Abstract
Insufficiency of potable water is acute in southwest (SW) coastal areas of Bangladesh. The local population ignores the depth to saltwater/freshwater interface causing many unsuccessful waters wells drilling. In this context, a combined use of borehole logs, geophysical well logs, vertical electrical soundings (VES), electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) and electrical conductivity (EC) of sampled waters was performed to identify saltwater/freshwater interface depths in this coastal part. The study shows that the depth to freshwater/saltwater interface varies from place to place occurring commonly between 190 to 285 m, and locally as shallow as 146 m. The shallow freshwater/saltwater interface depth is greatly influenced by the upconing of fresh water from the deep aquifer (DA) near the major rivers and coast compared to the landward part and is mixed with more saline waters above. Vertically infiltrated saltwater is the main cause of brackish water in the upper shallow aquifer (USA), which is hydraulically connected with the lower shallow aquifer (LSA), and not directly recharged from the Bay of Bengal in the south. The study will contribute to find out the depth of the potential freshwater aquifer and assess the aquifer vulnerability in the coastal area of SW Bangladesh.
1. Introduction
The coastal areas of Bangladesh covering an area of 47,201 km2 accommodate approximately 46 million people. Knowing the depth at which fresh water occurs is of crucial importance to the people living in the saltwater-affected coastal area of SW Bangladesh. Different degrees of salinity (4000–25,000 µS/cm) affect more than 50% of the coastal areas of Bangladesh [1]. A total of 73% of the population in Bangladesh live in rural areas, and a majority of the rural people use hand-pump tubewell water for their drinking-water supply [2]. The diameter of the tubewell is normally 3.81 to 6.35 cm. Groundwater is abstracted from a tubewell by using a hand pump, as well as a centrifugal pump. The development of shallow or deep tubewells is sometimes limited because of the inaccessibility of aquifers [3,4]. About 61% of the population in the coastal area have serious health issues due to potable water shortage [5]. Mostly women and young girls suffer severely, as they have to collect water for domestic purposes. Hypertension, heart, and kidney disorders are common among them, as they drink insufficient water [6,7]. In some places, women and girls have to walk to a water source about five km away to collect fresh water for domestic purposes. There are some areas along the coast of Bangladesh, where water in both shallow hand-pump tubewells (SHTWs) and deep tubewells (DTWs) is not suitable for consumption due to excessive salinity. Tubewell failure is also a very common phenomenon in the coastal area, due to the unknown freshwater/saltwater interface depth in the aquifer. In many settlements, people store rainwater in manmade or natural ditches that serve as the only source of domestic water [3,8]. Sea-level change also affects the groundwater salinity and/or migration of salt water into groundwater aquifers in Bengal Basin [9]. That is another reason why delineation of the freshwater aquifer boundary in coastal areas is of particular importance is to establish a baseline. Extreme climatic events, sea-level fluctuations, and increased groundwater abstraction from coastal aquifers disrupt the natural groundwater equilibrium condition, resulting in shifting of the freshwater/saltwater interface inland, toward the abstraction well, and seawater upconing and/or moving locally upward [10,11,12,13,14].
The coastal aquifer’s water is inferior in terms of quality and often beyond the potable limits. Most of the tubewells constructed in this area are saline [15,16]. Seawater intrusion in the freshwater zone and impact of saltwater upon public health and agriculture have been investigated by some researchers [17,18,19,20,21,22], but the exact depth of salt/freshwater boundary has yet to be resolved. This interface depth can be detected by downhole geophysical well logs, for example, electrical resistivity logging, and water sampling or by indirect surface methods, such as VES or ERT [23]. Both direct and indirect methods have been used successfully to determine aquifer characteristics and monitor saltwater intrusion in groundwater research because of the impact of salinity on EC [24,25,26,27,28,29,30]. There is almost no work done yet to find out the actual depth of the saltwater–freshwater interface in the coastal areas of Bangladesh. In this study, geophysical well logging, VES, ERT, and water chemistry were integrated to locate this interface in this area. This will certainly be helpful in planning and implementation of safe and cost-effective drinking-water facilities in the SW coast of Bangladesh.
2. Study Area
2.1. Hydrology and Climate
The study area is situated in the lower part of the Ganges River tidal floodplain in the southwestern part of the Bengal basin bordered by the Bay of Bengal in the south (Figure 1). It comprises of two coastal districts: Barguna and Patuakhali. The rivers flowing in the area include Payra in the north, Bishkhali and Baleshwar in the west, Buriswar in the middle, and Tetulia in the east. Other small rivers and channels include the Andharmanik, Galachipa, Kajol, Bhairob, Kopotakkho, Palla, and Rabnabad. Furthermore, the Ganges River flows to the northwest–northeast of the study area. Mostly dendritic pattern distributaries of the major rivers, and irregularly distributed ponds and beels (a lake like wetland) are present throughout the study area. In total 200,984 small and 494 big ponds are situated in this area [31]. Some of the ponds are being used as the sources of domestic water supply, especially during the dry season. All the rivers and channels are influenced by the low tide (1 m) and high tide (3.1 m) with respect to mean lower low water (MLLW) each day in the SW part [32]. Tropical monsoon is dominant in Bangladesh, with a huge amount of rainfall occurring from June to October and moderate-to-high temperature and humidity. The annual average temperature is 25 °C. Relative humidity is around 60% in the dry season and 98% during the monsoon. The average annual rainfall for the period 2000–2014 was 2570 mm [22].
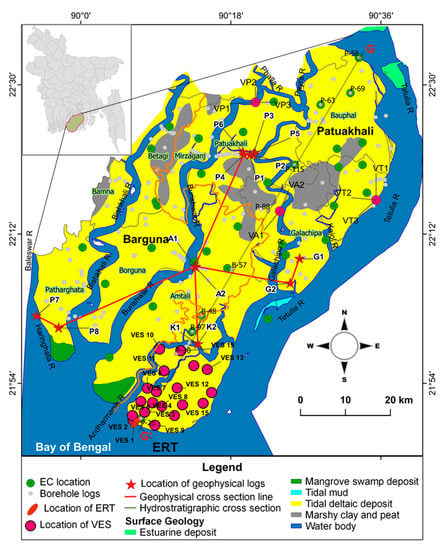
Figure 1.
Geological map of the study area with location of the boreholes, geophysical borehole logs, VES, ERT, and EC. The solid line G–G′ is the hydrostratigraphic cross-section line.
2.2. Geology and Hydrogeology
The study area, a part of the Bengal basin, has relatively flat topography with very gentle slope. The surface geology is mainly formed by the tidal deltaic and marshy peat and clay deposits. The Recent sediments primarily deposited by the Ganges form the area with a complex interfingering of very fine to coarse sediments from several regressions and transgressions in the past.
Borehole log data were collected from the aquifer database inventory program of the Department of Public Health Engineering (DHPE) of Bangladesh, and Bangladesh Water Development Board (BWDB) and surface geological data were collected from the Geological Survey of Bangladesh (GSB). These data reveal that the subsurface sediments are composed of a complex mixture of sand, silt, and clay. In the hydrogeological cross-section G-G’ (Figure 2, localized in Figure 1), all sands ranging from very fine sand to coarse sand were considered as an aquifer, and, on the other hand, clay and silt were considered as an aquitard. There is a clay/silty clay layer present discontinuously over the study area at the top. This layer serves as the upper aquitard, with variable thickness ranging from a few meters to maximum 75 m. Less sand content is observed in the SW to central part of the study area compared to the northeastern part. The top sand layer with thickness from a few meters to 50 m is named the USA and is underlain by a discontinuous aquitard. The sand layer below the USA that is called the LSA. The LSA is semiconfined or consists of interconnected stratified layer. The clay layer of variable thickness below the LSA is defined as the lower aquitard. The sand layer found mostly deeper than 200 m is termed the DA. Recharge mostly occurs in the northern part of the study area and in areas where the upper aquitard is absent and the water discharges into the Bay of Bengal. Regionally, groundwater flows from north to south in both seasons. Sarker et al. [22] estimated an average discharge and recharge in the study area of 54.97 mm/yr and 55.56 mm/yr, respectively. The study area is mostly rural. A total of 533,134 tubewells, mostly from the DA, are currently in use in this area [33]. The shallow aquifers are saline, and therefore, they are not in use. Interactions are observed among rainfall, groundwater level, and river stage. The river water level in the SW part is higher than the groundwater level, while an opposite pattern is observed in the northern part. The lower groundwater level in the SW is due to high evapotranspiration and reduced downstream groundwater flow during the dry season. The average hydraulic conductivity (K) and transmissivity (T) values of the DA calculated from pumping tests by the Cooper and Jacob [34] method are 110 m/day and 888 m2/day, respectively [35]. According to the Gheorghe [36] classification, the DA is highly potential for groundwater abstraction. The average hydraulic conductivity values of the USA, LSA, and DA estimated by oscillation slug tests [37] are about 117, 10.6, and 7.8 m/day, respectively. Radial hydraulic conductivity obtained by Horslev’s tests [38] for all aquifers ranges from 1.7 to 7.2 m/day, as is typical of sandy alluvial aquifers. The storage coefficient values of the DA are estimated to be between 1.07 × 10−4 and 0.0165 [35]. According to Kruseman et al. [39], based on the calculated storage coefficient, the aquifers seem to be unconfined to semi-confined in nature.
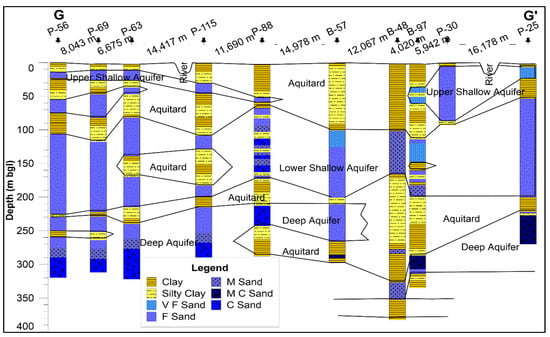
Figure 2.
Hydrostratigraphic cross-section along the line G-G’ (Figure 1).
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Geophysical Prospection
The subsurface information for depth, geometry, and characteristics of a source aquifer can be determined by using geophysical surveys [40,41]. Studies related to saltwater investigations frequently use geophysical resistivity surveys because of the direct sensitivity to the water salinity [42,43,44,45].
3.1.1. Geophysical Well Logs
The natural gamma ray (GR) log measures the natural emission of total gamma radiation from a geological formation in a borehole [46]. The emission depends on the mineral composition of the rock or sediment. Sands (quartz) tend to be less radioactive than clays and fine-grained sediments. GR log is most frequently used for lithologic and stratigraphic correlation. Results of the natural GR logs are reported in counts per second (CPS), commonly used by mineral industry, or API units if calibrated [46,47].
Two electrodes typically spaced 16 or 64 inches apart during electrical resistivity logging in the borehole, called short normal (SN) and long normal (LN) resistivity log, respectively, are used in combination with two electrodes located at the surface. They measure the apparent resistivity in ohmmeters (Ω.m) and are used to detect water quality (mainly the salinity) and lithology (mainly the clay content). The SN log is more strongly influenced by the invaded zone. It is useful for detecting thin beds (>16 inch) and sometimes to measure formation porosity. The LN log measures an intermediate resistivity, which may permit calculation of both invaded zone resistivity () and true rock resistivity (). GR and LN logs were combined to deduce the aquifer properties up to the depth of 380 m below the ground level (bgl). In this study, 14 natural GR and LN resistivity logs were used. The combined use of short and long normal may be very helpful in identifying intruded zones. However, SN is more influenced by the drilling fluid in the invaded zone, which may misinterpret the results. When SN shows higher resistivity than LN, this indicates a high resistivity mud has been used (Rmf > Rw). We have carefully checked both the SN and LN. We observed that SN has lower resistivity compared to LN in our studied resistivity logs. Because it is more influenced by the resistivity farther away from the borehole (and thus less disturbed by borehole effects), LN usually provides a good approximation of formation resistivity (comprising matrix and pore water). We, therefore, usually emphasized LN only for this study. The SN was not used in this study, as it is strongly influenced by the invaded zone. These data were collected from the archive of DHPE, Dhaka, Bangladesh.
The qualitative interpretation of GR log was based on the identification of the sand (minimum cps) and shale (maximum cps) lines, in relatively constant zones of the log, from which a scale from 0 to 100% shale can be made. The shale line indicates a low permeability unit (clay or shale), and a deflection towards lower values indicates a decrease in the shale content and a higher permeability unit, such as sand and coarse grain sediments. The deflection in the LN log occurs towards left when ρw < ρmf and right when ρw > ρmf, where ρw and ρmf are formation water resistivity and mud-filtrate resistivity, respectively. At the same time, high resistivity indicates fresh water and the absence of clay/shale, whereas low resistivity identifies the presence of salt water/brackish water and/or shale/clay. Furthermore, the natural GR deflections were correlated with borehole log data to identify the different hydrostratigraphic boundaries. The deflections were also correlated with electrical resistivity data to identify fresh water and saline zones. For example, a saltwater sandy zone with higher total dissolved solids (TDSs) would be indicated by decrease in both natural gamma response and resistivity values, whereas freshwater-bearing aquifers with low TDSs would be delineated by increase in resistivity values and low gamma response. All the GR and LN resistivity logs were interpreted in the depth range from 50 to 380 m bgl (see Figure 3). The resistivity values for different lithological units were obtained from the LN resistivity log of the same borehole. The resistivity of pore water in a lithological unit was determined from the resistivity value of this unit by making use of Table 1. For example (Figure 3), when LN resistivity curve encompasses the sand and clay/clayey zones, the corresponding resistivity values are correlated with the formation resistivity (sand) and formation resistivity (clay) shown in Table 1, respectively. Following this correlation, we identified a series of water-resistivity values, such as B, MB, MF, and so on, from top to bottom of the log (see Figure 3 for an example). Saltwater/freshwater interface depth was then defined at the bottom of lithological unit containing saltwater and above the lithological unit containing fresh groundwater. The cross-sections were then constructed in different directions, as shown in Figure 1, to identify dominant litho-hydrologic units.
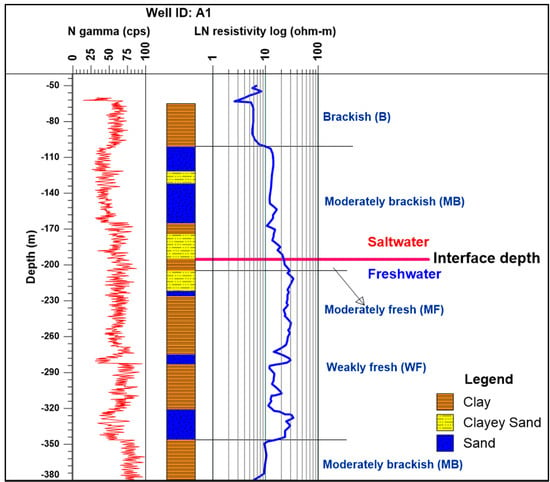
Figure 3.
An example delineation of saltwater–freshwater interface in well A1.

Table 1.
Relation between groundwater resistivity and formation resistivity for the water-quality classes defined by De Moor and De Breuck [63].
3.1.2. Resistivity Ground Surveys
Normally, a direct current (DC) is sent into the earth through a pair of current electrodes, and the resulting potential difference is then measured with the help of a pair of potential electrodes at the surface. The magnitude of the potential difference is closely related to the distribution of current in the subsurface. For a Schlumberger array configuration, where the current electrodes separation is much longer than the potential electrodes separation, Equation (1) is used to calculate apparent resistivity [48].
where a is the distance between the current electrode and the centre of the array, b the separation between potential electrodes, and R the resistance = .
When the electrode separation increases, the apparent resistivity is influenced by the resistivity of deeper layers. The Schlumberger array was used to conduct all the VES.
In the case of the Wenner configuration, the array spacing expands about the array midpoint, while maintaining an equivalent spacing between two adjacent electrodes, and Equation (2) is used to calculate apparent resistivity.
where is the electrode spacing.
In this study, VES 1 to VES 19 were conducted by a McOHM (Model-2115) OYO corporation, Japan, and taken from the MoST report, 2016 [49]. The rest of the VES and ERT were conducted by using a SYSCAL-R2 resistivity meter. This device is a high-power fully automated resistivity meter for DC electrical survey. The measuring process was adjusted to get the highest possible accuracy in the field conditions. The length of the current electrode spacing (AB/2) varies from 170 to 495 m, depending on the access to the survey area. ERT was carried out over a distance of 960 m, with 40 m unit electrode spacing. Soundings at 27 stations and one ERT were carried out to understand the groundwater quality and the geological structure of the area.
- 1-D inversion
Obvious outliers were first removed from the measured resistivity data. The filtered data were then inverted in terms of 1-D multilayer earth models. The starting model was obtained from the available geological and hydrogeological information about the study area, followed by refinement of the initial model, using an iterative approach. Finally, the IPI2WIN-1D computer program [50] was used to obtain the final resistivity model. The inverse problem is solved by using the minimum number of layers required to fit the data (blocky inversion) and the regularized fitting minimizing algorithm, using Tikhonov’s approach to solve ill-posed problems [51]. The results from the blocky inversion were considered to generate sharp contrast during inversion. A priori information about different layers depths and resistivities was used for regularizing the inversion and get more realistic solution [52].
- ERT
Electrical imaging is a popular geophysical method in hydrogeology, given its sensitivity to crucial parameters, such as salinity and clay content [53]. ERT measurements were collected by repeating resistivity measurements with different electrode spacing at different locations. In contrast to VES, it can thus be used to characterize subsurface lateral resistivity variations, as well. For this study, a Wenner electrode configuration was used, and the apparent resistivity was calculated by Equation (2). The survey was carried out in the north–south direction perpendicular to the coast of the Bay of Bengal, starting approximately 50 m from the seashore (Figure 1). The Res2DInv software was used to invert the measured apparent resistivity data to create a model of the subsurface resistivity based on the iterative smoothness-constrained least-squares method [54,55].
- Depth of Investigation (DOI) Index
The DOI can be defined by the depth below which the electrical resistivity of the subsurface no longer affects the measured resistivity data [56]. The sensitivity of ERT data decreases with increasing depth. The decreasing trend of resolution and sensitivity with depth is well documented [57]. Therefore, it should be addressed in calculation to avoid any misinterpretation or overestimation of subsurface resistivity structures. This is particularly more important in saline grounds. The electrical current flow tends to concentrate in highly conductive zones which will significantly decrease the DOI [58]. The DOI was calculated following the Equation (3) by Oldenburg and Li [56]. In the DOI method, two model inversions ( and ) were carried out with different reference models ( and ). The values of 0.1 and 10 times the average apparent resistivity values were taken for and , respectively.
The discrepancy of the inverted model is insignificant when the value of DOI is approaching zero [56], and then the inverted model can be considered as a reliable model. In contrast, the DOI value around 1 indicates significant discrepancy of the inverted model. The DOI values between 0.1 and 0.2 are often used to delimit the reliable part of the inverted model [56,57,58,59,60]. In this study, we used the subjective value 0.1 to define the DOI of the inverted model.
3.2. Determination of Pore-Water Resistivity
We used the LN measured apparent resistivity, as an approximation of the formation resistivity, . Archie’s law [24] describes the bulk resistivity () as being related to pore-water resistivity () through the formation factor, F, as in Equation (4).
This relation works well in sandy formations. However, in shaly formations, the relationship between and is more complex, since the surface conductivity of clay particles must be accounted for. Patnode and Willie [61] prescribed an additional term to include the resistivity of the sediment/rock matrix.
In this study, for clayey deposits, we used a formation factor () equal to 2 and matrix resistivity of 50 Ωm, as deduced from detailed studies in the coastal plain of Belgium (e.g., Reference [62]). Table 1 shows the relation we used between groundwater resistivity and formation resistivity for the different water-quality classes that were defined by De Moor and De Breuck [63]. We extended the table given by Walraevens et al. [64] for sands with F = 4 to include also the case for clayey deposits.
Depth-wise lithological zones have been defined based on natural GR response and validated them with available nearest borehole. Shallow aquifers are affected by the presence of salt water. Both salinity and clay in the formation reduce the bulk resistivity and will lead to low resistivity values. The low resistivity values indicating saltwater intrusion might be equivocal. Nonetheless, it should be noted that the low resistivity value of clay may indicate freshwater condition, according to the Equation (5).
The resistivity values for different lithological units were obtained from the LN resistivity log of the same borehole. The resistivity of pore water was determined from the corresponding resistivity value of the same lithological units, according to Table 1. For example (Figure 3), when the LN resistivity curve encompasses the sand and clay/clayey zone, the corresponding resistivity values are correlated with the formation resistivity (sand) and formation resistivity (clay), as described in the Table 1, respectively.
A similar technique has been applied for the interpretation of VES. Each VES having different zones of resistivity was checked carefully and correlated with the nearby borehole log. The depth at which the resistivity value of pore water obtained from VES becomes more than 6 Ω.m was taken as the beginning of freshwater depth. Usually, there is a steep change in resistivity at the interface between the VES layers, and 6 Ω.m is mostly a trustworthy value to differentiate them: layers saturated with fresh water will show higher resistivity, while layers with saline water will show lower resistivity [65]. The transition thus corresponds to a resistivity limit of 6 Ω.m and is referred to as the freshwater–saltwater interface depth, where the upper part is saline (<6 Ω.m) and the lower part is freshwater (>6 Ω.m) in the study area. The interface depth thus represents the depth at which fresh water can be found.
The detailed lithology of the sampled tubewells was studied. EC of water samples from the nested wells (a set of tubewells having different depths and drilled very near to each other) was also examined. EC of the sampled tubewells was assumed to be the same for the whole lithologic unit (well screen is placed in the lower part of the sand layer); the top of that lithologic unit was chosen as the starting depth of the fresh water. EC values from sampled tubewells were converted to resistivity values by considering the formation factor 4 (well screen in the sand layer). These resistivity values were then correlated with different water-quality types given in Table 1. The formations having pore-water resistivity more than 6 Ω.m in the abovementioned datasets were termed as freshwater zone, and formations with resistivity less than 6 Ω.m were termed as saline water zone.
3.3. Saltwater–Freshwater Interface Map
This is the first attempt to construct a saltwater and freshwater interface map of the study area by considering geophysical logs, geophysical survey, groundwater flow direction, water chemistry, and the borehole logs with chloride data. Firstly, 14 resistivity logs, 27 VES, 1 ERT, and water EC of the 36 selected tubewells were examined. Considering the resistivity values, local geology, geomorphology, and other influencing factors, such as population growth centers, we produced a map of the freshwater–saltwater interface depth. Firstly, all points with the interface depths were posted on a plain piece of paper. The contour lines were then drawn manually and scanned and finally digitized to present a version, using QGIS 3.16. The depth of the saltwater–freshwater interface was differentiated by a series of colors ranging from dark green to red, where the dark green color represents the shallowest and red color represents the largest depth to fresh water.
4. Results
4.1. Geophysical Cross-Section
Example cross-sections are given in Figure 4A–C. In these sections, three distinctive layers of different salinity types are identified, following the hydrostratigraphy of the study area. In all cross-sections, the upper part is mostly brackish (B), with its actual depth levels varying from place to place. This zone extends on average up to 120 m, although it starts at around 100 m and ends at 200 m near the coast. A less saline (moderately brackish (MB)) zone up to the depth of around 245 m is present below the top zone. The thickness of this zone is higher in the P7/P8 section than that in the G2/G1 section. This zone is absent near the coast and reaches a maximum depth of 240 m in the Patuakhali town. A layer of weakly fresh (WF) water is present below 180 m depth in the Patuakhali town and at 200 m in the coast. The presence of a moderately brackish (MB) zone below 350 m depth indicates either saline pockets or a saline-water zone (Figure 4B,C). There is not any evidence of direct seawater intrusion observed in any part of the study area. Some more exploratory DTWs below 350 m with geophysical logs and water sampling are needed, especially in the coastal area, to confirm this interpretation.
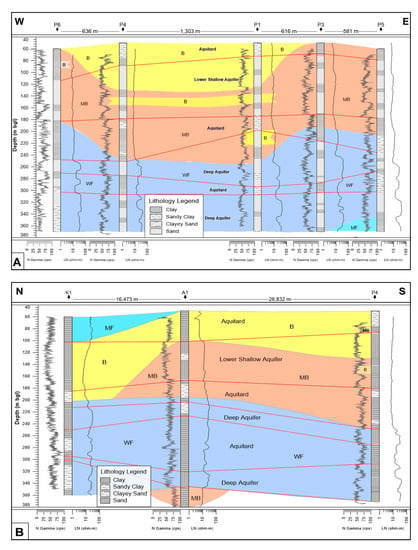
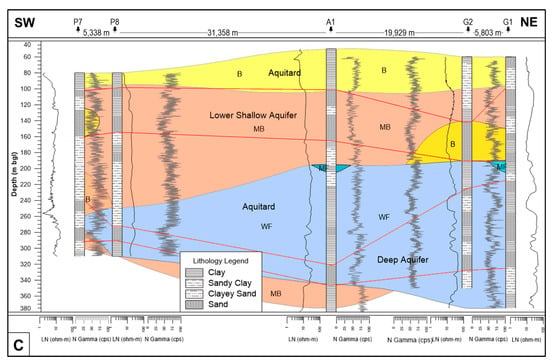
Figure 4.
The cross-sections based on the natural gamma and LN resistivity logs. (A) cross-section along the line P6/P4/P3/P1/P5; (B) cross-section along the line K1/A1/P4; (C) cross-section along the line P7/P8/A1/G2/G1. In each cross-section, the water quality is shown by different colors (MF = blue, WF = light blue, B = light yellow, and MB = peach puff). The location of the cross-section lines is shown in Figure 1.
From these sections, it is also evident that seawater is not coming directly from the sea, but rather is leaching from the surface. Some recent studies [22,66,67] have shown that high salinity in the study area up to depth of ca. 200 m bgl is due to vertical infiltration of dissolved evaporite salts, rather than direct saltwater intrusion from the Bay of Bengal.
4.2. VES
The 1-D models obtained from VES show that the investigated subsurface comprises five or six geo-electric layers, showing different salinity zones, with a maximum investigation depth of less than 285 m. The topmost zone up to ca. 15 m depth from the VES located near the rivers has relatively high resistivity values in T1-3, P1-3, A1-2, VES 13, and VES 14. In groundwater-quality class, this corresponds to a WF zone. This can be the effect of freshwater invasion from the surrounding surface freshwater bodies. There are some layers of very low resistivity values underneath the topmost soil up to larger depth. The markedly low resistivity values of these layers could be attributed to the effect of seawater intrusion, but the main water table is mostly above the sea level and has a flowing trend from the recharge area in the north to the Bay of Bengal in the south [22]. The water-quality class of these layers varies from B to S in some cases. The resistivity sounding curves at different locations show different behaviours; the inversion results are also different. This may be due to the different levels of saltwater effects and lithological variation in the study area. It is evident from the model that resistivity is very low (0.98 to 1.68 Ω.m), up to 100 m depth. The presence of clay and silt layers inhibits a rapid downward movement of saltwater. Below this zone, there is a zone of pore-water resistivity values around 6 Ω.m at the bottom of the model, indicating the possible presence of fresh water below ~200 m depth.
The root-mean-square (rms) errors between the calculated and observed resistivity values range from 2.4% to 12%. Example models obtained at the measured points VES T1 and VES 19 are given in Figure 5, where the model response presents a good fit with measured data and there are notable variations from zone to zone in resistivity values obtained by 1-D inversion. The 1-D models of the investigated VES reveal six geo-electrical layers. The model layers show an alternation of clayey and sandy materials from top to bottom. The soundings show decreased resistivity up to ca. 200 m bgl, followed by a rising resistivity trend. The deepest layer (layer six), having relatively high resistivity values, could be attributed to the freshwater-bearing formation. The VES T1 is located just a few meters from a river and shows a relatively high resistivity value (ca. 6 Ω.m), up to 17 m in depth. On the other hand, VES 19 is located ca. 500 m meters away from a river and shows low values, up to 22 m, compared to VES T1. The relatively high resistivity value (18.4 Ω.m) is observed at the former site below 146 m, while, at the latter site, below 205 m in depth.
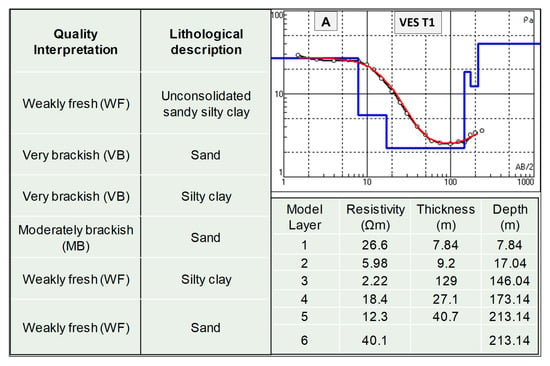
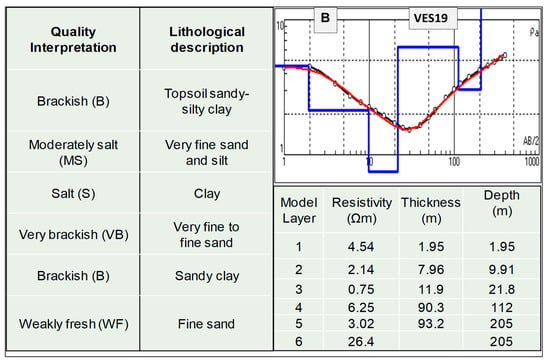
Figure 5.
Example 1-D models obtained from inversion of resistivity data at VES T1 (A) and VES 19 (B) located in the northeast and south of the study area, respectively. Open circles with black line and the red line are the measured VES data and calculated VES data, respectively. The solid blue line is the estimated subsurface resistivity of the geo-electric layers.
4.3. ERT
Figure 6A shows the inverted resistivity model after four iterations, with a 2.6% final RMS error. The model shows that the site is characterized by relatively low background resistivity (1–6 Ω.m), depicting a general trend of low to high resistivity values from top to bottom. The low resistivity values in the profile infer the presence of high salinity. Very low (<1.75 Ω.m) but irregularly distributed resistivity is observed from the ground surface to 120 m depth. Extremely low resistivity (~1 Ω.m) observed locally in two places in the upper part of model is due to infiltration of saltwater. The presence of a pond in the middle of the profile is indicated by a relatively high resistivity value (>2 Ω.m). The gradual increase of resistivity with depth is observed below 120 m depth. The saline-water-filled pores of fine-grain-size sediments are responsible for the low resistivity values. The extent of saltwater movement is mainly controlled by the vertical infiltration. There is no evidence of lateral migration of salt water directly from the Bay of Bengal in the south of the profile.
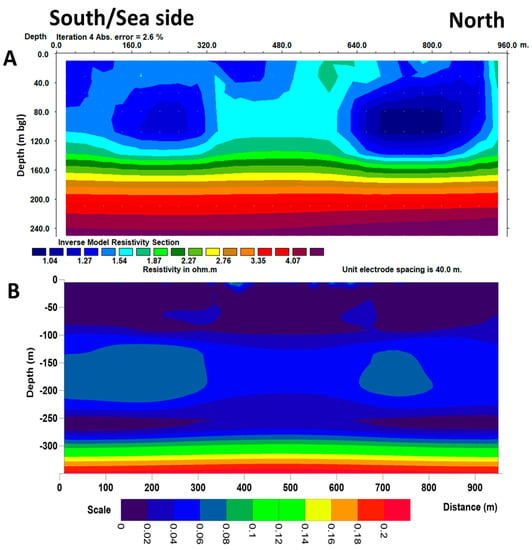
Figure 6.
Interpreted inverse 2-D resistivity model section near the shoreline of the Bay of Bengal (A). Bottom image is a DOI map (B). Profile lies below the DOI index of 0.1, indicating well-resolved regions controlled by the data.
The DOI for the inverted profile is shown in Figure 6B. The DOI map shows that the 0 value is observed close to the surface, down to about 100 m depth below the ground surface. Two isolated zones of relatively high DOI (0.06) are located between 140 and 220 m depths, indicating slight discrepancies between the two inverted models. However, the DOI of these two isolated points is below our threshold level (0.1). Below 300 m depth, the DOI increases sharply, indicating the maximum depth of investigation, considering our threshold value (0.1). The result is less well controlled by the resistivity data below a 300 m depth.
5. Discussion
The potential of an aquifer for freshwater extraction depends on the hydraulic conductivity, storativity, transmissivity, and the quality of water. The varying lithology in the studied borehole logs includes alternating clay, clayey sand, silt, silty clay, very fine sand, fine sand, and medium sand. It is typical of the SW coast of Bangladesh [22]. The coastal plain sand below 200 m depth is the major source of fresh groundwater for domestic purposes in the study area.
The integrated study of natural gamma and resistivity logs, VES, ERT, and EC of sampled waters in this study revealed three hydrostratigraphic sections. The top section is USA, corresponding to low-resistivity brackish water to moderately salt water in some places. Its thickness is around 100 m on average, and it rests on a moderately brackish LSA zone. A few VESs near the rivers indicate the USA top reflected by high resistivity values. These localized high resistivity values may be due to the effect of dry soil, heavy monsoon downpour, and infiltration from the surrounding rivers, ponds, and lakes. This zone extends down to maximum 15 m in depth. However, extracting groundwater from this zone will not be suitable for drinking and domestic use and should be discouraged because of the potential risk of pollution due to poor sanitation and agricultural activities [68].
The second zone, extending between 100 and 220 m, represents a moderately brackish water zone. The transition between the high-salinity upper zone and relatively lower-salinity middle zone is gradual. The zone below ca. 200 m in depth has higher resistivity values, indicating weakly fresh water. Most of the pumping water wells are located in this zone to provide water for domestic purposes. The depth to this weakly freshwater zone varies from place to place, generally between 190 and 285 m, with a minimum depth of 146 m (Figure 7A). The relatively shallow interface depth is observed mainly along the rivers and near the coast. The groundwater flow system of the study area is somewhat complex, but we find some kind of fresh groundwater upconing in the areas of major rivers. The zoomed in section of the southern part (Figure 7B) shows a similar pattern of upconing of fresh groundwater from the DA, and that is mixed with some more saline groundwater above. The map (Figure 7B) also clearly shows that the interface depth decreases near the main rivers and coast, whereas the depth relatively increases towards the continental part of the study area. The water-salinity-type profiles (Figure 8A,B) based on VES show a general trend of decreasing salinity with depth. The salinity along the major rivers and coast is low compared to the landward part. This phenomenon also indicates the upconing of fresh groundwater from the DA and mixing with saltwater from the shallow aquifers above. We would recommend to further investigate the hypothesis with different scenarios, such as GW abstraction, sea-level rises due to climate change, etc. The use of radiocarbon (14C), along with stable isotopes, could be very helpful to reveal the age and recharge mechanisms of the water in the study area, and we plan to perform this in the future.
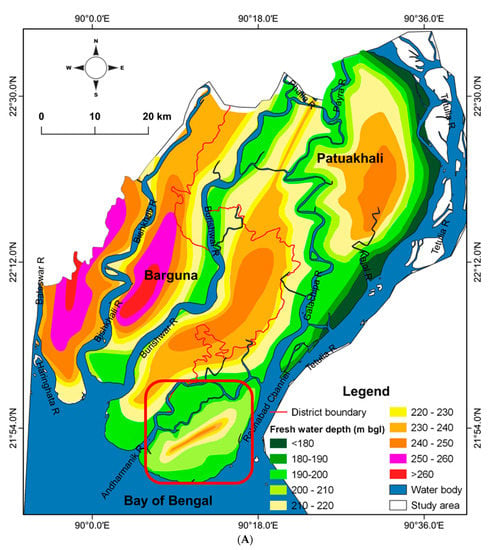
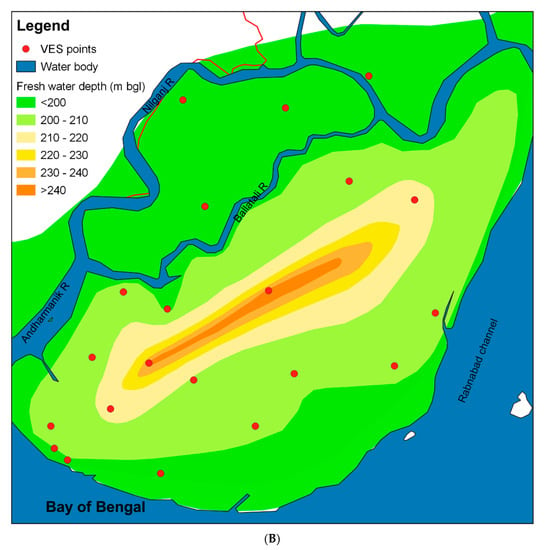
Figure 7.
(A) Map depicting the depth to the saltwater–freshwater interface in the study area. (B) Saltwater–freshwater interface zoomed in within the limit of the red rectangle in Figure 7A for clarity of displaying trend of interface depth in the study area.
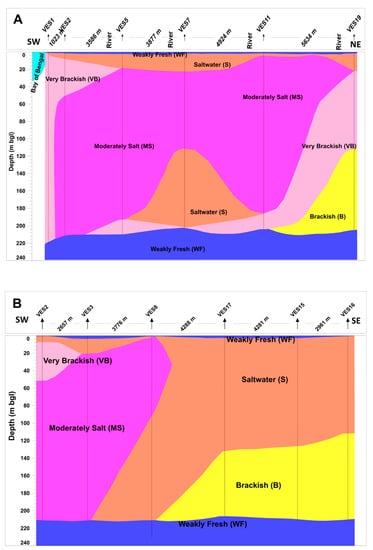
Figure 8.
Water-salinity-class profiles based on VES in the southern part of the study area. The profiles (A,B) are directed SW-NE and SW-SE, respectively. The location of the VES was shown in Figure 1.
The presence of some saltwater-contaminated ponds corresponds to low resistivity values at shallow depth. It is worth noting that there is no sign of saltwater movement from the sea to the landward side of the study area. Rather, saltwater is infiltrating from the top layers downwards. Extensive pumping from the deeper aquifers, especially in the towns and population growth centers, causes vertical infiltration of salt water from the upper aquifers and is also responsible for the salinization of the DA. The salinity in the top layer is the result of the leaching of evaporite deposited on the depressed/low-lying areas and mixing with marine-induced flood water [22,66]. Some authors [69,70] also showed that lateral seawater intrusion is slow compared to the downward infiltration of saltwater as a natural phenomenon in the coastal area of SW Bangladesh. This could also be a cause of variation of the depth to saltwater–freshwater boundary in the study area. Groundwater flows from recharge areas having high hydraulic heads to low hydraulic heads in the coastal area. Low-density fresh water tends to remain above high-density salt water, and this probably can explain the presence of some freshwater zone due to accumulation of rainwater at the top of the upper shallow unconfined aquifers, where water is mostly brackish in some studied VESs. Many researchers [71,72,73,74,75,76] have documented repeated sea-level changes that influence and change the direction of groundwater flow in the coastal area of Bangladesh. The presence of saline water below 300 m in depth in some studied resistivity logs in the SW corner of the study area results from the Holocene marine transgression between 10,000 and 6000 BP, when the sea level increased fast, and the flow situation may have changed severely. At this time, seawater was trapped in the back-barrier dunes and lagoon environments.
The interface depth was plotted against the distance to the important rivers (Figure 9). This graph illustrates that the interface depth drops with increasing distance to the river, indicating that the salinity depth distribution is influenced locally by the upward flow of fresh groundwater from the deep aquifer. A noticeable upward flow of fresh groundwater from the deep aquifer is marked vertically up to 150 m and laterally within 1500 m distance from the rivers. Beyond 1500 m from the river, the interface depth remains practically constant (Figure 9). The presence of fresh groundwater at a shallow depth in some studied VESs in the northern part of the study area near the river indicates freshening by river water and rainwater in the upper part of the shallow water table aquifer. Very similar results were also observed by Sarker et al. [22], using chloride profiles, where the depths of groundwater samples were 30 m to ca. 100 m, acquired perpendicular to the rivers in six different locations over the study area.
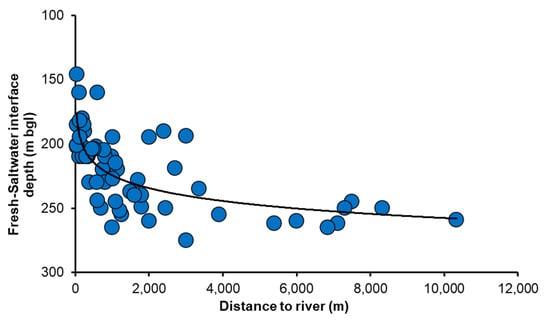
Figure 9.
Graph showing freshwater–saltwater interface depth versus distance to the rivers.
6. Conclusions
Knowing the depth at which fresh water occurs is of crucial importance to the people living in the saltwater-affected coastal area of SW Bangladesh. Geophysical well logs (natural GR and LN electrical resistivity) are integrated with borehole logs, VES, and ERT from the SW coastal area of Bangladesh to infer the source and location of subsurface saltwater and freshwater zones. We were able to identify the existence of three major aquifers with different water qualities. The upper aquifer above 100 m bgl depth is mostly brackish and sometimes highly to moderately saline in nature and prone to surface contamination. High salinity in this aquifer is not due to lateral saltwater intrusion from the Bay of Bengal revealed by ERT and VES. The discontinuous aquitard below the USA allows saltwater movement to the hydraulically connected LSA at depths of 100–200 m; it bears mostly moderately brackish water. In this aquifer, the salinity level is a bit lower compared to the upper aquifer. A continuous clay/silty clay layer below the LSA inhibits saline-water migration to the DA encountered below 200 m bgl. Water quality in this aquifer is weakly fresh. The presence of salt water below 300 m in the SW corner of the study area revealed in some resistivity logs, VES, and EC of the sampled groundwater probably results from the influence of sea-level rise during the Holocene transgression. From the equivalent EC of water in the aquifer, estimated from the geophysical and hydrochemical data, we mapped the salinity in the aquifer qualitatively and determined the saltwater/freshwater interface depth. The maps show that the shallowest interface depth is observed along the major rivers and coast, due to upconing of fresh groundwater from the DA. A relatively higher depth of interface is observed in the landward part of the study area. The interface depth versus distance to the major rivers shows a positive correlation; that is, the interface depth is increasing with increasing distance to the river, indicating that the freshwater distribution is influenced by the upward flow of DA water. The salinity profiles indicate a general trend of decreasing salinity with depth, but, more importantly, near the major rivers compared to the more landward part. This also indicates the vertical flow of DA water, and that is mixed with more saline waters above. It is recommended that the future groundwater exploitation be done in the DA, 200 m bgl.
This study, therefore, indicates the importance of the combined use of geophysics and hydrochemistry in delineating accurate water-quality type in aquifers useful in well design, construction, development, and groundwater abstraction, especially in complex hydrogeological coastal area.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M.R.S. and K.W.; methodology, M.M.R.S. and K.W.; software, M.M.R.S., T.H., M.V.C., D.H. and M.I.; validation, M.M.R.S., T.H., M.V.C., D.H. and K.W.; formal analysis, M.M.R.S., T.H., M.V.C., M.I. and K.W.; investigation, M.M.R.S., D.H., M.Z.U., N.A., M.A.Q.B. and M.M.K.; resources, M.M.R.S.; data curation, M.M.R.S. and M.I.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M.R.S.; writing—review and editing, T.H., M.V.C., D.H. and K.W.; visualization, M.M.R.S. and K.W.; supervision, K.W.; funding acquisition, M.M.R.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Bangabandhu Science and Technology Fellowship Trust, Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the GSB for assistance with the fieldwork and Md. Yakub Hossain, Electronic Officer of GSB, for his support during the geophysical field campaign. DPHE and BWDB are also thanked for providing necessary data. Thanks to ASM Woobaidullah, Professor, Department of Geology, Dhaka University, for providing access to VES data. Special thanks to Jill Van Rey-brouck, Laboratory for Applied Geology and Hydrogeology, Department of Geology, Ghent Uni-versity for analyzing water samples. The authors are also grateful to Muhammad Arifuzzaman, Director, and Sultana Nasrin Nury, Deputy Director of GSB, for their cooperation in conducting the geophysical field survey. Thanks to Cong-Thi Diep for her help in calculating the DOI. Thanks to Md. Abdur Rahim, Md. Atequr Rahman, and Md. Kutub Uddin for their help during field-work. The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their comments and sugges-tions in improving the quality of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Karim, Z. Salinity Problems and Crop Intensification in the Coastal Regions of Bangladesh. Soil Publ. No. 33, 1990. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/264419412_Salinity_Problems_and_Crop_Intensification_in_the_Coastal_Regions_of_Bangladesh (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), Bangladesh MICS 2012-2013: Water Quality Thematic Report. Government of Bangladesh, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics, and UNICEF, 2018. Available online: https://www.unicef.org/bangladesh/sites/unicef.org.bangladesh/files/2018-10/Drinking%20Water%20Quality%20in%20Bangladesh.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Kamruzzaman, A.; Ahmed, F. Study of Performance of Existing Pond Sand Filters in Different Parts of Bangladesh. In Proceedings of the 32nd WEDC International Conference, Colombo, Sri Lanka, 13–17 September 2006; Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/2134/29649 (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Islam, M.; Chou, F.F.; Kabir, M.R.; Liaw, C.H. Rainwater: A Potential Alternative Source for Scarce Safe Drinking and Arsenic Contaminated Water in Bangladesh. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 3987–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedin, A.; Habiba, U.; Shaw, R. Community Perception and Adaptation to Safe Drinking Water Scarcity: Salinity, Arsenic, and Drought Risks in Coastal Bangladesh. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2014, 5, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.E.; Ireson, A.; Kovats, S.; Mojumder, S.K.; Khusru, A.; Rahman, A.; Vineis, P. Drinking Water Salinity and Maternal Health in Coastal Bangladesh: Implications of Climate Change. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1328–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.E.; Scheelbeek, P.F.D.; Shilpi, A.B.; Chan, Q.; Mojumder, S.K.; Rahman, A.; Haines, A.; Vineis, P. Salinity in Drinking Water and the Risk of (Pre)Eclampsia and Gestational Hypertension in Coastal Bangladesh: A Case-Control Study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alam, A.; Rahman, M.; Islam, S. Performance of modified design pond sand filters. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.-Aqua 2011, 60, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, B.; Islam, A.; Majumder, A. Seawater intrusion into groundwater and its impact on irrigation and agriculture: Evidence from the coastal region of West Bengal, India. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 44, 101751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, P.M. Ground Water in Freshwater-Saltwater Environments of the Atlantic Coast; Geological Survey (USGS): Sunrise Valley Drive, Reston, VA, USA, 2003; Volume 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meisler, H.; Leahy, P.P.; Knobel, L.L. Effect of Eusta108715tic Sea-Level Changes on Saltwater-Freshwater Relations in the Northern Atlantic Coastal Plain; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1984; Volume 2255. [Google Scholar]
- Jimoh, R.A.; Bankole, O.M.; Ahmed, K.; Christopher, O.A.; Adeniji, M.A.; Ebhodaghe, J.; Sedara, S.O.; Obende, P.W.; Alebu, O.; Ezima, E.A. Use of geophysical logs in hydrogeological studies and borehole designs: Case study of Apapa coastal area, Lagos, Nigeria. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Camp, M.; Mtoni, Y.; Mjemah, I.C.; Bakundukize, C.; Walraevens, K. Investigating seawater intrusion due to groundwater pumping with schematic model simulations: The example of the Dar es Salaam coastal aquifer in Tanzania. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2014, 96, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walraevens, K.; Mjemah, I.C.; Mtoni, Y.; Van Camp, M. Sources of salinity and urban pollution in the Quaternary sand aquifers of Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2015, 102, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedin, M.; Habiba, U.; Shaw, R. Chapter 10 Health: Impacts of Salinity, Arsenic and Drought in South-western Bangladesh; Emerald Group Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2012; pp. 165–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woobaidullah, A.; Rahman, M.; Romer, A.; Arndt, R. Geoelectric resistivity survey for suitable freshwater aquifer identification in the coastal Belt of south-west Bangladesh. Jb Geol BA 1996, 139, 127–137. [Google Scholar]
- Afroza, R.; Mazumder, Q.H.; Jahan, C.S.; Kazi, M.A.I.; Ahsan, M.A.; Al-Mansur, M.A. Hydrochemistry and origin of salinity in groundwater in parts of Lower Tista Floodplain, northwest Bangladesh. J. Geol. Soc. India 2009, 74, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, P.K.; Froehlich, K.; Basu, A.; Poreda, R.; Kulkarni, K.; Tarafdar, S.; Mohamed, A.; Nasir, A.; Alamgir, H.; Mizanur, R. A Report on Isotope Hydrology of Groundwater in Bangladesh: Implications for Characterization and Mitigation of Arsenic in Groundwater; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2000; 61p. [Google Scholar]
- Bahar, M.M.; Reza, M.S. Hydrochemical characteristics and quality assessment of shallow groundwater in a coastal area of Southwest Bangladesh. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 61, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.Q. Hydrochemistry of lowlands water of southwest Bangladesh. Lowl. Technol. Int. Off J. Int. Assoc. Lowl. Technol. 2000, 2, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, T.; Mirza, A.; Rahman, S.H.; Majumder, R.K. Groundwater quality for irrigation of deep aquifer in southwestern zone of Banglades. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2012, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Sarker, M.R.; van Camp, M.; Islam, M.; Ahmed, N.; Walraevens, K. Hydrochemistry in coastal aquifer of southwest Bangladesh: Origin of salinity. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melloul, A.; Goldenberg, L. Monitoring of Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers: Basics and Local Concerns. J. Environ. Manag. 1997, 51, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Archie, G.E. The Electrical Resistivity Log as an Aid in Determining Some Reservoir Characteristics. Trans. AIME 1942, 146, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, D.K. Some case histories of geophysical downhole logging to examine borehole site and regional groundwater movement in Celtic regions. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spéc. Publ. 2000, 182, 219–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, D.K.; Hinsby, K.; Manzano, M. Application of geophysical borehole logging techniques to examine coastal aquifer palaeohydrogeology. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spéc. Publ. 2001, 189, 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallenburg, J.K. Geophysical Logging for Mineral and Engineering Applications; PennWell Publishing: Tulsa, Oklahoma, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Mares, S.; Zboril, A.; Kelly, W. Logging for determination of aquifer hydraulic properties. Log Anal. 1994, 35, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Repsold, H. Well logging in groundwater development. Heise 1989, 9, 136. [Google Scholar]
- Cong-Thi, D.; Dieu, L.; Thibaut, R.; Paepen, M.; Ho, H.; Nguyen, F.; Hermans, T. Imaging the Structure and the Saltwater Intrusion Extent of the Luy River Coastal Aquifer (Binh Thuan, Vietnam) Using Electrical Resistivity Tomography. Water 2021, 13, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (BBS). Statistical Yearbook of Bangladesh; Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics, Ministry of Planning: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Website. Available online: http://www.tides4fishing.com/as/bangladesh/sundarban (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (BBS). Population and Housing Census. In Socio-Economic and Demographic Report, National Series; Ministry of Planning, Statistics and Informatics Division (SID): Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2011; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, H., Jr.; Jacob, C.E. A generalized graphical method for evaluating formation constants and summarizing well-field history. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1946, 27, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, M.M.R. Hydrogeology and Hydrochemistry in a Coastal Aquifer: A Case Study from Southwestern Part of Bangladesh. Master’s Thesis, Universiteit Brussel and Universiteit Gent, Ghent, Belgium, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gheorghe, A. Processing and Synthesis of Hydrogeological Data; Abacus Press: Hachette, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Ferris, J.G.; Knowles, D.; Brown, R.; Stallman, R.W. Theory of Aquifer Tests; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1962.
- Hvorslev, M.J. Time Lag and Soil Permeability in Ground-Water Observations; Corps of Engineers, US Army: Washington, DC, USA, 1951. [Google Scholar]
- Kruseman, G.P.; de Ridder, N.A.; Verweij, M.J. Analysis and Evaluation of PumpingTest Data; International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1970; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- Boughriba, M.; Melloul, A.; Zarhloule, Y.; Ouardi, A. Extension Spatiale de la Salinisation des Ressources en eau et Modèle Conceptuel des Sources Salées Dans la Plaine des Triffa (Maroc Nord-Oriental). Comptes Rendus Geosci. 2006, 338, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guasmia, M. Caracterisation de la Geometrie des Aquiferes Alluvionnaires, Neogene Sableux et Cretace Carbonate du Bassin de Gafsa par les Methods Geophysiques. Ph.D. Thesis, Universite de Sfax, Sfax, Tunisia, 2008; 220p. [Google Scholar]
- Adepelumi, A.A.; Ako, B.D.; Ajayi, T.R.; Afolabi, O.; Omotoso, E.J. Delineation of saltwater intrusion into the freshwater aquifer of Lekki Peninsula, Lagos, Nigeria. Environ. Earth Sci. 2008, 56, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.; Ingham, M.; McConchie, J. The applicability of earth resistivity methods for saline interface definition. J. Hydrol. 2006, 316, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, F.; Kemna, A.; Antonsson, A.; Engesgaard, P.; Kuras, O.; Ogilvy, R.; Gisbert, J.; Jorreto, S.; Pulido-Bosch, A. Characterization of seawater intrusion using 2D electrical imaging. Near Surf. Geophys. 2009, 7, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goebel, M.; Pidlisecky, A.; Knight, R. Resistivity imaging reveals complex pattern of saltwater intrusion along Monterey coast. J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keys, W.S. A Practical Guide to Borehole Geophysics in Environmental Investigations; Routledge: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Belknap, W.B.; Dewan, J.T.; Kirkpatrick, C.; Mott, W.E.; Pearson, A.; Rabson, W. API calibration facility for nuclear logs. In Drilling and Production Practice; American Petroleum Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, J.M. An Introduction to Applied and Environmental Geophysics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Science and Technology (MoST). Government of People’s Republic of Bangladesh, Evaluation and Monitoring the Consequences of Saline Water Intrusion and Land Erosion-Accretion on the South-Central Coastal Ecosystem of Bangladesh; MoST: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2014–2016. [Google Scholar]
- IPI2WIN-1D Program. In Programs Set for 1D VES Data Interpretation; Moscow University: Moscow, Russia, 2000.
- Tikhonov, A.N.; Arsenin, V.Y. Solutions of ill-posed problems. SIAM Rev. 2012, 21, 266–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caterina, D.; Hermans, T.; Nguyen, F. Case studies of incorporation of prior information in electrical resistivity tomography: Comparison of different approaches. Near Surf. Geophys. 2014, 12, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loke, M.; Chambers, J.; Rucker, D.; Kuras, O.; Wilkinson, P. Recent developments in the direct-current geoelectrical imaging method. J. Appl. Geophys. 2013, 95, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, M.; Barker, R. Rapid least-squares inversion of apparent resistivity pseudosections by a quasi-Newton method1. Geophys. Prospect. 1996, 44, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, M. Rapid 2D Resistivity Forward Modeling Using the Finite-Difference and Finite-Element Methods; Geotomo Software: Penang, Malaysia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Oldenburg, D.W.; Li, Y. Estimating depth of investigation in dc resistivity and IP surveys. Geophysics 1999, 64, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caterina, D.; Beaujean, J.; Robert, T.; Nguyen, F. A comparison study of different image appraisal tools for electrical resistivity tomography. Near Surf. Geophys. 2013, 11, 639–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paepen, M.; Hanssens, D.; Smedt, P.D.; Walraevens, K.; Hermans, T. Combining resistivity and frequency domain electromagnetic methods to investigate submarine groundwater discharge in the littoral zone. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 3539–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsekian, A.D.; Claes, N.; Singha, K.; Minsley, B.J.; Carr, B.; Voytek, E.B.; Harmon, R.; Kass, A.; Carey, A.; Thayer, D.; et al. Comparing Measurement Response and Inverted Results of Electrical Resistivity Tomography Instruments. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2017, 22, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marescot, L.; Loke, M.; Chapellier, D.; Delaloye, R.; Lambiel, C.; Reynard, E. Assessing reliability of 2D resistivity imaging in mountain permafrost studies using the depth of investigation index method. Near Surf. Geophys. 2002, 1, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnode, H.; Willie, M. The presence of borehole geophysics to water resources investigations. In Techniques of Waterresources Investigations of the USGS; Book 2; U.S. Geological Survey: Seattle, WA, USA, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- Vlieghe, C. Hydrogeologische Studie van het Poldergebied in de Omgeving van Booitshoeke. Master’s Thesis, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- de Moor, G.; de Breuck, W. De freatische waters in het Oostelijk Kustgebied en in de Vlaamse Vallei. Natuurwet. Tijdschr. 1969, 51, 3–68. [Google Scholar]
- Walraevens, K.; Lebbe, L.; van Camp, M.; Angius, G.; Serra, M.; Vacca, A.; Massidda, R.; Debreuck, W. Salt fresh-water flow and distribution in a cross-section at Oostduinkerke (Western Coastal-Plain of Belgium). Study Model. Saltwater Intrusion Aquifers 1993, 407–420. [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbohede, A.; Walraevens, K.; de Breuck, W. What does the interface on the fresh-saltwater distribution map of the Belgian coastal plain represent? Geol. Belg. 2015, 18, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Sarker, M.M.R.; van Camp, M.; Hossain, D.; Islam, M.; Ahmed, N.; Karim, M.M.; Bhuiyan, M.A.Q.; Walraevens, K. Groundwater salinization and freshening processes in coastal aquifers from southwest Bangladesh. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, M.M.R.; Camp, M.V.; Hossain, D.; Islam, M.; Bhuiyan, M.A.Q.; Ahsan, M.A.; Bennett, G.; Walraevens, K. Understanding the Hydrogeochemical Evolution of Groundwater in Coastal Aquifers of Southwest Bangladesh. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts 2021, online. 19–30 April 2021; EGU21-9767. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5194/egusphere-egu21-9767 (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Islam, M.; Siddika, A.; Khan, M.; Goldar, M.; Sadique, M.A.; Kabir, A.; Huq, A.; Colwell, R. Microbiological analysis of tube-well water in a rural area of Bangladesh. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 3328–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Faneca Sànchez, M.; Bashar, K.; Janssen, G.; Vogels, M.; Snel, J.; Zhou, Y.; Stuurman, R.J.; Essink, G.O. SWIBANGLA: Managing Salt Water Intrusion Impacts in Coastal Groundwater Systems of Bangladesh. 2015. Available online: https://www.deltares.nl/app/uploads/2015/04/1207671-000-BGS-0016-r-SWIBANGLA-def.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Michael, H.A.; Voss, C.I. Controls on groundwater flow in the Bengal Basin of India and Bangladesh: Regional modeling analysis. Hydrogeol. J. 2009, 17, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, M.; Khan, S.; Goodbred, S.; Kuehl, S. Stratigraphic evolution of the late Holocene Ganges–Brahmaputra lower delta plain. Sediment. Geol. 2003, 155, 317–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodbred, S., Jr.; Kuehl, S.A. The significance of large sediment supply, active tectonism, and eustasy on margin sequence development: Late Quaternary stratigraphy and evolution of the Ganges–Brahmaputra delta. Sediment. Geol. 2000, 133, 227–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umitsu, M. Late Quaternary sedimentary environment and landform evolution in the Bengal lowland. Geogr. Rev. Jpn. Ser. B 1987, 60, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Umitsu, M. Late quaternary sedimentary environments and landforms in the Ganges Delta. Sediment. Geol. 1993, 83, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbridge, R.W. Eustatic changes in sea level. Phys. Chem. Earth 1961, 4, 99–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.R.; Islam, B. Holocene stratigraphy of the lower Ganges-Brahmaputra river delta in Bangladesh. Front. Earth Sci. China 2008, 2, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).