Performance Evaluation of Different Combined Drainage Forms on Flooding and Waterlogging Removal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
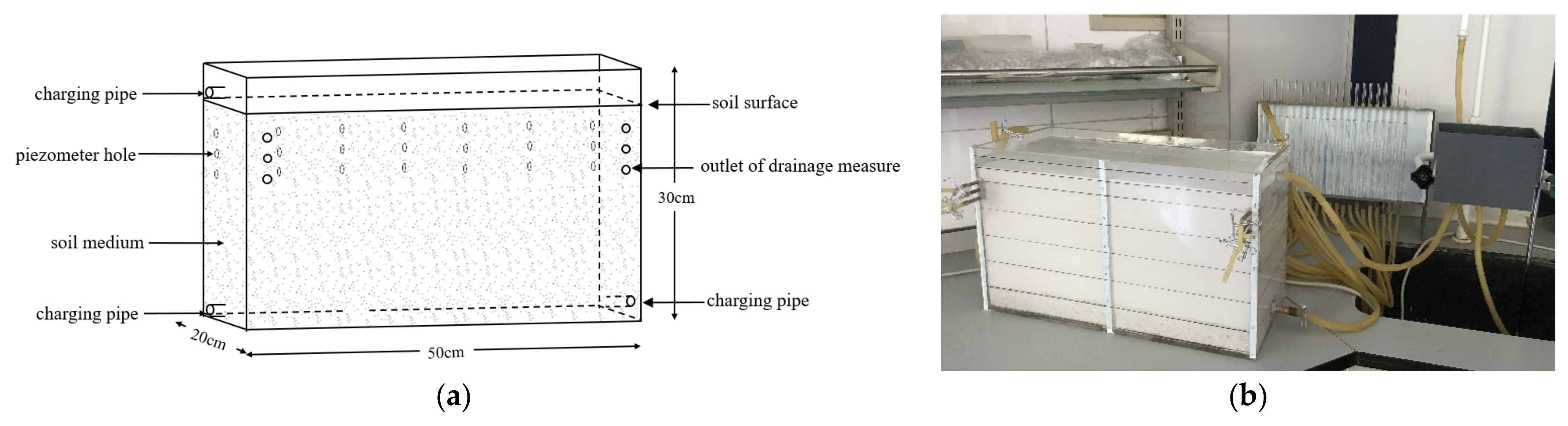
2.1. Experimental Structure
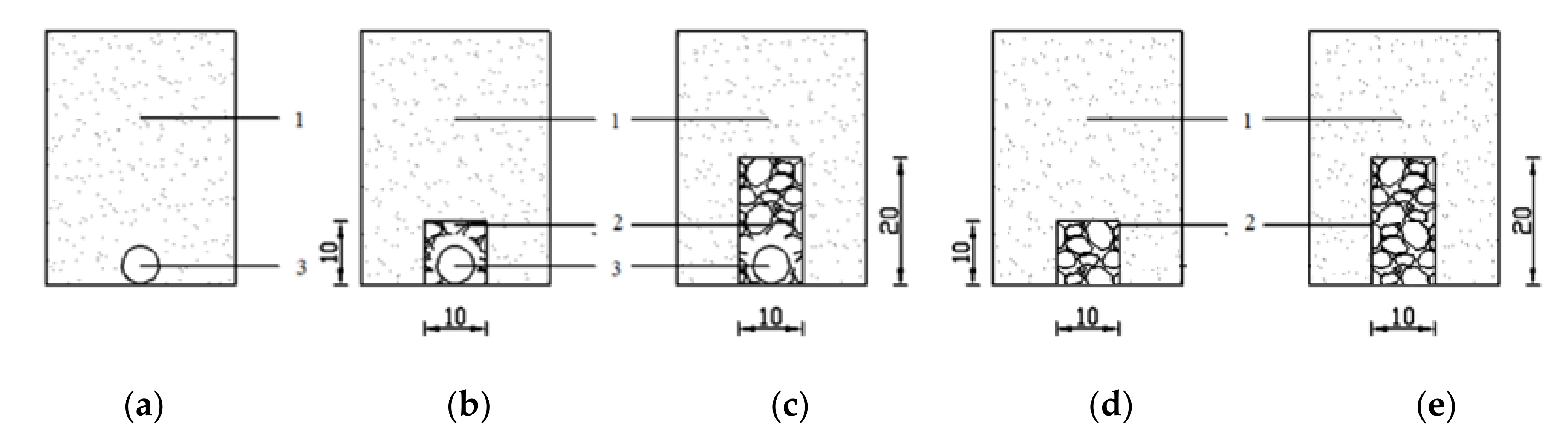
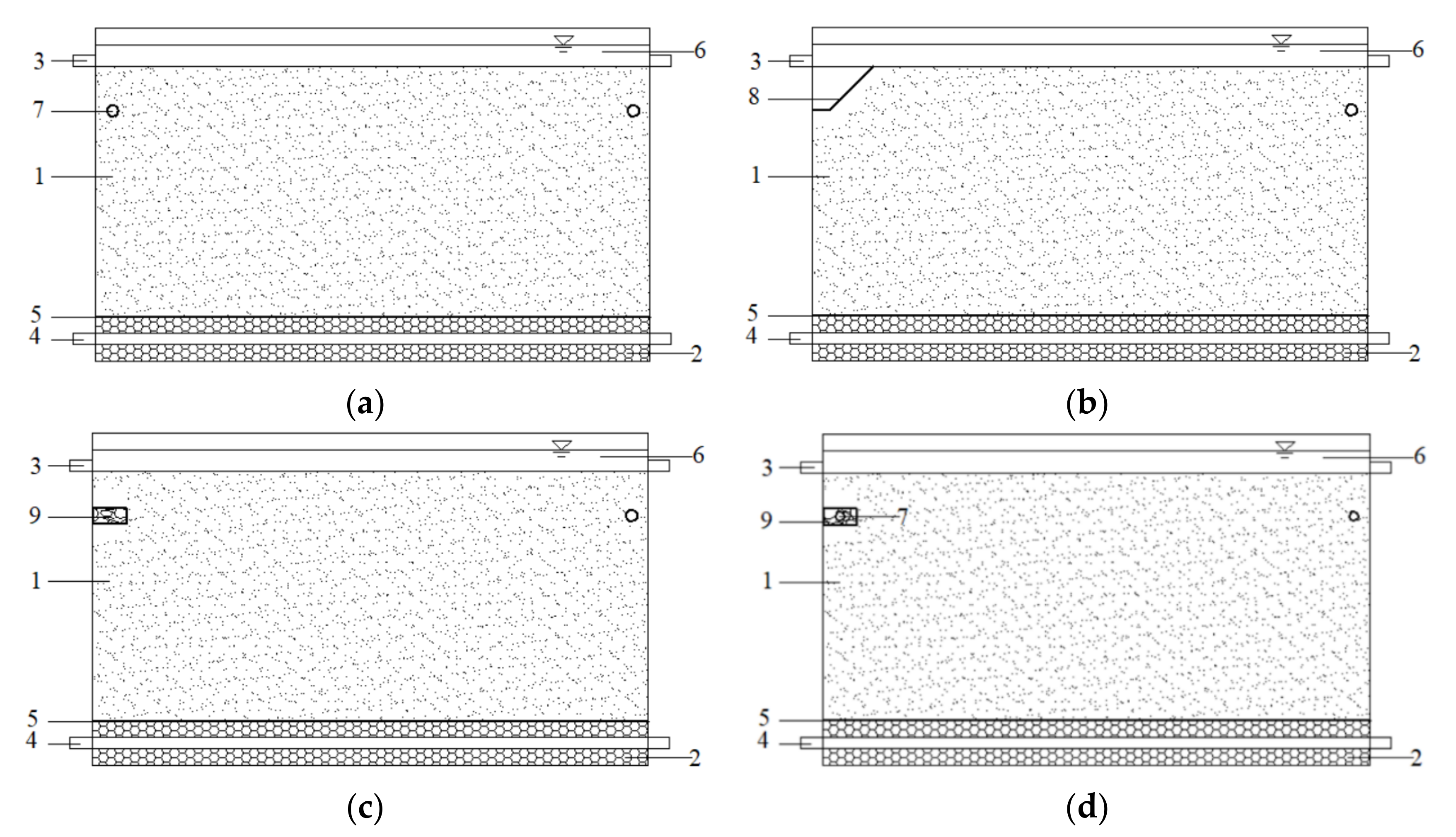
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Observation Method
3. Results
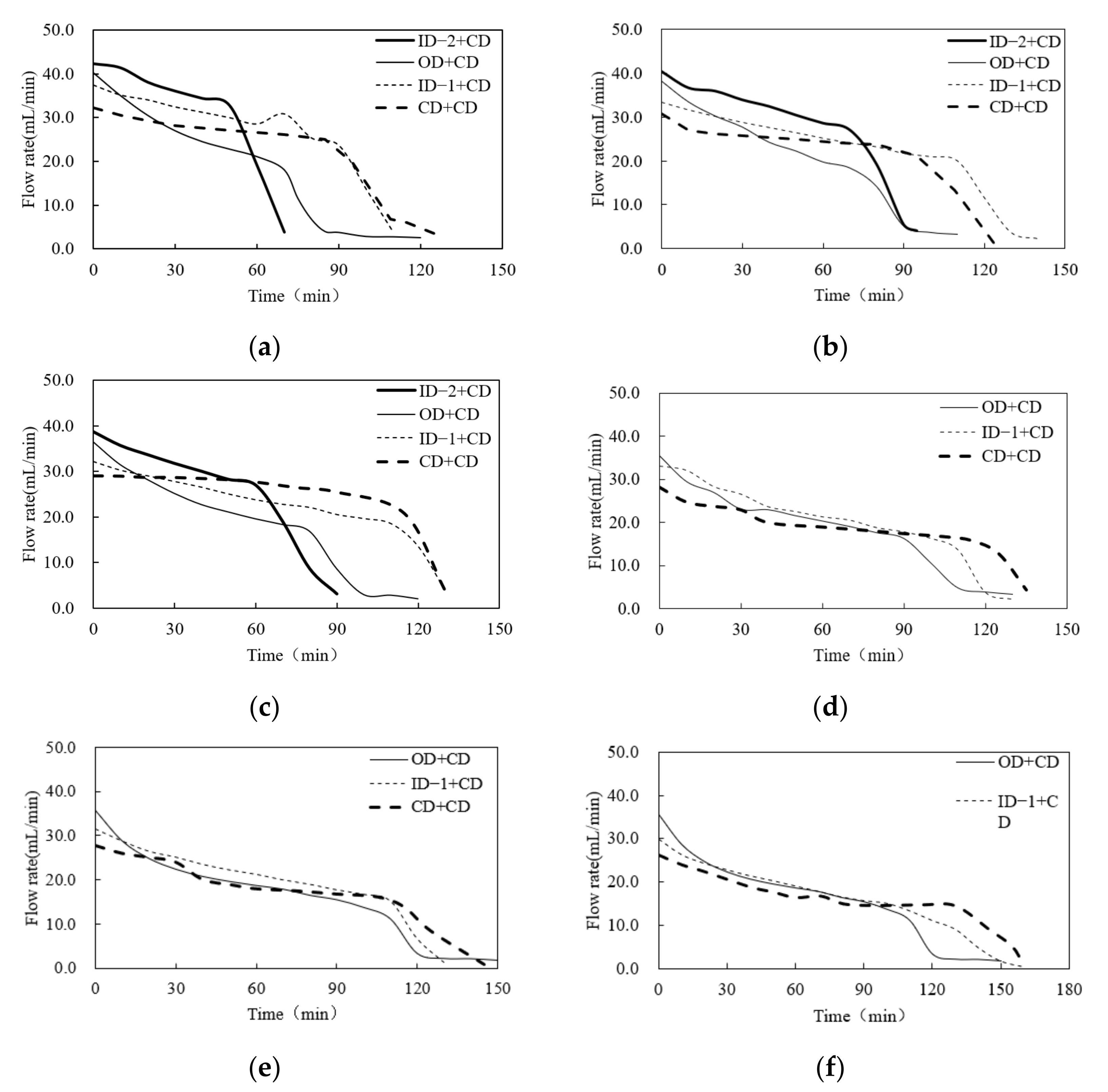
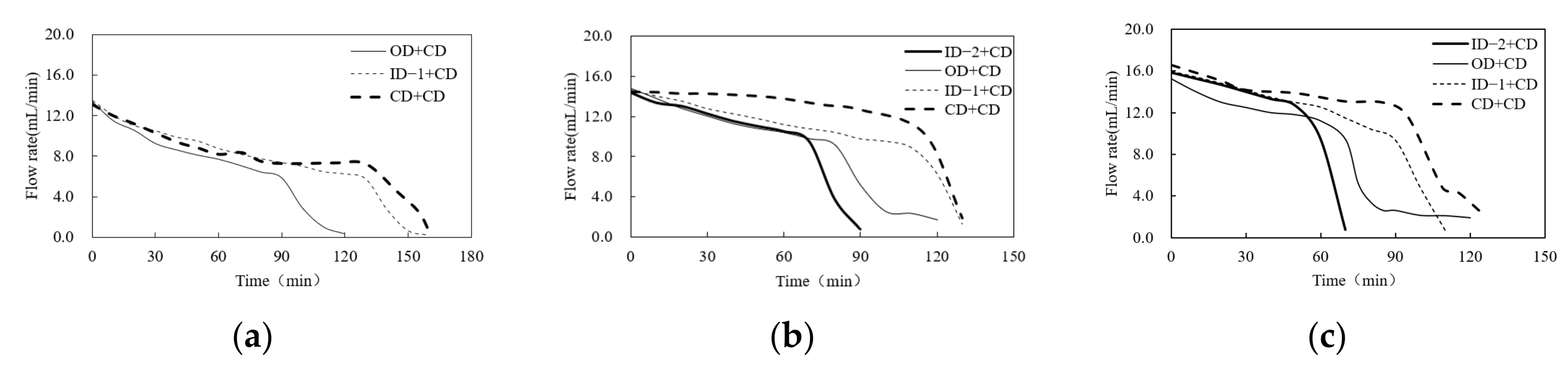
3.1. Flow Rate of Different Combinations under Stable Ponding Water
3.2. Flow Rate of Different Combinations under the Receded Water Condition
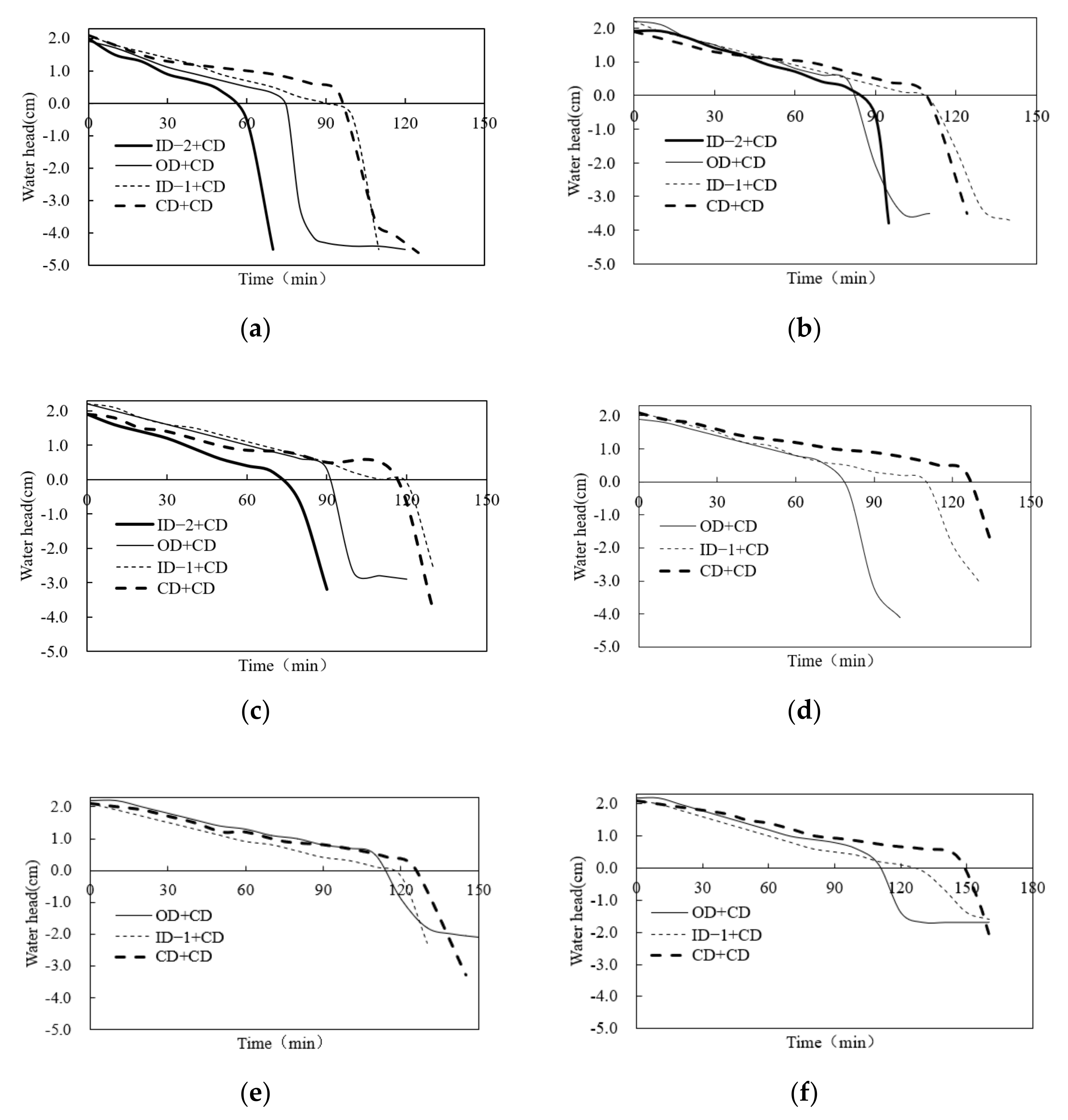
3.3. Effect of Flooding and Waterlogging Removal
3.4. Contribution Degree of Different Drainage Measures in Combined Drainage Forms
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yue, X.-L.; Gao, Q.-X. Contributions of natural systems and human activity to greenhouse gas emissions. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2018, 9, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, H.; Shen, Z.; Sun, P. Double increase in precipitation extremes across China in a 1.5 °C/2.0 °C warmer climate. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 746, 140807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Dai, A.; Rasmussen, R.M.; Parsons, D.B. The Changing Character of Precipitation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 84, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). The State of Food and Agriculture: Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security. 2018. Available online: www.fao.org/publications (accessed on 4 November 2020).
- China Meteorological Administration. Yearbook of Meteorological Disasters in China. 2017. Available online: http://www.cma.gov.cn/2011xwzx/2011xmtjj/201701/t20170112_386200.html (accessed on 4 November 2020).
- Corwin, D.L. Climate change impacts on soil salinity in agricultural areas. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 72, 842–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, D.W.; Das, T.; Cayan, D.R.; Maurer, E.P.; Miller, N.L.; Bao, Y.; Kanamitsu, M.; Yoshimura, K.; Snyder, M.A.; Sloan, L.C.; et al. Probabilistic estimates of future changes in California temperature and precipitation using statistical and dynamical downscaling. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 40, 839–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trenberth, K. Changes in precipitation with climate change. Clim. Res. 2011, 47, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahlown, M.A.; Marri, M.K.; Azam, M. Design, construction and performance evaluation of small tile drainage systems in the Indus Basin. Irrig. Drain. 2007, 56, S217–S225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, M.; Kulkarni, S.A. Agricultural land drainage in India. Irrig. Drain. 2007, 56, S59–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, D.; Qu, X. Experiment and analysis on flow rate of improved subsurface drainage with ponded water. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 177, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, D.; Yuan, H.; Chen, H. Field and numerical experiment of an improved subsurface drainage system in Huaibei plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 194, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maalim, F.K.; Melesse, A.M. Modelling the impacts of subsurface drainage on surface runoff and sediment yield in the Le Sueur Watershed, Minnesota, USA. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 570–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filipović, V.; Mallmann, F.J.K.; Coquet, Y.; Šimůnek, J. Numerical simulation of water flow in tile and mole drainage systems. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 146, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Xu, D.; Chen, H.; Han, S.; Jiao, P. Review on research of farmland drainage technology. J. Drain. Irrig. Ma-Chinery Eng. 2014, 32, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, D.; Qu, X. Effect of Structure-type on Improved Subsurface Drainage Performance. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2016, 47, 113–118, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madramootoo, C.A.; Johnston, W.R.; Ayars, J.E.; Evans, R.O.; Fausey, N.R. Agricultural drainage management, quality and disposal issues in North America. Irrig. Drain. 2007, 56, S35–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzon, I.; Helenius, J. Agricultural drainage ditches, their biological importance and functioning. Biol. Conserv. 2008, 141, 1171–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y. The Performance Experiment and Theory Analysis of an Improved Subsurface Drainage. Ph.D. Thesis, College of Water Conservancy and Hydropower Engineering, Hohai University, Nanjing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, M.K.; Koga, K. Mole drainage: Prospective drainage solution to Bangkok clay soils. Agric. Water Manag. 1995, 28, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaboosi, K.; Liaghat, A.; Hosseini, S.H. The Feasibility of Rice Husk Application as Envelope Material in Subsurface Drainage Systems. Irrig. Drain. 2012, 61, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuohy, P.; Humphreys, J.; Holden, N.; Fenton, O. Runoff and subsurface drain response from mole and gravel mole drainage across episodic rainfall events. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 169, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari-Talukolaee, M.; Ritzema, H.; Darzi-Naftchali, A.; Shahnazari, A. Subsurface Drainage to Enable the Cultivation of Winter Crops in Consolidated Paddy Fields in Northern Iran. Sustainability 2016, 8, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christen, E.; Skehan, D. Design and Management of Subsurface Horizontal Drainage to Reduce Salt Loads. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2001, 127, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukolaee, M.J.; Naftchali, A.D.; Parvariji, L.Z.; Ahmadi, M.Z. Investigating long-term effects of subsurface drainage on soil structure in paddy fields. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 177, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornbuckle, J.; Christen, E.; Faulkner, R. Evaluating a multi-level subsurface drainage system for improved drainage water quality. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 89, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F. Calculation method of combining open channel and pipe drainage for controlling concurrent wa-terlogging and water table rising. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2001, 12, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Xu, H. Experiment on Reconstruction of Waterlogged Paddy Field by combined drainage of dark pipe and rat ca-nal. J. Irrig. Drain. 1992, 3, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, M. Effect and Simulation of Double-layer Subsurface Pipe Drainage Lay out on Water and Nitrogen Transport of Farmland. J. Water Resour. Archit. Eng. 2014, 12, 39–44, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Gupta, S.; Singh, K.; Chauhan, H. An analytical solution for design of bi-level drainage systems. Agric. Water Manag. 1998, 37, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zhou, H. Experiment on reforming saline-alkali wasteland by drainage technology of double layer concealed pipe. China Rural Water Hydropower 1997, 10, 33–34. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, J.; Wang, Q.; Guo, S. Combined Drainage Engineering Formations and Design for Comprehensive Treatment of Water Logging and Waterlogged in the Northern Huai River Plain. J. Xi’an Univ. Technol. 2009, 25, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogino, Y.; Ota, S. The evolution of Japan’s rice field drainage and development of technology. Special Issue: Drainage—An essential element of integrated water management. Irrig. Drain. 2007, 56, S69–S80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, P.; Qi, J. Model test and numerical simulation on the development of artificially freezing wall in sandy layers considering water seepage. Transp. Geotech. 2019, 21, 100293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Kuwano, R. Suffusion and clogging by one-dimensional seepage tests on cohesive soil. Soils Found. 2015, 55, 1427–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirkham, D. Flow of ponded water into drain tubes in soil overlying an impervious layer. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1949, 30, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, D.; Guan, X.; Ji, M.; Liu, J. Theoretical analysis and experimental verification of the improved subsurface drainage discharge with ponded water. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X. Calculation of Discharge and Correcting Factor on the Partial Penetration of Open Drains and Pipe Drains. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1982, 4, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, D. Experimental Study of Clogging Defense Measures for Improved Subsurface Drainage. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2016, 47, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Wang, S.; Guan, X.; Xu, D.; Chen, H.; Ji, M. Study on Characteristics of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Loss under an Improved Subsurface Drainage. Water 2019, 11, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, W.B.; Li, M.S.; Li, Y.F.; Liu, H.G. Proposed Gravel Filters for Pipe-drain to Improve the Efficacy of the Drainage System under Drip Irrigation. J. Irrig. Drain. 2017, 36, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
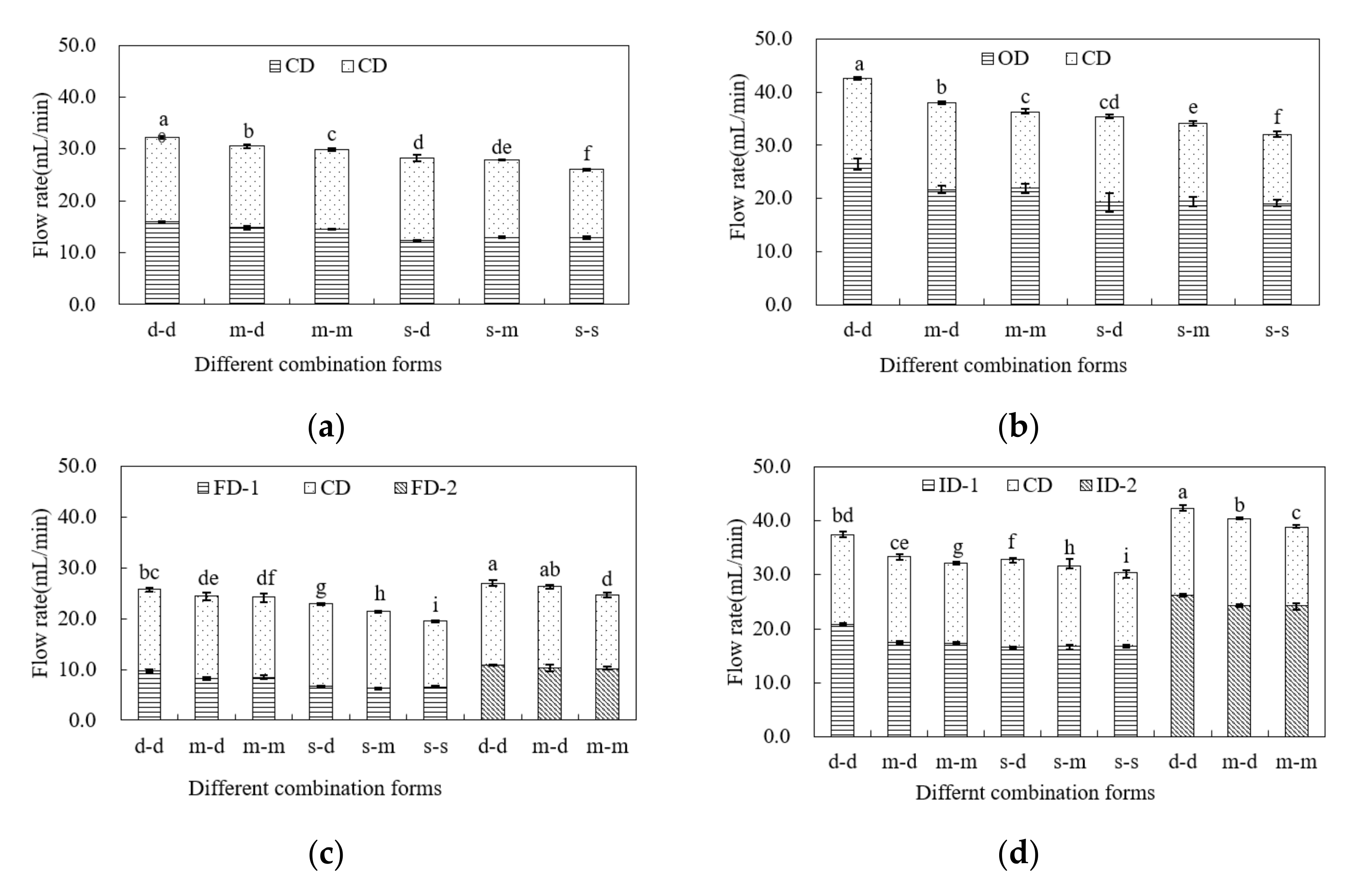
| Drain Depth on the Left Sidewall of the Sand Tank (CD, OD, FD, and ID) | Drain Depth on the Right Sidewall of Sand Tank (CD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Shallow | Medium | Deep | |
| Shallow | s-s | s-m | s-d |
| Medium | — | m-m | m-d |
| Deep | — | — | d-d |
| Combination | Drainage | Drain Depth | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s-s | s-m | s-d | m-m | m-d | d-d | ||
| OD + CD | OD | 51.3% | 48.2% | 49.0% | 51.3% | 49.8% | 54.4% |
| CD | 48.7% | 51.8% | 51.0% | 48.7% | 50.2% | 45.6% | |
| ID-1 + CD | ID-1 | 53.7% | 49.5% | 45.7% | 53.0% | 50.1% | 56.7% |
| CD | 46.3% | 50.5% | 54.3% | 47.0% | 49.9% | 43.3% | |
| ID-2 + CD | ID-2 | — | — | — | 61.0% | 57.5% | 61.3% |
| CD | — | — | — | 39.0% | 42.5% | 38.7% | |
| Combination | Flow Rate (mL/min) | Drain Depth | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s-s | s-m | s-d | m-m | m-d | d-d | ||
| CD + CD | Measured value | 26.1 | 27.9 | 28.2 | 29.2 | 30.6 | 32.2 |
| Theoretical value | 25.2 | 27.1 | 29.1 | 27.9 | 29.9 | 32.9 | |
| Relative error (%) | 3.4 | 3.0 | −2.9 | 4.6 | 2.2 | −2.0 | |
| OD + CD | Measured value | 32.1 | 34.1 | 35.4 | 36.3 | 38.0 | 42.6 |
| Theoretical value | 30.8 | 32.7 | 34.5 | 36.4 | 38.5 | 42.4 | |
| Relative error (%) | 4.1 | 4.3 | 2.7 | −0.4 | −1.2 | 0.4 | |
| ID-1 + CD | Measured value | 30.3 | 31.6 | 32.8 | 32.1 | 33.4 | 37.4 |
| Theoretical value | 29.6 | 31.5 | 33.0 | 32.4 | 34.3 | 36.8 | |
| Relative error (%) | 2.2 | 0.4 | −0.5 | −0.8 | −2.7 | 1.7 | |
| ID-2 + CD | Measured value | — | — | — | 38.8 | 40.4 | 42.3 |
| Theoretical value | — | — | — | 37.6 | 39.3 | 41.6 | |
| Relative error (%) | — | — | — | 3.1 | 2.7 | 1.7 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, X.; Wang, S.; Yang, P.; Tao, Y.; Chen, H. Performance Evaluation of Different Combined Drainage Forms on Flooding and Waterlogging Removal. Water 2021, 13, 2968. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13212968
Ren X, Wang S, Yang P, Tao Y, Chen H. Performance Evaluation of Different Combined Drainage Forms on Flooding and Waterlogging Removal. Water. 2021; 13(21):2968. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13212968
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Xiaolei, Shaoli Wang, Peiling Yang, Yuan Tao, and Haorui Chen. 2021. "Performance Evaluation of Different Combined Drainage Forms on Flooding and Waterlogging Removal" Water 13, no. 21: 2968. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13212968
APA StyleRen, X., Wang, S., Yang, P., Tao, Y., & Chen, H. (2021). Performance Evaluation of Different Combined Drainage Forms on Flooding and Waterlogging Removal. Water, 13(21), 2968. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13212968









