Effects of Artificial Reefs on Phytoplankton Community Structure in Baiyangdian Lake, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
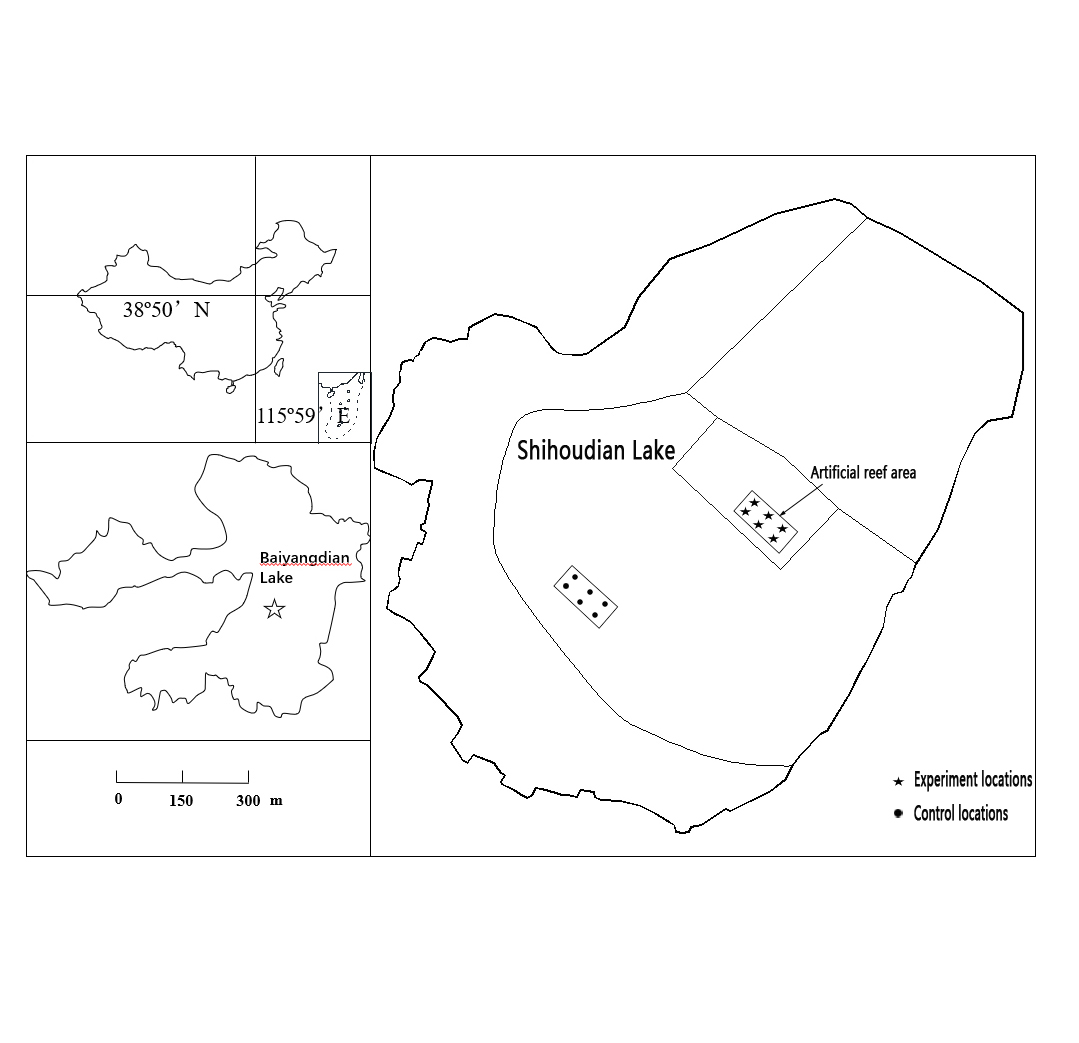
2.1. Study Area and Station Locations
2.2. Design and Layout of Artificial Reefs
2.3. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.4. Data Processing
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Factors of the Water
3.2. Phytoplankton Composition
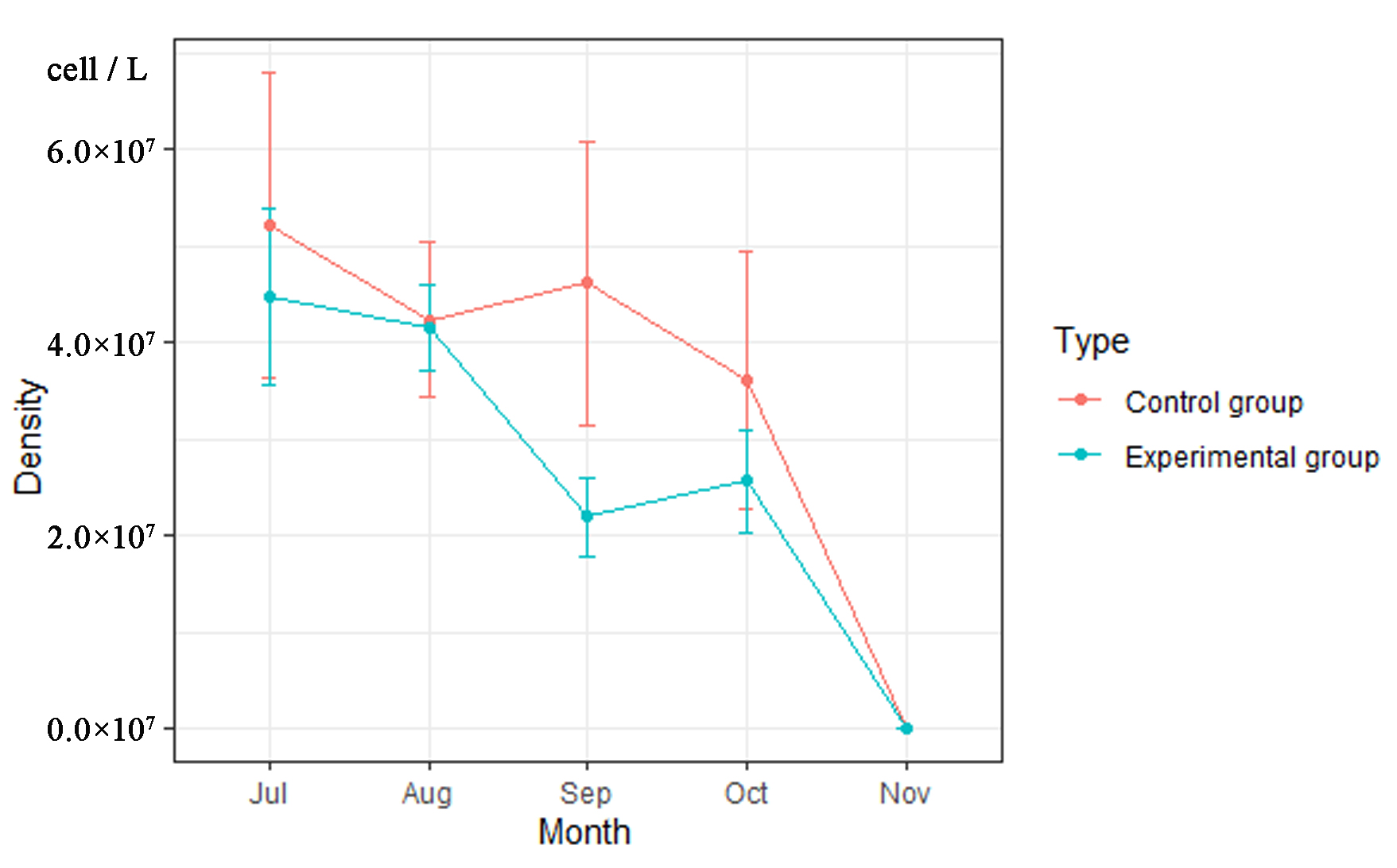
3.3. The Density of Phytoplankton
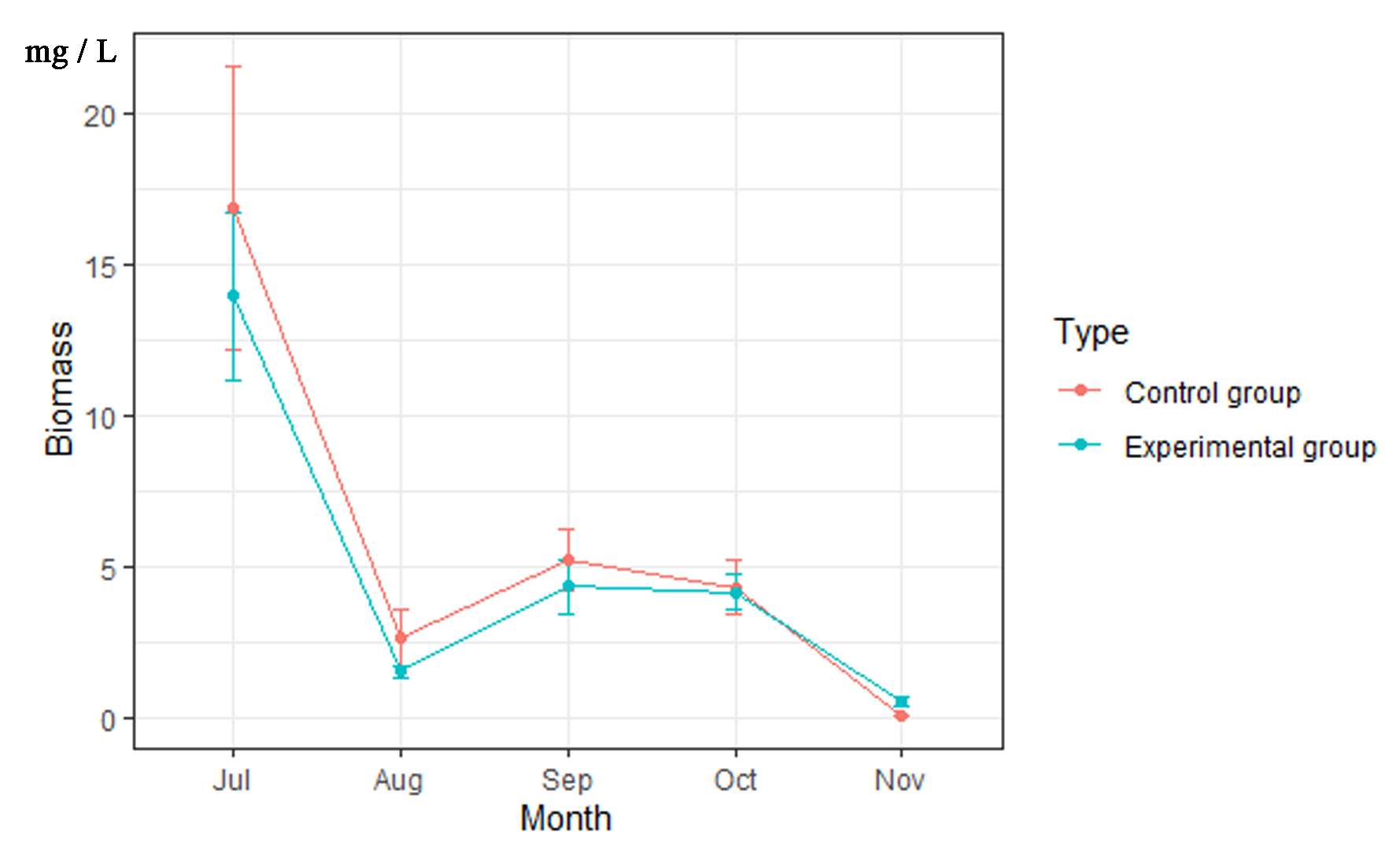
3.4. Phytoplankton Biomass
3.5. Phytoplankton Diversity Indices
3.6. The Density and Biomass of Attached Phytoplankton
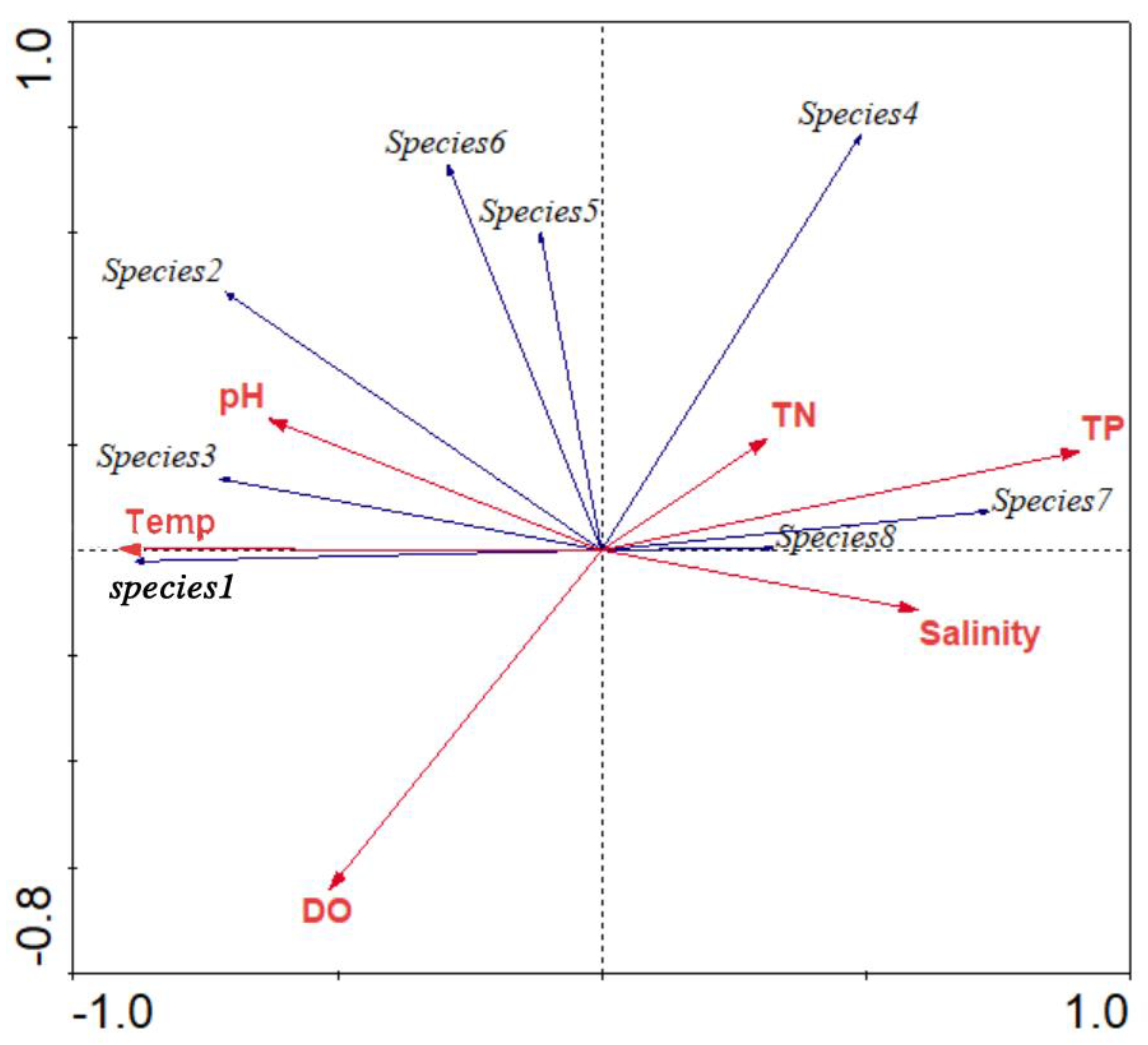
3.7. The Relationship between the Phytoplankton Community and Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Artificial Reefs on the Surrounding Water
4.2. Changes in Artificial Reef Attachments
4.3. Application Prospects of Artificial Reefs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Tang, C.; Song, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, R. The impacts of a linear wastewater reservoir on groundwater recharge and geochemical evolution in a semiarid area of the Lake Baiyangdian watershed. North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 482–483, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, X.G.; Cheng, S.P. Phytoplankton community structure and water quality assessment in an ecological restoration area of Baiyangdian Lake, China. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 18, 1529–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Cao, K.; Chen, X.L.; Ye, S.W. Effect of ecological suspended bed measures on water environment restoration in Baiyangdian Lake. Fish. Mod. 2020, 47, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.; Yi, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zerizghi, T.; Wang, X.; Cui, X.; Duan, P. Planktonic indicators of trophic states for a shallow lake (Baiyangdian Lake, China). Limnologica 2019, 78, 125712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yang, Z. Integrating ecosystem-service tradeoffs into environmental flows decisions for Baiyangdian Lake. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 71, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.F.; Wang, S.A. Ecological analysis of fish species composition in Baiyangdian Lake after the restoration of its water level. Hebei Fish. 1991, 6, 8–11. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.L.; Xiao, G.H.; Luo, N.T.; Yuan, Q.Y.; Deng, P.C. Analysis of the current fish species composition in Baiyangdian Lake. Hebei Fish. 2007, 11, 49–50. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, B.K.; Enderson, B.; Spieler, R.E. Fish assemblages associated with artificial reefs of concrete aggregates or quarry stone offshore Miami Beach, Florida, USA. Aquat. Living Resour. 2002, 15, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, B. Artificial reefs: A review of their design, application, management and performance. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2001, 44, 241–259. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z.Q.; Zhang, S.Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Wang, K.; Liang, J. Growth variation and rational utilization of small yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis) in artificial reef areas of Shengsi, Zhejiang Province. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2010, 18, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yang, W.; Liu, C.; Tang, Y.; Song, X.; Fang, G. Relationships between Community Structure and Environmental Factors in Xixiakou Artificial Reef Area. Ocean. Coast. Sea Res. 2020, 19, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creque, S.M.; Raffenberg, M.J.; Brofka, W.A.; Dettmers, J.M. If You Build It, Will They Come? Fish and Angler Use at a Freshwater Artificial Reef. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2006, 26, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.S.; Huang, X.F. Research Methods of Freshwater Plankton; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Hillebrand, H.; Dürselen, C.D.; Kirschtel, D.; Pollingher, U.; Zohary, T. Biovolume calculation for pelagic and benthic microalgae. J. Phycol. 1999, 35, 403–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wei, Y. The Freshwater Algae of China: Systematics, Taxonomy and Ecology; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.J.; He, W.; Liu, W.X.; Qin, N.; Ouyang, H.L.; Wang, Q.M.; Kong, X.Z.; He, Q.S.; Yang, C.; Yang, B.; et al. The seasonal and spatial variations of phytoplankton community and their correlation with environmental factors in a large eutrophic Chinese lake (Lake Chaohu). Ecol. Indic. 2014, 40, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amri, S.; Samar, M.F.; Sellem, F.; Ouali, K. Seasonal antioxidant responses in the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus (Lamarck 1816) used as a bioindicator of the environmental contamination in the South-East Mediterranean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Li, X.; Fang, H.; Dong, Y.; Huang, Z.; Chen, J. Calanoid copepods assemblages in Pearl River Estuary of China in summer: Relationships between species distribution and environmental variables. Estuar. Coast Shelf Sci. 2011, 93, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Margalef, R. Information theory in ecology. Int. J. Gen. Syst. 1958, 2, 36–71. [Google Scholar]
- Muylaert, K.; Sabbe, K.; Vyverman, W. Spatial and temporal dynamics of phytoplankton communities in a freshwater tidal estuary (Schelde, Belgium). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2000, 50, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyene, A.; Addis, T.; Kifle, D.; Legesse, W.; Kloos, H.; Triest, L. Comparative study of diatoms and macroinvertebrates as indicators of severe water pollution: Case study of the Kebena and Akaki rivers in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Ecol. Indic. 2009, 9, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.D.; Liang, J.; Zhang, S.Y. Influence of artificial reef construction on nutrition and water quality in off-shore area of Shengsi, Zhejiang. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2010, 34, 78–87. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcao, M.; Santos, M.N.; Drago, T.; Serpa, D.; Monteiro, C. Effect of artificial reefs (southern Portugal) on sediment-water transport of nutrients: Importance of the hydrodynamic regime. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 83, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhu, K.W.; Sun, M.C. Species composition and biomass variation in phytoplankton in artificial reef area in Haizhou Bay. J. Dalian Fish. Univ. 2006, 21, 134–140. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Li, C.H.; Jia, X.P.; Chen, P.M.; Fang, L. Effects of environmental factors on the distribution of attached organisms on artificial reef in Daya Bay. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2009, 8, 4053–4060. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.H.; Chang, J.J.; Sun, P.S. Phosphorus cycle of algae during its growth and death process: Phosphorus uptake and release. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2013, 22, 1250–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Littler, M.M.; Littler, D.S.; Brooks, B.L. The effects of nitrogen and phosphorus enrichment on algal community development: Artificial mini-reefs on the Belize Barrier Reef sedimentary lagoon. Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Huang, Z.G.; Zheng, C.X. A preliminary study of attached organisms on artificial reef in Daya Bay. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 1991, 2, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Hong, J.Z.; Li, H.Q. Fouling communities on neighboring artificial and natural reefs in Zhu Island, Pearl River estuary. South China Fish. Sci. 2013, 2, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Moura, A.; Boaventura, D.; Curdia, J.; Carvalho, S.; Monteiro, C.C. Effect of depth and reef structure on early macrobenthic communities of the Algarve artificial reefs (southern Portugal). Hydrobiologia 2007, 580, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristina, F.G.; Emilio, M. Effect of temperature on the unimodal size scaling of phytoplankton growth. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Lu, X.H.; Chen, Y.W. Long-term evolution of planktonic diatoms and their relationships with environmental factors in Lake Taihu. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2012, 32, 821–827. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.S.; Yan, G.L. The impact of microalgae in industrial river-crab seeding. Freshw. Fish. 2001, 31, 34–35. [Google Scholar]
- Neely, K.L.; Ziegler, T.A.; Peloso, M.; Hooper, M.; O’Briant, C.; Wise, M.; Rittschof, D. Enhancing artificial reef fish populations by providing invertebrate prey refugia. Fish. Res. 2021, 241, 106003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanthi, M.; Patterson, E.J.K.; Malleshappa, H.; Gladwin, G.A.N.; Mathews, G.; Diraviya, R.K.; Deepak, S.B.; Ashok, K.T.K.; Sannasiraj, S.A. Perforated trapezoidal artificial reefs can augment the benefits of restoration of an island and its marine ecosystem. Restor. Ecol. 2020, 28, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.; Ortizc, M.; Rodríguez-Zaragozad, F. Evaluating the macroscopic system properties of kelp species planted on two artificial reefs: Implications for the restoration of perturbed subtidal areas. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 252, 107266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitmarsh, D.; Santos, M.N.; Ramos, J.; Monterio, C.C. Marine habitat modification through artificial reefs off the Algarve (southern Portugal): An economic analysis of the fisheries and the prospects for management. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2008, 51, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, S.G.; Bushnell, S.L. Socio-economic aspects of artificial reefs: Considerations for the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2007, 50, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.R.; Liang, X.Y.; Zeng, J. Preliminary study on the effects of attached organisms on artificial reef material. South China Fish. Sci. 2006, 2, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Einbinder, S.; Perelberg, A.; Ben-Shaprut, O.; Foucart, M.; Shashar, N. Effects of artificial reefs on fish grazing in their vicinity: Evidence from algae presentation experiments. Mar. Environ. Res. 2006, 61, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
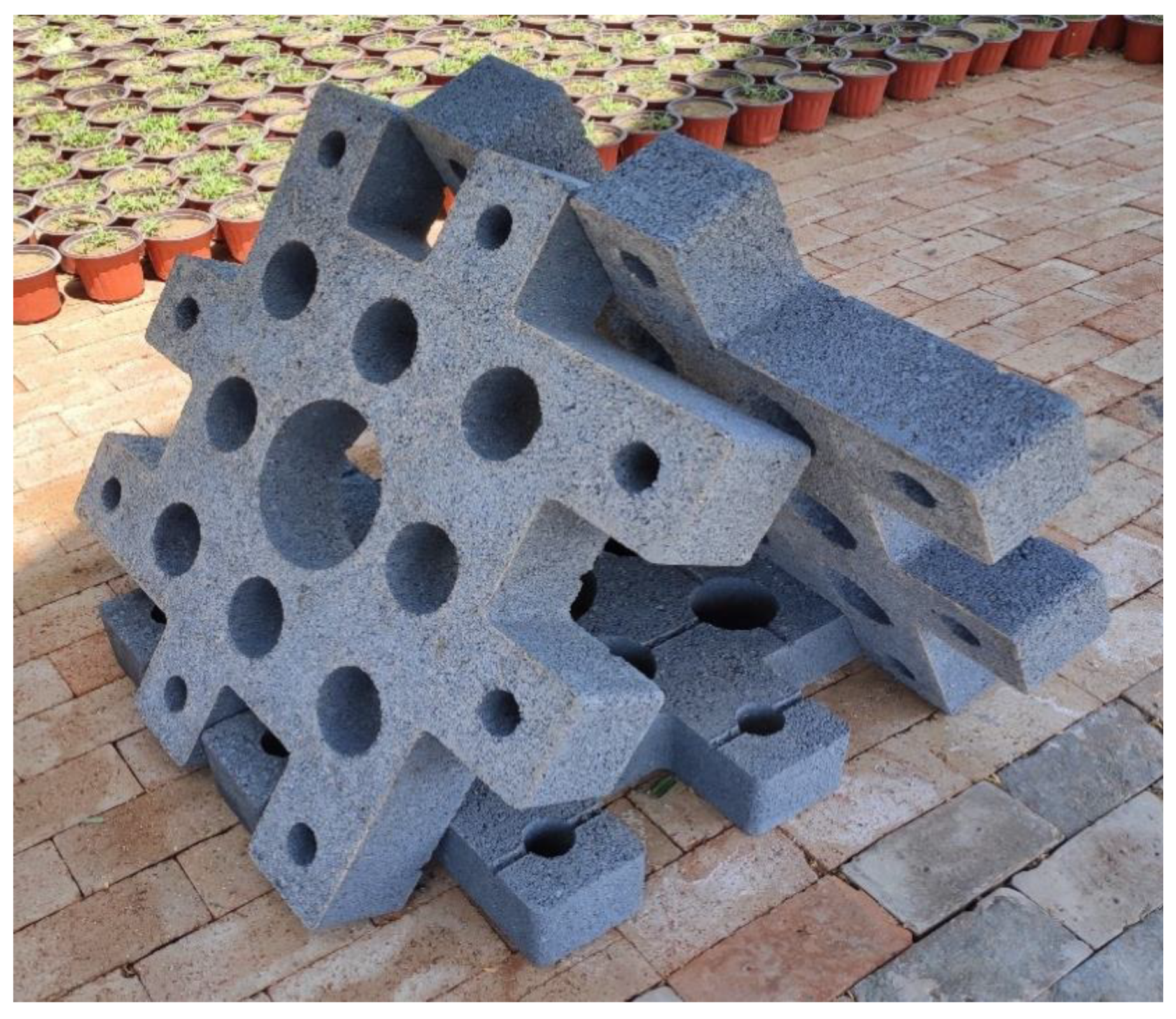


| Name | Technical Parameter |
|---|---|
| Material | Biomass filler |
| Structural requirements | Specific surface area 9.7 m2/g |
| Porosity | 50–81% |
| Dissolution rate in hydrochloric acid | <1.0% |
| Compressive strength | >3.0 MPa |
| Impurity content | <3.0% |
| Time of biofilm formation | 3–7 days |
| Chemical oxygen demand loading rate | <60 g/(m2·d) |
| Hydraulic loading | 0.3–0.6 m3/(m2·d) |
| July | August | September | October | November | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control Area | Reef Area | Control Area | Reef Area | Control Area | Reef Area | Control Area | Reef Area | Control Area | Reef Area | |
| Water temperature °C | 29.28 ± 0.35 | 29.85 ± 0.53 | 31.0 ± 0.75 | 30.7 ± 0.43 | 28.4 ± 0.25 | 27.6 ± 0.05 | 19.6 ± 0.04 | 19.2 ± 0.05 | 13.5 ± 0.07 | 13.8 ± 0.27 |
| Salinity ‰ | 0.73 ± 0.00 | 0.748 ± 0.00 | 0.69 ± 0.00 | 0.68 ± 0.00 | 0.73 ± 0.00 | 0.72 ± 0.00 | 0.76 ± 0.00 | 0.75 ± 0.00 | 0.77 ± 0.00 | 0.76 ± 0.00 |
| pH | 8.63 ± 0.01 | 8.71 ± 0.01 | 8.68 ± 0.08 | 8.94 ± 0.03 | 8.62 ± 0.03 | 8.97 ± 0.06 | 8.72 ± 0.02 | 8.46 ± 0.16 | 8.09 ± 0.05 | 8.4 ± 0.03 |
| Dissolved oxygen mg/L | 10.73 ± 0.20 | 10.67 ± 0.37 | 13.73 ± 0.60 | 14.54 ± 0.45 | 6.91 ± 0.92 | 7.8 ± 0.53 | 10.69 ± 0.52 | 7.03 ± 0.68 | 7.24 ± 0.28 | 8.84 ± 0.54 |
| Total nitrogen mg/L | 1.77 ± 0.21 | 2.23 ± 0.11 | 2.03 ± 0.49 | 1.43 ± 0.09 | 2.09 ± 0.30 | 1.95 ± 0.19 | 1.53 ± 0.16 | 2.77 ± 0.39 | 1.94 ± 0.33 | 2.25 ± 0.21 |
| Total phosphorus mg/L | 0.09 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 0.37 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 0.11 ± 0.04 | 0.04 ± 0.06 | 0.53 ± 0.01 |
| July | August | September | October | November | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prochlorophyta | 22 | 32 | 35 | 19 | 12 |
| Bacillariophyta | 7 | 4 | 11 | 5 | 3 |
| Cyanophyta | 4 | 2 | 10 | 7 | 6 |
| Cryptophyta | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0 |
| Euglenophyta | 3 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 0 |
| Pyrrophyta | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Xanthophyta | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| Total | 39 | 41 | 68 | 36 | 23 |
| July | August | September | October | November | Code | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anabaena sp. | 0.98 | - | - | - | - | Species1 |
| Merismopedia sp. | - | 0.93 | 0.78 | 0.28 | - | Species2 |
| Chlorella sp. | - | 0.02 | - | - | - | Species3 |
| Phormidium sp. | - | - | 0.08 | 0.64 | 0.11 | Species4 |
| Phacus sp. | - | - | 0.02 | - | - | Species5 |
| Cryptomonas erosa | - | - | 0.03 | - | - | Species6 |
| Merismopedia elegans | - | - | - | - | 0.06 | Species7 |
| Peridinium sp. | - | - | - | - | 0.72 | Species8 |
| July | August | September | October | November | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyanophyta | 26,452.36 | 19,033.16 | 11,681.87 | 7296.73 | 7.41 |
| Proportion % | 98.54 | 94.81 | 88.72 | 95.16 | 19.84 |
| Prochlorophyta | 307.57 | 940.59 | 590.22 | 267.66 | 2.84 |
| Proportion % | 1.15 | 4.69 | 4.48 | 3.49 | 7.60 |
| Bacillariophyta | 30.51 | 52.72 | 130.36 | 43.66 | 0.28 |
| Proportion % | 0.11 | 0.26 | 0.99 | 0.57 | 0.75 |
| Cryptophyta | 10.56 | 34.75 | 427.76 | 33.67 | 0 |
| Proportion % | 0.04 | 0.17 | 3.25 | 0.44 | 0 |
| Euglenophyta | 24.36 | 0 | 298.57 | 3.49 | 0 |
| Proportion % | 0.09 | 0 | 2.27 | 0.05 | 0 |
| Pyrrophyta | 18.14 | 13.99 | 13.62 | 2.54 | 26.77 |
| Proportion % | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 71.67 |
| Xanthophyta | 0 | 0 | 24.05 | 19.86 | 0.05 |
| Proportion % | 0 | 0 | 0.18 | 0.26 | 0.13 |
| Total | 26,843.5 | 20,075.21 | 13,166.45 | 7667.61 | 37.35 |
| July | August | September | October | November | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyanophyta | 39.616 | 4.874 | 4.822 | 10.627 | 0.0088 |
| Proportion % | 93.53 | 66.63 | 18.56 | 85.41 | 0.54 |
| Prochlorophyta | 0.37 | 0.949 | 0.812 | 0.332 | 0.0028 |
| Proportion % | 0.87 | 12.97 | 3.12 | 2.67 | 0.17 |
| Bacillariophyta | 0.277 | 0.531 | 1.296 | 0.613 | 0.0048 |
| Proportion % | 0.65 | 7.26 | 4.99 | 4.93 | 0.30 |
| Cryptophyta | 0.057 | 0.121 | 7.727 | 0.673 | 0 |
| Proportion % | 0.13 | 1.65 | 29.74 | 5.41 | 0 |
| Euglenophyta | 0.949 | 0 | 10.34 | 0.035 | 0 |
| Proportion % | 2.24 | 0 | 39.80 | 0.28 | 0 |
| Pyrrophyta | 1.088 | 0.8398 | 0.817 | 0.152 | 1.6064 |
| Proportion % | 2.57 | 11.48 | 3.14 | 1.22 | 98.99 |
| Xanthophyta | 0 | 0 | 0.168 | 0.0099 | 0.000023 |
| Proportion % | 0 | 0 | 0.65 | 0.08 | 0 |
| Total | 42.357 | 7.3148 | 25.982 | 12.4419 | 1.622823 |
| July | August | September | October | November | Mean | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon–Weaver diversity index (H′) | 0.16 | 0.44 | 1.09 | 0.63 | 1.26 | 0.71 |
| Pielou’s evenness index (J) | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.30 | 0.21 | 0.51 | 0.24 |
| Margalef’s richness index (D) | 0.88 | 1.56 | 2.11 | 1.20 | 0.98 | 1.35 |
| First Sampling | Second Sampling | Third Sampling | Mean | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyanophyta | 63.12 | 55.97 | 12.03 | 43.70 |
| Proportion % | 38.54 | 21.36 | 3.93 | 21.28 |
| Prochlorophyta | 44.16 | 30.62 | 34.33 | 36.37 |
| Proportion % | 26.96 | 11.69 | 11.20 | 16.62 |
| Bacillariophyta | 49.53 | 154.7 | 238.35 | 147.53 |
| Proportion % | 30.24 | 59.05 | 77.76 | 55.68 |
| Cryptophyta | 4.45 | 8.02 | 0.16 | 4.21 |
| Proportion % | 2.72 | 3.06 | 0.05 | 1.94 |
| Euglenophyta | 0 | 1.37 | 4.86 | 2.08 |
| Proportion % | 0 | 0.52 | 1.59 | 0.70 |
| Pyrrophyta | 2.52 | 11.3 | 1.8 | 5.21 |
| Proportion % | 1.54 | 4.31 | 0.59 | 2.15 |
| Xanthophyta | 0 | 0 | 14.99 | 5.00 |
| Proportion % | 0 | 0 | 4.89 | 1.63 |
| Total | 163.77 | 261.99 | 306.53 |
| August | September | October | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cyanophyta | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.01 |
| Proportion % | 7.23 | 1.91 | 0.17 |
| Prochlorophyta | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.08 |
| Proportion % | 3.65 | 1.05 | 2.51 |
| Bacillariophyta | 0.86 | 1.55 | 2.26 |
| Proportion % | 73.36 | 53.45 | 71.03 |
| Cryptophyta | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0 |
| Proportion % | 2.95 | 3.18 | 0 |
| Euglenophyta | 0 | 0.49 | 0.72 |
| Proportion % | 0 | 17.03 | 22.66 |
| Pyrrophyta | 0.15 | 0.68 | 0.11 |
| Proportion % | 12.81 | 23.37 | 3.40 |
| Xanthophyta | 0 | 0 | 0.01 |
| Proportion % | 0 | 0 | 0.24 |
| Total | 1.18 | 2.90 | 3.18 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, H.; Liu, X.; Cheng, S.; Wang, J. Effects of Artificial Reefs on Phytoplankton Community Structure in Baiyangdian Lake, China. Water 2021, 13, 1802. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131802
Zhu H, Liu X, Cheng S, Wang J. Effects of Artificial Reefs on Phytoplankton Community Structure in Baiyangdian Lake, China. Water. 2021; 13(13):1802. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131802
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Hao, Xingguo Liu, Shuiping Cheng, and Jie Wang. 2021. "Effects of Artificial Reefs on Phytoplankton Community Structure in Baiyangdian Lake, China" Water 13, no. 13: 1802. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131802
APA StyleZhu, H., Liu, X., Cheng, S., & Wang, J. (2021). Effects of Artificial Reefs on Phytoplankton Community Structure in Baiyangdian Lake, China. Water, 13(13), 1802. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131802








