Evidence of Anthropogenic Gadolinium in Triangle Area Waters, North Carolina, USA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
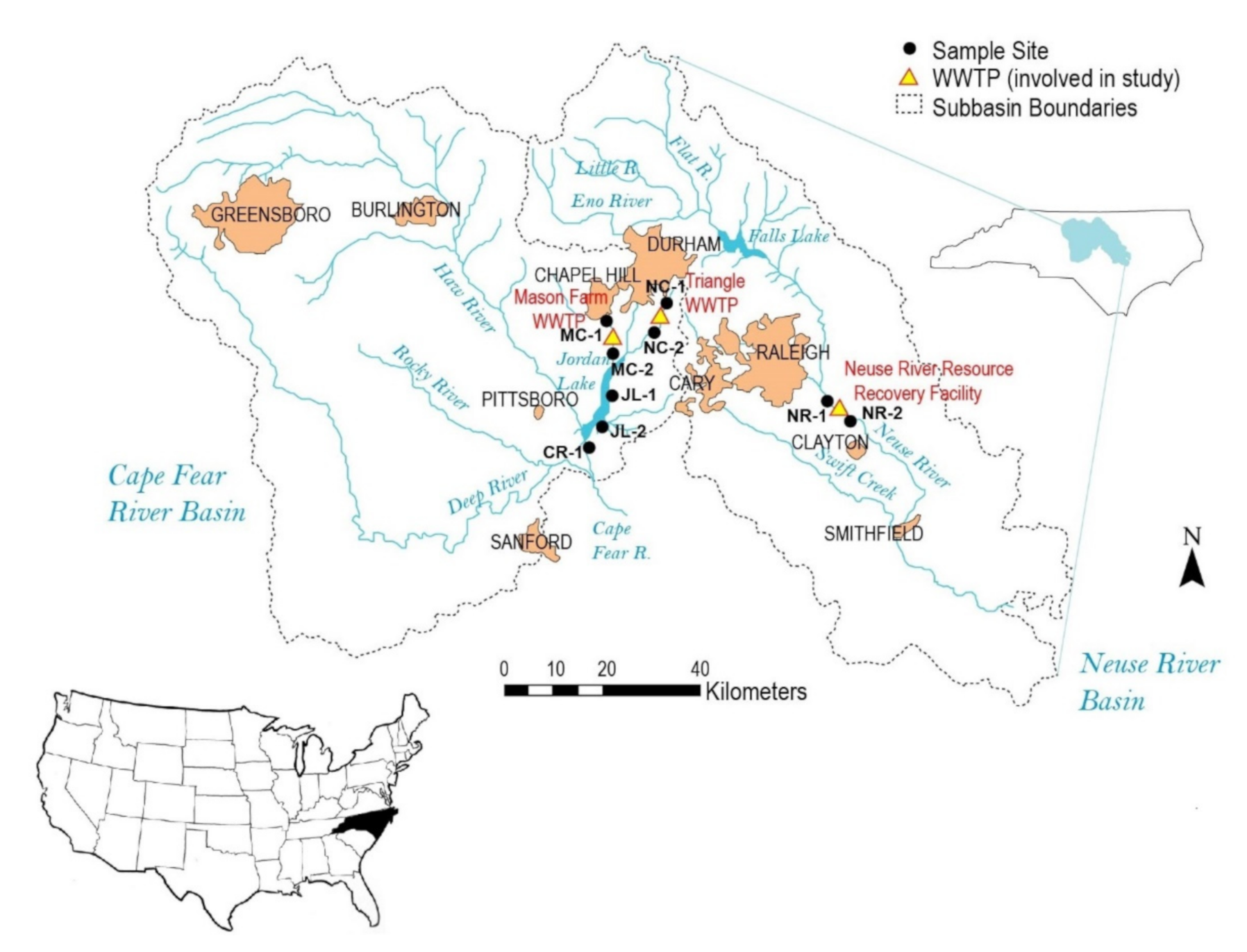
2.1. Location of Study
2.2. Sampling and Analyses
3. Results
3.1. REE + Y Concentrations
3.2. PAAS-Normalization and Anthropogenic Gd
4. Discussion
4.1. Anthropogenic Gd and Its Sources
4.2. Health and Ecotoxicological Effects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, C.; Liu, X.M. Spatial and temporal distribution of rare earth elements in the Neuse River, North Carolina. Chem. Geol. 2018, 488, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hardisty, D.S.; Lyons, T.W.; Swart, P.K. Evaluating the fidelity of the cerium paleoredox tracer during variable carbonate diagenesis on the Great Bahamas Bank. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2019, 248, 25–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Liu, X.; Bataille, C.P.; Liu, C. What do Ce anomalies in marine carbonates really mean? A perspective from leaching experiments. Chem. Geol. 2020, 532, 119413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M.; Dulski, P. Anthropogenic origin of positive gadolinium anomalies in river waters. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1996, 143, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, Y.; Lerche, D.; Alibo, D.S.; Tsutsumi, M. Dissolved indium and rare earth elements in three Japanese rivers and Tokyo Bay: Evidence for anthropogenic Gd and In. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 3975–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knappe, A.; Möller, P.; Dulski, P.; Pekdeger, A. Positive gadolinium anomaly in surface water and ground water of the urban area Berlin, Germany. Chem. Erde Geochem. 2005, 65, 167–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verplanck, P.L.; Taylor, H.E.; Nordstrom, D.K.; Barber, L.B. Aqueous stability of gadolinium in surface waters receiving sewage treatment plant effluent Boulder Creek, Colorado. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6923–6929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bau, M.; Knappe, A.; Dulski, P. Anthropogenic gadolinium as a micropollutant in river waters in Pennsylvania and in Lake Erie, northeastern United States. Chem. Erde Geochem. 2006, 66, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiet, M.; Brissaud, F.; Seidel, J.L.; Pistre, S.; Elbaz-Poulichet, F. Positive gadolinium anomalies in wastewater treatment plant effluents and aquatic environment in the Hérault watershed (South France). Chemosphere 2009, 75, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulaksiz, S.; Bau, M. Anthropogenic dissolved and colloid/nanoparticle-bound samarium, lanthanum and gadolinium in the Rhine River and the impending destruction of the natural rare earth element distribution in rivers. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 362, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Campos, F.F.; Enzweiler, J. Anthropogenic gadolinium anomalies and rare earth elements in the water of Atibaia River and Anhumas Creek, Southeast Brazil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Shin, W.J.; Ryu, J.S.; Shin, H.S.; Chung, H.; Lee, K.S. Anthropogenic rare earth elements and their spatial distributions in the Han River, South Korea. Chemosphere 2017, 172, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Q.; An, Y.; Jia, H.; Shen, Y. Anthropogenic rare earth elements: Gadolinium in a small catchment in Guizhou Province, Southwest China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merschel, G.; Bau, M.; Baldewein, L.; Dantas, E.L.; Walde, D.; Bühn, B. Tracing and tracking wastewater-derived substances in freshwater lakes and reservoirs: Anthropogenic gadolinium and geogenic REEs in Lake Paranoá, Brasilia. Comptes Rendus Geosci. 2015, 347, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbaz-Poulichet, F.; Seidel, J.L.; Othoniel, C. Occurrence of an anthropogenic gadolinium anomaly in river and coastal waters of Southern France. Water Res. 2002, 36, 1102–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulaksiz, S.; Bau, M. Contrasting behaviour of anthropogenic gadolinium and natural rare earth elements in estuaries and the gadolinium input into the North Sea. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 260, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatje, V.; Bruland, K.W.; Flegal, A.R. Increases in Anthropogenic Gadolinium Anomalies and Rare Earth Element Concentrations in San Francisco Bay over a 20 Year Record. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4159–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, R.L.B.; Hatje, V.; Pedreira, R.M.A.; Böning, P.; Pahnke, K. REE fractionation and human Gd footprint along the continuum between Paraguaçu River to coastal South Atlantic waters. Chem. Geol. 2020, 532, 119303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.G.; Ort, C.; Keller, J. Detection of anthropogenic gadolinium in treated wastewater in South East Queensland, Australia. Water Res. 2009, 43, 3534–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulaksiz, S.; Bau, M. Anthropogenic gadolinium as a microcontaminant in tap water used as drinking water in urban areas and megacities. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 1877–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepe, N.; Romero, M.; Bau, M. High-technology metals as emerging contaminants: Strong increase of anthropogenic gadolinium levels in tap water of Berlin, Germany, from 2009 to 2012. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 45, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.; Bau, M.; Merschel, G.; Tepe, N. Anthropogenic gadolinium in tap water and in tap water-based beverages from fast-food franchises in six major cities in Germany. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 1401–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aime, S.; Caravan, P. Biodistribution of gadolinium-based contrast agents, including gadolinium deposition. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2009, 30, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- OECD. Health at a Glance 2019: OECD Indicators; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Stuckey, J. North Carolina: Its Geology and Mineral Resources; Department of Conservation and Development: Raleigh, NC, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- NCDEQ Jordan Lake Water Supply Allocation. Available online: https://deq.nc.gov/about/divisions/water-resources/planning/basin-planning/map-page/cape-fear-river-basin-landing/jordan-lake-water-supply-allocation/jordan-lake-water-supply-allocation-background-info (accessed on April 2020).
- McLennan, S.M. Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks: Influence of provenance and sedimentary processes. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 1989, 21, 169–200. [Google Scholar]
- De Baar, H.J.W.; Brewer, P.G.; Bacon, M.P. Anomalies in rare earth distributions in seawater: Gd and Tb. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1985, 49, 1961–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Byrne, R.H. Complexation of trivalent rare earth elements (Ce, Eu, Gd, Tb, Yb) by carbonate ions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 295–302. [Google Scholar]
- Sherry, D.; Caravan, P.; Lenkinski, R.E. A primer on gadolinium chemistry. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2010, 30, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tedeschi, E.; Caranci, F.; Giordano, F.; Angelini, V.; Cocozza, S.; Brunetti, A. Gadolinium retention in the body: What we know and what we can do. Radiol. Med. 2017, 122, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inoue, K.; Fukushi, M.; Furukawa, A.; Sahoo, S.K.; Veerasamy, N.; Ichimura, K.; Kasahara, S.; Ichihara, M.; Tsukada, M.; Torii, M.; et al. Impact on gadolinium anomaly in river waters in Tokyo related to the increased number of MRI devices in use. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 154, 111148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaichick, S.; Zaichick, V.; Karandashev, V.; Nosenko, S. Accumulation of rare earth elements in human bone within the lifespan. Metallomics 2011, 3, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, S.; Marckmann, P.; Scherer, S.; Abraham, J. Multiorgan gadolinium (Gd) deposition and fibrosis in a patient with nephrogenic systemic fibrosis-an autopsy-based review. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 3616–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merschel, G.; Bau, M. Rare earth elements in the aragonitic shell of freshwater mussel Corbicula fluminea and the bioavailability of anthropogenic lanthanum, samarium and gadolinium in river water. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 533, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzbecher, E.; Knappe, A.; Pekdeger, A. Identification of degradation characteristics-exemplified by Gd-DTPA in a large experimental column. Environ. Model. Assess. 2005, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Yu, J.; Ye, B.; Liang, T. Rare earth elements in human hair from a mining area of China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 96, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charalampides, G.; Vatalis, K.; Karayannis, V.; Baklavaridis, A. Environmental Defects and Economic Impact on Global Market of Rare Earth Metals. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 161, 012069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, S.; Xiaorong, W.; Zhaozhe, H.; Chonghua, W.; Liansheng, W. Bioconcentration and elimination of five light rare earth elements in carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Chemosphere 1996, 33, 1475–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; He, X.; Bai, W.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chai, Z.; Zhao, Y. Ecotoxicological assessment of lanthanum with Caenorhabditis elegans in liquid medium. Metallomics 2010, 2, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhang, Z.; Bai, W.; Zhang, L.; He, X.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chai, Z. Effects of rare earth elements La and Yb on the morphological and functional development of zebrafish embryos. Environ. Health Toxicol. 2012, 24, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample 1 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ∑REE | Y | ∑REY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ppt | ppt | ppt | ppt | ppt | ppt | ppt | ppt | ppt | ppt | ppt | ppt | ppt | ppt | ppb | ppt | ppb | |
| MC-1 | 115 | 170 | 28.4 | 116 | 22.4 | 9.73 | 26.4 | 3.71 | 21.8 | 4.85 | 13.0 | 2.08 | 14.5 | 2.28 | 0.550 | 143 | 0.693 |
| MC-2 | 184 | 272 | 44.2 | 181 | 35.6 | 12.5 | 390 | 5.86 | 42.6 | 9.70 | 30.1 | 4.69 | 33.6 | 5.03 | 1.25 | 272 | 1.52 |
| NC-1 | 1376 | 2831 | 360 | 1412 | 294 | 72.2 | 289 | 43.0 | 254 | 44.3 | 113 | 16.6 | 106 | 14.8 | 7.23 | 1223 | 8.45 |
| NC-2 | 346 | 746 | 91.1 | 355 | 70.8 | 18.2 | 186 | 10.4 | 61.6 | 11.6 | 28.9 | 4.71 | 30.5 | 13.5 | 1.97 | 387 | 2.36 |
| NR-1 | 212 | 271 | 46.4 | 179 | 34.4 | 10.5 | 41.3 | 4.65 | 31.0 | 6.30 | 17.0 | 2.76 | 17.1 | 2.62 | 0.877 | 212 | 1.09 |
| NR-2 | 276 | 392 | 61.3 | 241 | 50.5 | 13.3 | 71.5 | 6.56 | 40.2 | 7.99 | 21.4 | 3.17 | 20.2 | 3.28 | 1.21 | 249 | 1.46 |
| NR-3 | 88.6 | 126 | 22.5 | 101 | 21.6 | 7.17 | 31.8 | 3.15 | 20.9 | 4.93 | 15.6 | 2.31 | 16.2 | 3.02 | 0.465 | - | - |
| NR-4 | 77.6 | 101 | 20.0 | 90.2 | 19.1 | 6.15 | 61.2 | 2.83 | 18.2 | 4.29 | 13.9 | 2.23 | 15.4 | 2.91 | 0.435 | - | - |
| JL-1 | 105 | 222 | 21.9 | 79.6 | 12.1 | 6.72 | 35.1 | 1.40 | 7.52 | 1.62 | 5.17 | 1.00 | 6.74 | 1.37 | 0.507 | 64.8 | 0.572 |
| JL-2 | 216 | 492 | 49.3 | 188 | 39.6 | 10.6 | 122 | 4.17 | 26.6 | 5.03 | 13.5 | 2.13 | 13.2 | 2.46 | 1.19 | 176 | 1.36 |
| CR-1 | 319 | 677 | 81.9 | 326 | 67.7 | 21.7 | 96.3 | 9.60 | 55.9 | 11.0 | 30.3 | 4.55 | 26.5 | 3.90 | 1.73 | 338 | 2.07 |
| MF-I | 3.16 | 7.20 | 0.647 | 3.51 | 0.704 | 3.59 | 390 | 0.164 | 0.386 | 0.154 | 0.353 | 0.089 | 2.24 | 0.265 | 0.413 | 4.98 | 0.418 |
| MF-E | 4.00 | 11.0 | 1.20 | 5.28 | 0.763 | 0.614 | 690 | 0.319 | 1.24 | 0.469 | 1.47 | 0.273 | 5.26 | 0.567 | 0.723 | 10.4 | 0.733 |
| T-I | 31.1 | 30.4 | 3.29 | 14.6 | 3.74 | 6.93 | 413 | 0.291 | 2.80 | 0.574 | 1.41 | 0.274 | 4.49 | 2.18 | 0.516 | 46.5 | 0.521 |
| T-E | 12.3 | 33.4 | 3.69 | 16.9 | 4.05 | 1.85 | 165 | 0.444 | 4.32 | 1.11 | 3.95 | 0.881 | 9.21 | 16.5 | 0.273 | 129 | 0.402 |
| Sample 1 | LaSN/YbSN | GdSN/GdSN* | Gdanth | %Gdanth |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC-1 | 0.498 | 1.29 | 3.90 | 14.7 |
| MC-2 | 0.346 | 12.0 | 354 | 90.9 |
| NC-1 | 0.819 | 1.17 | 17.1 | 5.92 |
| NC-2 | 0.717 | 3.10 | 120 | 64.5 |
| NR-1 | 0.785 | 1.50 | 11.1 | 26.9 |
| NR-2 | 0.863 | 1.82 | 28.3 | 39.5 |
| NR-3 | 0.346 | 1.75 | 11.9 | 37.3 |
| NR-4 | 0.319 | 3.78 | 43.4 | 70.9 |
| JL-1 | 0.048 | 4.00 | 25.4 | 72.5 |
| JL-2 | 0.437 | 4.49 | 91.9 | 75.5 |
| CR-1 | 0.085 | 1.73 | 35.0 | 36.3 |
| MF-I | 0.987 | 473 | 389 | 99.8 |
| MF-E | 1.04 | 481 | 689 | 99.8 |
| T-I | 0.759 | 191 | 411 | 99.4 |
| T-E | 0.089 | 58.0 | 161 | 98.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zabrecky, J.M.; Liu, X.-M.; Wu, Q.; Cao, C. Evidence of Anthropogenic Gadolinium in Triangle Area Waters, North Carolina, USA. Water 2021, 13, 1895. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13141895
Zabrecky JM, Liu X-M, Wu Q, Cao C. Evidence of Anthropogenic Gadolinium in Triangle Area Waters, North Carolina, USA. Water. 2021; 13(14):1895. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13141895
Chicago/Turabian StyleZabrecky, Jordan M., Xiao-Ming Liu, Qixin Wu, and Cheng Cao. 2021. "Evidence of Anthropogenic Gadolinium in Triangle Area Waters, North Carolina, USA" Water 13, no. 14: 1895. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13141895
APA StyleZabrecky, J. M., Liu, X.-M., Wu, Q., & Cao, C. (2021). Evidence of Anthropogenic Gadolinium in Triangle Area Waters, North Carolina, USA. Water, 13(14), 1895. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13141895






