Deep Neural Network and Polynomial Chaos Expansion-Based Surrogate Models for Sensitivity and Uncertainty Propagation: An Application to a Rockfill Dam
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Surrogate Models
2.1.1. Polynomial Chaos Expansion (PCE)
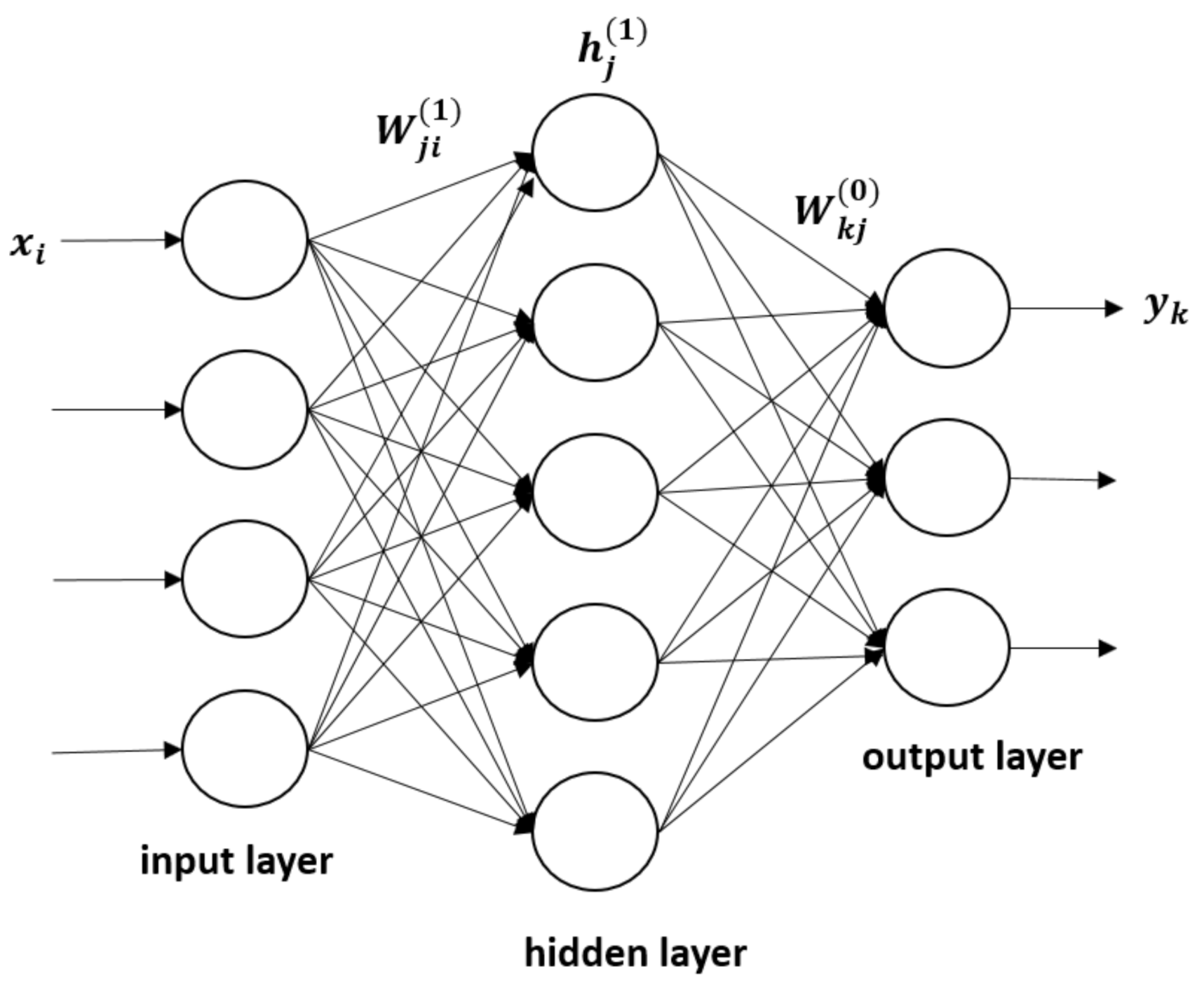
2.1.2. Deep Neural Networks
2.1.3. Ensemble of Models
2.2. Global Sensitivity Analysis
3. Case Study: Application to Romaine-2 Dam
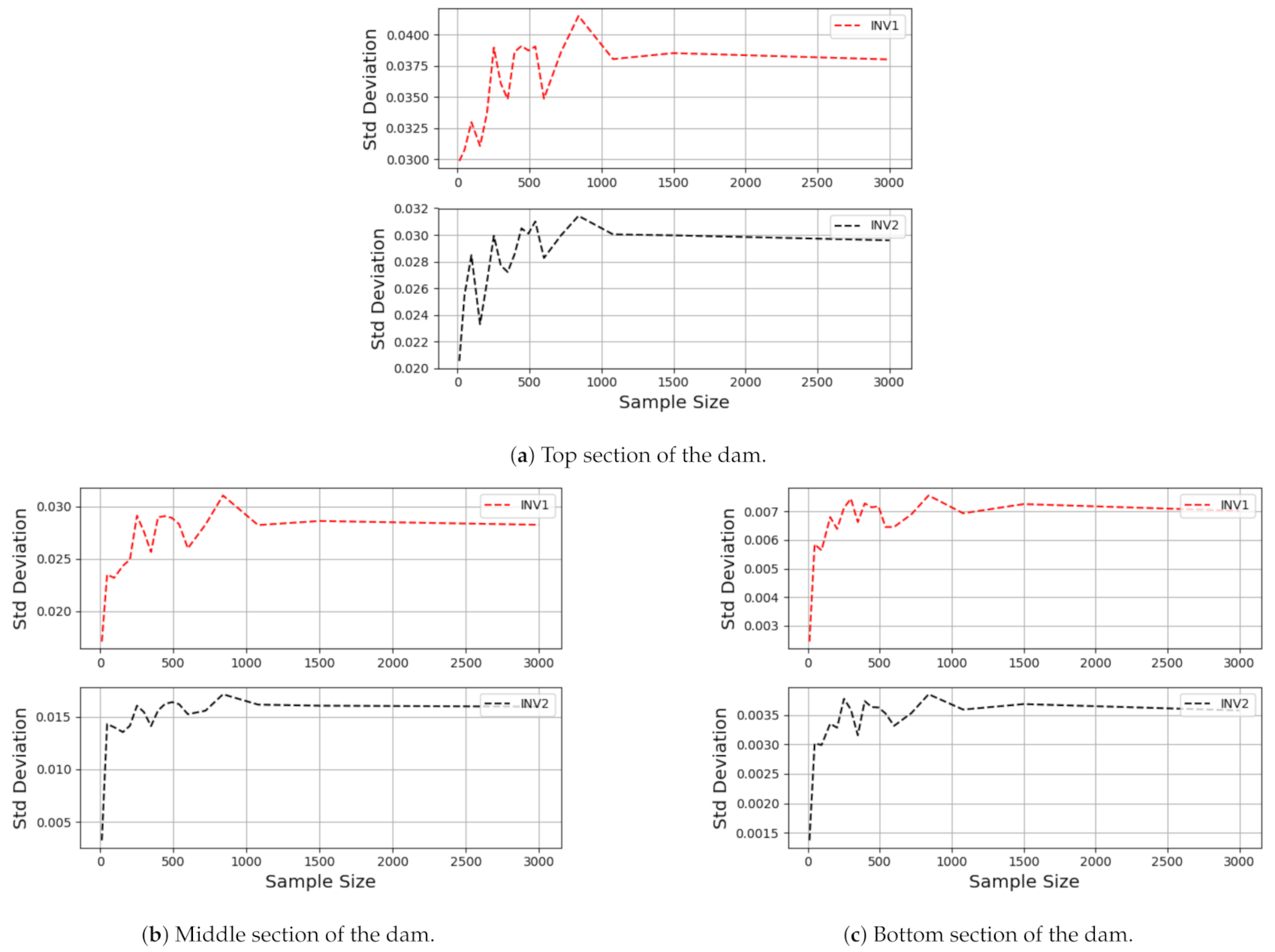
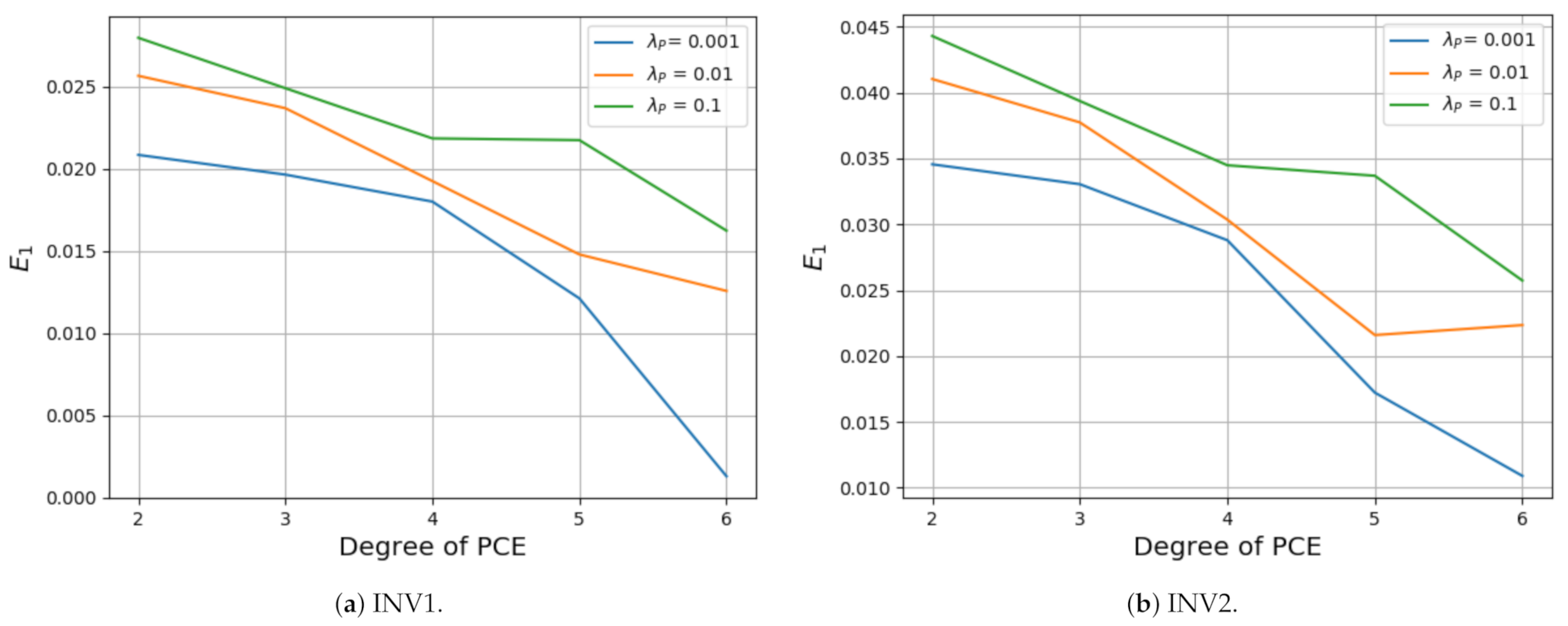
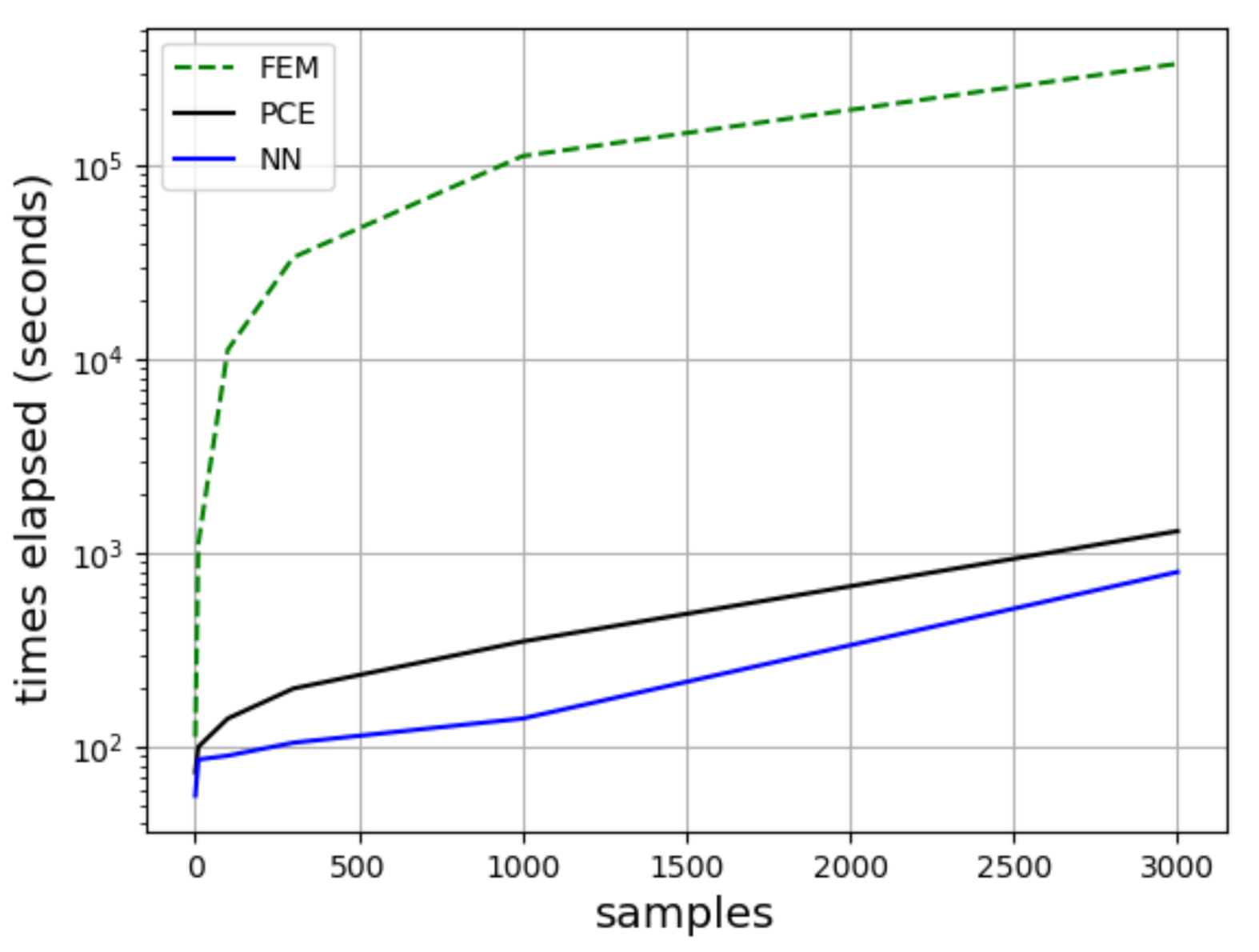
3.1. Sample Size Convergence Study
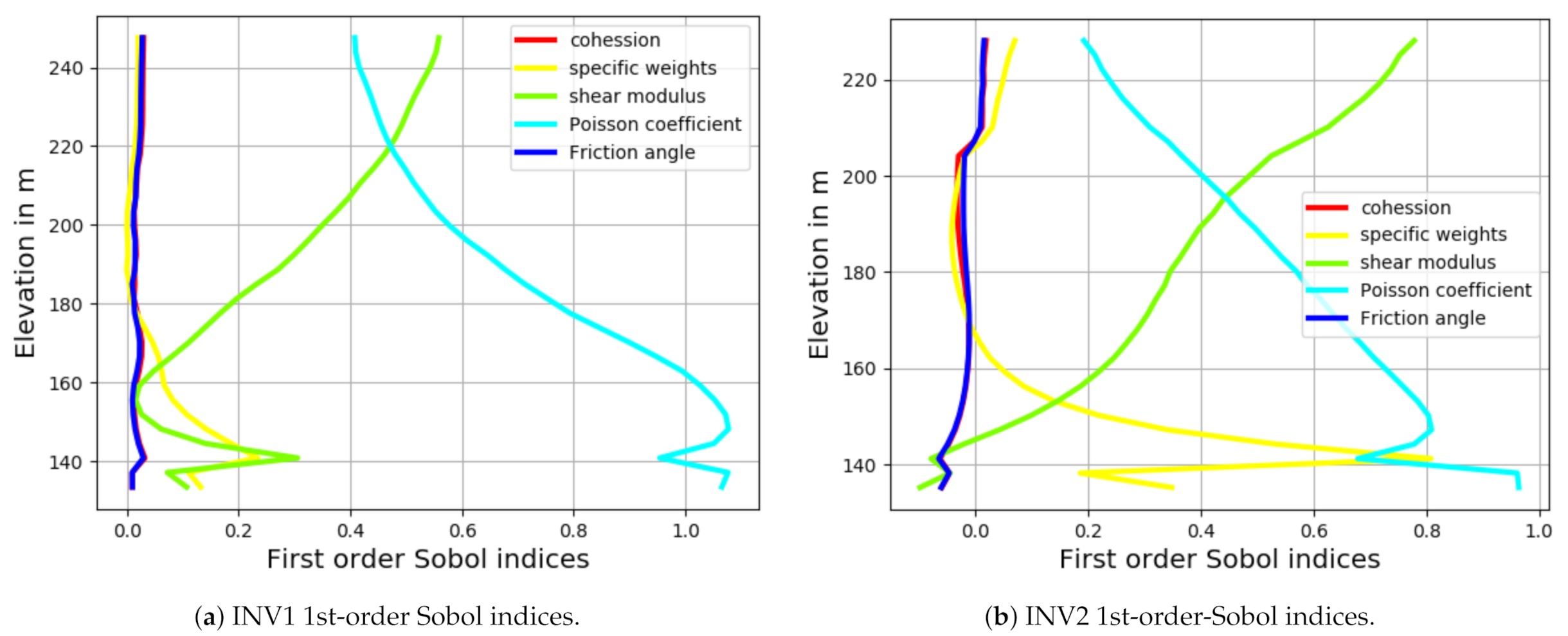
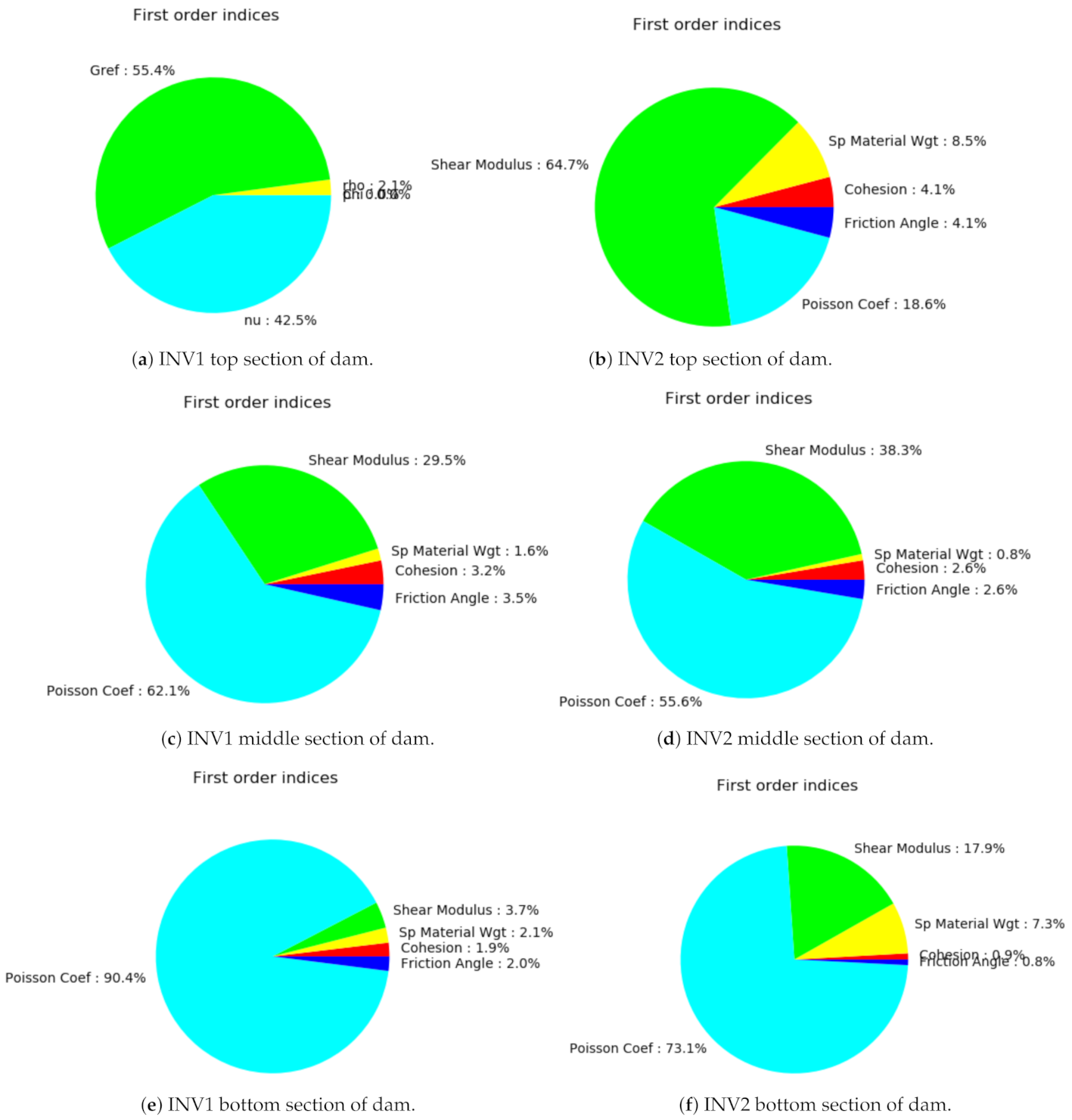
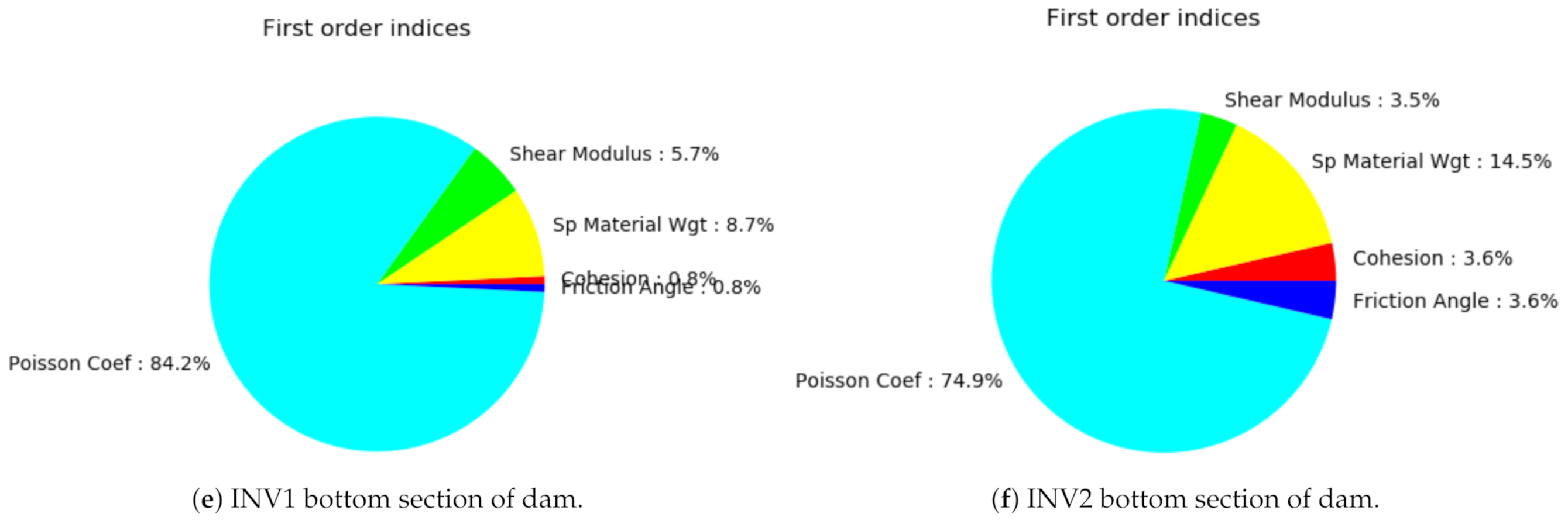
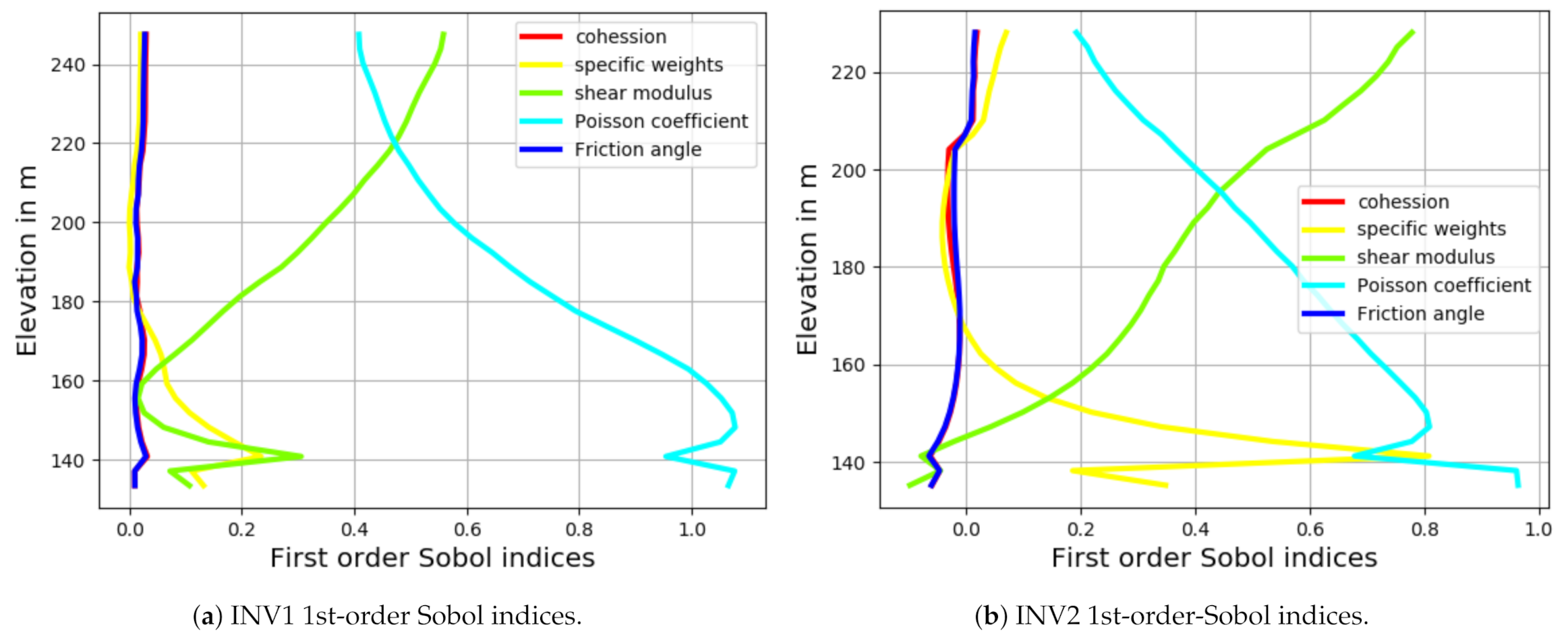
3.2. Sobol Indices
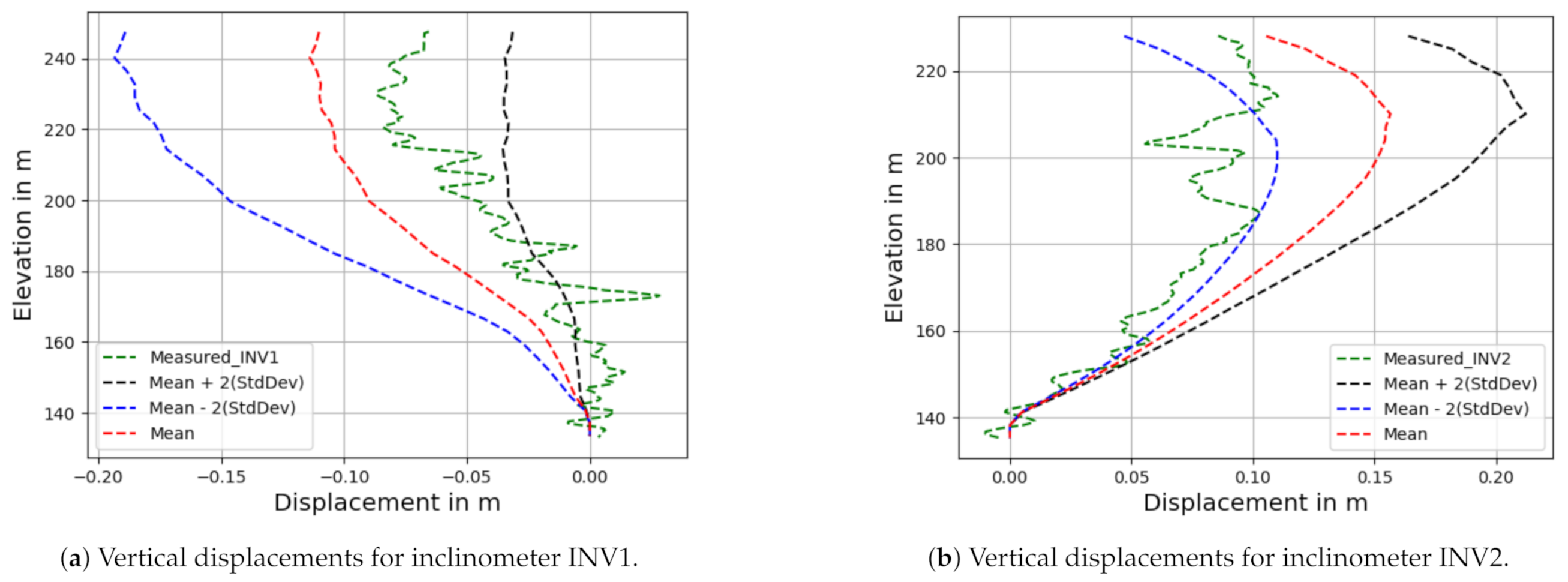
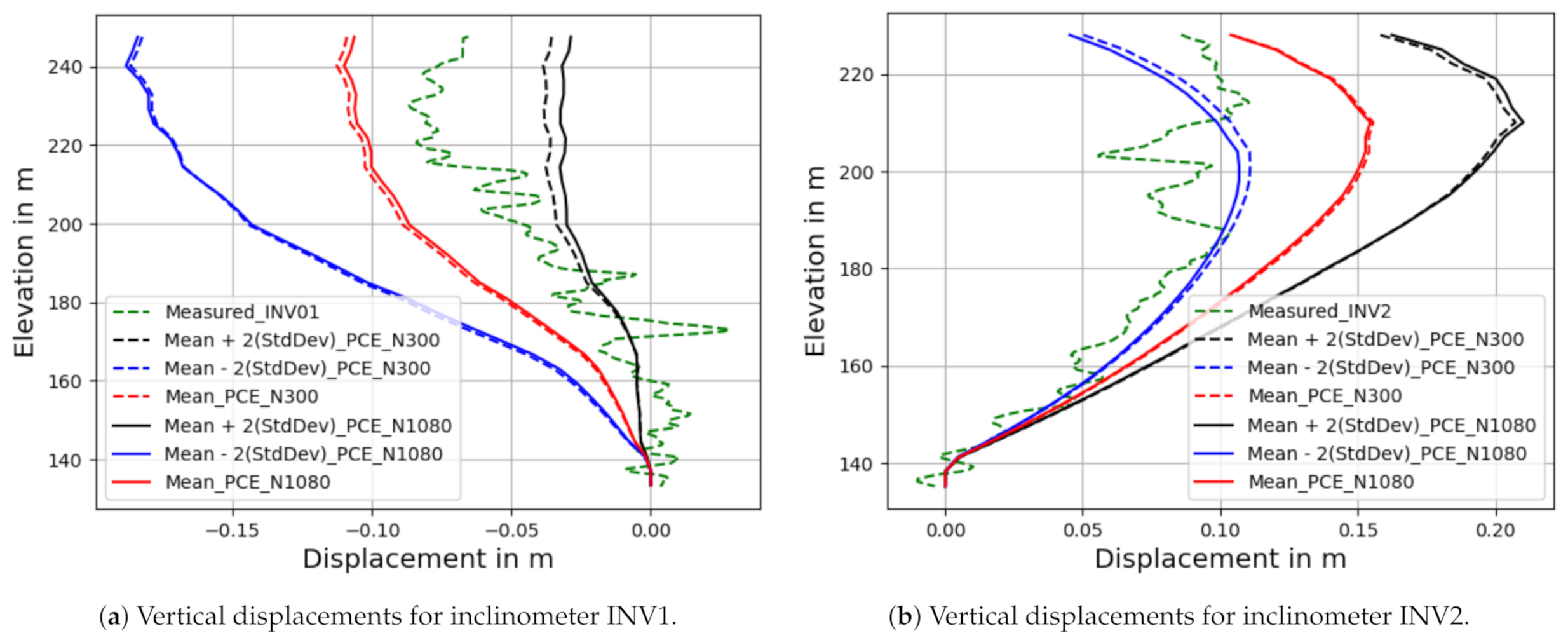
3.3. Surrogate Modeling
3.3.1. Polynomial Chaos Expansion (PCE)
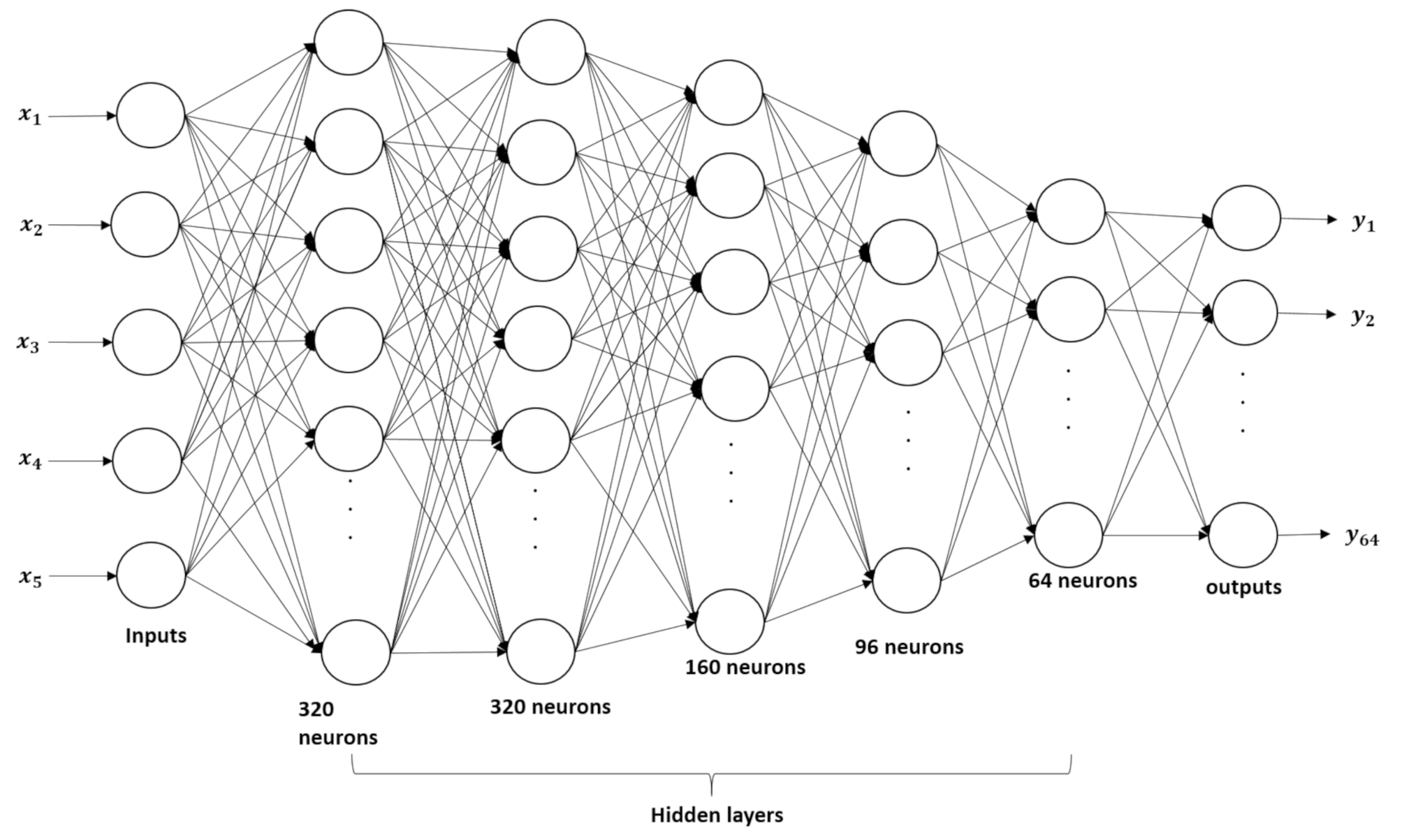
3.3.2. Deep Neural Network Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bowles, L. Foundation Analysis and Design; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Calvello, M.; Finno, R.J. Selecting parameters to optimize in model calibration by inverse analysis. Comput. Geotech. 2004, 31, 410–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, T.; Saltelli, A. Importance measures in global sensitivity analysis of nonlinear models. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 1996, 52, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltelli, A.; Ratto, M.; Andres, T.; Campolongo, F.; Cariboni, J.; Gatelli, D.; Saisana, M.; Tarantola, S. Global Sensitivity Analysis: The Primer; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cacuci, D.G.; Ionescu-Bujor, M.; Navon, I.M. Sensitivity and Uncertainty Analysis, Volume II: Applications to Large-Scale Systems; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Dimov, I.; Georgieva, R. Monte carlo algorithms for evaluating sobol’sensitivity indices. Math. Comput. Simul. 2021, 81, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, R.L.; Miquel, B.; Paultre, P.; Padgett, J.E. Accounting for uncertainties in the safety assessment of concrete gravity dams: A probabilistic approach with sample optimization. Water 2021, 13, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branbo, R.S.; Hassan, I. Seepage sensitivity analysis through a homogeneous dam within the unsaturated soil zone. J. Eng. And Computer Sci. JECS 2020, 21, 64–74. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Radi, B.; Hami, A.E. Uncertainty analysis of deep drawing using surrogate model based probabilistic method. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 86, 3229–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Dias, D. Kriging based reliability and sensitivity analysis: Application to the stability of an earth dam. Comput. Geotech. 2020, 120, 103411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargsyan, K. Surrogate Models for Uncertainty Propagation and Sensitivity Analysis, Handbook of Uncertainty Quantification; Ghanem, R., Higdon, D., Owhadi, H., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Stephens, D.; Gorissen, D.; Crombecq, K.; Dhaene, T. Surrogate based sensitivity analysis of process equipment. Appl. Math. Model. 2011, 35, 1676–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forrester, A.; Sobester, A.; Keane, A. Engineering Design via Surrogate Modelling: A Practical Guide; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hariri-Ardebili, M.A.; Mahdavi, G.; Abdollahi, A.; Amini, A. An rf-pce hybrid surrogate model for sensitivity analysis of dams. Water 2021, 13, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, J.M. State of the art: Limit equilibrium and finite-element analysis of slopes. J. Geotech. Eng. 1996, 122, 577–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, D.; Hinton, E. Finite Elements in Plasticity; Technical Report; Pineridge Press Limited: Swansea, UK, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Pietruszczak, S. Fundamentals of Plasticity in Geomechanics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pramthawee, P.; Jongpradist, P.; Kongkitkul, W. Evaluation of hardening soil model on numerical simulation of behaviors of high rockfill dams. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2011, 33, 325–334. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, D.M. Soil Behaviour and Critical State Soil Mechanics; Cambridge University Press: Melbourne, Australia, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Labuz, J.F.; Zang, A. Mohr–coulomb failure criterion. In The ISRM Suggested Methods for Rock Characterization, Testing and Monitoring: 2007–2014; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 227–231. [Google Scholar]
- Schanz, T.; Vermeer, P.; Bonnier, P. The Hardening Soil Model: Formulation and Verification, Beyond 2000 in Computational Geotechnics; A.A. Balkema: Avereest, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 281–296. [Google Scholar]
- Dige, N.; Diwekar, U. Efficient sampling algorithm for large-scale optimization under uncertainty problems. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2018, 115, 431–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burhenne, S.; Jacob, D.; Henze, G.P. Sampling based on sobol’sequences for monte carlo techniques applied to building simulations. In Proceedings of the Building Simulation 2011: 12th Conference of International Building Performance Simulation Association, Sydney, Australia, 14–16 November 2011; pp. 1816–1823. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Bagging predictors. Mach. Learn. 1996, 24, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, C.M. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, W.W. Machine Learning Methods in the Environmental Sciences: Neural Networks and Kernels; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Blatman, G.; Sudret, B. An adaptive algorithm to build up sparse polynomial chaos expansions for stochastic finite element analysis. Probabilistic Eng. Mech. 2010, 25, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, D.; Karniadakis, G.E. The wiener–askey polynomial chaos for stochastic differential equations. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2002, 24, 619–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariri-Ardebili, M.A.; Sudret, B. Polynomial chaos expansion for uncertainty quantification of dam engineering problems. Eng. Struct. 2020, 203, 109631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosder, S.; Walters, R.; Balch, M. Efficient sampling for non-intrusive polynomial chaos applications with multiple uncertain input variables. In Proceedings of the 48th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–26 April 2007; p. 1939. [Google Scholar]
- Abdedou, A.; Soulaimani, A. A non-intrusive b-splines bézier elements-based method for uncertainty propagation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2019, 345, 774–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratley, P.; Fox, B.L. Algorithm 659: Implementing sobol’s quasirandom sequence generator. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. TOMS 1988, 14, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrun, R.; Dutfoy, A. A generalization of the nataf transformation to distributions with elliptical copula. Probabilistic Eng. Mech. 2009, 24, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, I.; Ehre, M.; Straub, D. Pls-based adaptation for efficient pce representation in high dimensions. J. Comput. Phys. 2019, 387, 186–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, M.; Agarwal, A.; Barham, P.; Brevdo, E.; Chen, Z.; Citro, C.; Corrado, G.S.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; et al. Tensorflow: Large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous distributed systems. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.04467. [Google Scholar]
- Beale, M.; Hagan, M.; Demuth, H. Matlab Deep Learning Toolbox Users Guide: Pdf Documentation for Release r2019a; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jacquier, P.; Abdedou, A.; Delmas, V.; Soulaimani, A. Non-intrusive reduced-order modeling using uncertainty-aware deep neural networks and proper orthogonal decomposition: Application to flood modeling. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.13506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Soulaimani, A. Global Sensitivity Analysis in the Design of Rockfill Dams; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M. Rockfill settlement measurement and modelling of the romaine-2 dam during construction. In Proceedings of the 25th International Congress on Large Dams, ICOLD, Stavanger, Norway, 14–20 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Vannobel, P.; Smith, M.; Lefebvre, G.; Karray, M.; Éthier, Y. Control of Rockfill Placement for the Romaine-2 Asphaltic Core Dam in Northern Quebec. In Proceedings of the Canadian Dam Association, Annual Conference, Montreal, QC, Canada, 5–10 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Plaxis, B. Reference Manual for Plaxis 2d; Bentley Institute Press: Exton, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hamed, A.A. Predictive Numerical Modeling of the Behavior of Rockfill Dams. Ph.D. Thesis, École de Technologie Supérieure, Montreal, QC, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Joe, S.; Kuo, F.Y. Constructing sobol sequences with better two-dimensional projections. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2008, 30, 2635–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Rabitz, H.; Yelvington, P.E.; Oluwole, O.O.; Bacon, F.; Kolb, C.E.; Schoendorf, J. Global sensitivity analysis for systems with independent and/or correlated inputs. J. Phys. Chem. 2010, 114, 6022–6032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiener, N. The homogeneous chaos. Am. J. Math. 1938, 60, 897–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Soulaimani, A. Non-deterministic methods and surrogates in the design of rockfill dams. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


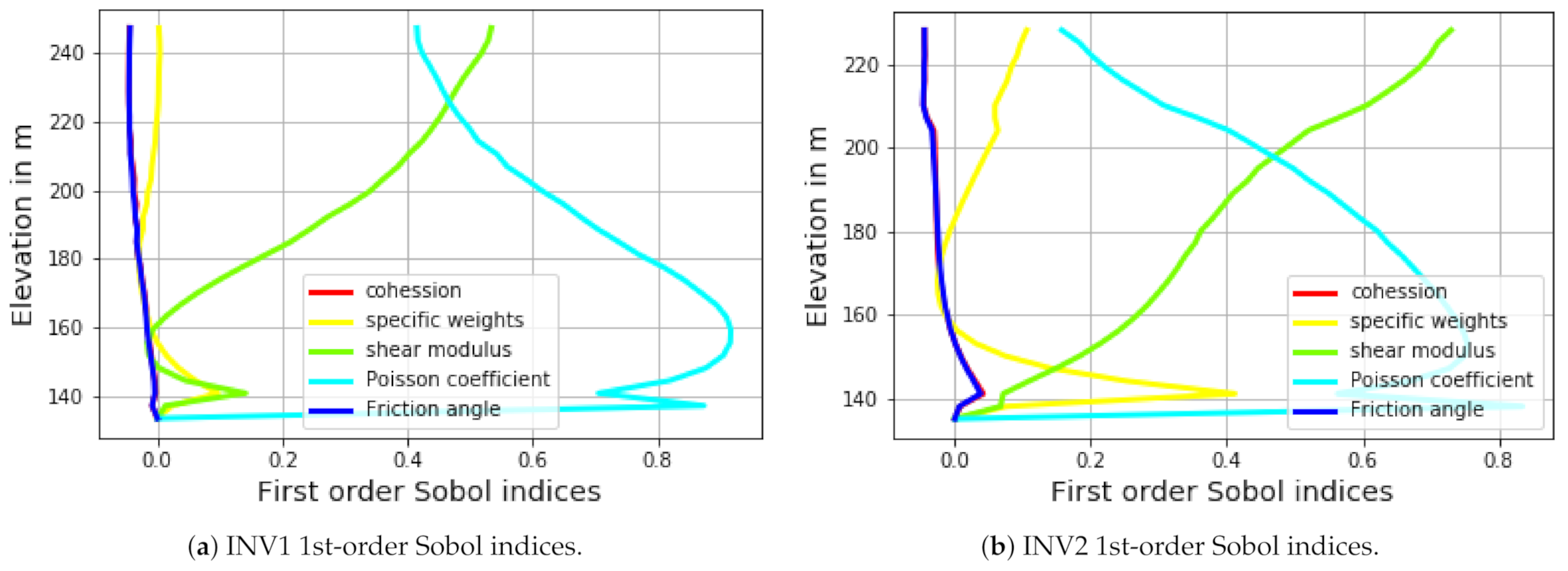
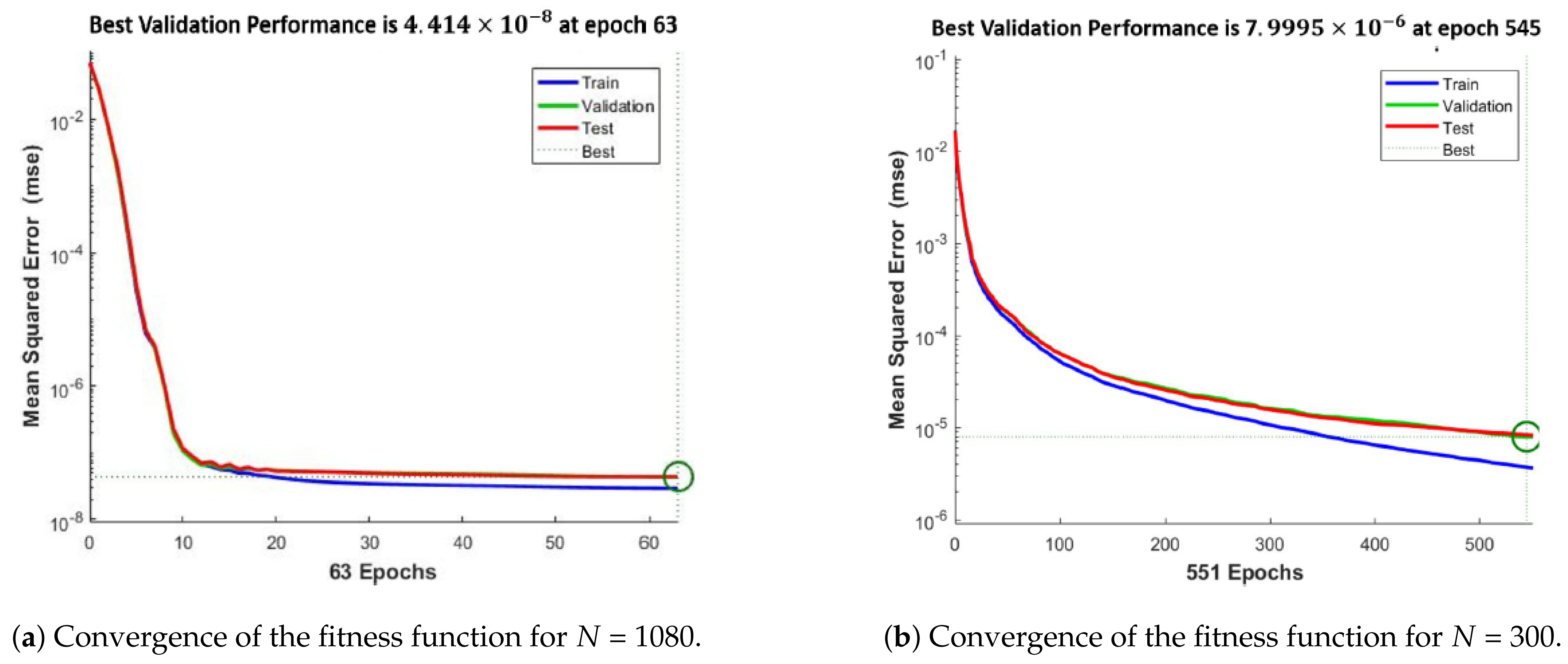
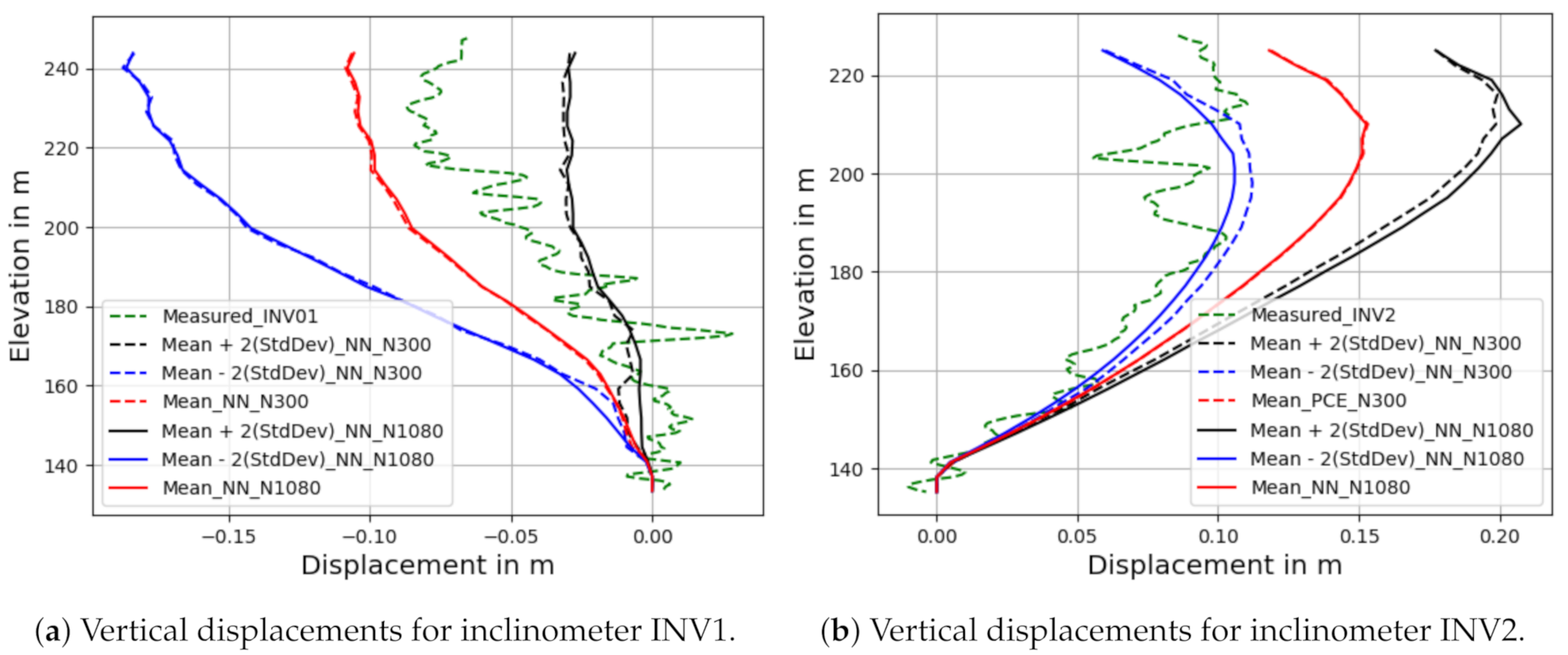
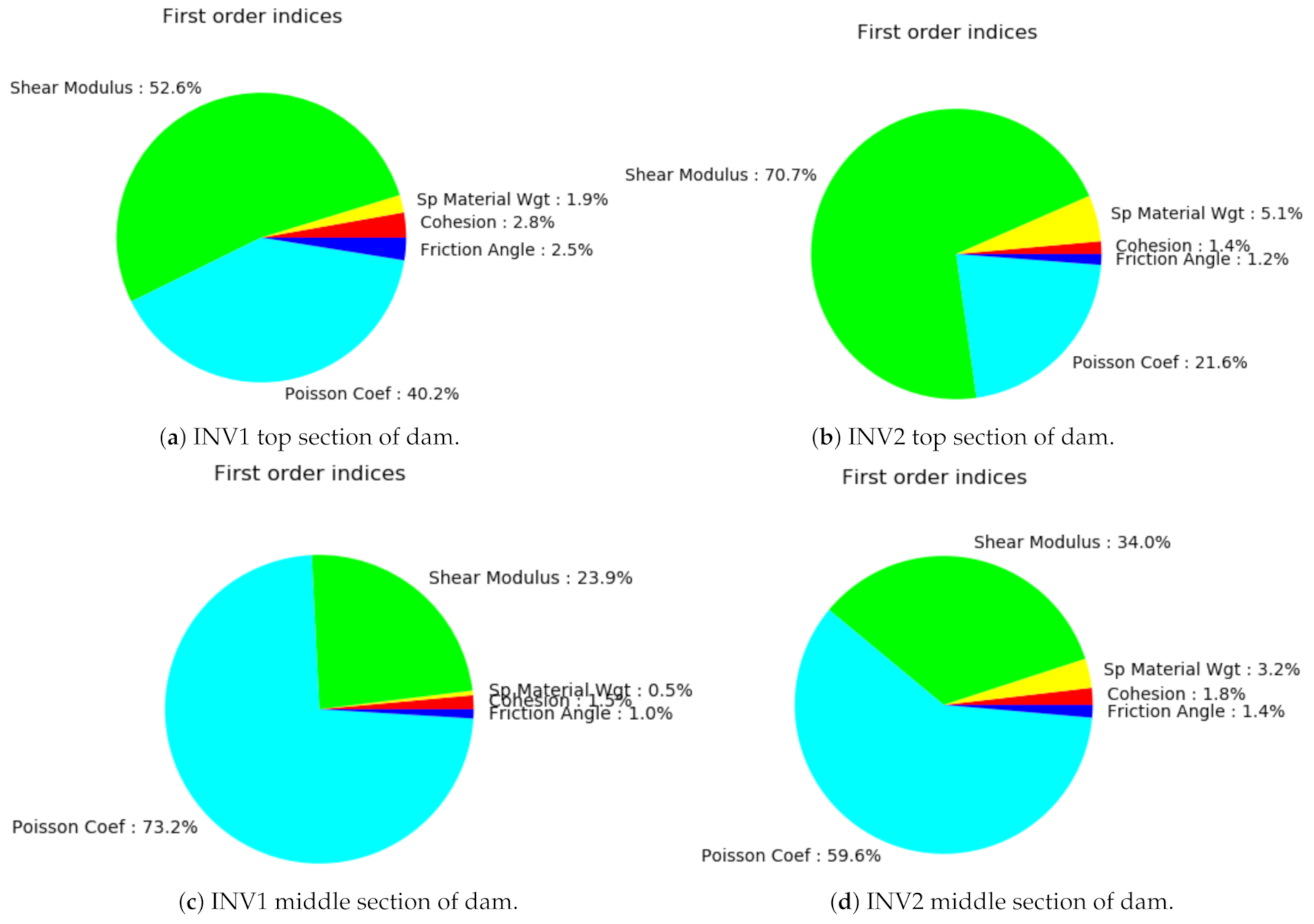
| Soil Parameters | Units | P | N | O | M | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||||
| Cohesion | KNm | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Specific weights | KNm | 21.375 | 23.625 | 23.7 | 22.5 | 24.5 |
| Shear modulus | KNm | 25,000 | 35,000 | 64,000 | 45,000 | 110,000 |
| Poisson coefficient | 0.234 | 0.3465 | 0.33 | 0.22 | 0.33 | |
| Friction angle | degree | 40.85 | 45.15 | 47 | 45 | 47 |
| Inclinometers | INV1 | INV2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approach | Top | Middle | Bottom | Top | Middle | Bottom |
| Statistical approach (MCS) | 0.0388 | 0.0282 | 0.0043 | 0.0292 | 0.0161 | 0.0028 |
| Polynomial Chaos Expansion (PCE) | 0.0364 | 0.0291 | 0.0084 | 0.0313 | 0.0238 | 0.0079 |
| Ensemble of Deep neural networks | 0.0387 | 0.0311 | 0.00121 | 0.0285 | 0.0189 | 0.0042 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shahzadi, G.; Soulaïmani, A. Deep Neural Network and Polynomial Chaos Expansion-Based Surrogate Models for Sensitivity and Uncertainty Propagation: An Application to a Rockfill Dam. Water 2021, 13, 1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131830
Shahzadi G, Soulaïmani A. Deep Neural Network and Polynomial Chaos Expansion-Based Surrogate Models for Sensitivity and Uncertainty Propagation: An Application to a Rockfill Dam. Water. 2021; 13(13):1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131830
Chicago/Turabian StyleShahzadi, Gullnaz, and Azzeddine Soulaïmani. 2021. "Deep Neural Network and Polynomial Chaos Expansion-Based Surrogate Models for Sensitivity and Uncertainty Propagation: An Application to a Rockfill Dam" Water 13, no. 13: 1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131830
APA StyleShahzadi, G., & Soulaïmani, A. (2021). Deep Neural Network and Polynomial Chaos Expansion-Based Surrogate Models for Sensitivity and Uncertainty Propagation: An Application to a Rockfill Dam. Water, 13(13), 1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131830






