Multi Frequency Isotopes Survey to Improve Transit Time Estimation in a Situation of River-Aquifer Interaction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
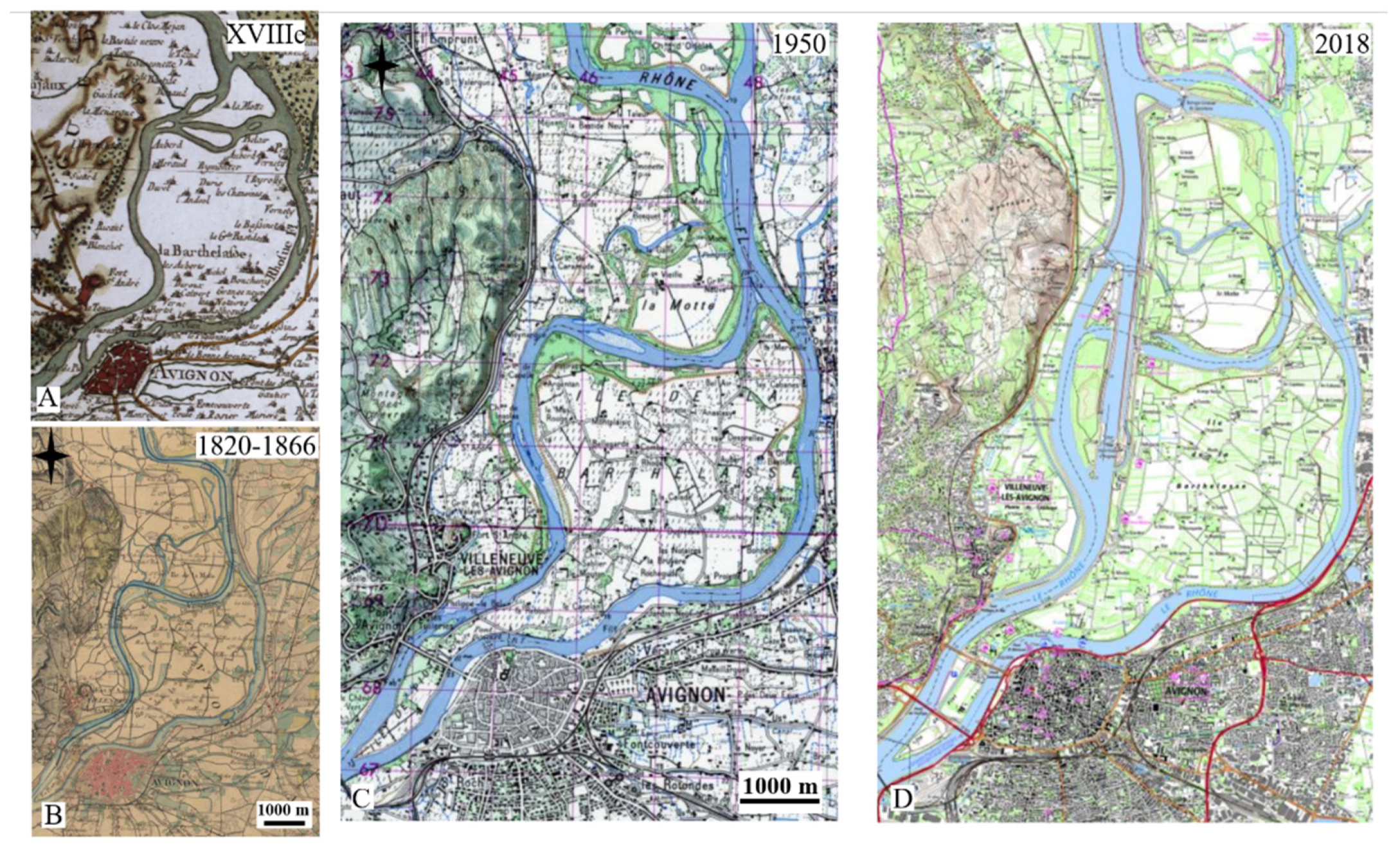
2.1. Study Site
2.1.1. Location and Climate
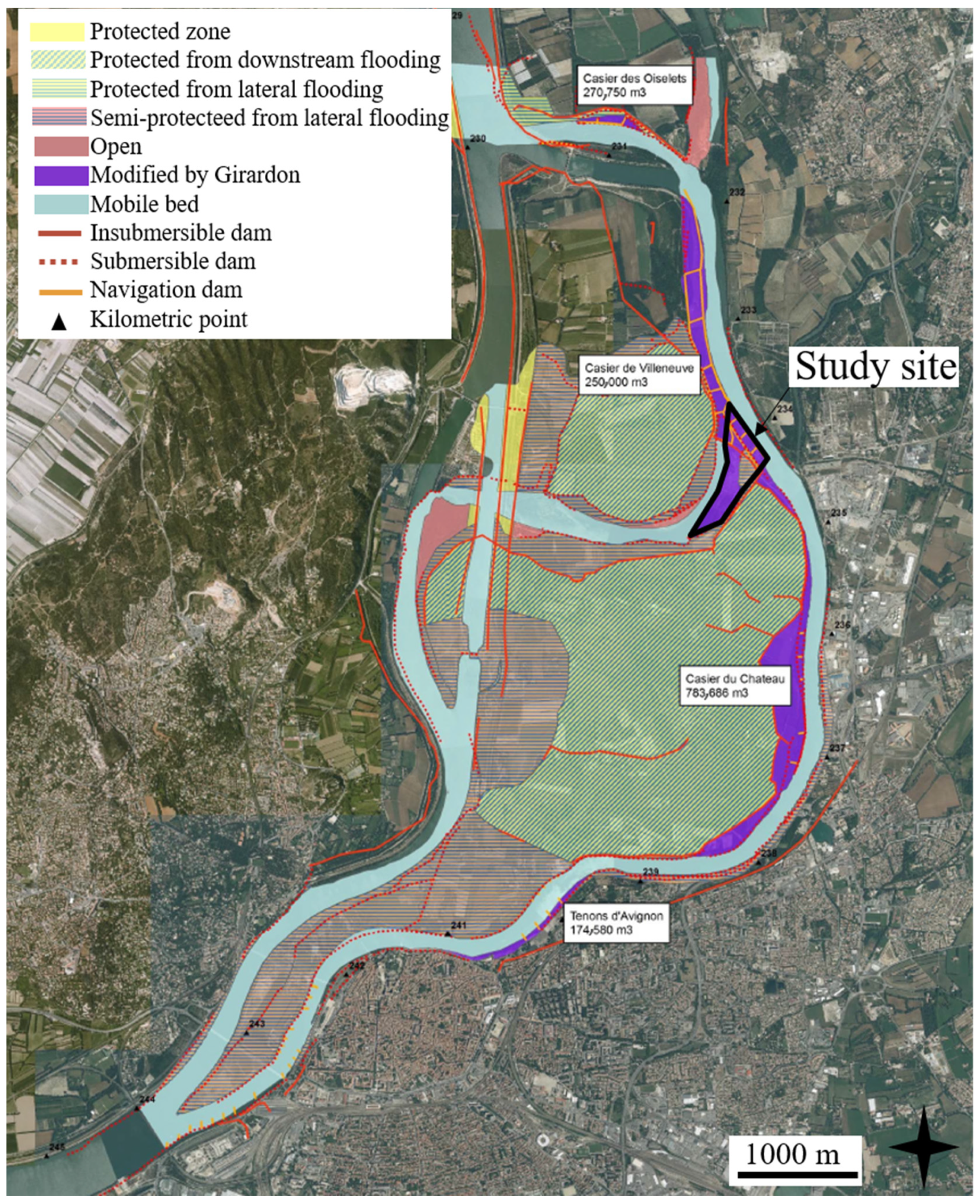
2.1.2. Complex Hydraulic Management
2.1.3. Geological Context
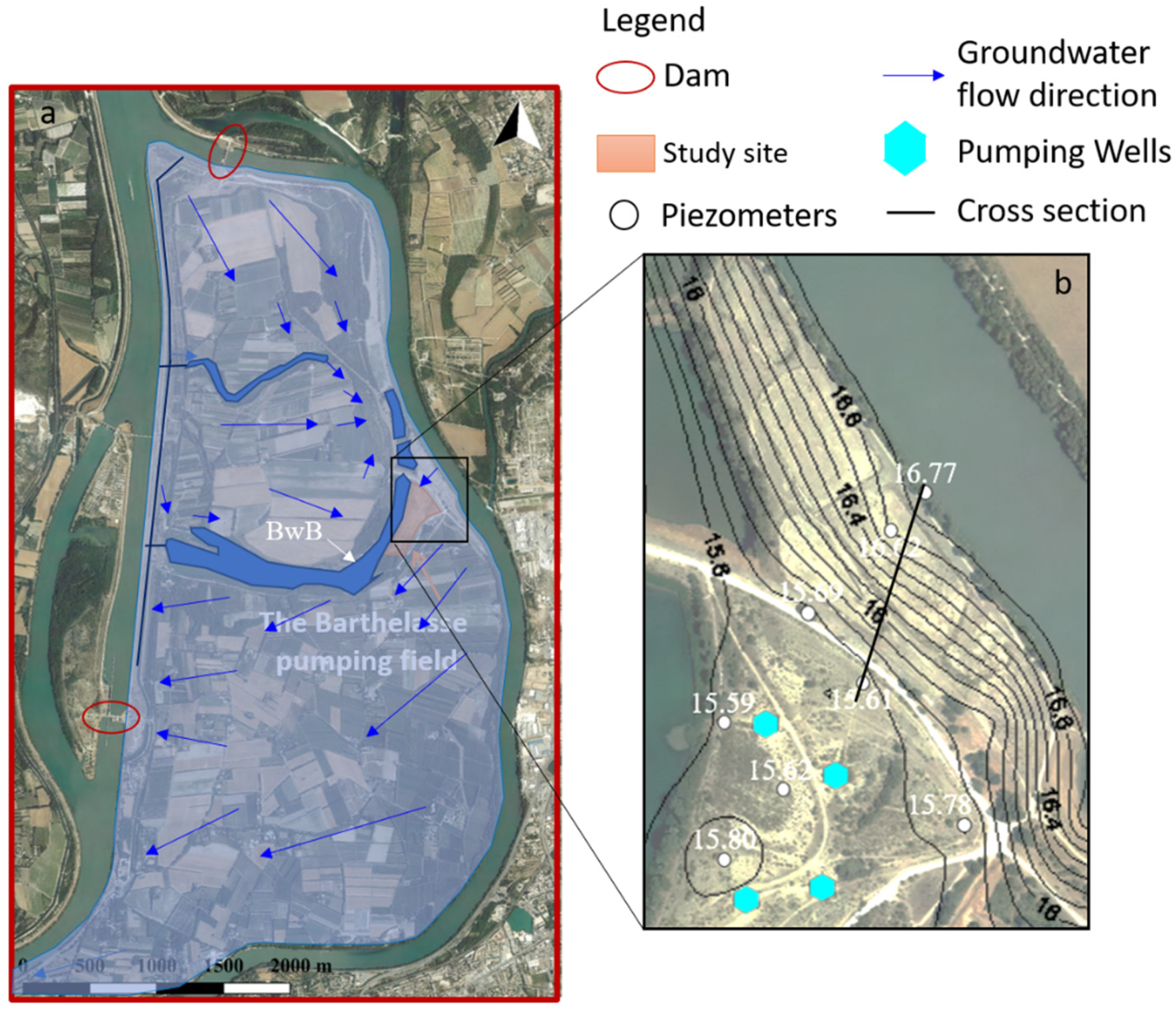
2.1.4. Hydrogeological Background
2.2. Theory
2.2.1. Lumped Parameter Models
2.2.2. Validation
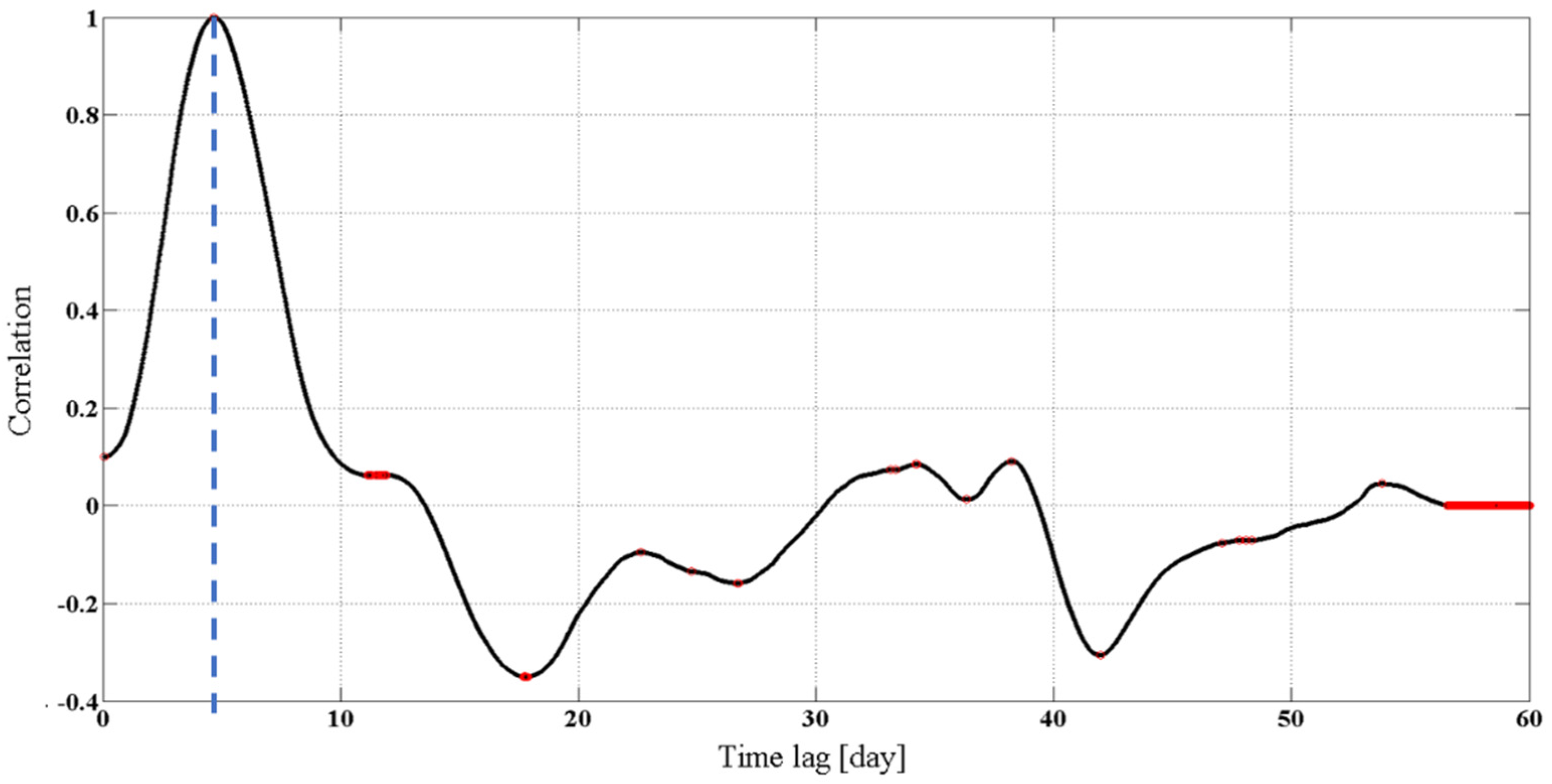
2.2.3. Cross-Correlation Analysis EC
3. Results
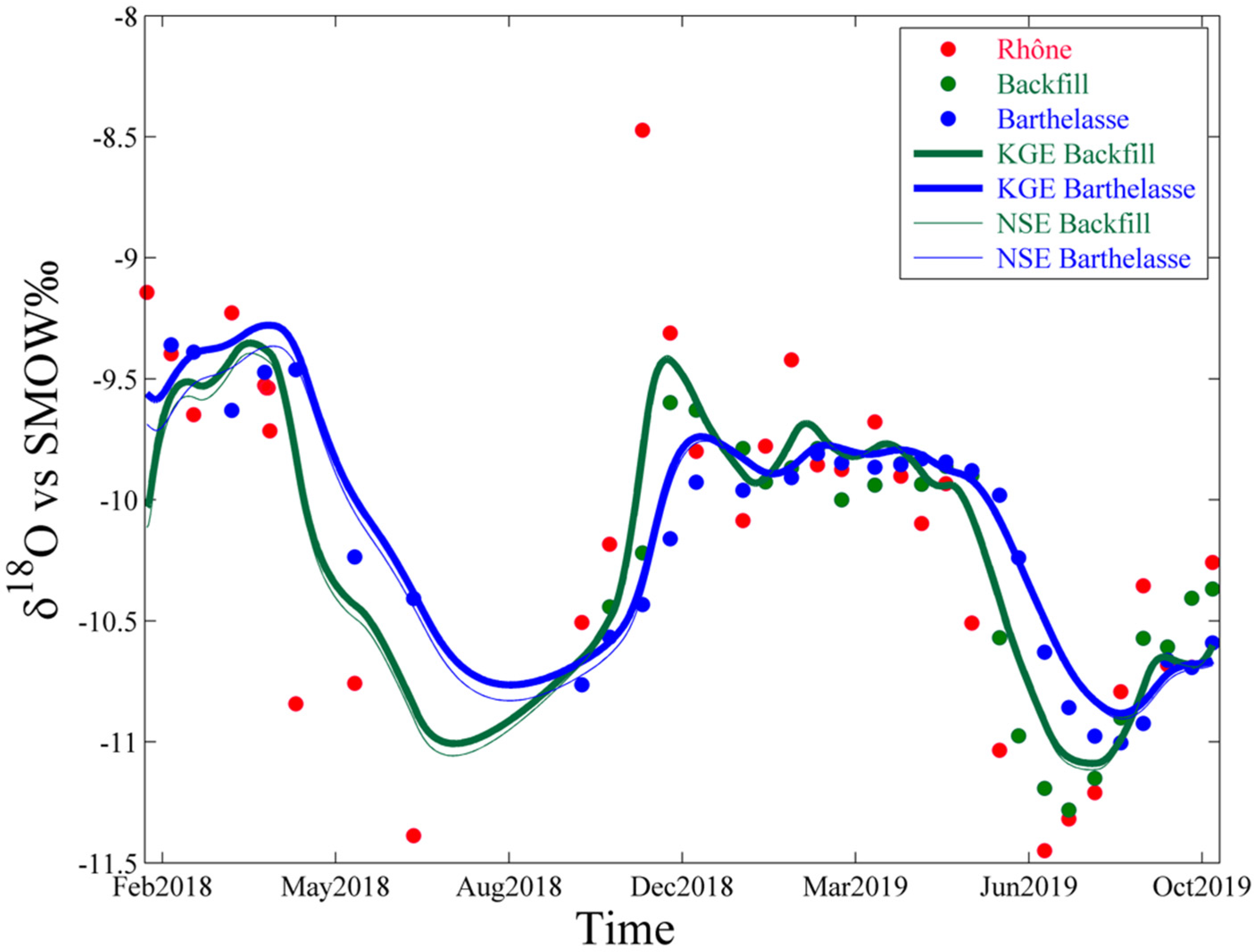
3.1. Annual Scale Monitoring
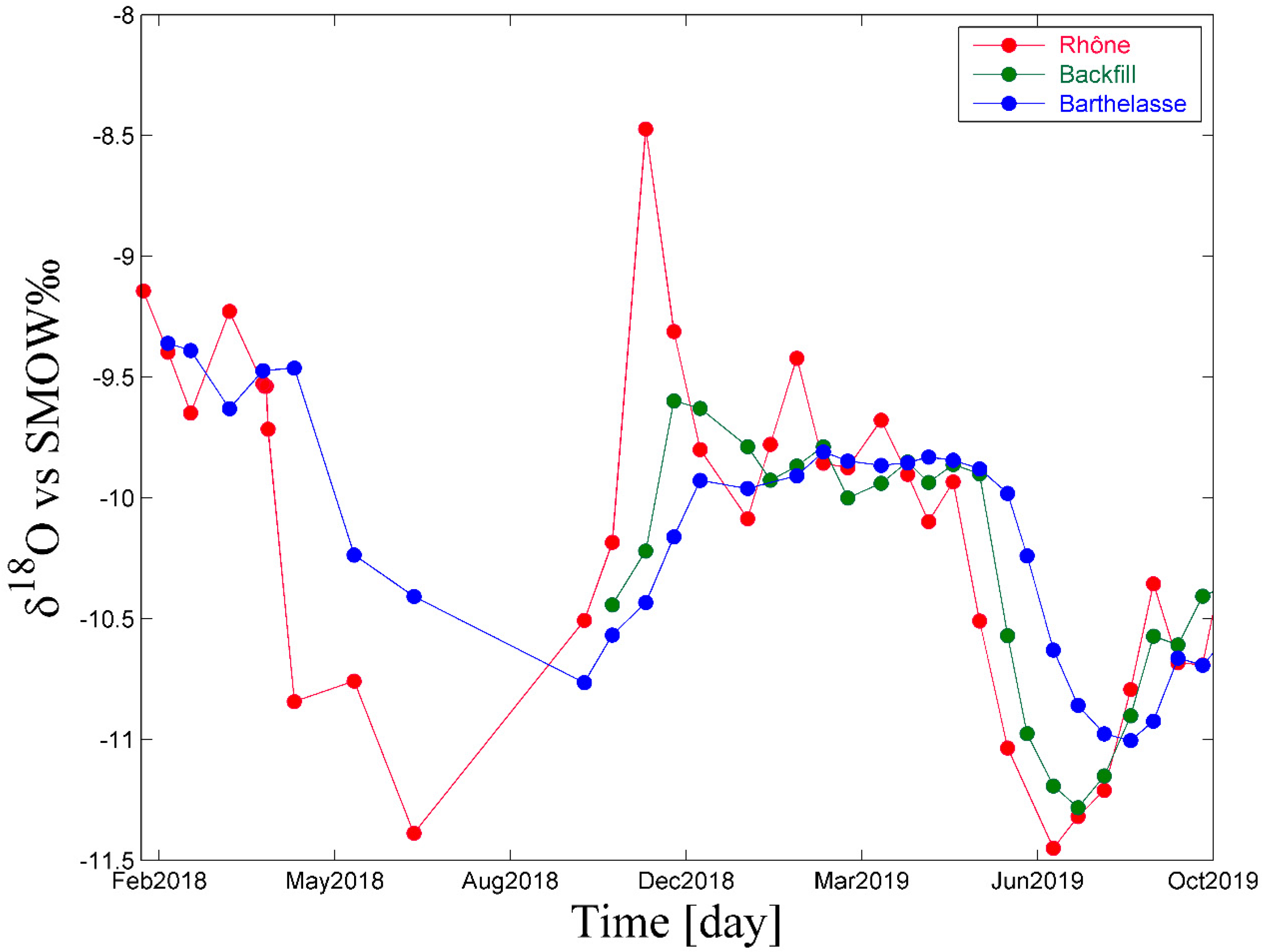
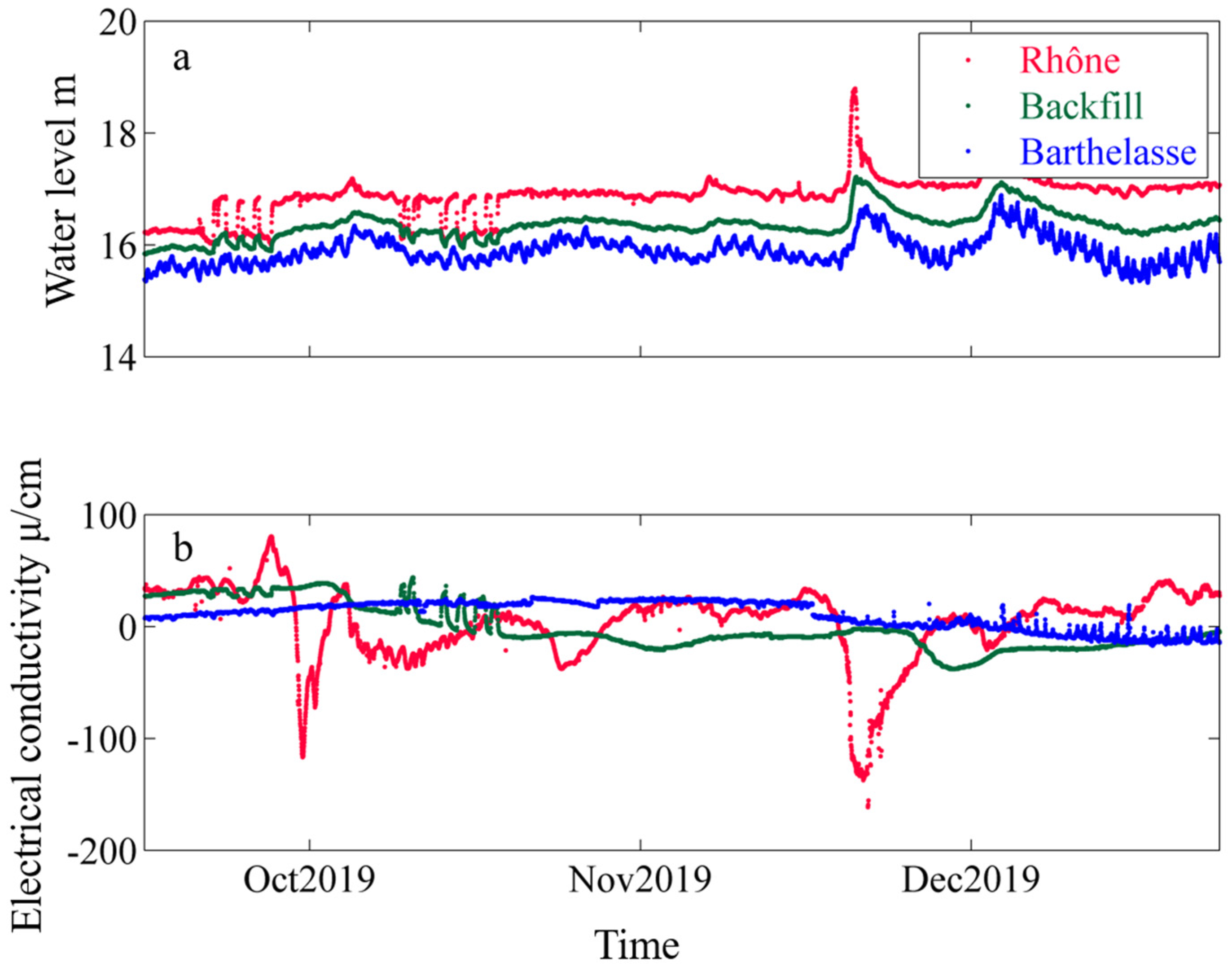
3.1.1. Isotopic Variations over Time
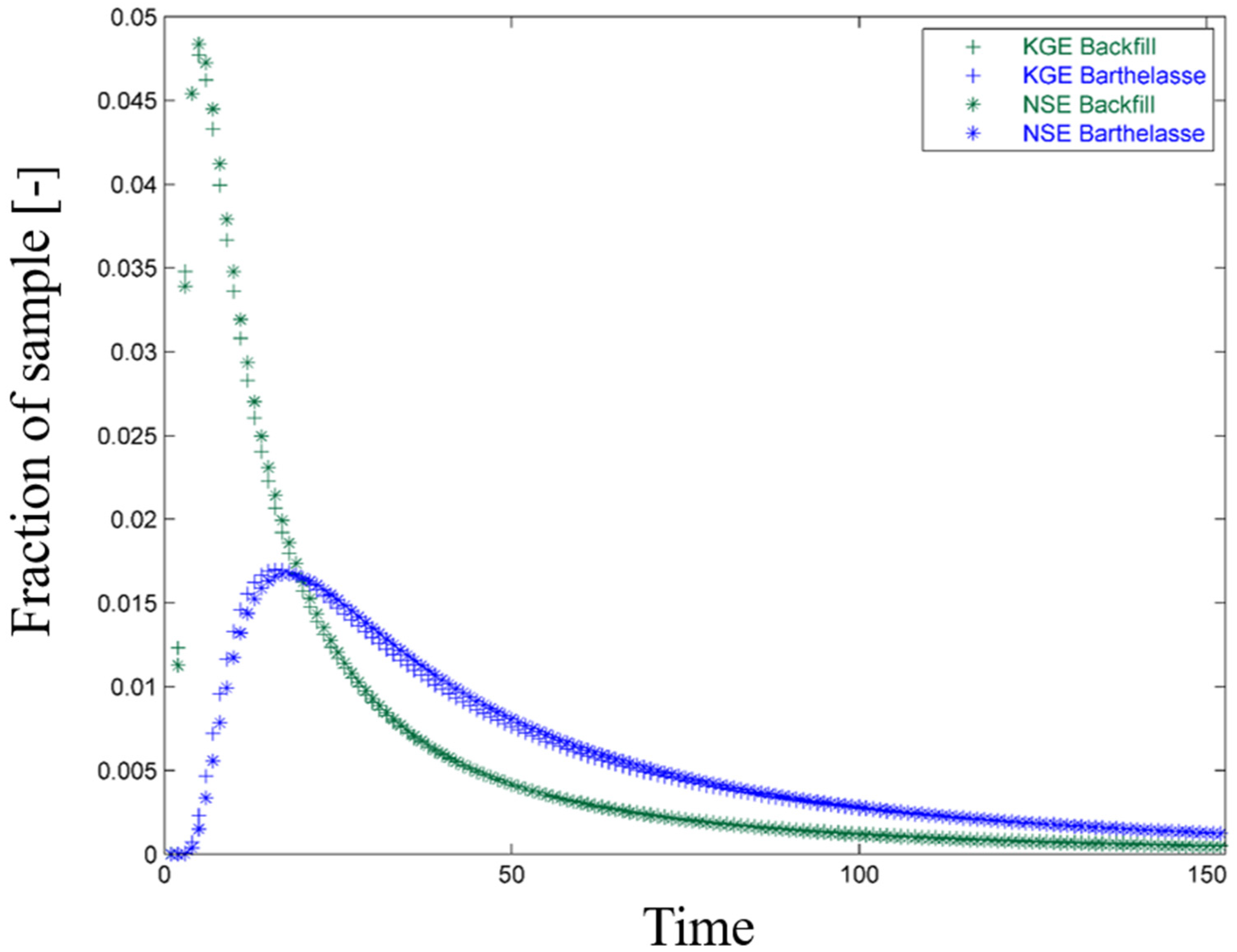
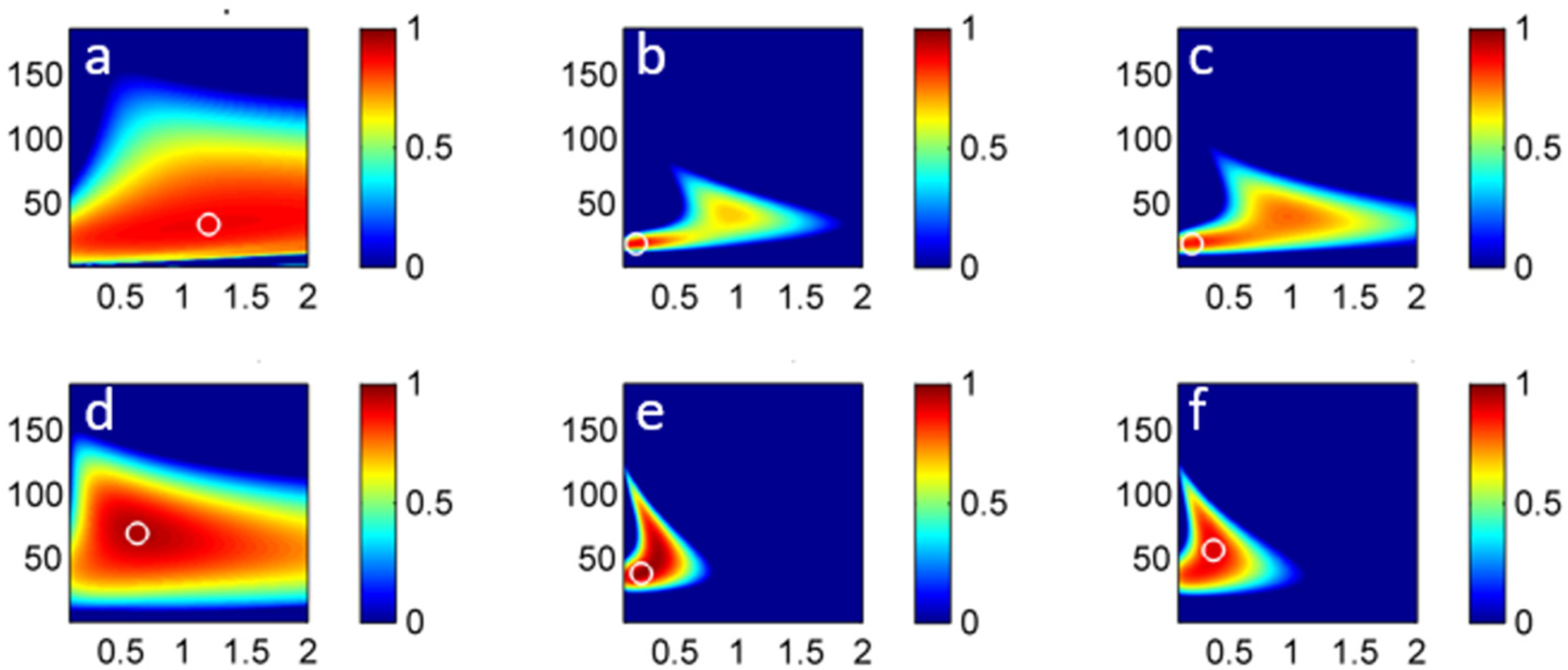
3.1.2. Applications of Lumped Parameters Models
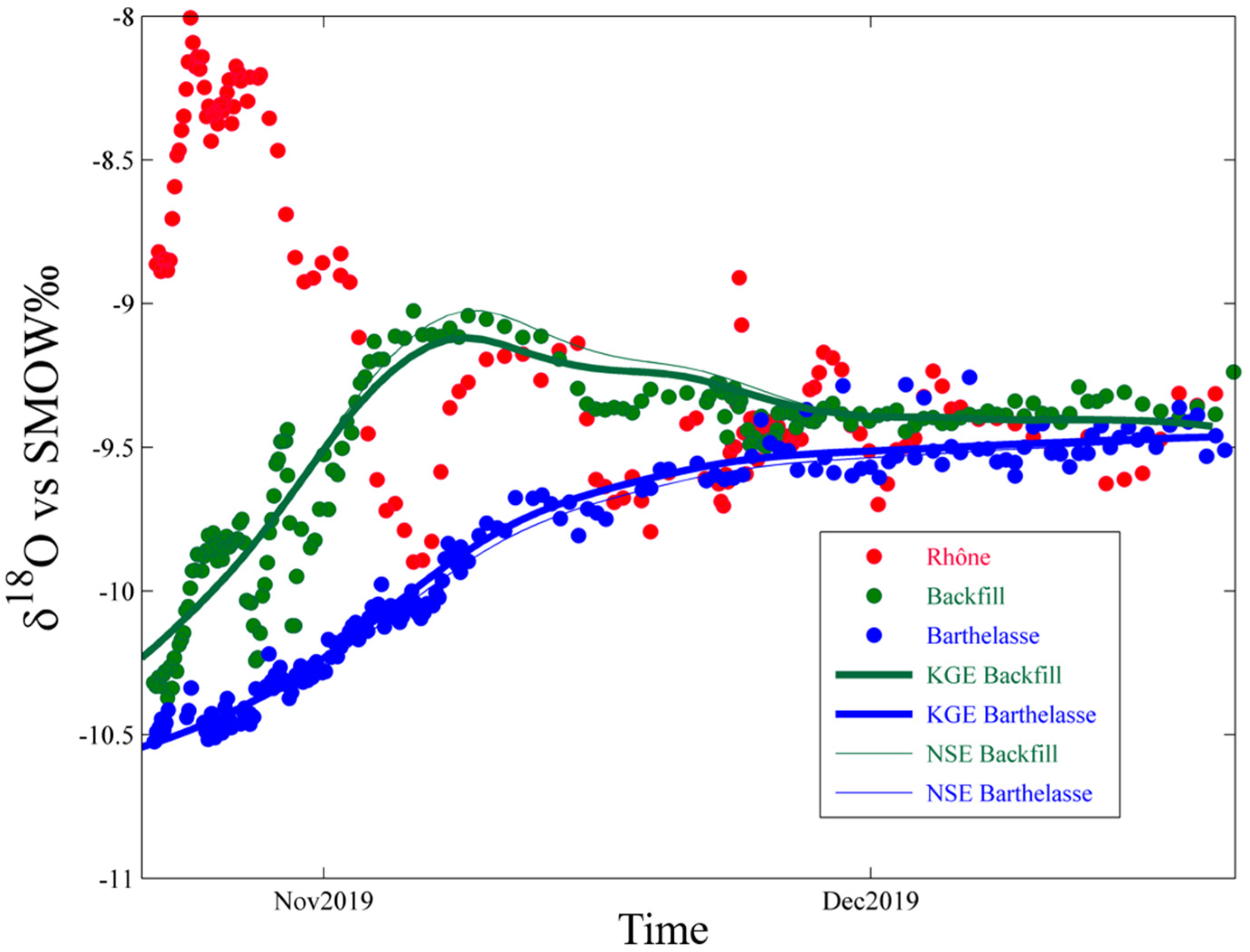
3.2. Event Scale Monitoring
3.2.1. Isotopic Variations over Time
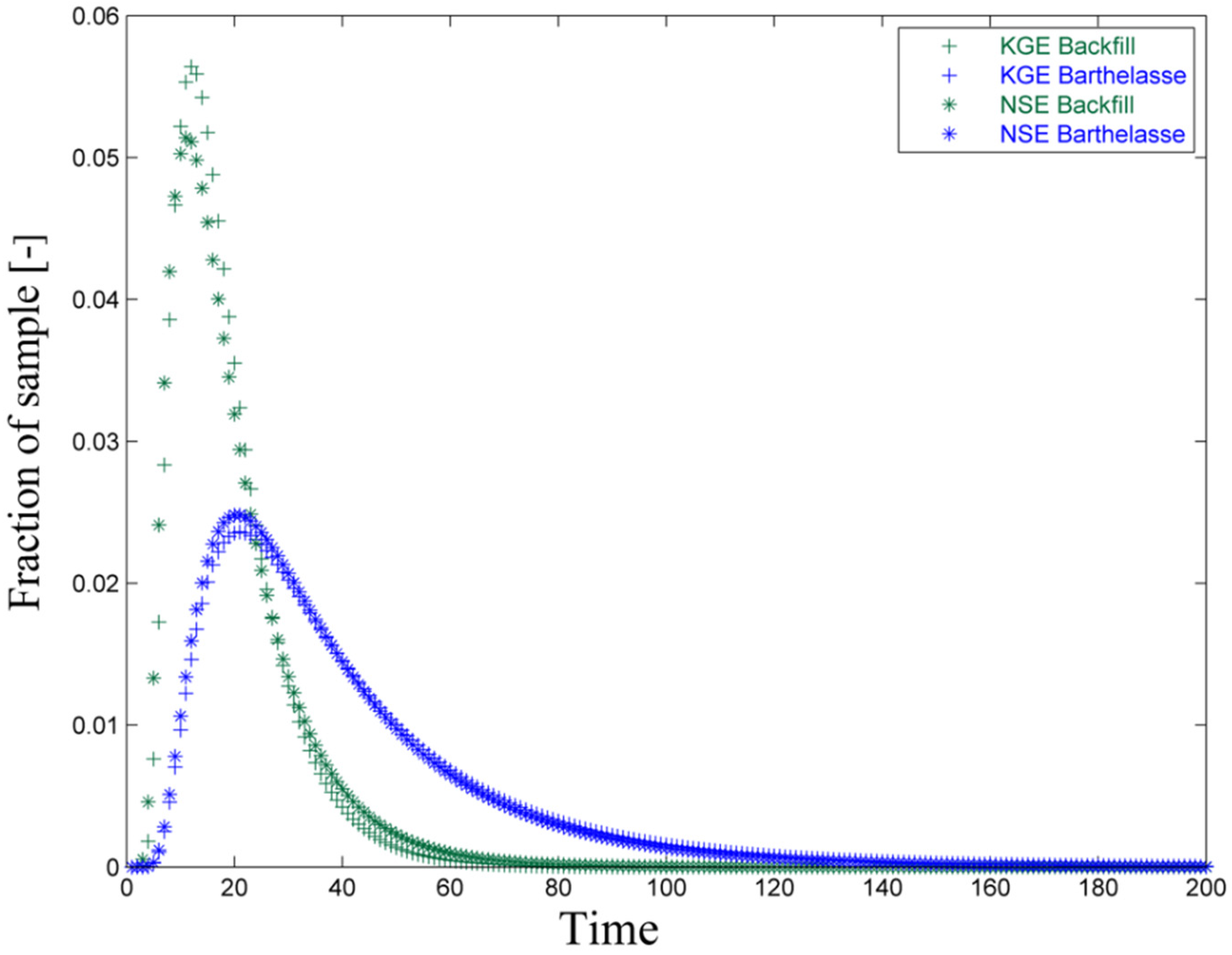
3.2.2. Applications of Lumped Parameters Models
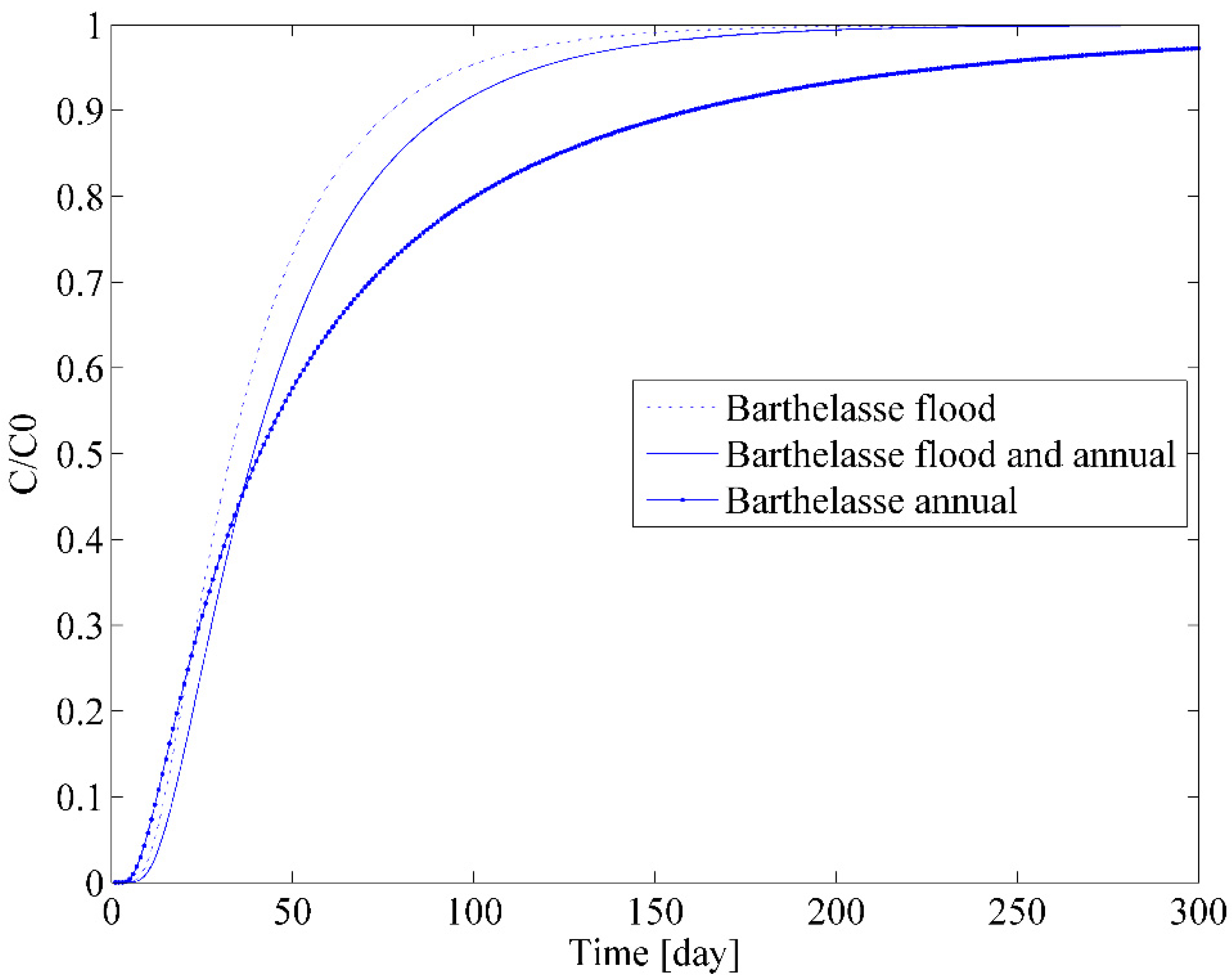
3.3. Combining Annual Scale and Event Scale Monitoring
3.4. EC Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Vulnerability of the Pumping Field and Role of the Backfill
4.2. Rhône Dynamics and Impact on Sampling Frequency
4.3. Choice of Optimisation Criteria
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hérivaux, C.; Maréchal, J.-C. Prise En Compte Des Services Dépendants Des Aquifères Dans Les Démarches d’évaluation Des Services Écosystémiques—Rapport Final; BRGM (Bureau de Recherches géologiques et minières) (Bureau de Recherches géologiques et minières): Orléans, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand, G.; Siergieiev, D.; Ala-Aho, P.; Rossi, P.M. Environmental Tracers and Indicators Bringing Together Groundwater, Surface Water and Groundwater-Dependent Ecosystems: Importance of Scale in Choosing Relevant Tools. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 813–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, I.D.; Fritz, P. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997; ISBN 978-1-56670-249-2. [Google Scholar]
- Das, B.K.; Kakar, Y.P.; Moser, H.; Stichler, W. Deuterium and Oxygen-18 Studies in Groundwater of the Delhi Area, India. J. Hydrol. 1988, 98, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herczeg, A.L.; Barnes, C.J.; Macumber, P.G.; Olley, J.M. A Stable Isotope Investigation of Groundwater-Surface Water Interactions at Lake Tyrrell, Victoria, Australia. Chem. Geol. 1992, 96, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, B.G.; Coplen, T.B.; Bullen, T.D.; Davis, J.H. Use of Chemical and Isotopic Tracers to Characterize the Interactions Between Ground Water and Surface Water in Mantled Karst. Groundwater 1997, 35, 1014–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloszewski, P. Lumped-Parameter Models as a Tool for Determining the Hydrological Parameters of Some Groundwater Systems Based on Isotope Data; IAHS Publication, IAHS, UKCEH: Wallingford, UK, 2000; Volume 262, pp. 271–276. [Google Scholar]
- Maloszewski, P.; Külls, C.; Leibundgut, C. Tracers in Hydrology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-1-119-96501-5. [Google Scholar]
- Stichler, W.; Maloszewski, P.; Bertleff, B.; Watzel, R. Use of Environmental Isotopes to Define the Capture Zone of a Drinking Water Supply Situated near a Dredge Lake. J. Hydrol. 2008, 362, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Su, X.; Dai, Z.; Yang, F.; Zhu, P.; Huang, Y. Multi-Tracer Investigation of River and Groundwater Interactions: A Case Study in Nalenggele River Basin, Northwest China. Hydrogeol. J. 2017, 25, 2015–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kármán, K.; Maloszewski, P.; Deák, J.; Fórizs, I.; Szabó, C. Transit Time Determination for a Riverbank Filtration System Using Oxygen Isotope Data and the Lumped-Parameter Model. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2014, 59, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloszewski, P.; Zuber, A. Lumped Parameter Models for the Interpretation of Environmental Tracer Data. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/etdeweb/biblio/439998 (accessed on 27 February 2020).
- Marçais, J.; Gauvain, A.; Labasque, T.; Abbott, B.W.; Pinay, G.; Aquilina, L.; Chabaux, F.; Viville, D.; de Dreuzy, J.-R. Dating Groundwater with Dissolved Silica and CFC Concentrations in Crystalline Aquifers. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jafari, T.; Kiem, A.S.; Javadi, S.; Nakamura, T.; Nishida, K. Using Insights from Water Isotopes to Improve Simulation of Surface Water-Groundwater Interactions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 798, 149253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fórizs, I.; Berecz, T.; Molnár, Z.; Süveges, M. Origin of shallow groundwater of Csepel Island (south of Budapest, Hungary, River Danube): Isotopic and chemical approach. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 3299–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.P. Heat as a Ground Water Tracer. Groundwater 2005, 43, 951–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirpka, O.A.; Fienen, M.N.; Hofer, M.; Hoehn, E.; Tessarini, A.; Kipfer, R.; Kitanidis, P.K. Analyzing Bank Filtration by Deconvoluting Time Series of Electric Conductivity. Groundwater 2007, 45, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoehn, E. Hydrogeological Issues of Riverbank Filtration—A Review. In Riverbank Filtration: Understanding Contaminant Biogeochemistry and Pathogen Removal; Ray, C., Ed.; NATO Science Series; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 17–41. ISBN 978-94-010-0479-4. [Google Scholar]
- Sheets, R.A.; Darner, R.A.; Whitteberry, B.L. Lag Times of Bank Filtration at a Well Field, Cincinnati, Ohio, USA. J. Hydrol. 2002, 266, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, T.; Hoehn, E.; Schneider, P.; Cirpka, O.A. Investigation of bank filtration in gravel and sand aquifers using time-series analysis. Grundwasser 2009, 14, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dudley-Southern, M.; Binley, A. Temporal Responses of Groundwater-Surface Water Exchange to Successive Storm Events. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 1112–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- González-Pinzón, R.; Ward, A.S.; Hatch, C.E.; Wlostowski, A.N.; Singha, K.; Gooseff, M.N.; Haggerty, R.; Harvey, J.W.; Cirpka, O.A.; Brock, J.T. A Field Comparison of Multiple Techniques to Quantify Groundwater–Surface-Water Interactions. Freshw. Sci. 2015, 34, 139–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slater, L.D.; Ntarlagiannis, D.; Day-Lewis, F.D.; Mwakanyamale, K.; Versteeg, R.J.; Ward, A.; Strickland, C.; Johnson, C.D.; Lane, J.W. Use of Electrical Imaging and Distributed Temperature Sensing Methods to Characterize Surface Water–Groundwater Exchange Regulating Uranium Transport at the Hanford 300 Area, Washington. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unland, N.P.; Cartwright, I.; Andersen, M.S.; Rau, G.C.; Reed, J.; Gilfedder, B.S.; Atkinson, A.P.; Hofmann, H. Investigating the Spatio-Temporal Variability in Groundwater and Surface Water Interactions: A Multi-Technique Approach. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 3437–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slimani, R.; Guendouz, A.; Trolard, F.; Moulla, A.S.; Hamdi-Aïssa, B.; Bourrié, G. Identification of Dominant Hydrogeochemical Processes for Groundwaters in the Algerian Sahara Supported by Inverse Modeling of Chemical and Isotopic Data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 1669–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AERMC Nappe Alluviale Du Rhône Identification et Protection Des Ressources En Eau Souterraine Majeures Pour l’alimentation En Eau Potable. Volume 3. (Télécharger Le Document). Available online: https://www.eaurmc.fr/jcms/dma_40370/fr/nappe-alluviale-du-rhone-identification-et-protection-des-ressources-en-eau-souterraine-majeures-pour-l-alimentation-en-eau-potable-volume-3 (accessed on 18 August 2021).
- Nofal, S. Étude Du Fonctionnement Hydrodynamique de La Nappe Alluviale d’Avignon: Impact de l’usage Du Sol Sur Les Mécanismes de Recharge. Ph.D. Thesis, Avignon Unisersité, Avignon, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Nofal, S.; Travi, Y.; Cognard-Plancq, A.-L.; Marc, V. Impact of Infiltrating Irrigation and Surface Water on a Mediterranean Alluvial Aquifer in France Using Stable Isotopes and Hydrochemistry, in the Context of Urbanization and Climate Change. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 2211–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulain, A.; Marc, V.; Gillon, M.; Mayer, A.; Cognard-Plancq, A.-L.; Simler, R.; Babic, M.; Leblanc, M. Enhanced Pumping Test Using Physicochemical Tracers to Determine Surface-Water/Groundwater Interactions in an Alluvial Island Aquifer, River Rhône, France. Hydrogeol. J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentric, J.; Langumier, J. Inondations des villes, inondations des champs: Norme et territoire dans la prévention des inondations sur l’île de la Barthelasse (Avignon). Nat. Sci. Soc. 2009, 17, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Räpple, B. Patrons de sédimentation et Caractéristiques de la Ripisylve dans les Casiers Girardon du Rhône: Approche Comparative Pour une Analyse des Facteurs de Contrôle et une évaluation des Potentialités écologiques. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Lyon, Lyon, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Thorel, M.; Piégay, H.; Barthelemy, C.; Räpple, B.; Gruel, C.-R.; Marmonier, P.; Winiarski, T.; Bedell, J.-P.; Arnaud, F.; Roux, G.; et al. Socio-Environmental Implications of Process-Based Restoration Strategies in Large Rivers: Should We Remove Novel Ecosystems along the Rhône (France)? Reg. Environ. Chang. 2018, 18, 2019–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaydou, P. Schéma Directeur de Réactivation de la Dynamique Fluviale des Marges du Rhône; CNRS: Lyon, France, 2013; p. 79. [Google Scholar]
- Abiven, R.; Blavoux, B. Dir. de thèse Etude Hydrochimique Du Fer et Du Manganèse Dans l’aquifère Alluvial d’Avignon (Vaucluse); France. 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Gourdin, T. Champ de Captage de l’île de La Motte Pompage d’essai, Résultats, Interprétation; France. 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River Flow Forecasting through Conceptual Models Part I—A Discussion of Principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.V.; Kling, H.; Yilmaz, K.K.; Martinez, G.F. Decomposition of the Mean Squared Error and NSE Performance Criteria: Implications for Improving Hydrological Modelling. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogata, A.; Banks, R.B. A Solution of the Differential Equation of Longitudinal Dispersion in Porous Media: Fluid Movement in Earth Materials; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Etchevers, P.; Golaz, C.; Habets, F. Simulation of the Water Budget and the River Flows of the Rhone Basin from 1981 to 1994. J. Hydrol. 2001, 244, 60–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golaz-Cavazzi, C. Modelisation Hydrologique a l’echelle Regionale Appliquee Au Bassin Du Rhone: Comparaison de Deux Modes de Calcul Des Bilans Hydriques de Surface et Etude de Sensibilite a Une Perturbation Des Forcages Climatiques; ENMP: Paris, France, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Golaz-Cavazzi, C.; Etchevers, P.; Habets, F.; Ledoux, E.; Noilhan, J. Comparison of Two Hydrological Simulations of the Rhone Basin. Phys. Chem. Earth Part B Hydrol. Ocean. Atmos. 2001, 26, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, S.; Hannah, D.M.; Fleckenstein, J.H.; Heppell, C.M.; Kaeser, D.; Pickup, R.; Pinay, G.; Robertson, A.L.; Wood, P.J. Inter-Disciplinary Perspectives on Processes in the Hyporheic Zone. Ecohydrology 2011, 4, 481–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oudin, L.; Andréassian, V.; Mathevet, T.; Perrin, C.; Michel, C. Dynamic Averaging of Rainfall-Runoff Model Simulations from Complementary Model Parameterizations. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpalatha, R.; Perrin, C.; Moine, N.; Andréassian, V. A Review of Efficiency Criteria Suitable for Evaluating Low-Flow Simulations. J. Hydrol. 2012, 420, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vos, N.J.; Rientjes, T.H.M.; Gupta, H.V. Diagnostic Evaluation of Conceptual Rainfall–Runoff Models Using Temporal Clustering. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 2840–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Backfill | Barthelasse | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dp | τs(j) | Criterion | Dp | τs(j) | Criterion | |
| RMSE | 0.99 | 12 | 0.18 | 0.5 | 61 | 0.11 |
| KGE | 1.4 | 38 | 0.94 | 0.75 | 74 | 0.97 |
| NSE | 1.21 | 34 | 0.88 | 0.4 | 70 | 0.95 |
| Backfill | Barthelasse | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dp | τs(j) | Criterion | Dp | τs(j) | Criterion | |
| RMSE | 0.18 | 20 | 0.09 | 0.23 | 40 | 0.06 |
| KGE | 0.15 | 18 | 0.93 | 0.25 | 41 | 0.99 |
| NSE | 0.20 | 19 | 0.88 | 0.24 | 39 | 0.97 |
| Transect | Rhône-Backfill | Rhône-Barthelasse | Backfill- Barthelasse | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flood | Annual | Both | Flood | Annual | Both | Flood | Annual | Both | |
| Effective Velocity (m/d) | 3.72 | 1.76 | 3.35 | 4.02 | 2.35 | 3.37 | 4.26 | 2.72 | 3.38 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poulain, A.; Marc, V.; Gillon, M.; Cognard-Plancq, A.-L.; Simler, R.; Babic, M.; Leblanc, M. Multi Frequency Isotopes Survey to Improve Transit Time Estimation in a Situation of River-Aquifer Interaction. Water 2021, 13, 2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192695
Poulain A, Marc V, Gillon M, Cognard-Plancq A-L, Simler R, Babic M, Leblanc M. Multi Frequency Isotopes Survey to Improve Transit Time Estimation in a Situation of River-Aquifer Interaction. Water. 2021; 13(19):2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192695
Chicago/Turabian StylePoulain, Angélique, Vincent Marc, Marina Gillon, Anne-Laure Cognard-Plancq, Roland Simler, Milanka Babic, and Marc Leblanc. 2021. "Multi Frequency Isotopes Survey to Improve Transit Time Estimation in a Situation of River-Aquifer Interaction" Water 13, no. 19: 2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192695
APA StylePoulain, A., Marc, V., Gillon, M., Cognard-Plancq, A.-L., Simler, R., Babic, M., & Leblanc, M. (2021). Multi Frequency Isotopes Survey to Improve Transit Time Estimation in a Situation of River-Aquifer Interaction. Water, 13(19), 2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13192695







