Integrated Treatment at Laboratory Scale of a Mature Landfill Leachate via Active Filtration and Anaerobic Digestion: Preliminary Results
Abstract
:Highlights
- The sustainable management of landfill leachate (LL) is particularly problematic.
- Mature LL contains NH3-N and humic substances (HSs) that are potentially valuable.
- Mature LL also contains toxic substances such as heavy metals (HMs).
- Filtration on ZVI/GAC and ZVI/lapillus mixtures has been tested for removing HM.
- Pre-treated LL is used for integration of NH3-N in anaerobic digestion of cellulose.
1. Introduction
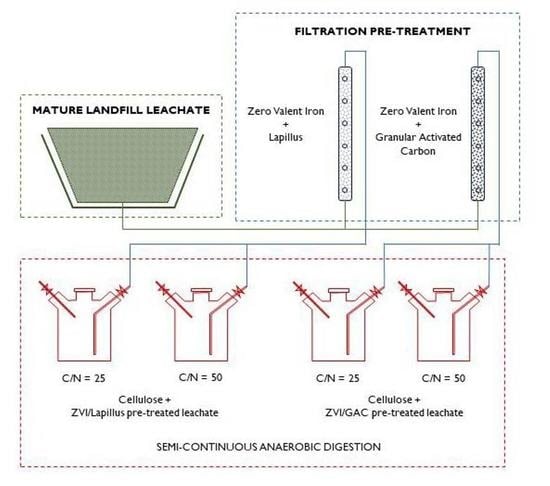
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthetic MLL
2.2. Pre-Treatment Tests
2.3. Semicontinuous AD Tests
3. Results and Discussion
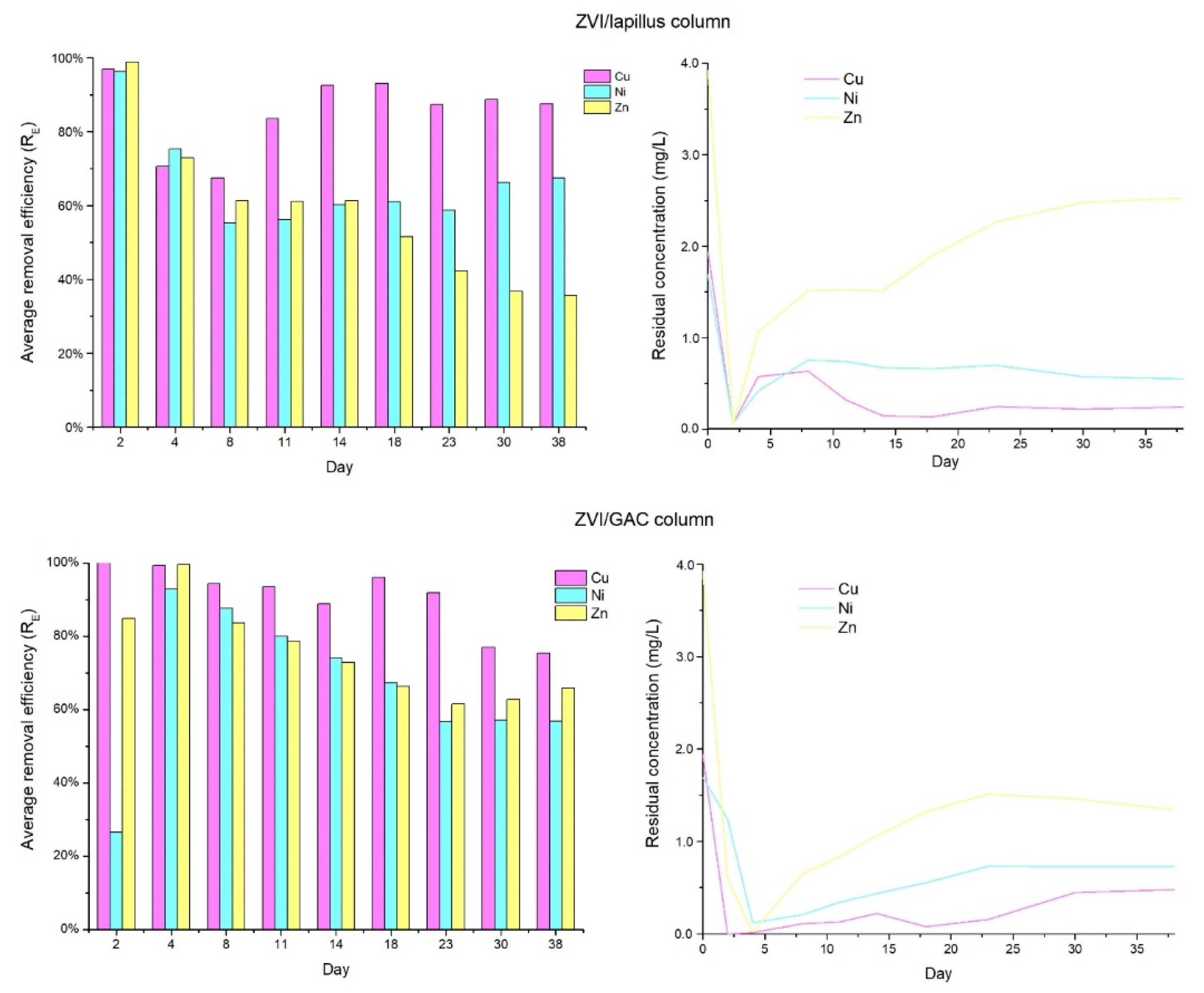
3.1. Pre-Treatment Tests
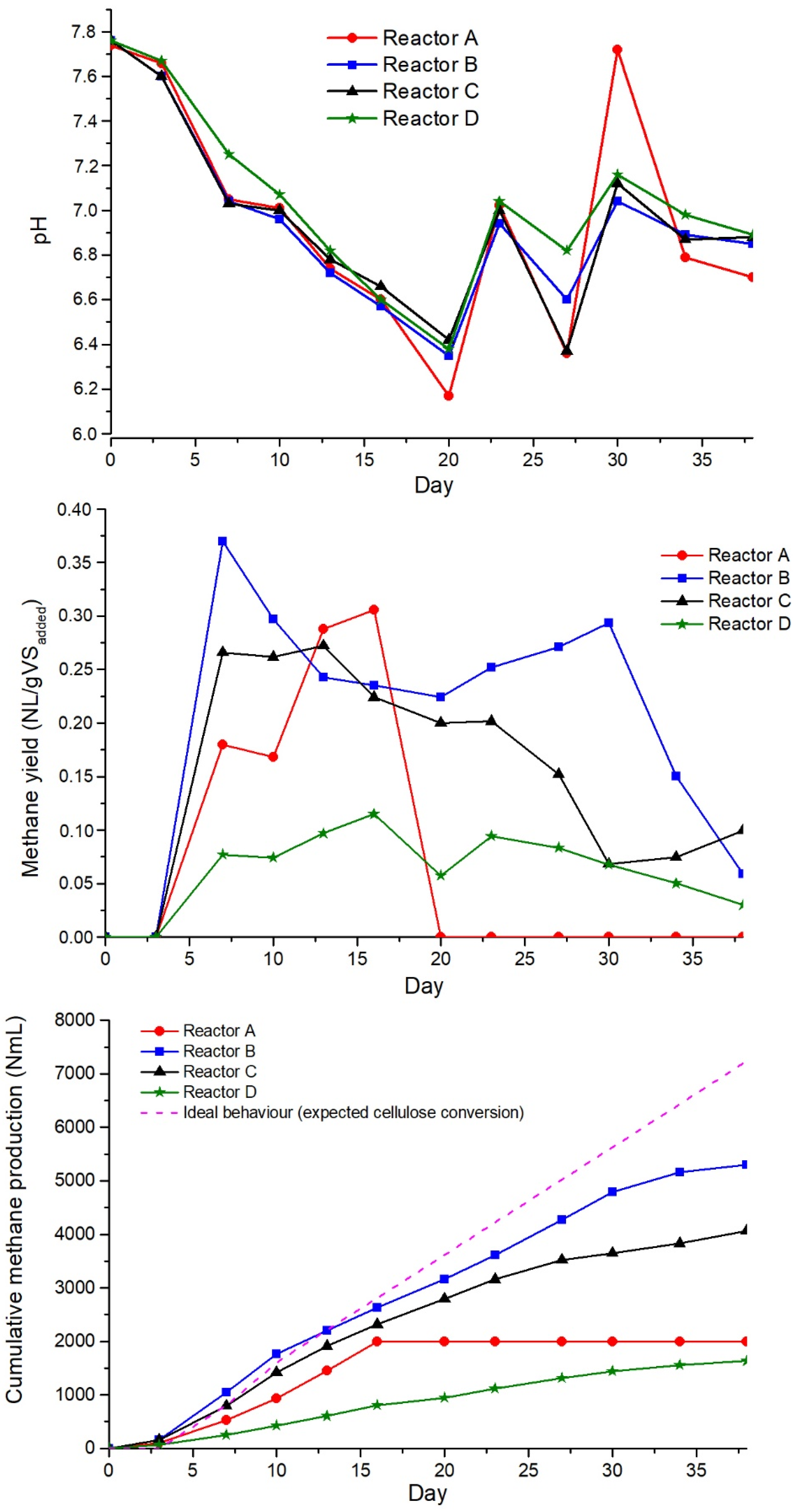
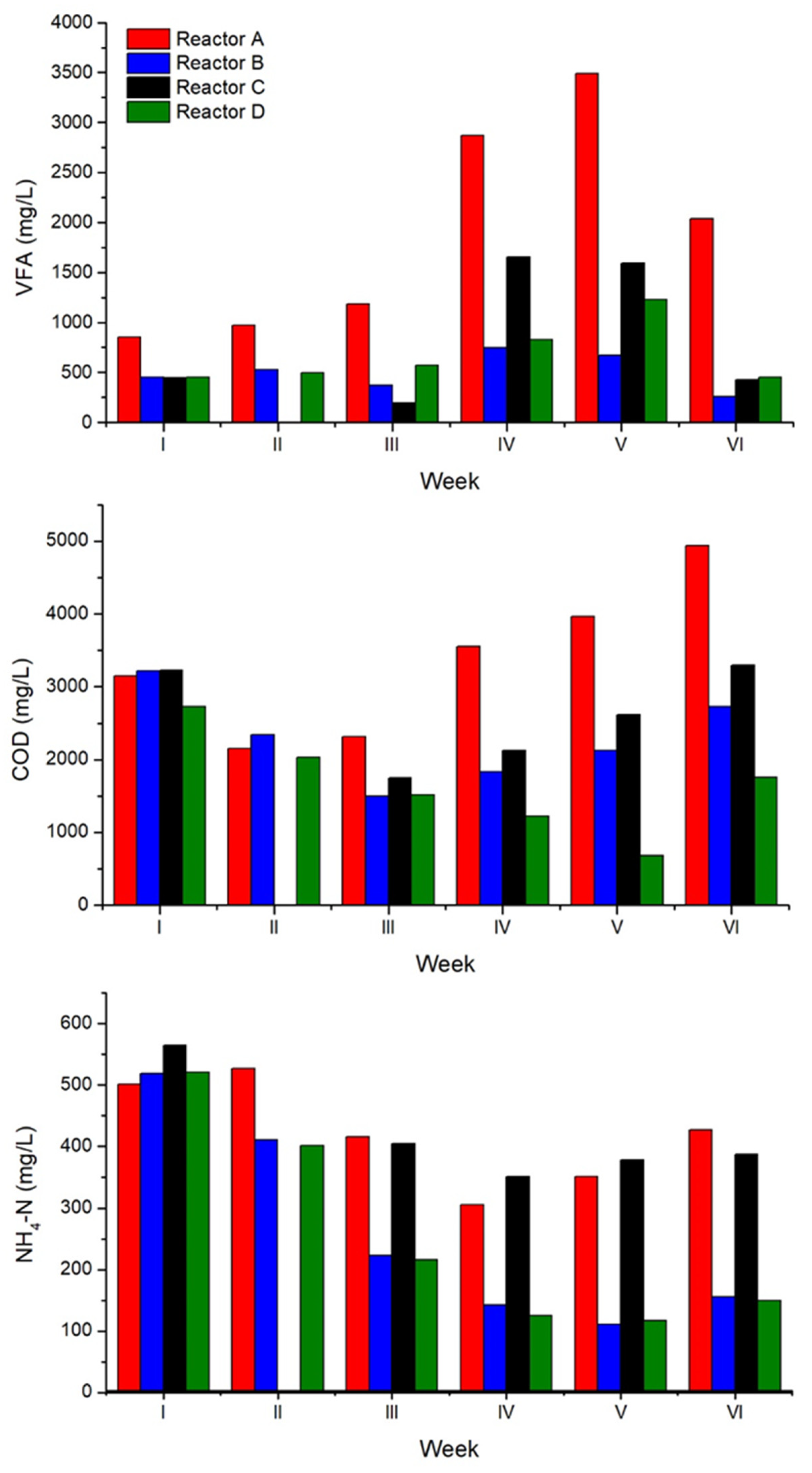
3.2. Semicontinuous AD Tests
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, J.; Oloibiri, V.; Chys, M.; Audenaert, W.; Decostere, B.; He, Y.; Van Langenhove, H.; Demeestere, K.; Van Hulle, S.W.H. The present status of landfill leachate treatment and its development trend from a technological point of view. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 14, 93–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leary, P.R.O. Chapter 14 Landfilling. In Handbook of Solid Waste Management; Mcgraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 1–94. [Google Scholar]
- Renou, S.; Givaudan, J.G.; Poulain, S.; Dirassouyan, F.; Moulin, P. Landfill leachate treatment: Review and opportunity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 150, 468–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, T.H.; Kjeldsen, P. Basic Biochemical Processes in Landfills; Academic Press Ltd.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, S.A.Q.; Watson-Craik, I.A. Ammonia and nitrogen fluxes in landfill sites: Applicability to sustainable landfilling. Waste Manag. Res. 1998, 16, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youcai, Z. Leachate Generation and Characteristics. Pollut. Control Technol. Leachate Munic. Solid Waste 2018, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Council Directive 1999/31/EC on the landfill. Off. J. Eur. Commu. 1999, L182/1-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. EPA. Solid Waste Disposal Facility Criteria; Final Rule. Federal Register, 40CFR Part 258, Part II Environmental Protection Agency, Volume 56, Number 196, 9 October, Rules and Regulations; US Department of Commerce: Washington, DC, USA, 1991.
- Laner, D.; Crest, M.; Scharff, H.; Morris, J.W.F.; Barlaz, M.A. A review of approaches for the long-term management of municipal solid waste landfills. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 498–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, A.A.; Jingsong, G.; Ping, L.Z.; Ya, P.Y.; Al-Rekabi, W.S. Review on landfill leachate treatments. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2009, 6, 672–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrig, H.J.; Robinson, H. Landfilling: Leachate Treatment; Christensen, T.H., Ed.; Solid Waste Technology and Management; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2010; Volume 2, pp. 858–897. ISBN 9781405175173. [Google Scholar]
- Amor, C.; De Torres-Socías, E.; Peres, J.A.; Maldonado, M.I.; Oller, I.; Malato, S.; Lucas, M.S. Mature landfill leachate treatment by coagulation/flocculation combined with Fenton and solar photo-Fenton processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 286, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torretta, V.; Ferronato, N.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Tolkou, A.K.; Airoldi, M. Novel and conventional technologies for landfill leachates treatment: A review. Sustainability 2017, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.; Chen, W.; Gu, Z.; Li, Q. A review of the characteristics of Fenton and ozonation systems in landfill leachate treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilardi, S.; Calabrò, P.S.; Greco, R.; Moraci, N. Selective removal of heavy metals from landfill leachate by reactive granular filters. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilardi, S.; Calabrò, P.S.; Greco, R.; Moraci, N. Removal of heavy metals from landfill leachate using zero valent iron and granular activated carbon. Environ. Technol. 2020, 41, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilardi, S.; Calabrò, P.S.; Moraci, N. The removal efficiency and long-term hydraulic behaviour of zero valent iron/lapillus mixtures for the simultaneous removal of Cu2+, Ni2+ and Zn2+. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 675, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, R.C.; Goyal, M. Activated Carbon Adsorption; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; ISBN 0-8247-5344-5. [Google Scholar]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. An overview of landfill leachate treatment via activated carbon adsorption process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelidaki, I.; Alves, M.; Bolzonella, D.; Borzacconi, L.; Campos, J.L.; Guwy, A.J.; Kalyuzhnyi, S.; Jenicek, P.; Van Lier, J.B. Defining the biomethane potential (BMP) of solid organic wastes and energy crops: A proposed protocol for batch assays. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holliger, C.; Alves, M.; Andrade, D.; Angelidaki, I.; Astals, S.; Baier, U.; Bougrier, C.; Buffière, P.; Carballa, M.; De Wilde, V.; et al. Towards a standardization of biomethane potential tests. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 2515–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkalay, D.; Guerrero, L.; Lema, J.M.; Mendez, R.; Chamy, R. Review: Anaerobic treatment of municipal sanitary landfill leachates: The problem of refractory and toxic components. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1998, 14, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleszkiewicz, J.A.; Sharma, V.K. Stimulation and inhibition of anaerobic processes by heavy metals—A review. Biol. Wastes 1990, 31, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wei, Y.; Leng, X. Improving biogas production using additives in anaerobic digestion: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Majeed, S.; Xu, R.; Zhang, K.; Kakade, A.; Khan, A. Heavy metals interact with the microbial community and a ff ect biogas production in anaerobic digestion: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 240, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fermoso, F.G.; Van Hullebusch, E.; Collins, G.; Roussel, J.; Mucha, A.P.; Esposito, G. Trace Elements in Anaerobic Biotechnologies; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 9781789060218. [Google Scholar]
- Steinhauser, A.; Deublein, D. Biogas from Waste and Renewables Energy; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; ISBN 9783527327119. [Google Scholar]
- Azman, S.; Khadem, A.F.; Zeeman, G.; van Lier, J.B.; Plugge, C.M. Mitigation of humic acid inhibition in anaerobic digestion of cellulose by addition of various salts. Bioengineering 2015, 2, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Hao, X.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Luo, Y.; Cao, D. Effect of humic acids on batch anaerobic digestion of excess sludge. Water Res. 2019, 155, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrò, P.S.; Gori, M.; Lubello, C. European trends in greenhouse gases emissions from integrated solid waste management. Environ. Technol. 2015, 36, 2125–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, C.; Orzi, V.; Carozzi, M.; Acutis, M.; Boccasile, G.; Lonati, S.; Tambone, F.; D’Imporzano, G.; Adani, F. Short-term experiments in using digestate products as substitutes for mineral (N) fertilizer: Agronomic performance, odours, and ammonia emission impacts. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 547, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Melo, B.A.G.; Motta, F.L.; Santana, M.H.A. Humic acids: Structural properties and multiple functionalities for novel technological developments. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 62, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qasim, S.R.; Chiang, W. Sanitary landfill leachate: Generation, Control and Treatment; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; ISBN 9781351417747. [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldsen, P.; Barlaz, M.A.; Rooker, A.P.; Baun, A.; Ledin, A.; Christensen, T.H. Present and Long-Term Composition of MSW Landfill Leachate: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 32, 297–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilardi, S.; Calabró, P.S.; Moraci, N. Simultaneous removal of CU II, NI II and ZN II by a granular mixture of zero-valent iron and pumice in column systems. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 55, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malara, A.; Paone, E.; Frontera, P.; Bonaccorsi, L.; Panzera, G.; Mauriello, F. Sustainable exploitation of coffee silverskin in water remediation. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Cheng, J.J.; Creamer, K.S. Inhibition of anaerobic digestion process: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4044–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA; AWWA; WEF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; Rice, E.W., Baird, R.B., Eaton, A.D., Eds.; American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; ISBN 9780875530130. [Google Scholar]
- Calabrò, P.S.; Fazzino, F.; Folino, A.; Scibetta, S.; Sidari, R. Improvement of semi-continuous anaerobic digestion of pre-treated orange peel waste by the combined use of zero valent iron and granular activated carbon. Biomass Bioenergy 2019, 129, 105337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrò, P.S.; Fazzino, F.; Folino, A.; Paone, E.; Komilis, D. Semi-Continuous Anaerobic Digestion of Orange Peel Waste: Effect of Activated Carbon Addition and Alkaline Pretreatment on the Process. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ammary, B.Y. Nutrients requirements in biological industrial wastewater treatment. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2004, 3, 236–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buchauer, K. A comparison of two simple titration procedures to determine volatile fatty acids in influents to waste-water and sludge treatment processes. Water SA 1998, 24, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Liebetrau, J.; Pfeiffer, D.; Thrän, D. (Eds.) Collection of Measurement Methods for Biogas—Methods to Determine Parameters for Analysis Purposes and Parameters That Describe Processes in the Biogas Sector; Series of the Funding Programme “Biomass Energy Use”; Deutsches Biomasseforschungszentrum gemeinnützige GmbH: Leipzig, Germany, 2016; Volume 7, ISSN 2364-897X. Available online: https://www.energetische-biomassenutzung.de/fileadmin/user_upload/Downloads/Ver%C3%B6_entlichungen/07_MMS_Biogas_en_web.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2021).
- Halim, A.A.; Aziz, H.A.; Johari, M.A.M.; Ariffin, K.S. Comparison study of ammonia and COD adsorption on zeolite, activated carbon and composite materials in landfill leachate treatment. Desalination 2010, 262, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Kim, B.J. Ammonia removal of activated carbon fibers produced by oxyfluorination. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 291, 597–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morawe, B.; Ramteke, D.S.; Vogelpohl, A. Activated carbon column performance studies of biologically treated landfill leachate. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 1995, 34, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Huang, J.; Li, X.; Flores, G.; Kamon, M. Column test-based optimization of the permeable reactive barrier (PRB) technique for remediating groundwater contaminated by landfill leachates. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2014, 168, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad-Pajooh, E.; Turcios, A.E.; Cuff, G.; Weichgrebe, D.; Rosenwinkel, K.H.; Vedenyapina, M.D.; Sharifullina, L.R. Removal of inert COD and trace metals from stabilized landfill leachate by granular activated carbon (GAC) adsorption. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 228, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Lo, W.H.; Chan, G.Y.S. Physico-chemical treatments for removal of recalcitrant contaminants from landfill leachate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 129, 80–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Guan, C.Y.; Griswold, N.; Hou, L.Y.; Fang, X.; Hu, A.; Hu, Z.Q.; Yu, C.P. Zero-valent iron-based technologies for removal of heavy metal(loid)s and organic pollutants from the aquatic environment: Recent advances and perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaffari, M.G.M.G.; Bilardi, S.; Calabrò, P.S.P.S.; Moraci, N. Nickel removal by zero valent iron/lapillus mixtures in column systems. Soils Found. 2017, 57, 745–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasay, S.A.; Barrington, S.; Tokunaga, S. Efficiency of GAC for treatment of leachate from soil washing process. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 1999, 116, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, B.E. Identification of Removal Mechanisms for Lead in Granular Activated Carbon (GAC) Columns. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1995, 30, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.P.; Wang, X. Removing copper, zinc, and lead ion by granular activated carbon in pretreated fixed-bed columns. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2000, 19, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modin, H.; Persson, K.M.; Andersson, A.; van Praagh, M. Removal of metals from landfill leachate by sorption to activated carbon, bone meal and iron fines. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 189, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilardi, S.; Calabrò, P.S.; Moraci, N.; Madaffari, M.G.; Ranjbar, E. A comparison between Fe 0/pumice and Fe 0/lapillus mixtures in permeable reactive barriers. Environ. Geotech. 2020, 7, 524–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, M.B.; Freitas, A.V.; Leitão, R.C.; Pinto, G.A.S.; Santaella, S.T. Anaerobic digestion of crude glycerol: A review. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2012, 1, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenigün, O.; Demirel, B. Ammonia inhibition in anaerobic digestion: A review. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Element | Reagent | C [mg/L] |
|---|---|---|
| Cu2+ | CuCl2, Sigma-Aldrich (purity ≥ 99.99%) | 2 |
| Ni2+ | NiCl2∙6H2O, Alfa Aesar (purity = 99.95%) | 2 |
| Zn2+ | ZnCl2, Fluka (purity > 98%) | 5 |
| NH4+ | NH4Cl, Acros Organics (purity > 99%) | 900 |
| Cl− | see the reagents above | 3100 |
| COD | 90% of humic acids, Haifa Italia 10% of acetic acid, Fisher Chemical (purity ≥ 99.7%) | 3500 |
| Pre-Treated Leachate | ||
|---|---|---|
| ZVI/Lapillus 20:80 | ZVI/GAC 40:60 | |
| pH | 7.5 | 7.1 |
| COD [mg/L] | 2363 | 1533 |
| NH4-N [mg/L] | 838.7 | 827.3 |
| Cl− [mg/L] | 3067 | 3013 |
| Cu [mg/L] | 0.30 | 0.41 |
| Ni [mg/L] | 0.52 | 0.55 |
| Zn [mg/L] | 1.64 | 0.97 |
| Week I (Acclimation) | Week II-VI (Regime Phase) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reactor | Leachate | COD/NH4-N | Pre-Treated Leachate [mL/d] | Dilution Water [mL/d] | Pre-Treated Leachate [mL/d] | Dilution Water [mL/d] |
| A | ZVI/lapillus | 25 | 35.8 | 0.0 | 35.8 | 24.2 |
| B | ZVI/lapillus | 50 | 17.9 | 12.1 | 17.9 | 42.1 |
| C | ZVI/GAC | 25 | 36.3 | 0.0 | 36.3 | 23.7 |
| D | ZVI/GAC | 50 | 18.1 | 11.9 | 18.1 | 41.9 |
| ZVI/Lapillus Column | ZVI/GAC Column | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day | Ammonium [mg/L] | Chloride [mg/L] | COD [mg/L] | Ammonium [mg/L] | Chloride [mg/L] | COD [mg/L] |
| Input leachate | 911 ± 1 | 3060 ± 20 | 3535 ± 35 | 912 ± 14 | 3120 ± 40 | 3450 ± 30 |
| 2 | 395 ± 3 | 2880 ± 40 | 1455 ± 35 | 158 ± 14 | 3220 ± 20 | 1220 ± 60 |
| 8 | 898 ± 14 | 3100 ± 20 | 3475 ± 15 | 923 ± 13 | 3100 ± 20 | 2200 ± 10 |
| 14 | 897 ± 11 | 3220 ± 20 | 3335 ± 5 | 934 ± 26 | 3180 ± 20 | 2520 ± 10 |
| 23 | 900 ± 0 | 3080 ± 0 | 3355 ± 5 | 924 ± 30 | 3140 ± 20 | 2835 ± 25 |
| 38 | 887 ± 1 | 3100 ± 20 | 3435 ± 5 | 897 ± 5 | 3120 ± 0 | 2785 ± 25 |
| Cmax [mg/L] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reactor | Cu | Ni | Zn | Chloride |
| A | 0.18 | 0.31 | 0.98 | 1828.3 |
| B | 0.09 | 0.16 | 0.49 | 914.1 |
| C | 0.25 | 0.33 | 0.59 | 1821.1 |
| D | 0.12 | 0.17 | 0.29 | 910.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fazzino, F.; Bilardi, S.; Moraci, N.; Calabrò, P.S. Integrated Treatment at Laboratory Scale of a Mature Landfill Leachate via Active Filtration and Anaerobic Digestion: Preliminary Results. Water 2021, 13, 2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202845
Fazzino F, Bilardi S, Moraci N, Calabrò PS. Integrated Treatment at Laboratory Scale of a Mature Landfill Leachate via Active Filtration and Anaerobic Digestion: Preliminary Results. Water. 2021; 13(20):2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202845
Chicago/Turabian StyleFazzino, Filippo, Stefania Bilardi, Nicola Moraci, and Paolo S. Calabrò. 2021. "Integrated Treatment at Laboratory Scale of a Mature Landfill Leachate via Active Filtration and Anaerobic Digestion: Preliminary Results" Water 13, no. 20: 2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202845
APA StyleFazzino, F., Bilardi, S., Moraci, N., & Calabrò, P. S. (2021). Integrated Treatment at Laboratory Scale of a Mature Landfill Leachate via Active Filtration and Anaerobic Digestion: Preliminary Results. Water, 13(20), 2845. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202845