Application of Integrated Watershed Management Measures to Minimize the Land Use Change Impacts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
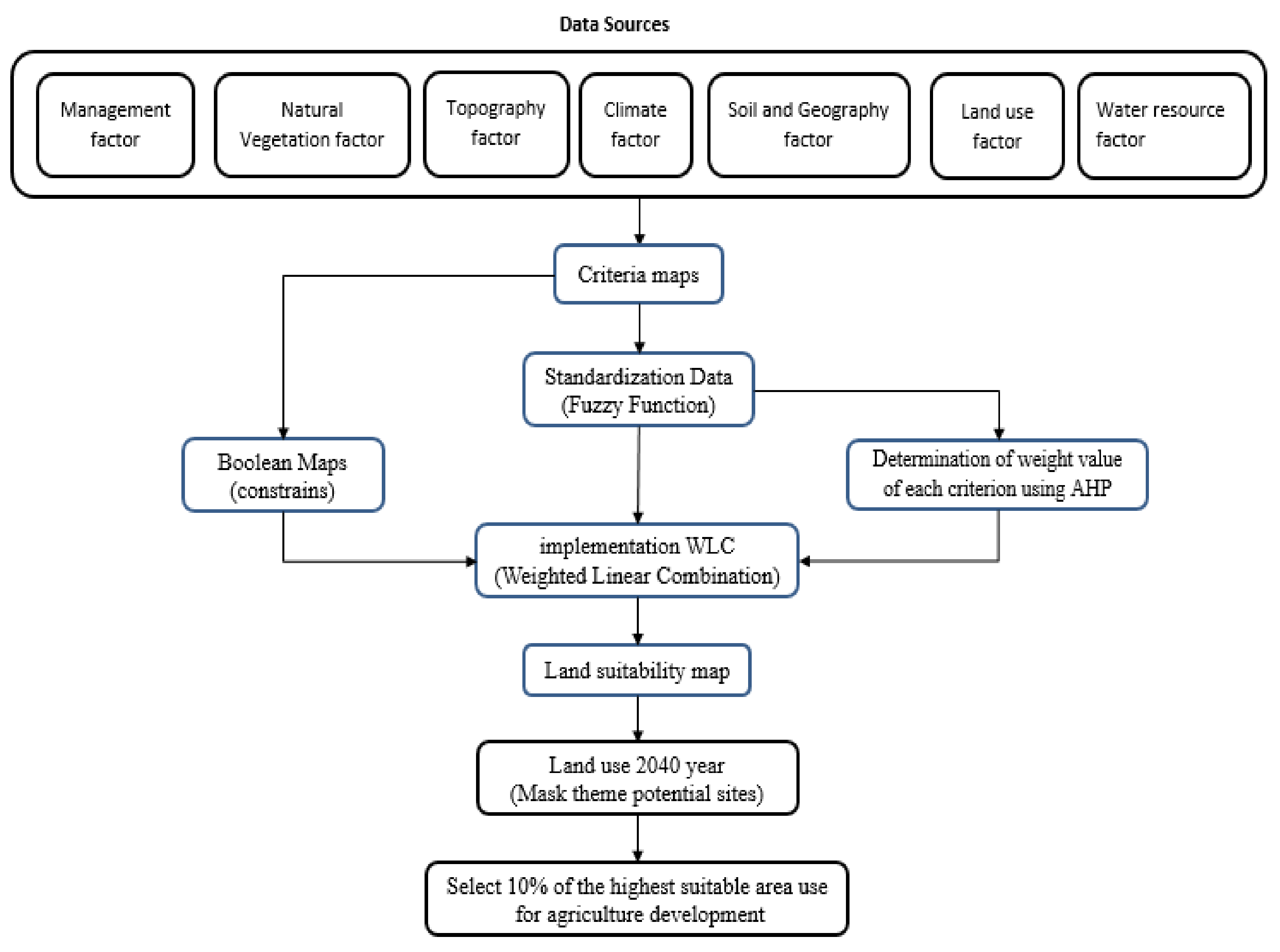
2. Materials and Methods
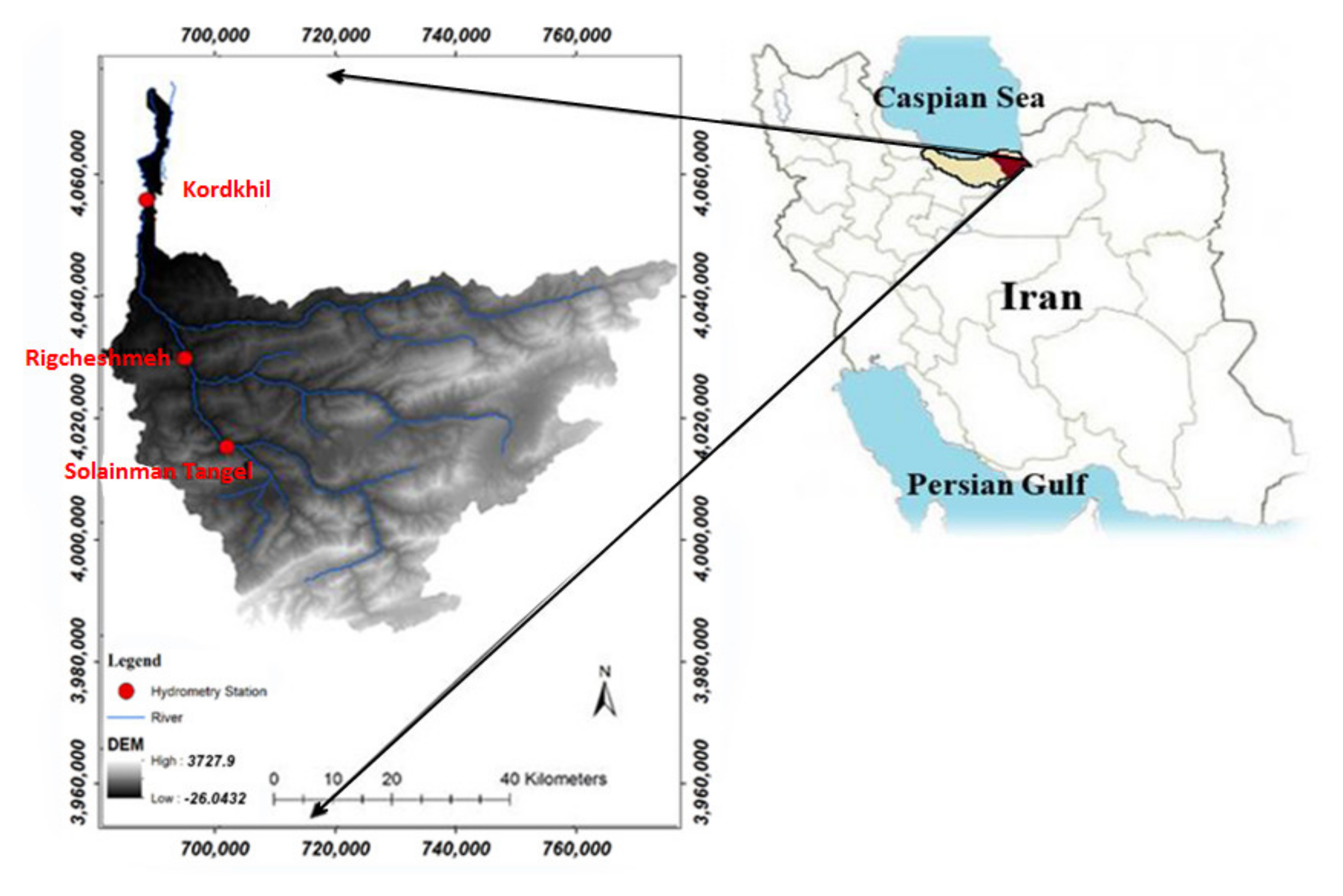
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Land Use/Land Cover Change Modeling
2.3. Future Land Use/Land Cover Scenarios
2.4. Watershed Modeling
3. Results and Discussion
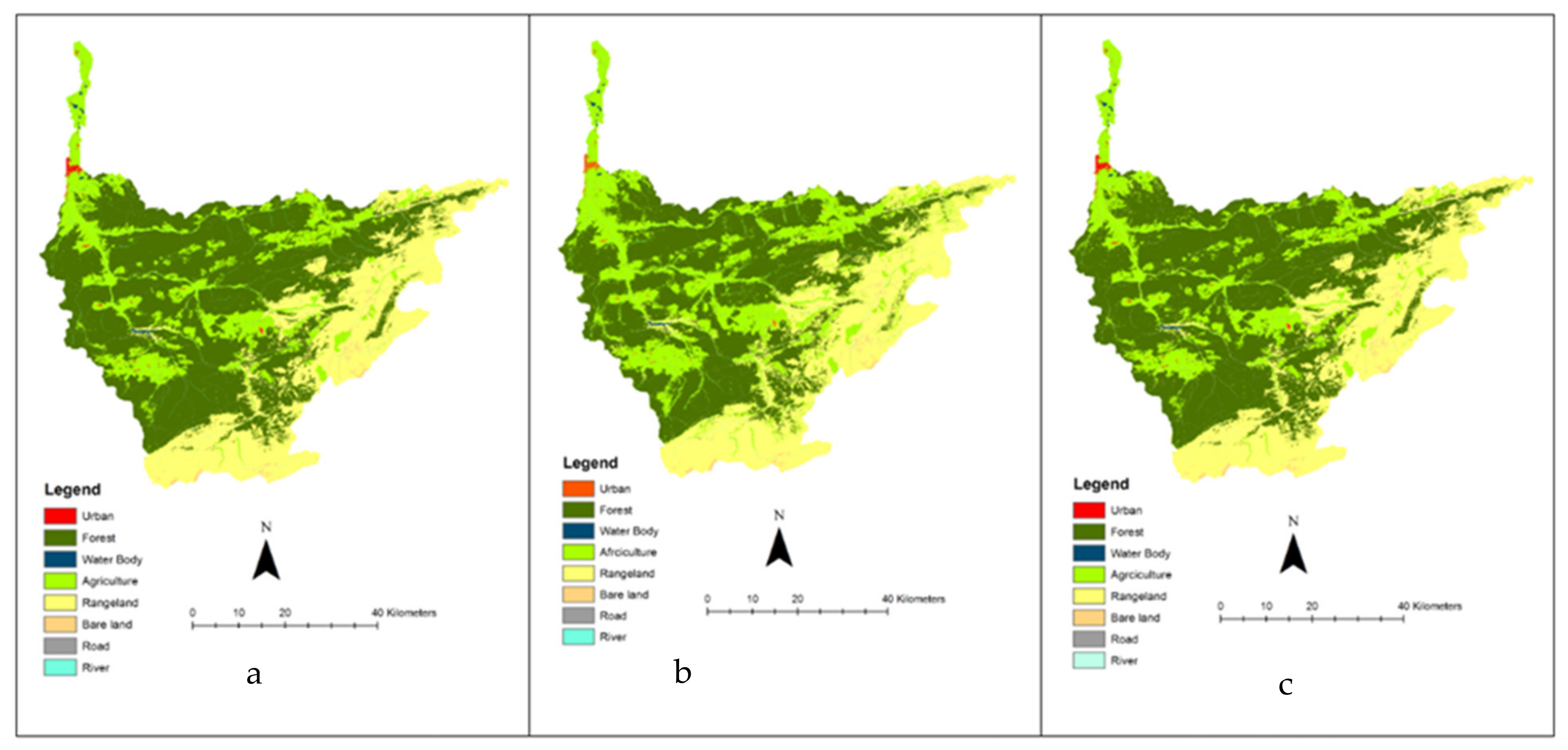
3.1. Land Use/Land Cover Change Modeling
3.2. Future Land Use Planning
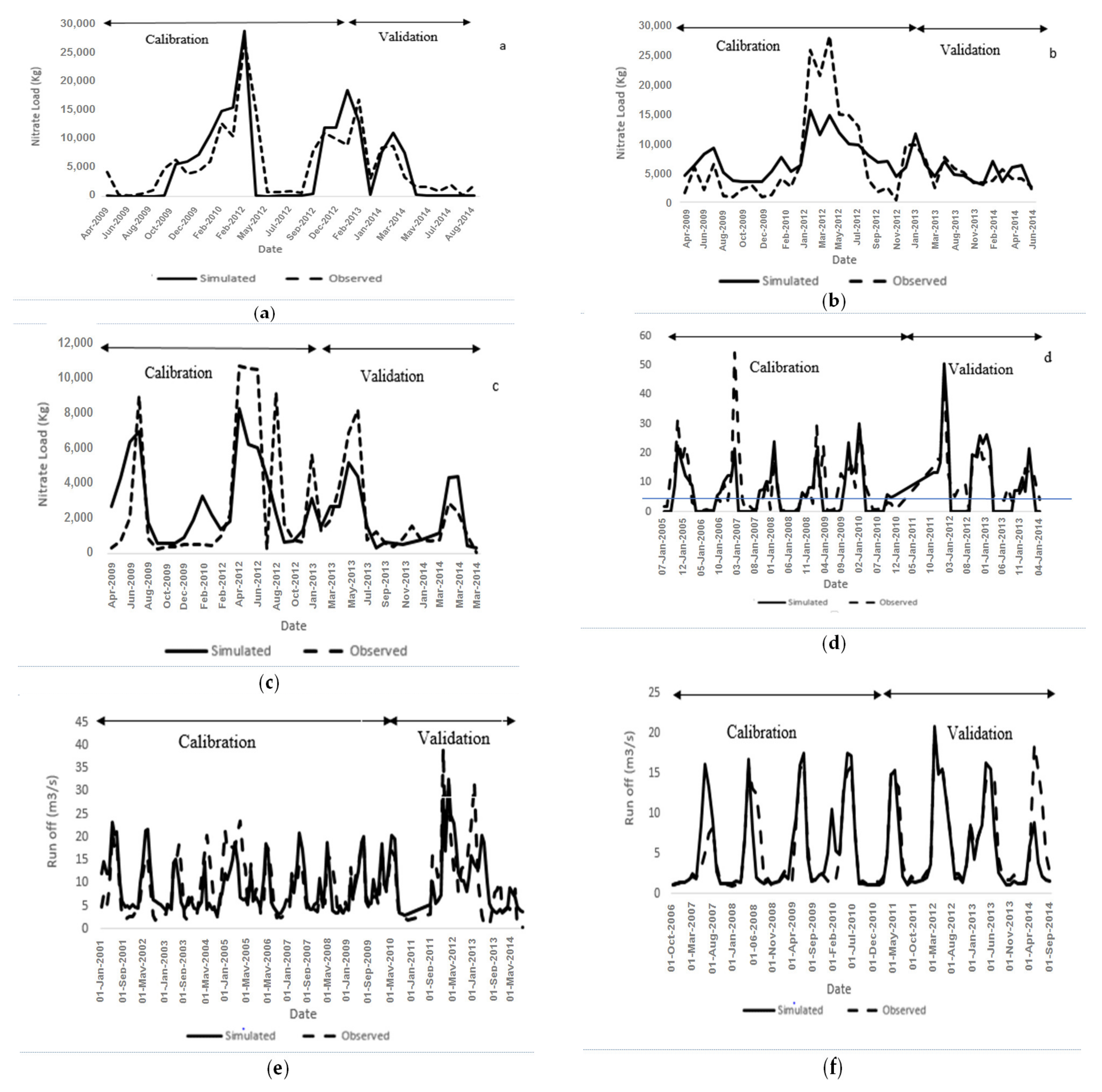
3.3. Land Use/Land Cover Change Impact on Nitrate Load
3.3.1. Projecting Annual Nitrate Loads
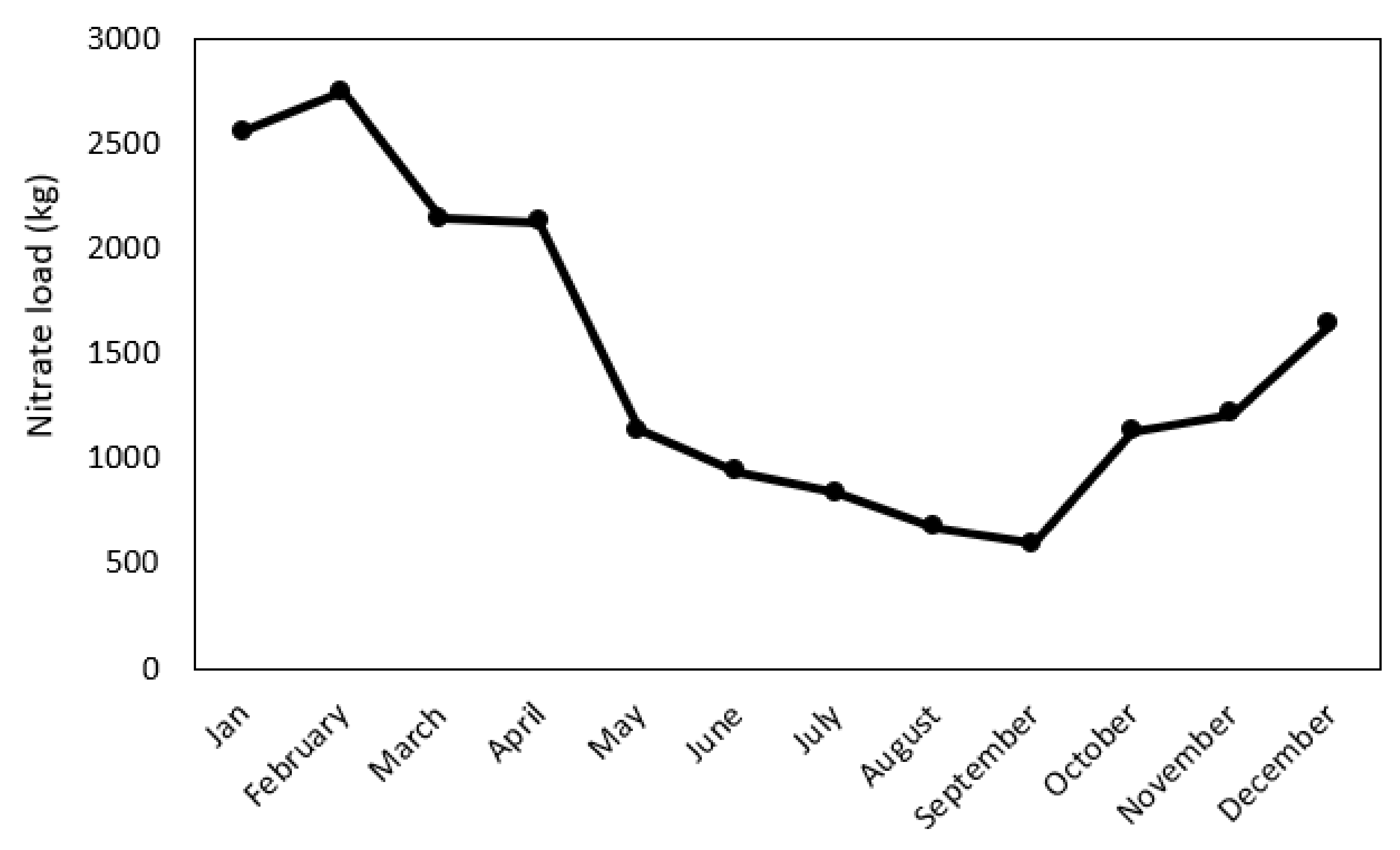
3.3.2. Projecting Monthly Nitrate Loads
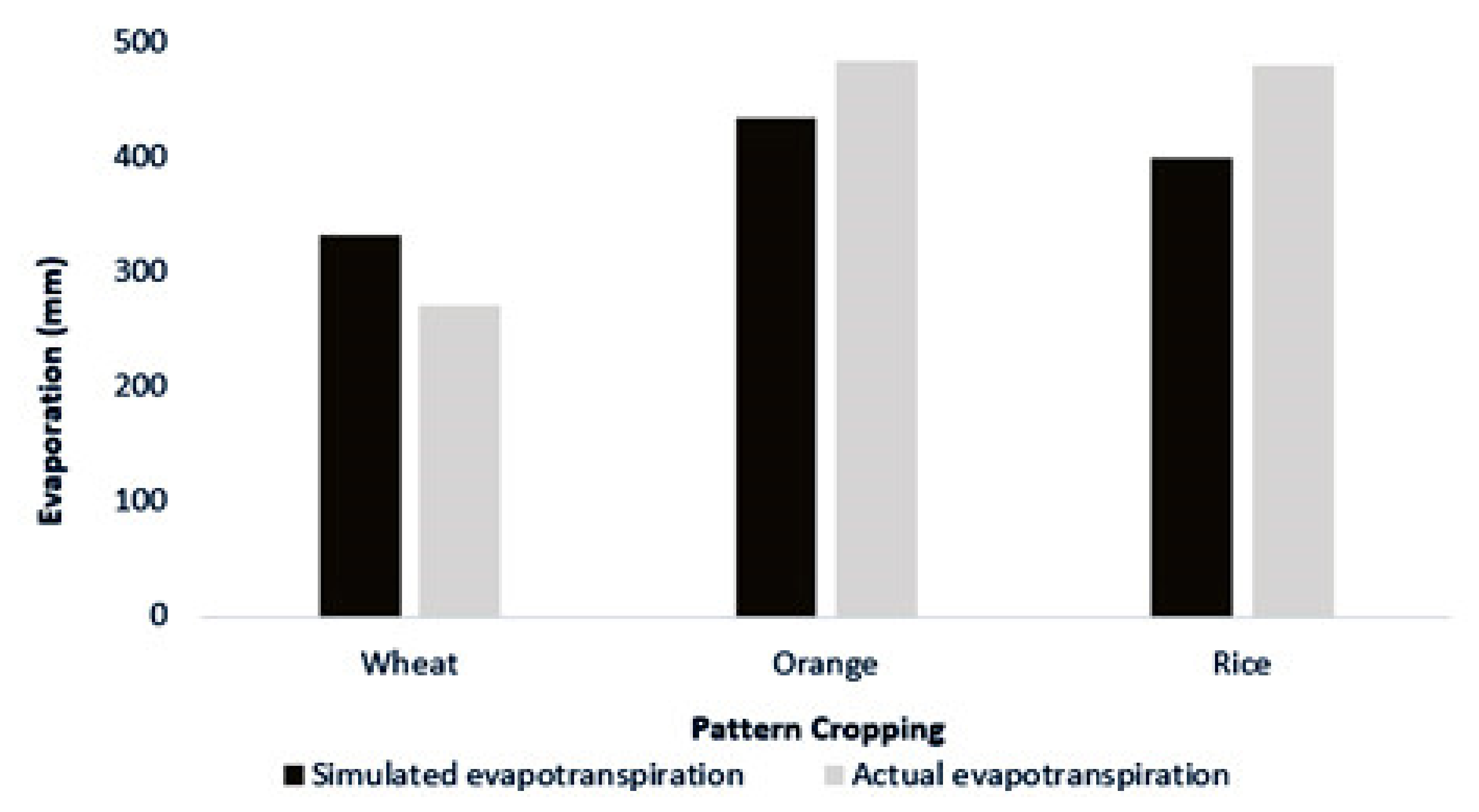
3.3.3. Components Related to Nitrate Losses
3.3.4. Limitations and Future Research
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO Global Forest Resources Assessment. Progress Towards Sustainable Forest Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Tingsanchali, T. Urban flood disaster management. Procedia Eng. 2012, 32, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IFRWMO Rport of Iran’s Forests, Range and Watershed Management Organization (2018). Repot 200. Available online: https://frw.ir/02/Fa/default.aspx (accessed on 8 June 2018).
- Rajaei, F.; Sari, A.E.; Salmanmahiny, A.; Randhir, T.O.; Delavar, M.; Behrooz, R.D.; Bavani, A.M. Simulating long-term effect of Hyrcanian forest loss on phosphorus loading at the sub-watershed level. J. Arid Land 2018, 10, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emadodin, I. Impacts of Land Management on Soil Formation and Soil Degradation during Middle and Late Holocene in Schleswig-Holstein (Germany). Ph.D. Thesis, Mathematisch-Naturwissenschaftliche Fakultät, Zürich, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gholamalifard, M.; Joorabian Shooshtari, S.; Hosseini Kahnuj, S.H.; Mirzaei, M. Land cover change modeling of coastal areas of Mazandaran Province using LCM in a GIS environment. J. Environ. Stud. 2013, 38, 109–124. [Google Scholar]
- Tavangar, S.; Moradi, H.; Massah Bavani, A.; Gholamalifard, M. A futuristic survey of the effects of LU/LC change on stream flow by CA--Markov model: A case of the Nekarood watershed, Iran. Geocarto Int. 2019, 36, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. The Analytic Hierarchy Process Mcgraw Hill, New York. Agric. Econ. Rev. 1980, 70, 109–121. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Hoyos, A.; Udías, A.; Rembold, F. Integrating multiple land cover maps through a multi-criteria analysis to improve agricultural monitoring in Africa. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 88, 102064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feizizadeh, B.; Blaschke, T. Land suitability analysis for Tabriz County, Iran: A multi-criteria evaluation approach using GIS. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2013, 56, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.A.; Singh, M.; Sahoo, R.N.; Ahmed, N.; Khanna, M.; Sarangi, A.; Mishra, A.K. Land suitability analysis for different crops: A multi criteria decision making approach using remote sensing and GIS. Researcher 2011, 3, 61–84. [Google Scholar]
- Neitsch, S.L.; Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Williams, J.R. Soil and Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation Version 2009; Texas Water Resources Institute Technical Repott No.406; Texas A&M University System: College Station, TX, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sigaroodi, S.K.; Ebrahimi, S. Effects of land use change on surface water regime (case study Orumieh Lake of Iran). Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salmani, H.; MOHSENI, S.M.; Rouhani, H.; Salajegheh, A. Evaluation of Land Use Change and Its Impact on the Hydrological Process in the Ghazaghli Watershed, Golestan Province; J. Watershed. Manag. Res. 2012, 3, 43–60. [Google Scholar]
- Zare, M.; Samani, A.A.N.; Mohammady, M.; Salmani, H.; Bazrafshan, J. Investigating effects of land use change scenarios on soil erosion using CLUE-s and RUSLE models. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 14, 1905–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arami, S.A.; Ownegh, M.; Mohammadian Behbahani, A.; Akbari, M.; Zarasvandi, A. Statistical Analysis of Spatio-Temporal Pattern of Dust Storms in West and Southwest of Iran. J. Water Soil Conserv. 2018, 25, 61–83. [Google Scholar]
- Fallah, M.; Farajzadeh, M. The assessment of land use and land cover change on abiotic characterises of Tajan River, Iran. Iran. J. Geogr. Res. 2008, 64, 89–104. [Google Scholar]
- Rajaei, F.; Sari, A.E.; Salmanmahiny, A.; Delavar, M.; Bavani, A.R.M.; Srinivasan, R. Surface drainage nitrate loading estimate from agriculture fields and its relationship with landscape metrics in Tajan watershed. Paddy Water Environ. 2017, 15, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodorevskaya, R.P.; Dovgopol, G.F.; Zhuravleva, O.L.; Vlasenko, A.D. Present status of commercial stocks of sturgeons in the Caspian Sea basin. In Sturgeon Biodiversity and Conservation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 209–219. [Google Scholar]
- Eastman, J.R. IDRISI Selva Manual; Clark labs-Clark University: Worcester, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Eastman, J.R.; Solórzano, L.A.; Van Fossen, M.E. Transition Potential Modeling for Land-Cover Change. GIS Spat. Anal. Modeling 2005, 17, 357–386. [Google Scholar]
- Shooshtari, S.J.; Gholamalifard, M. Scenario-based land cover change modeling and its implications for landscape pattern analysis in the Neka Watershed, Iran. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2015, 1, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J.R. IDRISI Andes guide to GIS and image processing; Clark University: Worcester, MA, USA, 2006; p. 328. [Google Scholar]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. In Fuzzy Sets, Fuzzy Logic, and Fuzzy Systems: Selected Papers by Lotfi A Zadeh; World Scientific: Binghamton University–SUNY: Binghamton, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 394–432. [Google Scholar]
- Malczewski, J. Fuzzy screening for land suitability analysis. Geogr. Environ. Model. 2002, 6, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malczewski, J. GIS-based land-use suitability analysis: A critical overview. Prog. Plann. 2004, 62, 3–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fang, C.; Wang, Z.; Ma, H. Urban construction land suitability evaluation based on improved multi-criteria evaluation based on GIS (MCE-GIS): Case of New Hefei City, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malczewski, J.; Rinner, C. Multicriteria Decision Analysis in Geographic Information Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jothibasu, A.; Anbazhagan, S. Modeling groundwater probability index in Ponnaiyar River basin of South India using analytic hierarchy process. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MOJA Iranian Ministry of Jahade-Agriculture (MOJA). Report 30 of Agricultural Statistics and the Information Center; Agricultural Statistics and the Information Center: Tehran, Iran, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Abbaspour, K.C.; Yang, J. Calibration and Uncertainty Analysis for SWAT Using SUFI2 with SWAT-SAI Interface, a User Manual; Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology: Dübendorf, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Gitau, M.W.; Pai, N.; Daggupati, P. Hydrologic and water quality models: Performance measures and evaluation criteria. Trans. ASABE 2015, 58, 1763–1785. [Google Scholar]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadisharaf, E.; Camacho, R.A.; Zhang, H.X.; Hantush, M.M.; Mohamoud, Y.M. Calibration and validation of watershed models and advances in uncertainty analysis in TMDL studies. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2019, 24, 3119001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oñate-Valdivieso, F.; Sendra, J.B. Application of GIS and remote sensing techniques in generation of land use scenarios for hydrological modeling. J. Hydrol. 2010, 395, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geist, H.J.; Lambin, E.F. What drives tropical deforestation. LUCC Rep. Ser. 2001, 4, 116. [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren, P. Global land use area change matrix. In Input to the Fourth Global Enviromental Outlook (GEO-4); FAO: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Václavik, T.; Rogan, J. Identifying trends in land use/land cover changes in the context of post-socialist transformation in central Europe: A case study of the greater Olomouc region, Czech Republic. GIScience Remote Sens. 2009, 46, 54–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosonuma, N.; Herold, M.; De Sy, V.; De Fries, R.S.; Brockhaus, M.; Verchot, L.; Angelsen, A.; Romijn, E. An assessment of deforestation and forest degradation drivers in developing countries. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 44009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Annunzio, R.; Sandker, M.; Finegold, Y.; Min, Z. Projecting global forest area towards 2030. For. Ecol. Manage. 2015, 352, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansen, M.C.; Potapov, P.V.; Moore, R.; Hancher, M.; Turubanova, S.A.; Tyukavina, A.; Thau, D.; Stehman, S.V.; Goetz, S.J.; Loveland, T.R.; et al. High-resolution global maps of 21st-century forest cover change. Science 2013, 342, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nepstad, D.C.; Stickler, C.M.; Filho, B.S.; Merry, F. Interactions among Amazon land use, forests and climate: Prospects for a near-term forest tipping point. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 1737–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammadi, J.; Shataee Joibary, S.; Yaghmaee, F.; Mahiny, A.S. Modelling forest stand volume and tree density using Landsat ETM+ data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 2959–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEA Millennium ecosystem assessment: Ecosystems and human well-being (volume 2). In Findings of the Scenarios Working Group, Millennium Ecosystem Assessment; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005.
- UNEP Global Environment Outlook 4 (GEO-4). United Nations Environment Programme, Nairobi. Available online: <http://www.unep.org/geo/geo4.asp> (accessed on 1 February 2015).
- Heidarlou, H.B.; Shafiei, A.B.; Erfanian, M.; Tayyebi, A.; Alijanpour, A. Effects of preservation policy on land use changes in Iranian Northern Zagros forests. Land Use policy 2019, 81, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, M.R.; Morid, S.; Delavar, M. Evaluating climate adaptation strategies on agricultural production in the Siminehrud catchment and inflow into Lake Urmia, Iran using SWAT within an OECD framework. Agric. Syst. 2016, 147, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacher, I.L.; Ahmadisharaf, E.; Fergus, C.; Akre, T.; Mcshea, W.J.; Benham, B.L.; Kline, K.S. Scale-dependent impacts of urban and agricultural land use on nutrients, sediment, and runoff. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadisharaf, E.; Lacher, I.L.; Fergus, C.; Benham, B.L.; Akre, T.; Kline, K.S. Projecting land use change impacts on nutrients, sediment and runoff in multiple spatial scales: Business-as-usual vs. stakeholder-informed scenarios. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.T.Y.; Chen, W. Modeling the relationship between land use and surface water quality. J. Environ. Manage. 2002, 66, 377–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-W.; Hwang, S.-J.; Lee, S.-B.; Hwang, H.-S.; Sung, H.-C. Landscape ecological approach to the relationships of land use patterns in watersheds to water quality characteristics. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 92, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Iwatsubo, G. Water chemistry in a number of mountainous streams of east Asia. J. Hydrol. 2000, 240, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piatek, K.B.; Christopher, S.F.; Mitchell, M.J. Spatial and temporal dynamics of stream chemistry in a forested watershed. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, C.O.; Weng, Q. Simulating the impacts of future land use and climate changes on surface water quality in the Des Plaines River watershed, Chicago Metropolitan Statistical Area, Illinois. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 4387–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Bhatta, B.; Shrestha, M.; Shrestha, P.K. Integrated assessment of the climate and landuse change impact on hydrology and water quality in the Songkhram River Basin, Thailand. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1610–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trisurat, Y.; Eawpanich, P.; Kalliola, R. Integrating land use and climate change scenarios and models into assessment of forested watershed services in Southern Thailand. Environ. Res. 2016, 147, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nohegar, A.; Kazemi, M. Evaluation of Water Erosion with ICONA Model Case study: Tange Bostanak watershed in Shiraz. Geogr. Res. 2013, 28, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Sanyal, J.; Densmore, A.L.; Carbonneau, P. Analysing the effect of land-use/cover changes at sub-catchment levels on downstream flood peaks: A semi-distributed modelling approach with sparse data. Catena 2014, 118, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Z.; Hou, X.; Li, W.; Aini, G.; Chen, L.; Gong, Y. Impact of landscape pattern at multiple spatial scales on water quality: A case study in a typical urbanised watershed in China. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, C.-Y.; Gao, Y.; Du, J. Hydrological response to urbanization at different spatio-temporal scales simulated by coupling of CLUE-S and the SWAT model in the Yangtze River Delta region. J. Hydrol. 2013, 485, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, A.S.H.; Azari, D.F.; Sadeghi, S.H.R.; Soufbaf, S.R. Study on Landscape Degradation in Neka Watershed Using Landscape Metrics. Envi. Sci. 2009, 6, 133–144. [Google Scholar]
- Jamshidi, M.; Tajrishy, M.; Maghrebi, M. Others Modeling of point and non-point source pollution of nitrate with SWAT in the Jajrood river watershed, Iran. Int. Agric. Eng. J. 2010, 19, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, R.; Cai, S.; Li, H.; Yang, G.; Li, Z.; Nie, X. Inferring land use and land cover impact on stream water quality using a Bayesian hierarchical modeling approach in the Xitiaoxi River Watershed, China. J. Environ. Manage. 2014, 133, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirmohammadi, A.; Chaubey, I.; Harmel, R.D.; Bosch, D.D.; Muñoz-Carpena, R.; Dharmasri, C.; Sexton, A.; Arabi, M.; Wolfe, M.L.; Frankenberger, J.; et al. Uncertainty in TMDL models. Trans. ASABE 2006, 49, 1033–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishra, A.; Ahmadisharaf, E.; Benham, B.L.; Wolfe, M.L.; Leman, S.C.; Gallagher, D.L.; Reckhow, K.H.; Smith, E.P. Generalized likelihood uncertainty estimation and Markov chain Monte Carlo simulation to prioritize TMDL pollutant allocations. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2018, 23, 5018025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharifi, A.; Yen, H.; Boomer, K.M.B.; Kalin, L.; Li, X.; Weller, D.E. Using multiple watershed models to assess the water quality impacts of alternate land development scenarios for a small community. Catena 2017, 150, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Criterion | Subcriteria | Weight (Pasture) | Weight (Forest) | Weight (Agriculture) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Vegetation | Rangeland condition | 0.18 | 0.03 | 0.062 |
| Vegetation density | 0.036 | 0.105 | 0.011 | |
| Forest type | ----- | 0.161 | ---- | |
| Geology | — | 0.019 | 0.052 | 0.025 |
| Soil | Soil texture | 0.062 | 0.15 | 0.162 |
| Sensitivity to erosion | 0.11 | 0.04 | 0.073 | |
| Climate | Temperature (°C) | 0 | 0.06 | 0.04 |
| Rainfall (mm) | 0.035 | 0.11 | 0.084 | |
| Water Resource | Distance to dam (m) | 0/058 | 0/005 | 0/091 |
| Distance to the stream and water channels and other water sources (m) | 0/110 | 0/035 | 0/122 | |
| Land use | 0/050 | 0/062 | 0/032 | |
| Topography | Elevation (m) | 0/008 | 0/030 | 0/003 |
| Slope (°) | 0/129 | 0/090 | 0/261 | |
| Aspect | ------ | 0/011 | 0/001 | |
| Distance from the human distributions | Distance to residential areas (m) | 0/109 | 0/030 | 0/011 |
| Natural Vegetation | Distance to roads (m) | 0/078 | 0/030 | 0/022 |
| Parameter | Description | Initial Range | Optimal Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| SOL_CBN | Organic carbon content | 0.05–10 | 0.44 |
| HLIFE_NGW | Half-life of nitrogen in groundwater (days) | 0–500 | 15.8 |
| SOL_AWC | Available water capacity of the soil layer (mm H2O/mm Soil) | 0–1 | 0.26 |
| HRU_SLP | Average slope steepness (m/m) | 0–1 | −0.7 |
| USLE_P | USLE equation support pra | 0–1 | 0.24 |
| CN2 | SCS runoff curve number for moisture condition | 35–98 | 75 |
| CANMX | Maximum canopy storage (mm) | 0–100 | 7 |
| BIOMIX | Biological mixing efficient | 0–1 | 0.29 |
| EPCO | Plant uptake compensation factor | 0–1 | 0.63 |
| ESCO | Outflow simulation option | 0–1 | 0.7 |
| GW_REVAP | Groundwater “revap” coefficient | 0.02–0.2 | 0.05 |
| GW_DELAY | Groundwater delay (days) | 0–500 | 170 |
| GWQMN | Threshold depth of water in the shallow aquifer required for return flow to occur (mm) | 0–5000 | 290 |
| SMTMP | Snow melt base temperature (°C) | −20–20 | 0 |
| ANION_EXCL | Fraction of porosity from which anions are excluded | 0.01–1 | 0.55 |
| Solaimantange Station | Rigcheshme Station | Kordkhil Station | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistic | Calibration (2006–2010) | Validation (2011–2014) | Calibration (2001–2010) | Validation (2011–2014) | Calibration (2005–2010) | Validation (2011–2014) |
| R2 | 0.67 | 0.78 | 0.53 | 0.58 | 0.50 | 0.77 |
| NSE | 0.58 | 0.75 | 0.52 | 0.5 | 0.53 | 0.47 |
| Stations | Solaimantange Station | Rigcheshme Station | Kordkhil Station | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistic | Calibration (2009–2013) | Validation (2013–2014) | Calibration (2009–2012) | Validation (2013–2014) | Calibration (2009–2013) | Validation (2013–2014) |
| R2 | 0.51 | 0.67 | 0.82 | 0.58 | 0.65 | 0.77 |
| NSE | 0.55 | 0.66 | 0.61 | 0.54 | 0.50 | 0.49 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rajaei, F.; Dahmardeh Behrooz, R.; Ahmadisharaf, E.; Galalizadeh, S.; Dudic, B.; Spalevic, V.; Novicevic, R. Application of Integrated Watershed Management Measures to Minimize the Land Use Change Impacts. Water 2021, 13, 2039. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13152039
Rajaei F, Dahmardeh Behrooz R, Ahmadisharaf E, Galalizadeh S, Dudic B, Spalevic V, Novicevic R. Application of Integrated Watershed Management Measures to Minimize the Land Use Change Impacts. Water. 2021; 13(15):2039. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13152039
Chicago/Turabian StyleRajaei, Fatemeh, Reza Dahmardeh Behrooz, Ebrahim Ahmadisharaf, Saman Galalizadeh, Branislav Dudic, Velibor Spalevic, and Rajko Novicevic. 2021. "Application of Integrated Watershed Management Measures to Minimize the Land Use Change Impacts" Water 13, no. 15: 2039. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13152039
APA StyleRajaei, F., Dahmardeh Behrooz, R., Ahmadisharaf, E., Galalizadeh, S., Dudic, B., Spalevic, V., & Novicevic, R. (2021). Application of Integrated Watershed Management Measures to Minimize the Land Use Change Impacts. Water, 13(15), 2039. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13152039







