Variability of δ2H and δ18O in Soil Water and Its Linkage to Precipitation in an East Asian Monsoon Subtropical Forest Plantation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
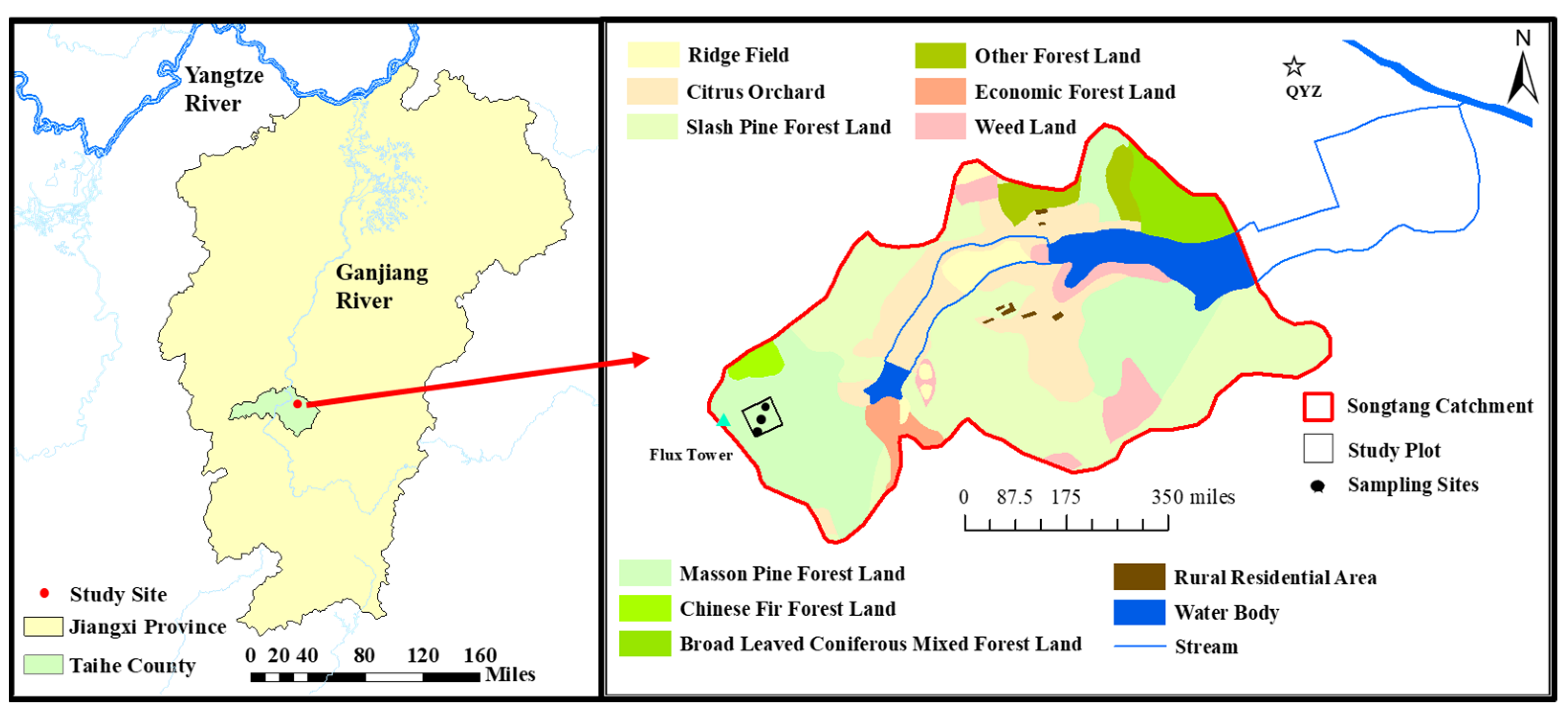
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Sample Collection and Measurements
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Critical Thresholds for Precipitation Recharge of Soil Water
2.3.2. Determining Residence Times of Precipitation in Soil
2.3.3. Calculations of δ2H and δ18O in Soil Water Source
- (1)
- Calculations of Soil Water Evaporation Line
- (2)
- δ2H and δ18O in Soil Water Source
2.3.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
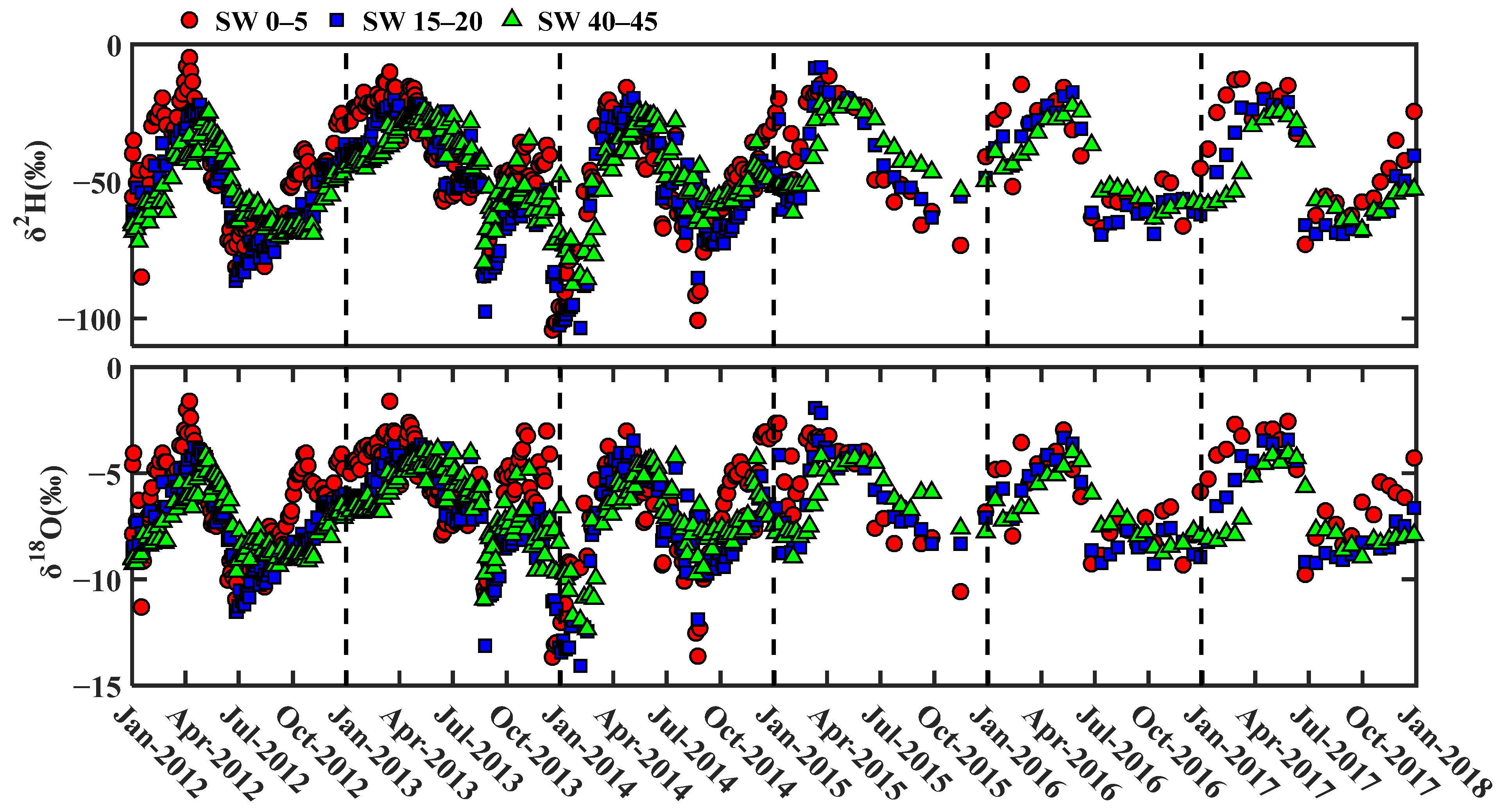
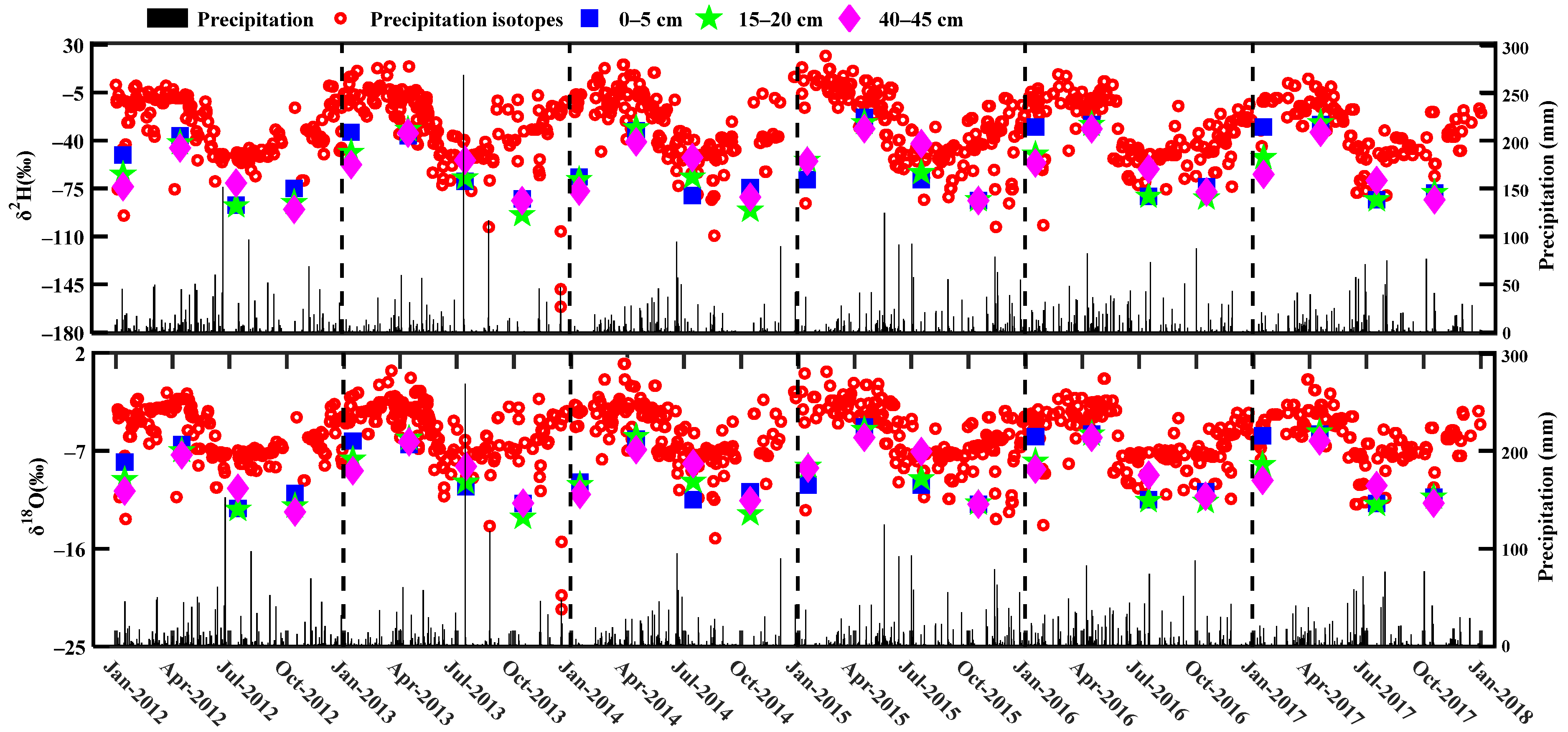
3.1. Seasonal Variability of δ2H and δ18O in Soil Water and Precipitation
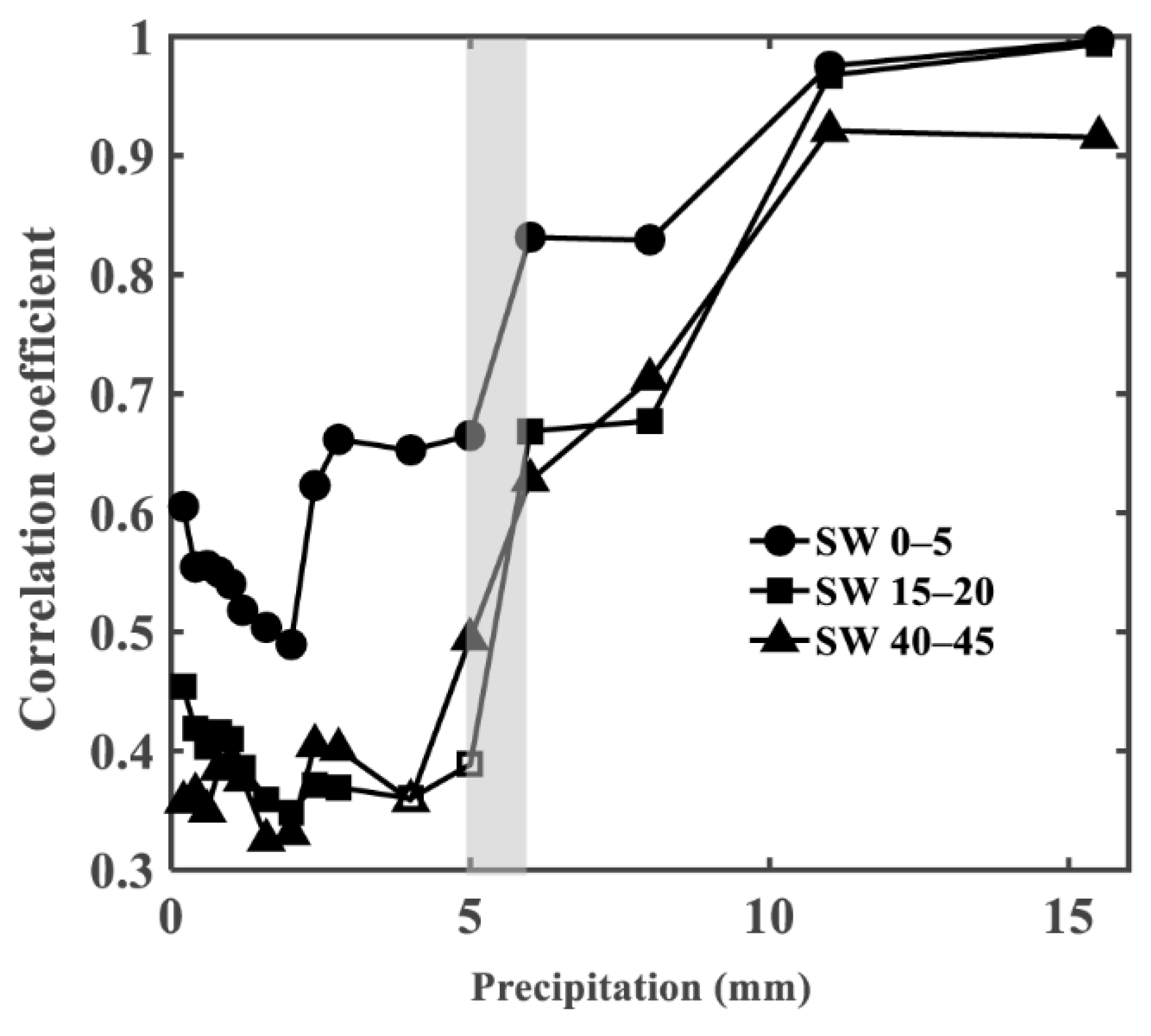
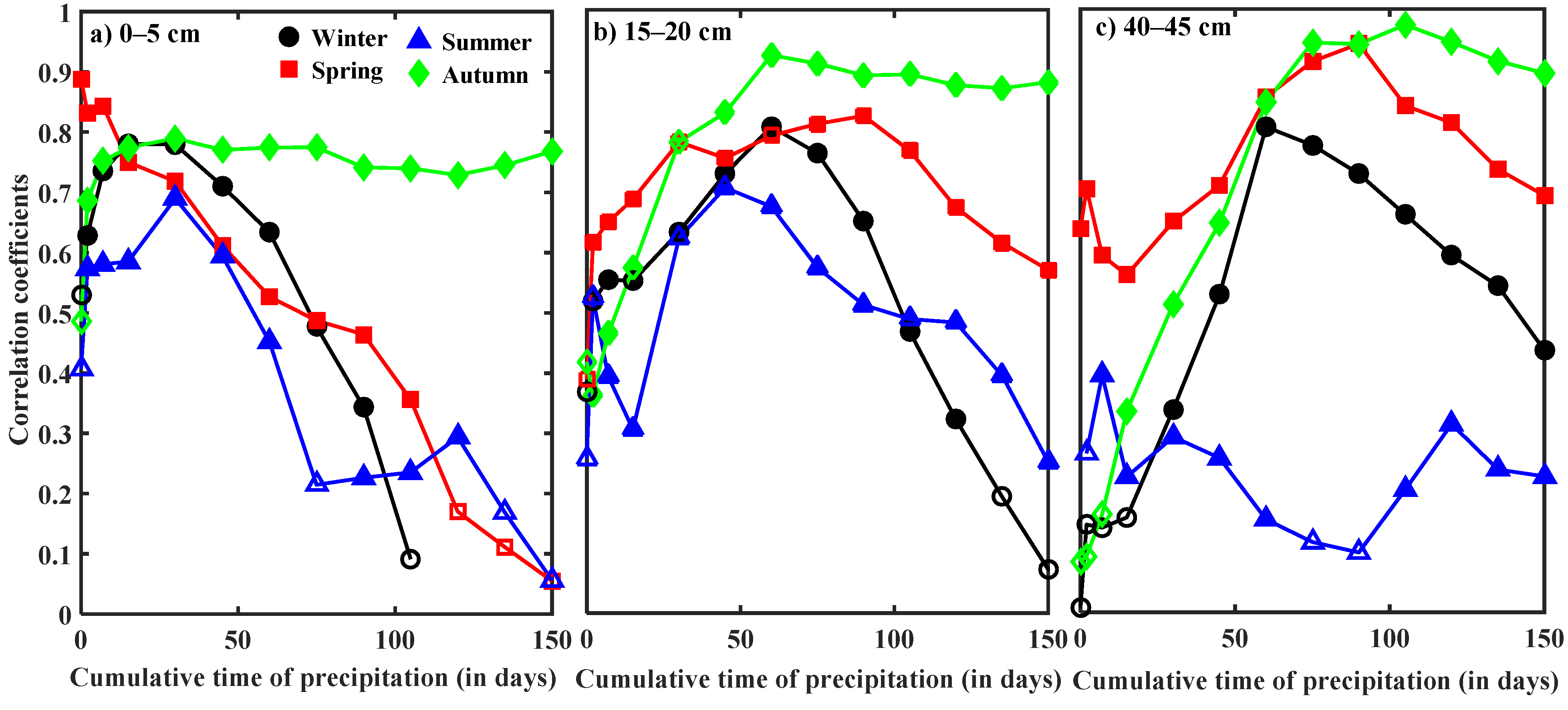
3.2. Critical Thresholds of Precipitation for Infiltration into the Soil Profile
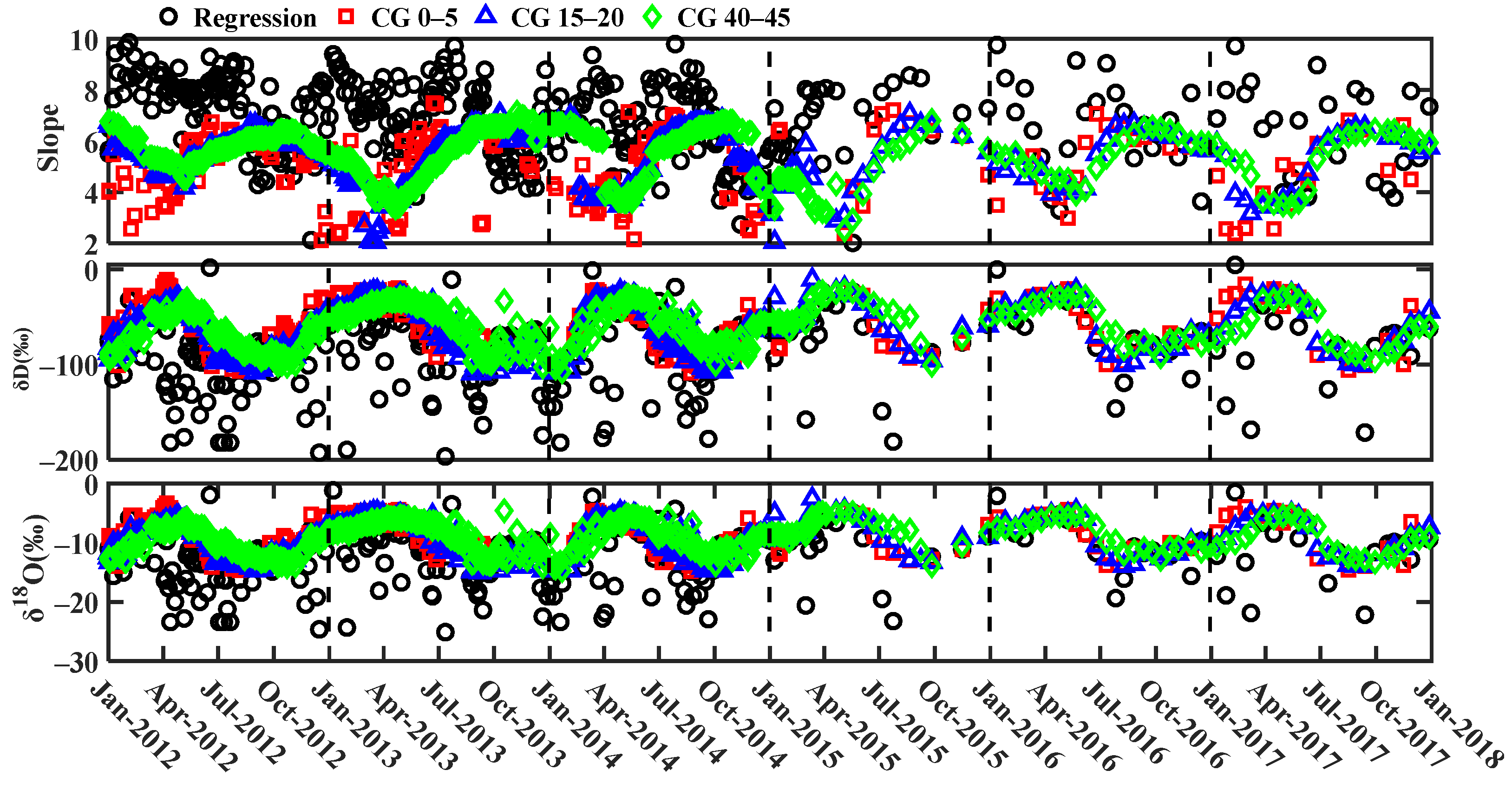
3.3. Seasonal Variability in Residence Times of Precipitation in Soil
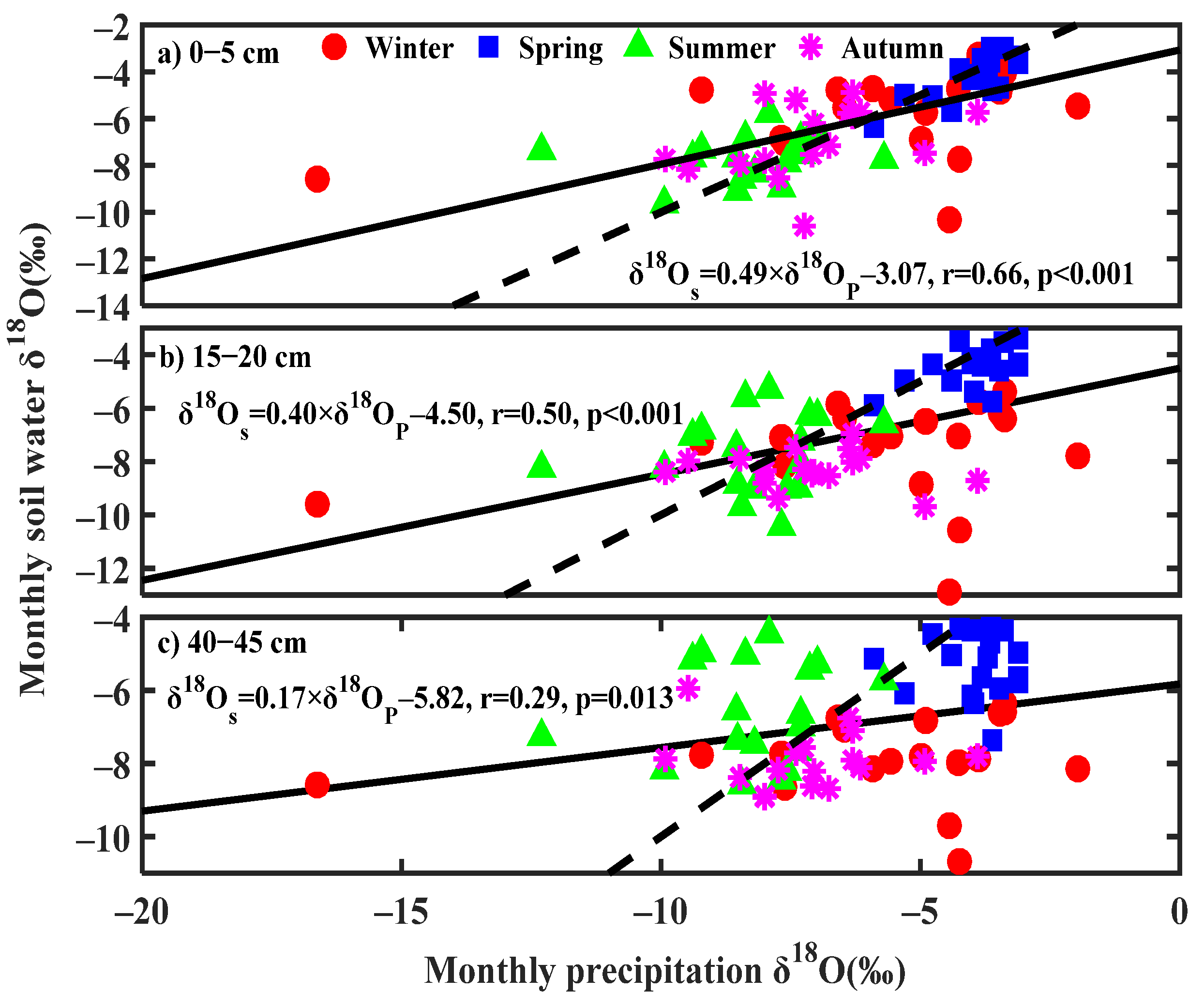
3.4. Seasonal Variability of δ2H and δ18O in Soil Water Source
4. Discussion
4.1. Responses of Soil Water to Rainfall Events
4.2. Influencing Factors of Residence Times of Precipitation in Soil
4.3. Seasonal Origins of Soil Water
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brooks, J.R. Water, bound and mobile. Science 2015, 349, 138–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mello, C.R.; Avila, L.F.; Lin, H.; Terra, M.C.N.S.; Chappell, N.A. Water balance in a neotropical forest catchment of southeastern Brazil. Catena 2019, 173, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColl, K.A.; Alemohammad, S.H.; Akbar, R.; Konings, A.G.; Yueh, S.; Entekhabi, D. The global distribution and dynamics of surface soil moisture. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, M.; Leistert, H.; Gimbel, K.; Weiler, M. Illuminating hydrological processes at the soil-vegetation-atmosphere interface with water stable isotopes. Rev. Geophys. 2016, 54, 674–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellsworth, P.Z.; Williams, D.G. Hydrogen isotope fractionation during water uptake by woody xerophytes. Plant Soil 2007, 291, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, S.; Wang, J.; Song, X.; Wen, X. The relationship of δD and δ18O in surface soil water and its implications for soil evaporation along grass transects of Tibet, Loess, and Inner Mongolia Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2021, 600, 126533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, M.; Tetzlaff, D.; Buttle, J.; Carey, S.K.; McNamara, J.P.; Laudon, H.; Shatilla, N.J.; Soulsby, C. Storage, mixing, and fluxes of water in the critical zone across northern environments inferred by stable isotopes of soil water. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 1720–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; He, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wei, S.; Yun, J.; Yue, X. The response of infiltration depth, evaporation, and soil water replenishment to rainfall in mobile dunes in the Horqin Sandy Land, Northern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 8699–8708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuartas, L.A.; Tomasella, J.; Nobre, A.D.; Hodnett, M.G.; Waterloo, M.J.; Munera, J.C. Interception water-partitioning dynamics for a pristine rainforest in Central Amazonia: Marked differences between normal and dry years. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2007, 145, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.J.; Zhang, X.P.; Luo, Z.D.; Wang, R.; Liu, Z.L.; He, X.G.; Rao, Z.G.; Guan, H.D. Variation of the stable isotopes of water in the soil-plant-atmosphere continuum of a Cinnamomum camphora woodland in the East Asian monsoon region. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, J.R.; Barnard, H.R.; Coulombe, R.; McDonnell, J.J. Ecohydrologic separation of water between trees and streams in a Mediterranean climate. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervé-Fernández, P.; Oyarzún, C.; Brumbt, C.; Huygens, D.; Bodé, S.; Verhoest, N.E.C.; Boeckx, P. Assessing the “two water worlds” hypothesis and water sources for native and exotic evergreen species in south-central Chile. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 4227–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, R.M.; Condon, L.E. Connections between groundwater flow and transpiration partitioning. Science 2016, 353, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprenger, M.; Stumpp, C.; Weiler, M.; Aeschbach, W.; Allen, S.T.; Benettin, P.; Dubbert, M.; Hartmann, A.; Hrachowitz, M.; Kirchner, J.W.; et al. The demographics of water: A review of water ages in the critical zone. Rev. Geophys. 2019, 57, 800–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, N.; Seeger, S.; Weiler, M.; Buchmann, N.; Eugster, W.; Kahmen, A. Employing stable isotopes to determine the residence times of soil water and the temporal origin of water taken up by Fagus sylvatica and Picea abies in a temperate forest. New Phytol. 2018, 219, 1300–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.T.; Kirchner, J.W.; Braun, S.; Siegwolf, R.T.W.; Goldsmith, G.R. Seasonal origins of soil water used by trees. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 1199–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, B.D.; Marttila, H.; Graham, S.L.; Evison, R.; Srinivasan, M.S. Water sources for woody shrubs on hillslopes: An investigation using isotopic and sapflow methods. Ecohydrology 2018, 11, e1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evaristo, J.; Jasechko, S.; McDonnell, J.J. Global separation of plant transpiration from groundwater and streamflow. Nature 2015, 525, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benettin, P.; Volkmann, T.H.M.; von Freyberg, J.; Frentress, J.; Penna, D.; Dawson, T.E.; Kirchner, J. Effects of climatic seasonality on the isotopic composition of evaporating soil waters. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sc. 2018, 22, 2881–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.; Evaristo, J.; Li, Z. Recharge mechanisms of deep soil water revealed by water isotopes in deep loess deposits. Geoderma 2020, 369, 114321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Chen, Z.; Piao, S.; Peng, C.; Ciais, P.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Zhu, X. High carbon dioxide uptake by subtropical forest ecosystems in the East Asian monsoon region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4910–4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Lyu, S.; Wen, X. Limitation of soil moisture on the response of transpiration to vapor pressure deficit in a subtropical coniferous plantation subjected to seasonal drought. J. Hydrol. 2020, 591, 125301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.K.; Wen, X.F.; Sun, X.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, H.M. The limiting effect of deep soil water on evapotranspiration of a subtropical coniferous plantation subjected to seasonal drought. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 31, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wen, X.; Sun, X. Seasonal variations in depth of water uptake for a subtropical coniferous plantation subjected to drought in an East Asian monsoon region. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 201, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Feng, Z.; Wang, H.; Dai, X.; Fu, X. Deep soil water extraction helps to drought avoidance but shallow soil water uptake during dry season controls the inter-annual variation in tree growth in four subtropical plantations. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 234, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.F.; Yu, G.R.; Sun, X.M.; Li, Q.K.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhang, L.M.; Ren, C.Y.; Fu, Y.L.; Li, Z.Q. Soil moisture effect on the temperature dependence of ecosystem respiration in a subtropical Pinus plantation of southeastern China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2006, 137, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.G.; Patrickson, S.J.; Ehleringer, J.R. Water extraction times for plant and soil materials used in stable isotope analysis. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 1317–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Lee, X.; Sun, X.; Wang, J.; Tang, Y.; Li, S.; Yu, G. Intercomparison of four commercial analyzers for water vapor isotope measurement. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2012, 29, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nelson, D.B.; Basler, D.; Kahmen, A. Precipitation isotope time series predictions from machine learning applied in Europe. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2024107118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, G.B. The relationship between O-18 and deuterium in water in sand columns undergoing evaporation. J. Hydrol. 1982, 55, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.J.; Birks, S.J.; Edwards, T.W.D. Global prediction of δA and δ2H-δ18O evaporation slopes for lakes and soil water accounting for seasonality. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 2008, 22, GB2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horita, J.; Wesolowski, D.J. Liquid-vapor fractionation of oxygen and hydrogen isotopes of water from the freezing to the critical-temperature. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 3425–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gat, J.R. Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in the hydrologic cycle. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1996, 24, 225–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, J.; Hughes, C.E.; Lykoudis, S. Alternative least squares methods for determining the meteoric water line, demonstrated using GNIP data. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 2331–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.M.; Jia, G.D.; Liu, Z.Q.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Yu, X.X.; Hao, P.Q. Field studies on the influence of rainfall intensity, vegetation cover and slope length on soil moisture infiltration on typical watersheds of the Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 4904–4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.D.; Guan, H.D.; Zhang, X.P.; Xu, X.; Dai, J.J.; Hua, M.Q. Examination of the ecohydrological separation hypothesis in a humid subtropical area: Comparison of three methods. J. Hydrol. 2019, 571, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, S.P.; Noone, D.; Bowen, G. Hydrologic connectivity constrains partitioning of global terrestrial water fluxes. Science 2015, 349, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radolinski, J.; Pangle, L.; Klaus, J.; Stewart, R.D. Testing the ‘two water worlds’ hypothesis under variable preferential flow conditions. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, e14252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knighton, J.; Souter-Kline, V.; Volkman, T.; Troch, P.A.; Kim, M.; Harman, C.; Morris, C.; Buchanan, B.; Walter, M.T. Seasonal and topographic variations in ecohydrological separation within a small, temperate, snow-influenced catchmet. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 6417–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, S.D.; Song, X.W.; Wen, X.F. Ecohydrologic separation of the mixing process between precipitation and soil water: A review. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 1797–1806. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, J.; Zheng, H.; Wang, P.F.; Liao, X.L.; Wang, C.; Hou, J.; Ao, Y.H.; Shen, M.M.; Liu, J.J.; Li, K. Assessing the ecohydrological separation hypothesis and seasonal variations in water use by Ginkgo biloba L. in a subtropical riparian area. J. Hydrol. 2017, 553, 486–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilusz, D.C.; Harman, C.J.; Ball, W.P. Sensitivity of catchment transit times to rainfall variability under present and future climates. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 10231–10256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evaristo, J.; Kim, M.; van Haren, J.; Pangle, L.A.; Harman, C.J.; Troch, P.A.; McDonnell, J.J. Characterizing the fluxes and age distribution of soil water, plant water and deep percolation in a model tropical ecosystem. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 3307–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockinger, M.P.; Luecke, A.; McDonnell, J.J.; Diekkrueger, B.; Vereecken, H.; Bogena, H.R. Interception effects on stable isotope driven streamwater transit time estimates. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 5299–5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetzlaff, D.; Buttle, J.; Carey, S.K.; Kohn, M.J.; Laudon, H.; McNamara, J.P.; Smith, A.; Sprenger, M.; Soulsby, C. Stable isotopes of water reveal differences in plant—Soil water relationships across northern environments. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, e14023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Guo, L.; Lin, H.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Chu, G.; Zhang, J. Soil moisture response to rainfall on the Chinese Loess Plateau after a long-term vegetation rehabilitation. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 1738–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Climate | Month | P (mm) | Ta (°C) | RH (%) | Pa (hPa) | WS (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 72.0 | 6.4 | 86.8 | 1013.1 | 2.5 | |
| 2 | 98.1 | 8.8 | 87.0 | 1010.3 | 3.0 | |
| 3 | 150.9 | 12.3 | 86.3 | 1007.4 | 2.9 | |
| 4 | 162.3 | 18.5 | 85.1 | 1003.1 | 3.0 | |
| 5 | 177.5 | 23.0 | 84.2 | 999.2 | 2.8 | |
| 6 | 217.0 | 26.3 | 84.0 | 995.5 | 2.7 | |
| 7 | 117.9 | 28.7 | 77.4 | 994.9 | 3.4 | |
| 8 | 138.9 | 28.0 | 81.5 | 995.6 | 2.6 | |
| 9 | 88.0 | 24.6 | 83.9 | 1000.7 | 2.5 | |
| 10 | 60.5 | 19.3 | 82.7 | 1006.8 | 2.4 | |
| 11 | 73.2 | 13.5 | 81.7 | 1010.0 | 2.4 | |
| 12 | 51.0 | 7.8 | 83.8 | 1013.2 | 2.3 | |
| Soil | pH | BD (g/cm3) | Sand (%) | Silt (%) | Clay (%) | Ts (°C) |
| 4.04–6.25 | 1.57 | 17 | 68 | 15 | 7.2–26.0 | |
| Vegetation | TD (stems/ha) | TB (t/ha) | LAImax (m2/m2) | |||
| 1463 | 106 | 5.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyu, S. Variability of δ2H and δ18O in Soil Water and Its Linkage to Precipitation in an East Asian Monsoon Subtropical Forest Plantation. Water 2021, 13, 2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202930
Lyu S. Variability of δ2H and δ18O in Soil Water and Its Linkage to Precipitation in an East Asian Monsoon Subtropical Forest Plantation. Water. 2021; 13(20):2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202930
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyu, Sidan. 2021. "Variability of δ2H and δ18O in Soil Water and Its Linkage to Precipitation in an East Asian Monsoon Subtropical Forest Plantation" Water 13, no. 20: 2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202930
APA StyleLyu, S. (2021). Variability of δ2H and δ18O in Soil Water and Its Linkage to Precipitation in an East Asian Monsoon Subtropical Forest Plantation. Water, 13(20), 2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202930






