Multivariate Analysis of Water Quality Data for Drinking Water Supply Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
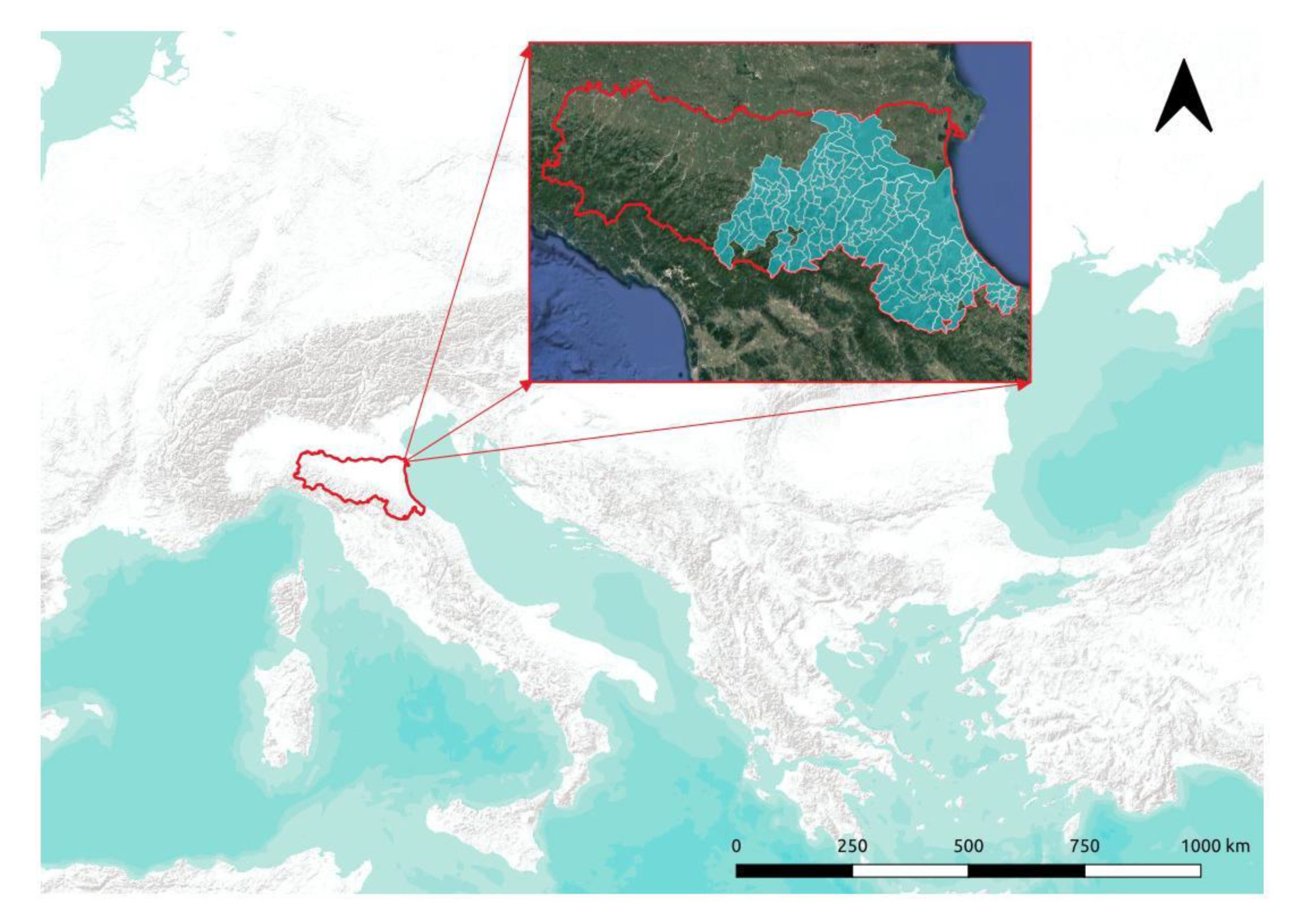
2.1. Case Study Area
2.2. Data
- Legislative Decree 2 February 2001, no. 31 “Implementation of directive 98/83/EC involving the quality of water for human consumption”;
- Legislative Decree 2 February 2002, no. 27 “Modifications and additions to Legislative Decree 2 February 2001, involving the implementation of directive 98/83/CE on the quality of water for human consumption”;
- Legislative Decree 3 April 2006, no. 152 “Norms on environmental matters”.
2.3. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
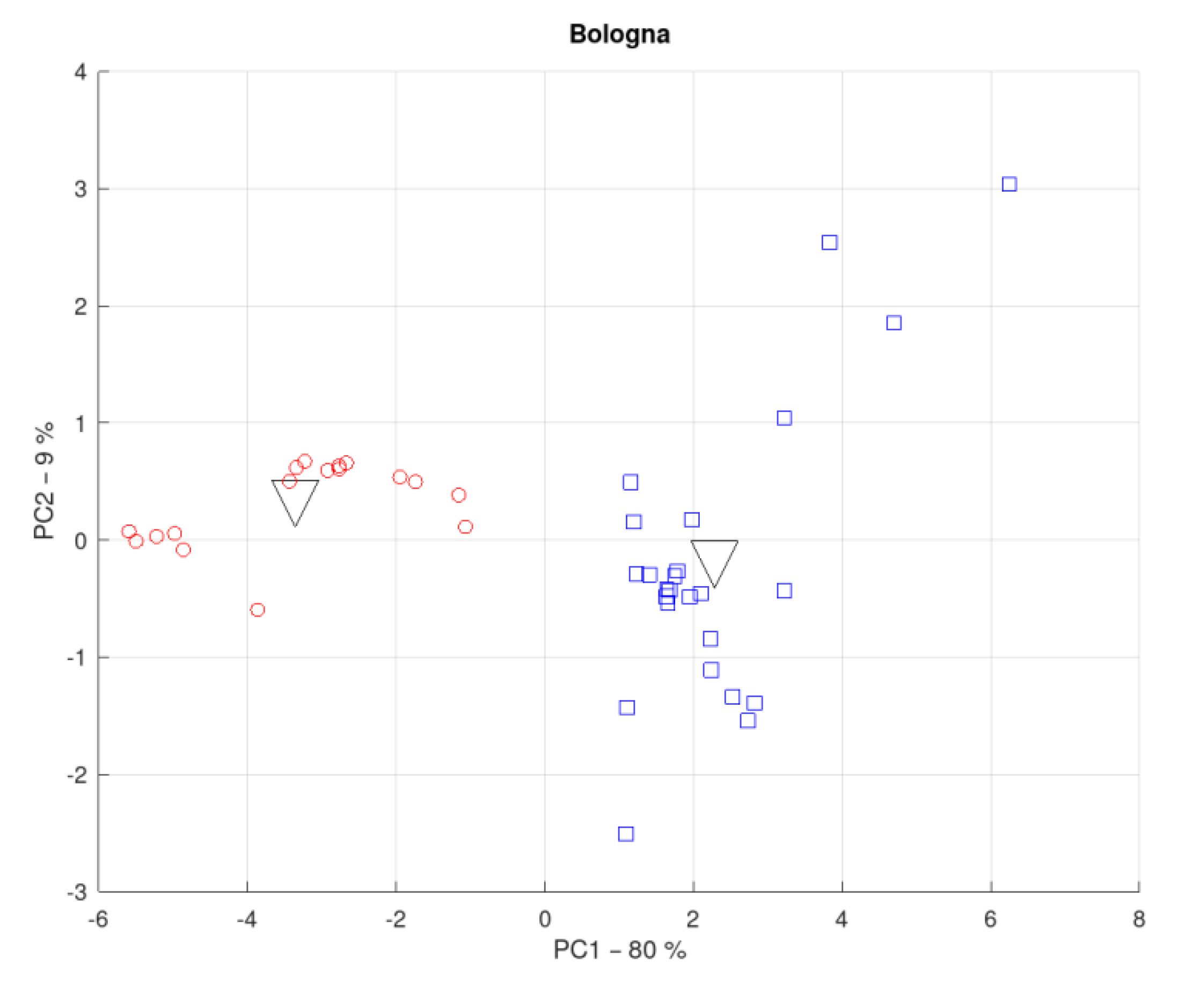
3.1. District of the Metropolitan City of Bologna
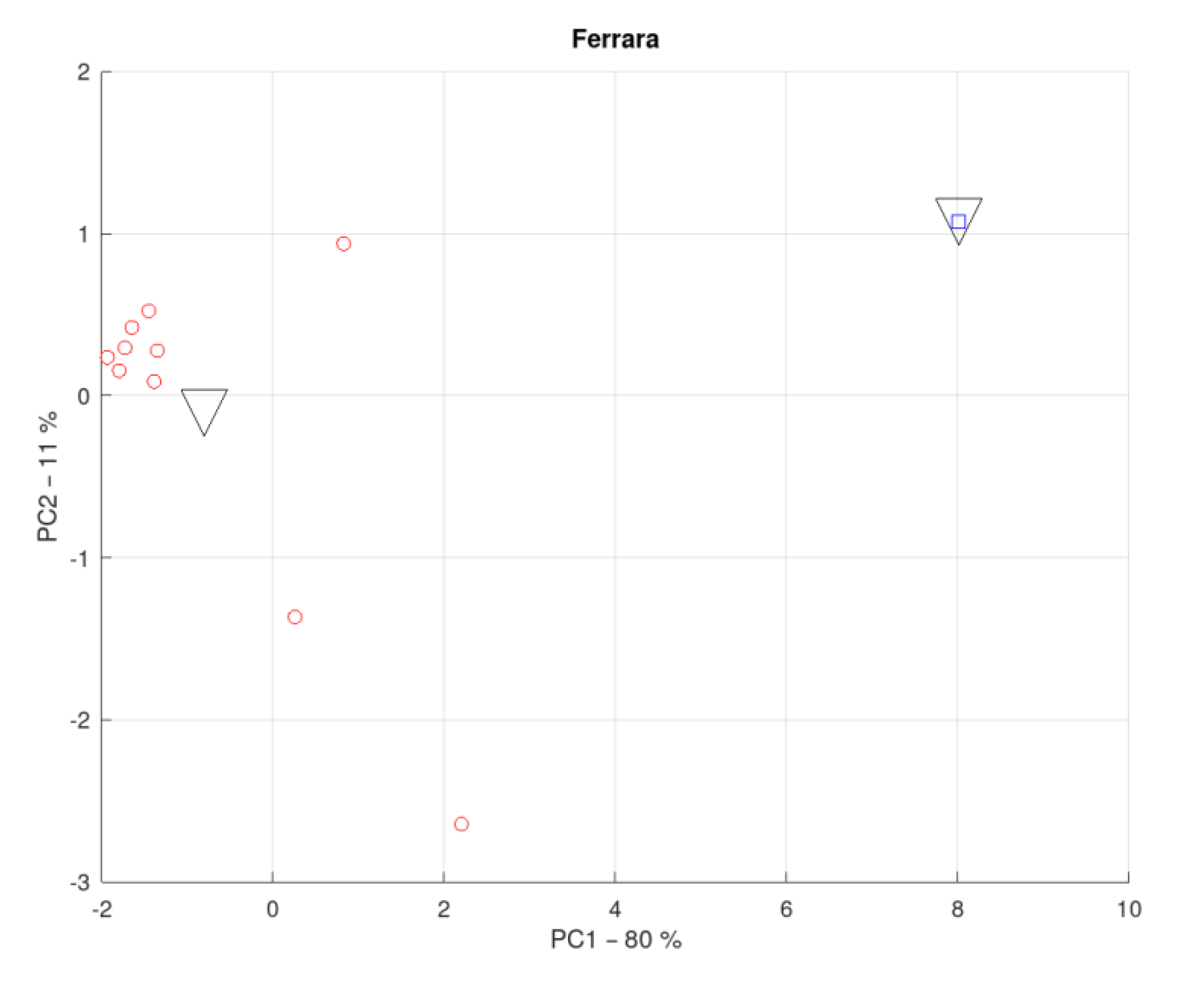
3.2. District of the Province of Ferrara
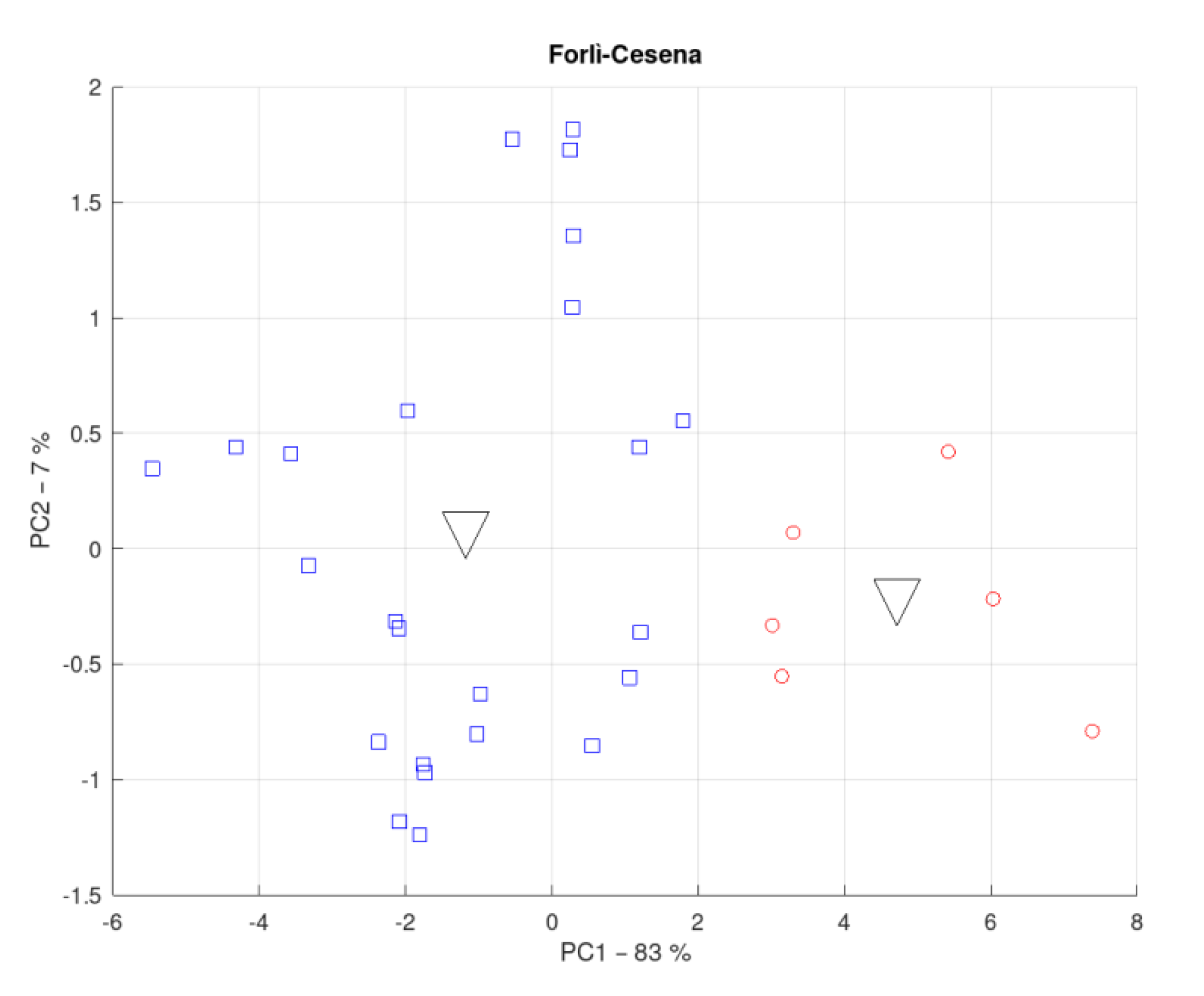
3.3. District of Forlì-Cesena
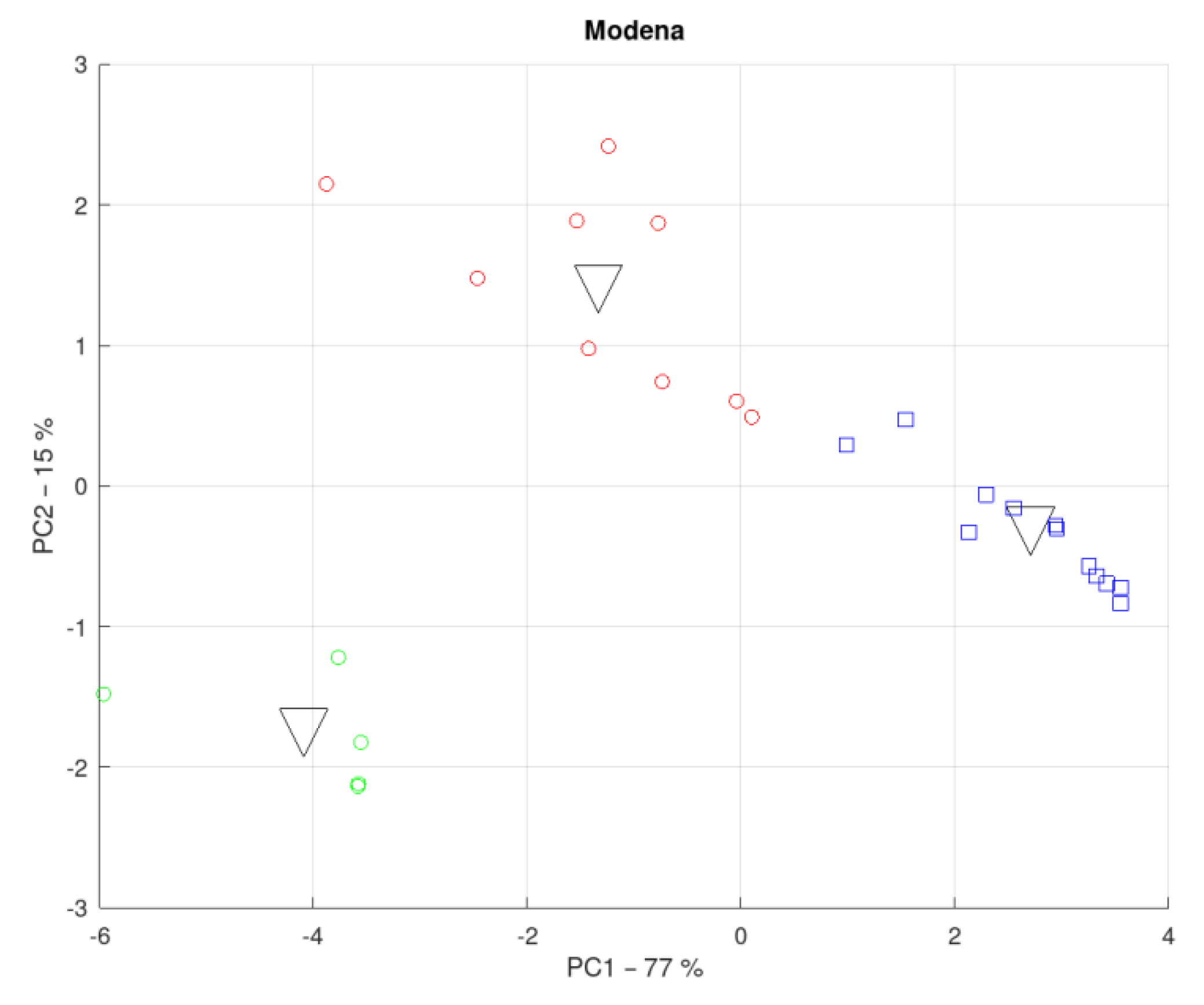
3.4. District of the Province of Modena
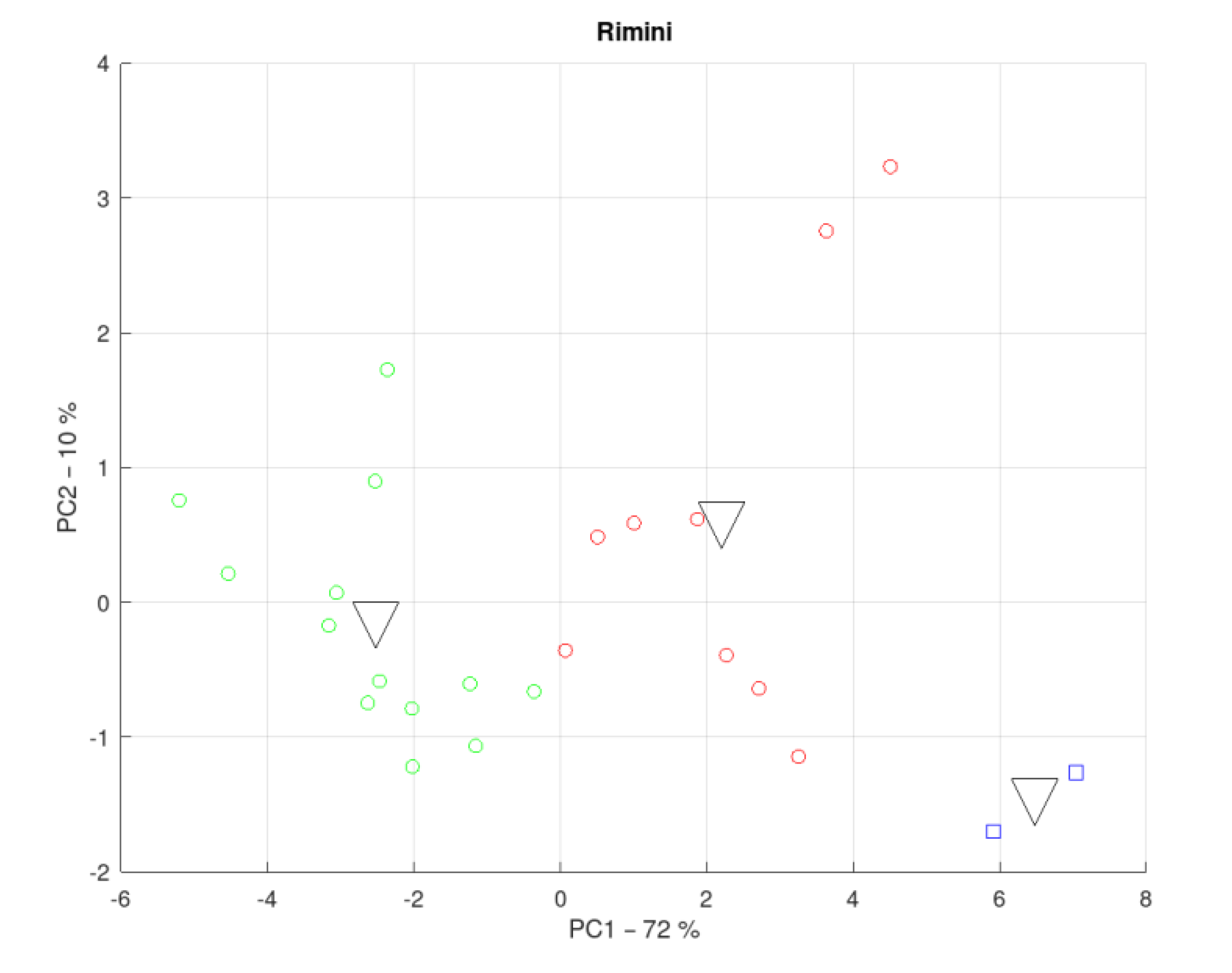
3.5. District of the Province of Rimini
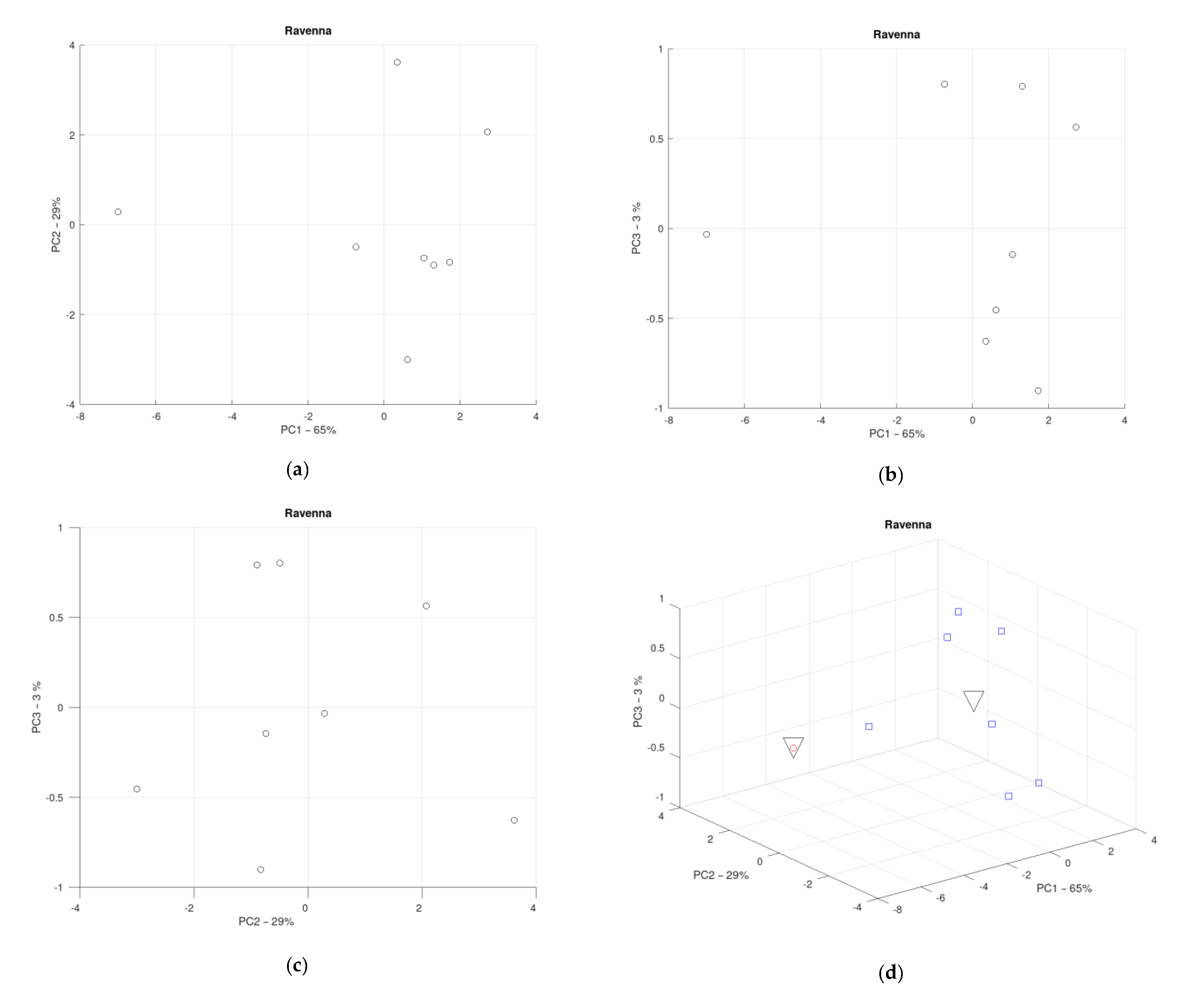
3.6. District of the Province of Ravenna
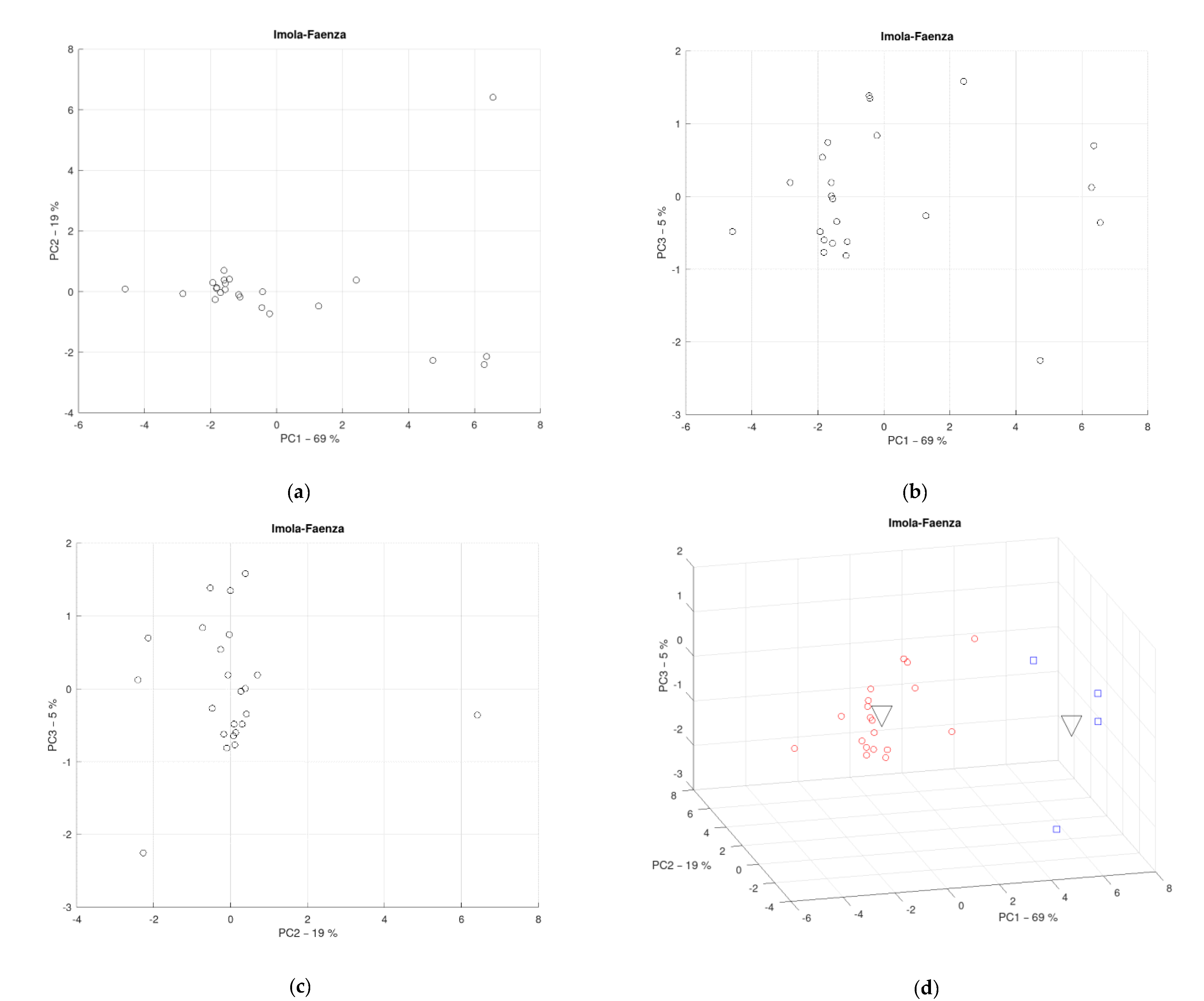
3.7. District of Imola-Faenza
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maiolo, M.; Pantusa, D. Sustainable Water Management Index, SWaM_Index. Cogent Eng. 2019, 6, 1603817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, B.; Lansey, K.; Kang, D. Resilience/Availability Analysis of Municipal Water Distribution System Incorporating Adaptive Pump Operation. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2013, 139, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, M.; Abraham, E.; Stoianov, I. A Graph-Theoretic Framework for Assessing the Resilience of Sectorised Water Distribution Networks. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 1685–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diao, K.; Sweetapple, C.; Farmani, R.; Fu, G.; Ward, S.; Butler, D. Global resilience analysis of water distribution systems. Water Res. 2016, 106, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maiolo, M.; Mendicino, G.; Pantusa, D.; Senatore, A. Optimization of Drinking Water Distribution Systems in Relation to the Effects of Climate Change. Water 2017, 9, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsefa, H.; Naghashzadegana, M.; Jamalia, A.; Farmani, R. Comparison of evolutionary multi objective optimization algorithms in optimum design of water distribution network. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2019, 10, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sophocleous, S.; Savi, D.; Kapelan, Z. Leak Localization in a Real Water Distribution Network Based on Search-Space Reduction. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2019, 145, 04019024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Malik, A.; Sinha, S. Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources of Gomti river (India) using multivariate statistical techniques—A case study. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 538, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gvozdić, V.; Brana, J.; Malatesti, N.; Roland, D. Principal component analysis of surface water quality data of the River Drava in eastern Croatia (24 year survey). J. Hydroinform. 2012, 14, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia, C.A.B.; Garcia, H.L.; Mendonça, M.C.S.; Ferreira da Silva, A.; do Patrocínio Hora Alves, J.; Lopes da Costa, S.S.; Araújo, G.O.; Santos Silva, I. Assessment of water quality using principal component analysis: A case study of the açude da Macela, Sergipe, Brazil. Water Resour. 2017, 3, 690–700. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, C.R.; Nayak, S.K. Assessment of seasonal variations in water quality of Brahmani river using PCA. Adv. Environ. Res. 2017, 6, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, D.; Wu, H.; Lin, A.; He, L. Using Principal Components Analysis and IDW Interpolation to Determine Spatial and Temporal Changes of Surface Water Quality of Xin’anjiang River in Huangshan, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioele, G.; De Luca, M.; Grande, F.; Durante, G.; Trozzo, R.; Crupi, C.; Ragno, G. Assessment of Surface Water Quality Using Multivariate Analysis: Case Study of the Crati River, Italy. Water 2020, 12, 2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, S.S.; Sahu, M.; Patel, R.K.; Panda, B.N. Prediction of Water Quality Using Principal Component Analysis. Water Qual. Expo. Health 2012, 4, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xia, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, F. Assessment of water quality in Baiyangdian Lake using multivariate statistical techniques. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 13, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Usman, U.N.; Toriman, M.E.; Juahir, H.; Abdullahi, M.G.; Rabiu, A.A.; Isiyaka, H. Assessment of Groundwater Quality Using Multivariate Statistical Techniques in Terengganu. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marghade, D.; Malpe, D.B.; Rao, N.S. Identification of controlling processes of groundwater quality in a developing urban area using principal component analysis. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 5919–5933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, L.; Bharadwaj, L.; Epp, T.; Waldner, C.L. Use of Principal Components Analysis and Kriging to Predict Groundwater-Sourced Rural Drinking Water Quality in Saskatchewan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chai, Y.; Xiao, C.; Li, M.; Liang, X. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Groundwater Quality Evaluation Based on Multivariate Statistical Analysis. Water 2020, 12, 2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praus, P. Urban water quality evaluation using multivariate analysis. Acta Montan. Slovaca 2007, 12, 150–158. [Google Scholar]
- Radzka, E.; Jankowska, J.; Rymuza, K. Principal Component Analysis and Cluster Analysis in Multivariate Assessment of Water Quality. J. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 18, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bancessi, A.; Catarino, L.; Silva, M.J.; Ferreira, A.; Duarte, E.; Nazareth, T. Quality Assessment of Three Types of Drinking Water Sources in Guinea-Bissau. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiouiouine, A.; Yameogo, S.; Valles, V.; Barbiero, L.; Dassonville, F.; Moulin, M.; Bouramtane, T.; Bahaj, T.; Morarech, M.; Kacimi, I. Dimension Reduction and Analysis of a 10-Year Physicochemical and Biological Water Database Applied to Water Resources Intended for Human Consumption in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur Region, France. Water 2020, 12, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hera Group. Available online: https://eng.gruppohera.it (accessed on 16 November 2020).
- Atersir. Agenzia Territoriale dell’Emilia-Romagna per i Servizi Idrici e Rifiuti (Territorial Agency of Emilia-Romagna for Water and Waste Services). Available online: https://www.atesir.it/argomento/servizio-idrico (accessed on 14 January 2021).
- Hera Group. Water Quality Reports and Archive. Available online: https://www.gruppohera.it/gruppo/attivita_servizi/business_acqua/qualità/qualita_acqua_hera_qualita_media_comuni/ (accessed on 12 January 2021).
- Pearson, K. On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. Philos. Mag. 1901, 6, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hotelling, H. Analysis of a complex of statistical variables into principal components. J. Educ. Psychol. 1033, 25, 417–441. [Google Scholar]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J. Principal Component Analysis. In Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Statistics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; p. 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I.T. Princypal Component Analysis, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002; ISBN 0-387-95442-2. [Google Scholar]
- Wold, S. Principal Component Analysis. In Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems; Elsevier Science Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; Volume 2, pp. 37–52, Printed in The Netherlands. [Google Scholar]
- Cattel, R.D. The scree test for the number of factors. Multivar. Behav. Res. 1966, 1, 245–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Likas, A.; Vlassis, N.; Verbeek, J. The global k-means clustering algorithm. Pattern Recognit. 2003, 36, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaiser, H.F. A second generation little jiffy. Psychometrika 1970, 35, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Territorial Operational District | Municipality Managed | Sources of Water | Network Length (km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metropolitan city of Bologna | 42 | groundwater and surface water | 9238 |
| District of the Province of Ferrara | 11 | groundwater and surface water | 2514 |
| District of the Province of Forlì-Cesena | 30 | surface water, groundwater, and springs (smaller share) | 4039 |
| District of the Province of Modena | 26 | groundwater and surface water (smaller share) | 4617 |
| District of the Province of Rimini | 24 | groundwater, followed by surface water and springs (smaller share) | 3006 |
| District of the Province of Ravenna | 8 | surface water | 3802 |
| District of the Province of Imola-Faenza | 23 | surface water | 3500 |
| Parameter | Unit | Health-Based Guideline Value WHO | Italian Standard Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bicarbonate alkalinity | mg/L | - | - |
| Total alkalinity | mg/L | - | - |
| Ammonia | mg/L | - | 0.50 |
| Arsenic | µg/L | 10 | 10 |
| Calcium | mg/L | - | - |
| Free residual chlorine | mg/L | 0.2 * | 0.2 |
| Chloride | mg/L | - | 250 |
| pH | - | - | >6.5–<9.5 |
| Conductivity at 20 °C | μ S/cm a 20 °C | - | 2500 |
| Water hardness | °F | - | 15–50 ** |
| Fluoride | mg/L | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Magnesium | mg/L | - | - |
| Manganese | mg/L | - | 50 |
| Nitrate (NO3) | mg/L | 50 | 50 |
| Potassium | mg/L | - | - |
| Dry residue at 180 °C | mg/L | - | 1500 * |
| Sodium | mg/L | - | 200 |
| Sulfate | mg/L | - | 250 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maiolo, M.; Pantusa, D. Multivariate Analysis of Water Quality Data for Drinking Water Supply Systems. Water 2021, 13, 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131766
Maiolo M, Pantusa D. Multivariate Analysis of Water Quality Data for Drinking Water Supply Systems. Water. 2021; 13(13):1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131766
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaiolo, Mario, and Daniela Pantusa. 2021. "Multivariate Analysis of Water Quality Data for Drinking Water Supply Systems" Water 13, no. 13: 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131766
APA StyleMaiolo, M., & Pantusa, D. (2021). Multivariate Analysis of Water Quality Data for Drinking Water Supply Systems. Water, 13(13), 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131766






