From Monitoring and Modeling to Management: How to Improve Water Quality in Brazilian Rivers? A Case Study: Piabanha River Watershed
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
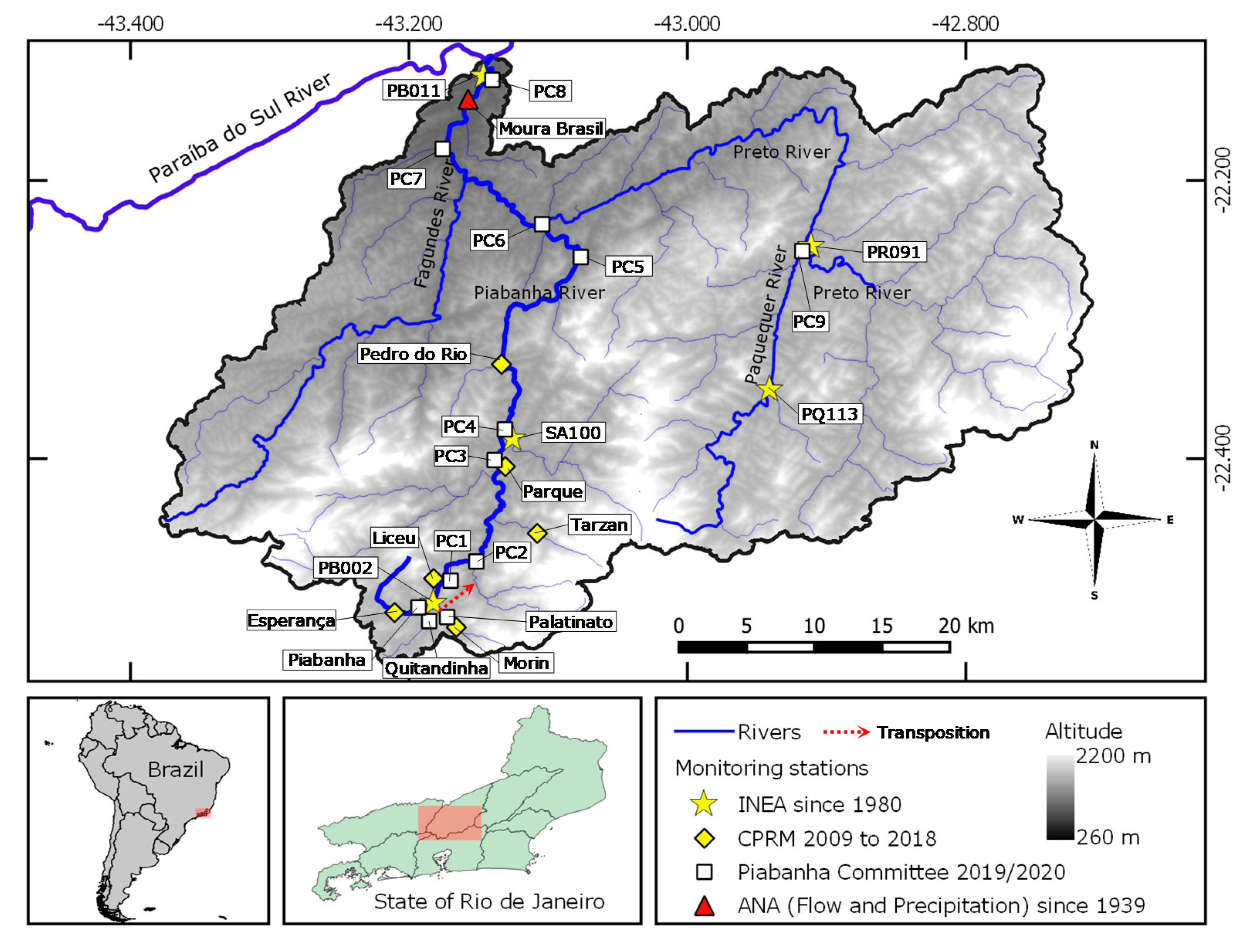
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets
2.2.1. Hydrological Data
2.2.2. Water Quality Time Series: Calibration Dataset
2.2.3. Water Quality Monitoring: Validation Dataset
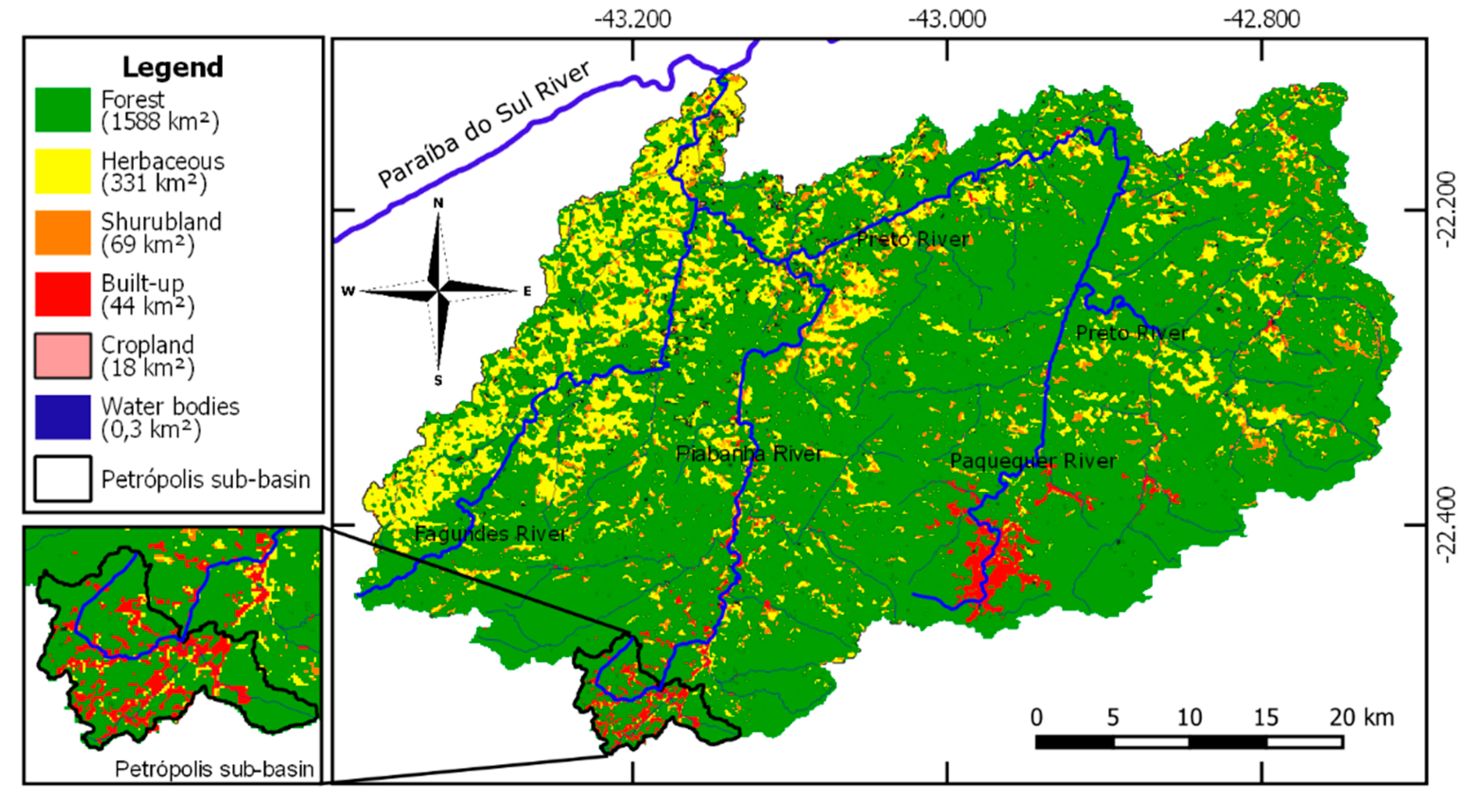
2.2.4. Land Cover and Water Uses
2.3. Water Quality Modeling
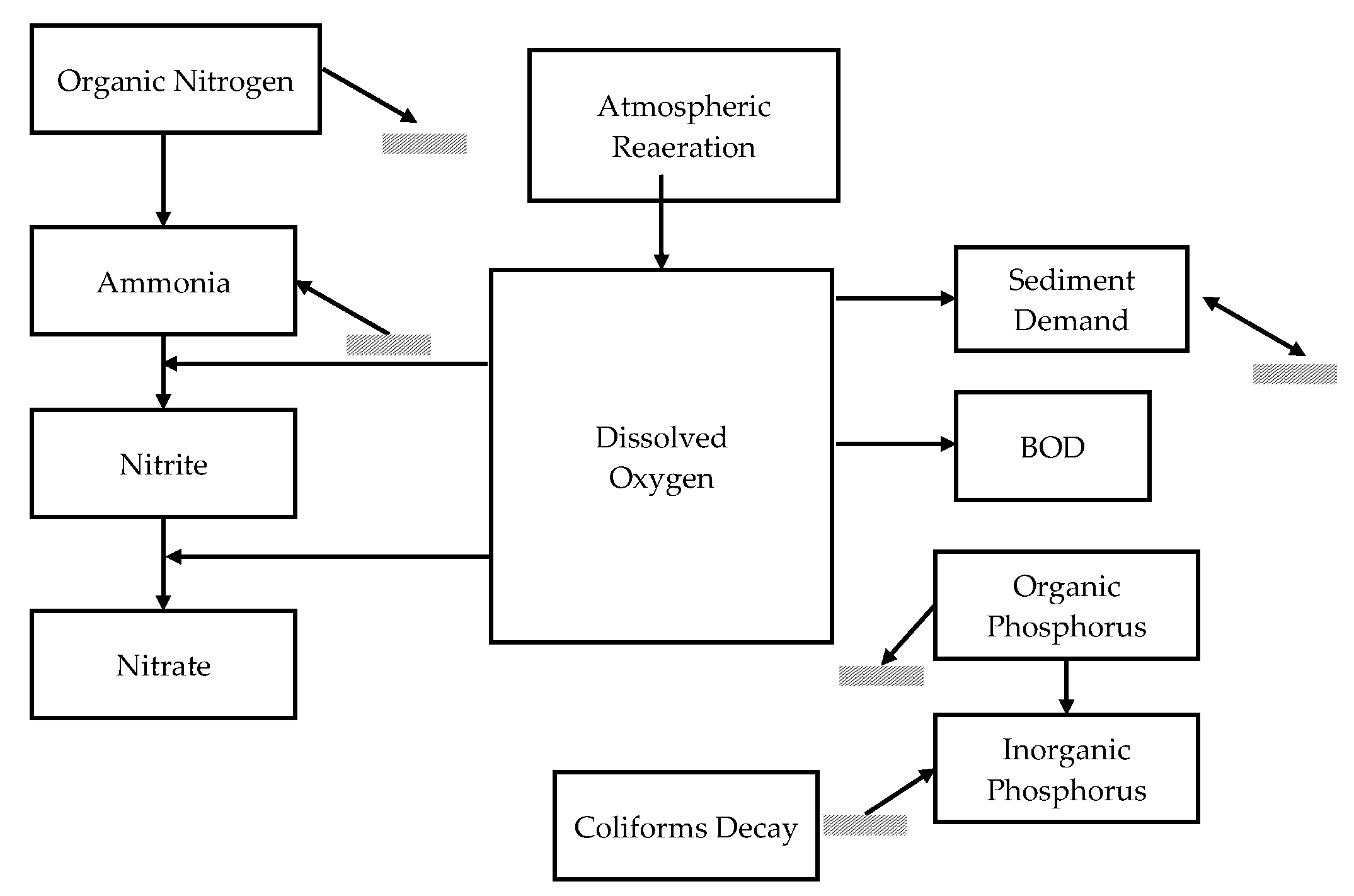
2.3.1. Model QUAL-UFMG
| = | Reaction constant (day−1); | |
| C | = | Constituents concentration (mg L−1 for most constituents and MPN 100 mL−1 for coliforms); |
| C0 | = | Initial constituents’ concentration (mg L−1 for most constituents and MPN 100 mL−1 for coliforms); |
| = | Time (days). |
2.3.2. Model Calibration, Validation, and Scenario Prognosis
| , | = | Mean long-term discharge and its respective organic concentration. |
| , | = | Flow with 95% permanence over time and its respective organic concentration. |
3. Results
3.1. Land Cover and Water Uses
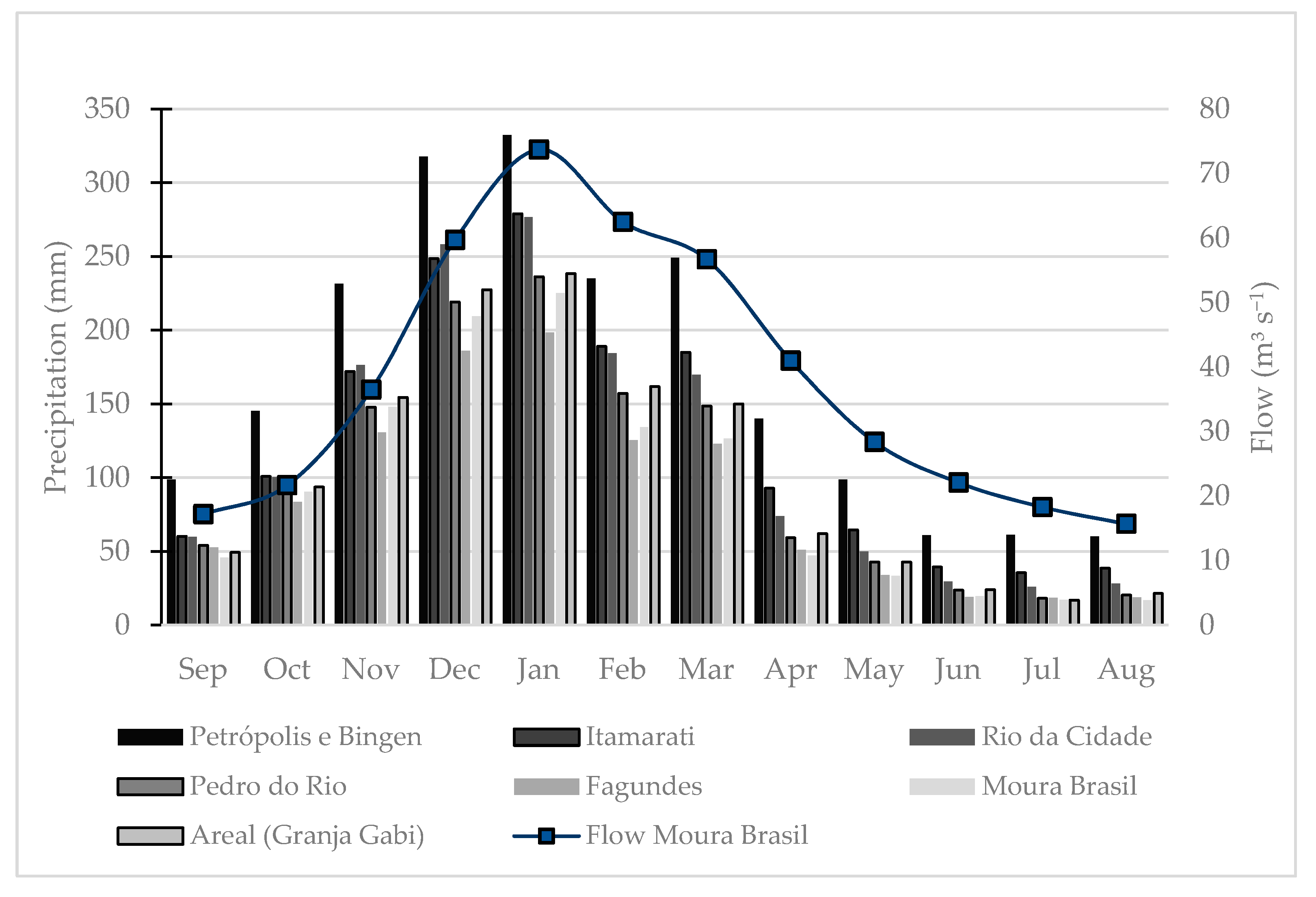
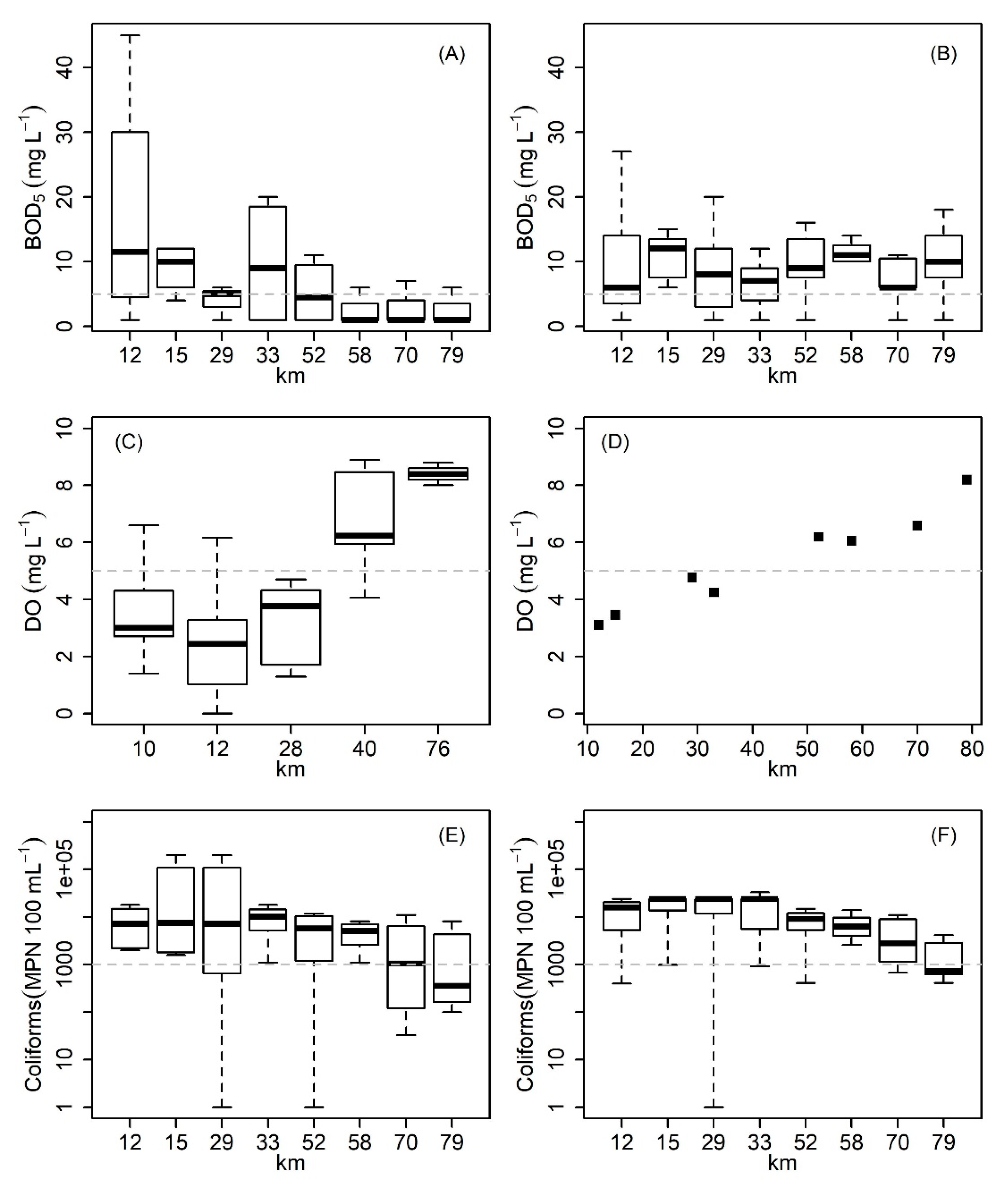
3.2. Seasonality in the Watershed and Water Quality Monitoring
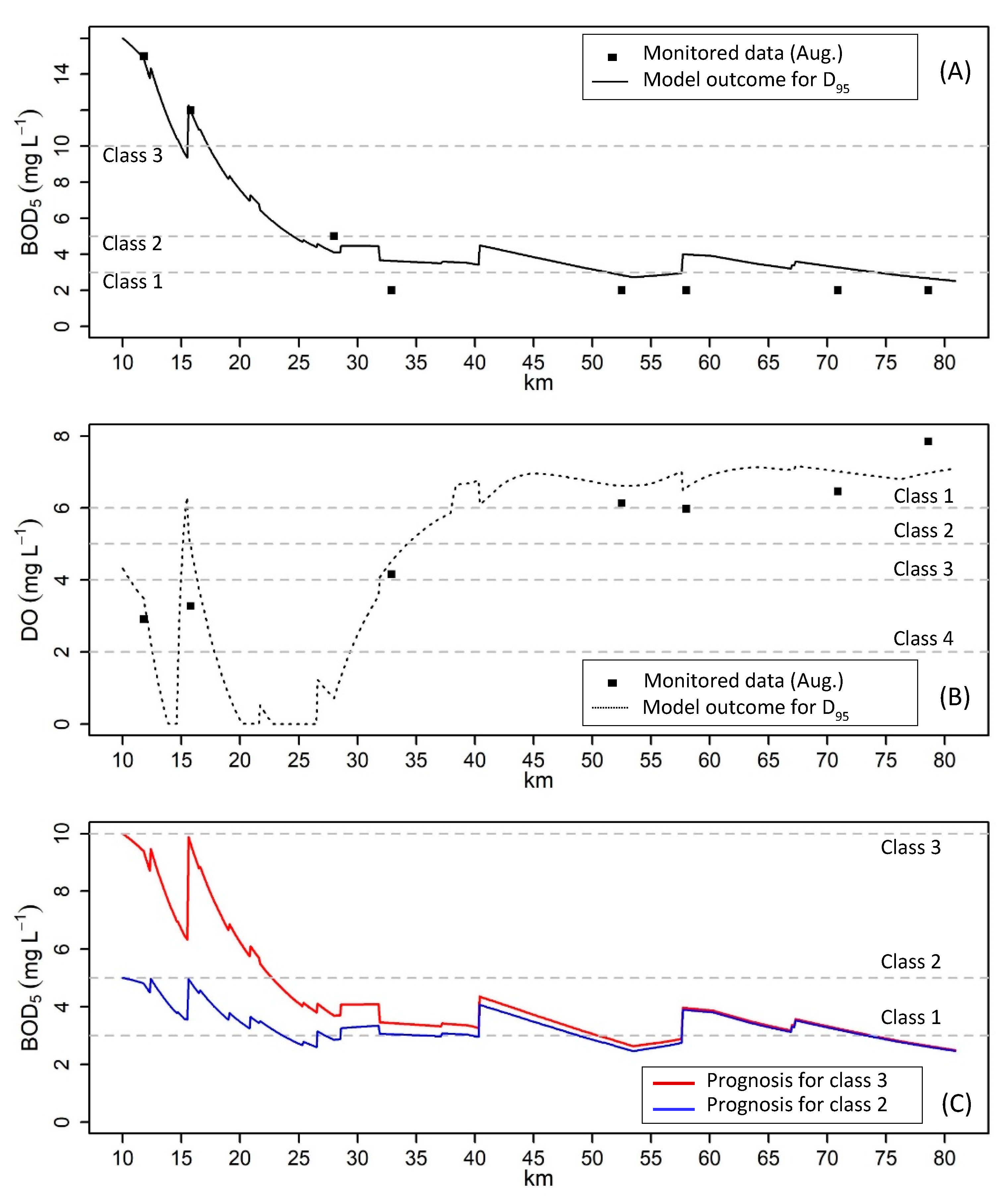
3.3. Water Quality Modeling Scenarios
4. Discussion
4.1. Water Quality Diagnosis
4.2. Model Performance and Pollution Load Reduction
4.3. Brazilian Water Resources Management and Some Recommendations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oliver, S.L.; Corburn, J.; Ribeiro, H. Challenges Regarding Water Quality of Eutrophic Reservoirs in Urban Landscapes: A Mapping Literature Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2018, 16, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mello, K.; Taniwaki, R.H.; De Paula, F.R.; Valente, R.A.; Randhir, T.O.; Macedo, D.R.; Leal, C.G.; Rodrigues, C.B.; Hughes, R.M. Multiscale land use impacts on water quality: Assessment, planning, and future perspectives in Brazil. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Xu, J.; Yin, H.; Jin, W.; Li, H.; He, Z. Urban river pollution control in developing countries. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, J.; Finlayson, B.L.; Chen, Z.; Webber, M.; Barnett, J.; Wang, M. Freshwater Supply to Metropolitan Shanghai: Issues of Quality from Source to Consumers. Water 2019, 11, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górski, J.; Dragon, K.; Kaczmarek, P.M.J. Nitrate pollution in the Warta River (Poland) between 1958 and 2016: Trends and causes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 26, 2038–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; He, P.; Shen, C.; Wu, Z. Effect of irrigation amount and fertilization on agriculture non-point source pollution in the paddy field. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 10363–10373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issaka, S.; Ashraf, M.A. Impact of soil erosion and degradation on water quality: A review. Geol. Ecol. Landsc. 2017, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Wei, R.; Luo, W.; Hu, L.; Li, B.; Di, Y.; Shi, H. Microplastic pollution in water and sediment in a textile industrial area. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, Z. Industrial water pollution, water environment treatment, and health risks in China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northey, S.; Mudd, G.M.; Saarivuori, E.; Wessman-Jääskeläinen, H.; Haque, N. Water footprinting and mining: Where are the limitations and opportunities? J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 135, 1098–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, G.W.; Goulart, F.F.; Ranieri, B.D.; Coelho, M.S.; Dales, K.; Boesche, N.; Bustamante, M.; Carvalho, F.A.; Carvalho, D.C.; Dirzo, R.; et al. Deep into the mud: Ecological and socio-economic impacts of the dam breach in Mariana, Brazil. Natureza & Conservação 2016, 14, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.D.A.; Assumpção, R.D.S.F.V.; De Azevedo, J.P.S.; Dos Santos, M.A. Dos instrumentos de gestão de recursos hídricos—O Enquadramento—Como ferramenta para reabilitação de rios. Saúde em Debate 2019, 43, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN Water. Sustainable Development Goal 6: Synthesis Report 2018 on Water and Sanitation; United Nations publications; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-92-1-101370-2. [Google Scholar]
- Behmel, S.; Damour, M.; Ludwig, R.; Rodriguez, M. Water quality monitoring strategies—A review and future perspectives. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 571, 1312–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brack, W.; Dulio, V.; Ågerstrand, M.; Allan, I.; Altenburger, R.; Brinkmann, M.; Bunke, D.; Burgess, R.M.; Cousins, I.; Escher, B.I.; et al. Towards the review of the European Union Water Framework Directive: Recommendations for more efficient assessment and management of chemical contamination in European surface water resources. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 576, 720–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altenburger, R.; Brack, W.; Burgess, R.M.; Busch, W.; Escher, B.I.; Focks, A.; Mark Hewitt, L.; Jacobsen, B.N.; De Alda, M.L.; Ait-Aissa, S.; et al. Future water quality monitoring: Improving the balance between exposure and toxicity assessments of real-world pollutant mixtures. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2019, 31, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, D.V.; Bradley, C.; Gettel, G.M.; Hatvani, I.G.; Hein, T.; Kovács, J.; Liska, I.; Oliver, D.M.; Tanos, P.; Trásy, B.; et al. Developments in water quality monitoring and management in large river catchments using the Danube River as an example. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 64, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Merritt, W.S.; Croke, B.F.W.; Weber, T.R.; Jakeman, A.J. A review of catchment-scale water quality and erosion models and a synthesis of future prospects. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 114, 75–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.M.D.S.B.; Marques, L.D.S.; Almeida, A.K.; Leite, I.R.; De Almeida, I.K. Applicability of water quality models around the world—a review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 36141–36162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN Agenda 21. In Proceedings of the United Nations Conference on Environment & Development, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 3–14 June 1992.
- United Nations; Environment Programme; United Nations; Development Programme. Status Report on the Application of Integrated Approaches To Water Resources Management; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2012; ISBN 978-92-807-3264-1. [Google Scholar]
- Boelee, E.; Geerling, G.; Van Der Zaan, B.; Blauw, A.; Vethaak, A.D. Water and health: From environmental pressures to integrated responses. Acta Trop. 2019, 193, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badham, J.; ElSawah, S.; Guillaume, J.H.A.; Hamilton, S.H.; Hunt, R.J.; Jakeman, A.J.; Pierce, S.A.; Snow, V.; Babbar-Sebens, M.; Fu, B.; et al. Effective modeling for Integrated Water Resource Management: A guide to contextual practices by phases and steps and future opportunities. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 116, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, L.; Henry, A.D.; Pivo, G. Integrated water management recommendations in practice: Coexistence of old and new ways in Arizona. Hydrol. Res. 2020, 22, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araral, E.; Wang, Y. Water Governance 2.0: A Review and Second Generation Research Agenda. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 3945–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodhouse, P.; Muller, M. Water Governance—An Historical Perspective on Current Debates. World Dev. 2017, 92, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, R. Disconnected dots?: A systematic review of governance challenges for natural resource management. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2019, 63, 1356–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, V. Reconciling global aspirations and local realities: Challenges facing the Sustainable Development Goals for water and sanitation. World Dev. 2019, 118, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, C.C.; Vikolainen, V.; Bressers, H. Water Governance Decentralisation and River Basin Management Reforms in Hierarchical Systems: Do They Work for Water Treatment Policy in Mexico’s Tlaxcala Atoyac Sub-Basin? Water 2016, 8, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WWAP. Leaving No One Behind; The United Nations World Water Development Report UNESCO World Water Assessment Programme: Paris, France, March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- WWAP. Wastewater, the Untapped Resource, The United Nations World Water Development Report; UNESCO World Water Assessment Programme: Paris, France, March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- ANA. SDG 6 in Brazil: ANA’s Vision of the Indicators; Brazilian National Water Agency: Brasília, Brazil, 2019.
- ANA. Brazilian Water Resources Report; National Water Agency: Brasília, Brazil, 2019.
- Brazilian National Congress. Brazilian National Water Resources Policy. Federal Law no. 9433. Brasília, Brazil, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- ANA. Brazilian Water Resources Report Full Report; National Water Agency: Brasília, Brazil, 2018.
- Brazilian National Environment Council (CONAMA). Resolution no. 357. Provides the classification of water bodies and environmental guidelines for their framework, as well as stablishes the conditions and standards for effluents discharge. Brasília, Brazil, 2005; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, D.D.A.; De Azevedo, J.P.S.; Dos Santos, M.A.; Assumpção, R.D.S.F.V. Water quality assessment based on multivariate statistics and water quality index of a strategic river in the Brazilian Atlantic Forest. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, P.E.A.M.; Da Hora, M. 20 Anos Da Lei No9.433/97: Percepções Dos Comitês De Bacia Hidrográfica E Dos Órgãos Gestores Acerca Do Enquadramento De Corpos D’água. Rev. Gestão Água da América Lat. 2019, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Valeriano, M.D.M.; Rossetti, D.D.F. Topodata: Brazilian full coverage refinement of SRTM data. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 32, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, C.H.P. Development of an Environmental Flow Approach Applied to the Piabanha River Watershed; Federal University of Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ/COPPE): Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Silva Junior, L.C.S. Analysis of Wastewater Impact on River Water Quality through Computational Modeling—Study Case in Piabanha River/RJ.; Federal University of Rio de Janeiro (COPPE/UFRJ): Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Villas-Boas, M.D.; Olivera, F.; De Azevedo, J.P.S. Assessment of the water quality monitoring network of the Piabanha River experimental watersheds in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, using autoassociative neural networks. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvim, B.R. Dinâmica do Nitrogênio e Fósforo em Águas Fluviais de Uma Bacia Hidrográfica com Diferentes Usos do Solo no Sudeste do Brasil; Universida de Federal Fluminense: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- National Water Agency (Brazil). Portal HidroWeb. Brazilian National Water Resources Information System. Available online: http://www.snirh.gov.br/hidroweb/ (accessed on 22 April 2020).
- de Almeida, H.A.; Freitas, R.C.; da Silva, L. Determinação de períodos secos e chuvosos em duas microregiões da Paraíba através da técnica dos quantis. Rev. Geogr. 2013, 30, 217–232. [Google Scholar]
- Cárdenas, O.L.; Peinado-Guevara, H.J.; Montoya, J.M.; Campos, M.N.; Ocampo, H.G.; León, S.C. Seasonal Trend Indicators and Return Periods of Meteorological Drought in the Northern States of Mexico. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2017, 26, 1471–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, J.P.S. Relatório Final do Projeto HIDROECO/Piabanha: Metodologia para Determinação de Vazões Ambientais Na Região Serrana Do RJ Integrando Aspectos Hidrometeorológicos, Ecológicos E Socioeconômico. Volume 1: Informações Quali-Quantitativas.; UFRJ: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Associação Pró-Gestão das Águas da Bacia Hidrográfica do Rio Paraíba do Sul (AGEVAP). Termo de Referência para contratação de empresa especializada para o monitoramento de rios na Região Hidrográfica Piabanha (RH-IV) [Term of Reference for hiring a specialized company to monitor rivers in the Piabanha Hydrographic Region (RH-IV)]. Available online: http://www.agevap.org.br/atos_view.php?id=597 (accessed on 22 April 2020).
- ANA. Enquadramento Dos Corpos D’água em Classes. Encarte Especial da Conjuntura Dos Recursos Hídricos no Brasil de 2019; National Water Agency: Brasília, Brazil, 2020.
- APHA. Standard Method for Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; ISBN 9780875530130. [Google Scholar]
- Buchhorn, M.; Smets, B.; Bertels, L.; Lesiv, M.; Tsendbazar, N.-E.; Masiliunas, D.; Linlin, L.; Herold, M.; Fritz, S. Copernicus Global Land Service: Land Cover 100m: Collection 3: Epoch 2019: Globe. (Version V3.0.1) [Data set]. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Water Agency (Brazil). Sistema Federal de Regulação de Uso—REGLA (Federal System for the Regulation of Uses). Available online: http://www.snirh.gov.br/cnarh/identificar.jsf (accessed on 22 April 2020).
- Weinberg, Á. Water Quality Control and Monitoring Prioritization Methodology as a Tool for Water Resourse Management; Federal University of Rio de Janeiro (COPPE/UFR): Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- ANA. Atlas Esgotos—Despoluição de Bacias Hidrográficas; Brazilian National Water Agency: Brasília, Brazil, 2017; ISBN 978-85-8210-050-9.
- von Sperling, M. Estudos E Modelagem Da Qualidade da Água em Rios, 2nd ed.; UFMG: Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2014; ISBN 978-85-423-0080-2. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, D.J.L.; Teixeira, D. Análise de incerteza em um modelo matemático de qualidade da água aplicado ao Ribeirão do Ouro, Araraquara, SP, Brasil. Ambient. e Agua—Interdiscip. J. Appl. Sci. 2011, 6, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Salla, M.R.; Pereira, C.E.; Filho, J.E.A.; De Paula, L.M.; Pinheiro, A.M. Estudo da autodepuração do rio Jordão, localizado na bacia hidrográfica do rio Dourados. Eng. Sanit. Ambient. 2013, 18, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Teodoro, A.; Ide, C.N.; Ribeiro, M.L.; Broch, S.A.O.; Da Silva, J.B. Implementação do conceito Capacidade de Diluiçãode Efluentes no modelo de qualidade da água QUAL-UFMG: Estudo de caso no Rio Taquarizinho (MS). Eng. Sanit. Ambient. 2013, 18, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calmon, A.; Souza, J.; Reis, J.; Mendonça, A. Uso combinado de curvas de permanência de qualidade e modelagem da autodepuração como ferramenta para suporte ao processo de enquadramento de cursos d-água superficiais. RBRH 2016, 21, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, S.H.R.; Guedes, H.A.S.; Siqueira, T.M.; Corrêa, L.B.; Andreazza, R.; Hüffner, A.N. Modelagem sazonal da qualidade da água do Rio dos Sinos/RS utilizando o modelo QUAL-UFMG. Eng. Sanit. e Ambient. 2018, 23, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, B.P.; Mamede, G.L.; Neto, I.E.L. Monitoramento e modelagem da qualidade de água em uma bacia hidrográfica semiárida. Eng. Sanit. e Ambient. 2018, 23, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringer, L.M.; Dos Reis, J.A.T.; Mendonça, A.S.F. Wastewater treatment systems selection inside watersheds by using multiobjective analysis. RBRH 2018, 23, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, S.R.; Junior, M.A.B.D.S.; De Lima, E.E.S. Analysis and modeling of water quality as a contribution to the preliminary framework proposal for the Una River (Pernambuco/Brazil). Ambient. Agua Interdiscip. J. Appl. Sci. 2018, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Sperling, M.; Von Sperling, E. Challenges for bathing in rivers in terms of compliance with coliform standards. Case study in a large urbanized basin (das Velhas River, Brazil). Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 2534–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filho, A.A.D.O.; Neto, I.E.L. Modelagem da qualidade da água do rio Poti em Teresina (PI). Eng. Sanit. e Ambient. 2017, 23, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, M.L.A. Subsidies For Piabanha River Framing Supported by Mathematical Modelling of Water Quality; Federal University of Rio de Janeiro (COPPE/UFRJ): Rio de Janeiro, Brzil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- de Paula, T.P. Analysis and Mathematical Modeling of the Water Quality in Strech of the River Piabanha/RJ; Federal University of Rio de Janeiro (COPPE/UFRJ): Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Gitau, M.W.; Pai, N.; Daggupati, P. Hydrologic and Water Quality Models: Performance Measures and Evaluation Criteria. Trans. ASABE 2015, 58, 1763–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Moriasi, D.N.; Gassman, P.W.; Abbaspour, K.C.; White, M.J.; Srinivasan, R.; Santhi, C.; Harmel, R.D.; Van Griensven, A.; Van Liew, M.W.; et al. SWAT: Model Use, Calibration, and Validation. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1491–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CPRM. Relatório-Síntese do Trabalho de Regionalização de Vazões da Sub-Bacia 58; Geological Survey of Brazil: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2003.
- INEA Resolution No. 162 of December 26, 2018 - Establishes criteria for determining the reference flow for purposes of calculating water availability for granting the right to use water resources and uses considered insignificant in the domain of the State of Rio de Janeiro. In (Resolução INEA No 162 De 26 De Dezembro De 2018 —Estabelece Critério Para A Determinação da Vazão De Referência Para Fins Do Cálculo De Disponibilidade Hídrica Para Outorga De Direito De Uso De Recursos Hídricos E Usos Considerados Insignificantes De Domínio do Estado do Rio de Janeiro); State Environmental Institute (INEA): Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2018; p. 3.
- Fries, A.S.; Coimbra, J.P.; Nemazie, D.A.; Summers, R.M.; De Azevedo, J.P.S.; Filoso, S.; Newton, M.; Gelli, G.; De Oliveira, R.C.N.; Pessoa, M.A.R.; et al. Guanabara Bay ecosystem health report card: Science, management, and governance implications. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2019, 25, 100474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, M.; Porto, R.L.L. Gestão de bacias hidrográficas. Estud. Avançados 2008, 22, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Junior, L.C.S.; Obraczka, M. Reúso de Efluentes de Estações de Tratamento de Esgoto no Beneficiamento de Concreto. Mix Sustentável 2020, 6, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.L.; Gelelete, D.S.; de Andrade Costa, D.; Barbosa, L.G.; Assis, M.M.C.; Guedes, R.B. Usos Múltiplos E Proposta De Revisão De Metodologia De Cobrança Pelo Uso Da Água (Multiple Water Uses and Methodological Proposal for Water Use Charging); AGEVAP: Resende, Brazil, 2018; ISBN 978-65-800-71-00-5. [Google Scholar]
- Royer, T.V.; David, M.B.; Gentry, L.E. Timing of Riverine Export of Nitrate and Phosphorus from Agricultural Watersheds in Illinois: Implications for Reducing Nutrient Loading to the Mississippi River. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 4126–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalu, T.; Wasserman, R.J.; Magoro, M.L.; Froneman, P.W.; Weyl, O.L. River nutrient water and sediment measurements inform on nutrient retention, with implications for eutrophication. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 684, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvim, R.B.; De Mello, W.Z.; Silveira, C.S.; Kligerman, D.C.; Ribeiro, R.P. Emissões de óxido nitroso em águas fluviais não poluídas e poluídas da Bacia do Rio Paquequer (Teresópolis, Rio de Janeiro). Eng. Sanit. Ambient. 2014, 19, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Araújo, L.M.N. Identification of Precipitation and Soil Moisture Hydrological Patterns at Piabanha River Basin. Ph.D. Thesis, Federal University of Rio de Janiero, Rio de Janiero, Brazil, November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gaur, V.K.; Gupta, S.K.; Pandey, S.D.; Gopal, K.; Misra, V. Distribution of heavy metals in sediment and water of river Gomti. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2005, 102, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngoye, E.; Machiwa, J.F. The influence of land-use patterns in the Ruvu river watershed on water quality in the river system. Phys. Chem. Earth, Parts A/B/C 2004, 29, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.M.; Chen, Y.; Xue, L.-G.; Fan, T.T.; Emaneghemi, B. Greater health risk in wet season than in dry season in the Yellow River of the Lanzhou region. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 644, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, M. BED MATERIAL TRANSPORT AND THE MORPHOLOGY OF ALLUVIAL RIVER CHANNELS. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2006, 34, 325–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuill, B.T.; Gasparini, N. Hydrologic controls on wash load sediment concentrations within a low-ordered, ephemeral watershed. J. Hydrol. 2011, 410, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigiak, O.; Grizzetti, B.; Udias-Moinelo, A.; Zanni, M.; Dorati, C.; Bouraoui, F.; Pistocchi, A. Predicting biochemical oxygen demand in European freshwater bodies. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 666, 1089–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jouanneau, S.; Recoules, L.; Durand, M.; Boukabache, A.; Picot, V.; Primault, Y.; Lakel, A.; Sengelin, M.; Barillon, B.; Thouand, G. Methods for assessing biochemical oxygen demand (BOD): A review. Water Res. 2014, 49, 62–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauvé, S.; Aboulfadl, K.; Dorner, S.; Payment, P.; Deschamps, G.; Prévost, M. Fecal coliforms, caffeine and carbamazepine in stormwater collection systems in a large urban area. Chemosphere 2012, 86, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhi, X.; Chen, L.; Shen, Z. Spatiotemporal variability and key influencing factors of river fecal coliform within a typical complex watershed. Water Res. 2020, 178, 115835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monfared, S.A.H.; Darmian, M.D.; Snyder, S.A.; Azizyan, G.; Pirzadeh, B.; Moghaddam, M.A. Water Quality Planning in Rivers: Assimilative Capacity and Dilution Flow. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 99, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Sun, S.; Fu, G.; Hall, J.W.; Ni, Y.; He, L.; Yi, J.; Zhao, N.; Du, Y.; Pei, T.; et al. Pollution exacerbates China’s water scarcity and its regional inequality. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khdhiri, H.; Potier, O.; Leclerc, J.-P. Aeration efficiency over stepped cascades: Better predictions from flow regimes. Water Res. 2014, 55, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Fu, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, T. Rate and Distribution of Sedimentation in the Three Gorges Reservoir, Upper Yangtze River. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2018, 144, 05018006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maavara, T.; Chen, Q.; Van Meter, K.; Brown, L.E.; Zhang, J.; Ni, J.; Zarfl, C. River dam impacts on biogeochemical cycling. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahipathy, M.V.; Puttaiah, E.T. Ecological characteristics of Vrishabhavathy River in Bangalore (India). Environ. Earth Sci. 2006, 49, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.Y.; Reddy, M.V. Assessment of seasonal effects of municipal sewage pollution on the water quality of an urban canal—A case study of the Buckingham canal at Kalpakkam (India): NO3, PO4, SO4, BOD, COD and DO. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 157, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerves-Cobo, R.; Benedetti, L.; Amerlinck, Y.; Lock, K.; De Mulder, C.; Van Butsel, J.; Cisneros, F.; Goethals, P.; Nopens, I. Integrated ecological modelling for evidence-based determination of water management interventions in urbanized river basins: Case study in the Cuenca River basin (Ecuador). Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 709, 136067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavijo, A.; Iribarnegaray, M.A.; Rodriguez-Alvarez, M.S.; Seghezzo, L. Closing the cycle? Potential and limitations of Water and Sanitation Safety Plans (WSSPs) for Latin American metropolitan areas. J. Water Sanit. Hyg. Dev. 2020, 10, 490–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stip, C.; Mao, Z.; Bonzanigo, L.; Browder, G.; Tracy, J. Water Infrastructure Resilience; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Devesa, F.; Matas, J.C.; Turon, C.; Freixó, A.; Carrasco, F.; Poch, M. Scenario analysis for the role of sanitation infrastructures in integrated urban wastewater management. Environ. Model. Softw. 2009, 24, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyola, A.; Padilla-Rivera, A.; Morgan-Sagastume, J.M.; Güereca, L.P.; Padilla, F.H. Typology of Municipal Wastewater Treatment Technologies in Latin America. CLEAN—Soil Air Water 2012, 40, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foresti, E.; Zaiat, M.; Vallero, M. Anaerobic Processes as the Core Technology for Sustainable Domestic Wastewater Treatment: Consolidated Applications, New Trends, Perspectives, and Challenges. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technology 2006, 5, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puga, B.P.; Junior, R.G.; Alexandre, G.M. Governança dos recursos hídricos na bacia do rio Jundiaí (São Paulo). Revibec Rev. Iberoam. Econ. Ecológica 2020, 32, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Braga, L.M.M. Sistemas Hídrico E Territorial Integrados A Partir Do Eixo Do Rio Jundiaí (Water and Territorial Systems Integrated from The Aixs of the Jundiaí River); Universida de Estadual de Campinas: Campinas, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- CNRH Resolution 181. In Approves the Priorities, Actions and Goals of the National Water Resources Plan for 2016–2020; Brazilian National Water Resources Council (CNRH): Brasil, Brazil, 2016; p. 15.
- CNRH Resolution n˚91. In Provides for General Procedures for Framing Surface and Underground Water Bodies; Brazilian National Water Resources Council (CNRH): Brasília, Brazil, 2008; pp. 1–5.
- Melo, D.D.C.D.; Anache, J.A.A.; Almeida, C.D.N.; Coutinho, J.V.; Filho, G.M.R.; Rosalem, L.M.P.; Pelinson, N.D.S.; Ferreira, G.L.R.A.; Schwamback, D.; Calixto, K.G.; et al. The big picture of field hydrology studies in Brazil. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2020, 65, 1262–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narzetti, D.A.; Marques, R.C. Models of Subsidies for Water and Sanitation Services for Vulnerable People in South American Countries: Lessons for Brazil. Water 2020, 12, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Motta, R.S.; Moreira, A. Efficiency and regulation in the sanitation sector in Brazil. Util. Policy 2006, 14, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresch, E.P.; Schneider, R. Political determinants of investment in water and sanitation: Evidence from Brazilian elections. Econ. Lett. 2020, 189, 109041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, K.; Dickin, S.; Rosemarin, A. Towards “Sustainable” Sanitation: Challenges and Opportunities in Urban Areas. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishi, S.A.S.; Martins, A.F.; Salvador, A.V.A.; de Azevedo Camargo, E.M.; Vianna, M.D.B. Ministério público resolutivo: Projeto Qualidade da Água e Projeto Conexão Água. Ministério Público e Sustentabilidade O Direito das Present. e Futur. Gerações 2017, 87–107. Available online: http://conexaoagua.mpf.mp.br/arquivos/artigos-cientificos/2017/03-ministerio-publico-resolutivo-projeto-qualidade-da-agua-e-projeto-conexao-agua.pdf (accessed on 22 April 2020).
- MPF. Efetivação das Metas de Qualidade das Águas no Brasil; Ministério Público Federal: Brasília, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, D.d.A.; Assumpção, R.d.S.F.V.; de Azevedo, J.P.S.; Leite, P.S.O.d.S.; Rosario, L.; Nunes, G.; Cinelli, W.S.; Montes, V.M.; Gouvêa, L.H.d.A. Delimitation Project of the Continues Riparian Protected Stripe to Piabanha River at the Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil. In Proceedings of the II International Conference on Research for Sustainable Development in Mountain Regions, Instituto Politécnico de Bragança, Nova Friburgo, Brazil, 10–14 December 2018; p. 298. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa, D.d.A.; Silva Junior, L.C.S.d.; Azevedo, J.P.S.d.; Santos, M.A.d.; Assumpção, R.d.S.F.V. From Monitoring and Modeling to Management: How to Improve Water Quality in Brazilian Rivers? A Case Study: Piabanha River Watershed. Water 2021, 13, 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020176
Costa DdA, Silva Junior LCSd, Azevedo JPSd, Santos MAd, Assumpção RdSFV. From Monitoring and Modeling to Management: How to Improve Water Quality in Brazilian Rivers? A Case Study: Piabanha River Watershed. Water. 2021; 13(2):176. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020176
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta, David de Andrade, Luis Carlos Soares da Silva Junior, José Paulo Soares de Azevedo, Marco Aurélio dos Santos, and Rafaela dos Santos Facchetti Vinhaes Assumpção. 2021. "From Monitoring and Modeling to Management: How to Improve Water Quality in Brazilian Rivers? A Case Study: Piabanha River Watershed" Water 13, no. 2: 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020176
APA StyleCosta, D. d. A., Silva Junior, L. C. S. d., Azevedo, J. P. S. d., Santos, M. A. d., & Assumpção, R. d. S. F. V. (2021). From Monitoring and Modeling to Management: How to Improve Water Quality in Brazilian Rivers? A Case Study: Piabanha River Watershed. Water, 13(2), 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020176





