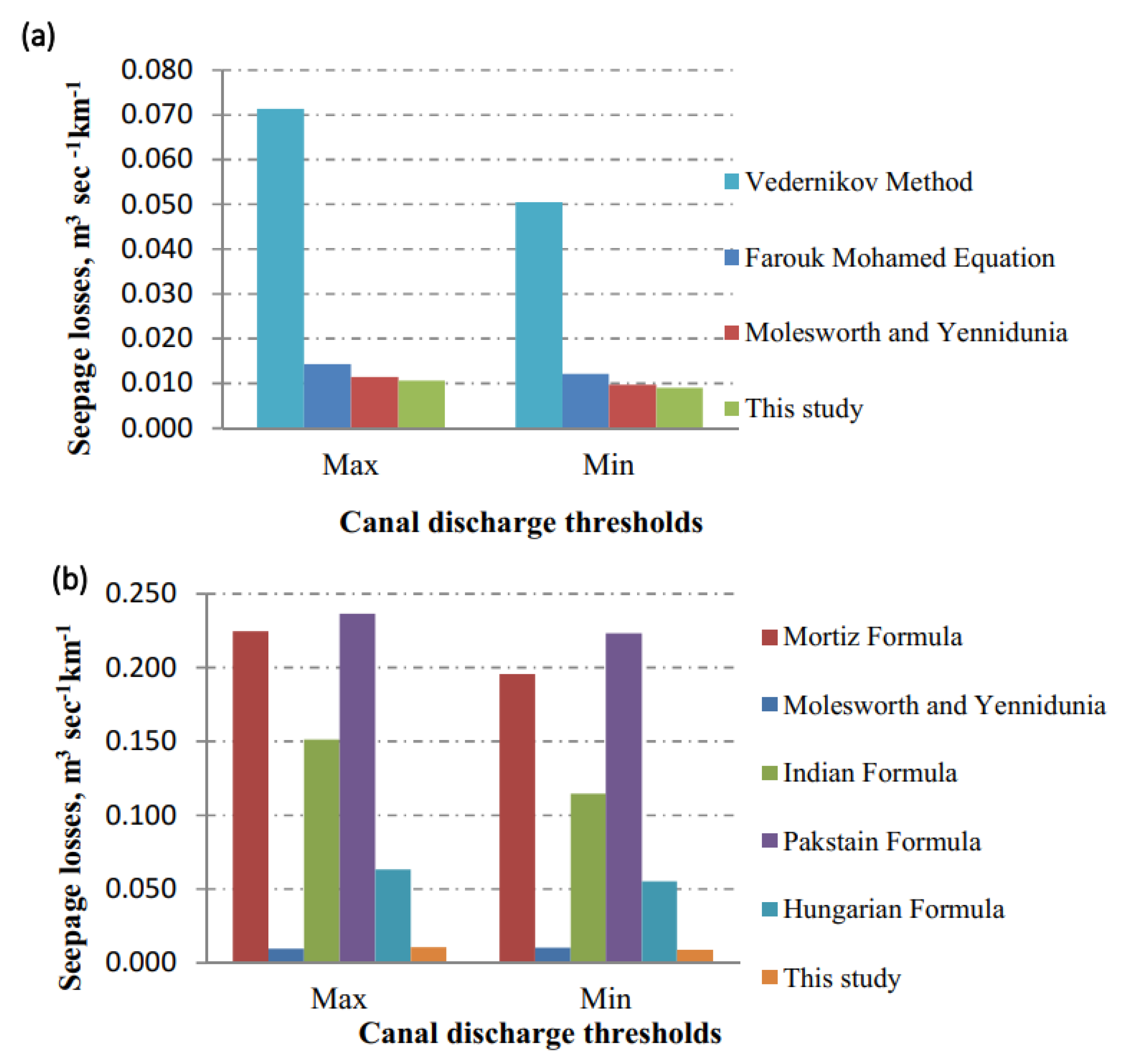
3.1. Seepage Losses for the Earth Canal
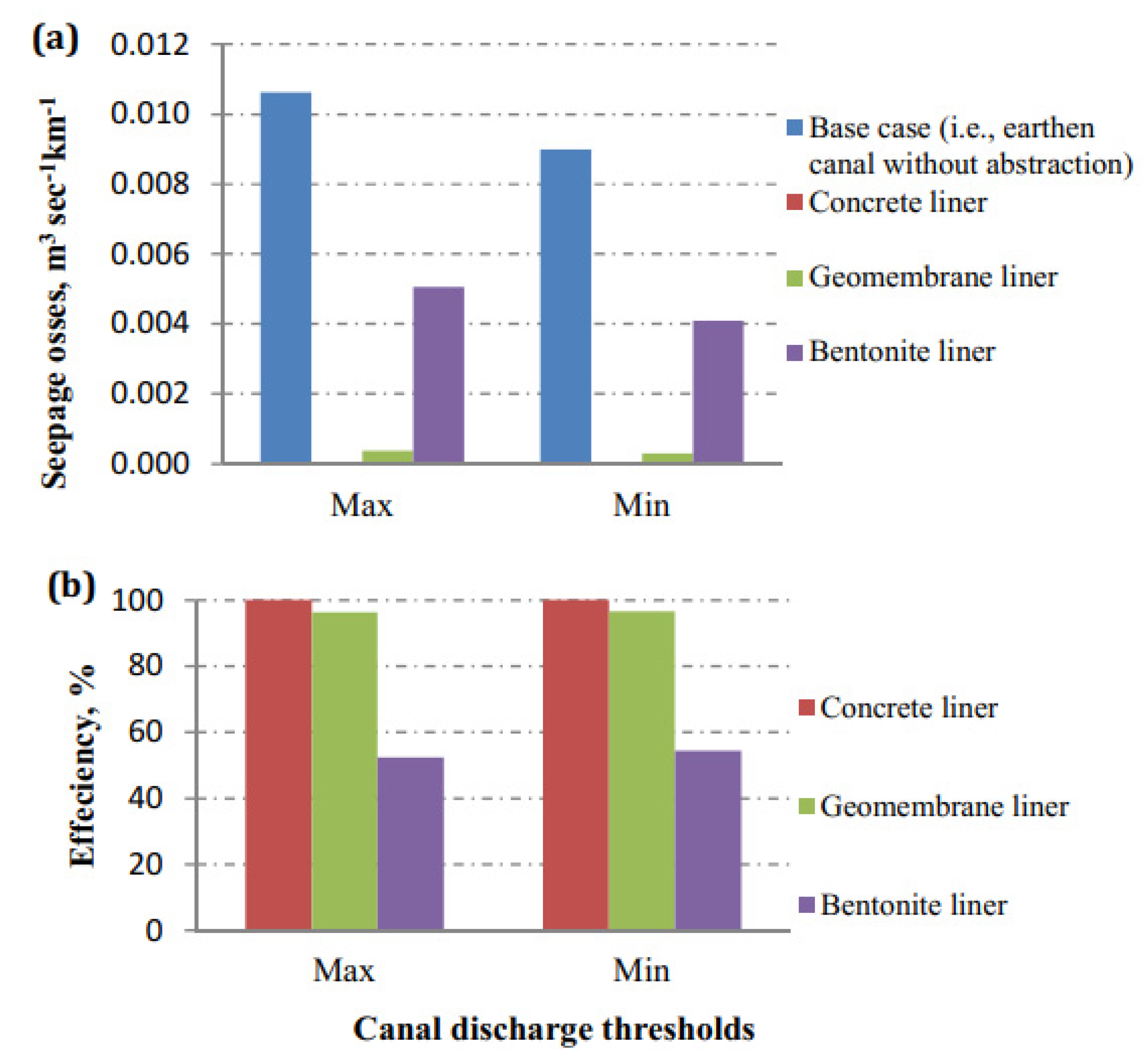
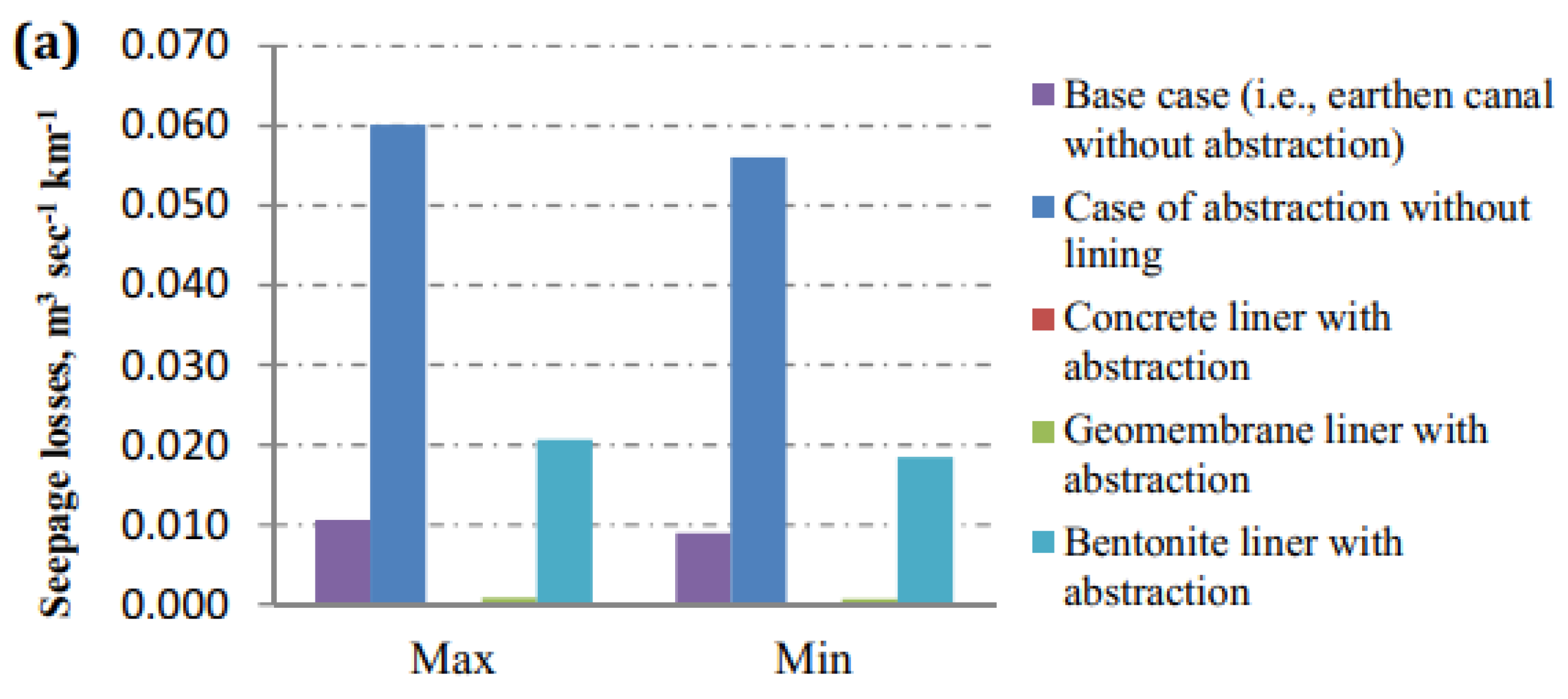
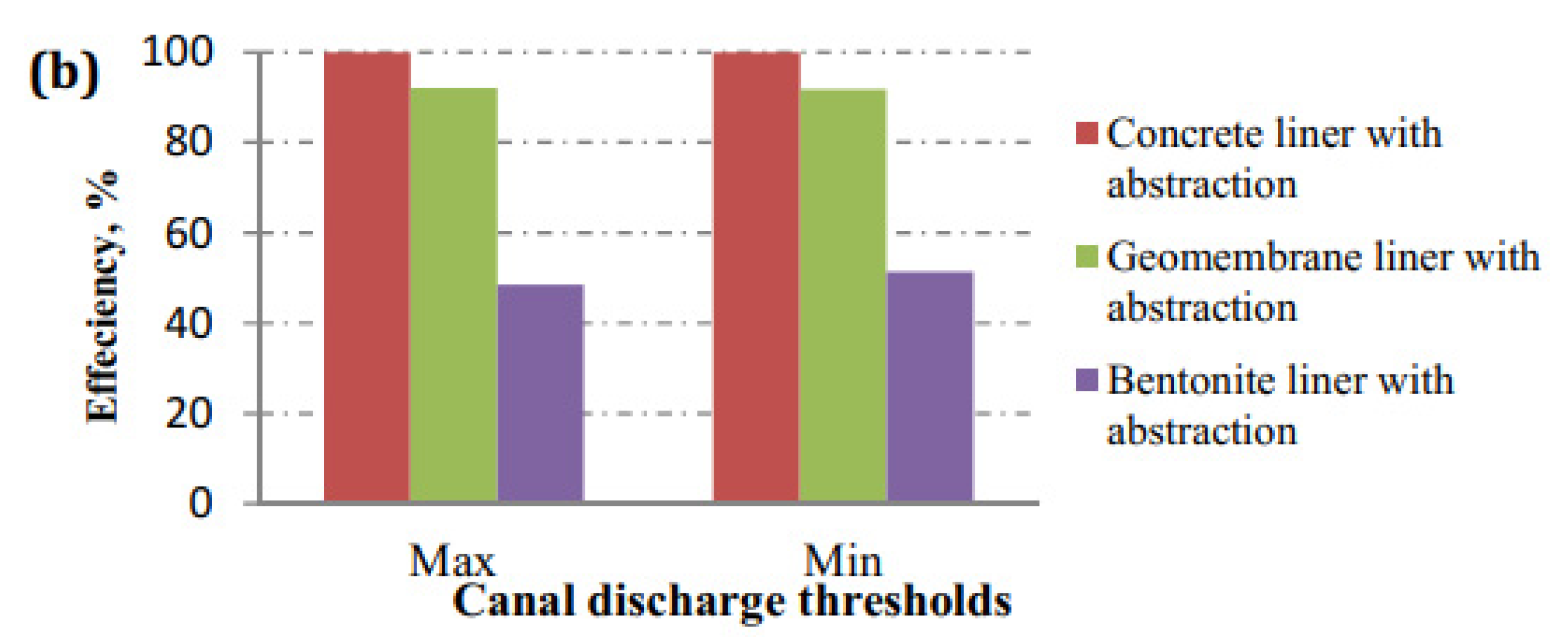
3.2. Seepage Losses from a Lined Canal
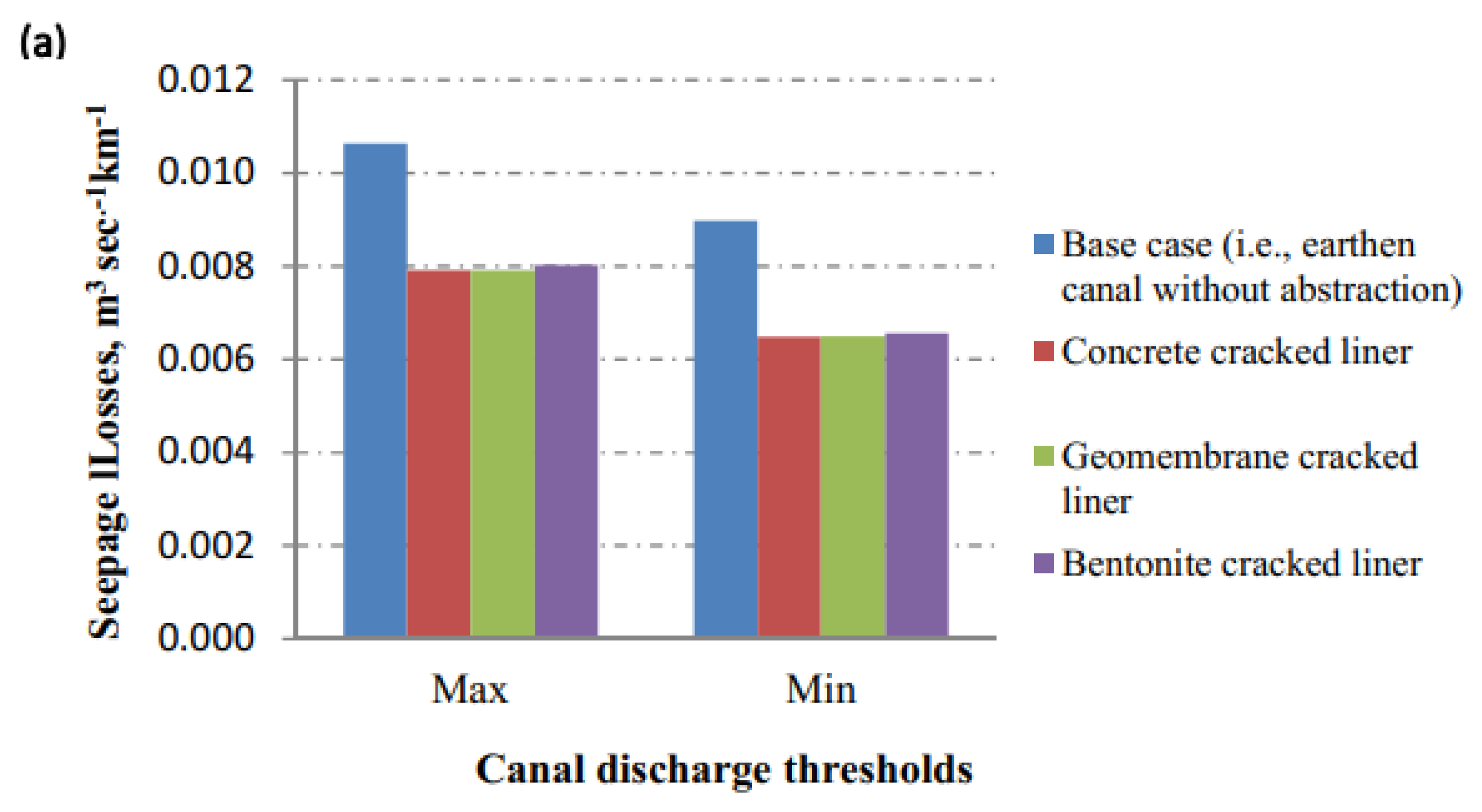
3.3. Seepage Losses from a Cracked Lined Canal
3.4. Cost Analysis for the Used Lining Materials
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Molla, D.A.; El-Molla, M.A. Seepage losses from trapezoidal earth canals with an impervious layer under the bed. Water Pract. Technol. 2021, 16, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, M.; Hagagg, K. Impact of reduced flow on 137Cs behavior in Ismailia Canal and surrounding groundwater systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 44279–44291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elhamid, H.; Abdelaty, I.; Sherif, M. Evaluation of potential impact of Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam on Seawater Intrusion in the Nile Delta Aquifer. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 2321–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waller, P.; Yitayew, M. Irrigation and Drainage Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Eltarabily, M.G.; Moghazy, H.E.; Abdel-Fattah, S.; Negm, A.M. The use of numerical modeling to optimize the construction of lined sections for a regionally-significant irrigation canal in Egypt. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowafy, M.H. Seepage losses in Ismailia canal. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Water Technology Conference, Alexandria, Egypt, 23–25 March 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Atmapoojya, S.L.; Ingle, R.N.; Kacimov, A.R.; Swamee, P.K.; Mishra, G.C.; Chahar, B.R. Design of minimum seepage loss canal sections. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2001, 127, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachyan, E.; Rushton, K.R. Water losses from irrigation canals. J. Hydrol. 1987, 92, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plusquellec, H. Overestimation of benefits of canal irrigation projects: Decline of performance over time caused by deterioration of concrete canal lining. Irrig. Drain. 2019, 68, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elhamid, H.F.; Said, A.M.; Abdelaal, G.M.; Abd-Elaty, I. Impact of polluted open-drain geometry on groundwater contaminant in unconfined aquifers. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzeid, T.S. Conveyance losses estimation for open channels in Middle Egypt case study: Almanna main canal, and its branches. JES J. Eng. Sci. 2021, 49, 64–84. [Google Scholar]
- Sarki, A.; Memon, S.; Leghari, M. Comparison of different methods for computing seepage losses in an earthen watercourse. Agric. Trop. Subtrop. 2008, 41, 197–205. [Google Scholar]
- Eshetu, B.D.; Alamirew, T. Estimation of seepage loss in irrigation canals of Tendaho sugar estate, Ethiopia. Irrig. Drain. Syst. Eng. 2018, 7, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Chai, J.; Xu, Z.; Qin, Y. Investigation of irrigation canal seepage losses through use of four different methods in Hetao irrigation district, China. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2017, 22, 05016035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Lal, C.; Shahi, N.C.; Chand, K. Estimation of canal seepage under shallow water table conditions. J. Acad. Ind. Res. 2013, 1, 571–575. [Google Scholar]
- El-Enany, M.; El-Alfy, K.S.A.E.-W.; Soheib, M.F.; Armanious, S.D.; Gergis, E.S. Modification of the improved irrigation system in the old lands in Egypt. (Dept. C). MEJ. Mansoura Eng. J. 2004, 29, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soothar, R.; Mirjat, M.S.; Mangrio, M.A.; Chandio, A.S.; Leghari, N. Estimating seepage losses in different size of earthen watercourses at farm level. Pak. J. Agric. Agric. Eng. Vet. Sci. 2015, 31, 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- Elkamhawy, E. Rehabilitation of Irrigation and Drainage Networks in Sharkia Irrigation Directorate. Master’s Thesis, Zagazig University, Zagazig, Egypt, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-Elhamid, H.F.; Abdelaal, G.M.; Abd-Elaty, I.; Said, A.M. Efficiency of using different lining materials to protect groundwater from leakage of polluted streams. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.-Aqua 2019, 68, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, T.; Hynes, J. Geomembranes for Canal Lining; Geosynthetics: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco, M.; Castillo, F.; Soriano, J.; Noval, A.M.; Touze-Foltz, N.; Pargada, L.; Rico, G.; Aguiar, E. Comparative Study of Three Different Kinds of Geomembranes (PVC-P, HDPE, EPDM) Used in The Waterproofing of Reservoirs. In Proceedings of the Eurogeo 5, Valencia, Spain, 16–19 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ojoawo, S.; Adegbola, A. The system dynamics modeling method in application of geo-membranes as landfill liners. Am. Int. J. Contemp. Res. 2012, 2, 138–144. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-Elaty, I.; Zelenakova, M.; Straface, S.; Vranayová, Z.; Abu-hashim, M. Integrated modelling for groundwater contamination from polluted streams using new protection process techniques. Water 2019, 11, 2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Available online: https://www.youm7.com/story/2021/6/12/%D8%AD%D9%8A%D8%A7%D8%A9-%D9%83%D8%B1%D9%8A%D9%85%D8%A9-%D8%AA%D8%A8%D8%B7%D9%8A%D9%86-85-%D9%83%D9%85-%D9%85%D9%86-%D8%AA%D8%B1%D8%B9-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%BA%D8%B1%D8%A8%D9%8A%D8%A9-%D8%AD%D9%81%D8%A7%D8%B8%D8%A7-%D8%B9%D9%84%D9%89/5351354 (accessed on 5 June 2021).
- Available online: https://www.geosynthetica.com/geosynthetics-agricultural-water-security/ (accessed on 20 June 2015).
- Available online: https://www.elaard.com/87592 (accessed on 15 March 2020).
- Sallouma, M.K.M. Hydrogeological and Hydrochemical Studies East of Nile Delta, Egypt. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Science, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt, 1983; 166p. [Google Scholar]
- Krahn, J. Seepage Modeling with SEEP/W: An Engineering Methodology; GEO-SLOPE International: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Elkamhawy, E.; Wang, H.; Zhou, B.; Yang, Z. Failure mechanism of a slope with a thin soft band triggered by intensive rainfall. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elaty, I.; Said, A.M.; Abdelaal, G.M.; Zeleňáková, M.; Jandora, J.; Abd-Elhamid, H.F. Assessing the impact of lining polluted streams on groundwater quality: A case study of the Eastern Nile Delta Aquifer, Egypt. Water 2021, 13, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elaty, I.; Kuriqi, A.; El Shahawy, A.E. Environmental rethinking of wastewater drains to manage environmental pollution and alleviate water scarcity. Nat. Hazards (Dordr.) 2021, 27, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elhamid, H.F.; Abd-Elmoneem, S.M.; Abdelaal, G.M.; Zeleňáková, M.; Vranayova, Z.; Abd-Elaty, I. Investigating and Managing the Impact of Using Untreated Wastewater for Irrigation on the Groundwater Quality in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.alibaba.com/product-detail/Hdpe-Geocell-Hdpe-Geocell-Earthwork-HDPE_60684636819.html?spm=a2700.pccps_detail.normal_offer.d_title.196f7179blSCfI&s=p (accessed on 10 August 2021).
- Available online: https://www.alibaba.com/product-detail/Hdpe-Geomembrane-Suppliers-for-Waste-Containment_1600232356483.html?spm=a2700.details.0.0.48d971779Yz4jD (accessed on 10 August 2021).
- Available online: https://www.alibaba.com/product-detail/Concrete-Canvas-Cement-Blanket-Concrete-Waterproof1600321346374.html?spm=a2700.galleryofferlist.normal_offer.d_title.69ce7b4eXPOvz6&s=p (accessed on 10 August 2021).
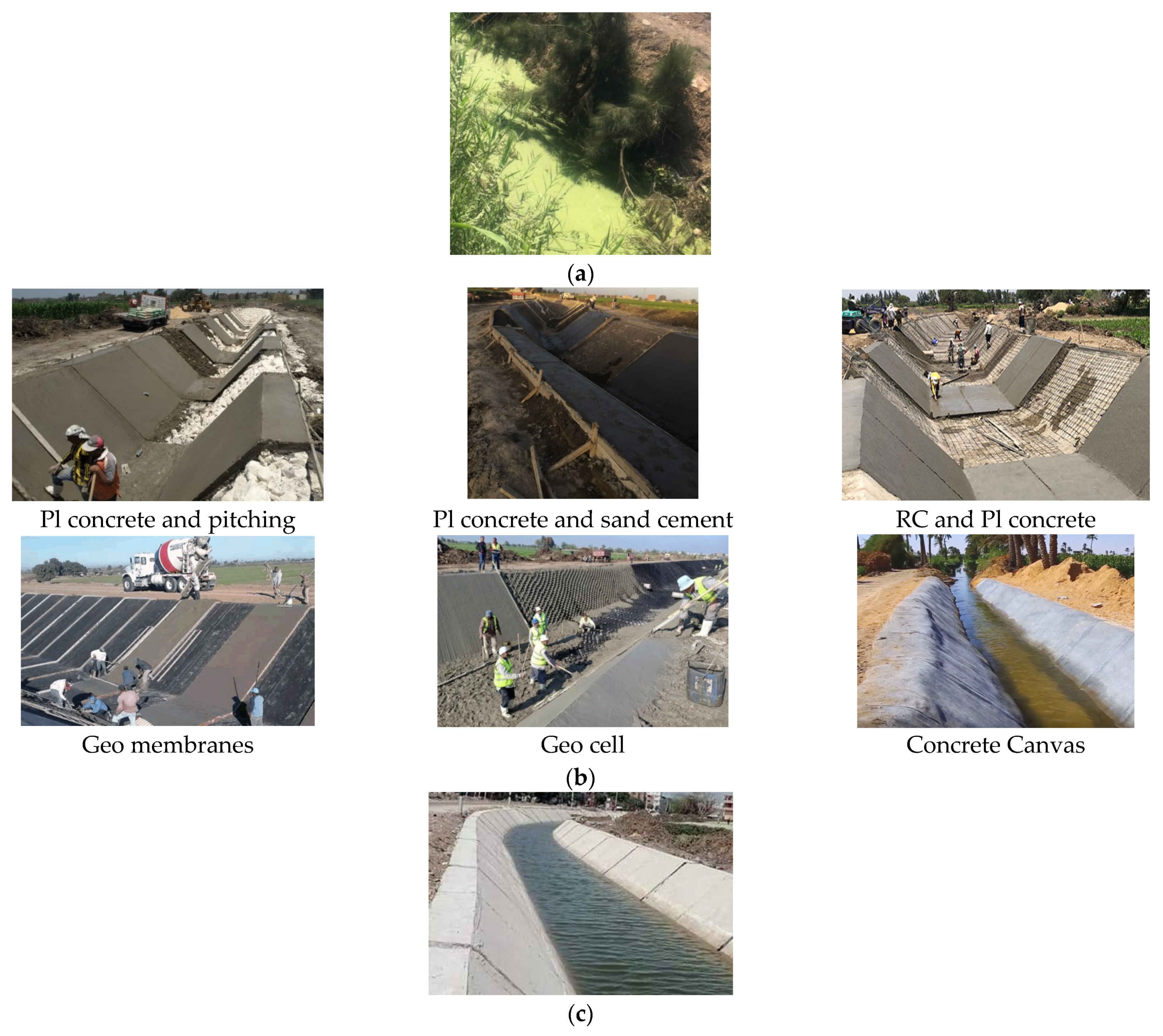


| Discharge, m3 s−1 | Case | Ksat, m s−1 | Well Extraction (0.00236 m3 s−1) | Cracks in Liner | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max. discharge 397.12 | Base case | 1.158 × 10−5 | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Concrete liner | 4.63 × 10−14 | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | |
| Geomembrane liner | 1.16 × 10−10 | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | |
| Bentonite liner | 3.82 × 10−8 | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | |
| Min. discharge 300.48 | Base case | 1.158 × 10−5 | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Concrete liner | 4.63 × 10−14 | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | |
| Geomembrane liner | 1.16 × 10−10 | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | |
| Bentonite liner | 3.82 × 10−8 | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | |
| Item | Lining Type | Material | Volume | Price ($/m2) | Study Area | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness (cm) | Price ($/m2) | |||||
| 1 | Plain concrete and pitching | Plain concrete | 1 m3 | 79 | 10 | 7.90 |
| Pitching without mortar | 1 m3 | 34 | 30 | 10.2 | ||
| Total price | - | - | - | 18.10 | ||
| Plain concrete and sand with cement | Plain concrete | 1 m3 | 79 | 15 | 11.85 | |
| Sand cement | 1 m3 | 31 | 20 | 6.20 | ||
| Total price | - | - | - | 18.05 | ||
| Reinforced concrete and sand with cement | Reinforced concrete | 1 m3 | 198 | 10 | 19.80 | |
| Sand cement | 1 m3 | 31 | 20 | 6.20 | ||
| Total price | - | - | - | 26 | ||
| 2 | Geomembrane and plain concrete | Plain concrete | 1 m3 | 79 | 20 | 15.80 |
| Sand cement | 1 m3 | 31 | 20 | 6.10 | ||
| High-density ploy ethylene geomembrane | 1 m2 | 4.50 | 0.10 | 4.50 | ||
| Total price | - | - | - | 26.40 | ||
| Geo cell and plain concrete | Plain concrete | 1 m3 | 79 | 20 | 15.80 | |
| High-density geo cell | 1 m2 | 7 | 0.10 | 7 | ||
| Total price | - | - | - | 22.80 | ||
| Concrete canvas and sand | Sand | 1 m3 | 7.50 | 20 | 1.50 | |
| Concrete canvas | 1 m2 | 28 | 1 | 28 | ||
| Total price | - | - | - | 29.50 | ||
| 3 | Bentonite and compacted soil | Compacted soil | 1 m3 | 9 | 30 | 2.70 |
| Bentonite | 1 m3 | 18 | 20 | 3.60 | ||
| Total price | - | - | - | 6.30 | ||
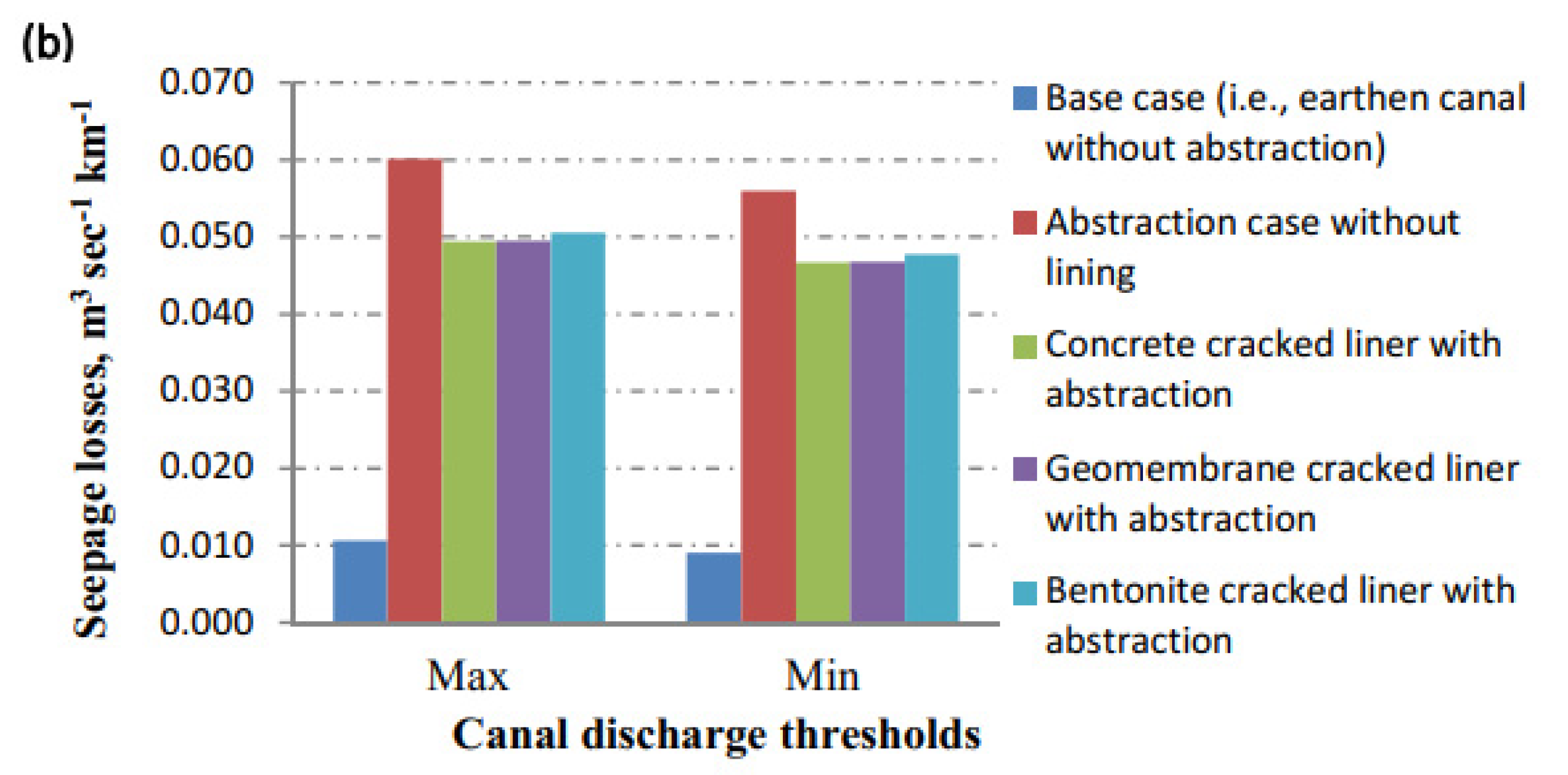
| Discharge, (m3 s−1) | Case | Without Extraction (m3 s−1 km−1) | With Extraction (m3 s−1 km−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max. discharge 397.12 | Base case | 0.0106274 | 0.060172 | |
| Concrete liner | Without crack | 1.59 × 10−7 | 6.13 × 10−7 | |
| With crack | 7.91 × 10−3 | 4.94 × 10−2 | ||
| Geomembrane liner | Without crack | 3.77 × 10−4 | 8.35 × 10−4 | |
| With crack | 7.92 × 10−3 | 4.95 × 10−2 | ||
| Bentonite liner | Without crack | 5.06 × 10−3 | 2.06 × 10−2 | |
| With crack | 8.01 × 10−3 | 5.06 × 10−2 | ||
| Min. discharge 300.48 | Base case | 0.008985 | 0.055996 | |
| Concrete liner | Without crack | 1.27 × 10−7 | 5.66 × 10−7 | |
| With crack | 6.48 × 10−3 | 4.66 × 10−2 | ||
| Geomembrane liner | Without crack | 3.02 × 10−4 | 7.39 × 10−4 | |
| With crack | 6.49 × 10−3 | 4.67 × 10−2 | ||
| Bentonite liner | Without crack | 4.09 × 10−3 | 1.85 × 10−2 | |
| With crack | 6.56 × 10−3 | 4.77 × 10−2 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elkamhawy, E.; Zelenakova, M.; Abd-Elaty, I. Numerical Canal Seepage Loss Evaluation for Different Lining and Crack Techniques in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions: A Case Study of the River Nile, Egypt. Water 2021, 13, 3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13213135
Elkamhawy E, Zelenakova M, Abd-Elaty I. Numerical Canal Seepage Loss Evaluation for Different Lining and Crack Techniques in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions: A Case Study of the River Nile, Egypt. Water. 2021; 13(21):3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13213135
Chicago/Turabian StyleElkamhawy, Elsayed, Martina Zelenakova, and Ismail Abd-Elaty. 2021. "Numerical Canal Seepage Loss Evaluation for Different Lining and Crack Techniques in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions: A Case Study of the River Nile, Egypt" Water 13, no. 21: 3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13213135
APA StyleElkamhawy, E., Zelenakova, M., & Abd-Elaty, I. (2021). Numerical Canal Seepage Loss Evaluation for Different Lining and Crack Techniques in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions: A Case Study of the River Nile, Egypt. Water, 13(21), 3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13213135







