Assessment of Land Use/Land Cover Change and Morphometric Parameters in the Keta Lagoon Complex Ramsar Site, Ghana
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
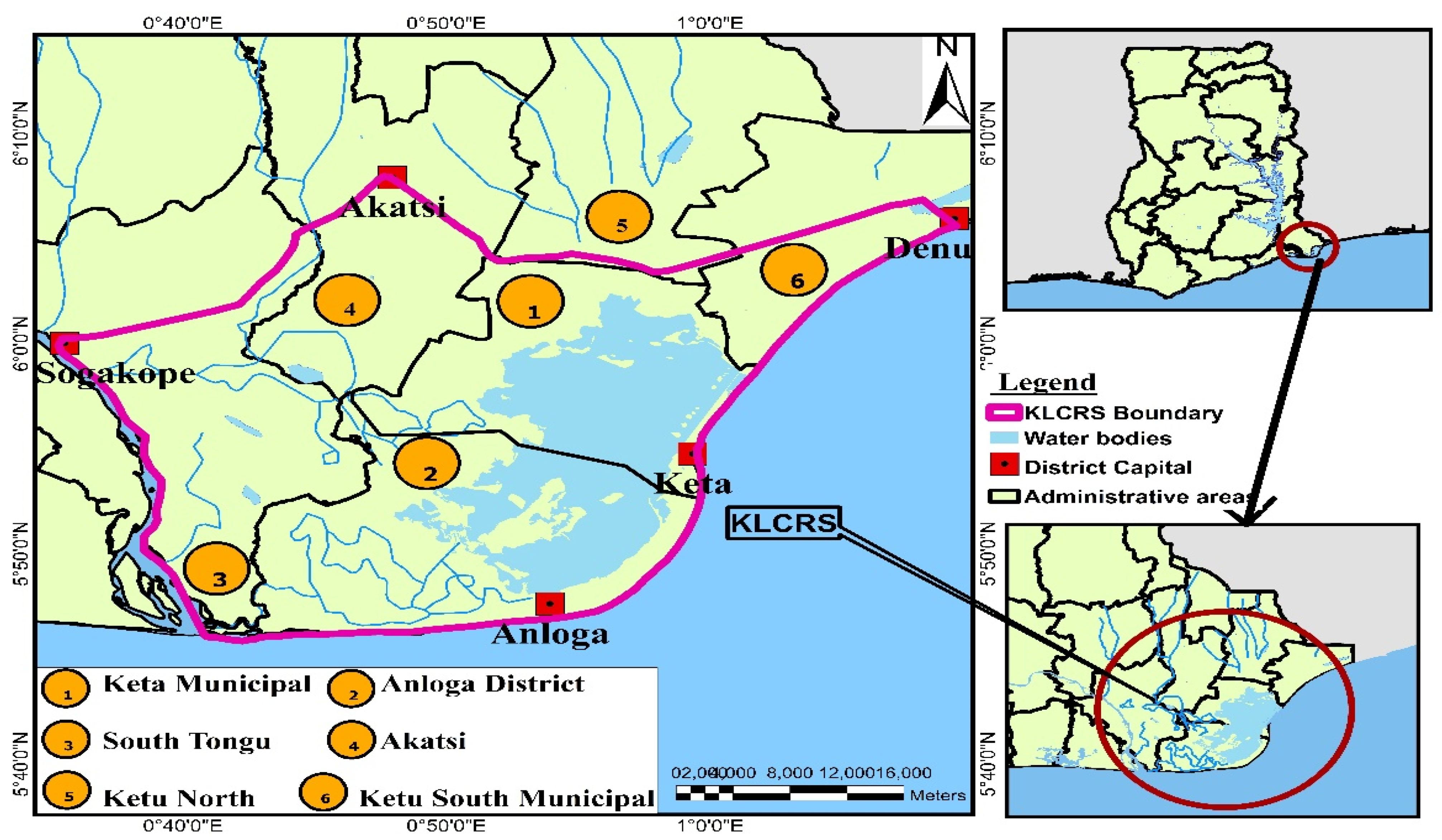
2.1. Study Area and Environmental Settings
2.2. Data and Sources
2.3. Satellite Data Preprocessing
2.4. Morphometric Analysis
2.5. Image Classification
2.6. Post-Classification
3. Results
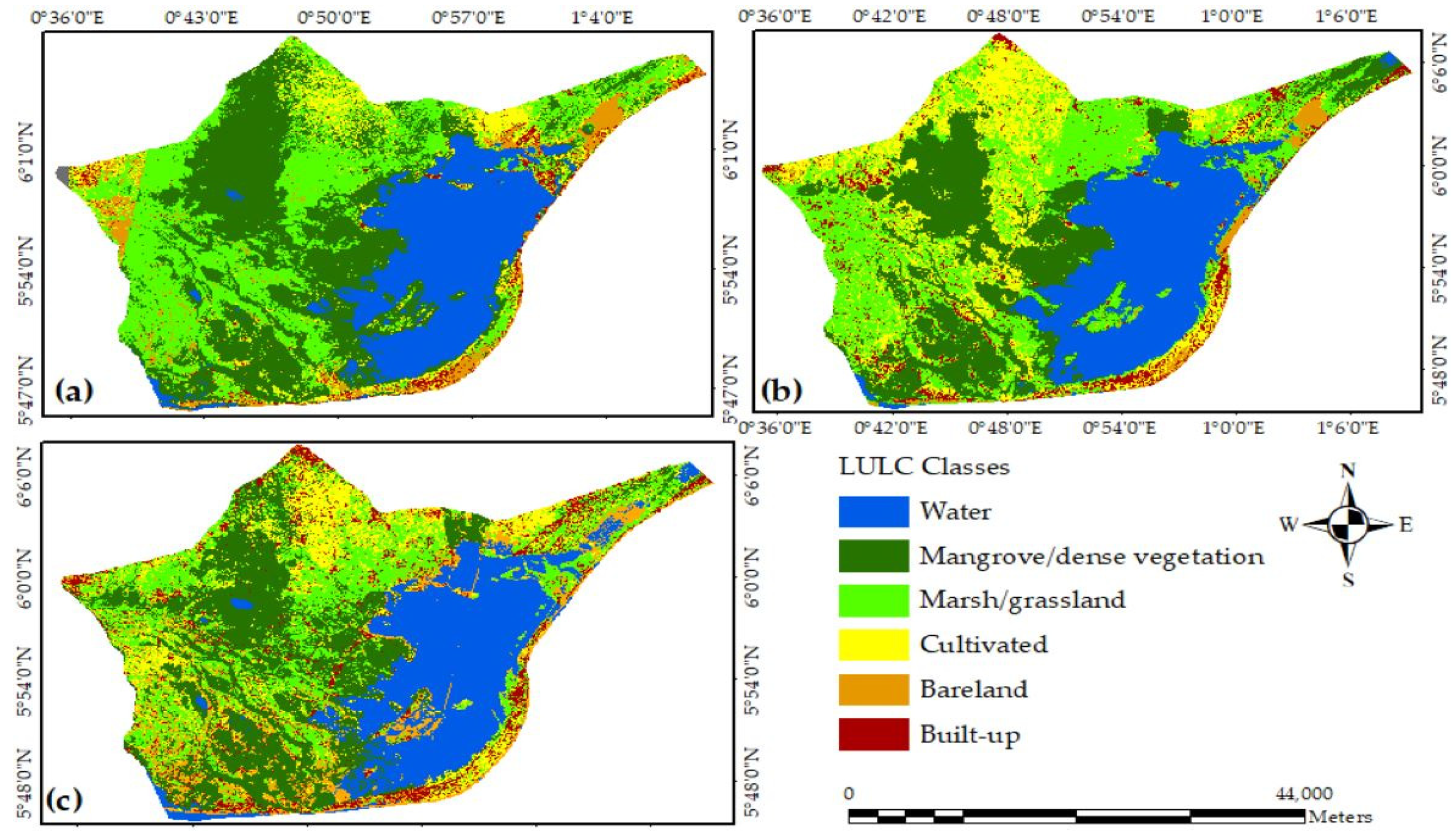
3.1. LULC Dynamics of Keta Lagoon Complex Ramsar from 1991 to 2020
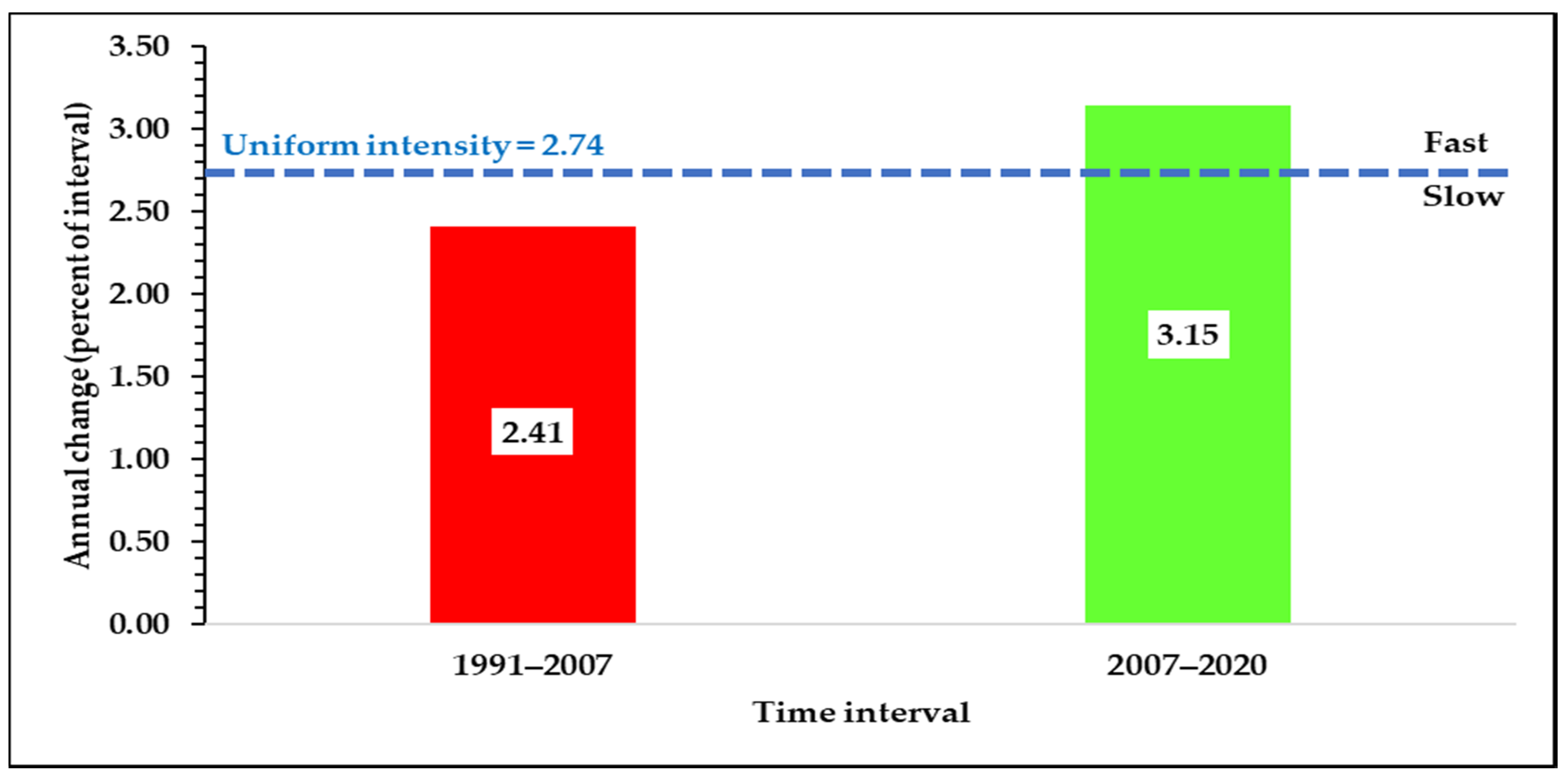
3.2. Interval Level Intensity Analysis
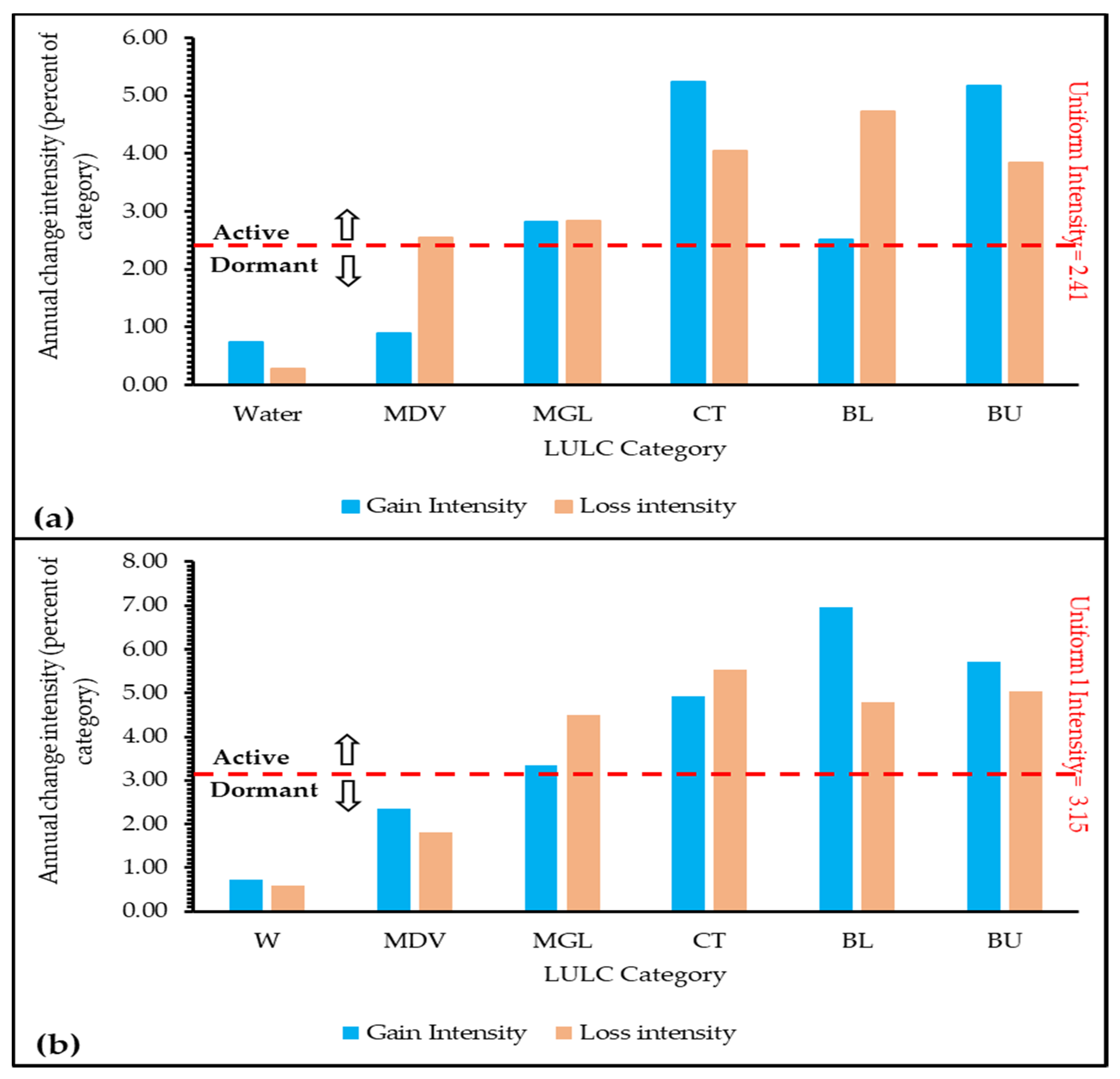
3.3. Category Level Intensity Analysis
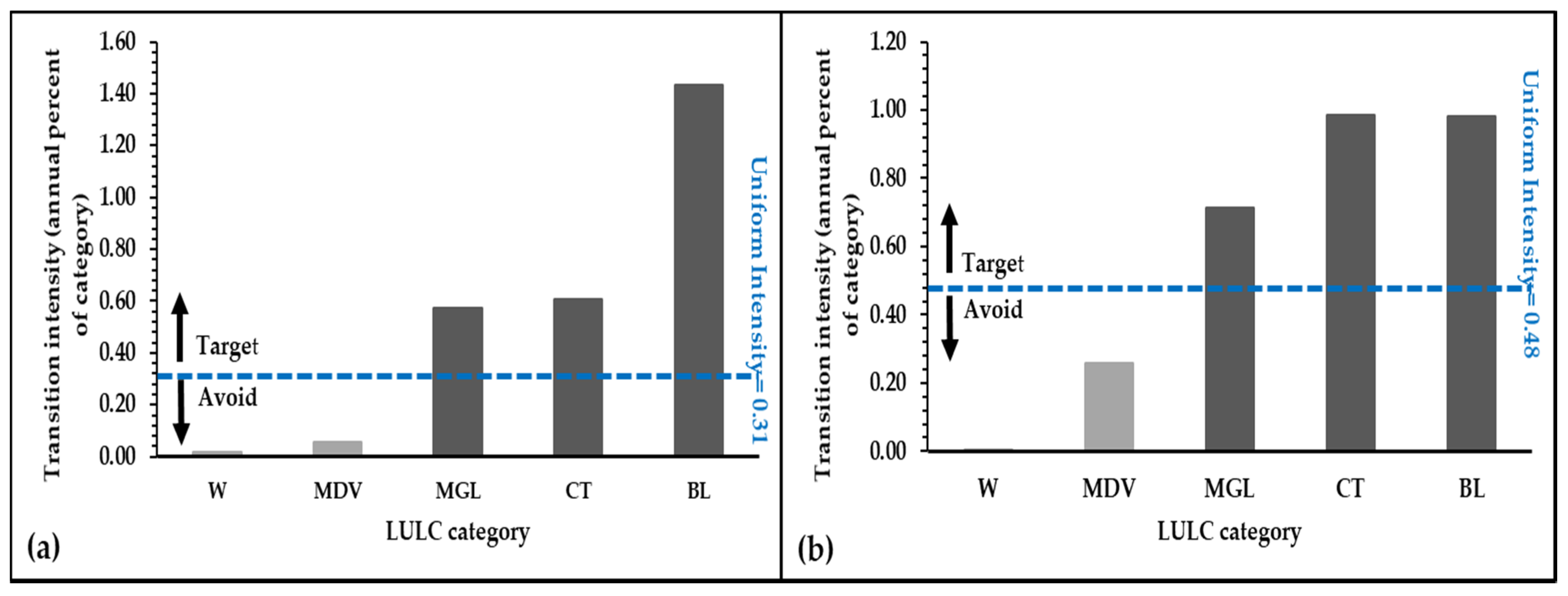
3.4. Transition Level Intensity Analysis
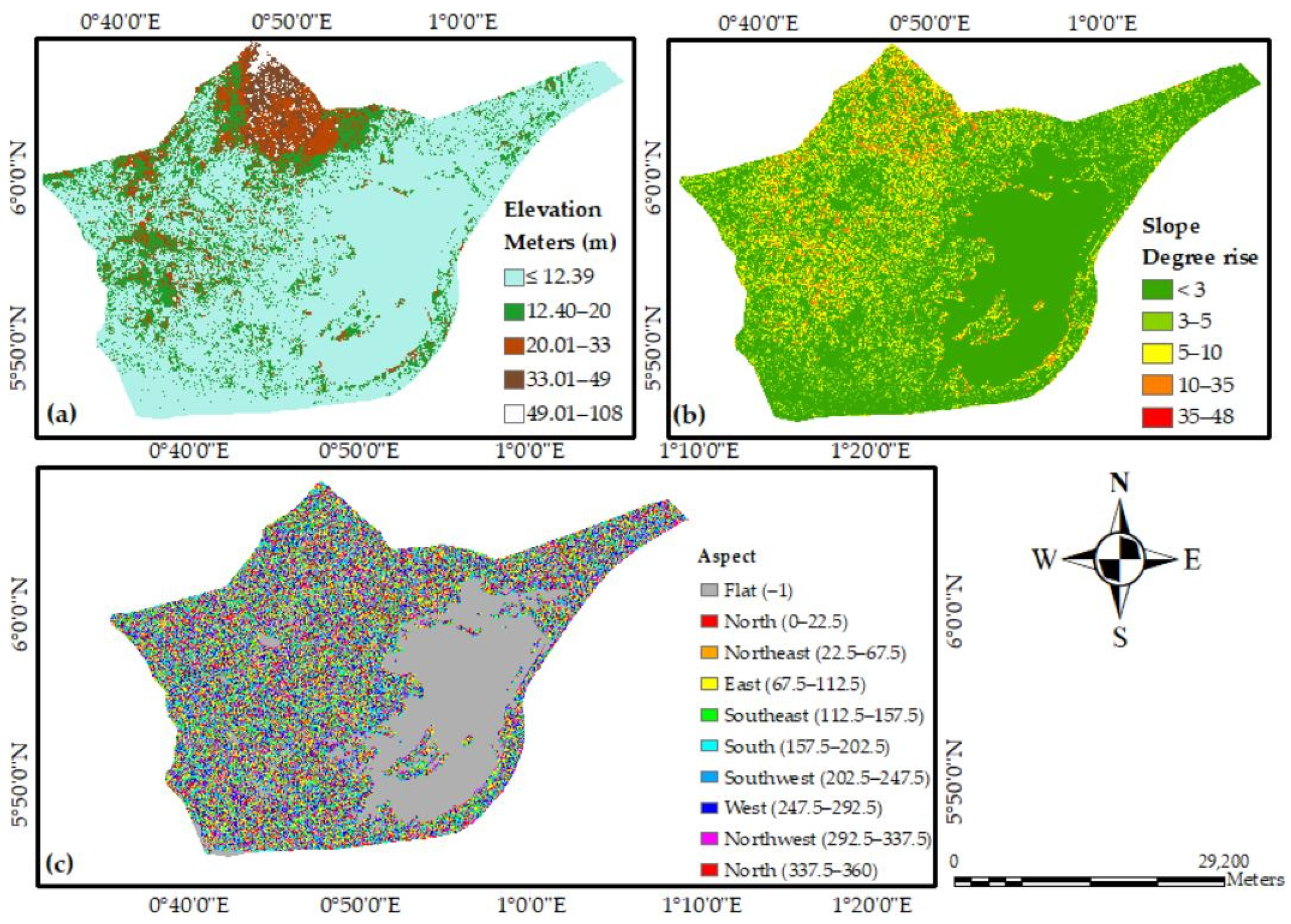
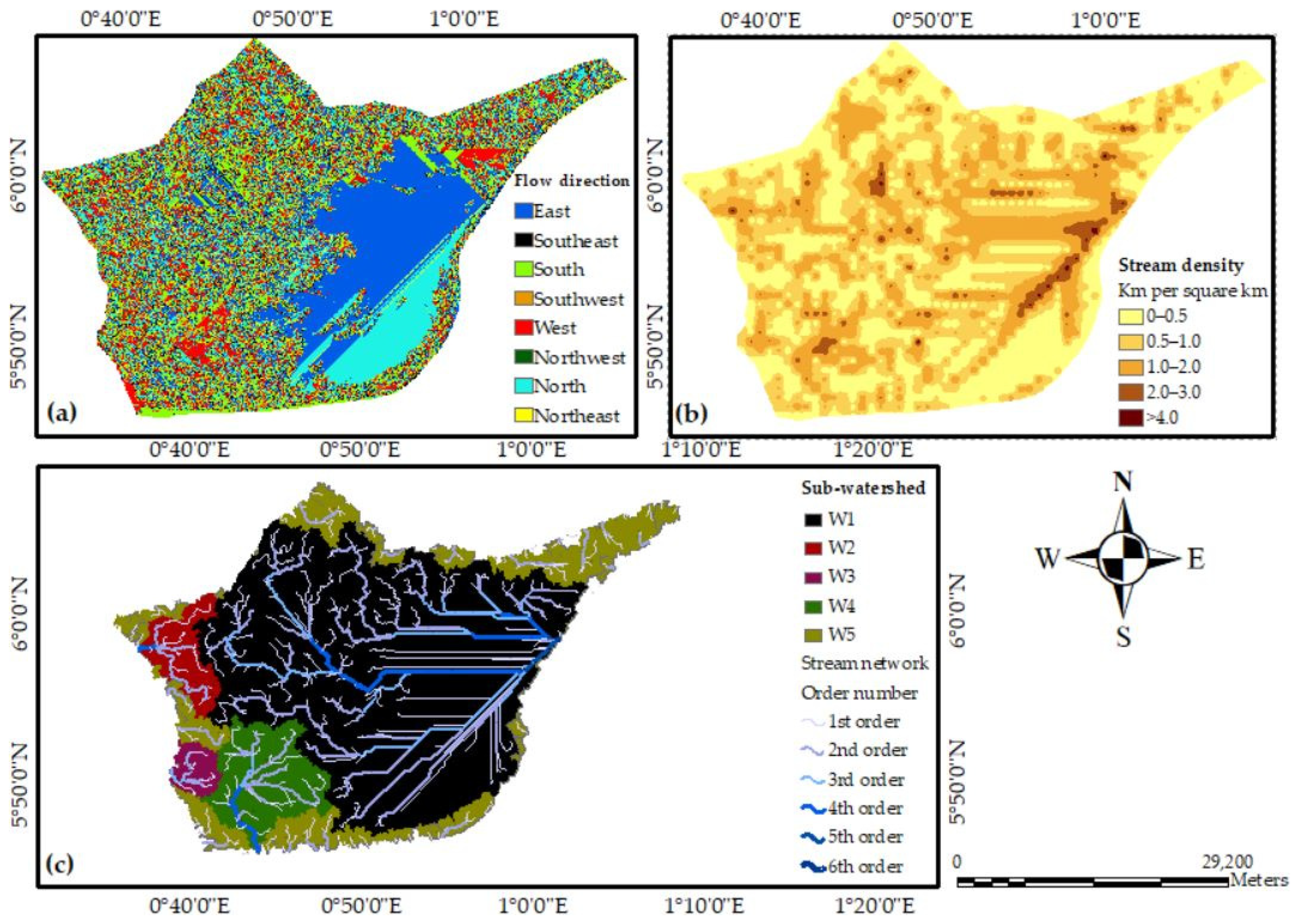
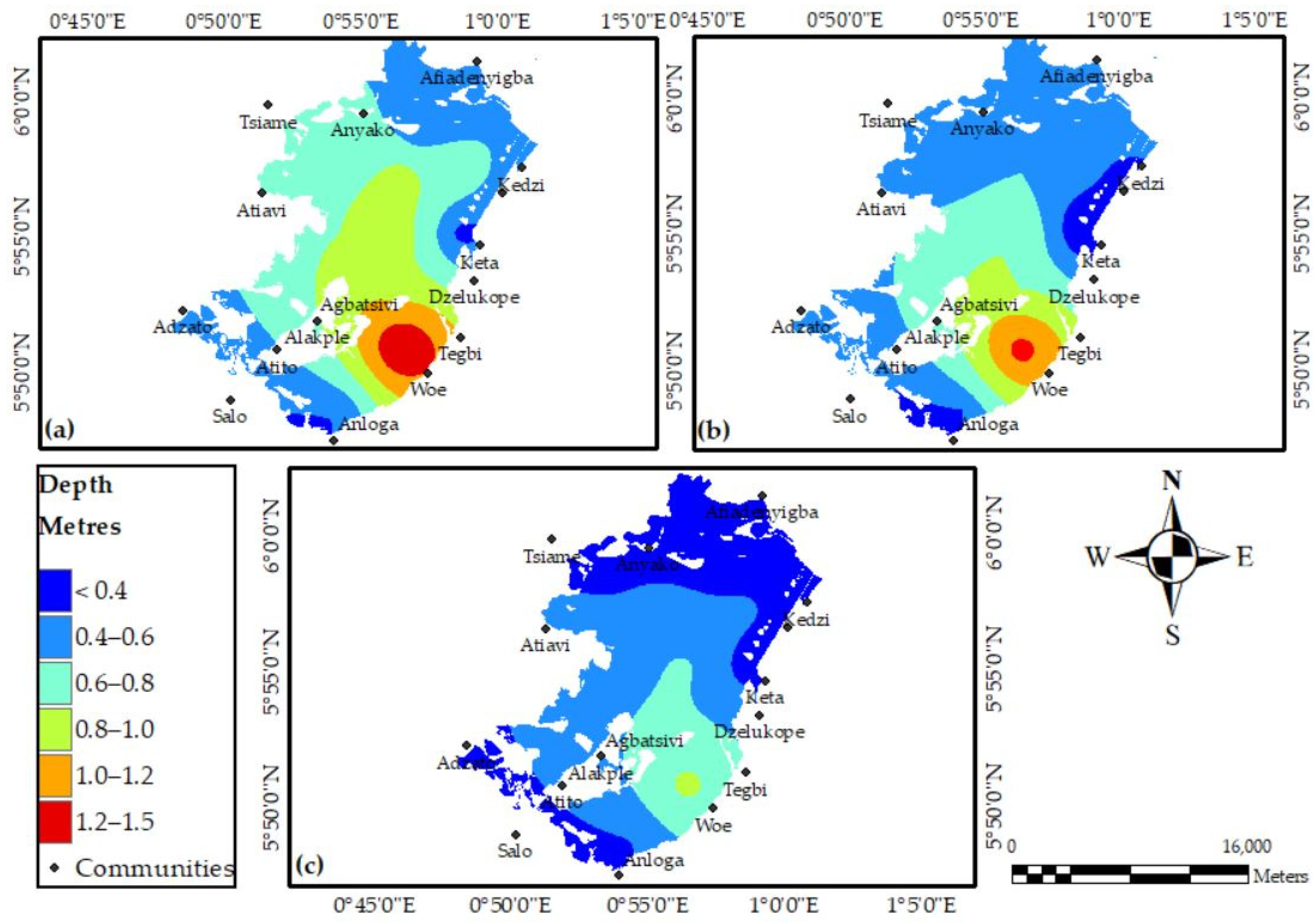
3.5. Digital Elevation Model and Morphometric Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Ethical Approval
References
- Finlayson, M.; Cruz, R.D.; Davidson, N.; Alder, J.; Cork, S.; de Groot, R.S.; Lévêque, C.; Milton, G.R.; Peterson, G.; Pritchard, D.; et al. Millennium Ecosystem Assessment: Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Wetlands and Water Synthesis; Island Press: Washington DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, N.C.; Fluet-Chouinard, E.; Finlayson, C.M. Global Extent and Distribution of Wetlands: Trends and Issues. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2018, 4, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davidson, N.C.; Dinesen, L.C.; Fennessy, S.D.; Finlayson, C.M. Trends in the Ecological Character of the World’ s Wetlands. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2020, 71, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Why are Wetlands Important? Available online: https://www.epa.gov/wetlands/why-are-wetlands-important (accessed on 19 June 2021).
- Orimoloye, I.R.; Kalumba, A.M.; Mazinyo, S.P.; Nel, W. Geospatial Analysis of Wetland Dynamics: Wetland Depletion and Biodiversity Conservation of Isimangaliso Wetland, South Africa. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2018, 32, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, J.; Ling, B.; Huang, W.; Liu, X.; Peng, W.; Zhang, J. Spatiotemporal Variations in Water Flow and Quality in the Sanyang Wetland, China: Implications for Environmental Restoration. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, K.; Pal, S. Hydrological and Landscape Dynamics of Floodplain Wetlands of the Diara Region, Eastern India. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 106961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Rasul, G.; Chettri, N. The Economic Value of Wetland Ecosystem Services: Evidence from the Koshi Tappu Wildlife Reserve, Nepal. Ecosyst. Serv. 2015, 12, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, R.B.; Ausseil, E.A.-G.; Gerbeaux, P. Wetland Ecosystem Services. In Ecosystem Services in New Zealand: Conditions and Trends; Dymond, J.R., Ed.; Manaaki Whenua Press: Lincoln, New Zealand, 2013; pp. 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, C.; Tao, Z.; Gao, D.; Wu, H. Wetland Mapping and Wetland Temporal Dynamic Analysis in the Nanjishan Wetland Using Gaofen One Data. Ann. GIS 2016, 22, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, L.; Dong, J. LUCC and Ecosystem Service Value Assessment for Wetlands: A Case Study in Nansi Lake, China. Water 2019, 11, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, M.; Gong, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, C.; Yang, Q.; Yin, Y. Landscape Pattern Evolution Processes of Wetlands and Their Driving Factors in the Xiong’an New Area of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4403. [Google Scholar]
- Ramsar Convention on Wetlands. Global Wetland Outlook: State of the World’s Wetlands and Their Services to People; Ramsar Convention Secretariat: Gland, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Bellerby, R.; Craft, C.; Widney, S.E. Coastal Wetland Loss, Consequences, and Challenges for Restoration. Anthr. Coasts 2018, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicholls, R.J. Coastal Flooding and Wetland Loss in the 21st Century: Changes under the SRES Climate and Socio-Economic Scenarios. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2004, 14, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, B.; Vafeidis, A.T.; Zimmermann, J.; Nicholls, R.J. Future Coastal Population Growth and Exposure to Sea-Level Rise and Coastal Flooding-A Global Assessment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ekumah, B.; Armah, F.A.; Afrifa, E.K.A.; Aheto, D.W.; Odoi, J.O.; Afitiri, A.R. Assessing Land Use and Land Cover Change in Coastal Urban Wetlands of International Importance in Ghana Using Intensity Analysis. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 28, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, N.C. How Much Wetland Has the World Lost? Long-Term and Recent Trends in Global Wetland Area. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2014, 65, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, R.S. Geospatial Technologies for Land Degradation Assessment and Management; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nasser, A.; Eid, M.; Olatubara, C.O.; Ewemoje, T.A.; El-hennawy, M.T.; Farouk, H. Inland Wetland Time-Series Digital Change Detection Based on SAVI and NDWI Indecies: Wadi El-Rayan Lakes, Egypt. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2020, 19, 100347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F. Land-Cover Change and Environmental Impact Analysis in the Greater Mankato Area of Minnesota Using Remote Sensing and GIS Modelling. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2008, 29, 1169–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Z.; Shabbir, R.; Ahmad, S.S.; Malik, A.H.; Aziz, N.; Butt, A.; Erum, S. Dynamics of Land Use and Land Cover Change (LULCC) Using Geospatial Techniques: A Case Study of Islamabad Pakistan. Springerplus 2016, 5, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akinyemi, F.O.; Pontius, R.G.; Braimoh, A.K. Land Change Dynamics: Insights from Intensity Analysis Applied to an African Emerging City. J. Spat. Sci. 2017, 62, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontius, R.G.; Gao, Y.; Giner, N.M.; Kohyama, T.; Osaki, M.; Hirose, K. Design and Interpretation of Intensity Analysis Illustrated by Land Change in Central Kalimantan, Indonesia. Land 2013, 2, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niya, A.K.; Huang, J.; Karimi, H.; Keshtkar, H.; Naimi, B. Use of Intensity Analysis to Characterize Land Use/Cover Change in the Biggest Island of Persian. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4396. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Li, J.; Huang, G.H. A Study on DEM-Derived Primary Topographic Attributes for Hydrologic Applications: Sensitivity to Elevation Data Resolution. Appl. Geogr. 2008, 28, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.K.; Mukherjee, S. Drainage Morphometry Using Satellite Data and GIS in Raigad District, Maharashtra. J. Geol. Soc. India 2005, 65, 577–586. [Google Scholar]
- Worqlul, A.W.; Dile, Y.T.; Jeong, J.; Adimassu, Z.; Lefore, N. Effect of Climate Change on Land Suitability for Surface Irrigation and Irrigation Potential of the Shallow Groundwater in Ghana Original Papers E Ff Ect of Climate Change on Land Suitability for Surface Irrigation and Irrigation Potential of the Shallow. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 157, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, C.; Gordon, C.; Ntiamoa-Baidu, Y.; Tumbulto, J.; Storrs, M. The Hydrobiology of the Songor and Keta Lagoons: Implications for Wetland Management in Ghana; Supervising Scientist Report 152; Environmental Research Institute of the Supervising Scientist, Australia: Darwin, Australia, 2000.
- Willoughby, N.; Grimble, R.; Ellenbroek, W.; Danso, E.; Amatekpor, J. The Wise Use of Wetlands: Identifying Development Options for Ghana’s Coastal Ramsar Sites. Hydrobiologia 2001, 458, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everard, M. National Wetland Policy: Ghana. In The Wetland Book: I: Structure and Function, Management, and Methods; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 785–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keta Lagoon Complex Ramsar Site. Available online: https://rsis.ramsar.org/ris/567 (accessed on 19 June 2021).
- Issaka, H.; Makinde, O.D.; Theuri, D.M. Dynamics of the Interaction of Species in the Keta-Anlo Wetland Ecosystem of Ghana. Glob. J. Pure Appl. Math. 2019, 15, 803–827. [Google Scholar]
- McPherson, J.M.; Sammy, J.; Sheppard, D.J.; Mason, J.J.; Brichieri-colombi, T.A.; Moehrenschlager, A. Integrating Traditional Knowledge When It Appears to Conflict with Conservation: Lessons from the Discovery and Protection of Sitatunga in Ghana. Ecol. Soc. 2016, 21, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brinks, R.J. Sustainable Tourism Development in the Keta Lagoon Complex Ramsar Site, Ghana. Master’s Thesis, Utrecht University, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Hou, X.; Li, X.; Song, B.; Wang, C. Assessing and Predicting Changes in Ecosystem Service Values Based on Land Use / Cover Change in the Bohai Rim Coastal Zone. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 111, 106004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, T.H.; Vølund, G.; Armah, A.K.; Christiansen, C.; Jensen, L.B.; Pedersen, J.T. Temporal and Spatial Varations in Concentrations of Sediment Nutrients and Carbon in the Keta Lagoon, Ghana. West. Afr. J. Appl. Ecol. 2003, 4, 91–105. [Google Scholar]
- Yidana, S.M.; Banoeng-yakubo, B.; Akabzaa, T.M. Analysis of Groundwater Quality Using Multivariate and Spatial Analyses in the Keta Basin, Ghana. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2010, 58, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamptey, A.M.; Ofori-Danson, P.K.; Abbenney-Mickson, S.; Breuning-Madsen, H.; Abekoe, M.K. The Influence of Land-Use on Water Quality in a Tropical Coastal Area: Case Study of the Keta Lagoon Complex, Ghana, West Africa. Open J. Mod. Hydrol. 2013, 3, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamptey, E.; Armah, A.K. Factors Affecting Macrobenthic Fauna in a Tropical Hypersaline Coastal Lagoon in Ghana, West Africa. Estuaries Coasts 2008, 31, 1006–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntiamoa-baidu, Y.; Gordon, C. Coastal Wetlands Management Plans: Ghana; Ghana Wildlife Division: Accra, Ghana, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Managing Ghana’s Wetlands: A National Wetlands Conservation Strategy; Ministry of Lands and Forestry: Accra, Ghana, 1999; Volume 1999.
- Tufour, K. Keta Lagoon Complex Ramsar Site Management Plan; Ghana Wildlife Division: Accra, Ghana, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Addo, K.A.; Walkden, M.; Mills, J.P. Detection, Measurement and Prediction of Shoreline Recession in Accra, Ghana. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 2008, 63, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Gupta, A.; Singh, M. Hydrological Inferences from Watershed Analysis for Water Resource Management Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Sp. Sci. 2014, 17, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danso, S.Y.; Ma, Y.; Adjakloe YD, A.; Addo, I.Y. Application of an Index-Based Approach in Geospatial Techniques for the Mapping of Flood Hazard Areas: A Case of Cape Coast Metropolis in Ghana. Water 2020, 12, 3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebola, A.; Adeseko, A.A. Drainage Basin Morphology and Terrain Analysis of the Nigerian Section of Lake Chad River Basin, Nigeria Using GIS and Remote Sensing. Conflu. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 10, 89–99. [Google Scholar]
- Medhi, B. Morphometric Analysis and Landuse Study of Gabharu River Basin using Remote Sensing and GIS. ADBU J. Eng. Technol. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Mossa, J.; Mao, L.; Almulla, M.; Wu, C.; Mossa, J. Comparison of Different Spatial Interpolation Methods for Historical Hydrographic Data of the Lowermost Mississippi River. Ann. GIS 2019, 25, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myslyva, T.; Sheluto, B.; Kutsaeva, O.; Naskova, S. Use of Geospatial Analysis Methods in Land Management and Cadastre. Balt. Surv. 2018, 9, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziez, O.; Remini, B.; Habi, M.; Ammari, A. Assessment of Groundwater Contamination by Different Interpolation Methods for Water Resources Management in the Mitidja Plain Aquifer (North-Center Algeria). Desalin. Water Treat. 2018, 132, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cláudia, M.V.; Sandra, O.; Sérgio, C.O.; Jorge, R. Land Use/Land Cover Change Detection and Urban Sprawl Analysis. In Spatial Modeling in GIS and R for Earth and Environmental Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 621–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judson, J.; Wynne, J.J. Cohen’s Kappa and Classification Table Metrics 2.0: An. ArcView 3x Extension for Accuracy Assessment of Spatially Explicit Models; U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report of 2005-1363; Southwest Biological Science Center: Flagstaff, AZ, USA, 2005.
- Thomlinson, J.R.; Bolstad, P.V.; Cohen, W.B. Coordinating Methodologies for Scaling Landcover Classifications from Site-Specific to Global: Steps toward Validating Global Map Products. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 70, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah, D.O.; Forkuo, E.K.; Bugri, J.T.; Development, R.; Borruso, G.; Kainz, W. Geo-Information. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2015, 4, 1265–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aldwaik, S.Z.; Pontius, R.G., Jr. Landscape and Urban Planning Intensity Analysis to Unify Measurements of Size and Stationarity of Land Changes by Interval, Category, and Transition. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2012, 106, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yan, F.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, M.; Su, F.; Cui, Y. Changes in Ecosystems and Ecosystem Services in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area since the Reform and Opening Up in China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1611. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Pontius, R.G., Jr.; Huang, J. Enhanced Intensity Analysis to Quantify Categorical Change and to Identify Suspicious Land Transitions: A Case Study of Nanchang, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryeetey, E.; Baah-boateng, W. Understanding Ghana’s Growth Success Story and Job Creation Challenges (No. 2015/140); University of Cape Town: Cape Town, South Africa, 2015; Volume 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lamptey, M.A.; Ofori-Danson, P. The Status of Fish Diversity and Fisheries of the Keta Lagoon, Ghana, West Africa. Ghana J. Sci. 2014, 54, 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Feka, N.Z.; Ajonina, G.N. Drivers Causing Decline of Mangrove in West- Central Africa: A Review. Int. J. Biodivers. Sci. Ecosyst. Serv. Manag. 2011, 7, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojang, F.; Ndeso-atanga, A. The Relevance of Mangrove Forests to African Fisheries, Wildlife and Water Resources. Nat. Faune 2009, 24, 1–143. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, T.J. Towards the Wise Use of Wetlands; Ramsar Convention Bureau: Gland, Switzerland, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Keta Municipal Assembly Comprehensive Annual Report on Projects and Programmes Implemented in 2016; Keta Municipal Assembly: Keta, Ghana, 2017.
- Ampim, P.A.Y.; Ogbe, M.; Obeng, E.; Akley, E.K.; MacCarthy, D.S. Land Cover Changes in Ghana over the Past 24 Years. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekumah, B.; Ato, F.; Afrifa EK, A.; Worlanyo, D.; Odoiquaye, J.; Afitiri, A. Geospatial Assessment of Ecosystem Health of Coastal Urban Wetlands in Ghana. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2020, 193, 105226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, I. An Assessment of the Physical Impacts of Sea-Level Rise and Coastal Adaptation: A Case Study of the Eastern Coast of Ghana. Clim. Chang. 2012, 114, 273–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenta, A.A.; Yasuda, H.; Shimizu, K.; Haregeweyn, N. Quantitative Analysis and Implications of Drainage Morphometry of the Agula Watershed in the Semi-Arid Northern Ethiopia. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 3825–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, V.P.; Yadav, S.; Yadava, R.N. (Eds.) Hydrologic Modeling: Select Proceedings of ICWEES-2016; Springer: Singapore, 2018; Volume 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjare, B.S.; Khan, S.; Jawadand, S.A.; Padhye, M.A. Watershed Prioritization of Wardha River Basin, Maharashtra, India Using Morphometric Parameters: A Remote Sensing and GIS-Based Approach. In Hydrologic Modeling Water Science and Technology Library; Singh, V., Yadav, S., Yadava, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, I. Spatial Planning in Coastal Regions: Facing the Impact of Climate Change; International Federation of Surveyors (FIG): Copenhagen, Denmark, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ntiamoa-baidu, Y.; Piersma, T.; Wiersma, P.; Poot, M.; Battley, P.; Gordon, C. Water Depth Selection, Daily Feeding Routines and Diets of Waterbirds in Coastal Lagoons in Ghana. Ibis 1998, 140, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Spacecraft ID | Sensor ID | Path/Raw | Acquisition Date (Year/Month/Day) | Image Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat-4 | TM | 192/056 | 1991/01/03 | 9 |
| Landsat-4 | TM | 193/056 | 1991/01/10 | 7 |
| Landsat-7 | ETM | 192/056 | 2007/01/15 | 9 |
| Landsat-7 | ETM | 193/056 | 2007/01/22 | 9 |
| Landsat-8 | OLI_TIRS | 192/056 | 2020/01/27 | 9 |
| Landsat-8 | OLI_TIRS | 193/056 | 2020/01/02 | 9 |
| 2007 | 1991–2007 | ||||||||
| LULC Category | W | MDV | MGL | CT | BL | BU | 1991 Total | GL | |
| 1991 | W | 277.57 | 5.18 | 3.94 | 0.26 | 3.24 | 0.88 | 291.07 | 13.5 |
| MDV | 31.57 | 290.69 | 94.31 | 68.53 | 1.37 | 4.41 | 490.88 | 200.19 | |
| MGL | 2.43 | 29.78 | 211.18 | 105.85 | 2.46 | 35.66 | 387.36 | 176.18 | |
| CT | 1.17 | 10.9 | 43.93 | 36.85 | 1.57 | 10.19 | 104.61 | 67.76 | |
| BL | 1.74 | 1.84 | 21.88 | 10.67 | 16.69 | 15.71 | 68.53 | 51.84 | |
| BU | 0.79 | 1.12 | 9.68 | 7.96 | 2.62 | 13.89 | 36.06 | 22.17 | |
| 2007 | Total | 315.27 | 339.51 | 384.92 | 230.12 | 27.95 | 80.74 | 1378.51 | 531.64 |
| 1991–2007 | GG | 37.7 | 48.82 | 173.74 | 193.27 | 11.26 | 66.85 | 531.64 | |
| 2020 | 2007–2020 | ||||||||
| LULC Category | W | MDV | MGL | CT | BL | BU | 2007 Total | GL | |
| 2007 | W | 291.15 | 13.91 | 0.25 | 3.43 | 6.28 | 0.25 | 315.27 | 24.12 |
| MDV | 13.74 | 259.65 | 27.23 | 17.81 | 9.71 | 11.37 | 339.51 | 79.86 | |
| MGL | 11.04 | 53.23 | 160.35 | 79.12 | 45.48 | 35.7 | 384.92 | 224.57 | |
| CT | 0.78 | 45.1 | 71.8 | 64.82 | 18.16 | 29.46 | 230.12 | 165.3 | |
| BL | 4.1 | 0.18 | 6.06 | 3.53 | 10.51 | 3.57 | 27.95 | 17.44 | |
| BU | 0.73 | 1.85 | 18.35 | 11.23 | 20.76 | 27.82 | 80.74 | 52.92 | |
| 2020 | Total | 321.54 | 373.92 | 284.04 | 179.94 | 110.9 | 108.17 | 1378.51 | 564.21 |
| 2007–2020 | GG | 30.39 | 114.27 | 123.69 | 115.12 | 100.39 | 80.35 | 564.21 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duku, E.; Mattah, P.A.D.; Angnuureng, D.B. Assessment of Land Use/Land Cover Change and Morphometric Parameters in the Keta Lagoon Complex Ramsar Site, Ghana. Water 2021, 13, 2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13182537
Duku E, Mattah PAD, Angnuureng DB. Assessment of Land Use/Land Cover Change and Morphometric Parameters in the Keta Lagoon Complex Ramsar Site, Ghana. Water. 2021; 13(18):2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13182537
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuku, Eric, Precious Agbeko Dzorgbe Mattah, and Donatus Bapentire Angnuureng. 2021. "Assessment of Land Use/Land Cover Change and Morphometric Parameters in the Keta Lagoon Complex Ramsar Site, Ghana" Water 13, no. 18: 2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13182537
APA StyleDuku, E., Mattah, P. A. D., & Angnuureng, D. B. (2021). Assessment of Land Use/Land Cover Change and Morphometric Parameters in the Keta Lagoon Complex Ramsar Site, Ghana. Water, 13(18), 2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13182537








