Hydrological Performance of Green Roofs in Mediterranean Climates: A Review and Evaluation of Patterns
Abstract
:1. Introduction
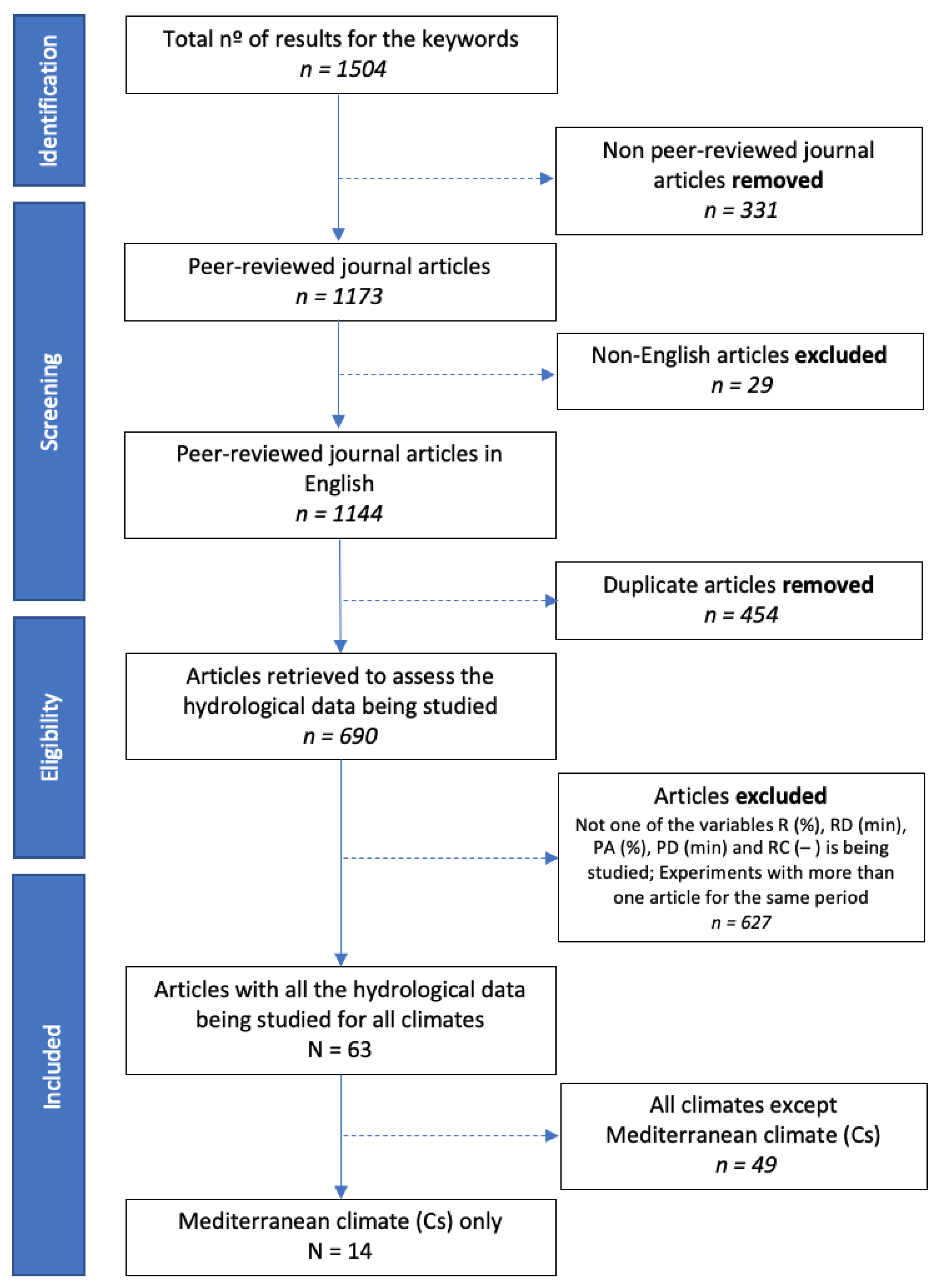
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Focus
- (a)
- Rainfall retention (R, %)
- (b)
- Runoff delay (RD, min)
- (c)
- Peak attenuation (PA, %)
- (d)
- Peak delay (PD, min)
- (e)
- Runoff coefficient (RC, −)
2.2. Methods of Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2. Statistical Analysis
3.2.1. Univariate Analysis
- Categorical variables
- Continuous variables
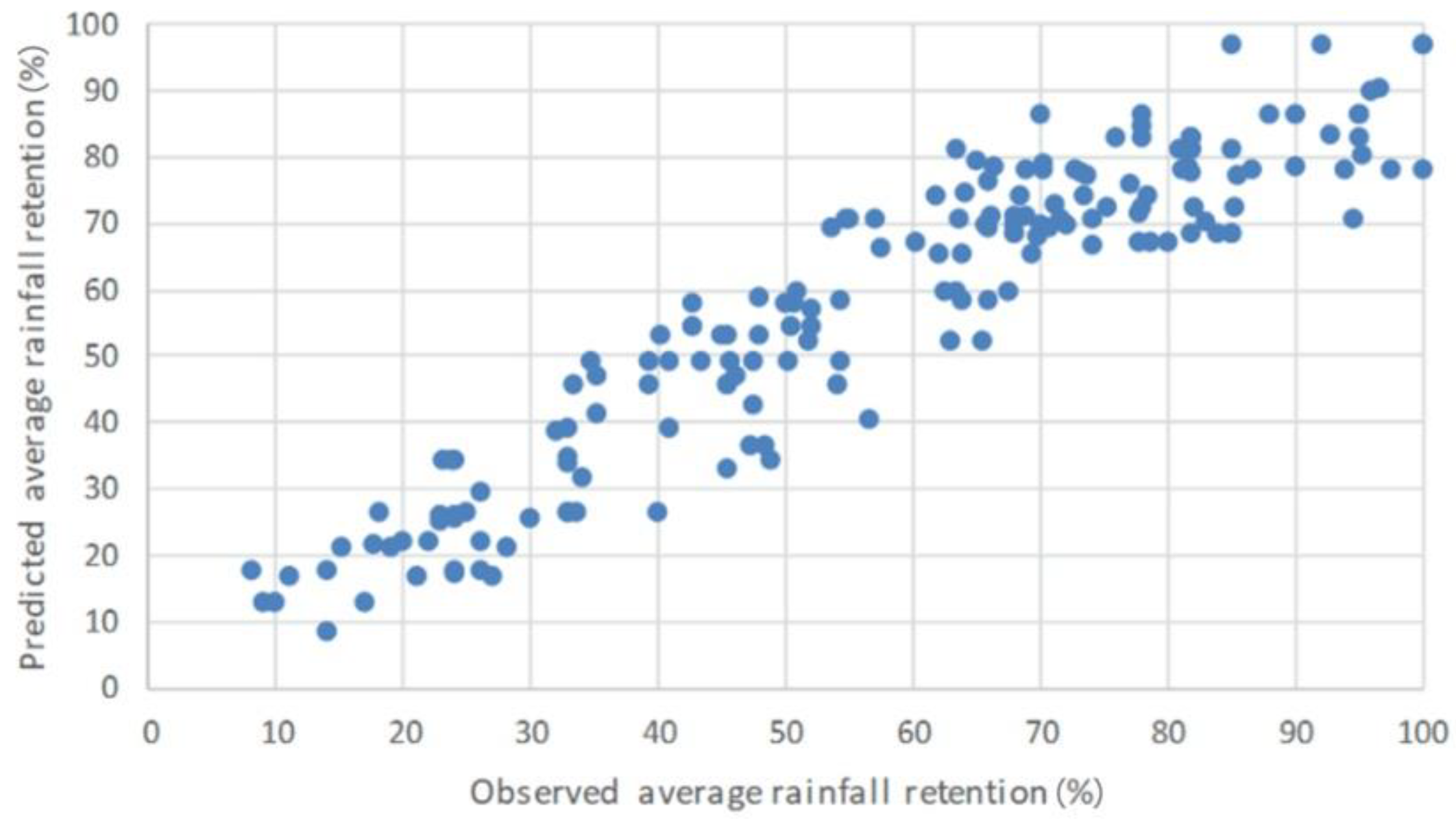
3.2.2. Multivariate Analysis
4. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Categorical Variables | No. of Groups | Groups | Parametric Statistical Test | Nonparametric Statistical Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate (Köppen–Geiger) | 2 | Csa | t-test | Wilcoxon |
| Csb | ||||
| System | 2 | Modules | t-test | Wilcoxon |
| Complete green roof | ||||
| Protection board (root barrier) | 2 | Yes | t-test | Wilcoxon |
| No | ||||
| Waterproofing layer | 2 | Yes | t-test | Wilcoxon |
| No | ||||
| Filtration layer (Geotextile) | 2 | Yes | t-test | Wilcoxon |
| No | ||||
| Substrate depth class | 3 | Class 1 (0–149 mm) | ANOVA | Kruskal–Wallis |
| Class 2 (150–249 mm) | ||||
| Class 3 (≥250 mm) | ||||
| Type of vegetation | 3 | Sedums and other succulents | ANOVA | Kruskal–Wallis |
| Perennial herbaceous plants and grasses | ||||
| Both | ||||
| Native | 3 | Native | ANOVA | Kruskal–Wallis |
| Not native | ||||
| Both | ||||
| Slope class | 3 | Class 1 (0–1.50%) | ANOVA | Kruskal–Wallis |
| Class 2 (1.51–8.80%) | ||||
| Class 3 (>8.80%) | ||||
| Type of green roof | 3 | Extensive | ANOVA | Kruskal–Wallis |
| Semi-intensive | ||||
| Intensive |
| Categorical Variables | Groups | w | p-Value | Hypothesis Testing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate (Köppen–Geiger) | Csa | 0.9663 | 0.2342 | H0 |
| Csb | 0.8798 | 0.0017 | H1 | |
| System | Modules | 0.9794 | 0.4247 | H0 |
| Complete green roof | 0.8068 | 0.0019 | H1 | |
| Root barrier | Yes | 0.9737 | 0.2383 | H0 |
| No | 0.8440 | 0.0068 | H1 | |
| Waterproofing layer | Yes | 0.9711 | 0.2150 | H0 |
| No | 0.8217 | 0.0011 | H1 | |
| Filtration layer (Geotextile) | Yes | 0.9486 | 0.0052 | H1 |
| No | 0.9588 | 0.7715 | H0 | |
| Substrate depth class | Class 1 | 0.9613 | 0.1457 | H0 |
| Class 2 | 0.9294 | 0.1064 | H0 | |
| Class 3 | 0.8891 | 0.2297 | H0 | |
| Type of vegetation | Perennial herbaceous plants and grasses | 0.9620 | 0.4323 | H0 |
| Sedums and other succulents | 0.9379 | 0.4307 | H0 | |
| Both | 0.8883 | 0.0037 | H1 | |
| Native | Native | 0.9712 | 0.3618 | H0 |
| Not native | 0.9348 | 0.4341 | H0 | |
| Both | 0.8899 | 0.0668 | H0 | |
| Slope class | Class 1 | 0.8922 | 0.0422 | H1 |
| Class 2 | 0.9763 | 0.6027 | H0 | |
| Type of green roof | Extensive | 0.9628 | 0.0870 | H0 |
| Semi-intensive | 0.9221 | 0.2674 | H0 | |
| Intensive | 0.8891 | 0.2297 | H0 |
| Categorical Variables | Groups | w | p-Value | Hypothesis Testing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate (Köppen–Geiger) | Csa | 0.8175 | 0.1117 | H0 |
| Csb | 0.9305 | 0.5837 | H0 | |
| Waterproofing layer | Yes | 0.9211 | 0.5130 | H0 |
| No | 0.7144 | 0.0135 | H1 | |
| Filtration layer (Geotextile) | Yes | 0.9766 | 0.9412 | H0 |
| No | 0.7267 | 0.0228 | H1 |
| Categorical Variables | Groups | w | p-Value | Hypothesis Testing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate (Köppen–Geiger) | Csa | 0.9721 | 0.4030 | H0 |
| Csb | 0.9348 | 0.6294 | H0 | |
| System | Modules | 0.9813 | 0.7643 | H0 |
| Complete green roof | 0.8171 | 0.0435 | H1 | |
| Waterproofing layer | Yes | 0.9820 | 0.7639 | H0 |
| No | 0.8874 | 0.3048 | H0 | |
| Type of vegetation | Perennial herbaceous plants and grasses | 0.9618 | 0.4998 | H0 |
| Sedums and other succulents | 0.9220 | 0.2667 | H0 | |
| Both | 0.9828 | 0.9488 | H0 | |
| Slope class | Class 1 | 0.8909 | 0.2796 | H0 |
| Class 2 | 0.9697 | 0.4538 | H0 |
| Rainfall Retention (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Categorical Variables | F value | Pr(>F) | hypothesis testing |
| Substrate depth class | 4.7389 | 0.0117 | H1 |
| Native | 2.1371 | 0.1261 | H0 |
| Type of green roof | 6.5091 | 0.0025 | H1 |
| Peak Attenuation (%) | |||
| Categorical Variables | F value | Pr(>F) | hypothesis testing |
| Climate (Köppen–Geiger) | 0.0277 | 0.8715 | H0 |
| Runoff Coefficient (−) | |||
| Categorical Variables | F value | Pr(>F) | hypothesis testing |
| Climate (Köppen–Geiger) | 0.6624 | 0.4201 | H0 |
| Waterproofing layer | 3.7784 | 0.0583 | H0 |
| Type of vegetation | 0.5702 | 0.5702 | H0 |
| Slope class | 1.7115 | 0.1985 | H0 |
| Continuous Variables | w | p-Value | Hypothesis Testing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rainfall retention (%) | 0.9487 | 0.0039 | H1 |
| Peak attenuation (%) | 0.9207 | 0.3244 | H0 |
| Runoff coefficient (‒) | 0.9715 | 0.3153 | H0 |
| Avg monthly precipitation (mm) | 0.8326 | 2.68 × 10−6 | H1 |
| SD monthly precipitation (mm) | 0.8852 | 9.10 × 10−5 | H1 |
| Avg monthly temperature (°C) | 0.8789 | 5.73 × 10−5 | H1 |
| SD monthly temperature (°C) | 0.9322 | 0.004458 | H1 |
| Substrate depth (mm) | 0.7904 | 3.02 × 10−9 | H1 |
| Plant coverage (%) | 0.8296 | 5.44 × 10−5 | H1 |
| Slope (%) | 0.5603 | 1.17 × 10−12 | H1 |
| Variables | Groups |
|---|---|
| Climate (Köppen–Geiger) | Am; BSh; BSk; Cfa; Cfb; Csa; Csb; Cwa; Dfa; Dfb; Dfc; Dwa; Dwb |
| System | Modules; complete green roof |
| Protection board (root barrier) | Yes; No |
| Waterproofing layer | Yes; No |
| Filtration layer (Geotextile) | Yes; No |
| Drainage layer | Yes; No |
| Substrate depth class | Class 1 (0–149 mm); class 2 (150–249 mm); class 3 (≥250 mm) |
| Type of vegetation | Sedums and other succulents; perennial herbaceous plants and grasses; both |
| Origin | Native; not native; both |
| Climate type | 1–real conditions; 2–simulated |
| Season | Spring; Summer; Fall; Winter; All; All except Winter; All except Summer; Spring/Summer; Summer/Fall; Fall/Winter; Winter/Spring; None |
| Author (Year) | ALocation |
|---|---|
| Razzaghmanesh and Beecham (2014) [44] | Adelaide, Australia |
| Beecham and Razzaghmanesh (2015) [13] | Adelaide, Australia |
| Brandão et al. (2017) [14] | Lisbon, Portugal |
| Palermo et al. (2019) [8] | Rende, Italy |
| Palla et al. (2011) [39] | Genoa, Italy |
| Andrés-Doménech et al. (2018) [11] | Benaguasil, Valencia, Spain |
| Piro et al. (2018) [42] | Rende, Italy |
| Soulis et al. (2017a) [52] | Athens, Greece |
| Soulis et al. (2017b) [53] | Athens, Greece |
| Garofalo et al. (2016) [6] | Rende, Italy |
| Schultz et al. (2018) [46] | Portland, Oregon, USA |
| Buccola and Spolek (2010) [15] | Portland, Oregon, USA |
| Schroll et al. (2011) [45] | Corvallis, Oregon, USA |
| Gnecco et al. (2013) [21] | Genoa, Italy |
References
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. The World’s Cities in 2018—Data Booklet (ST/ESA/ SER.A/417). 2018. Available online: https://digitallibrary.un.org/record/3799524 (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Jha, A.K.; Bloch, R.; Lamond, J. World Bank. Cities and Flooding: A Guide to Integrated Urban Flood Risk Management for the 21st Century. 2012. Available online: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/2241.
- Drobinski, P.; Ducrocq, V.; Alpert, P.; Anagnostou, E.; Béranger, K.; Borga, M.; Braud, I.; Chanzy, A.; Davolio, S.; Delrieu1, G.; et al. HYMEX, a 10-year Multidisciplinary Program on the mediterranean water cycle. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 1063–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Kong, F.; Dronova, I. Hydrological performance of extensive green roofs in response to different rain events in a subtropical monsoon climate. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 15, 297–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipolla, S.S.; Maglionico, M.; Stojkov, I. A long-term hydrological modelling of an extensive green roof by means of SWMM. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 876–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, G.; Palermo, S.; Principato, F.; Theodosiou, T.; Piro, P. The Influence of Hydrologic Parameters on the Hydraulic Efficiency of an Extensive Green Roof in Mediterranean Area. Water 2016, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.G.; Silva, C.M.; Valadas, A.S. Impact of Vegetation, Substrate, and Irrigation on the Energy Performance of Green Roofs in a Mediterranean Climate. Water 2019, 11, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palermo, S.A.; Turco, M.; Principato, F.; Piro, P. Hydrological Effectiveness of an Extensive Green Roof in Mediterranean Climate. Water 2019, 11, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charalambous, K.; Bruggeman, A.; Eliades, M.; Camera, C.; Vassiliou, L. Stormwater Retention and Reuse at the Residential Plot Level—Green Roof Experiment and Water Balance Computations for Long-Term Use in Cyprus. Water 2019, 11, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peel, M.C.; Finlayson, B.L.; McMahon, T.A. Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrés-Doménech, I.; Perales-Momparler, S.; Morales-Torres, A.; Escuder-Bueno, I. Hydrological Performance of Green Roofs at Building and City Scales under Mediterranean Conditions. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abualfaraj, N.; Cataldo, J.; Elborolosy, Y.; Fagan, D.; Woerdeman, S.; Carson, T.; Montalto, F.A. Monitoring and Modeling the Long-Term Rainfall-Runoff Response of the Jacob K. Javits Center Green Roof. Water 2018, 10, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beecham, S.; Razzaghmanesh, M. Water quality and quantity investigation of green roofs in a dry climate. Water Res. 2015, 70, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, C.; Cameira, M.D.R.; Valente, F.; de Carvalho, R.C.; Paço, T.A. Wet season hydrological performance of green roofs using native species under Mediterranean climate. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 102, 596–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccola, N.; Spolek, G. A Pilot-Scale Evaluation of Greenroof Runoff Retention, Detention, and Quality. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 216, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burszta-Adamiak, E.; Mrowiec, M. Modelling of green roofs’ hydrologic performance using EPA’s SWMM. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, T.B.; Marasco, D.E.; Culligan, P.J.; McGillis, W.R. Hydrological performance of extensive green roofs in New York City: Observations and multi-year modeling of three full-scale systems. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 024036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, T.L.; Rasmussen, T.C. Hydrologic behavior of vegetated roofs. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2006, 42, 1261–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrans, P.; Rey, C.; Pérez, G.; Sánchez, J.P.; Díaz-Granados, M. Effect of Green Roof Configuration and Hydrological Variables on Runoff Water Quantity and Quality. Water 2018, 10, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Getter, K.L.; Rowe, D.B.; Andresen, J.A. Quantifying the effect of slope on extensive green roof stormwater retention. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 31, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnecco, I.; Palla, A.; Lanza, L.G.; Barbera, P.L. A green roof experimental site in the Mediterranean climate: The storm water quality issue. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 1419–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Yin, D.; Fang, X.; Zhai, D.; Li, J. Rainwater retention effect of extensive green roofs monitored under natural rain-fall events—A case study in Beijing. Hydrol. Res. 2018, 49, 1773–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Yin, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Fang, X.; Shi, H.; Wang, Q. Performance assessment of extensive green roof runoff flow and quality control capacity based on pilot experiments. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 687, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grard, B.J.; Chenu, C.; Manouchehri, N.; Houot, S.; Frascaria-Lacoste, N.; Aubry, C. Rooftop farming on urban waste provides many ecosystem services. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 38, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gregoire, B.G.; Clausen, J.C. Effect of a modular extensive green roof on stormwater runoff and water quality. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, G.E.; Limmer, M.A.; Showalter, W.E.; Burken, J.G. Nine-month evaluation of runoff quality and quantity from an experiential green roof in Missouri, USA. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 78, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathaway, A.M.; Hunt, W.F.; Jennings, G.D. A Field Study of Green Roof Hydrologic and Water Quality Performance. Trans. ASABE 2008, 51, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Liu, L.; Cao, J.; Chen, N.; Wang, Z. Water Resilience by Centipedegrass Green Roof: A Case Study. Buildings 2019, 9, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jelinkova, V.; Dohnal, M.; Sacha, J. Thermal and water regime studied in a thin soil layer of green roof systems at early stage of pedogenesis. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 2568–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannessen, B.G.; Muthanna, T.M.; Braskerud, B.C. Detention and Retention Behavior of Four Extensive Green Roofs in Three Nordic Climate Zones. Water 2018, 10, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kemp, S.; Hadley, P.; Blanuša, T. The influence of plant type on green roof rainfall retention. Urban Ecosyst. 2019, 22, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ladani, H.J.; Park, J.-R.; Jang, Y.-S.; Shin, H.-S. Hydrological Performance Assessment for Green Roof with Various Substrate Depths and Compositions. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 23, 1860–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Lee, M.J.; Han, M. A pilot study to evaluate runoff quantity from green roofs. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 152, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linden, K.V.; Stone, M. Treatment Performance of an Extensive Vegetated Roof in Waterloo, Ontario. Water Qual. Res. J. 2009, 44, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Feng, Q.; Chen, W.; Wei, W.; Deo, R.C. The influence of structural factors on stormwater runoff retention of exten-sive green roofs: New evidence from scale-based models and real experiments. J. Hydrol. 2019, 569, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiola, C.; Mary, W.; Silva, L.P. Hydrological performance of modular-tray green roof systems forincreasing the resilience of mega-cities to climate change. J. Hydrol. 2019, 573, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickovski, S.B.; Buss, K.; McKenzie, B.M.; Sökmener, B. Laboratory study on the potential use of recycled inert construction waste material in the substrate mix for extensive green roofs. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 61, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, R.; McDonald, A.; Postoyko, S. Hydrological performance of a full-scale extensive green roof located in a temperate climate. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 82, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palla, A.; Sansalone, J.J.; Gnecco, I.; Lanza, L. Storm water infiltration in a monitored green roof for hydrologic restoration. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pęczkowski, G.; Kowalczyk, T.; Szawernoga, K.; Orzepowski, W.; Żmuda, R.; Pokładek, R. Hydrological Performance and Runoff Water Quality of Experimental Green Roofs. Water 2018, 10, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perales-Momparler, S.; Andrés-Doménech, I.; Hernández-Crespo, C.; Vallés-Morán, F.; Martín, M.; Escuder-Bueno, I.; Andreu, J. The role of monitoring sustainable drainage systems for promoting transition towards regenerative urban built environments: A case study in the Valencian region, Spain. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 163, S113–S124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piro, P.; Carbone, M.; De Simone, M.; Maiolo, M.; Bevilacqua, P.; Arcuri, N. Energy and Hydraulic Performance of a Vegetated Roof in Sub-Mediterranean Climate. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qianqian, Z.; Liping, M.; Huiwei, W.; Long, W. Analysis of the effect of green roof substrate amended with biochar on water quality and quantity of rainfall runoff. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaghmanesh, M.; Beecham, S. The hydrological behaviour of extensive and intensive green roofs in a dry climate. Sci. Total. Environ. 2014, 499, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroll, E.; Lambrinos, J.; Righetti, T.; Sandrock, D. The role of vegetation in regulating stormwater runoff from green roofs in a winter rainfall climate. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, I.; Sailor, D.J.; Starry, O. Effects of substrate depth and precipitation characteristics on stormwater retention by two green roofs in Portland OR. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 18, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafique, M.; Kim, R.; Kyung-Ho, K. Green Roof for Stormwater Management in a Highly Urbanized Area: The Case of Seoul, Korea. Sustainability 2018, 10, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sherrard, J.A.; Jacobs, J.M. Vegetated Roof Water-Balance Model: Experimental and Model Results. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2012, 17, 858–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, A.W.; Robinson, C.E.; Smart, C.C.; Voogt, J.; Hay, G.J.; Lundholm, J.T.; Powers, B.; O’Carroll, D.M. Retention performance of green roofs in three different climate regions. J. Hydrol. 2016, 542, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, A.W.; Robinson, C.E.; Smart, C.C.; O’Carroll, D.M. Mechanisms controlling green roof peak flow rate attenuation. J. Hydrol. 2019, 577, 123972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skala, V.; Dohnal, M.; Votrubová, J.; Jelínková, V. The use of simple hydrological models to assess outflow of two green roofs systems. Soil Water Res. 2019, 14, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soulis, K.; Ntoulas, N.; Nektarios, P.A.; Kargas, G. Runoff reduction from extensive green roofs having different substrate depth and plant cover. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 102, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulis, K.X.; Valiantzas, J.D.; Ntoulas, N.; Kargas, G.; Nektarios, P.A. Simulation of green roof runoff under different substrate depths and vegetation covers by coupling a simple conceptual and a physically based hydrological model. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 200, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speak, A.; Rothwell, J.; Lindley, S.; Smith, C. Rainwater runoff retention on an aged intensive green roof. Sci. Total. Environ. 2013, 461–462, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stovin, V.; Vesuviano, G.; Kasmin, H. The hydrological performance of a green roof test bed under UK climatic conditions. J. Hydrol. 2012, 414-415, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stovin, V.; Poë, S.; De-Ville, S.; Berretta, C. The influence of substrate and vegetation configuration on green roof hydrological performance. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 85, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stovin, V. The potential of green roofs to manage Urban Stormwater. Water Environ. J. 2010, 24, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorov, D.; Driscoll, C.T.; Todorova, S. Long-term and seasonal hydrologic performance of an extensive green roof. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 2471–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Seters, T.; Rocha, L.; Smith, D.; Macmillan, G. Evaluation of Green Roofs for Runoff Retention, Runoff Quality, and Leachability. Water Qual. Res. J. 2009, 44, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanWoert, N.D.; Rowe, D.B.; Andresen, J.A.; Rugh, C.L.; Fernandez, R.T.; Xiao, L. Green Roof Stormwater Retention. J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal, E.L.; Bengtsson, L. Response of a Sedum green-roof to individual rain events. Ecol. Eng. 2005, 25, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voyde, E.; Fassman-Beck, E.; Simcock, R. Hydrology of an extensive living roof under sub-tropical climate conditions in Auckland, New Zealand. J. Hydrol. 2010, 394, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, X. The influence of dual-substrate-layer extensive green roofs on rainwater runoff quantity and quality. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 592, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittinghill, L.J.; Rowe, D.B.; Andresen, J.A.; Cregg, B.M. Comparison of stormwater runoff from sedum, native prairie, and vegetable producing green roofs. Urban Ecosyst. 2015, 18, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, G.K.; Jim, C. Quantitative hydrologic performance of extensive green roof under humid-tropical rainfall regime. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 70, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Miao, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, D.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, B.; Sun, J.; Liu, J. The capacity of greening roof to reduce stormwater runoff and pollution. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 144, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhong, X.; Che, W.; Sun, H.; Zhang, H. A laboratory study to determine the use of polluted river sediment as a substrate for extensive green roofs. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 2247–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Szota, C.; Fletcher, T.D.; Williams, N.S.; Farrell, C. Green roof storage capacity can be more important than evapotranspiration for retention performance. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author (Year) | No. of Experiments | Climate |
|---|---|---|
| Andrés-Doménech et al. (2018) [11] | 1 | Csa |
| Abualfaraj et al. (2018) [12] | 1 | Cfa |
| Beecham, Razzaghmanesh (2015) [13] | 12 | Csb |
| Brandão et al. (2017) [14] | 3 | Csa |
| Buccola, Spolek (2010) [15] | 2 | Csb |
| Burszta-Adamiak, Mrowiec (2013) [16] | 3 | Dfb |
| Carson et al. (2013) [17] | 3 | Cfa |
| Carter, Rasmussen (2006) [18] | 1 | Cfa |
| Charalambous et al. (2019) [9] | 4 | BSh |
| Cipolla et al. (2016) [5] | 1 | Cfa |
| Ferrans et al. (2018) [19] | 6 | Cfb |
| Garofalo et al. (2016) [6] | 5 | Csa |
| Getter et al. (2007) [20] | 4 | Dfb |
| Gnecco et al. (2013) [21] | 1 | Csb |
| Gong et al. (2018) [22] | 7 | Dfa |
| Gong et al. (2019) [23] | 5 | Dfa |
| Grard et al. (2018) [24] | 2 | Cfb |
| Gregoire, Clausen (2011) [25] | 1 | Dfb |
| Harper et al. (2015) [26] | 2 | Cfa |
| Hathaway et al. (2008) [27] | 2 | Cfa |
| Hu et al. (2019) [28] | 1 | Cfa |
| Jelinkova et al. (2016) [29] | 2 | Dfb |
| Johannessen et al. (2018) [30] | 32 | Cfb; Dfb; Dfc |
| Kemp et al. (2018) [31] | 4 | Cfb |
| Ladani et al. (2019) [32] | 3 | Cfa |
| Lee et al. (2015) [33] | 2 | Dwa |
| Linden, Stone (2009) [34] | 1 | Dfb |
| Liu et al. (2019) [35] | 9 | Dwb |
| Loiola et al. (2019) [36] | 3 | Am |
| Mickovski et al. (2013) [37] | 3 | Cfb |
| Nawaz et al. (2015) [38] | 4 | Cfb |
| Palermo et al. (2019) [8] | 1 | Csa |
| Palla et al. (2011) [39] | 2 | Csb |
| Peczkowski et al. (2018) [40] | 2 | Dfb |
| Perales-Momparler et al. (2017) [41] | 1 | BSk |
| Piro et al. (2018) [42] | 1 | Csa |
| Qianqian et al. (2019) [43] | 2 | Dwa |
| Razzaghmanesh, Beecham (2014) [44] | 4 | Csb |
| Schroll et al. (2011) [45] | 4 | Csb |
| Schultz et al. (2018) [46] | 10 | Csb |
| Shafique et al. (2018) [47] | 1 | Dwa |
| Sherrard Jr., Jacobs (2012) [48] | 1 | Dfb |
| Sims et al. (2016) [49] | 3 | Dfb; Dfc |
| Sims et al. (2019) [50] | 2 | Dfb |
| Skala et al. (2019) [51] | 2 | Cfb |
| Soulis et al. (2017a) [52] | 30 | Csa |
| Soulis et al. (2017b) [53] | 4 | Csa |
| Speak et al. (2013) [54] | 5 | Cfb |
| Stovin et al. (2012) [55] | 5 | Cfb |
| Stovin et al. (2015) [56] | 2 | Cfb |
| Stovin, Virginia (2010) [57] | 1 | Cfb |
| Todorov et al. (2018) [58] | 1 | Dfb |
| Van Seters et al. (2009) [59] | 3 | Dfa |
| VanWoert et al. (2005) [60] | 4 | Dfb |
| Villarreal, Bengtsson (2005) [61] | 3 | Dfb |
| Voyde et al. (2010) [62] | 10 | Cfb |
| Wang et al. (2017) [63] | 7 | Dfa |
| Whittinghill et al. (2015) [64] | 3 | Dfb |
| Wong, Jim (2014) [65] | 20 | Cwa |
| Yin et al. (2019) [4] | 2 | Cfa |
| Zhang et al. (2015) [66] | 1 | Cwa |
| Zhang et al. (2018) [67] | 9 | Dfa |
| Zhang et al. (2019) [68] | 5 | Cfb |
| Categorical Variables | Groups |
|---|---|
| Climate (Köppen–Geiger) | Csa |
| Csb | |
| System | Modules |
| Complete green roof | |
| Protection board (root-barrier) | Yes |
| No | |
| Waterproofing layer | Yes |
| No | |
| Filtration layer (geotextile) | Yes |
| No | |
| Substrate depth class | Class 1 (0–149 mm) |
| Class 2 (150–249 mm) | |
| Class 3 (≥250 mm) | |
| Type of vegetation | Sedums and other succulents |
| Perennial herbaceous plants and grasses | |
| Both | |
| Native | Native |
| Not native | |
| Both | |
| Slope class | Class 1 (0–1.50%) |
| Class 2 (1.51–8.80%) | |
| Class 3 (>8.80%) | |
| Type of green roof | Extensive |
| Semi-intensive | |
| Intensive |
| Continuous Variables | Units |
|---|---|
| Avg monthly precipitation | mm |
| SD monthly precipitation | mm |
| Avg monthly temperature | °C |
| SD monthly temperature | °C |
| Substrate depth | mm |
| Plant coverage | % |
| Slope | % |
| Statistics | R (%) | RD (Min) | PA (%) | PD (Min) | RC (−) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 62.38% | 503.2 | 75.29% | 344.3 | 0.39 | ||
| Min | 13.98% | 52.10 | 44.30% | 29.4 | 0.00 | |
| Max | 100.00% | 1537.5 | 93.20% | 1132.0 | 0.86 | |
| 23.74% | 515.9 | 14.92% | 399.9 | 0.23 | ||
| Md | 66.99% | 184.1 | 74.40% | 143.7 | 0.37 | |
| Q1 | 46.85% | 141.9 | 66.30% | 45.2 | 0.22 | |
| Q3 | 81.52% | 1059.4 | 90.80% | 748.7 | 0.51 | |
| MAD | 21.66% | 453.1 | 12.08% | 335.9 | 0.19 | |
| Shapiro–Wilk test results | w | 0.9487 | 0.7694 | 0.9182 | 0.7509 | 0.9710 |
| p-value | 0.0040 | 0.0060 | 0.3035 | 0.0084 | 0.3013 | |
| hypothesis testing | H1 | H1 | H0 | H1 | H0 | |
| No. of articles | 12 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 7 | |
| No. of experiments | 76 | 10 | 11 | 8 | 46 | |
| Categorical Variables | Test | Populations | p-Value | Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate (Köppen–Geiger)–R (%) | Wilcoxon | nCsa = 43 | 0.8463 | The distributions of Csa R (%) and Csb R (%) are not significantly different |
| nCsb = 33 | ||||
| Climate (Köppen–Geiger)–PA (%) | t-test | nCsa = 5 | 0.3201 | There is not a statistically significant difference in mean PA (%) between groups |
| nCsb = 6 | ||||
| Climate (Köppen–Geiger)–RC (−) | t-test | nCsa = 41 | 0.6480 | There is not a statistically significant difference in mean RC (−) between groups |
| nCsb = 5 | ||||
| System–R (%) | Wilcoxon | nmodules = 58 | 5.28 × 10−7 | The distributions of modules R (%) and complete green roof R (%) are significantly different |
| ncomplete = 18 | ||||
| System–RC (−) | Wilcoxon | nmodules = 38 ncomplete = 8 | 0.0011 | The distributions of modules RC (−) and complete green roof RC (−) are significantly different |
| ncomplete = 8 | ||||
| Protection board (root barrier)–R (%) | Wilcoxon | nRTYes = 58 | 4.74 × 10−6 | The distributions of Yes R (%) and No R (%) are significantly different |
| nRTNo = 18 | ||||
| Waterproofing layer–R (%) | Wilcoxon | nWLYes = 54 | 0.3107 | The distributions of Yes R (%) and No R (%) are not significantly different |
| nWLNo = 22 | ||||
| Waterproofing layer–PA (%) | Wilcoxon | nWLYes = 6 | 0.0358 | The distributions of Yes PA (%) and No PA (%) are significantly different |
| nWLNo = 5 | ||||
| Waterproofing layer–RC (−) | t-test | nWLYes = 40 | 8.75 × 10−7 | There is a statistically significant difference in mean RC (−) between groups |
| nWLNo = 6 | ||||
| Filtration layer (Geotextile)–R (%) | Wilcoxon | nFLYes = 72 | 0.4852 | The distributions of Yes R (%) and No R (%) are not significantly different |
| nFLNo = 4 | ||||
| Filtration layer (Geotextile)–PA (%) | Wilcoxon | nFLYes = 7 | 0.0472 | The distributions of Yes PA (%) and are significantly different PA (%) are significantly different |
| nFLNo = 4 | ||||
| Substrate depth Class–R (%) | Kruskal–Wallis | nSubClass1 = 44 | 0.0002 | The difference between the groups medians R (%) is statistically significant |
| nSubClass2 = 23 | ||||
| nSubClass3 = 8 | ||||
| Type of vegetation–R (%) | Kruskal–Wallis | nSedums = 13 | 0.5482 | The difference between the groups medians R (%) is not statistically significant |
| nPerennial = 26 | ||||
| nBoth = 31 | ||||
| Type of vegetation–RC (−) | ANOVA | nSedums = 13 | 0.3010 | There is not a statistically significant difference between groups mean RC (−) |
| nPerennial = 23 | ||||
| nBoth = 5 | ||||
| Native–R (%) | ANOVA | nNative = 42 | 1.96 × 10−7 | There is a statistically significant difference between groups mean R (%) |
| nNotnative = 12 | ||||
| nBoth = 15 | ||||
| Slope Class–R (%) | Wilcoxon | nSlopeClass1 = 18 | 0.1996 | The distributions of class 1 R (%) and class 2 R (%) are not significantly different |
| nSlopeClass2 = 37 | ||||
| Slope Class–RC (−) | t-test | nSlopeClass1 = 7 | 9.04 × 10−7 | There is a statistically significant difference in mean RC (−) between groups |
| nSlopeClass2 = 34 | ||||
| Type of Green roof–R (%) | Kruskal–Wallis | nSExtensive = 55 | 1.61 × 10−5 | The difference between the groups medians R (%) is statistically significant |
| nSemi = 13 | ||||
| nIntensive = 8 |
| Variables | Test | Results | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rainfall retention (%) − Substrate depth class | Multiple pairwise comparison between groups | Class 1 | Class 2 | |
| Class 2 | 0.0153 | - | ||
| Class 3 | 0.0011 | 0.0157 | ||
| Rainfall retention (%) − Type of green roof | Multiple pairwise comparison between groups | Extensive | Intensive | |
| Intensive | 0.0007 | - | ||
| Semi-intensive | 0.0011 | 0.1578 | ||
| Rainfall retention (%) − Native | Tukey multiple comparisons of means | Native | Both | |
| Both | 2.00 × 10−7 | - | ||
| Not native | 0.0133 | 0.0670 | ||
| Continuous Variables | R (%) | PA (%) | RC (−) |
|---|---|---|---|
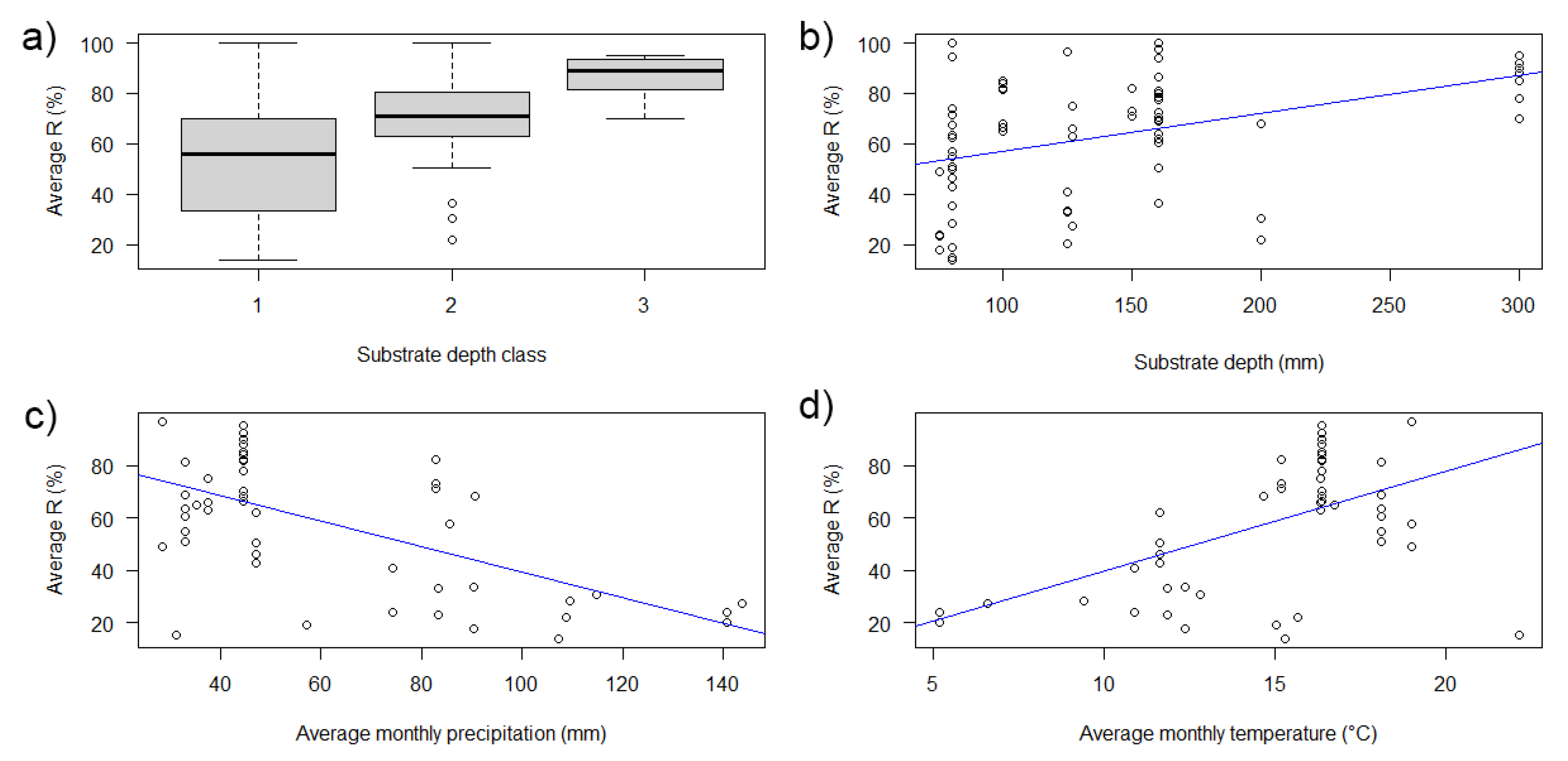
| Avg monthly precipitation (mm) | −0.4764 | 0.3335 | 0.4889 |
| SD monthly precipitation (mm) | −0.2843 | 0.04228 | 0.1767 |
| Avg monthly temperature (°C) | 0.4837 | −0.6060 | −0.3649 |
| SD monthly temperature (°C) | 0.2645 | −0.4181 | −0.4395 |
| Substrate depth (mm) | 0.4883 | 0.1301 | −0.4020 |
| Plant coverage (%) | 0.2587 | - | −0.2875 |
| Slope (%) | 0.2824 | - | - |
| Model | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
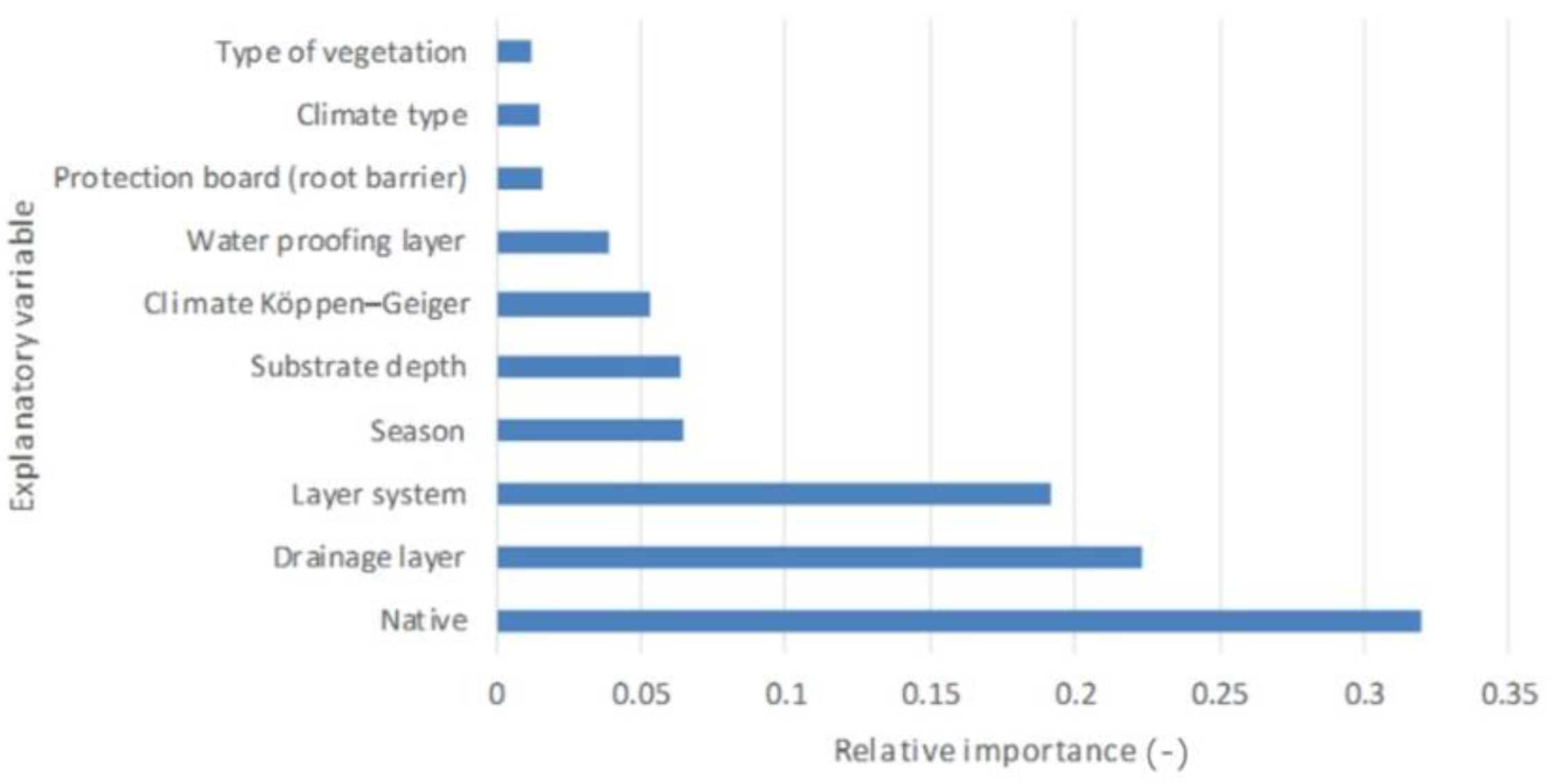
| Regression | 88,339.074 | 14 | 6309.934 | 79.115 | 0.000 |
| Native | 16,727.339 | 3 | 5575.780 | 69.910 | 0.000 |
| Drainage layer | 11,665.995 | 1 | 11,665.995 | 146.270 | 0.000 |
| Layer system | 10,042.667 | 1 | 10,042.667 | 125.916 | 0.000 |
| Season | 3390.489 | 2 | 1695.244 | 21.255 | 0.000 |
| Substrate depth | 3365.394 | 1 | 3365.394 | 42.196 | 0.000 |
| Climate Köppen–Geiger | 2773.797 | 1 | 2773.797 | 34.778 | 0.000 |
| Waterproofing layer | 2052.609 | 1 | 2052.609 | 25.736 | 0.000 |
| Protection board (root barrier) | 819.601 | 1 | 819.601 | 10.276 | 0.002 |
| Climate type | 765.462 | 1 | 765.462 | 9.597 | 0.002 |
| Type of vegetation | 615.326 | 2 | 307.663 | 3.858 | 0.023 |
| Residual | 12,761.051 | 160 | 79.757 | ||
| Total | 101,100.124 | 174 |
| Variable | Coefficient | Std. Error | t | Sig. | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper | Lower | |||||
| Intercept | 45.422 | 4.341 | 10.464 | 0.000 | 53.995 | 36.849 |
| Native = Both | 34.186 | 2.660 | 12.850 | 0.000 | 39.440 | 28.932 |
| Native = Native | 37.878 | 3.035 | 12.482 | 0.000 | 43.871 | 31.885 |
| Native = Not native | 22.350 | 3.132 | 7.137 | 0.000 | 28.534 | 16.165 |
| Native = Unknown | 0.000 | |||||
| Drainage layer = No | −32.152 | 2.658 | −12.094 | 0.000 | −26.901 | −37.402 |
| Drainage layer = Unknown, Yes | 0.000 | |||||
| Layer system = Multilayer | −32.967 | 2.938 | −11.221 | 0.000 | −27.165 | −38.769 |
| Layer system = Single layer | 0.000 | |||||
| Season = Spring/Summer | 8.967 | 3.171 | 2.828 | 0.005 | 15.230 | 2.704 |
| Season = Fall, Winter, Winter/Spring | −12.756 | 2.197 | −5.806 | 0.000 | −8.417 | −17.095 |
| Season = remaining options | 0.000 | |||||
| Substrate depth | 0.093 | 0.014 | 6.496 | 0.000 | 0.122 | 0.065 |
| Climate Köppen–Geiger = Cwa–dry-winter humid subtropical climate | 12.951 | 2.196 | 5.897 | 0.000 | 17.288 | 8.614 |
| Climate Köppen–Geiger = remaining options | 0.000 | |||||
| Waterproofing layer = No | −10.282 | 2.027 | −5.073 | 0.000 | −6.280 | −14.285 |
| Waterproofing layer = Unknown, Yes | 0.000 | |||||
| Protection board (root barrier) = Yes | 6.099 | 1.902 | 3.206 | 0.002 | 9.856 | 2.341 |
| Protection board (root barrier) = Unknown, No | 0.000 | |||||
| Climate type = 1 | 7.204 | 2.325 | 3.098 | 0.002 | 11.796 | 2.611 |
| Climate type = 2 | 0.000 | |||||
| Type of vegetation = Unknown | −1.090 | 5.273 | −0.207 | 0.836 | 9.322 | −11.503 |
| Type of vegetation = Sedums and other succulents; Perennial herbaceous plants and grasses | 4.541 | 1.665 | 2.728 | 0.007 | 7.828 | 1.253 |
| Type of vegetation = remaining options | 0.000 | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, J.; Paço, T.A.; Sousa, V.; Silva, C.M. Hydrological Performance of Green Roofs in Mediterranean Climates: A Review and Evaluation of Patterns. Water 2021, 13, 2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13182600
Silva J, Paço TA, Sousa V, Silva CM. Hydrological Performance of Green Roofs in Mediterranean Climates: A Review and Evaluation of Patterns. Water. 2021; 13(18):2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13182600
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Joana, Teresa A. Paço, Vítor Sousa, and Cristina M. Silva. 2021. "Hydrological Performance of Green Roofs in Mediterranean Climates: A Review and Evaluation of Patterns" Water 13, no. 18: 2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13182600
APA StyleSilva, J., Paço, T. A., Sousa, V., & Silva, C. M. (2021). Hydrological Performance of Green Roofs in Mediterranean Climates: A Review and Evaluation of Patterns. Water, 13(18), 2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13182600









