A Characterization of the Hydrochemistry and Main Controlling Factors of Lakes in the Badain Jaran Desert, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
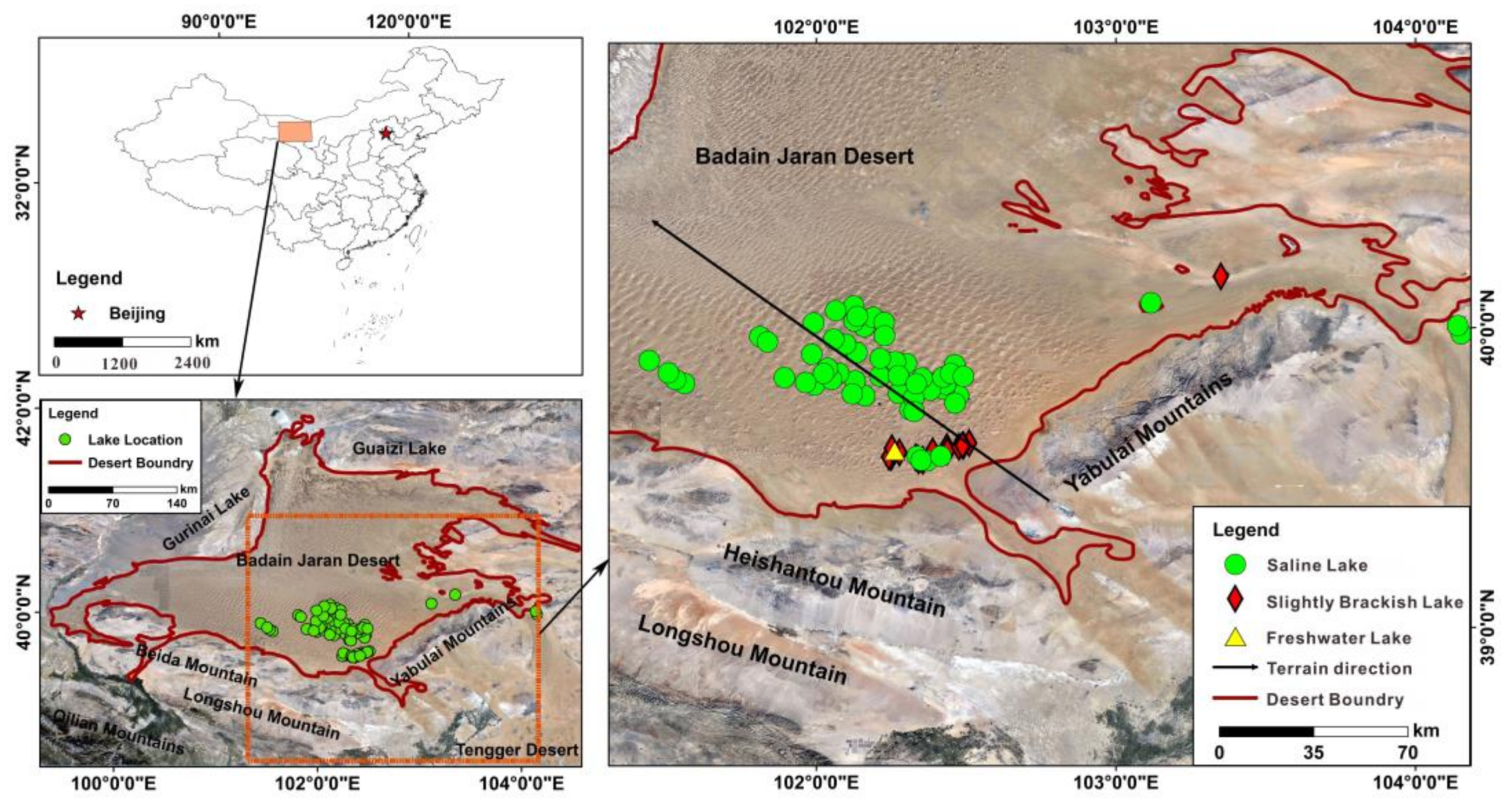
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Data Processing Method
3. Results
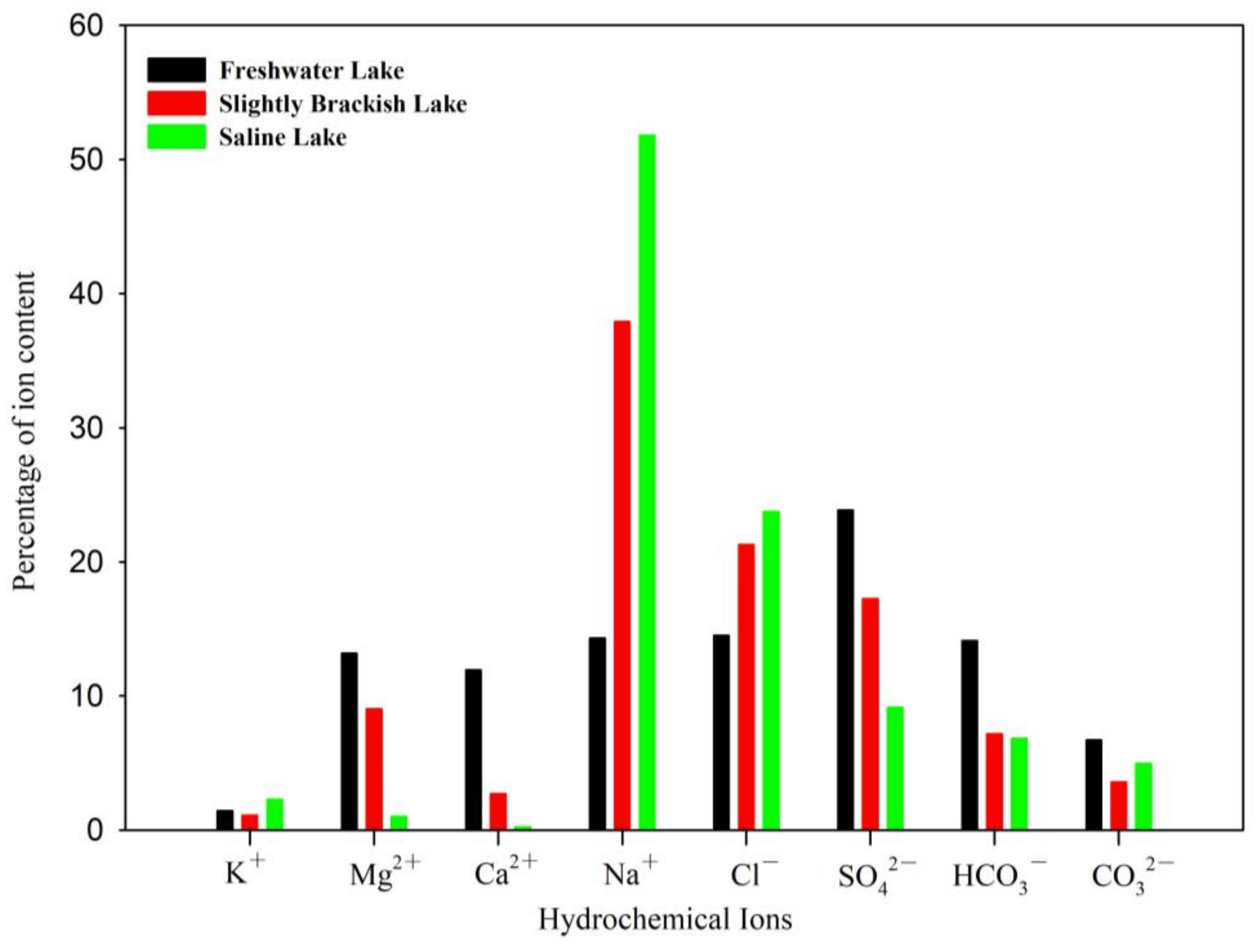
3.1. Hydrochemical Characteristics of Lakes in the Badain Jaran Desert
3.2. Hydrochemical Compositions and Types in the Badain Jaran Desert Lakes
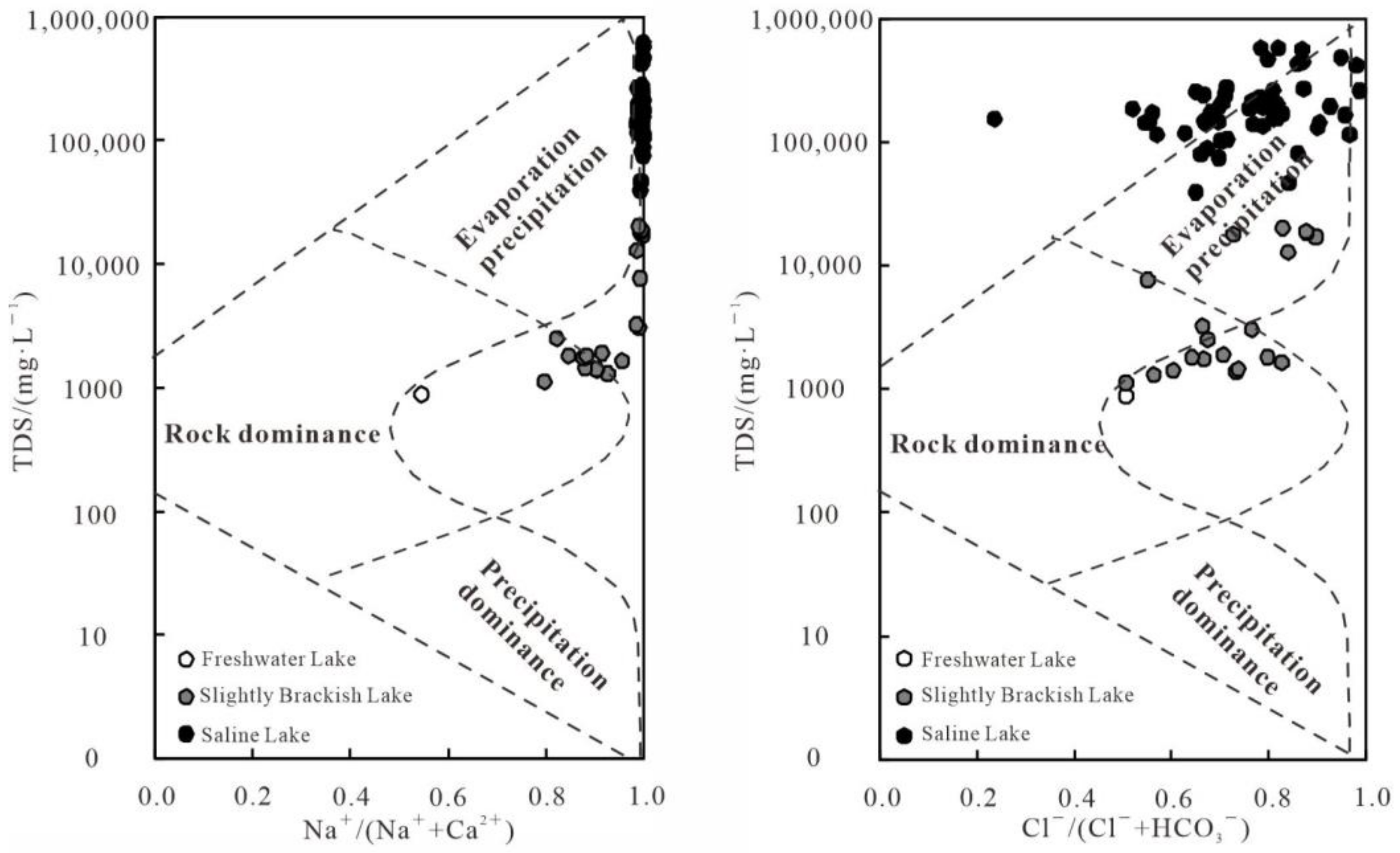
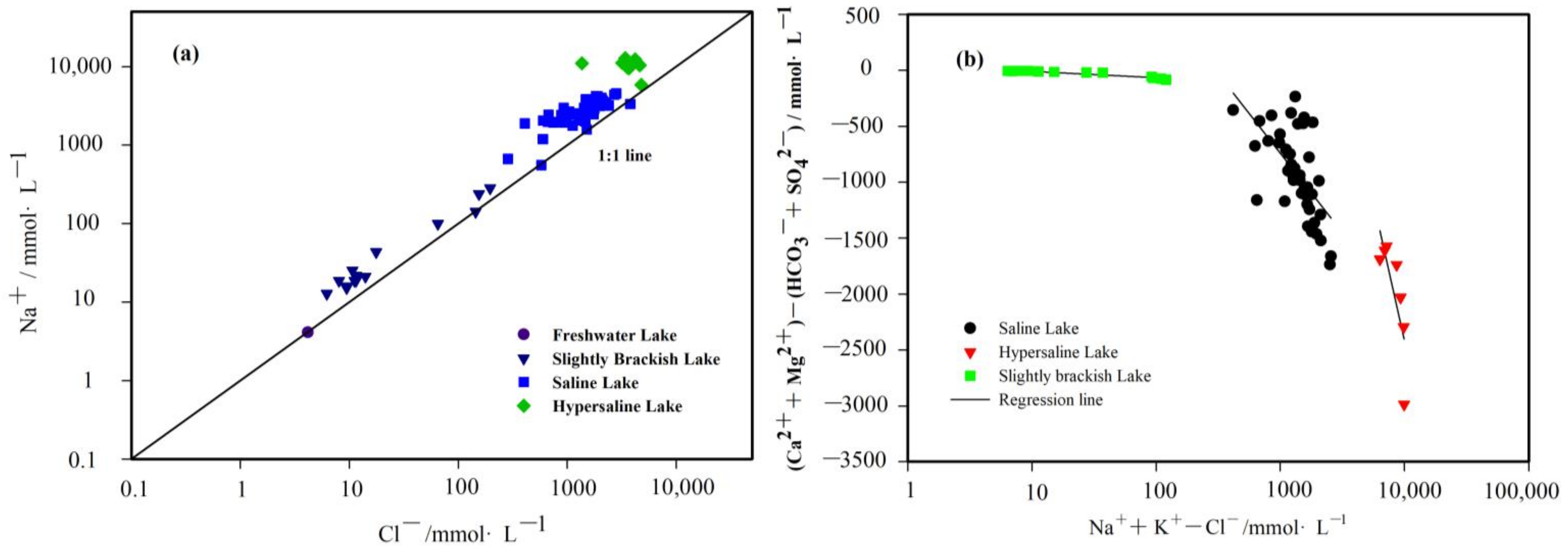
3.3. Mechanisms Controlling Hydrochemical Component
3.3.1. Rock Weathering, Evaporation, and Soil-Leaching
3.3.2. Ion Exchange
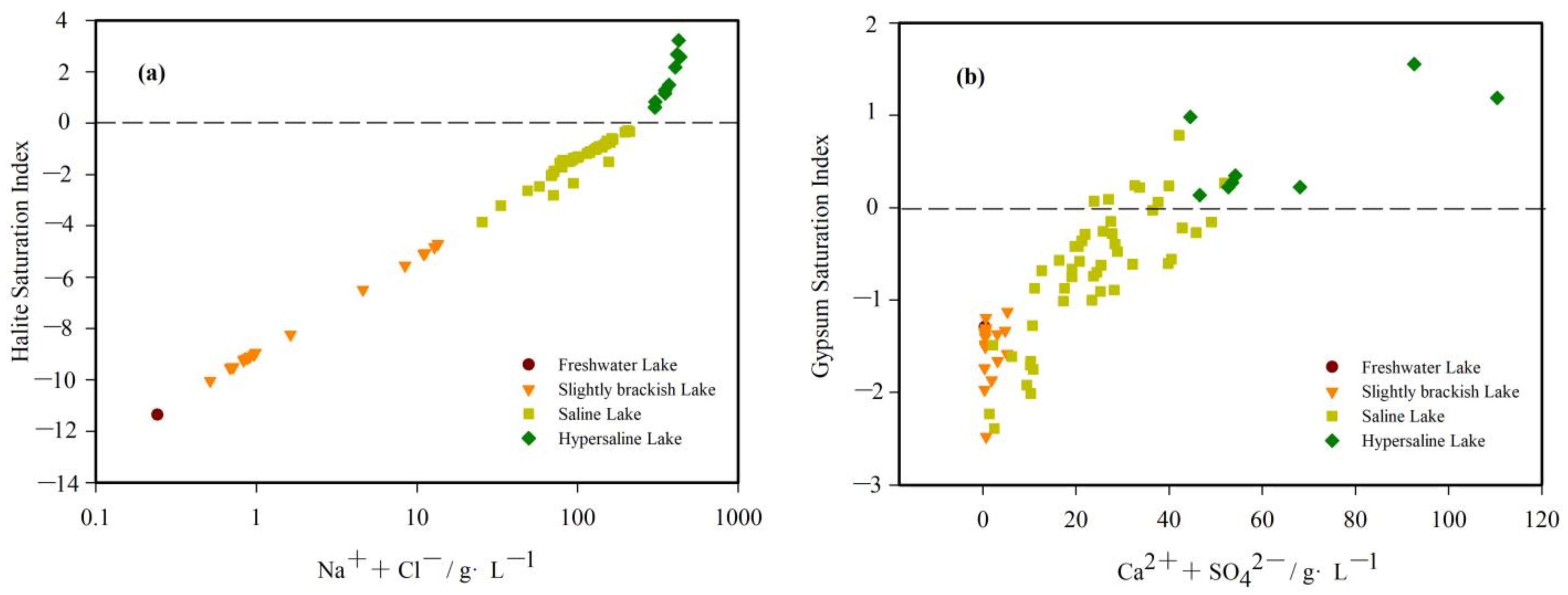
3.3.3. Precipitation and Dissolution
4. Discussion
4.1. Variation in Hydrochemical Composition between Lakes of Different Types
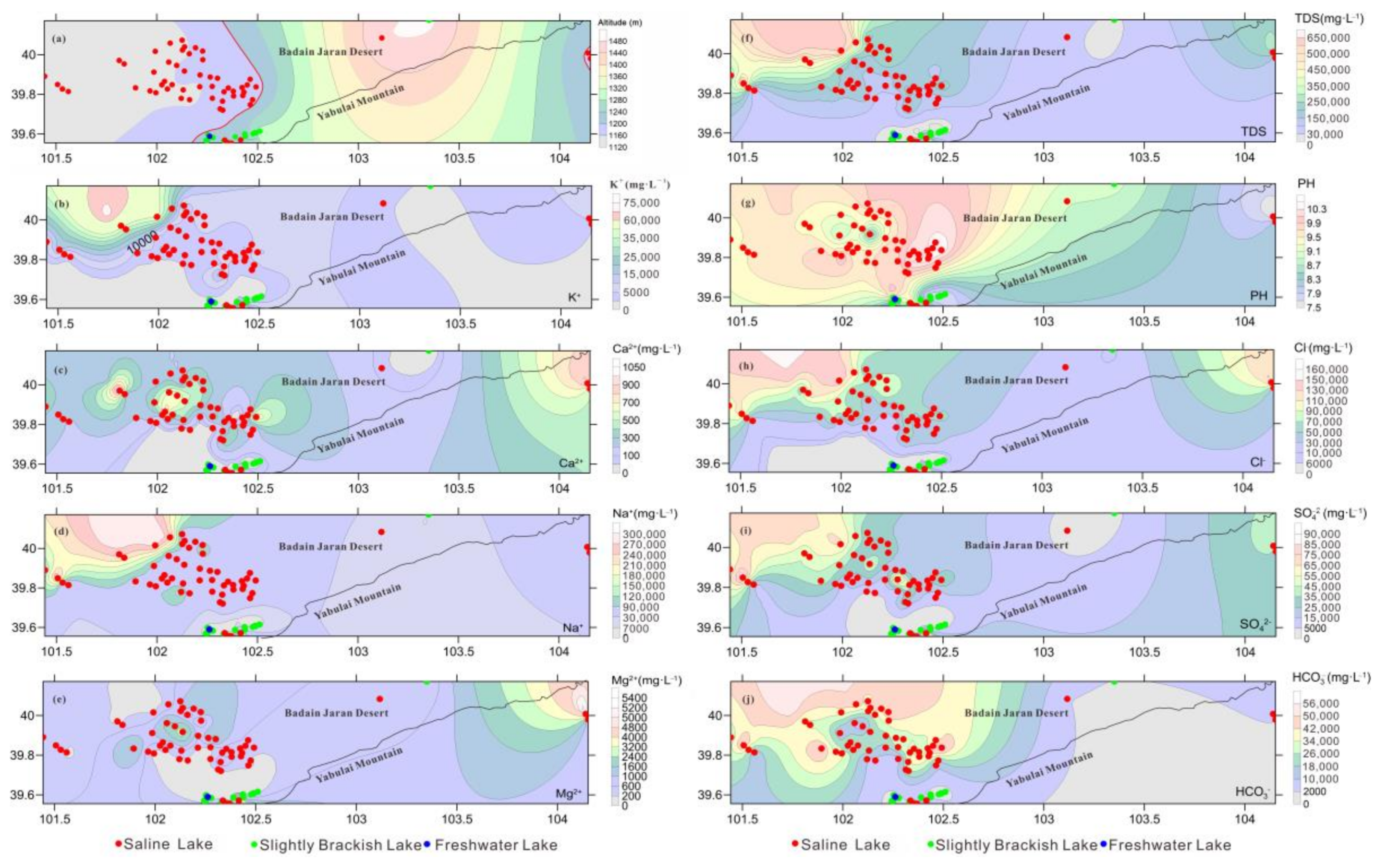
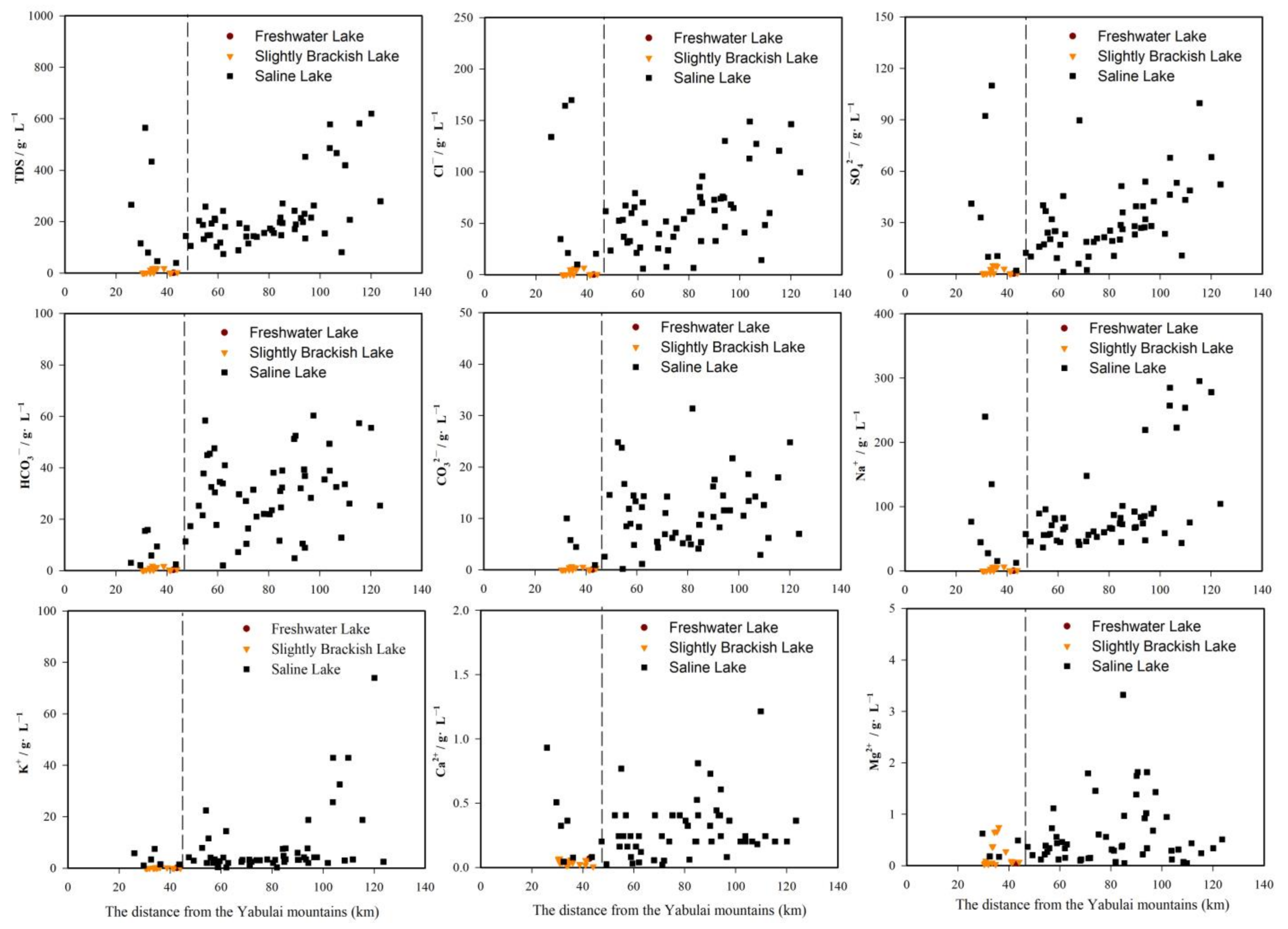
4.2. Evolution of the Spatial Distribution of Hydrochemical Parameters among Different Types of Lakes
4.3. Analysis of Mechanisms Contributing to the Hydrochemistry of Different Types of Lakes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, Z.; Zhang, L. Hydrochemistry of lakes in Xinjiang. Arid Zone Res. 1992, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, N.; Wang, N.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhu, J.; Dong, C. Analysis on Climate Change in the Northern and Southern Marginal Zones of the Badain Jaran Desert during the Period 1960–2009. Arid Zone Res. 2011, 28, 243–250. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, N.; Wang, N.; Zhu, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, H.; Dong, C. Climate Change around the Badain Jaran Desert in Recent 50 Years. J. Desert Res. 2011, 31, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar]
- Gulbostan, T.; Pang, Z.; Shang, Y. The Source of Lake Water Supply from the Comparison of Isotopic and Hydrochemical in Desert Area: Taking Mukainao Lake in Ordos Basin as an Example. Xinjiang Geol. 2020, 38, 546–551. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Dou, H.; Chen, K.; Wang, X.; Jiang, J. A General Survey of Lakes in China. Lakes in China, 1st ed.; Science Press: Beijing China, 1998; Volume 6, pp. 320–347. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, N.; Li, G.; Li, Z.; Dong, C.; Lu, J. Spatial distribution of lakes in Badain Jaran Desert. J. Lake Sci. 2010, 22, 774–782. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Edmunds, W.M.; Lu, Z.; Ma, J. Geochemistry of sediment moisture in the Badain Jaran desert: Implications of recent environmental changes and water-rock interaction. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 63, 235–247. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.S.; Li, L.; Wang, J.Y.; Barry, D.; Sheng, X.F.; Zu Gu, W.; Zhao, X.; Chen, L. Groundwater maintains dune landscape. Nature 2004, 432, 459–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Fan, Z.; Wang, J.; Gu, W.; Zhao, X. Isotope Methods for Studying the Replenishment of the Lakes and Downstream Groundwater in the Badain Jaran Desert. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2003, 24, 497–504. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Chen, F.; Zhao, H. Vadose geochemical records of groundwater recharge and climate change in the Badain Jaran Desert since 1000 years. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2004, 49, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Huang, T.; Ding, Z.; Edmunds, W. Environmental Isotopes as the Indicators of the Groundwater Recharge in the South Badain Jaran Desert. Adv. Earth Sci. 2007, 22, 922–930. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Huang, X.; Zhou, W. Methods of Lake Ecosystem Observation; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2005; ISBN 978780163745. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Qian, G.; Lv, P.; Hu, G. Investigation of the sand sea with the tallest dunes on Earth: China’s Badain Jaran Sand Sea. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2013, 120, 20–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Yang, G.; Duan, H.; Jiang, J.; Wang, S.; Feng, X.; Li, A.; Kong, F.; Xue, B.; Wu, J.; et al. The number, area and spatial distribu-tion of lakes in China. Sci. Sin. Terrae 2011, 41, 394–410. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, N.; Ma, N.; Dong, C.; Chen, L.; Shen, S. Lakes Area change in Badain Jaran Desert Hinterland and Its Influence Factors during the Recent 40 Years. J. Desert Res. 2012, 32, 1743–1750. [Google Scholar]
- Banda, J.F.; Lu, Y.; Hao, C.; Pei, L.; Du, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, P.; Dong, H. The Effects of Salinity and pH on Microbial Commu-nity Diversity and Distribution Pattern in the Brines of Soda Lakes in Badain Jaran Desert, China. Geomicrobiol. J. 2020, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Gao, Q.; Zou, X.; Li, B.; Yan, C. Climate change in southern Margin of Badain Jaran Desert since late Pleistocene. Chinese Sci. Bull. 1995, 40, 1214–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Nie, Z.; Jiang, G.; Liu, M.; He, P.; Tong, L.; Wang, J. Water Volume Change of Lakes in the Badain Jaran Desert and Its Causes Based on GF Satellite Remote Sensing Date. Yellow River 2020, 42, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Ma, N.; Dong, J.; Zhu, B.; Xu, B.; Ma, Z.; Liu, J. Recharge to the Inter-Dune Lakes and Holocene Climatic Changes in the Badain Jaran Desert, Western China. Quat. Res. 2010, 73, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liang, A.; Zhang, C.; Dong, Z. Gobi deposits play a significant role as sand sources for dunes in the Badain Jaran Desert, Northwest China. CATENA 2021, 206, 105530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Williams, M.A. The ion chemistry of lakes and late Holocene desiccation in the Badain Jaran Desert, Inner Mongolia, China. CATENA 2003, 51, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X. Water chemistry of the lakes in the Badain Jaran Desert and their holocene evolutions. Quat. Sci. 2002, 2, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, K.; Wang, N.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Bi, Z. Holocene vegetation history and environmental changes inferred from pollen records of a groundwater recharge lake, Badain Jaran Desert, northwestern China. PalaGeogr. Palae-Oclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2021, 577, 110538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, J.B.; Edmunds, W.M.; Darling, W.G.; Ma, J.; Pang, Z.; Young, A.A. Conceptual model of recharge to southeastern Badain Jaran Desert groundwater and lakes from environmental tracers. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 3519–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, N.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Lu, Y.; Lü, X.; Chang, J. Hydrochemical characteristics and recharge sources of Lake Nuoertu in the Badain Jaran Desert. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Lu, H.; Ma, Z. Research on the recharge of the lakes in the Badain Jaran Desert: Simulation study in the Sumu Jaran Lakes area. J. Lake Sci. 2017, 29, 467–479. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, J.; Joseph, S.; Thrivikramji, K. Hydrochemical variations of a tropical mountain river system in a rain shadow region of the southern Western Ghats, Kerala, India. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 63, 456–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Liu, C. Hydrogeochemistry of Wujiang River water in Guizhou Province, China. Chin. J. Geochem. 2001, 20, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, E. Hydrochemistry of inland rivers in the north Tibetan Plateau: Constrains and weathering rate estimation. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 461–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.-L.; Li, X.-Y.; Wei, X.-H. Isotope and hydrochemistry reveal evolutionary processes of lake water in Qinghai Lake. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Sun, D.; Chen, F.; Bloemendal, J.; Guo, F.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, X. Formation and evolution of the Badain Jaran Desert, North China, as revealed by a drill core from the desert center and by geological survey. PalaGeogr. Palae-Oclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2015, 426, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T. Formation and Evolution in the Badan Jaran Desert. J. Desert Res. 1990, 10, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Jin, X.; Hou, L.; Qian, R.; Wang, L. Interactions between groundwater and lakes in the Badan Jaran Desert. Earth Sci. Front. 2014, 21, 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Lu, H.; Gong, Y.; Wan, L. The macro- characteristics of groundwater flow in the Badain Jaran desert. J. Desert Res. 2015, 35, 774–782. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, X. The Surface Water. Principles of Hydrology, 1st ed.; China Water & Power Press: Beijing, China, 2004; ISBN 9787508421643. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, T.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z. Water Chemistry of the Lakes and Groundwater in the Badain Jaran Desert. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2011, 66, 662–670. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, Y. Investigating the mysteries of grounds in the Badain Jaran Desert, China. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 1639–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Wang, N.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Chen, L.; Ma, N. New obervational and experimental evidence for the re-charge mechanism of the lake group in the Alxa Desert, North-central China. J. Arid Environ. 2016, 124, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Lin, Z.; Niu, F.; Luo, J.; Liu, M.; Yin, G. Hydrochemistry and controlling mechanism of lakes in permafrost regions along the Qinghai-Tibet Engineering Corridor, China. Geomorphology 2017, 297, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Z.; Ma, J. Evolution of groundwater geochemistry in the Minqin Basin: Taking chloride as an indica-tor of groundwater recharge. Resour. Sci. 2011, 33, 416–421. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Ma, J.; Zhang, P.; Tian, L.; Zhu, G.; Edmunds, W.M.; Zhang, Q. Groundwater recharge environments and hydrogeo-chemical evolution in the Jiuquan Basin, Northwest China. Appl. Geochem. 2012, 27, 866–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Yang, X. Characteristics of hydrochemistry and environmental isotopes in the Badain Jaran Desert and its southeast-ern margin and their hydrological significance. Quat. Sci. 2008, 28, 702–711. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, X.; Wang, X. Research on Geomorphologic Evolution of East and West Badain Lake and the Impact on Water Body Features. Geoscience 2017, 31, 406–414. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, K.; Rao, W.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, F.; Wang, S. Strontium isotopic and hydrochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater and lake water in the Badain Jaran Desert, North China. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2021, 57, 516–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Enmunds, W. Groundwater and lake evolution in the Badain Jaran Desert ecosystem, Inner Mongolia. Hydrogeol. J. 2006, 14, 1231–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X. Chemistry and late Quaternary evolution of ground and surface waters in the area of Yabulai Mountains, western Inner Mongolia, China. CATENA 2006, 66, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, J. The lakes in the SE part of Badain Jaran Shamo, their limnology and geochemistry. Geowissenschaften 1996, 14, 275–278. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, R.; Wang, M.; Wang, S.; Song, X. Water transfer imposes hydrochemical impacts on groundwater by altering the in-teraction of groundwater and surface water. J. Hydrol. 2020, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Freshwater Lake | Slightly Brackish Lake | Saline Lakes | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | 1 | 20 | 59 | ||||||||||||
| Value | Min | Max | Mean | SD | CV | Kurtosis | Skewness | Min | Max | Mean | SD | CV | Kurtosis | Skewness | |
| g L−1 | g L−1 | g L−1 | g L−1 | g L−1 | g L−1 | ||||||||||
| PH | 7.93 | 7.65 | 10.1 | 8.47 | 0.75 | 0.09 | −0.76 | 0.54 | 7.54 | 10.52 | 9.60 | 0.58 | 0.06 | 2.63 | −1.21 |
| TDS | 0.88 | 1.13 | 20.21 | 6.76 | 7.57 | 1.12 | −0.91 | 0.98 | 39.44 | 619.74 | 221.54 | 137.96 | 0.62 | 1.68 | 1.52 |
| Na+ | 0.09 | 0.30 | 6.53 | 2.08 | 2.45 | 1.17 | −0.59 | 1.10 | 12.79 | 295.48 | 93.01 | 70.24 | 0.76 | 2.19 | 1.79 |
| K+ | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.31 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 1.18 | −0.09 | 1.29 | 0.25 | 73.97 | 8.75 | 14.04 | 1.61 | 9.26 | 2.95 |
| Mg2+ | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.75 | 0.22 | 0.25 | 1.15 | 0.08 | 1.24 | 0.05 | 7.13 | 0.81 | 1.22 | 1.51 | 14.77 | 3.57 |
| Ca2+ | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.47 | −1.18 | −0.04 | 0.02 | 1.21 | 0.30 | 0.23 | 0.78 | 3.75 | 1.68 |
| Cl− | 0.15 | 0.22 | 6.94 | 2.10 | 2.55 | 1.21 | −0.90 | 0.99 | 6.07 | 169.83 | 62.58 | 40.16 | 0.64 | 0.47 | 0.96 |
| SO42− | 0.33 | 0.31 | 5.21 | 1.67 | 1.84 | 1.10 | −0.25 | 1.17 | 1.33 | 110.05 | 32.52 | 23.67 | 0.73 | 2.29 | 1.46 |
| HCO3− | 0.25 | 0.15 | 1.86 | 0.66 | 0.56 | 0.85 | −0.21 | 1.10 | 1.97 | 60.33 | 27.69 | 15.69 | 0.57 | −0.72 | 0.19 |
| CO32− | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.67 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.99 | −1.14 | 0.67 | 0.21 | 31.37 | 10.82 | 6.64 | 0.61 | 0.81 | 0.87 |
| Anhydrite | Aragonite | Calcite | Dolomite | Epsomite | Gypsum | Magnesite | Mirabilite | Thenardite | Halite | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean value | −0.76 | 2.65 | 2.80 | 5.86 | −2.92 | −0.72 | 3.03 | −1.35 | −1.41 | −2.53 |
| Minimum value | −2.68 | −0.35 | −0.20 | −0.38 | −9.18 | −2.48 | −0.37 | −6.61 | −7.50 | −11.36 |
| Maximum value | 2.36 | 6.52 | 6.67 | 13.53 | −1.03 | 1.55 | 6.86 | 0.93 | 5.30 | 3.22 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, B.; Si, J.; Xi, H.; Qin, J. A Characterization of the Hydrochemistry and Main Controlling Factors of Lakes in the Badain Jaran Desert, China. Water 2021, 13, 2931. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202931
Jia B, Si J, Xi H, Qin J. A Characterization of the Hydrochemistry and Main Controlling Factors of Lakes in the Badain Jaran Desert, China. Water. 2021; 13(20):2931. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202931
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Bing, Jianhua Si, Haiyang Xi, and Jie Qin. 2021. "A Characterization of the Hydrochemistry and Main Controlling Factors of Lakes in the Badain Jaran Desert, China" Water 13, no. 20: 2931. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202931
APA StyleJia, B., Si, J., Xi, H., & Qin, J. (2021). A Characterization of the Hydrochemistry and Main Controlling Factors of Lakes in the Badain Jaran Desert, China. Water, 13(20), 2931. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202931







